
Chatbot-Based Dialogue for Early Psychosis Detection: Leveraging
Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF)
Astria Hijriani
1,2,* a
, Lailatus Salma
2
, Sulastri
3b
, Yohana Tri Utami
2c
and Yunda Heningtyas
3d
1
Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Unist-Gil 50, Ulsan, South Korea
2
Department of Computer Science, University of Lampung, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
3
Nursing Department, Politeknik Kesehatan Negeri Tanjungkarang, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
Keywords: Psychosis, Schizophrenia, Global Assessment of Functional, Chatbot, Mental Disorder.
Abstract: Mental disorders patients often make people restless because they have uncontrollable behavior and need
special rehabilitation. Not every patient's family knows how to handle them, and health workers find it
difficult to monitor their condition. Early detection of psychosis, specifically schizophrenia, is critical for
effective treatment and support. Existing studies have explored expert systems and mobile applications for
diagnosing mental disorders and depression. Still, none have concentrated on developing a system or
application for the early detection of psychosis based on its severity. This research seeks to significantly
contribute to the mental health field by improving the early detection of psychosis, ultimately enhancing the
lives of individuals affected by this condition using chatbot-based dialog. The Early detection of psychosis
features was developed using the Global Assessment of Functional (GAF) and integrated with the Jiwamuku
mobile application. This GAF was categorized into four classifications: not indicated, mild, medium, and
serious. This feature was tested on 15 respondents. The application shows that two people are not indicated:
11 are mild, one is medium, and one is severe. Of all the data taken, 14 tests are accurate. The result shows
that early detection of psychosis features with Global Assessment of Functioning can be detected with 93%
accuracy. This research underscores the critical importance of early detection of mental disorders, particularly
psychosis, by harnessing the potential of chatbot-based dialogue and the Global Assessment of Functioning
(GAF).
1 INTRODUCTION
Mentally healthy individuals do not display signs of
mental disorders and effectively manage life
challenges by handling stress and recognizing the
importance of mental health on par with physical
well-being. Mental health problems can stem not only
from heredity but also from overwhelming stress due
to life demands (Saputra, et al., 2018).
In Indonesia, approximately 27.3 million people
experienced mental health disorders in 2017, with 6.7
per 1000 households dealing with schizophrenia/
psychosis (Kemenkes, 2018). Schizophrenia, a
lifelong disorder affecting daily activities, disrupts
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6073-6517
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7363-7211
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1082-1622
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5401-9979
thought and perception patterns, impacting factors
like age, memory, and intellect (Sumner et al., 2018).
People with mental health disorders often exhibit
uncontrollable behavior, causing societal distress.
They may experience relapses and require specialized
rehabilitation. However, post-treatment relapses are
influenced by a lack of supervision and limited
knowledge among family members regarding patient
care.
Information system technology can assist in
monitoring post-treatment mental health patients.
Studies, such as the development of web-based
systems and the JiwaMuKu Android app, focus on
monitoring patients' health conditions via mobile
applications used by their families. Although these
Hijriani, A., Salma, L., Sulastri, , Utami, Y. T. and Heningtyas, Y.
Chatbot-Based Dialogue for Early Psychosis Detection: Leveraging Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF).
DOI: 10.5220/0013671300003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 271-277
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
271

systems can screen and provide progress graphs,
reminders, and reports, they have not progressed to
diagnosing disorders like psychosis.
In addition to post-medical care processes, early
detection of schizophrenia and other symptoms is
equally crucial. Early education and symptom
recognition processes are vital for personal
assessment and those close to the individual. If
identified early on, patients can seek assistance for the
mental health issues they are facing. Typically,
patients or their families may feel reluctant to disclose
the early symptoms to others or mental health
professionals. Other research explores using expert
systems for psychosis detection, schizophrenia, or
student depression. Nevertheless, there is ample room
for improvement in identifying the severity of early-
stage psychosis.
This research uses the Global Assessment of
Functioning (GAF) Scale to determine severity. The
study focuses on developing a feature for early
psychosis detection using the GAF scale through
chatbot-based dialogues. Choosing a chatbot dialog
aims to make the application more user-friendly, with
different constructions for self-assessment or
assessments by others.
2 RELATED WORKS
Mental health disorders are conditions in which an
individual has trouble adapting to their surroundings.
The inability to solve problems can lead to excessive
stress, making the mental health of the individual more
vulnerable and eventually diagnosed as a mental
health disorder (Lubis et al., 2014). Psychotic
disorders, on the other hand, are characterized by a
disturbance in assessing reality. Psychosis includes
various types, such as schizophrenia, schizoaffective
disorder, persistent delusional disorder, bipolar with
psychotic features, and depression with psychotic
features (Idaini et al., 2018).
Schizophrenia is a group of psychotic disorders
with distinctive distortions in thought processes.
Individuals with schizophrenia may sometimes feel
controlled by external forces, experience strange
delusions, perceptual disturbances, abnormal affect
integrated with real or actual situations, and autism.
Schizophrenia is the most common psychotic
disorder, affecting nearly 1% of the world's population
during their lifetime (Zahnia & Sumekar, 2016).
People with schizophrenia generally require
assistance from those around them, known as
caregivers. Caregivers help with the daily activities of
individuals needing care, such as the sick or children.
Caregivers can include family members or close
individuals who assist patients in their daily activities
(Farkhah & Suryani, 2017). The level of assistance
provided may vary for each patient.
Several studies have explored the use of
information systems in primary healthcare
institutions, including the development of web-based
systems for monitoring the recovery process of mental
health disorder survivors (Waskito, 2020),
(Adiyaksatama, 2020) and the JiwaMuKu Android-
based application (Syahputra, 2020). These systems
allow for tracking patients' health conditions,
integrated with a mobile application used by their
families.
Screenings can be performed in the mobile
application, and healthcare professionals can view the
results through a web application. The web application
can display patient progress graphs, provide
reminders, and generate patient reports. However,
these studies have not progressed to diagnosing
mental health disorders such as psychosis
(schizophrenia).
In 2018, Landung Sudarman and Febty Lestari
developed an expert system for diagnosing
schizophrenia (Sudarmana & Lestari, 2018) using a
forward chaining method and Dempster-Shafer
theory. (Widodo and Jaya, 2018) and (Anisa, 2018)
created an expert system for analyzing the level of
depression in students and schizophrenia detection
utilizing the certainty factor method. Another study
focused on early detection of psychosis using a mobile
application based on fingerprints. However, no
research has been conducted on developing a system
or application to detect early-stage psychosis based on
its severity.
This research utilized the Global Assessment of
Functioning (GAF) Scale to determine the severity
level based on weighted symptoms.
The GAF is used to assess the seriousness of
mental health disorders and measures the impact of
symptoms on daily life on a scale of 0-100 (Smith,
2021). GAF scores can be assessed through
interviews, questionnaires, medical records,
information from doctors, caregivers, or close
relatives, and police or court records documenting
violent or illegal behavior.
3 METHODS
3.1 Design
This study was to develop an early psychosis
detection feature on the JiwaMuKu (Jiwa Munyai
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
272
Jiwa Strong) platform in the form of an Android
application that general users can use.
3.2 Population and Sampling
The psychosis early detection feature is carried out by
several community groups, including five people
from the Sukarame neighborhood, five people who
are experiencing mental disorders, and five people
mental health professionals.
Testing with people with psychiatric disorders
was conducted in two different places. The first place
was at Wisma Ataraxis, while the second was at the
Yayasan Sinar Jati Kemiling. During the testing, they
were directly accompanied by mental health experts.
3.3 Procedure
Application development begins with a discussion
with the Ikatan Perawat Kesehatan Jiwa Indonesia
(IPKJI) to analyze the needs and definitions of the
application during development. After the discussion,
the application design was carried out by designing
the application's functional features, workflows, data
structures, and appearance. After that, the coding
stage is carried out based on the design that has been
made previously.
The next stage is black box testing to ensure
that all functions run smoothly before being used by
users. If the black-box test has met the expected
results, then testing with users is carried out. From
testing with users, it can be concluded how accurately
the application works.
4 RESULTS
The early detection of psychosis is a new feature that
will be added to the JiwaMuKu application.
Psychosis detection diagnoses its severity based on
the symptoms experienced using the Global
Assessment of Functioning (GAF) scale. The public
can access this feature, and it does not require login
beforehand. The questions asked are based on the
individual's conditions and experiences. As for the
answers provided, they indicate the level of
confidence in those events or conditions.
Like an expert system, this feature also utilizes
rules to conclude. Table 1 presents a list of symptoms
and rules for the early detection of psychosis features.
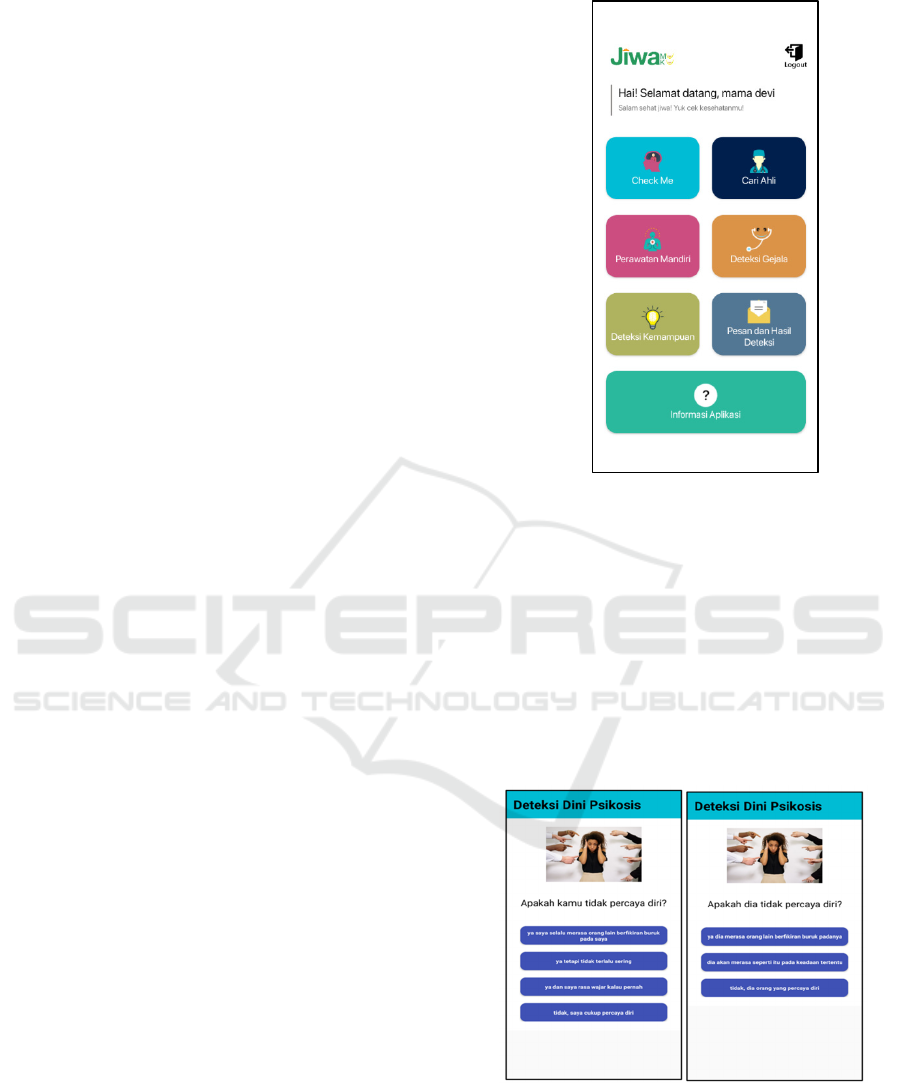
Meanwhile, figure 1 shows the main menu of the
Jiwamuku application.
Figure 1: Home menu for the user.
The "Check Me" menu is where users can
diagnose psychosis. To begin the test, options will be
presented for self-detection or detection of others.
The difference between these two options lies in the
questions' wording, which is based on the target being
detected. If conducting the test for oneself, the
questions will use the word 'kamu' (you), while for
testing someone else, the word 'dia' (he/she) will be
used. The answer and the calculation will also differ
based on the viewpoint.
Figure 2: Display Self-Doubt Questions for Oneself (Left)
and Self-Doubt Questions for Others (Right).
Figure 2 displays examples of questions related
to a lack of confidence. Feeling lacking in confidence
is something everyone may experience, and it's a
normal occurrence. However, if one consistently feels
Chatbot-Based Dialogue for Early Psychosis Detection: Leveraging Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF)
273

low in self-confidence and believes that others always
harbor negative thoughts about them, it falls under the
symptoms of psychosis.
After answering various displayed questions, a
summary page of the provided answers will appear.
Figure 3 shows the display of the resume answer. If
the answers seem appropriate, the user can view the
conclusion of the detection by pressing the Next
button. The displayed conclusion will be based on the
obtained score. There are four categories:
• The first category indicates no mental health
issues if the score is >91. Individuals in this
category show no symptoms, function optimally,
and have no unresolved problems.
• The second conclusion, with a score between 61-
90, indicates a mild condition. In this category,
individuals with mental health issues experience
temporary and manageable symptoms, like
everyday problems.
• The conclusion with a score between 51-60
indicates a moderate condition, where the
experienced symptoms are at a moderate level.
• The last conclusion, in the severe category, with
a score between 0-50, suggests that individuals
with mental health issues are in a persistent and
more serious state. This may include some
disabilities in communication and cognitive
functions, a risk of self-harm or harm to others,
and severe impairments in various functions.
Figure 3: Display of the summary page of the application.
When the application is ready, a system test is
conducted to ensure that all functions within the
application and system operate correctly using the
black box testing technique. Figure 4 shows the
documentation of black box testing.
Figure 4: Black box testing at the Sinar Jati Foundation in
Kemiling.
The system developers and healthcare personnel
perform black box testing on the JiwaMuKu
information system. The testing activities occurred at
the Kedaton Inpatient Health Center, the Rajabasa
Indah Health Center, the Sinar Jati Kemiling
Foundation, and the Way Halim Health Center.
The second testing involves accuracy testing to
determine the accuracy of early psychosis detection
and conclusion, as documented in Figure 5. Various
community members were involved in this testing.
There were five individuals in the Sukarame
community, five individuals experiencing moderate
mental disorders, and five mental health
professionals.
Figure 5: Testing activities for early detection of psychosis
conducted by Mr. E at the Sinar Jati Kemiling Foundation.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
274
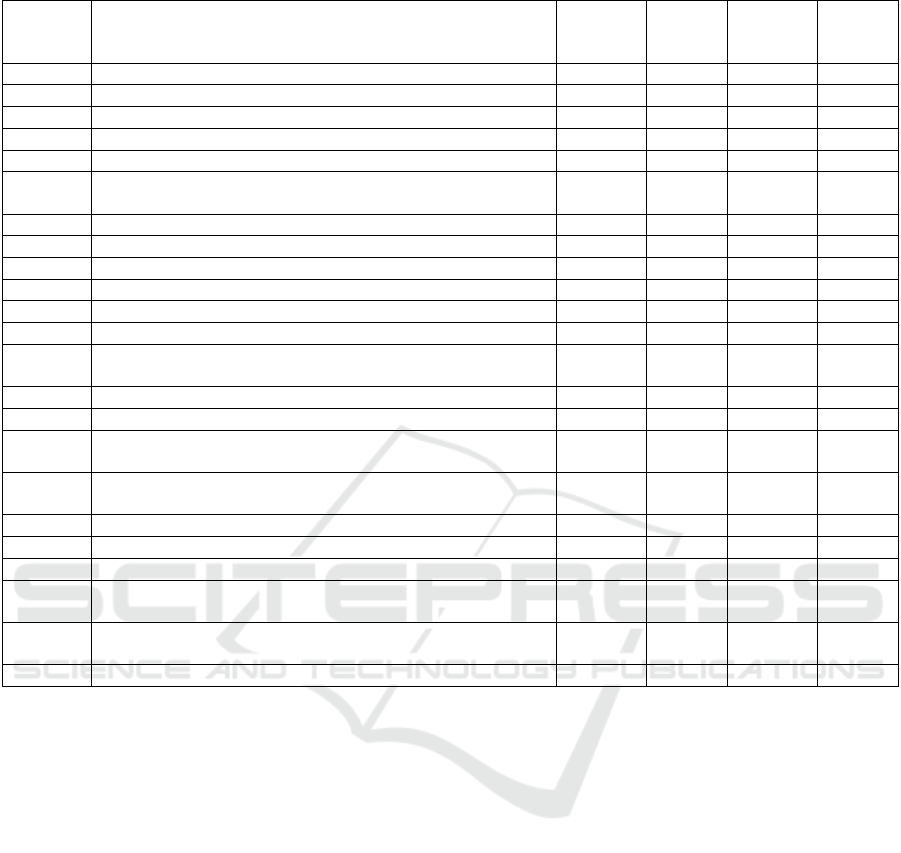
Table 2: Symptoms and Rules.
Code Explanation Not
Indicated
(
100-91
)
Mild
(91-61)
Moderate
(60-51)
Severe
(50-0)
G1 Men
g
asin
g
kan diri dari lin
g
kun
g
an sekita
r
oran
g
lain x x x
G2 Perilaku ketika makan tidak bai
k
x x
G3 Perubahan emosi secara signifikan x x x
G4 Perubahan pada pola tidu
r
xxx x
G5 Berteriak tiba-tiba dan marah tanpa alasan x x x
G6 Sulit berkonsentrasi (terlebih jika sedang membaca ataupun
menonton)
x x x
G7 Merasa cemas berlebihan x x x
G8 Kesulitan untuk membaca dan menulis x
G9 Sulit merasa senan
g
atau
p
uas x x
G10 Kehilan
g
an minat dan motivasi
p
ada berba
g
ai aktivitas x x x x
G11 Tidak peduli pada penampilan dan kebersihan diri x x
G12 Curiga dan tidak percaya dengan orang lain x x
G13 Sering merasakan/mendengar adanya suara yang mengancam
atau memberi
p
erintah
x x
G14 Meyakini bahwa dirinya menjadi sosok tertentu x x
G15 Ekspresi wajah dan nada bicara tidak sesuai dengan situasi x x
G16 Gerakan tubuh tidak teratur dan gerak tubuh yang tidak
normal atau sulit di
p
rediksi
x x
G17 Berkeinginan atau melakukan untuk mencederai diri sendiri
mau
p
un oran
g
lain
x
G18 Tidak
p
erca
y
a diri, takut dikritik atau dihakimi oran
g
lain x x
G19 Putus asa dan pesimis x x
G20 Merasa dirinya dikendalikan oleh orang lain x x
G21 Mendengar suara halusinasi yang berkomentar secara terus-
menerus
x x
G22 Merasa bersalah, tidak beguna, rasa terbebani, tidak berdaya
dan tidak ber
g
una
x
G23 Ber
p
ikir in
g
in mati x
5 DISCUSSIONS
The challenge in this research is how to transform the
language of symptoms into an early detection
language easily understood by users. The developed
chatbot dialog should also be able to view two
different sides, including self-assessment and
assessment by others.
Testing conducted at Wisma Ataraxis involved
two individuals facing mental health issues. The first
respondent, R, experienced mental health problems
with symptoms of anxiety, difficulty sleeping,
concentration issues, and withdrawal from social
environments. The conclusion from R's early
psychosis detection test indicated mild mental health
issues due to R's improved condition and ability to
communicate. The second respondent, Mr. M, had
mental health problems with symptoms of loss of
interest in hobbies, hallucinations, and suicidal risk.
Like R, Mr. M's results also showed mild mental
health issues, as his condition improved during the
test. The third and fourth respondents, both staff at
Wisma Ataraxis, showed no indications of mental
health issues.
The next testing location was conducted at
Yayasan Sinar Jati Kemiling, where early psychosis
detection tests were performed on three patients and
one staff member. The first respondent at Yayasan
Sinar Jati, a healthcare worker, received a mild result.
The second respondent, Mr. E, experiencing
symptoms of anxiety, emotional changes,
unexplained anger, and neglecting personal hygiene,
showed mild results. Mr. E had been mistreated by his
family and remained unaccepted by them despite two
years of treatment. Despite his tendency to raise his
voice, Mr. E was genuinely concerned about his
surroundings, leading to a mild psychosis detection
result.
The next respondent was Mr. R, with symptoms
of anxiety, emotional changes, difficulty
concentrating, neglect of personal hygiene,
suspicious feelings, hallucinations, and suicidal risk.
Chatbot-Based Dialogue for Early Psychosis Detection: Leveraging Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF)
275

He also faced family rejection and had been treated at
Yayasan Sinar Jati for four years. During the early
psychosis detection test, Mr. R scored 79, falling into
the mild category.
The final respondent from Yayasan Sinar Jati
Kemiling, identified as S, had been under treatment
for four years, experiencing symptoms of anxiety,
hallucinations, and suicidal risk. S's result indicated a
moderate level. Since direct interaction with the
patient was not allowed during data collection, there
was no documentation during the testing activities.
From the conducted tests, the application's
conclusions were compared with those of mental
health experts conducting direct psychosis detection.
Out of 15 test data, two individuals showed healthy
results, 11 showed mild results, 1 showed moderate
results, and 1 showed severe results.
Of the 14 accurate test data, the accuracy rate was
93%. Therefore, this feature can conclude with an
accuracy rate of 93%. The results from the collected
data do not represent the overall since the sampling
size was small. Hence, these results are used as a
reference, indicating that the application's displayed
results have an accuracy rate of 93%.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, this research emphasizes the
paramount significance of early detection in
addressing mental disorders, specifically psychosis.
Leveraging chatbot-based dialogue and the Global
Assessment of Functioning (GAF), our study has
demonstrated a promising approach to enhance the
detection and monitoring of mental health conditions.
Moving forward, there are several avenues for
future research in this domain. Firstly, developing
early psychosis detection systems could benefit from
applying expert system development methods such as
certainty factor, fuzzy logic, or other advanced
techniques. These methodologies can potentially
enhance the accuracy and efficiency of early
detection systems.
Furthermore, exploring chatbot-based solutions
for early psychosis detection presents an intriguing
avenue for future work. Integrating chatbots into
mental health diagnostics offers a user-friendly and
accessible approach, allowing individuals to engage
in conversations with the bot to diagnose psychosis.
This interactive and conversational model has the
potential to reach a broader audience, providing
timely and personalized assistance in mental health
assessments.
The research lays the foundation for innovative
approaches to mental health diagnostics, emphasizing
the importance of proactive measures in identifying
and addressing mental health issues. Integrating
technology, particularly chatbot-based systems, holds
promise in revolutionizing early detection methods
and facilitating more widespread access to mental
health support.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The researcher would like to extend gratitude to
Puskesmas Kedaton, Puskesmas Rajabasa Indah,
Puskesmas Way Halim, Wisma Ataraxis, and
Yayasan Sinar Jati Kemiling for their assistance and
collaboration in this research.
REFERENCES
Adiyaksatama, M. Y., 2020. Desain Antarmuka Dan
Implementasi User-Centered Design Pada Aplikasi dan
Sistem Informasi Jiwamuku (Jiwa Munyai Jiwa Kuat),
Minithesis, Bandar Lampung: Universitas Lampung.
Annisa, R., 2018. Sistem Pakar Metode Certainty Factor
Untuk Mendiagnosa Skizofrenia. IJCIT (Indonesian
Journal on Computer and Information Technology),
3(1), pp. 40–46.
Farkhah, L. & Suryani, S., 2017. Faktor Caregiver dan
Kekambuhan Klien Skizofrenia. Jurnal Keperawatan
Padjadjaran, 5(1), p. 37–46.
Idaini, S. et al., 2018. Prevalensi Psikosis di Indonesia
berdasarkan Riset Kesehatan Dasar. Jurnal Penelitian
dan Pengembangan Pelayanan Kesehatan, 3(1), pp. 9-
16.
Kementrian Kesehatan RI, "Laporan Riskesdas,"
Kementrian Kesehatan RI, Jakarta, 2018.
Lubis, N., Krisnani, H. & Fedryansyah, M., 2014.
Pemahaman Masyarakat Mengenai Gangguan Jiwa
Dan Keterbelakangan Mental. Share: Social Work
Journal, 4(2), pp. 137-144.
Saputra, F. A., Ranimpi, Y. Y. & Pilakoannu, T., 2018.
Kesehatan Mental dan Strategi Koping Studi
Sosiodemografi di Kudangan Kecamatan Delang
Kabupaten Lamandau Kalimantan Tengah. Jurnal
Keperawatan Jiwa., 2(1), pp. 63-74.
Smith, M., 2021. What Is the Global Assessment of
Functioning (GAF) Scale? [Online] Available at:
https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/gaf-scale-
facts#091e9c5e815efdfe-1-2
Sudarmana, L. & Lestari, F., 2018. Aplikasi Sistem Pakar
Untuk mendiagnosis Gangguan Jiwa Schizophrenia.
Jurnal Informatika: Jurnal Pengembangan IT (JPIT).,
3(1), pp. 40-44.
Sumner, C. B. et al., 2018. Process Evaluation of a Pilot
Intervention for Psychosocial Rehabilitation for Service
Users with Schizophrenia in Northwest Province, South
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
276

Africa. Community Mental Health Journal, Volume 54,
p. 1089–1096.
Syahputra, A., 2020. Pengembangan Aplikasi Jiwamuku
Berbasis Android Untuk Monitoring Proses Recovery
Survivor Gangguan Jiwa Pasca Perawatan, Minithesis,
Bandar Lampung: Universitas Lampung.
Widodo, E. & Jaya, S., 2018. Implementasi Sistem Pakar
Untuk Mendiagnosa Tingkat Depresi Pada Mahasiswa
Tingkat Akhir dengan Metode Certainty Factor. Jurnal
Teknologi Pelita Bangsa, 8(2), pp. 233-240.
Waskito, S. T., 2020. Pengembangan Sistem Informasi
Berbasis Web Untuk Monitoring Proses Recovery
Survivor Gangguan Jiwa Pasca Perawatan, Minithesis,
Bandar Lampung: Universitas Lampung.
Zahnia, S. & Sumekar, D. W., 2016. Kajian Epidemiologis
Skizofrenia. Medical Journal of Lampung University.,
4(4), pp. 160-166.
Chatbot-Based Dialogue for Early Psychosis Detection: Leveraging Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF)
277
