
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A
Meta-Analysis Study
Hanna Mutiara
1,2
, Agnes Kurniawan
2
and Lisawati Susanto
2
1
Section of Microbiology and Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Lampung, Indonesia
2
FKUI Clinical Parasitology Specialist Doctoral Education Study Programs, Indonesia
Keywords: Intestinal Worms, Intestinal Parasitic Infections, Meta-Analysis, Intestinal Protozoa, Stunting.
Abstract: Stunting is a child health problem that describes a chronic nutritional problem. One of the causes of stunting
is intestinal parasitic infection. Research related to the risk factors for stunting has been widely carried out,
but related to intestinal parasite infection as one of the determinants is still limited and still being debated.
Therefore, it is necessary to make a meta-analysis study. Search for published and unpublished articles
according to the flow on the Prisma diagram online through PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar,
Hindawi, Cochrane library, DOAJ, JSTOR, Public Library of Science (PLoS), UI repository, Unila and USU
in a timeframe 2016 to 2021 with Indonesian and English versions. The keywords used were intestinal
parasitic infection, soil transmitted helminth infection, intestinal protozoan, stunting, growth disorders,
children, intestinal parasitic infections, intestinal protozoa, short stature and children. The article search was
carried out using keywords and Mesh terminology using the Quatation mark "", the boolean operators "OR"
and "AND". The search results obtained 1042 journals and 2 theses. Then, screening and review were carried
out to obtain 6 suitable journals to be analyzed using review manager 5.4 software. The combined p-value of
the meta-analysis results was p=0.02 with an OR of 1.48 (95% CI 1.06-2.07). This means that there is an
effect of intestinal parasitic infection on the incidence of stunting in children.
1 INTRODUCTION
Stunting is a child health problem, not only in the
world, but also in Indonesia. In 2015, around 23.2%
or 159 million children under five experienced
stunting (Shekar, 2017). Data from 2017 shows that
55% of children under five are stunted in the world
originate from Asia and 39% live in Africa. The order
of proportion of stunted children under five in Asia is
South Asia (58.7%), Southeast Asia (14.9%), East
Asia (4.8%), West Asia (4.2%) and Central Asia
(0.9%). According to data from the World Health
Organization (WHO), the prevalence of stunted
toddlers in Indonesia in 2005-2017 was the third
highest in the Southeast Asia region or South-East
Asia Regional (SEAR), namely 36.4% (Ministry of
Health of the Republic of Indonesia, 2018; UNICEF,
2020).
Based on Nutrition Status Monitoring (PSG) data,
the highest prevalence of nutritional problems in
Indonesia is stunting, namely 27.5% in 2016 and
29.6% in 2017, while Basic Health Research
(Riskesdas) in 2018 produced prevalence data of
30.8% (Ministry of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia, 2018). Nutritional problems do not only
occur in toddlers, but also in children and adolescents.
Nationally, the prevalence of stunting in children
aged 5-12 years is 23.6% and in adolescents aged 13-
15 years is 25.7% (Ministry of Health of the Republic
of Indonesia, 2018).Handling stunting has been
designated as one of the priority programs (Ministry
of Health of the Republic of Indonesia, 2018; CPM,
2020).
Stunting is divided into two categories, namely
short with a Z score threshold of -3.0 to -2.0 standard
deviation (SD) and very short with a Z score threshold
of less than -3.0 SD (Ministry of Health of the
Republic of Indonesia, 2020; Harjatmo, 2017).
Stunting has serious impacts both in the short and
long term, including increasing child morbidity and
mortality. The incidence of stunting at an early age
can continue and there is a risk of short growth in
adolescence. Therefore, interventions to prevent
stunting growth are still needed even after exceeding
the First 1000 Days of Life (HPK) (Ministry of Health
of the Republic of Indonesia, 2018; Aryastami, 2017).
182
Mutiara, H., Kurniawan, A. and Susanto, L.
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0013667900003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 182-194
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

The causes of stunting consist of several factors,
namely basic causes, underlying causes and
immediate causes. Basic causes are adequate
household quality support (such as housing,
education, work, income and technology), socio-
cultural, economic and political conditions.
Underlying causes include household food security
conditions, parenting patterns, sanitation and health
of the household environment, and health services.
Immediate causes include food intake and infectious
diseases.
9
One of the infectious diseases is caused by
intestinal parasites which often affect children,
especially in tropical areas such as Indonesia
(Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia,
2018; Aryastami, 2017; Torlesse, 2016; Setiawan,
2018).
Intestinal parasitic infections can be caused by
intestinal protozoa and intestinal worms. The
intestinal protozoa that are often found are Giardia
lamblia, Blastocystis hominis, Entamoeba and
Cryptosporidium. The prevalence of intestinal
protozoan infections is still relatively high. Research
in Ethiopia on 500 children aged 1 to 5 years found a
prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections of 47%
and the highest was Giardia lamblia infection (22 %)
(Osman, 2020). Children with giardiasis are 3.5 times
more likely to be malnourished than those without
Giardia lamblia infection (Osman, 2020). Likewise,
in Mexico, 34% of children aged 6 months to 5 years
were infected with intestinal parasites, namely
Ascaris lumbricoides, Entamoeba histolytica and
Giardia lamblia (Gutiérrez-Jiménez, 2019). Research
in Bekasi, West Java, Indonesia also provided data on
the prevalence of Blastocystis hominis at 60.8%,
Giardia lamblia at 33.8% and Entamoeba histolytica
at 1.4% (Winita, 2016).
Intestinal protozoal infections are generally
water-borne diseases that are transmitted via the oral-
fecal route (Mahardianti, 2020). Transmission can
occur easily, especially in areas with low sanitation
and hygiene conditions. This causes high morbidity
rates which of course affect the sufferer's quality of
life. Manifestations of this disease can include
nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea
(Pramestuti, 2017). Intestinal protozoal infections can
cause problems with digestion and absorption of
nutrients. This is partly due to shortening and
dystrophy of the intestinal microvillus or the
formation of ulcers (Herbowo, 2016).
Intestinal worm infections are most often caused
by soil transmitted helminth (STH) worm parasites.
Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, and hook
worms ( Necator americanus and Ancylostoma
duodenale ) are nematodes that include STH
(Jourdan, 2018; Sutanto, 2008). Intestinal worm
infections generally are chronic and asymptomatic.
This parasite can affect the intake, digestion,
absorption and metabolism of food in the host's body.
The World Health Organization estimates that
worldwide STH infection sufferers are more than 1.5
billion people (24%). More than 600 million school-
age children and 270 million preschool-age children
live in areas with intensive parasite transition and are
therefore at high risk of infection (WHO, 2020). In
500 children aged under 5 years in Ethiopia, 15%
were infected with Ascaris lumbricoides (Osman,
2020). The prevalence in Indonesia varies, but is still
in the high range. Research conducted by Mutiara in
2014 at several state elementary schools in one sub-
district in the West Java region, found that the
prevalence of STH infection was 23.2% (Mutiara,
2014). Meanwhile, the prevalence in one of the state
elementary schools located in South Lampung
Regency was 43.1%. This infection is included in
neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) so attention
regarding its management, including management
and elimination efforts, is not yet optimal.
Research regarding risk factors for
stunting has
been widely carried out, however regarding intestinal
parasitic infections as one of the determinants is still
limited and still debated (Hailegebriel, 2018; Yoseph,
2020). In addition, treating intestinal parasitic
infections has not been a priority in implementing
stunting management programs in Indonesia.
Therefore, it is necessary to carry out systematic
reviews and meta-analysis research to synthesize data
related to the influence of intestinal parasite
infections on stunting in children.
2 THEORETICAL REVIEW
2.1 Child Nutritional Status
Stunting is a child health problem, not only in the
world, but also in Indonesia. Stunting is nutritional
status based on body length (PB) or body height (TB)
index according to age. This indicator provides an
indication of chronic nutritional problems. Another
anthropometric indicator for assessing the nutritional
status of toddlers is weight for height (WW/TB),
which provides an indication of acute nutritional
problems. The BB/TB and BMI/U indicators can be
used to identify thin and fat. The problem of being
thin and fat at an early age can result in the risk of
various degenerative diseases in adulthood (Ministry
of Health of the Republic of Indonesia, 2018).
Anthropometry is the measurement of the human
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study
183

body, while nutritional anthropometry relates to
various measurements of body dimensions and body
composition as well as age and nutritional levels. The
nutritional status assessment categories are presented
in table 1.
In growth there are 4 interrelated periods, namely
fetus, infancy, childhood and puberty. Age 6 to 24
months determines linear growth. Inadequate
nutrition can cause irreversible damage and lead to
impaired physical and cognitive growth. The first
thousand days have been declared a critical period for
nutritional interventions and addressing problems
that interfere with nutritional adequacy (Budge,
2019). The combined effects and interactions of
infection, environmental and dietary factors as
determinants of stunting in children have long been
considered very important.
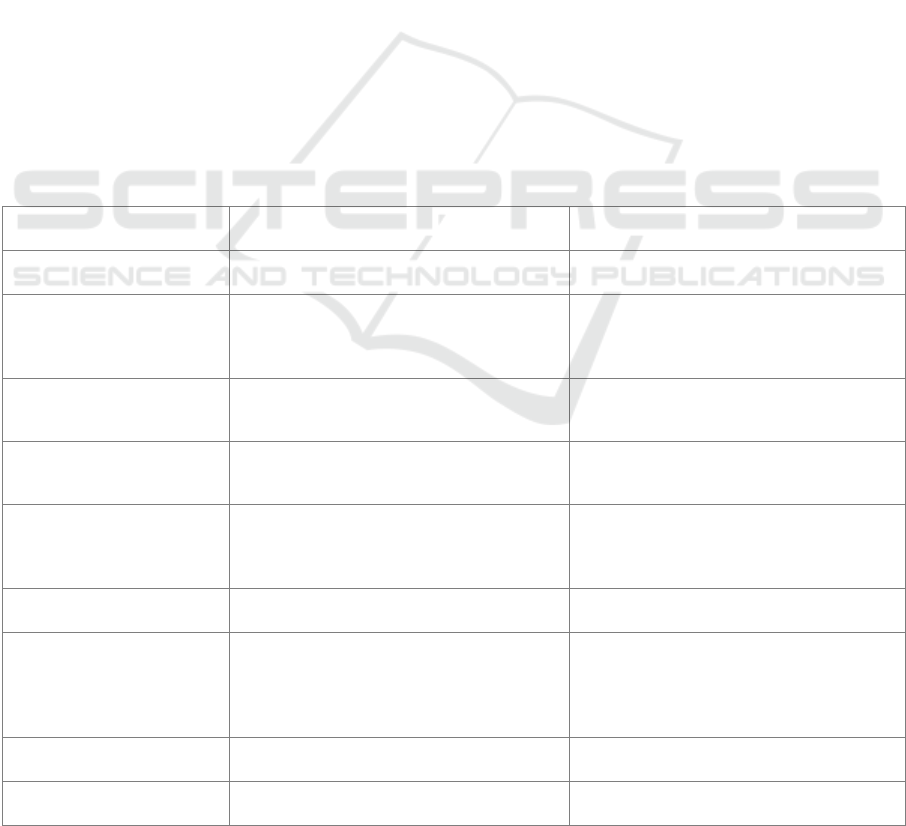
Table 1: Categories and Thresholds for Children's Nutritional Status Based on Index (Minister of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia, 2020)
Index Nutritional Status Category Threshold (Z-score)
Body weight according to age (WW/U)
Children aged 0-60 months
Extremely underweight <-3 SD
Underweight -3 SD to <-2 SD
Normal weight -2 SD to +1 SD
Risk of being overweight > +1 SD
Body length according to age (PB/U) or
Height according to age (TB/U)
Children aged 0-60 months
Very Short (severely stunted) <-3 SD
Short (stunted) -3 SD to <-2 SD
Normal -2 SD to +3 SD
Tall > +3 SD
Body weight according to body length
(BB/WW) or according to height
(WW/TB)
Children aged 0-60 months
Malnutrition (severely wasted) <-3 SD
Malnutrition (wasted) -3 SD to <-2 SD
Good (normal) nutrition -2 SD to +1 SD
Risk of overnutrition (possible
risk o
f
overwei
g
ht)
> +1 SD to +2 SD
Over nutrition (overweight) > +2 SD to +3 SD
Obesity (obese) > +3 SD
Body mass index according to age
(BMI/U)
Children aged 0-60 months
Malnutrition (severely wasted) <-3 SD
Malnutrition (wasted) -3 SD to <-2 SD
Good (normal) nutrition -2 SD to +1 SD
Risk of overnutrition (possible
risk o
f
overwei
g
ht)
> +1 SD to +2 SD
Over nutrition (overweight) > +2 SD to +3 SD
Obesity (obese) > +3 SD
Body mass index according to age
(BMI/U)
Children aged 5-18 years
Malnutrition (severe thinness) <-3 SD
Malnutrition (thinness) -3 SD to <-2 SD
Good (normal) nutrition -2 SD to +1 SD
Over nutrition (overweight) +1SD to +2 SD
Obesity (obese) > +2 SD
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
184

Diarrhea or parasitic infections are infections that
occur frequently and repeatedly and are associated
with an increased risk of stunting (Milward, 2017).
Exposure to pathogens can cause disruption of
intestinal structure and function. This condition is
known as environmental enteric dysfunction (EED)
which is characterized by villous atrophy of intestinal
mucosal cells, crypt hyperplasia, increased
permeability, and inflammatory cell infiltration. This
EED condition can result in disruption of the
intestinal immune response, reducing the delivery,
absorption and utilization of nutrients resulting in a
state of nutritional deficiency (Budge, 2019; Dewey,
2011).
2.2 Intestinal Parasitic Infections
Soil transmitted helminthiasis is an intestinal worm
infection that often occurs in children in tropical
areas, including Indonesia, especially in areas with
poor sanitation. This group of intestinal worms
requires moist and warm soil as a medium for the egg
stage to develop into an infective stage, either
infective eggs or infective larvae. Intestinal worms
included in this group are Ascaris lumbricoides,
Trichuris trichiura and hook worms (Ancylostoma
duodenale and Necator americanus) (Hadidjaja,
2011).
Protozoa are eukaryotic unicellular
microorganisms that resemble animals, are
heterotrophs and live as parasites in the bodies of
other organisms. Protozoa can survive in a free
environment by forming cysts, and in the body other
organisms move using means of movement in the
form of pseupodia, cilia and flagella. Protozoa is a
subdivision that comes from Kingdom Protista.
Based on movement or locomotion, the Protozoa
subdivision is divided into 4 phyla, namely
Sarcomastigophora, Ciliophora, Apicomplexa, and
Microspora. Protozoa can infect the intestines, blood,
lung tissue and other extraintestinal tissues. The
species of intestinal protozoa in hosts (humans),
especially in children, that are often found include
Entamoeba sp, Giardia sp, Blastocystis sp,
Balantidium sp, and Cryptosporidium sp.
Laboratory examination is an important aspect in
diagnosing parasitic diseases. Placing fixation labels,
use of special containers, where specimens are
collected and how they are disposed of need to be
considered. Fresh feces specimens are collected in a
clean container, with a wide mouth and a tight lid to
prevent spillage and maintain humidity. Stool
specimens should not be mixed with water and/or
urine. Each specimen sent to the laboratory must be
accompanied by the patient's name, identification
number, name of the doctor or specimen sender, date
and time of specimen collection. The specimen must
also be accompanied by a request form for the type of
laboratory examination requested. It is better if
accompanied by information about possible
diagnoses or certain characteristics, such as travel
history (Hadidjaja, 2011; Garcia, 2016).
To examine parasites in feces, it is recommended
to collect three specimens sent on different days or
one day apart but not more than 10 days apart. Two
specimens were collected after normal defecation
while another specimen was collected after laxative
administration. If you suspect intestinal amoebiasis
infection, six specimens should be taken. Liquid stool
specimens should be examined within 30 minutes of
the stool being passed while soft stools should be
examined within 1 hour. If this is not possible, then
the specimen must be given a preservative. Solid
stool specimens may be examined at any time within
24 hours of the stool being passed. Preservatives that
can be used include formalin, merthiolate
(thimerosal) iodine formalin (MIF), sodium acetate-
acetic acid-formalin (SAF), Schaudinn's solution and
polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (Garcia, 2016).
Specimen delivery must be carried out using a
double container. The inner container is an aluminum
cylinder with a screw cap which is then wrapped in
cotton to maintain moisture and absorb materials that
may escape due to leaks. Next, the container is placed
in an outer container made of cardboard.
Intestinal parasite examination methods that can
be used are direct preparation, concentration method
and removal preparation with permanent smear.
Direct preparations were made by mixing about 2 mg
of feces with a drop of 0.85% salt solution, then
covered with a 22x22 mm glass cover. The entire
surface of the cover glass was examined
systematically using 100x magnification and low
light intensity then with medium magnification
(400x). The concentration method is part of the
routine parasite examination procedure to detect
parasites that may not be found in a direct preparation
examination. There are two types of concentration
procedures, namely flotation and sedimentation. This
method is designed to separate protozoa and worm
eggs from feces through differences in specific
gravity. Permanent smear preparations not only allow
the examiner to store the preparation permanently,
but can also be used for further consultations. This
preparation is recommended for every stool sample
examination. There are several smear techniques,
namely the Heidenhain method of iron hematoxylin,
trichrome or modified iron hematoxylin.
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study
185
In providing therapy for intestinal worm
infections, especially STH, in children over 2 years,
WHO recommends albendazole 400 mg and
mebendazole 500 mg given as a single dose orally.
For children aged 1 year to 2 years, the dose of
Albendazole that can be given is 200 mg. However, it
seems that these therapy guidelines need to be
updated considering the large number of studies
regarding this anthelmintic regimen. It is now known
that benzimidazole drugs have limitations, namely
their low efficacy against Trichuris trichiura and
hookworms, as well as the emergence of the risk of
resistance. So now multiple drug therapy appears to
be a potential solution.
Moser's research on the combination of
anthelmintics for hookworm infections showed that
the administration of a three-drug regimen
(albendazole 400mg, pyrantel pamoate 20mg/kgBB,
and oxantel pamoat 20mg/kgBB) had the highest cure
rate (84.1%) compared to administration of
albendazole and oxantel pamoate or administering
pyrantel pamoate and oxantel pamoate at the same
dose. Studies in the Philippines also showed that
ivermectin plus albendazole had higher efficacy
against T. trichiura infections than monotherapy.
Other studies have also shown the benefit of dual drug
therapy including administration of oxantel and
tribendimidine in the treatment of infections with T.
trichiura and other STH species (Brooker, 2018;
Eshetu, 2020).
Therapy for intestinal protozoal infections
consists of several options. In Giardia lamblia
infection, metronidazole is an effective treatment.
Until 2002, treatment for cryptosporidiosis was
unsatisfactory, but now it has shown improvement.
Of the many drugs screened for having
anticryptosporidial activity, it is known that
paromomycin and nitazoxanide show clinical
improvement in patients (Farthing, 2006). In the
treatment of amoebic colitis, nitroimidazole
derivatives are the drugs of choice because they are
very effective in treating the trophozoite form.
Metronidazole can be given at a dose of 750-800 mg,
three times a day for 5-10 days, or tinidazole at a dose
of 2 g every day for 3 days. However, this drug has
little effect on amoebic cysts so it is recommended
that treatment be followed by administration of
paromomycin or diloxanide furoate which work on
organisms in the lumen (Farthing, 2006). These
procedures are summarized in table 2.
Table 2: Therapy for Diarrhea Caused by Protozoa (Farthing, 2006)
Intestinal Protozoa Therapy Alternative therapy
Giardia lamblia Metronidazole 1 g/dose for 3 days Tinidazole 2 g single dose
Cryptosporidium parvum
Nitazoxanide 500 mg twice daily for 3–
14 days
Albendazole 400 mg twice daily for 7–
14 days
Paromomycin 500 mg four times a day
for 7
–
14 days
Cyclospora cayetanensis
Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim 160 mg
and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg) twice
daily for 7 days
Ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily for 7
days
Isospora belli
Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim 160 mg
and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg) mg four
times a da
y
for 10 da
y
s
Ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice a day for 7
days
Entamoeba histolytica
Metronidazole 750 mg three times a day
for 5 days
Diloxanide furoate 500 mg three times a
day for 10 days
Paromomycin 25-35 mg/kgBB three
times a day for 7-10 days
Balantidium coli
Metronidazole 400 mg three times a day
for 10 days
Tetracycline 500 mg four times a day for
10 days
Blastocystis hominis
Nitazoxanide 500 mg twice a day for 3
days
Metronidazole 800 mg three times a day
for 5-10 days
Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim 160 mg
and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg) twice a
day for 7 days
Encephalitozoon intestinalis Albendazole 400 mg twice a day for 14-
28 days
Not yet available
Enterocytozoon bieneusi
Albendazole 400 mg twice a day for 28
days
Fumagillin 60 mg daily for 14 days
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
186
3 METHODS
The research was conducted in June 2021 – July
2021. Data or literature collection was carried out
through electronic media, namely in the form of
published and unpublished results of primary
research regarding intestinal parasitic infections on
the incidence of stunting in children. Literature
searches via electronic media were carried out online
via the Unila, UI and USU repositories, as well as via
PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, Hindawi,
Cochrane library, DOAJ, JSTOR, Public Library of
Science (PLoS). Some of the keywords used are
intestinal parasitic infection, soil transmitted
helminth infection, intestinal protozoan, stunting,
growth disorders, and children. Key words used in
searching through the repository were intestinal
parasitic infections, soil transmitted helminths,
intestinal protozoa, short stature, stunting and
children.
4 RESULT
Article searches were carried out using keywords and
Mesh terminology for each PICO component using
the Quatation mark "", Boolean operators "OR" and
"AND". The results of searching all sources using
keywords obtained 1042 journals and 2 theses.
Articles that experienced duplication were deleted
and then filtered based on the title and 182 suitable
journals were obtained. Then verification was carried
out through abstracts that met the inclusion criteria
and 21 suitable journals were obtained. Then content
verification was carried out and 9 appropriate
journals were obtained. Then an in-depth review was
carried out and it was found that 3 studies were not
relevant because the research data was prevalence
data and compared data between regions, not between
variables, so they did not meet the inclusion criteria.
Therefore, 6 articles were obtained that could be
analyzed in the meta-analysis. A description of the
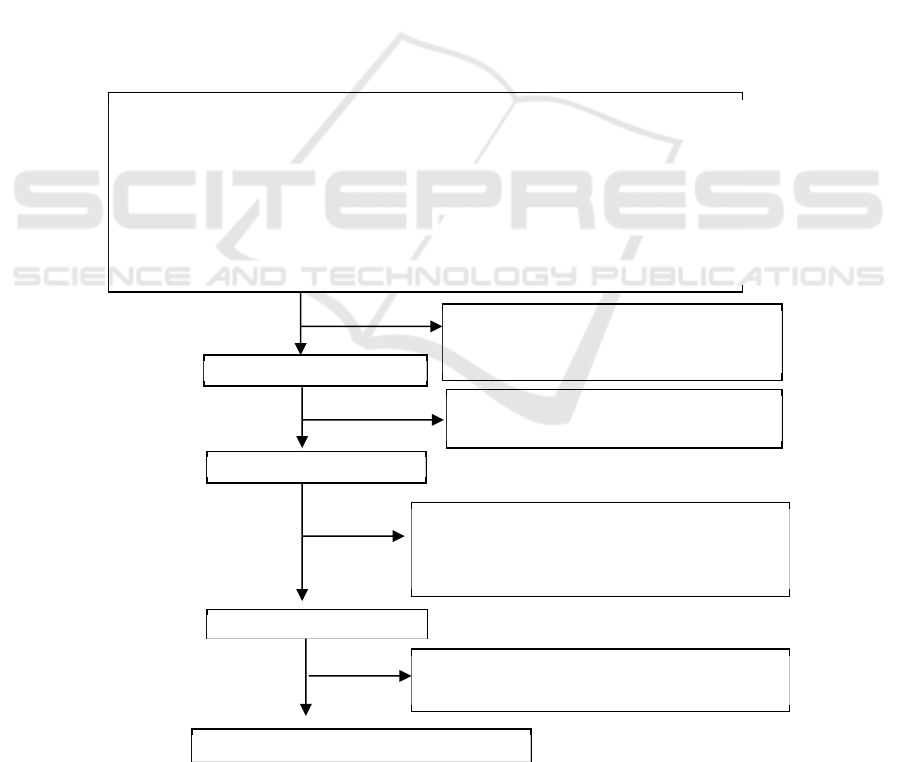
research search results is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1. PRISMA diagram of article selection flow
Literature searching (n = 1044)
Published (n = 1042) Unpublished (n = 2)
PubMed: 59 Repository UI: 0
Google Scholar: 655 Repository Unila: 1
Cochrane Library: 16 Repository USU: 1
DOAJ: 0
Hindawi: 5
Science Direct: 293
PLOS: 3
JSTOR: 11
Title’s reviewed:
Unrelevan studies (n= 858)
Double article (n=4)
Title
(
n = 182
)
Abstract’s reviewed:
Unrelevan studies (n= 161)
Abstract (n=21)
Full article (n=9)
Full article’s reviewed:
Not open access (n=4)
Unrelevan studies (n= 8)
Unrelevan dependent’s variable
Studies analysis (n=6)
Unrelevan studies 3 because:
Unrelevant data (only prevalence)
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study
187
Data analysis was carried out using review
manager 5.4 software. Selected articles were
published by PLOS, BioMed Central Public Health
(BMC), Sage Open medicine, and Journal of
Epidemiology and Public Health (JEPH). The
research was conducted in Nangapanda District,
Indonesia, Southern Ethiopia, Bahir Dar Ethiopia,
Southwest Ethiopia, and Pinrang District, South
Sulawesi, Indonesia. All subjects analyzed were 5,687
children aged 6 months to 18 years. The entire study
used a cross sectional design. The characteristics of
the research data in the article are presented in table 3.
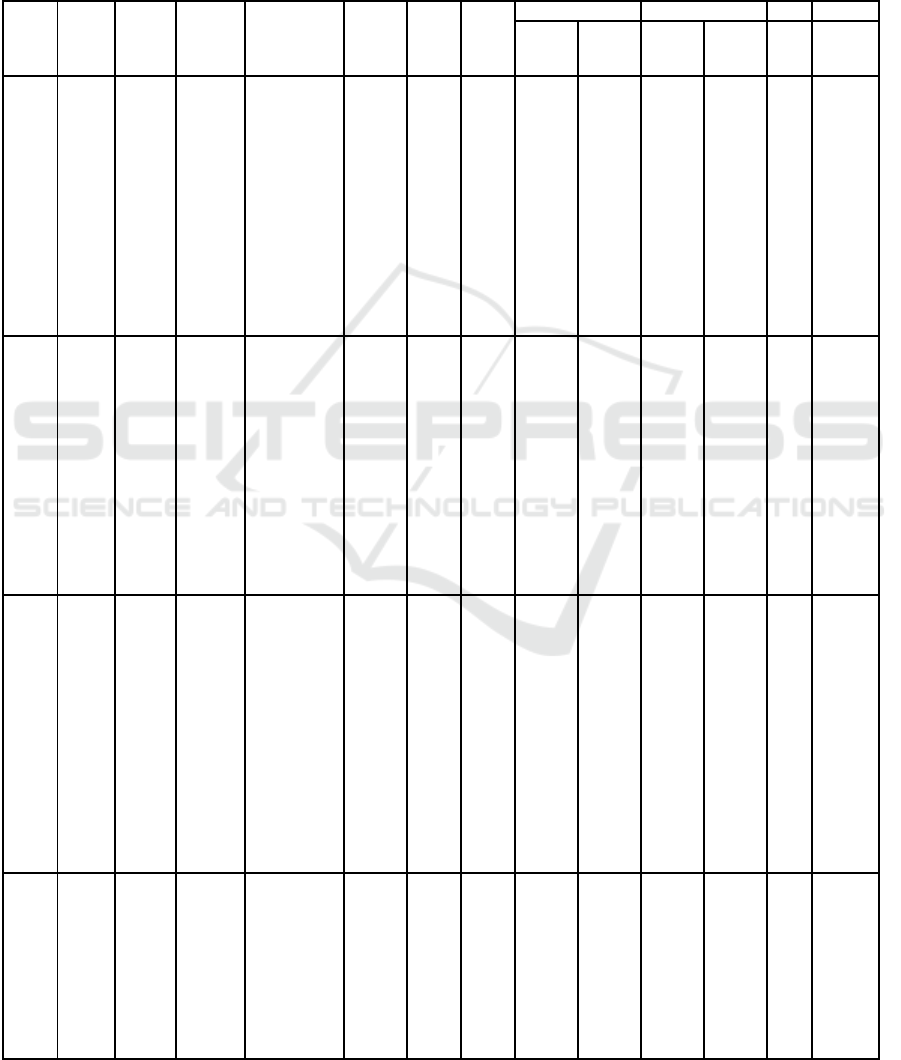
Table 3. Characteristics of Research Data
S
ource Type Year
of
publi-
cation
Writer Title Loca-
tion
n Sub-
ject's
age
Inspection Prevalence aOR 95%CI
Stun-
ting
Para-
site
Stun-
ting
Para-
site
PLOS
J
ournal
2021 Djuardi
Soil-
transmitted
helminth
infection,
anemia, and
malnutrition
among
preschool-
age children
in
Nangapand
a
subdistrict,
I
ndonesia
Indo-
nesia
393
1-5
yrs
HAZ
score
Kato
Katz
Metho
d
40.2%
58.8% 1.23
0.63-
2.39
PLOS
J
ournal
2017 Grimes
Sanitation,
hookworm,
anemia,
stunting,
and wasting
in primary
school
children in
southern
Ethiopia:
Baseline
results from
a study in 30
s
chools
Ethiop
ia
3686
5-18
yrs
HAZ
score
Kato
Katz
Metho
d
28% 23% 0.99
0.79-
1.25
BMC
J
ournal
2018 Hailege
briel
Undernutriti
on,
intestinal
parasitic
infection
and
associated
risk factors
among
selected
primary
school
children in
Bahir Dar,
Ethiopia
Ethiop
ia
382
7-13
yrs
HAZ
score
Forma
lin-
Ether
concen
tration
metho
d
18.3% 52.4% 1.1 0.65-
1.86
S
AGE
J
ournal
2020 Mekonn
en
Soil-
transmitted
helminth
infections
and
nutritional
status of
school
children in
g
overnment
Ethiop
ia
404
6-14
yrs
HAZ
score
Direct
wet
mount
and
McMa
ster
metho
ds
21% 55% 2 1.2-
3.33
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
188
elementary
schools in
Jimma
Town,
Southwester
n Ethiopia
JEPH
J
ournal
2020 Muslim
ah
Multilevel
Analysis
Association
of Soil
Transmitted
Helminths
and Stunting
in Children
Aged 6-12
Years Old in
Pinrang
District,
South
Sulawesi
Indone
sia
200
6-12
yrs
HAZ
score
Stool
exami
nation
(not
explai
ned
further
)
46.5% 41% 2.11 1.11-
4.01
BMC
J
ournal
2020 Joseph The high
prevalence
of intestinal
parasitic
infections is
associated
with
stunting
among
children
aged 6–59
months in
Boricha
Woreda,
Southern
Ethiopia: a
cross-
sectional
s
tudy
Ethiop
ia
622 6
mont
hs-5
years
HAZ
score
Direct
wet
mount
and
Kato
Katz
metho
ds
39.3% 48.7% 2.18 1.36-
3.49
Note: HAZ = Height-for-age-z-score with classification based on WHO guidelines
Analysis of variations between studies is aimed at
determining whether the studies are heterogeneous or
homogeneous. Between studies it is said to be
homogeneous if the p value in the heterogeneity test
is greater than 0.05 or the intuitive index (I
2
) and Tau
values are small. The results of the analysis show that
I
2
of this analysis is 67%, meaning that the variation
between studies is heterogeneous, so the model used
to calculate the combined effect is the random effect
model.
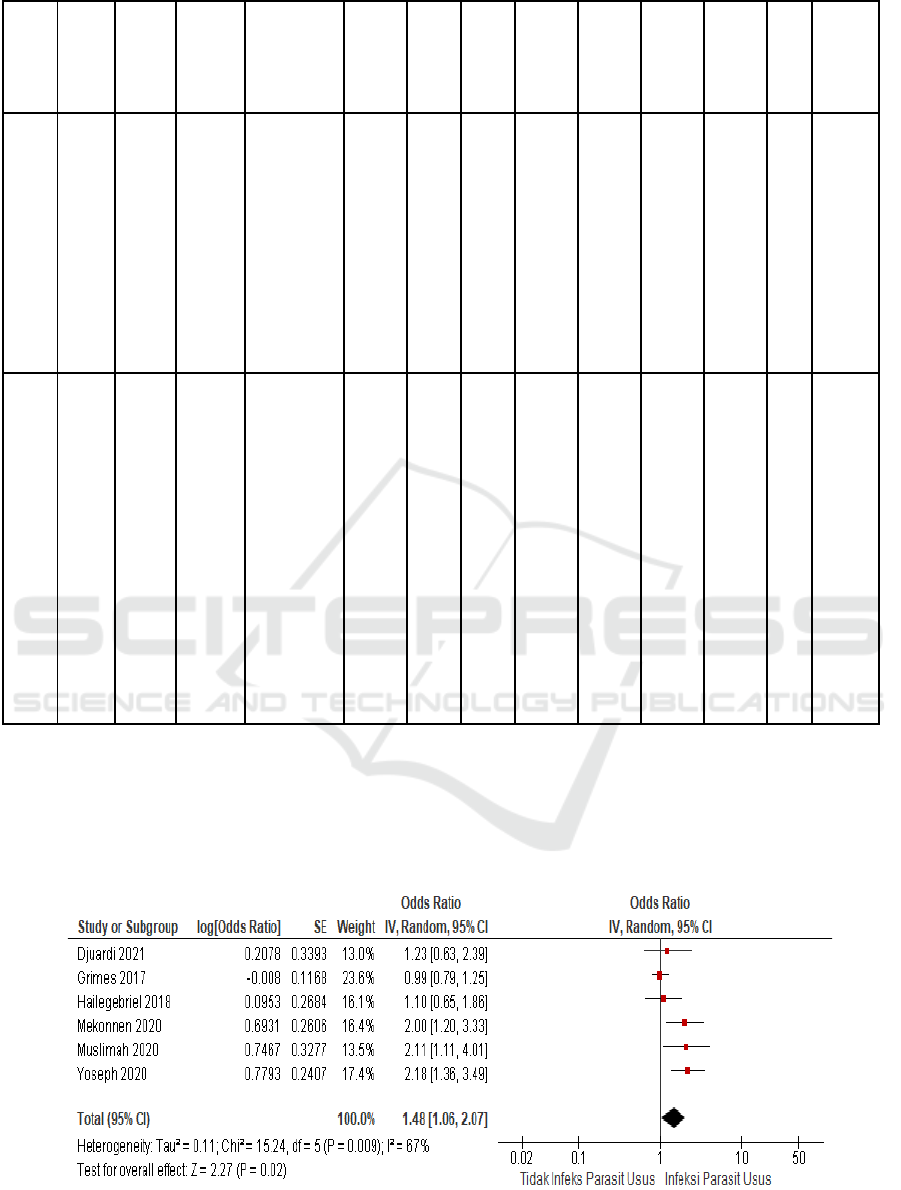
Figure 2. Forest Plot Random Effect Model.
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study
189
The forest plot shows the odds ratio for each study
with its confidence interval (horizontal line). The
combined odds ratio is depicted in a diamond shape
(black). The combined effect value from the results of
the analysis of these six studies was 1.48 with a 95%
confidence interval of 1.06-2.07. The combined
effect also produces a Z value of 2.27 and a p value
of 0.02. This means that there is an influence between
intestinal parasitic infections on the incidence of
stunting in children. Children with intestinal parasitic
infections are 2.27 times more stunted than children
without intestinal parasitic infections.
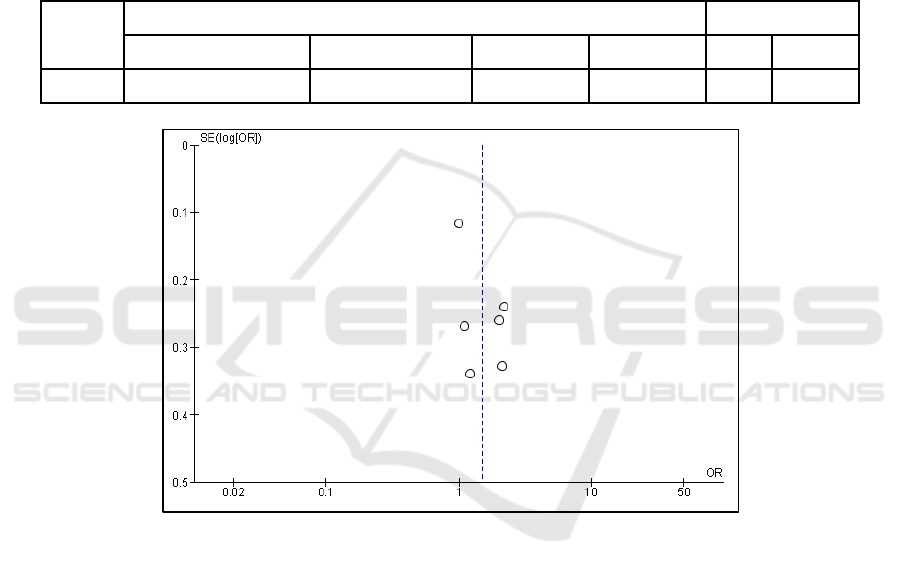
Funnel plots can be used to determine research
variation and publication bias. If the number of plots
on the left and right sides is balanced and the distance
between plots is balanced, it means there is no
publication bias. This means that if the analysis is
carried out on different populations, times, places and
conditions, the results will remain consistent. The
results of this meta-analysis show a balanced funnel
plot.
Table 4. Effect size of combined studies
Model
Effect Size and 95%CI Si
g
nificance test
Number of Research Combined Effects Lower limit Upper limit Z p
Rando
m
6 1.48 1.06 2.07 2.27 0.02
Figure 3. Funnel Plot
5 DISCUSSION
Many studies have been conducted regarding
intestinal parasitic infections and stunting, but have
produced varying results. Therefore, statistical
analysis was carried out using meta-analysis to prove
the quality of each research so that new quantitative
data could be obtained and more accurate conclusions
could be drawn.
These six studies were analyzed involving 5,687
research subjects and the combined effect results
concluded that there was an influence between
intestinal parasitic infections on the incidence of
stunting in children with an OR of 1.48 (CI 95%:
1.06-2.07). In determining stunting status, all
researchers used the same method, namely based on
height-for-age-z-score which was then classified
according to WHO guidelines. Intestinal parasite
examination is carried out using stool specimens and
then examined in the laboratory. Examination
methods in general are direct wet mount and the Kato
Katz method, except for the Hailegebriel study which
used the Formalin-Ether concentration method and
Mekonnen used the McMaster method (Hailegebriel,
2018; Yoseph, 2020; Mekonnen, 2020; Grim, 2017).
In research in Nangapanda, there were 58.8% of
intestinal parasitic infections which were
predominantly caused by Ascaris lumbricoides
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
190

(47.4%) followed by Trichuris trichiura (36.8%) and
hookworm (9.2%). A total of 28.7% of subjects
experienced multiple infections, namely 20.6%
coinfected with Ascaris lumbricoides with Trichuris
trichiura, 2.2% coinfected with Ascaris lumbricoides
with hookworm and 5.9% coinfected with the three
species. A single parasitic infection has been proven
to be related to the incidence of stunting. The same
thing with moderate intensity infections. However,
this is not the case with multiple parasitic infections,
mild and severe intensity. How this happens has not
been explained (Djuardi, 2021). The high prevalence
of A. lumbricoides and T. trichiura infections in this
study indicates that oral-fecal transmission is more
common than transmission through skin penetration
(in hookworm infections) especially in children.
Other factors examined in this study were difficult
access to health centers and/or midwives (81.9%),
lack of access to water sources (13.8%) and poor
sanitation (87.3%) which of course could contribute
to the high incidence of intestinal parasitic infections
and nutritional problems among children in the area
(Djuardi, 2021).
Research conducted by Grimers showed that the
prevalence of hookworm infection was 18%, Ascaris
lumbricoides 4.8%, Trichuris trichiura 0.6% and S.
mansoni 0.3%. The high number of hookworm
infections in this study is known to be related to
inadequate sanitation, namely the absence of latrines
and open defecation. Apart from that, data was also
obtained on the prevalence of anemia of 23%,
stunting of 28% and wasting of 14%. Statistically,
there is no significant relationship between sanitation
and hookworms or between hookworms and anemia,
stunting or wasting (Grimes, 2017).
In Hailegebriel's study, 52.4% of subjects were
positive for one or more intestinal parasites. The
prevalence of multiple intestinal parasitic infections
is quite large, namely 6.3%. The most frequently
detected intestinal parasitic infections were E.
histolytica/dispar (16.8%), hookworm (14.7%) and
A. lumbricoides (13.6%). Based on the multivariate
analysis that was carried out, the predictors of
intestinal parasitic infection in this study were
unclean nails, irregular hand washing habits and
maternal education.
Nutritional problems occurred in 41.6% of
subjects, consisting of 18.3% stunting, 26.7% wasting
and 25.9% were underweight. Almost half of the
study subjects experienced 2 or more nutritional
problems at one time. Of the 18.3% of subjects who
experienced stunting, 20% of them experienced
severe stunting (HAZ<-3SD). Based on further
analysis, it is known that subjects born to families
with a monthly income of less than 1500 birr (around
Rp. 479,000.00), the frequency of eating a maximum
of 3 times in 1 day and the presence of intestinal
parasitic infections are the main predisposing factors
for malnutrition in children (Hailegebriel, 2018).
Mekonnen's research showed that research
subjects were infected with 8 species of intestinal
parasites, namely Trichuris trichiura, Ascaris
lumbricoides, hookworm, H.nana, E.histolytica,
E.vermicularis, G.lamblia, and S.mansoni . The
highest prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections is
infection due to mild intensity STH, namely 55% with
the most infections caused by T. trichiura (34.9%).
Ascaris lumbricoides and hookworm were detected in
28.5% and 11.4%. The highest STH infection
occurred in children with dirty nails (63.5%).
Children who have the habit of defecating in the open
(52.7%) have a 1.9 times higher risk of developing
STH infection. Likewise, children who are
accustomed to not wearing footwear have a 2.2 times
higher risk of being infected with hookworms than
children who wear shoes. The prevalence of stunting
is 21%. The results of multivariate analysis show that
T. trichiura infection is the main predictor of stunting
in children (Mekonnen, 2020).
Muslimah research in 2020 gave results of a
stunting prevalence of 46.5% and intestinal worm
infections of 41% in children aged 6 to 12 years.
There is an effect of worm infections on the incidence
of stunting where children with worm infections have
a 2.11 times greater probability of experiencing
stunting than children without intestinal worm
infections (Muslimah, 2020).
Yoseph's research stated that the total prevalence
of intestinal parasitic infections was 48.7%,
consisting of Giardia lamblia infections (10.45%),
Entamoeba hystolitica (4.66%), Ascaris lumbricoides
(10.77%), hookworms (7.88%). %), Trichiura
trichiura (6.1%), Strongyloides stercoralis (1.6%)
and Taenia sp (1.3%). About a quarter (22%) of
children were moderately infected and 5.94% had
multiple intestinal parasitic infections. The
prevalence of stunting is 39.3% and 3.4% of them
experience severe stunting. Other nutritional
problems are underweight 24% and wasting 11.6%.
The prevalence of stunting in children infected with
intestinal parasites (59.4%) was significantly higher
than the prevalence in uninfected children (20.6%).
Almost all (92.53%) children infected with Ascaris
lumbricoides experienced stunting. Likewise, in other
intestinal parasitic infections, such as in people with
hookworm infections, the prevalence of stunting is
89.79%, in G. lamblia infections it is 86.20%, E.
histolytica is 72.24%, T. trichiura is 71%, Taenia sp.
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study
191

By 50% and Strongyloides stercoralis by 50%.
Statistically, there is a significant relationship
between stunting and infection with hookworms,
G.lamblia , E.histolytica and T.trichiura . Children
infected with intestinal parasites have a 5.45 times
greater risk of experiencing stunting compared to
those who are not infected (Yoeph, 2020).
Based on the results of these six studies, it is clear
that the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections is
still high. Intestinal parasitic infections occur in
various ages of children, even in babies as young as 6
months (Yoseph, 2020). The availability of adequate
sanitation facilities is very important because
otherwise it will be possible for contamination of
water and food with human waste, especially if the
habit of defecating in open fields continues. The habit
of not using footwear can occur because there is still
a lack of public knowledge and awareness about how
this intestinal parasite can infect humans.
Intestinal parasitic infections can cause various
impacts on the host. Intestinal worms can reduce a
child's appetite and cause competition between hosts
and parasites. Lack of carbohydrates, protein,
nutrients, and blood can reduce the adequacy needed
by the body, thereby reducing the quality of human
resources (Muslimah, 2020; Jourdan, 2018).
Intestinal protozoal infections often cause complaints
of diarrhea. Research shows that 25% of stunting
cases are associated with five or more episodes of
diarrhea (Millward, 2017). Exposure to these
pathogens can cause disruption of intestinal structure
and function called environmental enteric
dysfunction (EED). This condition is a reversible
condition, characterized by villous atrophy of
intestinal mucosal cells, crypt hyperplasia, increased
permeability, and inflammatory cell infiltration. This
can result in disruption of the intestinal immune
response, reducing the delivery, absorption and
utilization of nutrients resulting in a state of
nutritional deficiency. A state of nutritional
deficiency can then result in damage to epithelial
tissue renewal, maturation and proliferation of
intestinal cells and pancreatic b cells, thus disrupting
linear growth (Budge, 2019).
Increased intestinal permeability can be
determined from the lactose/mannitol ratio (Budge,
2019). Research shows that this ratio tends to be
higher in children with infections, especially
Cryptosporidium infections sp. and Giardia sp
(Budge, 2019). Choudhry's research has shown that
C. parvum infection can alter intestinal barrier
function by reducing the integrity of the intestinal
epithelium through reduced TER (Transepithelial
Electrical Resistance) associated with
downregulation of the claudin-4 protein (Choudry,
2021). In giardiasis there is malabsorption of fat,
xylose and vitamin B12. Mannose-binding lectin
mediates parasite adhesion to brush border
enterocytes. Increased apoptosis, loosening of
enterocyte adhesions at tight junctions, and damage
to the enterocyte membrane lumen contribute to
impaired digestion and nutrient absorption (Wright,
2012).
The six studies above also provide results that the
prevalence of nutritional problems in children is still
high, namely in the range of 18.3% to 46.5%.
Nutritional problems detected in the research subjects
included underweight, thinness, stunting, wasting and
anemia. Underweight, can also be called
underweight, is the child's nutritional status based on
body weight for age with a Z score of -3SD to -2SD.
Stunting is short stature, a child's nutritional status
based on length or height per age with a Z score of -
3SD to -2 SD. Wasting, which can also be called
undernutrition, is a child's nutritional status based on
weight per body length, weight per child's height, or
body mass index (BMI) per child aged 0 to 60 months
with a Z score of -3SD to -2SD . Thinnes, also called
malnutrition, is a category of children's nutritional
status based on BMI per child aged 5 to 18 years with
a Z score of -3SD to -2SD (Minister of Health of the
Republic of Indonesia, 2020).
Monitoring intestinal parasitic infections and
children's nutritional status is very important to pay
attention to because it greatly affects their health
condition and academic achievement (Hailegebriel,
2018). Apart from carrying out nutritional
interventions, it is also necessary to consider the
importance of carrying out environmental
interventions including water, sanitation and hygiene
to prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases,
including intestinal parasitic infections (Grimes,
2017).
5.1 Research Limitations
In this research there are still several limitations,
including that this research only accesses free
published journals. Sources for unpublished articles
are still limited because they are limited to digital
searches due to the COVID 19 pandemic which still
limits activities. Apart from that, this research is
limited to analyzing the relationship between only
two variables, namely intestinal parasitic infections
and the incidence of stunting in children. There are
still other variables such as intensity of parasite
infection, Hb levels, body weight and body mass
index that can be analyzed in further research.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
192

6 CONCLUSSION
Research that meets the criteria to be tested in meta-
analysis is six articles (journals) with heterogeneous
variations. The effect size used is the odds ratio
where the combined effect results show a p value
<0.05, which means there is an influence between
intestinal parasitic infections, namely intestinal worm
infections and intestinal protozoa on the incidence of
stunting in children. Further research is needed
regarding other nutritional status variables such as
underweight, thinness, and wasting. Apart from that,
it is also necessary to add reading sources, both text
books and related journals, to add references for
further research.
REFERENCES
Aryastami NK. Policy Study and Overcoming Stunting
Nutrition Problems in Indonesia. Health Researcher
Bul . 2017;45(4):233-240.
Brooker SJ. Soil-transmitted helminth treatment: multiple-
drug regimens. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(7):698-699.
Budge S, Parker AH, Hutchings PT, Garbutt C.
Environmental enteric dysfunction and child stunting.
Nutr Rev. 2019;77(4):240-253.
CDC. Soil transmitted helminthiases. Available from:
https://www.who.int/health-topics/soil-transmitted-
helminthiases#tab=tab_3
CDC. domestic intestinal parasites. Available from:
https://www.cdc.gov/immigrantrefugeehealth/guidelin
es/domestic/intestinal-parasites-domestic.html#tables1
Choudhry N, Scott F, Edgar M, Sanger GJ, Kelly P.
Reversal of Pathogen-Induced Barrier Defects in
Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Contra-pathogenic
Agents. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66(1):88-104.
CPM. Mother and Child Health Profile 2020. Central
Statistic Agency. 2020;53(9):1689-1699.
Dewey KG, Mayers DR. Original Article Early child
growth: how do nutrition and infection interact? Matern
Child Nutr. 2011;7(3):129-142.
Dharma YP, Mutiara H, Suwandi JF, Setyaningrum E.
Mapping where infected students live and the
relationship between socio-economic factors and
parental knowledge level with the incidence of soil-
transmitted helminth infections in elementary school
students in Natar District, South Lampung Regency.
Medulla. 2017;7(5):134-139.
Djuardi Y, Lazarus G, Stefanie D, Fahmida U, Ariawan I,
Supali T. Soil-transmitted helminth infection, anemia,
and malnutrition among preschool-age children in
Nangapanda subdistrict, Indonesia. PLoS Negl Trop
Dis . 2021;15(6):1-16.
Eshetu T, Aemero M, Zeleke AJ. Efficacy of a single dose
versus multiple dose regimen of MBZ agains
hookworm infection in a randomized open label trial.
BMC Infect Dis. 2020; 20:1-8.
Farthing MJG. Treatment options for the eradication of
intestinal protozoa. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 2006;3(8):436-445.
Garcia LS. Diagnostic Medical Parasitology. 6th ed. ASM
Press; 2016.
Grimes JET, Tadesse G, Gardiner IA, Yard E, Wuletaw Y,
Templeton MR, et al. Sanitation, hookworm, anemia,
stunting, and wasting in primary school children in
southern Ethiopia: Baseline results from a study in 30
schools. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(10):1-18.
Gutiérrez-Jiménez J, Luna-Cázares LM, Martínez-De la
Cruz L, Aquino-Lopez JA, Sandoval-Gomez D, Leon-
Ortiz AT, et al. Children from a rural region in the
Chiapas highlands, Mexico, show an increased risk of
stunting and intestinal parasitoses when compared with
urban children. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex.
2019;76(1):18-26.
Hadidjaja P, Margono SS. Basics of Clinical Parasitology.
FKUI Publishing Agency; 2011.
Hailegebriel T. Undernutrition, intestinal parasitic infection
and associated risk factors among selected primary
school children in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis.
2018;18(1):1-11.
Harjatmo TP, Par'i HM, Wiyono S. Assessment of
Nutritional Status. Ministry of Health of the Republic
of Indonesia; 2017.
Herbowo H, Firmansyah A. Diarrhea Due to Parasitic
Infections. Sari Pediatri. 2016;4(4):198.
Jourdan PM, Lamberton PHL, Fenwick A, Addiss DG.
Soil-transmitted helminth infections. Lancet.
2018;391(10117):252-265.
Mahardianti M, Kurniawan A, Sari IP. Potential
Transmission of Cryptosporidium sp. in Ciliwung River
Water, Jakarta. Indonesian Medical eJournal .
2020;8(2).
Mekonnen Z, Hassen D, Debalke S, Tiruneh A, Asres Y,
Chelkeba L, et al. Soil-transmitted helminth infections
and nutritional status of school children in government
elementary schools in Jimma Town, Southwestern
Ethiopia. SAGE Open Med. 2020; 8:1-10.
Millward DJ. Nutrition, infection and stunting: The roles of
deficiency of individual nutrients and foods and of
inflammation as determinants of reduced linear growth
of children Nutrition Research Reviews. Nutr Res Rev.
2017; 30: 50-72.
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. Stunting
Bulletin. Ministry of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia. 2018;301(5):1163-1178.
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. 2018
Riskesdas Report. 2018 Riskesdas National Report.
2018;53(9):154-165.
Minister of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. Regulation
of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Indonesia
Number 2 of 2020 concerning Child Anthropometric
Standards. Ministry of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia; 2020.
Muslimah PA, Salimo H, Dewi YLR. Multilevel Analysis
Association of Soil Transmitted Helminths and
Stunting in Children Aged 6-12 Years Old in Pinrang
Effect of Intestine Parasite Infection on Stunting in Children: A Meta-Analysis Study
193

District, South Sulawesi. J Epidemiol Public Health.
2020;5(3):372-383.
Mutiara H. Analysis of Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily
Gene Expression Profiles, Member 13B (TNFSF13B)
and Nuclear Factor-B1(NFB1) in Ascariasis Sufferers
in State Elementary Schools in Jatinangor District
[Thesis]. Bandung. 2014.
Osman KA, Zinsstag J, Tschopp R, Schelling E, Hattendorf
J, Umer A, et al. Nutritional status and intestinal
parasites among young children from pastoralist
communities of the Ethiopian Somali region. Matern
Child Nutr. 2020;16(3):1-11.
Pramestuti N, Saroh D. Blastocystis hominis: Potential
Intestinal Protozoa Causing Diarrhea. Cell J Health
Researcher. 2017;4(1):1-12.
Setiawan E, Machmud R, Masrul M. Factors Associated
with the Incident of Stunting in Children Aged 24-59
Months in the Andalas Community Health Center
Working Area, East Padang District, Padang City in
2018. J Health Andalas . 2018;7(2):275.
Shekar M, Kakietek J, D'Alimonte MR, Rogers HE,
Eberwein JD, Akuoku JK, et al. Reaching the global
target to reduce stunting: An investment framework.
Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(5):657-668.
Sutanto I, Ismid I, Sjarifudin P, Sungkar S. Textbook of
Medical Parasitology 4th Edition. 4th ed. FKUI
Publishing House; 2008.
Torlesse H, Cronin AA, Sebayar SK, Nandy R.
Determinants of stunting in Indonesian children:
Evidence from a cross-sectional survey indicates a
prominent role for the water, sanitation and hygiene
sector in stunting reduction. BMC Public Health.
2016;16(1):1-11.
UNICEF, WHO, World Bank. Levels and Trends in Child
Malnutrition: Key Findings of the 2020 Edition of the
Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates. 2020;24.
UNICEF. Improving Child Nutrition The Achievable
Imperative for Global Progress. 2013;18.
World Health Organization (WHO). Soil-transmitted
helminth infections. Published 2020. Available from:
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-
sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections
Winita R, Huda MK AH. Intestinal Parasite Infections in
Children and Their Relationship with Work as a
Scavenger Rawina. Maj FK UKI. 2016;32(3):113-119.
Wright SG. Protozoan Infections of the Gastrointestinal
Tract. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2012;26(2):323-339.
Yoseph A, Beyene H. The high prevalence of intestinal
parasitic infections is associated with stunting among
children aged 6-59 months in Boricha Woreda,
Southern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. BMC
Public Health. 2020;20(1):1-13.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
194
