
Inhibiting and Supporting Factors in Reporting Patient Safety
Incidents Among Healthcare Workers: A Literature Review
Ika Novianna Wardani
a
, Betta Kurniawan
b
and Bayu Anggileo Pramesona
*
c
Master of Public Health Program, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Lampung, Bandar Lampung, 35145, Indonesia
Keywords: Patient Safety Incidents, Inhibiting Factors, Supporting Factors, Literature Review.
Abstract: Reporting hospital incidents is still a matter of pros and cons in its implementation, both from the perspective
of patients and hospital staff. However, this is detrimental if it is not immediately corrected by building and
strengthening a safety culture. The present study aimed to determine the inhibiting and supporting factors in
reporting patient safety incidents among healthcare workers. This study used a literature review method by
collecting online literature data sources and obtained 5 (five) pieces of literature related to inhibiting and
supporting factors in reporting patient safety incidents among healthcare workers. Inhibiting factors consist
of individual aspects (feelings of fear of being blamed and threats of intimidation), psychological aspects
(worries about worsening the hospital's image), organizational aspects (lack of safety culture), and
government aspects (no laws to protect whistle-blowers). Meanwhile, supporting factors include supportive
organizational support, developing and strengthening a patient safety culture, hospitals regulating reporting
patient safety incidents, continuous evaluation in implementing patient safety training, and support for
government laws and regulations protecting staff. Efforts to support the reporting of patient safety incidents
by fostering and strengthening a culture of patient safety through a culture of learning, a culture of reporting,
a culture of fairness, and a culture of information openness in hospitals can support the realization of reporting
patient safety incidents safely and comfortably.
1 INTRODUCTION
Patient safety is crucial in implementing health
services as a benchmark for providing the best health
services and avoiding or reducing patient accidents
(Canadian Patient Safety Institute, 2020). It can act as
a reference or hospital procedure in providing health
services to patients by trying to avoid or at least
reduce the risk of accidents in the hope that patients
can feel safe and secure. Apart from that, patient
safety is also touched upon in the hospital
accreditation assessment provisions according to
Ministry of Health standards with a focus on patient
safety. Patient safety itself has 6 (six) target parts,
including accurate patient identification, increasing
effective communication, increasing the safety of
drugs that must be alert (high-alert), ensuring the right
location, proper procedure, suitable patient operation,
reducing the risk of service-related infections. Health
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-9859-8187
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8775-7708
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9242-7129
and reducing the risk of patient falls (Ministry of
Health Republic Indonesia, 2022). The goals of
patient safety are realizing a culture of patient safety
in hospitals, increasing hospital accountability
towards patients and the community, reducing the
number of adverse events in hospitals, and
implementing prevention programs to prevent the
recurrence of adverse events (Ministry of Health
Republic Indonesia, 2008). However, the fact is that
the fear of being blamed, punished, and threatened
with intimidation is still a 'threat' for health workers,
as well as the fear of worsening the hospital's image
in reporting patient safety incidents. In fact, with open
and fair reporting of patient safety incidents, health
workers, hospitals, and patients can improve patient
safety efforts and obtain positive benefits. The
present study aimed to determine the inhibiting and
supporting factors in reporting patient safety
incidents.
Wardani, I. N., Kurniawan, B. and Pramesona, B. A.
Inhibiting and Supporting Factors in Reporting Patient Safety Incidents Among Healthcare Workers: A Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0013667200003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 151-155
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
151
2 METHODS
This research uses a literature review method by
specifically reviewing or summarizing literature from
online data sources in Google Scholar with a
publication period of 2020 – 2023 to provide a more
comprehensive understanding of the inhibiting and
supporting factors in reporting patient safety
incidents. The keywords in searching for this data
source are inhibiting factors in reporting patient
safety incidents and supporting factors in reporting
patient safety incidents. The inclusion criteria in
screening data sources are that the period of research
literature to be reviewed is limited to the last four
years (2020-2023), English and Indonesian language
journals, full-text journals, and journal research
objects are inhibiting and supporting factors in
reporting patient safety incidents. Meanwhile, the
exclusion criteria for this research are journals other
than English and Indonesian and paid journals. The
articles included are research articles conducted in
Indonesia and Japan. It can be seen from the year of
publication that there are two articles published in
2023, one published in 2022, one published in 2021,
and one published in 2020. Of these articles, three use
literature reviews, one use quantitative observational,
and one use descriptive quantitative.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Result
The literature reviewed in this research was published
from 2019 to 2023 in 5 (five) journals. Then, a study
was drawn up regarding inhibiting and supporting
factors in reporting patient safety incidents, and the
conclusions in each journal obtained several results,
including the following:
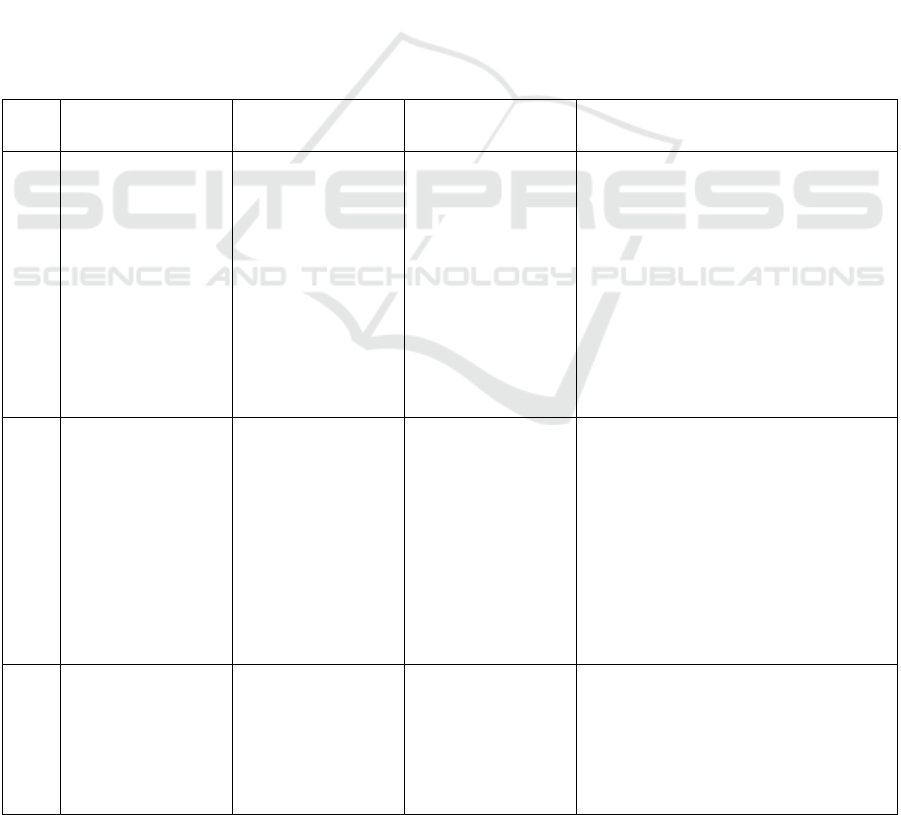
Table 1: Summary of research results based on research type
No Author and Year Title Methods Results
1 Nofita Tudang
Rombeallo, Takdir
Tahir and Ariyanti
Saleh (2022)
Faktor Penyebab
Rendahnya
Pelaporan Insiden
Keselamatan Pasien
di Rumah Sakit:
Literature Review
Literature Review Barriers for health workers in reporting
patient safety incidents in hospitals come
from the individuals themselves:
a. Feelings of fear of being punished,
blamed, judged incompe-tent, reputation
damage, and intimida-tion if reporting an
incident
b.Lack of knowledge, skills, and abilities in
reporting incidents
To support incident reporting, commitment
from policymakers is needed to improve
the patient safety incident reporting system
(Rombeallo, Tahir and Saleh, 2022)
2 Astari Ekaning-tyas
and Nasiatul Aisyah
Salim (2023)
Factors Associated
with Reporting
Patient Safety
Incidents by Nurses
at Panemba-han
Senopati Hospital
Bantul Yogya-karta
Observa-tional
Quantita-tive
Inhibiting factors: lack of non-punitive
response to errors, open communication,
feedback due to feelings of fear and guilt if
reporting incidents
However, there are supporting factors to
foster a non-punitive response, namely,
developing and strengthening a culture of
patient safety through a culture of learning,
justice, and reporting.
It also allows patients and their families to
report their experiences while in the
hospital. (Ekaningtyas and Salim 2023).
3 Tamaamah Habibah
and Inge Dhamanti
(2020)
Faktor yang
Mengham-bat
Pelaporan Insiden
Keselamat-an
Pasien di Rumah
Sakit: Literature
Review
Literature Review Barriers to incident reporting, namely:
a.Individual, namely feelings of fear of
intimidation or punishment
b.Organiza-tion, namely low feedback on
incident reporting and never investigating
the root cause of the problem
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
152
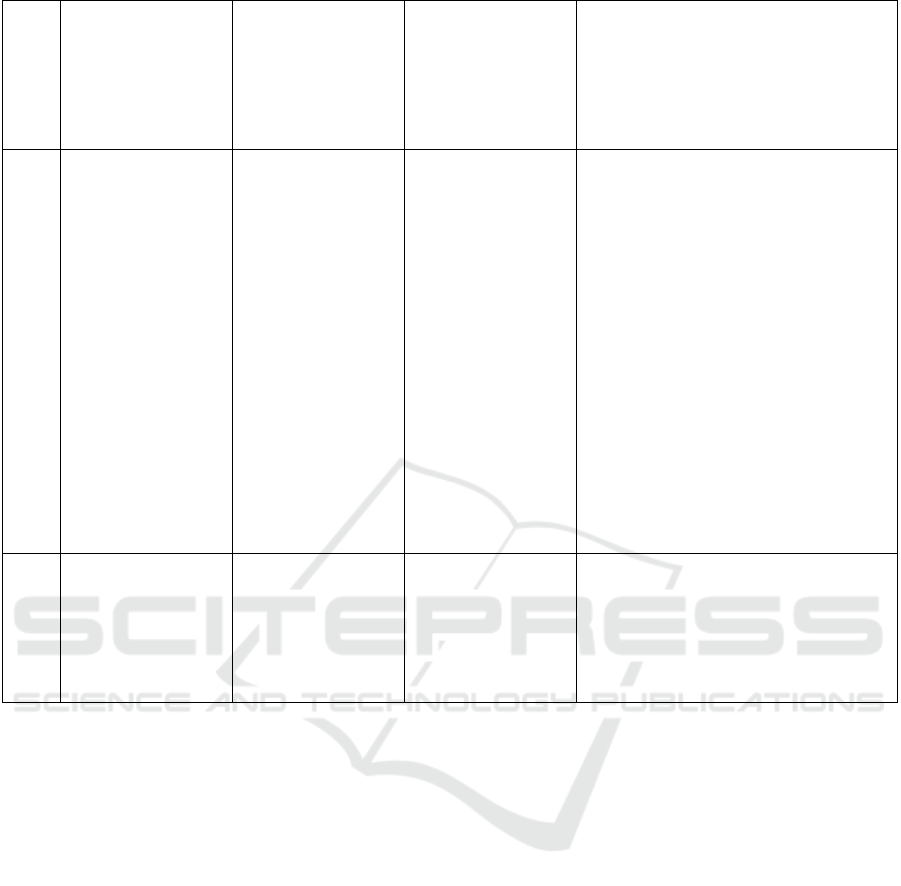
c.Govern-ment, namely the absence of laws
that protect health workers who report
medical errors
To support incident reporting, further
evaluation of implementing patient safety
incident reporting in hospitals is needed.
(Habibah and Inge, 2020).
4 Salsabila Nurislami,
Bayu Anggileo
Pramesona, Risal
Wintoko and Rasmi
Zakiah Oktarlina
(2023)
Factors Influencing
Reporting of Patient
Safety Incidents:
Literature Review
Literature Review Factors that influence the reporting of
patient safety incidents generally come
from three factors, namely:
a.Individual, including knowledge, skills,
and abilities in carrying out reports and
awareness of patient safety
b.Psychology, including perceptions,
attitudes, and beliefs that patient safety is
beneficial, putting aside feelings of fear of
being blamed or punished because of
protecting colleagues and the reputation of
the workplace
c. As one of the supporting factors in
reporting incidents, the organization
includes a supportive environment and no-
blame work culture, availability of a patient
safety team, guidelines and report format,
anonymity of reports, and good feedback in
the form of further investigation and
corrective action. (Nurislami et al., 2023).
5 Masaru Kurihara,
Yoshimasa Nagao, and
Yasuharu Tokuda
(2021)
Incident reporting
among physicians-in-
training in Japan: A
national survey
Quantita-tive descript-
tive
Of the 6,164 doctors undergoing training, it
was found that although 78% had taken
patient safety training, 44% had not
submitted an incident report in the previous
year, and 40.6% did not know how to
submit an incident report. (Kurihara,
Nagao, and Tokuda, 2021).
3.2 Discussion
Based on the results of this research, several
inhibiting and supporting factors were obtained in
reporting patient safety incidents. These factors are
for various reasons but are generally related to patient
safety culture. Patient safety culture is the primary
and most important basis for reporting safety
incidents. This culture has a significant impact on
individuals and organizations. For example, one of
the inhibiting and dominating factors in reporting
patient safety incidents is that which originates from
individuals. Feelings of fear, worry about being
blamed, not knowing how to report, and threats of
intimidation if they report a patient safety incident
(Habibah and Inge, 2020; Rombeallo, Tahir and
Saleh, 2022; Nurislami et al., 2023). As a result,
individuals choose not to report it. Even though
reporting this incident has a positive impact and
benefit on patient safety and fosters a positive image
for the organization. Meanwhile, not all individuals
share this view because they are trapped in fear and
worry.
Apart from the feelings of fear that individuals
have, some organizations lack non-punitive responses
(Ekaningtyas and Salim 2023), Moreover, they are
not investigating the root causes of patient safety
problems (Habibah and Inge 2020). This particular
condition can occur due to the perception
(psychological aspect) that reporting patient safety
incidents gives the organization a bad image
(Habibah and Inge 2020; Nurislami et al. 2023). In
fact, on the contrary, an investigation into the root of
the problem can result in improvements for the
organization to protect its image and patient safety.
Moreover, hospitals are essential in supporting
patient safety efforts as a health organization. Then,
from a government perspective, it was found that
there was no law to protect health workers who
reported medical errors (Habibah and Inge 2020).
This effort also prevents an atmosphere of non-
punitive attitudes from being realized. There is a
blaming culture and feelings of discomfort with
fellow health workers to maintain conducive working
Inhibiting and Supporting Factors in Reporting Patient Safety Incidents Among Healthcare Workers: A Literature Review
153

relationships. So, it would be better to have policies
or laws that protect health workers who report
medical errors or patient safety incidents, hoping to
encourage and strengthen a patient safety culture.
Regarding individual knowledge, it was found
that the cause of delays in reporting patient safety
incidents was a lack of knowledge, abilities, and skills
(Rombeallo, Tahir and Saleh, 2022; Nurislami et al.,
2023). This condition is also related to patient safety
culture, which means there are obstacles to its
implementation. This aspect of knowledge can be
improved by strengthening the patient safety culture
through a learning culture. Health workers can
acquire this learning culture through training
programs in hospitals. However, it is not just about
carrying out training; monitoring must be done by
evaluating patient safety training and alternative
methods through a reporting culture. The aim is to
strengthen the patient safety culture. As one example,
the first national survey on incident reporting in Japan
found that half of junior residents had not submitted
patient safety incident reports due to residents' lack of
experience in making patient safety incident reports,
even though 96% of residents had taken patient safety
training, so alternative methods through
strengthening were needed patient safety reporting
culture (Kurihara, Nagao, and Tokuda 2021).
Some of these inhibiting factors can be overcome
with supporting factors for reporting patient safety
incidents, including supportive organizational
support. Hospitals can play their role in establishing
regulations and fostering and strengthening a patient
safety culture so that health workers have the
confidence or courage to be open because they do not
have fear or are threatened with intimidation in
reporting patient safety incidents. Hospitals also
participate in creating patient safety training
programs, such as learning culture, reporting culture,
fair culture, and patient safety culture. In this way, an
atmosphere of openness will be created and benefit
patients and hospitals.
Second, develop and strengthen a patient safety
culture. This effort can be achieved by the strength of
hospital regulations regarding patient safety culture,
providing patient safety training programs, and
monitoring and evaluating the implementation of
patient safety culture when providing health services
to patients. Third, hospitals regulate regulations
regarding reporting patient safety incidents
(including format, reporting system, and patient
safety team) to avoid a culture of blaming each other,
which leads to feelings of fear and the threat of
intimidation—fourth, continuous and ongoing
evaluation in implementing patient safety training.
Without monitoring (evaluation), hospitals cannot
make continuous improvements to improve patient
safety culture so that the hospital's image will have a
positive value. Fifth, government support in
protecting health workers when reporting medical
errors or patient safety through legislation. The
existence of legal protection for medical personnel in
reporting medical errors or patient safety incidents
not only gives officers a sense of confidence but also
provides a deterrent effect on parties who are
negligent in providing services that are not oriented
toward patient safety.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results and discussion above, it can be
concluded that inhibiting and supporting factors in
reporting patient safety incidents have their role.
Inhibiting factors (individual, psychological,
organizational, and governmental aspects) can create
negative value for the hospital, in contrast to
supporting factors (supportive organizational
support; developing and strengthening a patient
safety culture; the hospital regulates regulations
related to reporting patient safety incidents; ongoing
evaluation- continuous and continuous
implementation of patient safety training; and support
for government laws and regulations in protecting
health workers) provide positive value for hospitals.
This supporting factor should be adopted or used in
health service activities not only in hospitals but all
health facilities can also apply it. Implementing
patient safety incident reporting means that patient
safety culture can be fulfilled so patients feel safe,
comfortable, and safe.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank all parties who
contributed to this research, both supervisors and
other research colleagues, for the reference material
that can be used in this research.
REFERENCES
Canadian Patient Safety Institute. 2020. Patient Safety
Incident. Institut Canadien Pour La Securite Des
Patients.
Ekaningtyas, Astari, and Nasiatul Aisyah Salim. 2023.
‘Factors Associated with Reporting Patient Safety
Incidents by Nurses at Panembahan Senopati Hospital
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
154

Bantul Yogyakarta’. Jurnal Surya Muda 5(1): 90–103.
Habibah, Tamaamah, and Dhamanti Inge. 2020. ‘Factors
Inhibiting Reporting of Patient Safety Incidents in
Hospitals: Literature Review’. Jurnal Kesehatan
Andalas 9(4): 449–60.
Kurihara, Masaru, Yoshimasa Nagao, and Yasuharu
Tokuda. 2021. ‘Incident Reporting among Physicians-
in-Training in Japan: A National Survey’. Journal of
General and Family Medicine 22(6): 356–58.
Ministry of Health Republic Indonesia. 2008. National
Guide of Hospital Patient Safety. Jakarta: Bakti Husada.
———. 2022. Hospital Accreditation Standards. Jakarta:
Direktorat Jenderal Pelayanan Kesehatan Kementerian
Kesehatan RI.
Nurislami, Salsabila, Bayu Anggileo Pramesona, Risal
Wintoko, and Rasmi Zakiah Oktarlina. 2023. ‘Factors
Influencing Reporting of Patient Safety Incidents:
Literature Review’. Jurnal Penelitian Perawat
Profesional 5(2): 551–58.
Rombeallo, Nofita Tudang, Takdir Tahir, and Ariyanti
Saleh. 2022. ‘Factors Causing Low Reporting of Patient
Safety Incidents in Hospitals: Literature Review’.
Jurnal Keperawatan 14(S3): 657–66.
Inhibiting and Supporting Factors in Reporting Patient Safety Incidents Among Healthcare Workers: A Literature Review
155
