
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Ogan Tribes in
Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia to Treat Degenerative
Diseases
Arif Setiawansyah
1a
, Abdul Rohim
1
and Muhammad Andre Reynaldi
2b
1
Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Kader Bangsa, Jl. Mayjend HM Ryacudu No. 88, Palembang, Indonesia
2
Department of Pharmacy, STIKES Arjuna, Jl. YP Arjuna, Toba Regency, Indonesia
Keywords: Degenerative Disease, Ethnobotanical Study, Medicinal Plants, Ethnomedicine.
Abstract: Degenerative disease is one of the non-communicable diseases characterized by progressive loss of cell
function, leading to an early organ defect and aging. Ethnobotanical study can be a promising approach to
explore potential plants that have been used traditionally based on local knowledge for the treatment of
degenerative disease. This study was implemented to uncover the unspooled knowledge of the Ogan tribes in
utilizing medicinal plants to treat degenerative diseases. An observational descriptive study was undertaken
to collect the data and information regarding the medicinal plants used for the management of several
degenerative diseases. Information and data collection was carried out via questionaries and direct interview
with traditional healers and local people on the type of ingredients, ways of making, dosage and frequency of
usage. The ethnobotanical survey revealed 36 different types of medicinal herbs included in 5 disease
categories including uric acid (16 medicinal herbs), hypertension (17 medicinal herbs), hyper-cholesterol (13
medicinal herbs), diabetes mellitus (11 medicinal herbs), and stroke (7 medicinal herbs) with a total of 64
plant species were utilized for the treatment of each health problem. The usage of medicinal herbs is quite
diverse such as direct consumption, infusion, and juicing with different frequencies of utilization (i.e., once
and twice daily). The survey has shown that Ogan tribes in Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia have
empirically implemented the local knowledge of medicinal herbs for the treatment of several degenerative
diseases. However, scientific proof should be undertaken for the medicinal herbs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Degenerative diseases are the term used for numerous
disorders caused by progressive loss of cell functions
that leads to an early organ damage and aging,
generally occurred in elderly. Even though it does not
rule out the possibility of occurring at the young age,
several main risk factor can be a potential trigger for
degenerative disease to be suffered by the
community, including lack of activity, ultra-
processed food, and oxidative stress (Richardson,
1926). Approximately 50 types of degenerative
diseases have been identified in the present time,
some of which are cancer, stroke, diabetes mellitus,
coronary heart problem, and hypercholesterolemia
(Wirasisya et al., 2020). The current managements of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1443-8666
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7827-5261
various degenerative diseases implement both the
non-pharmacology and pharmacology treatment by
modifying the lifestyle and consuming the clinically
approved synthetic drugs (Moriguchi et al., 2016).
However, the use of synthetic drugs often experiences
the number of adverse effects, leading to the
emergence of various health problems (Helleday,
2017; Miller et al., 2010). High negative effect of the
synthetic drugs increases the needs to discover new
drug candidate pointed out as the degenerative
diseases therapy that is more safe with low toxicity.
Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by
the local people in certain areas is one of the
promising approaches in discovering the new drug
candidates, in view of the fact that traditional herbal
medicine has been extensively utilized since ancient
time (Iwu, 2002). The local knowledge of medicinal
Setiawansyah, A., Rohim, A. and Reynaldi, M. A.
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Ogan Tribes in Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia to Treat Degenerative Diseases.
DOI: 10.5220/0013666700003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 107-115
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
107
plants can be an appropriate source of information as
a basis of drug discovery and development
(Mahmood et al., 2013). Numerous scientific reports
have shown the fundamental role of the traditional
knowledge in development of new drug candidates
that have provided a real substitute in the primary
healthcare of the rural communities in developing
countries (Cordel et al., 2012; Hayta et al., 2014).
Approximately 80% of the developing countries
population rely on the herbal medicines with a total
of 85% of the traditional medicinal herbs have been
extensively utilized globally, making it as a global
indigenous heritage (WHO, 2002; Farnsworth, 1988).
The documentation of the traditional knowledge
on medicinal plants is a key aspect to conserve the
global empirical heritage. It has also been
implemented by the Indonesian government through
the Ministry of Health by upscaling the use of
Indonesian traditional herbal medicine, specifically
known as Jamu, to be integrated into the primary
healthcare system (The Indonesia’s Ministry of
Health, 2010). This study, therefore, transcribes the
empirical information of the Ogan tribes living in
Lempuing Jaya, Ogan Komering Ilir district, South
Sumatera, Indonesia on medicinal herbs for the
management of several degenerative disease. This
ethnobotanical survey is the first ethnomedicinal
assessment and listing of medicinal plant data,
specifically for degenerative diseases in this area.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
The ethnobotanical survey used a technique adopted
from Wirasisya et al. (2020). The documentation of
the local knowledge used an observational descriptive
study supported by participative ethnobotany
appraisal approach including scheduled and semi-
structured direct interview.
2.1 Survey Location
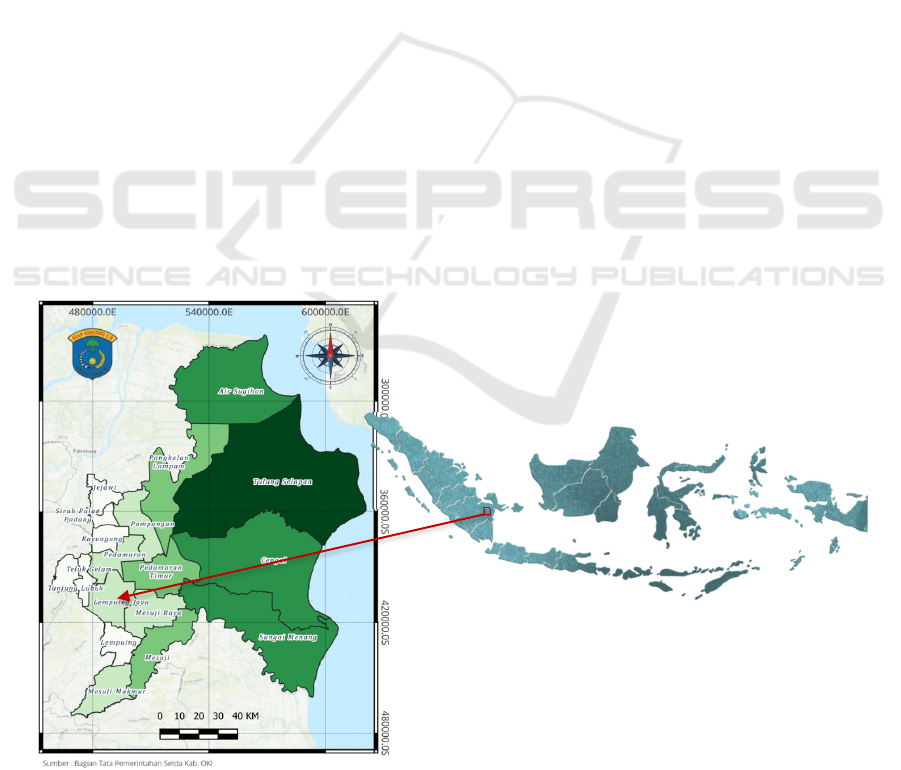
The ethnobotanical survey was conducted in January
– April 2023 located in Lempuing Jaya, Ogan
Kemering Ilir district, South Sumatera, Indonesia as
depicted in Figure 1.
2.2 Documentation and Interview
The semi-structured direct interview was
implemented to document the data and local
knowledge with the informant criteria as follows:
1. Knowledgeable on the utilization of medicinal
herbs/plants and medicinal plant ingredients for
management of health problem.
2. The local inhabitants or enculturated person.
3. Known as knowledgeable on the utilization of
medicinal herbs/plants and medicinal plant
ingredients for management of health problem.
The information regarding informant biodata,
medicinal plant species, local name, the usage, part of
usage, formulation and preparation.
(Map was courtesy from Governance Section, Ogan Komering Ilir District)
Figure 1: Ethnobotanical survey location.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
108
2.3 Data Analysis
Descriptive and quantitative analysis was carried out
to analyse the data and information. The descriptive
analysis was undertaken on the characteristics of the
informant and the medicinal herbs, while the
quantitative analysis was carried out to the medicinal
plant data by quantified the ethnobotanical index
including the use value (UV) and fidelity level (FL)
as explained by Hoffman and Gallaher (2007).
Use Value (UV)
𝑈𝑉 =
𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡
Fidelity level (FL)
𝐹𝐿 =
𝐼𝑝
𝐼𝑢
𝑥 100%
I
p
: Informant using specific plant for certain
disease
I
u
: Total informant usin
g
specific plants
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Location and Respondent
Demographic
The survey was carried out in Lempuing Jaya, Ogan
Kemering Ilir (OKI) district, South Sumatera,
Indonesia specifically at three villages including SP 6
Suka Maju, SP7 Suka Jaya, and Tanjung Sari II which
was selected based on the high number of traditional
healing practice by the local people. A total of 100
participants were obtained that meets the criteria with
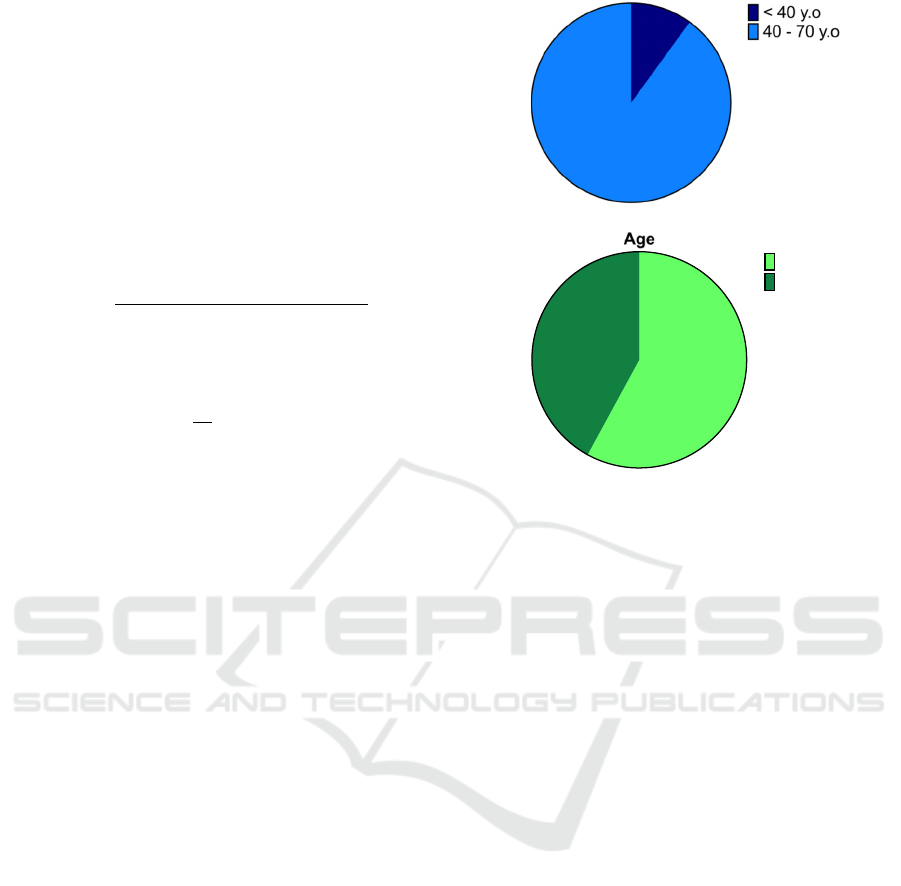
the informant demographic as depicted in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Informant demographic of ethnobotanical survey
location
Figure 2 illustrates most of informants are male
with the age ranging from 40-70 years old, and only
10% of respondents are 35-40 years old. This
indicates that Lempuing Jaya inhabitants that are
under 35 years old do not have any knowledge
regarding the medicinal herbs. The main source of
their medicinal plant’s knowledge (75%) was
empirically passed down from their ancestors and
25% of the rest were obtained from self-experiences
of using the medicinal plants to manage their health
problems.
3.2 Medicinal Plants
Ethnobotanical survey revealed 36 types of medicinal
herbs included in five disease categories such as uric
acid (16 medicinal herbs), hypertension (17 medicinal
herbs), hyper-cholesterol (13 medicinal herbs),
diabetes mellitus (11 medicinal herbs), and stroke (7
medicinal herbs). A total of 64 medicinal herbs have
been documented for the medicinal herb preparations
and all of the have been identified botanically. The
plant species used by the Ogan tribes summarized in
Table 1.
1
0
%
Gender
Male
Female
58%
42%
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Ogan Tribes in Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia to Treat Degenerative
Diseases
109
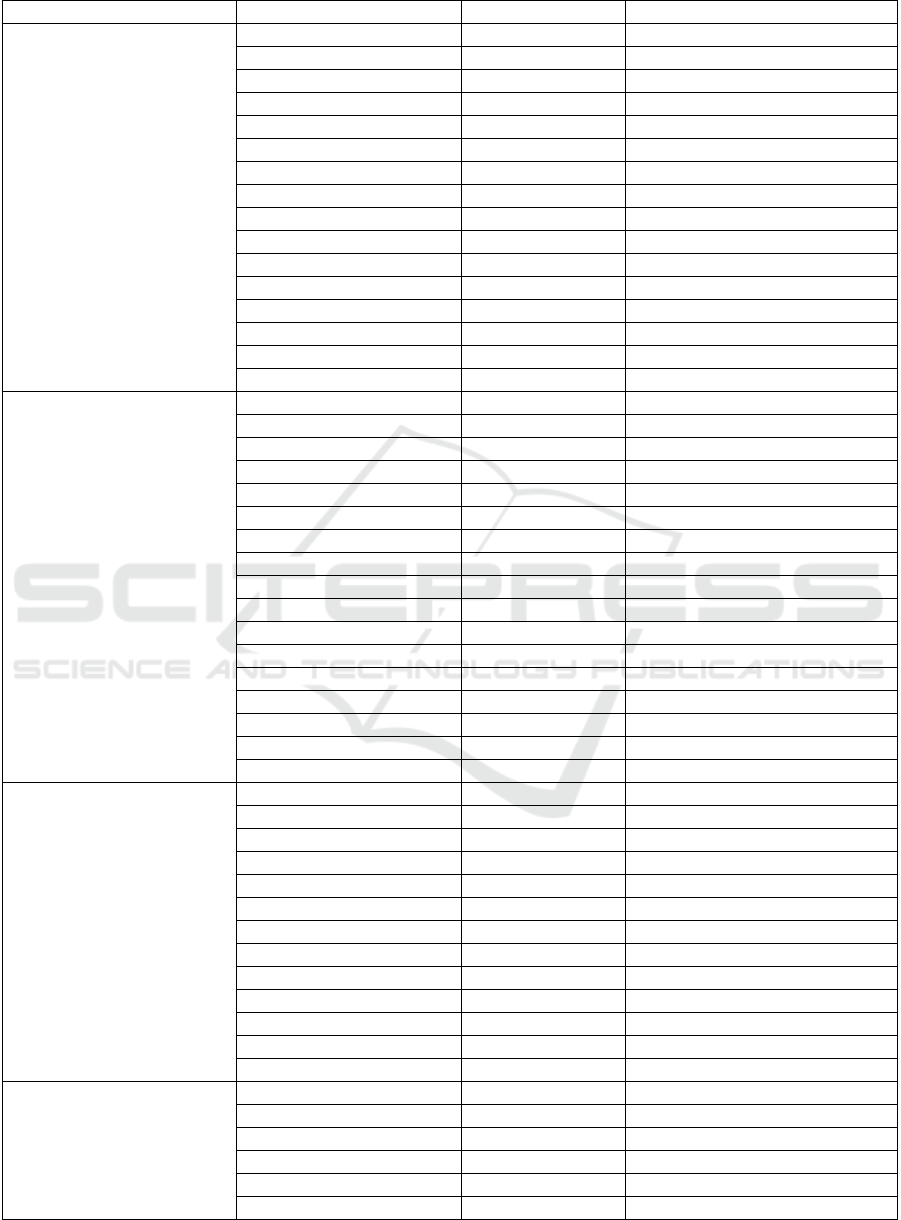
Table 1: Medicinal plants based on disease category.
Disease categories Local name The used part Species
Uric acid
Salam Leaf Syzygium polianthum
Sirsak Leaf Annona muricata
Sirih Leaf Piper betel
Bawang putih Tuber Allium sativum
Alang-alang Herbs Imperata cylindrica
Kumis Kucing Leaf Orthosiphon aristatus
Putri malu Leaf Mimosa pudica
Sirih cina Leaf Peperomia pellucida
Jahe merah Rhizome Zingiber officinale
Sambiloto Herbs Androgarphis paniculata
Kelor Leaf Moringa oleifera
Binahong Herbs Anredera cordifolia
Ciplukan Leaf Physalis angulata
Kunyit Rhizome Curcuma longa
Pinah Fruit Areca catechu
Brotowali Herbs Tinospora cordifolia
Hypertension
Sirsak Leaf Annona muricata
Sirih Cina Leaf Peperomia pellucida
Tumulawak Rhizome Curcuma xanthorriza
Kumis Kucing Leaf Orthosiphon aristatus
Belimbing Wuluh Fruit Averrhoa bilimbi
Bawang Putih Tuber Allium sativum linn
Seledri Leaf Apium graveolens
Jahe Rhizome Zingber officinale
Salam Leaf Syzygium polyanthum
Nangka Leaf Artocarpus heterophyllus
Sambiloto Herbs Andrographis paniculata
Kelor Leaf Moringa oleifera
Timun Fruit Cucumis sativus
Asam Jawa Fruit Tamarindus indica
Kayu Manis Lignum Cinnamomum burmani
Alang – alang Herbs Imperata cylidnrica
Bawang merah Tuber Alium cepa
Hyper-cholesterol
Seledri Herbs Apium graveolens
Mengkudu Fruit Morinda citrifolia
Sambiloto Herbs Andrographis paniculata
Kelor Leaf Moringa oleifera
Ketumbar Leaf and Seed Coriandrum sativum
Sirih Leaf Piper betle
Seri Fruit Muntingia calabura
Belimbing manis Fruit Averrhoa carambola
Salam Leaf Syzygium polyanthum
Bawang Putih Tuber Allium sativum
Wortel Roots Daucus carota
Tumulawak Rhizome Curcuma xanthorrhiza
Buncis Seed Phaseolus vulgaris
Diabetes mellitus
Sirih Cina Leaf Peperomia pellucida
Seri Fruit Muntingia calabura
Nanas Fruit Ananas comosus
Jahe Rhizome Zingiber officinale
Kayu Manis Lignum Cinnamomum verum
Pare Fruit Momordica charantia
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
110
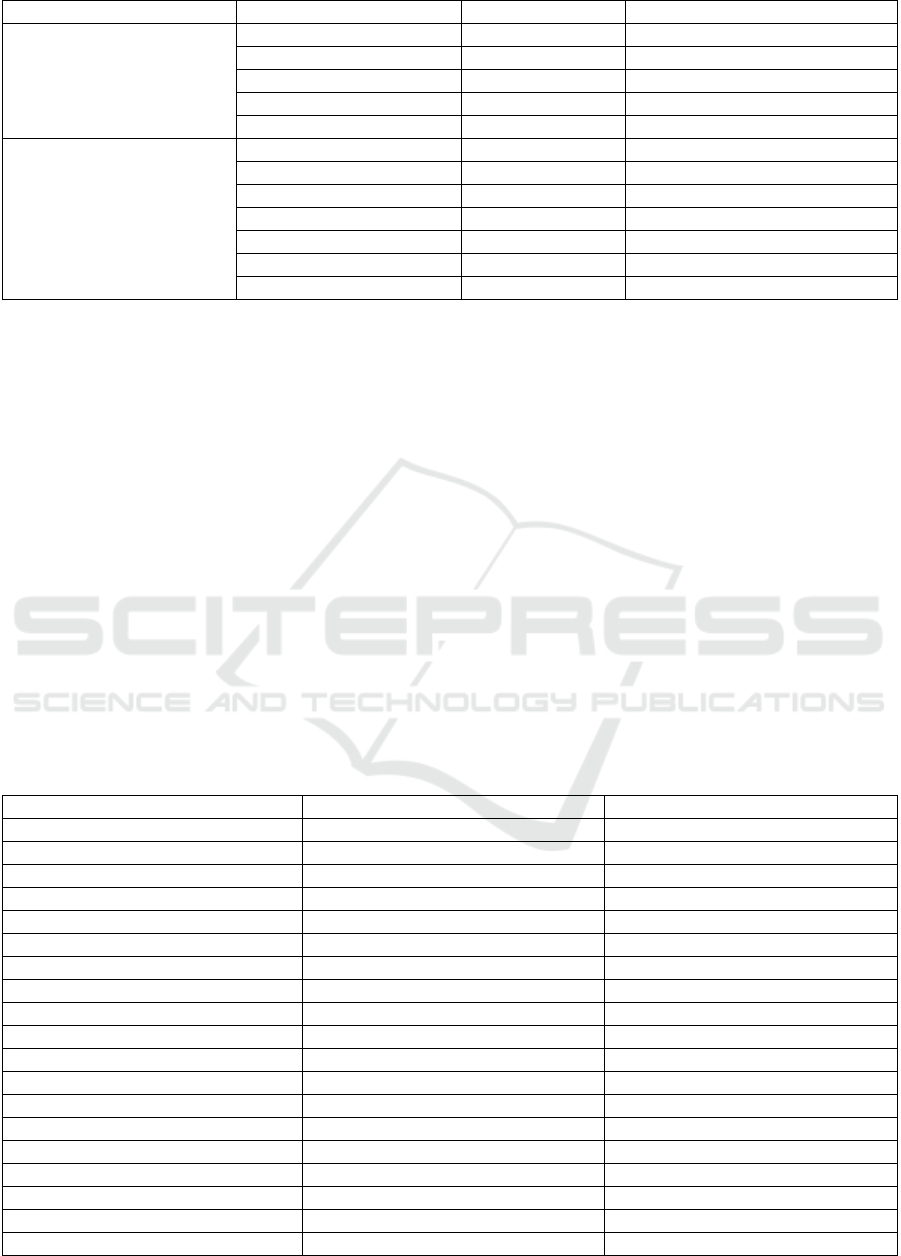
Disease categories Local name The used part Species
Salam Leaf Syzygium polyanthum
Sirsak Leaf Annona muricata
Manggis Fruit peel Garcinia mangostana
Sambiloto Herbs Andrographis paniculata
Gingseng Radix Panax gingseng
Stroke
Sirih Cina Leaf Peperomia pellucida
Serai Leaf Cymbopogon nardus
Kelor Leaf Moringa oleifera
Ciplukan Leaf Physalis angulata
Sambiloto Herbs Andrographis paniculata
Seledri Herbs Apium graveolens
Bawang Putih Tuber Allium sativum
3.3 Dosage and Preparation
The most common way of use of the medicinal
plant/herbs at the ethnobotanical study location is by
infusion the plants. However, several methods were
also found including juicing and direct consumption.
The simple preparation and convenience of the
infusion methods makes this herbal preparation
technique highly used by the local people. The used
of medicinal plant in Lempuing Jaya sometimes
combined with other ingredients i.e., sugar, salt, and
honey to increase a good savour.
The frequency and duration of usage was also
diverse depending on the medicinal herbs and the
severity level of diseases. The use of medicinal herbs
indicated for curative purposes shows an intense use
(three times a day) than palliative and preventive
purposes which only use once and twice daily for
seven days or more. In addition, the local inhabitants
of Lempuing Jaya have a unique dosage for
preparation of medicinal herbs. They apply the odd
number in every dosage of the medicinal plant
ingredients.
3.4 Ethnobotanical Index
3.4.1 Use Value (UV)
UV is an index that can describes the level of use
value of species for treating diseases based on
predetermined categories (Silalahi, 2016). The UV
value indicate how frequent the medicinal plants
species were utilized by the community. The UV
value of medicinal plant used by the local inhabitant
of Lempuing Jaya is described in table 2.
Table 2: The use value index of medicinal plants
Local Name Species UV Index
Salam Syzygium polyanthum 0,2
Sirsak Annona muricata 0,18
Sirih Piper betle 0,04
Alang-alang Imperata cylindrica 0,06
Bawang putih Allium sativum 0,09
Kumis kucing Orthosiphon aristatus 0,17
Putri malu Mimosa pudica 0,01
Sirih cina Peperomia pellucida 0,17
Jahe merah Zingiber officinale 0,04
Sambiloto Andrographis paniculata 0,10
Kelor Moringa oleifera 0,09
Binahong Anredera cordifolia 0,03
Ciplukan Physalis angulate 0,03
Kunyit Curcuma longa 0,01
Pinang Areca catechu 0,01
Brotowali Tinospora cordifolia 0,01
Tumulawak Curcuma xanthorrhiza 0,07
Belimbing wuluh Averrhoa bilimbi 0,03
Seledri Apium graveolens 0,15
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Ogan Tribes in Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia to Treat Degenerative
Diseases
111
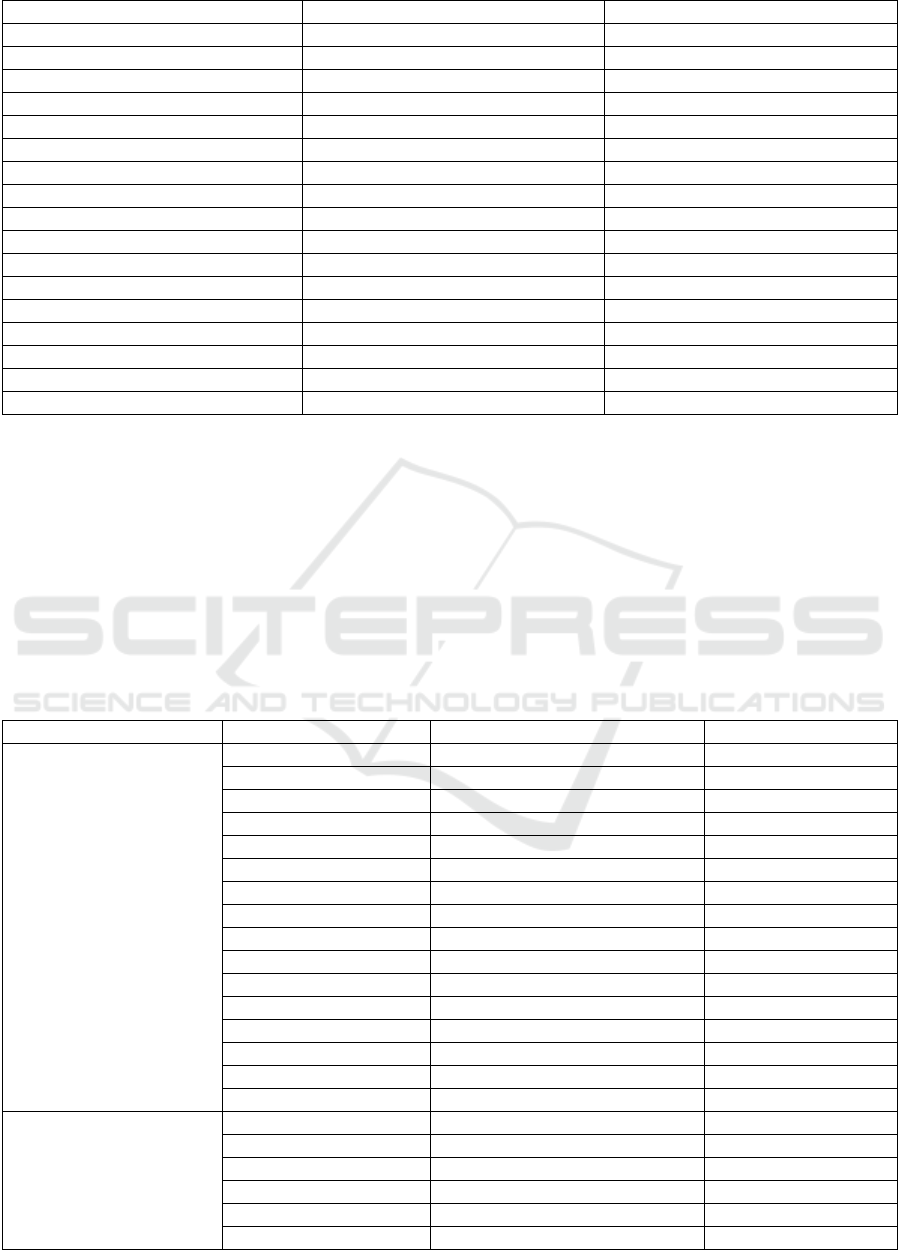
Local Name Species UV Index
Jahe Zingiber officinale 0,04
Nangka Artocarpus heterophyllus 0,03
Timun Cucumis sativus 0,01
Asam jawa Tamarindus indica 0,01
Kayu manis Cinnamomum burmani 0,01
Bawang merah Alium cepa 0,01
Mengkudu Morinda citrifolia 0,03
Ketumbar Coriandrum sativum 0,01
Seri Muntingia calabura 0,04
Belimbing manis Averrhoa carambola l 0,03
Wortel Daucus carota 0,03
Buncis Phaseolus vulgaris 0,04
Serai Cymbopogon nardus 0,01
Nanas Ananas comosus 0,01
Pare Momordica charantia 0,01
Manggis Garcinia mangostana 0,01
Gingseng Panax gingseng 0,01
The UV index calculation showed that Syzygium
polianthhum provide the highest UV index indicating
this plant species is the most commonly used by the
local inhabitants of Lempuing Jaya in their daily
purposes, not only for the management of their health
problem, but also for other purposes including daily
consumption. The traditional healers and local
inhabitants claim that Syzygium polianthum can be
used for the treatment of several diseases including
uric acid, hypertension, hyper-cholesterol, diabetes
mellitus, and stroke.
3.4.2 Fidelity Level (Fl)
FL was used to quantify the importance of the plant
species for treatment of certain diseases in which the
higher the FL of the medicinal plant species, the more
trusted the plant species to be used for the treatment
of a disease category (Hoffman & Gallaher, 2007).
Table 3: The fidelity level index of medicinal plant species
Disease categories Local name Species FL
Uric acid
Salam Syzygium polianthum 18,75
Sirsak Annona muricata 62,5
Sirih Piper betel 6,25
Bawang putih Allium sativum 6,25
Alang-alang Imperata cylindrica 18,75
Kumis Kucing Orthosiphon aristatus 13,5
Putri malu Mimosa pudica 6,25
Sirih cina Peperomia pellucida 18,75
Jahe merah Zingiber officinale 18,75
Sambiloto Androgarphis paniculata 12,5
Kelor Moringa oleifera 12,5
Binahong Anredera cordifolia 12,5
Ciplukan Physalis angulata 6,25
Kunyit Curcuma longa 6,25
Pinah Areca catechu 6,25
Brotowali Tinospora cordifolia 6,25
Hypertension
Sirsak Annona muricata 11,76
Sirih Cina Peperomia pellucida 23,52
Tumulawak Curcuma xanthorriza 5,88
Kumis Kucing Orthosiphon aristatus 35,29
Belimbing Wuluh Averrhoa bilimbi 11,76
Bawang Putih Allium sativum linn 5,88
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
112
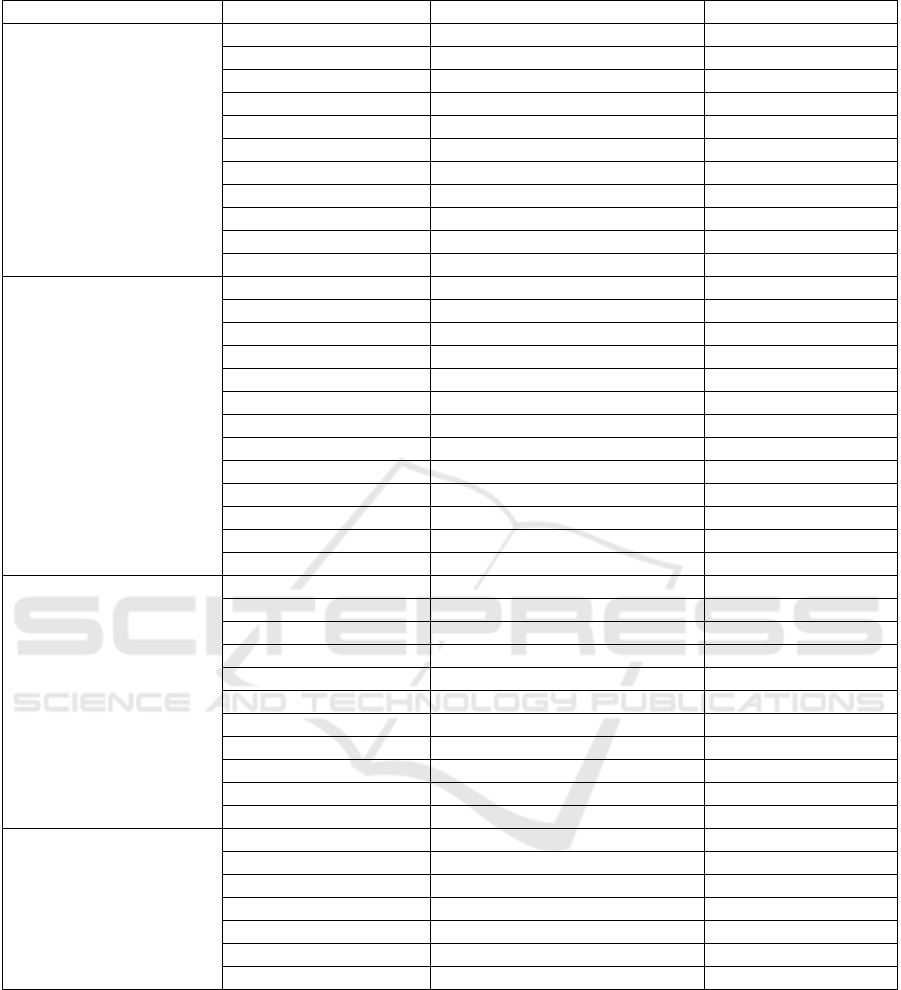
Disease categories Local name Species FL
Seledri Apium graveolens 35,29
Jahe Zingber officinale 5,88
Salam Syzygium polyanthum 58,82
Nangka Artocarpus heterophyllus 11,76
Sambiloto Andrographis paniculata 5,88
Kelor Moringa oleifera 11,76
Timun Cucumis sativus 5,88
Asam Jawa Tamarindus indica 5,88
Kayu Manis Cinnamomum burmani 5,88
Alang – alang Imperata cylidnrica 5,88
Bawang merah Alium cepa 5,88
Hyper-cholesterol
Seledri Apium graveolens 7,69
Mengkudu Morinda citrifolia 15,38
Sambiloto Andrographis paniculata 23
Kelor Moringa oleifera 7,69
Ketumbar Coriandrum sativum 7,69
Sirih Piper betle 7,69
Seri Muntingia calabura 15,38
Belimbing manis Averrhoa carambola l. 7,69
Salam Syzygium polyanthum 15,38
Bawang Putih Allium sativum 23
Wortel Daucus carota 15,38
Tumulawak Curcuma xanthorrhiza 30,76
Buncis Phaseolus vulgaris 23
Diabetes mellitus
Sirih Cina Peperomia pellucida 9
Seri Muntingia calabura 9
Nanas Ananas comosus 9
Jahe Zingiber officinale 18,18
Kayu Manis Cinnamomum verum 9
Pare Momordica charantia 9
Salam Syzygium polyanthum 27,27
Sirsak Annona muricata 9
Manggis Garcinia mangostana 9
Sambiloto Andrographis paniculata 9
Gingseng Panax gingseng 9
Stroke
Sirih Cina Peperomia pellucida 14,28
Serai Cymbopogon nardus 14,28
Kelor Moringa oleifera 14,28
Ciplukan Physalis angulata 14,28
Sambiloto Andrographis paniculata 14,28
Seledri Apium graveolens 14,28
Bawang Putih Allium sativum 14,28
By considering the UV and FL for each disease
categories, several medicinal plant species have been
pointed out as the priority to be used including uric
acid (Annona muricata, Syzygium polyanthum,
Peperomia pellucida, Zingiber officinale),
hypertension (Syzygium polianthum, Orthosiphon
aristatus, Apium graveolens), hyper-cholesterol
(Curcuma xanthorriza, Morinda citrifolia, Phaseolus
vulgaris, Syzygium polyanthum), diabetes mellitus
(Syzygium polyanthum, Zingiber officinale), and
stroke (Androgarphis paniculate, Apium graveolens,
Moringa oleifera). Several pictures of selected
medicinal plant species are depicted in Figure 3.
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Ogan Tribes in Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia to Treat Degenerative
Diseases
113
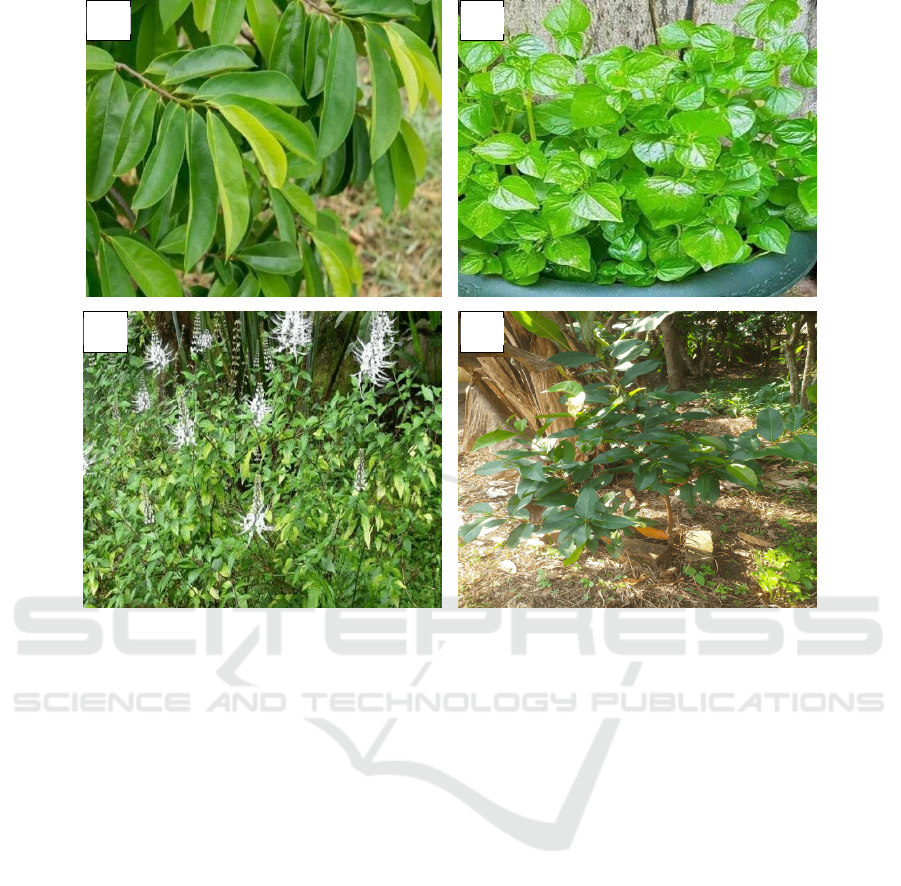

Figure 3: Several selected medicinal plant species. (A) Annona muricata, (B) Peperomia pellucida, (C) Orthosiphon aristatus,
and (D) Syzygium polyanthum.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A total of 64 medicinal herbs have been successfully
documented along with 36 plant species have been
identified. This shows Ogan tribes in Lempuing Jaya,
Specifically in SP 6 Suka Maju, SP7 Suka Jaya, and
Tanjung Sari II have empirically implemented the
local knowledge of medicinal herbs for the treatment
of several degenerative diseases. The documentation
of the local knowledge regarding the traditional
medicinal herbs is necessary to be implemented to
avoid the loss of the local knowledge. Furthermore,
the scientific proof of the use of the traditional herbal
medicine should be undertaken.
REFERENCES
Faruque, M. O., Uddin, S. B., Barlow, J. W., Hu, S., Dong,
S., Cai, Q., Li, X., & Hu, X. (2018). Quantitative
ethnobotany of medicinal plants used by indigenous
communities in the Bandarban district of Bangladesh.
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9(FEB).
https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00040
Farnsworth NR. (1988). Screening plants for new
medicines. In: Wilson E.O., Ed., Chapter 9 in
Biodiversity, National Academy Press, Washington
DC.
Helleday, T. (2017). Chemotherapy-induced toxicity-A
secondary effect caused by released DNA? Annals of
Oncology, 28(9), 2054–2055.
https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx349
Hoffman, B., & Gallaher, T. (2007). Importance Indices in
Ethnobotany. Ethnobotany Research and Applications,
5, 201–218.
Iwu, M. M. (2002). Ethnobotanical approach to
pharmaceutical drug discovery: strengths and
limitations. In M. M. Iwu & J. C. Wootton (Eds.),
Advances in Phytomedicine (Vol. 1, pp. 309–320).
Elsevier. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1572-
557X(02)80034-4
Miller, R. P., Tadagavadi, R. K., Ramesh, G., & Reeves, W.
B. (2010). Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity.
Toxins, 2(11), 2490–2518.
https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2112490
A B
C D
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
114

Moriguchi, Y., Alimi, M., Khair, T., Manolarakis, G.,
Berlin, C., Bonassar, L. J., & Härtl, R. (2016).
Biological Treatment Approaches for Degenerative
Disk Disease: A Literature Review of in Vivo Animal
and Clinical Data. In Global Spine Journal (Vol. 6,
Issue 5, pp. 497–518). Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1571955
Richardson, A. M. (1926). Book Review: The Degenerative
Diseases: Their Causes and Prevention. The Family,
7(6), 194–195.
https://doi.org/10.1177/104438942600700607
Silalahi, M. (2016). Studi Etnomedisin Di Indonesia dan
Pendekatan Penelitiannya. Jurnal Dinamika
Pendidikan, 9(3), 117- 124.
WHO. (2002). Traditional Medicinen and Alternative
Medicines. Geneva. Fact Sheet. No. 271.
Wirasisya, D. G., Hanifa, N. I., & Hajrin, W. (2020).
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used to Treat
Degenerative Disease in East Lombok. Jurnal Biologi
Tropis, 20(3), 423–431.
https://doi.org/10.29303/jbt.v20i3.2119.
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by Ogan Tribes in Lempuing Jaya, South Sumatera-Indonesia to Treat Degenerative
Diseases
115
