
Global Recent Trends Research of Herbal Medicine for Diabetes
Mellitus in a Decade (2014-2023): A Bibliometric Analysis
and Scientific Mapping
Nanang Wiyono
1,5,* a
, Ratih Dewi Yudhani
2b
, Brian Wasita
3c
and Anggraeni Janar Wulan
4
1
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
3
Department of Anatomical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine. Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
4
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Lampung, Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
5
Research Group of Brain, Degenerative Disease and Cancer, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta,
Indonesia
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus, Herbal Medicine, Bibliometric.
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a prevalent health issue on a global scale, characterized by the presence of persistent
hyperglycemia due to compromised insulin synthesis, usage, or both. Oral antidiabetic medications and
insulin have been the mainstay of diabetes treatment. A increasing body of research suggests that herbal
therapies may enhance or even replace diabetes medications. Objective: The objective of this study is to find
and assess diabetes-related herbal medicine research. This study examines publication patterns, renowned
authors, scientific publications, research contributions' geographical distribution and the important research
topics. Scopus was used to find herb research for DM papers. Use the database's "Search document"
functionality to collect basic publication and citation information, including title, abstract, and key functions.
The full bibliographic data was imported to Vosviewer for analysis. To illustrate title and abstract ideas and
notions, visualization maps were created. Based on a decade-long dataset spanning from 2014 to 2023, this
study reveals that there were 3,226 publications. The findings indicate that the growth and development of
herbs for DM experienced a notable increase. The Journal of Ethnopharmacology, with 241 scholarly articles,
is a leading herbal medication for DM journal. China leads the world in herbal diabetes research with 574
papers. With 18 articles, G. Zengin is the most prolific author in this field. The co-occurrence classification
of herbs for DM field development map yields six clusters. Diabetes mellitus, antioxidants, and herbal therapy
dominate the network. The bibliometric data shows that herbal diabetic treatments are becoming more popular.
The use of natural diabetic therapies is expected to change. Herbal medicine research is growing and becoming
more accessible.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus is a pressing issue in worldwide
health, characterized by a rising prevalence and
consequential mortality (Lin et al., 2020; Robert &
Dawish, 2020). The prevalence of diabetes mellitus
has escalated to epidemic proportions, presenting
substantial obstacles to global public health systems
(Fang et al., 2022). Research findings have indicated
a concerning rise in the occurrence of diabetes
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0396-4337
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6781-8251
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5501-3541
mellitus, observed in both industrialized and
developing nations (Katulanda & Sheriff, 2009)
(Abebe et al., 2014). The impact of diabetes mellitus
goes beyond death, since it is also associated with
decreased life expectancy and heightened
susceptibility to complications (Lin et al., 2020). A
comprehensive comprehension of the patterns in
diabetes mellitus is of utmost importance in order to
facilitate efficient strategies for prevention,
94
Wiyono, N., Yudhani, R. D., Wasita, B. and Wulan, A. J.
Global Recent Trends Research of Herbal Medicine for Diabetes Mellitus in a Decade (2014-2023): A Bibliometric Analysis and Scientific Mapping.
DOI: 10.5220/0013666500003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 94-100
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
treatment, and distribution of healthcare resources
(Campbell & Shokrani, 2016).
Traditional medicinal plants have been
recognized and utilized for the treatment and
management of diabetes mellitus (Gaonkar &
Hullatti, 2020). For thousands of years, herbs such as
fenugreek and rhubarb have been used in various
traditional medical systems to treat diabetes mellitus
(Alsanad et al., 2018; Shad & Haghighi, 2018). These
medicinal plants contain active components that have
shown potential in regulating blood glucose levels
and gene expression related to diabetes (Salehi et al.,
2019). Additionally, the use of herbal remedies for
diabetes mellitus is prevalent among patients, who
often turn to these alternatives due to the challenges
of adhering to conventional therapeutic regimens
(Mekuria et al., 2018). Medicinal plants provide a
hopeful opportunity for the creation of novel orally
effective substances for treating diabetes mellitus
(Farzaei et al., 2017; Akram, 2013).
2 METHODS
2.1 Data Collection
Scopus, being the preeminent and extensive scientific
database presently accessible, provides a diverse
range of peer-reviewed journal articles, thereby
ensuring the reliability and caliber of the obtained
literature. The selection of Scopus as the electronic
database for this research was made. Data on virtual
reality and augmented reality in anatomy education
were searched by topic using the search strategy: TS
= (("herbal medicine" OR "traditional medicine" OR
"herbal therapy" OR "herb therapy" AND "diabetes
mellitus" OR dm OR diabetes OR diabetic)).
A total of 8059 documents have been published
from 1961 to 2023. The scope of the studies is
restricted to the period from 2014 to 2023, including
the last 10 years. These papers were collected to
investigate the worldwide research patterns in herbal
medicine for diabetes mellitus. Following retrieval,
only original publications in their final state,
published in English journals, were selected for
further analysis. There were 3,226 original articles
included. Data used in this study were lastly updated
on November 2, 2023.
2.2 Data Analysis
In order to gain an understanding of research growth
patterns, the most prolific authors, the nation with the
most publications, and the most cited journals are
extracted from the Scopus database via the analyzed
results menu and then downloaded as necessary.
Articles were downloaded in CSV format and then
processed using Vosviewer 1.6.19 (van Eck and
Waltman, 2022) and Bibliometrix (Aria and
Cuccurullo, 2017) to visualize and analyze trends in
the form of bibliometric maps. Vosviewer and
Bibliometrix can make keywords maps based on
shared networks.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Research Developments in the Field
of Herbal Medicine for Diabetes
Mellitus
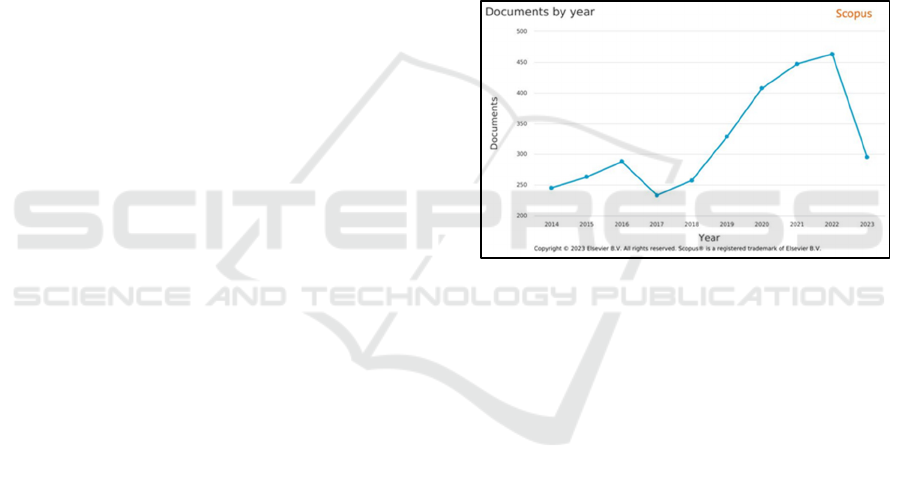
Figure 1: Trend research of herbal medicine for diabetes
mellitus in the worldwide for 10 years.
There are 3.226 documents in journal published
from 2014-2023 with average annual growt are 2.08
%. The are increasing in scientific publications in the
field of herbal medicine for diabetes mellitus
demonstrates a worldwide rise in the number of
researchers in one decade (2014-2013).The most
significant increases happened in 2018-2019, 27.62
percent and 2019-2020, 24.08 percent.
3.2 The Most Profilic Authors in the
Publication of Herbal Medicine for
Diabetes Mellitus
A total of 13,990 authors were involved in all
articles related to herbal medicine for diabetes
mellitus. The top ten contributors to publications
published in Scopus journals showed in figure 2.
Zengin, G. is the most profilic author on the list,
having published approximately eighteen works.
Thong, X. has authored thirdteen publications,
followed by Eddouks, M., Li, P., and Rafliean-
Kopaeri, M., who have twelve written eight papers.
Global Recent Trends Research of Herbal Medicine for Diabetes Mellitus in a Decade (2014-2023): A Bibliometric Analysis and Scientific
Mapping
95
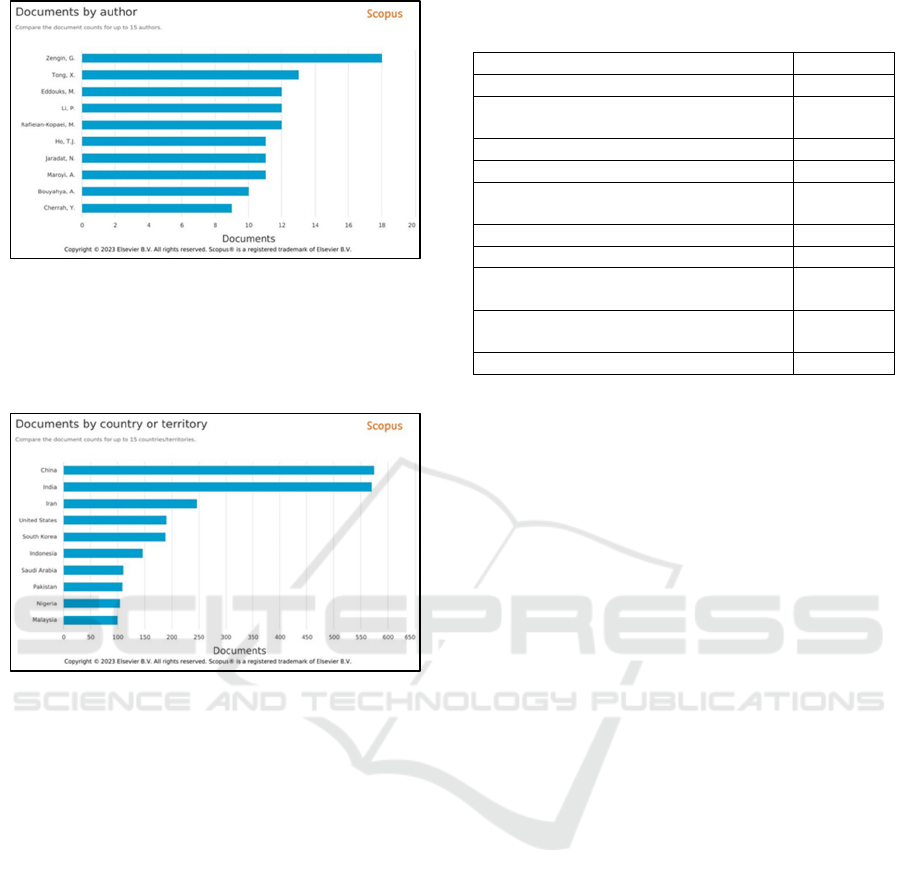
Figure 2: Top Ten Contributing Authors in the area of
herbal medicine for diabetes mellitus research worldwide
3.3 Top Ten Countries of Author Based
on Publication Number
Figure 3: Top Ten Countries in the area of herbal medicine
for diabetes mellitus research worldwide
The country with the most publications is China with
574 documents (17.79 percent), second place is India
with 570 documents (17.66 percent) and third is Iran
with 246 documents (7.62 percent).
3.4 The Core Journal of Herbal
Medicine for Diabetes Mellitus
Table 1 lists the top ten peer-reviewed journals that
have published the most cited articles in the field of
herbal medicine in diabetes mellitus for one decade rs
(2014-2023). The journal with the most cited papers
is Journal of Ethnopharmacology, which has 241
citations. Then, Evidence Based Complementary and
Alternative Medicine contributes to the publication
with 88 citations, and Frontiers in Pharmacology with
publication of 60 citations, making it a leading
scientific publication worldwide.
Table 1: Topten journal by citation in herbal medicine for
diabetes mellitus research.
Source Title Citation
Journal of Ethnopharmacolog
y
241
Evidence Based Complementary and
Alternative Medicine
88
Frontiers in Pharmacolog
y
60
Molecules 56
BMC Complementary and Alternative
Medicine
53
Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 45
Plos One 38
Research Journal of Pharmacy and
Technolog
y
38
BMC Complementary Medicine and
Thera
p
ies
33
Heli
y
on 28
3.5 Topic Area Visualization Using
Vosviewer
In Vosviewer, the default visualization method for
keywords related to herbal medicine in diabetes
mellitus research themes is to tag and display them as
circles. The significance of an item or keyword is
directly proportional to its frequency of occurrence,
resulting in a larger circle as it appears more
frequently. The frequency of repetition impacts the
magnitude of the objects. Unsurprisingly, the
research issue that received the most attention was
diabetes mellitus, as it had the highest frequency of
occurrence. Once the color is allocated to the
elements, each circle is assigned a distinct color
corresponding to its cluster. The result was derived by
analyzing the frequency of author keywords in
bibliographic data using Vosviewerm (van Eck and
Waltman, 2022).
A keyword minimum occurrence number of 10
was defined. Then we got 7555 keywords and merely
150 keywords that satisfied the condition. After
analyzing the outcome, we collected 6 groupings as
study subjects trends virtual reality in the anatomy
education sector denoted by different colors.
The network visualization illustrates six distinct
clusters and their interconnections among the
identified topic areas. Each cluster comprises
multiple keywords that exhibit a strong correlation
within the structure of the map. Each cluster has
distinct high-frequency instances of terms that
indicate the research topic that has been explored in
previous research. There are the top three clusters
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
96

Figure 4: Network Visualization of herbal medicine for diabetes mellitus field publication co-occurrence map using
Vosviewer.
with the most frequency of occurrence in the top three
keywords. For example, with the most frequent of
occurrence the first cluster has the most frequent
terms: antioxidant (168), antidiabetic (109), and α-
glucosidase (72). The second cluster has oxidative
stress (120), type 2 diabetes (103), and inflammation
(77) as the most prominent common term. The third
cluster includes the most prominent words, such as
diabetes mellitus (272), streptozotocin (91), and
insulin (34).
3.6 The Most Frequent Keywords of
Herbal Medicine in Diabetes
Mellitus Publication
Keywords are crucial for conducting research on
trends. In addition to serving as a keyword research
trend, it also facilitates the discovery of topics
relevant to researchers and readers in their respective
fields. The meticulous selection of these words will
significantly influence the accessibility of searches
and the ongoing discourse topics. Each monoword or
biword keyword will determine the scope of the
literature search and inquiry.
The predominant keywords in the domain of herbal
medicine for diabetes mellitus are displayed in Figure
4. Based on the data shown in Figure 5, the phrases
that had the highest frequency were diabetes (376
occurrences), diabetes mellitus (273 occurrences),
antioxidant (168 occurrences), herbal medicine (161
occurrences), traditional medicine (147 occurrences),
oxidative stress (120 occurrences), medicinal plants
(116 occurrences), antidiabetic (110 occurrences),
type 2 diabetes (103 occurrences), and streptozotocin
(91 occurrences). Put simply, the prevailing subjects
for publishing in the field of herbal medicine and
diabetes mellitus are diabetes mellitus, antioxidants,
and herbal medicine.
Figure 5: The most used keywords of herbal medicine in diabetes mellitus
Global Recent Trends Research of Herbal Medicine for Diabetes Mellitus in a Decade (2014-2023): A Bibliometric Analysis and Scientific
Mapping
97

3.7 Thematic Map Analysis of Herbal
Medicine in Diabetes Mellitus
Publication
Furthermore, this discovery can be utilized to
formulate a captivating concept that can be published
in this domain, specifically pertaining to diabetic
mellitus, antioxidant, and herbal medication. The
Thematic Map study, depicted in Figure 6, provides
evidence to corroborate this finding. The research
topic highlighted in the red circle represents a
thematic trend that holds potential for future
development.
The implementation of the multi-disciplinary
theme is a fascinating concept in this subject. Figure
6 illustrates various potential clusters, such as
diabetes mellitus, anti-oxidant, inflammation and
medicinal herbs. Based on the field or herbal
medicine in diabetes mellitus, various subjects related
to green, blue, pink, and purple colours are suggested
as potential areas for further research.
4 DISCUSSIONS
The management of diabetes mellitus holds
significant relevance, with traditional herbal
medicine being acknowledged for its potential in
addressing this condition. Several scholarly
investigations have underscored the efficacy of
botanical resources in the therapeutic intervention
and control of diabetes (Gaonkar and Hullatti,
2020)(Farzaei et al., 2017).Tran et al. have reported
that these particular botanical species possess
bioactive constituents that have demonstrated
potential efficacy in the management of
diabetes(Tran, Bao and Le, 2020). Nevertheless, it is
imperative to acknowledge and confront the
deceptive endorsement of conventional herbal
remedies as a remedy for diabetes within the
community (Rutebemberwa et al., 2013). According
to (Farzaei et al., 2017), the utilization of
complementary and alternative medicine, such as
herbal medications, has the potential to be beneficial
in the management of diabetes. According to a recent
study conducted by (Putrimarlin et al., 2022), it has
been observed that plants containing flavonoid
components, such as genistein and quercetin, had the
ability to enhance insulin production. Consequently,
these plants hold potential for utilization in the
management and treatment of diabetes. Moreover, the
aqueous extract derived from the seeds of
Tamarindus indica has demonstrated promise in
ameliorating hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia
associated with diabetes, as reported by (Maiti, Das
and Ghosh, 2005). Herbs have been recognized as a
potential adjunct to pharmacological interventions for
managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (Proboningsih et
al., 2020). However, it is crucial to acknowledge that
the efficacy of certain herbs, such as rhubarb, in
regulating hyperglycemia can exhibit variability
(Shad and Haghighi, 2018). In general, the utilization
of traditional medicinal plants shows potential in the
treatment of diabetes mellitus. However, additional
investigation is required to comprehensively
comprehend their underlying mechanisms and
enhance their efficacy (Prabhakar and Doble, 2008;
Mallick et al., 2007).
Figure 6: Thematic map analysis of herbal medicine in diabetes mellitus research
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
98

5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on data from a decade (2014-2023) we get
3,226 articles, this study suggests that the growth
development in herbs for DM with the most
significant Scopus index occurred in 2020, which
reached 24.08 percent. The Journal of
Ethnopharmacology is the most international
publications in herbs for DM with 241 documents.
The Journal of Ethnopharmacology is also the most
influential, with 7,223 citations. China is the country
that has the most research papers on herbs for DM
(574 documents), while Zengin, G is the most prolific
writer (18 documents). Herbs for DM field
development map based on co-occurrence is
classified into six clusters, and diabetes mellitus,
antioxidants, herbal medicine are the most
highlighted term throughout the entire network.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful to Universitas Sebelas Maret
for supporting this research. This work was supported
by the Research Group Funding 2023 (grant number
228/UN27.22/PT.01.03/2023).
REFERENCES
Abebe, S. M., Berhane, Y., Worku, A., & Assefa, A.
(2014). Diabetes Mellitus in North West Ethiopia: A
Community Based Study. BMC Public Health.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-97
Akram, M. (2013). Diabetes Mellitus Type II: Treatment
Strategies and Options: A Review. Journal of Diabetes
& Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-
6156.1000304
Alsanad, S. M., Aboushanab, T., Khalil, M., & Alkhamees,
O. A. (2018). A Descriptive Review of the Prevalence
and Usage of Traditional and Complementary Medicine
Among Saudi Diabetic Patients. Scientifica.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6303190
Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool
for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal
of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOI.2017.08.007
Campbell, M. R., & Shokrani, M. (2016). Diabetes
Management and Future Trends. American Society for
Clinical Laboratory Science.
https://doi.org/10.29074/ascls.29.2.122
Fang, Z., Liu, M., & Kong, L. (2022). Association Between
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width‐to‐albumin Ratio
and Diabetic Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical
Laboratory Analysis.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24351
Farzaei, F., Morovati, M. R., Farjadmand, F., & Farzaei, M.
H. (2017). A Mechanistic Review on Medicinal Plants
Used for Diabetes Mellitus in Traditional Persian
Medicine. Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary
& Alternative Medicine.
https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587216686461
Gaonkar, V. P., & Hullatti, K. (2020). Indian Traditional
Medicinal Plants as a Source of Potent Anti-Diabetic
Agents: A Review. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic
Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00628-
8
Katulanda, P., & Sheriff, M. H. R. (2009). The Diabetes
Epidemic in Sri Lanka – A Growing Problem. Ceylon
Medical Journal.
https://doi.org/10.4038/cmj.v51i1.1373
Lin, X., Xu, Y., Pan, X., Xu, J., Ding, Y., Sun, X., Song,
X., Ren, Y., & Shan, P. (2020). Global, Regional, and
National Burden and Trend of Diabetes in 195
Countries and Territories: An Analysis From 1990 to
2025. Scientific Reports.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71908-9
Maiti, R., Das, U. K., & Ghosh, D. (2005). Attenuation of
Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia in Streptozotocin-
Induced Diabetic Rats by Aqueous Extract of Seed of
Tamarindus Indica. Biological and Pharmaceutical
Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.28.1172
Mallick, C., Mandal, S., Barik, B. R., Bhattacharya, A., &
Ghosh, D. (2007). Protection of Testicular
Dysfunctions by MTEC, a Formulated Herbal Drug, in
Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rat. Biological and
Pharmaceutical Bulletin.
https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.30.84
Mekuria, A. B., Belachew, S. A., Tegegn, H. G., Ali, D. S.,
Netere, A. K., Lemlemu, E., & Erku, D. A. (2018).
Prevalence and Correlates of Herbal Medicine Use
Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Teaching Hospital
in Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC
Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2147-3
Prabhakar, P. K., & Doble, M. (2008). A Target Based
Therapeutic Approach Towards Diabetes Mellitus
Using Medicinal Plants. Current Diabetes Reviews.
https://doi.org/10.2174/157339908786241124
Proboningsih, J., Joeliantina, A., Novitasari, A., &
Purnamawati, D. (2020). Complementary Treatment to
Reduce Blood Sugar Levels of Type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus Patients. International Journal of Public Health
Science (Ijphs).
https://doi.org/10.11591/ijphs.v9i3.20434
Putrimarlin, I., Hasanuddin, H., Safrida, S., Wardiah, W.,
& Andayani, D. (2022). Utilization of Plant as a Drug
for Diabetes Mellitus by the Community of Beutong
District, Nagan Raya Regency. Biosaintifika Journal of
Biology & Biology Education.
https://doi.org/10.15294/biosaintifika.v14i2.36480
Robert, A. A., & Dawish, M. A. Al. (2020). The Worrying
Trend of Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: An Urgent
Call to Action. Current Diabetes Reviews.
https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399815666190531093735
Global Recent Trends Research of Herbal Medicine for Diabetes Mellitus in a Decade (2014-2023): A Bibliometric Analysis and Scientific
Mapping
99

Rutebemberwa, E., Muhamadi, L., Katureebe, S. K.,
Oundo, A., Kiweewa, F., & Mukanga, D. (2013). Use
of Traditional Medicine for the Treatment of Diabetes
in Eastern Uganda: A Qualitative Exploration of
Reasons for Choice. BMC International Health and
Human Rights. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-698x-13-
1
Salehi, B., Ata, A., N, A. K., Sharopov, F., Ramírez‐
Alarcón, K., Ruíz-Ortega, A. M., Ayatollahi, S. A.,
Fokou, P. V. T., Kobarfard, F., Zakaria, Z. A., Iriti, M.,
Taheri, Y., Martorell, M., Sureda, A., Setzer, W. N.,
Durazzo, A., Lucarini, M., Santini, A., Capasso, R., …
Sharifi‐Rad, J. (2019). Antidiabetic Potential of
Medicinal Plants and Their Active Components.
Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100551
Shad, F. S., & Haghighi, M. (2018). Study of the Effect of
the Essential Oil (Extract) of Rhubarb Stem (Shoot) on
Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Fasting Blood Glucose
Levels in Patients with Type II Diabetes. Biomedicine.
https://doi.org/10.1051/bmdcn/2018080424
Tran, N., Bao, P. T., & Le, L. (2020). Bioactive Compounds
in Anti-Diabetic Plants: From Herbal Medicine to
Modern Drug Discovery. Biology.
https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9090252
Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2022). VOSviewer manual
1.6.18. CWTS Meaningful metrics. Universiteit
Leiden.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
100
