
Potential Drug-Drug Interactions and Associated Factors on
Ambulatory Patients with Hypertension of a Secondary Care Hospital
in Bandar Lampung
Noni Zahwa Salsabila, Citra Yuliyanda Pardilawati
*
, Dwi Aulia Ramdini and Oktafany
Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Lampung, Indonesia
Keywords: Hypertension, Drug Interaction, Associated Factor.
Abstract: Hypertensive patients are often given combination therapy according to the patient's condition, the drugs used
have a high risk of potential drug interactions. The aim of this research is to determine potential drug-drug
interactions and associated factors on ambulatory patients with hypertension of a secondary care hospital in
Bandar Lampung. This research is a cross-sectional study. Data were collected from patient’s medical
records. Evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions refers to Drugs.com. The associated factors are
analyzed by Chi-Square test. Of the 135 prescriptions, there are 90 (66,67%) prescriptions that have the
potential for drug-drug interactions. Potential drug-drug interactions based on severity levels are major
(6,88%), moderate (72,10%) and minor (21,01%). Bivariate statistical analysis showed that there was an
influence of age and number of medications on potential drug-drug interactions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Hypertension is a disease condition that occurs due to
an increase in systolic blood pressure exceeding 140
mmHg and diastolic blood pressure exceeding 90
mmHg (Hastuti, 2020). Hypertension is a health
problem in the world because it is a major risk factor
for cardiovascular disease. An estimated 1.28 billion
adults aged 30-79 years worldwide suffer from
hypertension15. Various drugs used to reduce blood
pressure such as diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE
inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs),
calcium antagonists, and vasodilators (PERHI, 2021).
This can cause the drugs and antihypertensive therapy
used by hypertension sufferers to vary and there is a
risk of drug interactions (Chalik, 2021).
Drug interactions can cause effects in the form of
increasing or decreasing activity or producing new
effects that were not present before. The occurrence
of drug interactions can also affect the body's
response, thereby affecting the desired therapeutic
outcome (Mahamudu, 2017). Treatment therapy
needs to be carried out optimally by selecting the best
treatment so that it can provide benefits to patients by
improving quality of life (Whittlesea, 2019). One way
that can be done to achieve this goal is to identify,
reduce and prevent potential drug interactions that
can occur, thus having an impact on the success of
therapy (Parulian, 2019).
Therefore, this research was conducted to
determine the potential for drug interactions and the
factors that influence the potential for drug
interactions in hypertensive patients. This research
aims to ensure that potential drug interactions are
more carefully considered and prevented, so the
incidence of drug interactions can be minimized.
2 METHOD
This research is a descriptive-analytic study with a
cross-sectional approach, carried out retrospectively
on the medical records of ambulatory patients with
hypertension of a secondary care hospital in Bandar
Lampung. The data used medical record for the
period January – June 2023. The sample size was
determined using the purposive sampling method.
Determination of the minimum sample size in this
study was determined based on the proportion
estimation formula.
Salsabila, N. Z., Pardilawati, C. Y., Ramdini, D. A. and Oktafany,
Potential Drug-Drug Interactions and Associated Factors on Ambulatory Patients with Hypertension of a Secondary Care Hospital in Bandar Lampung.
DOI: 10.5220/0013101600003873
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Science and Health (ICOMESH 2023), pages 21-24
ISBN: 978-989-758-740-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
21
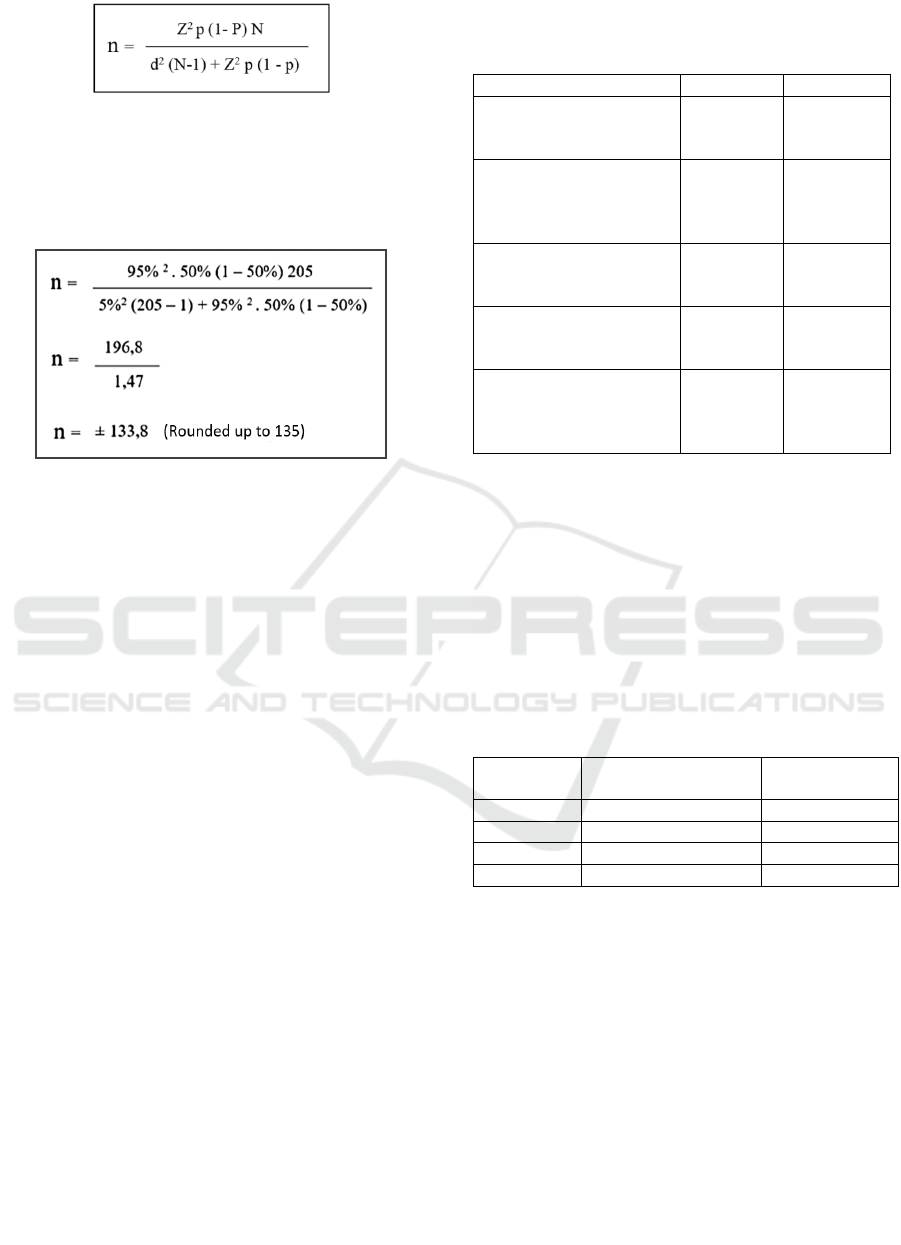
Explanation:
𝑛: Number of samples
N: Number of populations
Z: Degree of trust
p: The proportion of cases to the population
d: The degree of deviation from the desired population
The population of ambulatory patients with
hypertension of a secondary care hospital in Bandar
Lampung on 2023 is 205 patients. The minimum
sample size for this research is 135 samples. In this
study, the inclusion criteria applied were patients
aged ≥ 18 years and having medical records with
complete information. The exclusion criteria applied
were patient who get <2 types of drugs.
The main guidelines that will be used as a guide in
assessing drug interactions are Drugs.com. In
bivariate analysis using the Chi-Square analysis
method with a categorical measurement scale
(Dahlan, 2014).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The sociodemographic characteristic on Ambulatory
Patients with Hypertension of a Secondary Care
Hospital in Bandar Lampung on January – June 2023
was showed in table 1. Hypertensive patients at a
secondary care hospital in Bandar Lampung tends to
be more common in women, namely 78 (57.78%)
patients compared to male patients, namely 57
(42.22%) patients. In the age category, the highest
number of hypertension cases was in individuals aged
≥59 years with 58 (42.96%) patients followed by the
>45-59 years age category with 54 (40%) patients
while the lowest number of cases was recorded in the
age 19-45 years with 23 (17.04%.) patients. There
were 79 (58.52%) prescriptions that used 2-4 drugs
and there were 56 (41.48%) prescriptions that used ≥5
drugs. Patients involved in this study had
comorbidities, with 108 (80%) patients.
Table 1. Sociodemographic characteristics on Ambulatory
Patients with Hypertension of a Secondary Care Hospital in
Bandar Lampung on January – June 2023
Variable Fre
q
uenc
y
Percenta
g
e
Gender
Male
Female
57
78
42.22%
57.78%
Age
19 – 45 years
> 45 - 59 years
> 59
y
ears
23
54
58
17.04%
40.00%
42.96%
Number of Medications
2 – 4 drugs
> 4 dru
g
s
79
56
58.52%
41.48%
Commorbid condition
Present
Absent
108
27
80%
20%
Potential Drug-drug
Interaction
Present
Absent
90
45
66.67%
33.33%
Based on table 1, it is explained that the drug-drug
interactions from 135 samples contained 90 (66.67%)
cases with potential drug interactions and 45
(33.33%) cases without potential drug interactions.
Patients suffering from hypertension have a high risk
of experiencing drug interactions due to long-term
treatment and are often given combination therapy.
Table 2: Severity Levels of Potential Drug-drug
Interactions on Ambulatory Patients with Hypertension of
a Secondary Care Hospital in Bandar Lampung on January
– June 2023
Level of
Interaction
Number of Potential
Interactions
Percentage
(%)
Majo
r
19 6,89%
Moderate 199 72,10%
Mino
r
58 21,01%
Total 276 100 %
Table 2 shows the results of the evaluation of
potential drug-drug interactions of moderate severity.
It was found that these interactions were the most
common. At major severity levels, the potential drugs
found are combinations that all involve
antihypertensive drugs. The most potential drug-drug
interactions that occur in the combination of
amlodipine and simvastatin are 15 potential
interactions. For major interactions between
amlodipine and simvastatin it can cause a potential
increase in the risk of myopathy (Baxter, 2010).
Amlodipine may significantly increase plasma
concentrations of simvastatin and its active
metabolite and increase the risk of statin-induced
myopathy (Baxter, 2010).
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
22

Then the most moderate interactions occur when
using amlodipine together with bisoprolol. The use of
amlodipine and bisoprolol together has a potential
interaction mechanism. Amlodipine can inhibit the
oxidative metabolism of beta blockers and additive
pharmacological effects by reducing blood pressure
and heart rate (Pikir, 2015). This is in accordance with
research at RSUP Haji Adam Malik Medan which
states that the highest interaction based on severity
level is moderate at 69.8% (Dasopang, 2015).
There are 58 (21,01%) potential minor
interactions. An example of a minor interaction
between amlodipine and lisinopril may have additive
hypotensive effects. Although these drugs are often
safe to use together, careful monitoring of systemic
blood pressure is recommended during
coadministration, especially during the first one to
three weeks of therapy (Triyanto, 2014).
Awareness and understanding of potential drug
interactions needs to be the main focus for doctors
and pharmacists. Regular monitoring by assessing the
patient's clinical signs and, if possible, checking for
drugs in the blood. This action is very important to
reduce the risk of possible drug interactions that may
arise.
Based on the bivariate analysis test between age
of patient and potential drug-drug interactions carried
out using chi-square test, p-value of 0.008 was
obtained. The same thing was shown in research by
Khairiyah et al. (2022) who stated that interactions
commonly occur in geriatric patients, especially
pharmacodynamic interactions caused by additive or
synergistic interactions. Therefore, it can be
concluded that there is a relationship between age of
patient and potential drug-drug interactions in
hypertensive patients at a secondary care hospital in
Bandar Lampung on 2023.
Table 3. Associated Factors of Potential Drug-drug
Interactions on Ambulatory Patients with Hypertension of
a Secondary Care Hospital in Bandar Lampung on January
– June 2023
Factor
Potential Drug-drug
Interaction
p-
value
Yes No
Age
19 – 45 years
> 45 - 59 years
> 59 years
9 (6.67%)
38 (28.15%)
43 (31.85%)
14 (10.37%)
16 (11.85%)
15 (11.11%)
0,008
Number of
medications
2 – 4 drugs
> 4 drugs
44 (32.59%)
46 (34.07%)
34 (25.19%)
11 (8.15%)
0,003
Comorbid
condition
Present
Absent
75 (55.55%)
15 (11.11%)
33 (24.44%)
12 (8.88%)
0,171
The results of the analysis of the relationship
between the number of medications and the potential
drug-drug interactions carried out using chi-square
test showed p-value of 0.003, so it can be concluded
that there is a significant relationship between the
number of medication and the potential drug-drug
interactions. In research conducted by Parulian et al.
(2019), the number of medications that had a
relationship with the number of interactions obtained
a positive correlation (very strong correlation),
namely the greater the number of drugs, the more
interactions that occurred.
Then the results of the analysis of the relationship
between comorbid condition and potential drug-drug
interactions using the chi-square test obtained p-value
of 0.171, so it can be concluded that there is no
significant relationship between comorbid condition
and potential drug interactions. In contrast to previous
research at RSU X in Makassar City, it showed a
significant influence on potential drug-drug
interactions. These results indicate that the number of
medications prescribed is the factor that has the
greatest influence on the potential for drug
interactions.
4 CONCLUSION
The results of the evaluation of potential drug
interactions on 135 prescriptions assessed using tools,
namely drugs.com, showed that in patients receiving
antihypertensive drugs, there were 90 prescriptions
that experienced potential drug interactions, which
were divided into three based on the level of severity,
namely 19 potential major level interactions (6.88% )
interaction potential, moderate level interaction
potential is 199 (72.10%) interaction potential, minor
level interaction potential is 58 (21.01%) interaction
potential.
There is a relationship between the number of
medications and age of patient on potential drug-drug
interactions in hypertensive patients, but there is no
relationship between comorbid condition and
potential drug-drug interactions in hypertensive
patients. The variable most related to potential drug-
drug interactions on ambulatory patients with
hypertension of a secondary care hospital in Bandar
Lampung on January – June 2023 is the number of
medications with p-value of 0.003.
Potential Drug-Drug Interactions and Associated Factors on Ambulatory Patients with Hypertension of a Secondary Care Hospital in Bandar
Lampung
23

REFERENCES
Baxter, K., & Stockley, I. (2010). Stockley ’s Drug
Interactions Ninth edition. In Pharmaceutical Press
(Ninth Edit). Pharmaceutical Press.
Chalik, R., Karim, D., Dewi, S. T. R., & Hidayati, H.
(2021). Analisis Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Terhadap
Kejadian Interaksi Obat Pada Pasien Hipertensi Di
Rumah Sakit Umum X Kota Makassar. Media Farmasi,
17(1), 55.
Dahlan, S. (2014). Statistik untuk Kedokteran dan
Kesehatan Seri 1 Edisi 6 (Ed.6). Jakarta: Salemba
Medika.
Dasopang, E., Harahap, U., & Lindarto, D. (2015).
Polipharmacy and Drug Interactions in Elderly Patients
with Metabolic Diseases. Indonesian Journal of Clinical
Pharmacy, 4(4), 235–241.
Hastuti, A. P. (2020). Hipertensi. Jateng: Lakeisha.
Khairiyah, U., Yuswar, M. A., & Purwanti, N. U. (2022).
Pola Penggunaan Obat Antihipertensi Pada Pasien
Hipertensi Di Instalasi Rawat Jalan Rumah Sakit. Jurnal
Syifa Sciences And Clinical Reasearch (JSSCR), 4,
609–617.
Mahamudu, Y. S., Citraningtyas, G., & Rotinsulu, H.
(2017). Kajian Potensi Interaksi Obat Antihipertensi
Pada Pasien Hipertensi Primer Di Instalasi Rawat Jalan
Rsud Luwuk Periode January – Maret 2016. Jurnal
Ilmiah Farmasi, 6(3), 1–9.
Parulian, L. (2019). Indonesian Journal of Pharmacy and
Natural Product. Indonesian Journal of Pharmacy and
Natural Product, 02(July), 4–7.
PERHI, K. (2021). Konsensus Penatalaksanaan Hipertensi:
Update Konsensus PERHI 2019. I-Hefcard.Com, 118.
Pikir, B. S., Aminuddin, M., Subagjo, A., Darmadati, B. B.,
Suryawan, I. G. R., & P, J. N. E. (2015). Hipertensi
Menejemen Komprehensif. Surabaya: Airlangga
University Press.
Setyoningsih, H., & Zaini, F. (2022). Hubungan Interaksi
Obat Terhadap Efektivitas Obat Antihipertensi Di Rsud
Dr. R. Soetrasno Rembang. Cendekia Journal Of
Pharmacy, 6(1), 76–88.
Triyanto, E. (2014). Pelayanan Keperawatan bagi Penderita
Hipertensi secara terpadu. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu.
Well, B. G., Dipiro, J., Schwinghammer, T. L., & DiPiro,
C. V. (2015). Pharmacotherapy Handbook (Ninth Edit).
MC Graw Hill Education.
Whittlesea, C., & Hodson, K. (2019). Clinical Pharmacy
and Therapeutic (Sixth Edit). Elsevier.
ICOMESH 2023 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MEDICAL SCIENCE AND HEALTH
24
