
Studying the Acceleration of Wound Healing with Channa Striata
Extract on Post Sectio Caesarea Patients: Literature Review
Dian Angger Suaner and Ida Paulina
Magister Program, Faculty Pharmacy, Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta,
Jl Santer Permai Raya, Jakarta, 14350, Indonesia
Keywords: Channa Striata, Wound Healing, SC.
Abstract: Caesarean section delivery can have specific impacts on the mother, particularly injuries to the perineal area.
During the injury recovery process, it is common to experience illness. Therefore, it is important for mothers
to have a good intake of food, especially protein, which can increase the speed of wound healing.
Postoperative hematological changes are characterized by leukocytosis in the inflammatory phase due to a
lack of blood fluid. Infections can occur during the postpartum period due to inadequate nutrition in mothers,
which can hinder the healing process of caesarean section wounds. The lack of protein is a major contributor
to the problem of postpartum mothers with caesarean section wounds, as it inhibits the healing process. This
research aims to determine the impact of protein utilization on the healing process of caesarean section surgery
patients. The research methodology employed in this study is a literature review. The regulations provide a
detailed description of the cycle for conducting regular audits. The survey of 7 journals revealed that this
administration had high protein utilization, produced significant results, and had a significant impact on the
injury healing process in post-cesarean section patients. The majority of respondents who received high
protein utilization medication were able to process complex repairs more quickly than those who did not
receive medication.
1 INTRODUCTION
The postpartum period is the time from the delivery of
the placenta until the woman's return to her pre-
pregnancy state. This period typically lasts around 4
and a half months. The requirements during the
postpartum period depend on the woman's birth
history, with special consideration given to those who
have undergone Cesarean delivery. It is worth noting
that Indonesia still has a high birth rate. Most delivery
methods used in Indonesia are unrestricted, but a
significant proportion of births occur via caesarean
section. In 2019, 62.7% of births in Indonesia were
without complications, while 28.9% were via
caesarean section. This high incidence rate increases
the risk of complications, including contamination of
the caesarean wound. A 2020 study conducted by Nih
Luh Putu at Sanglah General Hospital in Denpasar
involved 554 mothers with various indications who
underwent caesarean section. During the postpartum
period, proper wound healing is greatly influenced by
post-delivery care.
The recommended rate for caesarean sections in a
country is between 5-15% per 1000 births worldwide,
a figure that remains unknown to the World Health
Organization (WHO) (WHO, 2021). The rate of
caesarean section deliveries in private clinics is higher
than that in government health clinics, with private
clinics accounting for over 30% of deliveries, while
government clinics account for only 11%. For
instance, in Indonesia, 15.3% of 20,591 mothers who
gave birth in the last 5 years did so via caesarean
section, exceeding the WHO's recommended
maximum of 5-15% (RI, 2020). Caesarean section
(SC) procedures increase the risk of death twofold
compared to vaginal births due to infection, blood
loss, and damage to internal organs. Additionally,
deliveries by caesarean section have a higher
morbidity rate.
One variable related to caesarean section (CS) is
the level of weakness (Memon et al., 2022). CS can
result in respiratory problems, decreased body
temperature, impaired digestive function, and
significant blood loss during medical procedures,
which can lead to weakness (Titi & Aminah, 2022).
Iron deficiency in post-pregnancy mothers can
interfere with their ability to carry out maternal duties,
Suaner, D. and Paulina, I.
Studying the Acceleration of Wound Healing with Channa Striata Extract on Post Sectio Caesarea Patients: Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0012642600003821
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023), pages 235-240
ISBN: 978-989-758-691-0; ISSN: 2828-853X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
235

including cooperation with their child and lactation
cycle. This is due to tiredness and paleness caused by
the deficiency, which can also disrupt nutritional
status (Primadina et al., 2019). Postoperative
discharge is often caused by infections, particularly
uterine disease or endometritis, bladder and liver
injuries. Crooked repair after caesarean section (SC)
can take several weeks assuming no disease occurs
and can last for one year or more until the scar
strengthens. The risk of contamination or sepsis often
increases after the fifth day of care for SC wounds,
which are usually difficult to treat. Therefore, careful
wound stitching is necessary (Sale et al., 2020).
Local factors such as wound management
practices, hypovolemia, infection, and the presence of
foreign objects in the wound can influence wound
healing. Additionally, wound-related factors like
infection, edema, and bleeding can also impact
healing. Other common factors that can affect healing
include age, nutrition, steroid use, sepsis, maternal
diseases such as anemia and diabetes, medications,
and indications for spontaneous cesarean delivery
(Safitri, 2022). Pharmacological treatment for
preventing disease and accelerating wound healing
has so far involved the administration of anti-infective
drugs. In addition to anti-infective drugs, postpartum
women require high-quality, nutritious food with
sufficient calories to aid in the healing of wounds after
a cesarean section. The diet should include vegetables
and organic products, particularly those high in
protein. Consuming protein-rich foods can aid in the
healing of surgical wounds for postpartum mothers
(Mayang & Dewi, 2023). This is because protein is
essential for the formation of new tissue and plays a
crucial role in the wound healing process.
According to Marliana Ginting's 2019 research at
the Binjai TNI Emergency Clinic, 15.35% of the
general public lacked information on treating liver
injuries resulting from caesarean sections. This lack of
information can increase the risk of infection in the
caesarean section wound. One issue during pregnancy
via caesarean section is contamination of the liver
wound, which can spread to other tissues such as
salpingitis and peritonitis. Efforts that can support
wound healing include ensuring adequate nutrition
and minerals, maintaining cleanliness of caesarean
section wounds, and proper preparation. The post-
pregnancy period following a cesarean delivery
requires good and proper care, including nutrition.
Several studies conducted by Dian Zuitna in 2021
have shown that protein supplements, particularly
those containing egg and snakehead fish, can aid in the
healing of caesarean section wounds. The research
indicates that snakehead fish has higher protein levels,
which can accelerate the wound healing process.
Snakehead fish contains 25.2 grams of egg white
protein per 100 grams, which is 60% more than that
found in plasma (3.3-5.5 gr/dl). In relation to this
investigation, scientists are interested in providing
Evidence-Based Case Report mediation to post-
Caesarean section patients by consuming snakehead
fish. Snakehead fish is easily accessible to the general
public and is not difficult to consume.
2 METHODS
This literature review examines the relationship
between dietary restrictions and the length of healing
of caesarean section wounds. Only articles that were
available in full text form were included in the study.
The search for articles was conducted on several
databases, including ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google
Scholar, and EBSCO. The inclusion criteria were
strictly followed, and the selected articles were
systematically collected and examined. The search
was limited to articles published between 2015 and
2020. The search process yielded seven articles that
met the inclusion and exclusion criteria for this
systematic review. The inclusion criteria require full-
text journals with abstracts, introductions, research
methods, research results and discussions, as well as
conclusions and suggestions. The research method
employed a systematic review approach using the
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews
and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The article search yielded 30 results, which were then
filtered using inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Ultimately, 7 articles from 30 journals were selected
that met the research criteria.
Based on the review of the seven journals, it was
found that the intervention groups that consumed
snakehead fish and eggs showed significant
improvement in the wound healing process of post-
cesarean section mothers due to high protein
consumption. The treatment was administered at
varying frequencies of 3 to 24 days with different
amounts of protein consumption. Both snakehead fish
and eggs are effective in the wound healing process.
Out of the 7 reviewed journals, 4 did not specify the
number of interventions given to the treatment group,
while the other 6 stated that the number of treatments
given varied.
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
236
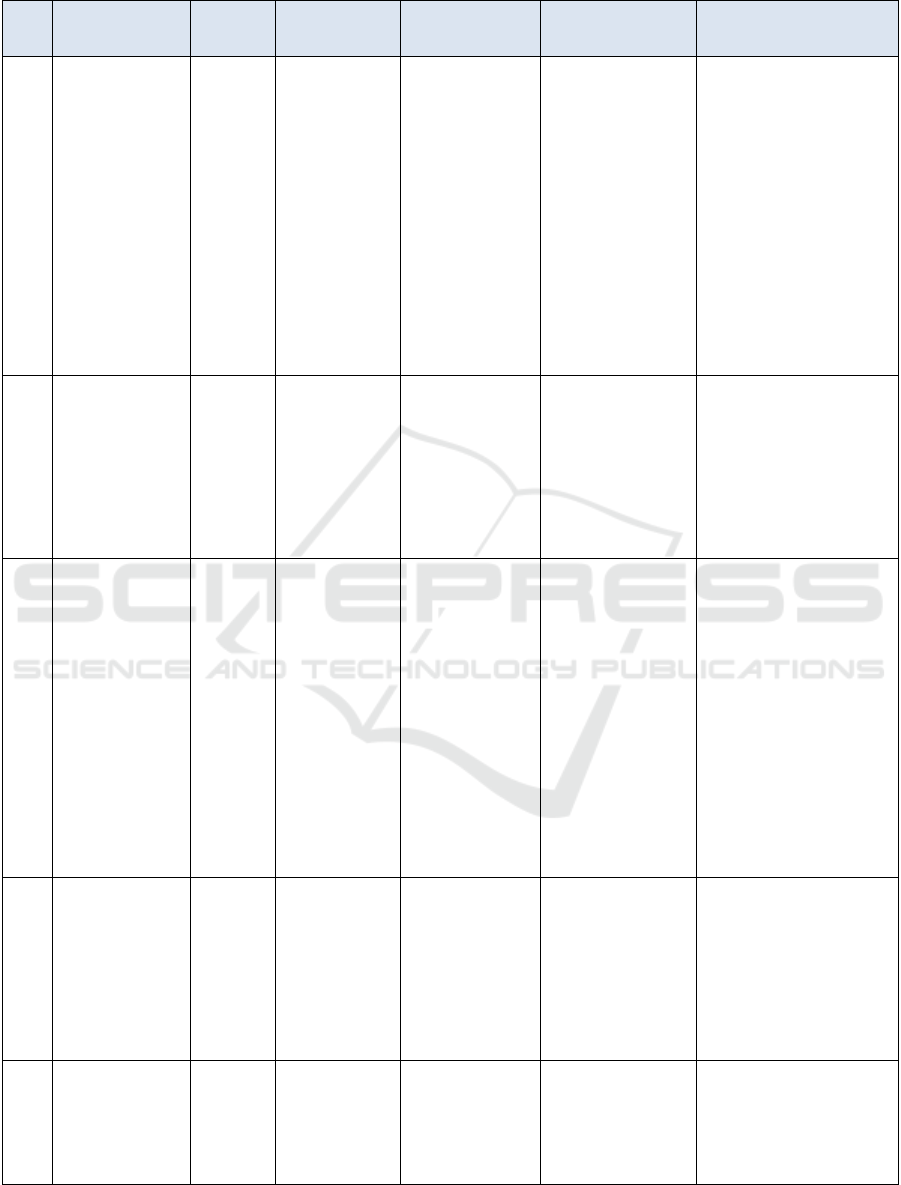
Table 1.
No Title Author,
Year
Aim Method Sample Result
1. Healing Post
Sectio Cesarea
(SC) Wounds
With Snakehead
Fish Extract
(Channa Striata)
Ummah &
Ningrum.
2020
analyzing the
effect of
snakehead fish
extract on Post
Sectio Cesarea
(SC) wound
healing
The research
design uses quasi-
experimental with
pretest-posttest
control group
design
The population was
all 30 post-SC
postpartum mothers
at Permata Hati
Hospital Malang, a
sample of 30 people
divided into 2 groups
(15 people each in
the treatment and
control groups).
The results showed that
there was a difference in the
reduction of wound status (p
= 0.001 < 0.05).
Statistically, it can be
concluded that there is an
effect of administering
snakehead fish (Channa
striata) extract on the
healing of post-sectio-
caesarea (SC) wounds in
postpartum mothers.
Snakehead fish has the
highest albumin content,
speeding up the wound
healing process.
2. The Effect of
Giving Gabus Fish
on the Healing
Process of
Postoperative
Sectio Caesarean
Tetty
Junita
Purba et
al., 2020
The study aims
to determine the
effect of Gabus
fish on the
healing process
of sectio
caesarean
This research uses
a quasi-
experimental
method, data is
analyzed using the
Fisher's Exact Test
with the Spearman
correlation test.,
The sample in this
study consisted of 34
mothers who gave
birth by CS
The results obtained were
that most of the intervention
group experienced fast
wound healing, 14 people
(82.4%) and the control
group experienced slow
wound healing, 13 people
(76.5%). The statistical test
results show p value = 0.002
3. The Effect of
Snakehead Fish
(Channa Striata)
Extract on Blood
Leukocyte
Number and
Cesarean Section
Wound Healing
Suryanti.
Et al.,
2019
to explain the
effect of
snakehead fish
extract on blood
leukocyte counts
and wound
healing in post-
cesarean section
patients.
The research
method used is
True-experiment
Design. The
instrument for
measuring the
number of
leukocytes is the
Hematology
Analyzer Method,
while wound
healing uses the
REEDA Scale
The sample
consisted of 26
postpartum mothers
who were divided
into 2 groups, 13
mothers were
included in the
intervention group
(receiving snakehead
fish extract) and the
remaining 13 were
included in the
control group
(receiving standard
therapy).
Administration of
snakehead fish extract
affected the number of
blood leukocytes with a p-
value of 0.003. On average,
wound healing occurred on
day 8 with a p-value of
0.001. Based on the results
above, it can be concluded
that administering
snakehead fish extract 700
mg 2 1 for 7 days to patients
after caesarean section has
an effect on the number of
blood leukocytes and
wound healing.
4. Correlation of
Cock Fish
Consumption to
Healing
Circumcision
Wounds in Desa
Lestari Dadi-
Pegajahan
Serdang Bedagai
Andilala
et al.,
2022
to find out how
the relationship
between the
influence of
snakehead fish
consumption on
wound healing
after
circumcision
The research
method used in
this scientific work
is a grounded
method, using a
qualitative
approach
Community of the
Whole Village
(Dadi-Pegajahan
Sustainable Village)
Through direct observation
on the sixth day it was
discovered that the protein
content in snakehead fish
was higher than other types
of fish, the albumin content
in snakehead fish reached
6.22%
5. The Effect of
Consuming
Snakehead Fish on
Sectio Caesarea
Wound Healing
Gurusinga
. 2022
determine the
effect of
snakehead fish
on SC wound
healing
Pretest and
posttest quasi-
experimental
design method,
Sample of 16 post
partum SC mothers
on days 2-14
The results obtained were
that there was an effect of
snakehead fish
consumption on wound
healing with a p value of
0.02<0.05.
Studying the Acceleration of Wound Healing with Channa Striata Extract on Post Sectio Caesarea Patients: Literature Review
237
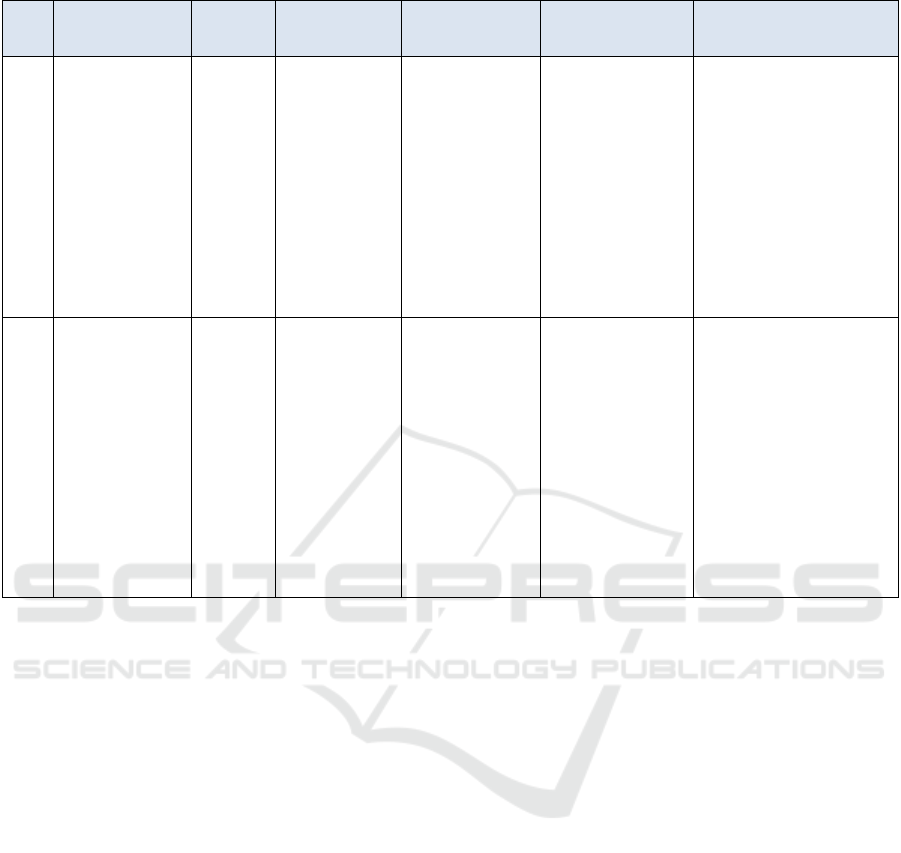
Table 1 (cont).
No Title Author,
Year
Aim Method Sample Result
6. The Effect of
Giving Snakehead
Fish on the
Healing of Sectio
Caesarea Wounds
in Postpartum
Mothers in the
Working Area of
the Ciasem
Subang Health
Center in 2020
Nurhikma
h et al.,
2020
to determine the
effect of giving
snakehead fish
on the speed of
SC wounds in
postpartum
mothers in the
working area of
the Ciasem
Subang
Community
Health Center in
2020
Quasi
Experimental
research design
which is Posttest
With Control
Group
The sample in this
study consisted of 32
women giving birth
by CS, consisting of
16 treatment groups
and 16 control
groups
The statistical test results
showed that the SC wound
acceleration score for the
treatment group on day 7
was an average of 2.25;
while in the control group
the average was 3.69.
7. The Effect of
Consuming
Snakehead Fish
Floss to
Accelerate
Healing of
Perineal Wounds
in Postpartum
Women
Selvianti
&
Nilawati.
2021
to determine the
effect of
consuming
snakehead fish
floss on the
healing of
perineal wounds
in postpartum
mothers
using a
Nonequivalent
Control Group
quasi-
experimental
design.
A sample of 40
postpartum mothers
who would consume
snakehead fish floss
was obtained
through purposive
sampling.
The average wound healing
time for the case group was
4.73 days, while in the
control group the average
wound healing time was
6.68 days. Statistical tests
using the independent
simple T-Test obtained a
value of ρ value = 0.000 <
0.05, so it can be concluded
that snakehead fish floss has
an effect on healing perineal
wounds in postpartum
wome
n
Several previous studies have suggested a
correlation between abstinence and the healing time
of Sectio Caesarea wounds. The review found 10
diary entries that explored the relationship between
dietary restrictions and the healing time of Sectio
Caesarea wounds, with differences in strategy and
testing being assessed. Furthermore, mothers who
have recently given birth are expected to receive
information regarding the healing process of a
Caesarean section incision. It is imperative that
healthcare professionals are able to provide clear
explanations to mothers who have undergone this
medical procedure in order to meet their health needs,
as it directly impacts the healing process of the
incision. Complications that can occur shortly after a
Caesarean section include post-operative infections
such as uterine contamination or endometritis, urinary
tract infections, and liver injury. These infections are
responsible for approximately 90% of post-operative
complications and can increase the maternal mortality
rate (MMR) (Daniati, 2022).
Women who undergo the Caesarean section
medical procedure may face a risk of vaginal health-
related diseases ranging from 5% to 20%. The
incidence of disease after undergoing the Caesarean
section medical procedure is significant, as it causes
pain to the mother (Wulan Anggraeni, 2019). Proper
nutrition is essential for injury recovery, as the
physiological process of wound healing depends on
the availability of protein, nutrients (especially
vitamins A and C), and minerals. Collagen is a protein
composed of amino acids obtained by fibroblasts
from the protein they consume. L-ascorbic acid is
expected to aid in collagen synthesis. Vitamin A can
mitigate the negative effects of steroids on injury
healing. Zinc, a minor component, is crucial for
epithelial structure, collagen synthesis, and collagen
fiber integration (Anwar & Safitri, 2022). Adequate
nutrition is necessary for the body to heal after
medical procedures. The process of wound healing is
dependent on the availability of protein, vitamins
(particularly vitamins A and C), and minerals.
Therefore, proper nutrition is usually required for
wound healing (Rusnedy et al., 2023). Good nutrition
for the wound healing process includes fat, protein,
carbohydrates, vitamin A, zinc, and vitamin C. These
nutrients play a crucial role in the wound healing
process, the duration of the healing process, the
strengthening of wound tissue, and the prevention of
infection. Proper nutrition is crucial, especially for
postpartum mothers with perineal or caesarean
wounds. It is important to consider not only the
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
238

amount of food consumed but also the nutrients it
provides. The frequency, quantity, and timing of
meals all play a role in maintaining good nutrition.
Fish, eggs, and meat are good sources of essential
nutrients for the body.
Breastfeeding mothers require additional calories
to support both the healing process and the production
of breast milk for their babies (Solehati, 2020). Adult
women typically require 2200 kilocalories, while
breastfeeding mothers require an additional 700
kilocalories during the first six months after giving
birth (Solehati, 2020). Mothers who have undergone
a cesarean section and restrict their diet, as advised by
their parents, may experience a slower healing
process. This can be attributed to a decrease in
nutritional intake. Conversely, mothers who have
adequate sustenance will experience a faster injury
recovery cycle. Conversely, mothers who have
adequate sustenance will experience a faster injury
recovery cycle. Conversely, mothers who have
adequate sustenance will experience a faster injury
recovery cycle. These findings were reported by
Haerani et al. (2021). Dietary forbearance is a
behavioural practice of abstaining from certain foods
due to social taboos that have been passed down
through generations. Certain groups have legends
about restricted food sources, such as breastfeeding.
Despite lacking scientific evidence, some still believe
that consuming certain foods while breastfeeding can
cause negative effects, such as festering wounds and
bad-tasting breast milk (Yanti, 2019).
4 CONCLUSION
The nutritional status of postpartum mothers has a
significant impact on the wound healing process.
Nutritional status refers to the body's condition
resulting from food consumption and nutritional
intake. Nutrients aid in metabolic processes and the
maintenance and formation of new tissue (Viyana,
2023). Nutritional status is a reflection of the balance
between the body's need for nutrients to maintain
normal bodily functions, produce energy, and obtain
other nutritional intake. Following surgery, the body
requires nutrition to aid in maintaining health and
healing wounds. These nutrients can be obtained from
foods that contain protein, carbohydrates, and fat,
which are available from various animal and
vegetable sources. These nutrients can be obtained
from foods that contain protein, carbohydrates, and
fat, which are available from various animal and
vegetable sources. These nutrients can be obtained
from foods that contain protein, carbohydrates, and
fat, which are available from various animal and
vegetable sources.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors express gratitude to the study participants
for their valuable contribution. This research can serve
as a reference for further analysis on the effectiveness
of other plants in healing post-Caesarean patients.
REFFERENCES
Anwar, C., & Safitri, F. (2022). Perawatan Masa Nifas Di
Rumah Sakit Bhayangkara Banda Aceh. Jurnal
Pengabdian Masyarakat (Kesehatan), 4(1), 61–69.
Barid, M. (2022). Pengaruh Konsumsi Protein Tinggi
Terhadap Proses Penyembuhan Luka Pada Pasien
Pasca Operasi Sectio Caesarea. Jurnal Keperawatan
dan Kesehatan, 13(2), 90-96.
Daniati, D. (2022). Asuhan Kebidanan Kehamilan:
Panduan Praktis untuk Bidan. Yogyakarta: Jejak
Pustaka.
Darmawati, Cut Husna, Aida Fitri, Dahrul Munira5, And
1graduate. (2019). “The Effectiveness Of High Protein
Nutrient To The.” Jurnal Medika Veterinaria 13(2):
192–99.
Deni Imam. (2019). “Pengaruh Pendidikan Kesehatan
Tentang Nutrisi Melalui Media Visual Interaktif
Terhadap Budaya Pantang Makan (Tarak) Pada Pasien
Diabetik Foot Ulcer Di Kabupaten Bojonegoro.” 17(1):
40–49.
Desi Ratna Sari. (2019). “Faktor Yang Memengaruhi
Keputusan Sectio Faktor Yang Memengaruhi
Keputusan Caesarea (Sc) Pada Ibu Bersalin Di Rsu.
Mitra (Sc) Pada Ibu Bersalin Di Rsu. Mitra Medika
Tanjung Mulia Tahun 2019.” : 1–7.
Fatah, U., Nuraini, I., & Hubaedah, A. (2023). Perbedaan
Pemberian Ekstrak Ikan Gabus Dan Rebusan Daun
Binahong Terhadap Penyembuhan Luka Post Operasi
Section Caesarea. SNHRP, 5, 2394-2401.
Gurusinga, R. (2022). The Effect Of Consumption Of Cock
Fish On Sectio Caesarea Wound Healing. JURNAL
KEBIDANAN KESTRA (JKK), 5(1), 137-141.
Haerani, Hidayah Bokhari, N., Wahyuni, S., Ariani Nur, N.,
Misnawaty, & Basri, F. (2021). Hubungan Antara
Status Gizi Dengan Pemulihan Masa Nifas Hari Ke-Iii
Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah (Rsud) Kabupaten
Jeneponto. Medika Alkhairaat : Jurnal Penelitian
Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan, 3(1), 16–20.
https://doi.org/10.31970/ma.v3i1.68
Lia Dharmayanti. (2019). “Pengaruh Konsumsi Putih Telur
Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Luka Jahitan Post
Sectio Caesarea.” Jurnal Keperawatan Dan
Kebidanan: 6–10.
Listyanto, N., & Andriyanto, S. (2019). Ikan Gabus
(Channa Striata) Manfaat Pengembangan Dan
Studying the Acceleration of Wound Healing with Channa Striata Extract on Post Sectio Caesarea Patients: Literature Review
239

Alternatif Teknik Budidayanya. Media Akuakultur, 4,
18–25
Maesaroh. (2019). “Jurnal Kesehatan Pertiwi Pengaruh
Status Gizi Ibu Nifas Terhadap Penyembuhan Luka
Post Partum Operasi Sectio Caesaria.” Jurnal
Kesehatan Pertiwi Politeknik Kesehatan Bhakti Pertiwi
Husada I: 1–7.
Malawat, R. (2022). Literatur Review: Pengaruh Pemberian
Ekstrak Ikan Gabus (Channa Striata) Terhadap
Penyembuhan Luka Post Sectio Sesarea. Jurnal
Keperawatan Indonesia Timur (East Indonesian
Nursing Journal), 2(2), 96-111.
Mayang, C., & Dewi, E. S. M. (2023). Gizi Dalam
Kesehatan Reproduksi. Surabaya: Deepublish.
Memon, W., Qazi, S., Naqvi, N., Bai, M., Bala, M., &
Memon, N. (2022). Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
Associated with Preterm Caesarean Delivery. Journal
of Research in Medical and Dental Science, 10(1), 281–
284.
Mutmainnah, M., & Wintarsih, W. (2023). Efektifitas
Konsumsi Ikan Gabus (Channa Starata) terhadap
Penyembuhan Luka Perineum pada Ibu Post
Partum. Jurnal Farmasetis, 12(3), 285-292.
Nurhikmah, A., Widowati, R., & Kurniati, D. (2020).
Pengaruh Pemberian Ikan Gabus Terhadap
Penyembuhan Luka Sectio Caesarea Pada Ibu
Pospartum Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Ciasem
Subang Tahun 2020. Syntax Idea, 2(8), 302-314.
Purba, T. J., & Manalu, A. B. (2020). Percepatan
Penyembuhan Luka Post Operasi Sectio Caesarea
Dengan Konsumsi Ikan Gabus (Channa Striata) Di
Rumah Sakit Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Deli
Serdang. Jurnal Doppler, 4(2), 55-60.
Rusnedy, R., Febrina, M., & Sari, C. P. (2023). Uji
Aktivitas Wound Healing Ekstrak Etanol Buah
Averrhoa bilimbi L. (Belimbing Wuluh ) Pada Mencit
Putih Jantan ( Mus musculus ) Wound Healing Activity
Test Averrhoa bilimbi L . Fruit Ethanol Extract in Male
White Mice ( Mus musculus ). 20(1), 50–60.
Safitri, E. W. (2022). Buku Ajar Gizi dan Diet untuk D3
Keperawatan: Sesuai Kurikulum AIPViKI Updated-
2022. Pekalongan: PT. Nsya Expanding Management.
Sale, H. O., Sutriyani, T., & Sari, D. K. (2020). Hubungan
Infeksi Keputihan Dan Kecemasan Dalam Kehamilan
Dengan Kejadian Ketuban Pecah Dini. Biomed Science,
8(1), 37–44.
Tetti Solehati, Cecilia Destiani Ekautami Putri, Pitria Sri
Pujhiyani. (2020). “Pengaruh Pendidikan Kesehatan
Nutrisi Pada Tingkat Pengetahuan Ibu Post Partum.”
Jurnal Kesehatan masyarakat, 7(1).
Titi, H. S. S., & Aminah, N. S. (2022). Studi Kasus Pada
Ny. S Dengan Post Sectio Caesarea (Sc) Atas Indikasi
Pre-Eklamsia Di Ruang Siti Hajar Rsu Islam Klaten.
2020, 210–218.
Viandika, Nurya, And Ratih Mega Septiasari. (2020).
“Pengaruh Continuity Of Care Terhadap Angka
Kejadian Sectio Cessarea.” 3(1): 1–8.
Viyana, A. (2023). Hubungan Pengetahuan, Status Gizi,
dan Mobilisasi Dini Terhadap Penyembuhan Lukaa
Post Sectio Caesarea ddi RS Permata Pamulang Tahun
2023. SENTRI: Jurnal Riset Ilmiah, 2(4), 1275--1289
Wulan Anggraeni. (2019). “Gambaran Penyembuhan Luka
Post Operasi Sectio Caesarea Dengan Pemberian
Antibiotik Ceftizoxime Sebagai Profilaksis Dosis
Tunggal Di Rumah Sakit Singaparna Medika
Citrautama Kabupaten Tasikmalayatahun 2018.”
Jurnal Bidkesmas 02.
Yanti, Desi Ari Madi. (2019). “Hubungan Asupan Protein
Dengan Kecukupan Asi.” Jurnal Kesehatan Panca
Bhakti Lampung VII(1): 8–16.
Yuli Suryanti. (2020). “The Effect Of Snakehead Fish
(Channa Striata ) Extract On Blood Leukocyte Number
And Cesarean Section Wound Healing.” 443(Iset
2019): 596–98.
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
240
