
Corporate Governance and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Disclosure Among Commercial Banks in an Emerging Economy:
Evaluative Perspectives
Padam Dongol
a
and Sajeeb Kumar Shrestha
b
Lincoln University College, Petaling Jaya, Malaysia
Keywords: Corporate Governance, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Commercial Banks, Board Characteristics.
Abstract: The confluence of corporate governance (CG) and corporate social responsibility (CSR) has become
increasingly significant in the contemporary banking landscape of emerging economies. The collaboration
between gender diversity and financial leverage in shaping CSR disclosure has not been comprehensively
explored in this context. The corporate governance factors evaluated including board meetings, the age of the
board, the percentage of women on the board, and the size of the audit committee. The dataset was collected
from 432 individuals. We utilize multivariate analysis techniques to assess the relationships between CG
variables, including board composition, ownership structure, and CSR disclosure. As a result, we found that
board composition, gender diversity, financial leverage, and industry type were significantly influenced by
CSR disclosure among commercial banks in the emerging economy. When regulators, policymakers, and
bank stakeholders know these connections, they may collaborate to raise corporate governance standards and
encourage ethical banking practices, which will help the emerging economy grow sustainably.
1 INTRODUCTION
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) and corporate
governance (CG), two interrelated business practices,
are receiving more and more attention from
academics, practitioners, and politicians in today's
global business environment. The renewed attention
was especially relevant in emerging economies,
where rapid economic expansion, diversified
stakeholder dynamics, and changing regulatory
settings provide a complex environment for corporate
activity. Emerging economies have seen a substantial
change in recent years. These economies are
distinguished by their distinctive combination of
economic prospects and obstacles. Economic entities,
especially corporations and financial institutions,
must navigate a complex environment where societal
effects and financial performance are intertwined in
the changing climate. Commercial enterprises are at
the heart of these economies; thus, their governance
procedures and CSR programs are in the public eye
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-5398-9372
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5227-771X
and significantly impact the socioeconomic
landscape as a whole (Chen, 2023).
1.1 Growing CSR Trends in Emerging
Economies
The CSR environment in emerging economies was
unique since they frequently have a variety of
cultural, economic, and regulatory circumstances. In
these contexts, the CSR paradigm goes beyond
traditional charitable undertakings and compliance-
driven activities. It includes a broader range of moral
principles, environmental responsibility, and a
dedication to stakeholders' interests other than
shareholders (Khojastehpour and Jamali, 2021).
1.2 The Function of Corporate
Governance
Banks' CSR frameworks are built upon corporate
governance frameworks, which include board
composition, ownership structure, and regulatory
Dongol, P. and Shrestha, S.
Corporate Governance and Cor porate Social Responsibility (CSR) Disclosure Among Commercial Banks in an Emerging Economy: Evaluative Perspectives.
DOI: 10.5220/0012492600003792
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR 2023), pages 521-528
ISBN: 978-989-758-687-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
521

monitoring. The foundation for ethical behaviour,
risk management, and sensible decision-making is
laid through effective governance procedures. As a
result, they significantly impact how intensely and in
what direction banks engage in CSR. In emerging
economies, corporate governance acquires a
particular relevance as the foundation of ethical
corporate behaviour (Velte, 2023). A corporation's
commitment to CSR and ethical corporate behaviour
was greatly influenced by the make-up, operation,
and oversight of its boards of directors (BoD) and
executive leadership teams. However, due to
elements including ownership arrangements, rules
and regulations, and cultural quirks, corporate
governance processes in emerging economies may
differ dramatically from those in mature markets (de
Villiers and Dimes, 2021).
1.3 The Strategic Need for CSR
CSR has gone from being a side issue to a strategic
requirement for companies in emerging economies
due to the changing demands of stakeholders,
including investors, consumers, and regulatory
authorities. Corporations are rapidly realizing that
CSR was more than a compliance concern but an area
of competitive advantage as the demand for
accountability and transparency grows. Sustainable
development, social inclusion, and ethical
governance are all included in CSR programs, which
reflect a broader societal commitment that is in line
with the varied and dynamic contexts of growing
economies (Abugre and Anlesinya, 2020).
The study investigates how board composition,
ownership structure, and other aspects of corporate
governance affect CSR disclosure (CSRD) among
commercial banks in emerging economies. It also
examines how gender diversity and financial leverage
affect these disclosure practices.
The remainder of the study was divided into the
following sections: We provide background
information on the research environment in Section 2,
focusing on corporate governance and CSR activities
in the banking industry; Section 3 delves into the
study's theoretical framework, presents a summary of
pertinent literature, and develops our hypotheses. The
data and our study technique are described in Section
4, respectively. The paper's concluding thoughts are
included in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORKS
(Orazalin,2019) examined CSR reporting procedures
in Kazakhstan's banking industry and how board
qualities affect CSRDs. The information on CSRDs
was collected manually from the yearly reports of
banks registered on the KASE. The findings
demonstrate that gender diversity on boards
positively impacts CSR reposting. However,
independence from management and board size have
no bearing on the volume of CSRDs. Data constraints
and the period selected could impact the
completeness of the analysis. Recognizing the
importance of CSR worldwide, (TRAN, et al, 2020)
examined the effects of corporate governance
determinants on CSRDs in Vietnamese commercial
banks. The corporate governance variables are
compared to CSRD using data from time series and
OLS (Ordinary Least Squares) regression analysis.
The findings indicate three problems with corporate
governance have positively impacted the disclosure
of CSR among Vietnamese commercial banks. They
use OLS regression, which makes specific statistical
assumptions that might not always hold in real-world
situations. (Matuszak, et al, 2019) found a link
between the corporate governance practices of these
institutions and their CSR statements. The gathered
data was subjected to procedures for analysis of panel
data. The findings demonstrate that throughout the
investigation, the banks under scrutiny enhanced their
CSR reporting procedures. It could restrict how
widely outcomes can be applied to a given time
period and region of the world.
(Duong, et al, 2023) better understand how state
ownership and strong CEOs affect Vietnam's
commercial banks' CSR. Vietnam was a developing
market in Asia. The analysis' indigeneity and
heterogeneity issues are addressed using an evolving
system, the GMM (Generalized Method of
Moments). The findings show that solid CEOs are
detrimental to CSR initiatives because they tend to
devote less money to CSR investments because of the
potential loss of operating free cash flow. Their focus
on the Vietnamese banking industry may limit the
applicability of results to other sectors or
geographical areas. (Abdelnur, 2021) evaluated the
degree of CSRD in On the Khartoum stock exchange
(KSE), annual reports of commercial banks in Sudan
are traded. 61 yearly filings from 10 registered
financial companies during a seven-year period were
reviewed using a content analysis technique. The
findings of all of the banks studied disclosed CSR
data in their yearly filings. The analysis does not
evaluate the influence or efficacy of CSR programs;
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
522

instead, it was based on the substance of annual
reports. In Malaysia, (Lui and Zainuldin, 2022)
compared CSRD degrees between domestic and
foreign banks. It uses robust regressions and OLS to
analyze the data. The findings show that Malaysian
local banks tend to provide more CSR data than their
multinational rivals. The concentration of the study
on a particular period and geographical area may limit
the generalizability of results.
(Miah, et al, 2019) focused on IBBL's efforts to
address societal and financial issues through
humanitarian aid, education, health, sports, the arts,
and culture initiatives. To improve the social welfare
of underdeveloped areas, the study examines the
growth rates in several CSR sectors and highlight’s
locations that may need further funding. Other
sectors' growth rates were lower, indicating that more
money was needed elsewhere to support social
welfare initiatives. The limitations, which include its
emphasis on a single financial institution (IBBL) and
a narrow time window, may make it difficult to
generalize its results to other banks and areas. (Ho,
Liang, and Tumurbaatar, 2019) how CSR impacts
Corporate Financial Performance (CFP) in
Mongolian institutions. To evaluate the CFP, they
developed a CSRD index and examined several
financial variables. They emphasize the importance
of taking the precise moment of financial crises into
account when examining this relationship. They find
correlations but do not prove a connection or explore
the precise mechanisms by which CSR affects
financial performance.
(BUI, 2021) focused on the one-way relationship
between Vietnamese commercial banks' financial
performance and CSR. The analysis makes use of
dynamic panel methods, a collection of Vietnamese
commercial banks, a two-step GMM estimator, and
regressions. In contrast to private banks, state-owned
commercial banks are less positively impacted by
CSRD in terms of their financial performance. The
concentration of the study on a particular geographic
area and ownership structure may limit the
applicability of the results to other contexts. With a
focus on developing economies, (Nwude, and
Nwude, 2021) intends to empirically analyze the
association between firm board features and CSRD in
the Nigerian banking sector. Multiple regression
analysis was used in the study using panel data from
the audited financial records of the chosen
institutions. The banks with more giant boards, fewer
board members who work outside of the bank's
operations and more female directors generally
disclose their CSR activities more frequently. The
drawback includes its emphasis on a single sector
(Nigerian banking) and the possible need for
generalizability to other industries or geographical
areas.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Development of Hypothesis
A crucial stage of the research process is the creation
of hypotheses. It entails creating verifiable
hypotheses or educated predictions regarding the
expected correlations between study variables.
Research is given a distinct direction by hypotheses,
which direct data collecting and analysis. They enable
systematic testing and evaluation of the results that
researchers expect to uncover, assisting in
formulating predictions that lead to empirical
findings regarding the research subject being
investigated.
3.1.1 Age of Board
The mean age of the board members can be used to
gauge the amount of experience of the committee
members. A board with a greater average age is more
significant and experienced, while a board with a
smaller mean age is younger and less experienced.
Older directors are often thought to bring more
wisdom and well-honed decision-making abilities,
frequently favoring traditional and risk-averse
corporate strategies. In contrast, younger directors,
having received more recent education, tend to be
more inclined toward risk-taking and are often drawn
to innovative business ideas, including those related
to CSR activities. Although the research has explored
the influence of board age on a firm's performance, its
connection to CSRD has received less attention.
While the studies have found insignificant effects,
younger board members had a higher propensity to
support contemporary business practices than their
more senior colleagues, such as CSRD. Thus, the
hypothesis emerges that:
Hypothesis 1: The degree of CSRD is negatively
correlated with board age.
3.1.2 Board Meeting
A corporate board's problem-solving capability and
diligence can be assessed by analyzing the number of
annual board meetings. Board members participate in
many meetings with increased opportunities for in-
depth discussions, workload distribution, and idea
Corporate Governance and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Disclosure Among Commercial Banks in an Emerging Economy:
Evaluative Perspectives
523

sharing. A responsive board pleases the owners and
improves the organization's reputation among
stakeholders. However, it is essential that
commonplace meetings may disrupt business
operations and reduce the quality of interactions
among board members. Formulating an effective
CSR strategy and policy is a complex process that
requires a collaborative effort and demands time from
board members. The complexity results from several
factors, including the need for a sustainable culture,
prior knowledge, resistance to transformation, and the
attitude of business leaders. A robust CSR plan
requires the board to address these issues and develop
a comprehensive CSR strategy. Therefore, boards
with regular meetings have more opportunities to
deliberate on garnering stakeholder support and CSR
plans. While the research has explored the impact of
board meetings on CSRD and found an encouraging
but statistically unimportant correlation, this study
posits that a superior frequency of meetings is
conducive to developing CSR initiatives.
Consequently, the study proposes the following
hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: The amounts of CSRD and board
meetings positively correlate.
3.1.3 Audit Committee
Making sure that the financial records of a business
are accurate is crucially dependent on the audit
committee. The competence of this committee hinges
on the composition of its members and experience. A
larger audit committee, composed of more skilled and
seasoned individuals, is essential for its effectiveness.
The audit committee's effectiveness has a beneficial
effect on the disclosure's level of quality.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of both voluntary
disclosure and financial audit committees is presently
increased. An influential audit committee contributes
to enhancing the quality of financial reporting. These
observations align with the principles of Agency
Theory, which asserts that having a board
committee's independent directors can balance out the
information. The current study suggests that a
sizeable audit committee of competent and
experienced members can effectively monitor
managerial performance, especially concerning
social and environmental activities. That can elevate
the quality of CSRD. Therefore, the hypothesis of this
research proposes that:
Hypothesis 3: The level of CSRD is positively
correlated with the audit committee's size.
3.1.4 Gender Diversity on the Board
The prominence of gender diversity on corporate
boards in India has been highlighted by recent
regulatory reforms introduced in the Companies Act of
2013. These reforms mandate that for every listed
company, at least one board member must be a female.
Although there is evidence between gender diversity
and financial performance, the influence on CSRD has
not been extensively studied. Gender diversity can
enhance board independence, as individuals with
different backgrounds, genders, ethnicities, and
cultures offer diverse perspectives rooted in their
experiences. Female directors differ from their male
counterparts in several ways. Companies with a higher
representation of females on their boards often engage
in more social and charitable activities than those with
fewer females in leadership positions. This has an
optimistic effect on corporate reputation and ratings of
CSR. According to these findings, current studies have
been supported by evidence that the presence of
females on corporate boards improves CSRD.
However, it is essential to note that some studies
present a contrasting relationship between the
participation of females on boards and CSRD. In light
of these findings, this study anticipates that the
inclusion of females on the board will strengthen the
CSR programs of the company and result in increased
CSRD. Consequently, the researcher proposes the
following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 4: Females on board have a good
relationship with the amount of CSRD.
3.2 Data Acquisition
The activists employed a quantitative descriptive
research approach and strategy for their investigation.
They highlighted using computer techniques to
measure data objectively obtained through survey
questions. It concentrated on accumulating numerical
data and using it to explain a particular viewpoint or
generalize it across groups of people. There were 432
respondents to the study, who were officials and staff
from the commercial banks. The study employed a
self-created survey questionnaire as a data collection
tool to sort quantitative data for analysis. The tool's
primary goal is to pinpoint the elements influencing
the sample commercial banks' corporate philanthropy
and, ultimately, to realize the value of publishing
these actions regularly.
The questions were written in a way that would
make it simple for responders to respond. The
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
524
respondents were forced to form an opinion since a 5-
point Likert scale or forced Likert scale was utilized.
A forced Likert scale was utilized to analyse the
correlation between CSR and disclosure in the
commercial banks' financial performance. The impact
of CSR and disclosure on the operations of
commercial banks was assessed using the composite
mean. The following scale was used to interpret the
study's findings: Strongly Agree (SA), Agree (A),
neutral (NS), Disagree (D), and Strongly Disagree
(SD) are all measured. Based on the weighted mean
of the index, the ranking was also utilized to
determine which index was the highest and lowest.
3.3 Variables
In corporate governance (CG), several factors that
can be considered as independent variables include
the audit committee's size, the average age of the
board members, the annual count of board sessions,
the frequency of board meetings, and the gender
makeup of the board. The other factors, including
industry, promoter ownership, financial leverage,
board age, board size, return on asset (ROA), is used
as controls. Company age is regarded as a controlling
factor since more established businesses are familiar
with the area and setting in which they function and
recognize that CSRD attracts new customers and
fosters goodwill. Therefore, it is expected that firm
age has a beneficial impact on CSRD. Financial
leverage refers to using debt to finance operations,
and companies with high debtors often face superior
pressure to provide detailed information to creditors.
It follows that a positive association between CSRD
and financial leverage is anticipated. Return on assets
(ROA), which reflects a firm's profitability, is often
higher for socially responsible companies. Profitable
firms tend to demonstrate their commitment to
society and are more likely to provide extensive
CSRDs, indicating a positive association between
ROA and CSRD. Based to the legitimacy theory,
organizations working in politically and ecologically
sensitive industries are more inclined to share
information about CSR than those in non-sensitive
industries in order to maintain their good reputations.
A favorable correlation between the kind of industry
and CSRD is expected. Table 1 lists the independent
variables that were used in the research.
Using Eviews 9, the following model examines
how the explanatory variable affects the disclosure
score on the Likert scale.
(1)
-dependent variable,
Where-company, - time - Board age on
average, - Board meeting, - audit committee's
size, -Women on board, - is financial
leverage, and - Return of asset.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 2 provides a statistical summary of the sample
data. The average disclosure of ESG score is 27.44,
with a maximum score of 61.57 and a median score
of 22.72. Table 3 presents Pearson's Correlation
Coefficient along with the variables of independence
and their respective importance levels. The results
indicate that the correlations between the variables of
independent fall within acceptable ranges, suggesting
that multi-collinearity is not a significant concern.
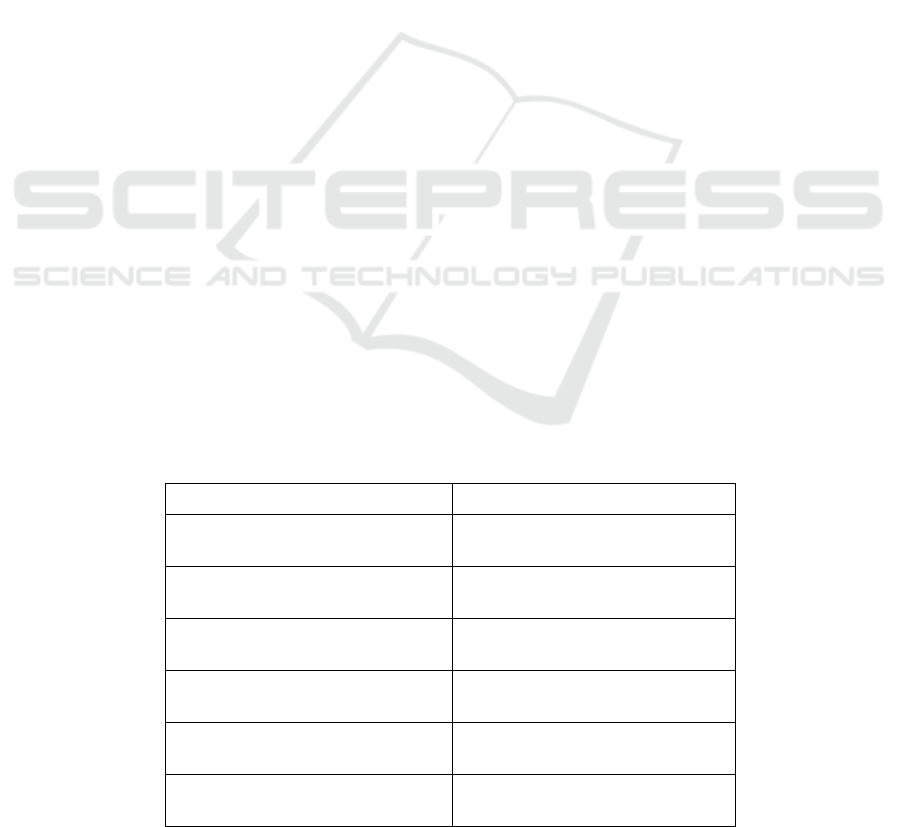
Table 1: Independent variables.
Independent variables
Description
Women on board
Percentage of women directors on
board
Board meeting
Number of board meeting per year
Size of audit committee
Number of audit committee
members
Board age
Average age of board members
Financial leverage
Debt-equity ratio
ROA
Asset return (profitability of the
company)
Corporate Governance and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Disclosure Among Commercial Banks in an Emerging Economy:
Evaluative Perspectives
525
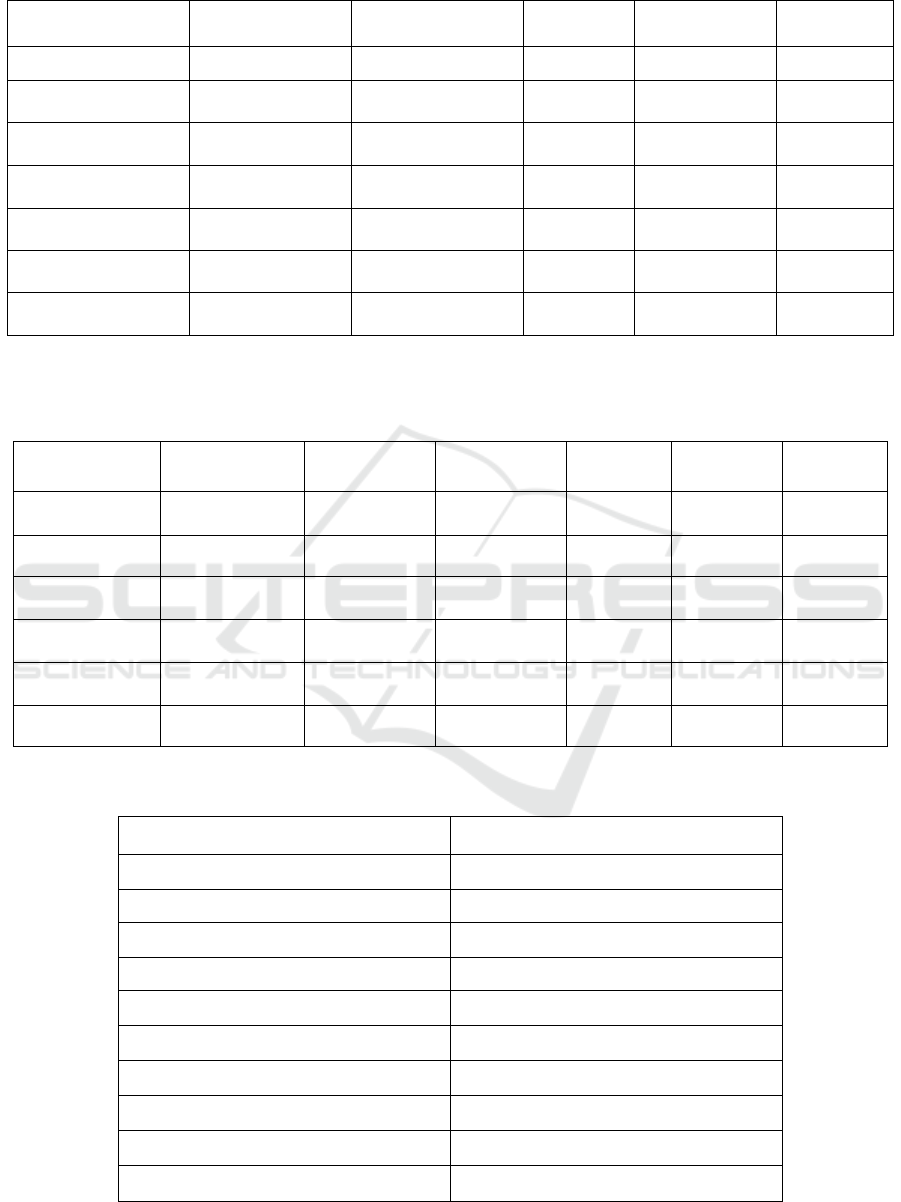
Table 2: Descriptive data analysis.
Variables
Maximum
Minimum
SD
Median
Mean
ROA
57.44
-45.31
10.11
06.21
08.70
ESGDS
61.58
04.55
15.05
22.73
27.45
FLEV
578.6
00.01
28.45
02.47
05.32
BAGE
74.58
47.51
04.15
62.00
61.17
BM
21.00
04.00
03.29
07.00
07.41
SAC
11.00
03.00
01.03
05.00
03.93
WB
33.34
00.01
07.52
06.67
06.73
Note: ROA- Return on asset, BM- Board meeting, FLEV- Financial leverage, BAGE- Average age of board member, WB-
Women on board, SAC- Size of audit committee.
Table 3: Matrix of correlation.
Variables
BAGE
BM
SAC
WB
FLEV
ROA
BAGE
0.084
0.171**
0.094*
-0.074
0.038
1.000
BM
0.023
-0.008
-0.006
-0.045
1.000
SAC
0.027
0.041
0.119**
1.000
WB
-0.038**
0.265**
1.000
FLEV
-0.193***
1.000
ROA
1.000
Table 4: Regression analysis of panel data.
Variables
ESGDS Model
ROA
0.118**
FLEV
0.012***
BAGE
− 0.429**
BM
0.202
SAC
− 0.502
WB
− 0.158**
Adjusted R
2
0.865
Constant
− 76.83***
F stat
37.94***
N
432
Note: *** (0.001%), ** (0.005%).
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
526

4.1 Discussion
The model's findings (Table 4) illustrate how
corporate governance factors affect CSRD. Board age
and CSRD are negatively correlated, meaning there is
a probability for greater CSRD if the average age of
the board is lower. Younger directors attempt to
include more CSR activities than senior directors
since they are more motivated and supportive of new
market ideas. Hypothesis 1 is therefore approved. The
outcome supports Hypothesis 3 and provides
evidence that the sustainability committee and the
CSRD have a beneficial relationship. A distinct
committee's existence indicates that the company has
a strong attitude toward socially responsible business
practices. Such companies must also have high social
values and increase their CSRD. The level of CSRD
is significantly negatively impacted by the presence
of women directors (hypothesis 4), proving that
having women on the board and the board committee
has detrimental effects on CSRD due to the reality
that both countries' involvement rates for women in
public activities are significantly lower than those of
other developed nations. Board meetings and CSRD
have a negligible correlation, which suggests that the
board meeting frequency has no bearing on the
disclosure of CSR. Our conclusion contradicts
Hypothesis 2, which also came to a similar conclusion
and supported it by claiming that the committee of
directors does not participate in the critical decisions
but merely makes them, the phase of putting CSR
policy into practice. Firm size, financial leverage, and
age demonstrate a substantial beneficial impact on
CSRD compared to control variables.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
SCOPE
The study explored the confluence of CG and CSR in
the banking landscape of emerging economies,
focusing on the role of gender diversity and financial
leverage in shaping CSR disclosure. Employing a
dataset of 432 individuals from commercial banks in
the selected emerging economy, we used multivariate
analysis techniques to examine the relationships
between CG variables, including CSR disclosure,
board composition and ownership structure. They
outcome indicated that board composition, gender
diversity, financial leverage, and industry type
significantly influence CSR disclosure among
commercial banks in the emerging economy. These
finding underscored the importance of fostering
diverse and responsible governance practices within
banks. Recognizing these connections, regulators,
policymakers, and bank stakeholders can collaborate
to elevate corporate governance standards and
promote ethical banking practices, ultimately
contributing to sustainable economic growth in the
emerging economy. However, it is essential to
acknowledge the study's limitations, such as the
specific focus on a single emerging economy, and
future research could expand upon these findings by
exploring cross-cultural variations and trends in CG
and CSR practices among banks in diverse emerging
economies.
REFERENCES
Abdelnur, O.A.O., (2021). Corporate Social Responsibility
Disclosure by Sudanese Listed Commercial Banks.
International Review of Management and Marketing,
11(1), p.60.
Abugre, J.B. and Anlesinya, A., (2020). Corporate social
responsibility strategy and economic business value of
multinational companies in emerging economies: The
mediating role of corporate reputation. Business
Strategy & Development, 3(1), pp.4-15.
BUI, HTT, (2021). The relationship between corporate
social responsibility and corporate financial
performance: an empirical study of commercial banks
in Vietnam. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics
and Business, 8(10), pp.373–383.
Chen, F. (2023). The Impact of Corporate Governance
mechanism on firms’ Financial Performance and
Corporate Social Responsibility Conduct in China.
de Villiers, C. and Dimes, R., (2021). Determinants,
mechanisms, and consequences of corporate
governance reporting: a research framework. Journal of
Management and Governance, 25, pp.7-26.
Duong, K.D., Tran, P.M.D. and Pham, H., (2023). CEO
overpower and corporate social responsibility of
commercial banks: The moderating role of state
ownership—Cogent Economics & Finance, 11(1),
p.2171609.
Ho, A.Y.F., Liang, H.Y. and Tumurbaatar, T., (2019). The
impact of corporate social responsibility on financial
performance: Evidence from commercial banks in
Mongolia. In Advances in Pacific Basin Business,
Economics and Finance (pp. 109-153). Emerald
Publishing Limited.Khojastehpour, M. and Jamali, D.,
(2021). Institutional complexity of host country and
corporate social responsibility: Developing vs
developed countries. Social Responsibility Journal,
17(5), pp.593-612.
Lui, T.K. and Zainuldin, M.H., (2022). Do foreign banks
disclose corporate social responsibility practices more
than their local counterparts? Empirical evidence of an
emerging market context. Corporate Social
Corporate Governance and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Disclosure Among Commercial Banks in an Emerging Economy:
Evaluative Perspectives
527

Responsibility and Environmental Management, 29(5),
pp.1855-1870.
Matuszak, Ł., Różańska, E. and Macuda, M., (2019). The
impact of corporate governance characteristics on
banks’ corporate social responsibility disclosure:
Evidence from Poland. Journal of Accounting in
Emerging Economies, 9(1), pp.75-102.
Miah, M.T., Saha, K.B. and Karim, R., (2019). The Role of
Private Commercial Bank in Corporate Social
Responsibility concerning Islami Bank Bangladesh
Limited. Open Access Library Journal, 6(5), pp.1-14.
Nwude, E.C. and Nwude, C.A., (2021). Board structure and
corporate social responsibility: evidence from
developing economy. Sage Open, 11(1),
p.2158244020988543.
Orazalin, N., (2019). Corporate governance and corporate
social responsibility (CSR) disclosure in an emerging
economy: evidence from commercial banks of
Kazakhstan. Corporate Governance: The International
Journal of Business in Society, 19(3), pp.490–507.
RAN, Q.T., LAM, T.T. and LUU, C.D., (2020). Effect of
corporate governance on corporate social responsibility
disclosure: empirical evidence from Vietnamese
commercial banks. The Journal of Asian Finance,
Economics and Business (JAFEB), 7(11), pp.327-333.
Velte, P., (2023). Institutional ownership and board
governance. A structured literature review on the
heterogeneous monitoring role of institutional
investors. Corporate Governance: The International
Journal of Business in Society.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
528
