
Machine Learning Models for Prostate Cancer Identification
Elias Dritsas
1 a
, Maria Trigka
2 b
and Phivos Mylonas
2 c
1
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Patras, Greece
2
Department of Informatics and Computer Engineering, University of West Attica, Greece
Keywords:
Prostate Cancer, Data Analysis, Machine Learning, Prediction, Ensemble Models, SMOTE.
Abstract:
In the present research paper, we focused on prostate cancer identification with machine learning (ML) tech-
niques and models. Specifically, we approached the specific disease as a 2-class classification problem by
categorizing patients based on tumour type as benign or malignant. We applied the synthetic minority over-
sampling technique (SMOTE) in our ML models in order to reveal the model with the best predictive ability
for our purpose. After the experimental evaluation, the Rotation Forest (RotF) model overcame the others,
achieving an accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-score of 86.3%, and an AUC equal to 92.4% after SMOTE
with 10-fold cross-validation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The prostate is a small gland that produces and stores
a component of male sperm. It is located under the
bladder and surrounds the urethra, which is why even
in the case of a significant increase in size, urination
problems are caused. A common result is prostate
cancer (Verze et al., 2016; Mottet et al., 2015).
Prostate cancer is nowadays one of the dominant
health problems faced by the male population. It is the
most frequent cancer in men in the Western world and
the second leading cause of death after lung cancer. It
usually develops slowly and is initially limited to the
prostate gland. Some forms of prostate cancer can be
very aggressive and metastasize rapidly. If detected
in time, it has good prospects for effective treatment
(Pernar et al., 2018; Rawla, 2019).
In addition, it is already known that the risk factors
for the occurrence of prostate cancer are age, family
history, the existence of metabolic syndrome, arterial
hypertension, increased waist circumference, obesity,
diabetes, smoking and high alcohol consumption.
Prostate cancer can appear on many faces and evolve
at different rates. Thus, there are men with prostate
cancer with no symptoms, while others present with
urination, ejaculation disorders, erectile dysfunction,
frequent urge to urinate, especially at night, bleeding
or even bone pain (Perdana et al., 2017; Leitzmann
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5647-2929
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7793-0407
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6916-3129
and Rohrmann, 2012).
This disease mainly concerns older men and is rel-
atively rare in men under 40 years of age. The diag-
nosis of prostate cancer is made by a competent doc-
tor, who is the urologist-andrologist. Clinical exam-
ination and imaging testing with digital rectal exam-
ination and Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) testing
via blood test are required. If necessary, an addi-
tional ultrasound check, prostatic tissue sample col-
lection - biopsy and magnetic resonance imaging are
performed (Bechis et al., 2011; Descotes, 2019).
Reduced intake of saturated fatty acids (red meat),
increased consumption of vegetables and dietary in-
take of vitamins E and D, selenium, lycopene, soy
proteins and fish oils have been proven to have a
protective effect. In addition, choosing a Mediter-
ranean diet based on fruits and vegetables, exercising
regularly, and maintaining a stable and healthy body
weight are contributing factors to avoiding the occur-
rence of prostate cancer (Gandaglia et al., 2021; Mat-
sushita et al., 2020).
As mentioned above, early diagnosis plays a key
role in prevention. ML now plays a decisive and,
at the same time, a complementary role towards this
direction. Medical science has an important tool
for better and more accurate prediction of various
diseases such as diabetes (as classification (Fazakis
et al., 2021b; Dritsas and Trigka, 2022a) or regres-
sion task for continuous glucose prediction (Dritsas
et al., 2022a; Alexiou et al., 2021)), cholesterol (Faza-
kis et al., 2021a; Dritsas and Trigka, 2022c), hyper-
Dritsas, E., Trigka, M. and Mylonas, P.
Machine Learning Models for Prostate Cancer Identification.
DOI: 10.5220/0012236800003598
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2023) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 421-428
ISBN: 978-989-758-671-2; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
421
tension (Dritsas et al., 2021a; Dritsas et al., 2022d),
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Dritsas et al.,
2022c), covid-19 (Dritsas and Trigka, 2022f), stroke
(Dritsas and Trigka, 2022e), chronic kidney dis-
ease (Dritsas and Trigka, 2022d), cardiovascular dis-
eases (Dritsas and Trigka, 2023a; Trigka and Dritsas,
2023a; Dritsas et al., 2022b), sleep disorders (Kon-
stantoulas et al., 2021; Konstantoulas et al., 2022),
lung cancer (Dritsas and Trigka, 2022b), liver dis-
ease (Dritsas and Trigka, 2023b), breast cancer (Drit-
sas et al., 2023), metabolic syndrome (Dritsas et al.,
2022e; Trigka and Dritsas, 2023b), etc.
This study was based on a publicly available
dataset that provides morphological descriptions to
discriminate the type of prostate tumour and facili-
tate the classification process. These data were ex-
ploited to build high-performance ML models. More
specifically, a key step of the adopted methodology
was the application of SMOTE (Chawla et al., 2002)
for training ensemble ML models on class-balanced
data. The models were evaluated in terms of accuracy,
precision, recall, f1-score and AUC. The model which
overcame the others in the aforementioned metrics
was the Rotation Forest. Finally, a discussion on re-
lated works in the same concept is presented.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
In Section 2 the main parts of the methodology for
prostate cancer identification are noted. In particu-
lar, in Section 3 a discussion of the results and re-
lated works for the subject under consideration are
provided. Finally, in Section 4 the conclusions are
outlined.
2 METHODOLOGY
In this section, we note the dataset’s characteristics in
which our ML models were evaluated. Also, we de-
scribe the adopted methodology, and finally, we cap-
ture the ensemble models we experimented with, as
well as the metrics for their evaluation.
2.1 Dataset Description
The dataset (Dat, ) on which our experimental evalu-
ation was performed contains information on 100 pa-
tients suffering from prostate cancer. Each sample
is represented by eight independent variables - pre-
dictors (radius, texture, area, perimeter, compactness,
smoothness, fractal dimension, symmetry) and one
dependent variable that captures the diagnosis result.
The class output takes two values: “B” for benign tu-
mours and “M” for malignant tumours.
Table 1: Statistical analysis of the dataset.
Attribute
Description
Min Max Mean±stdDev
radius 9 25 16.85±4.879
texture 11 27 18.23±5.193
perimeter 52 172 96.78±23.676
area 202 1878 702.88±319.711
smoothness 0.07 0.143 0.103±0.015
compactness 0.038 0.345 0.127±0.061
symmetry 0.135 0.304 0.193±0.031
fractal dimension 0.053 0.097 0.065±0.008
2.2 Data Processing and Analysis
Following an exploratory data analysis, a statistical
description of the features in the whole dataset is
given in Table 1. Also, for each feature, their values
among the involved patients are shown in Figure 1.
Moreover, the Pearson correlation coefficient is
used to estimate the degree of linear association be-
tween the features including the target class. Table
2 demonstrates the outcomes of this coefficient based
on the equation of (Liu et al., 2020) defined as fol-
lows:
ρ
X,Y
=
E [(X − µ
x
)(Y − µ
y
)]
σ
X
σ
Y
,
where X, Y are the variables that capture the compared
features values, E[·] denotes the expectation operator
and µ
x
, σ
x
and µ
y
, σ
y
are the mean values and vari-
ances of the X, Y , respectively. Based on this coeffi-
cient, the features’ importance is ordered as: “perime-
ters, area, compactness, symmetry, smoothness, ra-
dius (the minus shows a negative correlation with the
class variable), texture and fractal dimension”. Also,
it was observed that the features of area and perimeter
indicated the highest positive linear association. From
a medical point of view, the considered features are
necessary for concretely representing the tumour type
and thus the patient’s status. So, all of them will be
considered for the models’ training and evaluation.
The application of SMOTE is an important step in
the process to ensure that the employed ML models
will be trained on data with uniform class distribu-
tion (Dritsas et al., 2021b). Algorithm 1 provides the
steps that SMOTE considers exploiting the K-Nearest
Neighbours method with K equal to 5 (default param-
eter in the WEKA environment where we worked)
(Dritsas and Trigka, 2022f). The use of SMOTE was
combined with 10-fold cross-validation since the size
of the dataset is quite limited; it consists of 100 sam-
ples, where 62 belong to the “Malignant” class and 38
to the “Benign” class. The ML models were trained
and evaluated in each fold, and the outcomes from
both classes and all folds were averaged to obtain the
final prediction (or, else, classification performance).
KDIR 2023 - 15th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
422
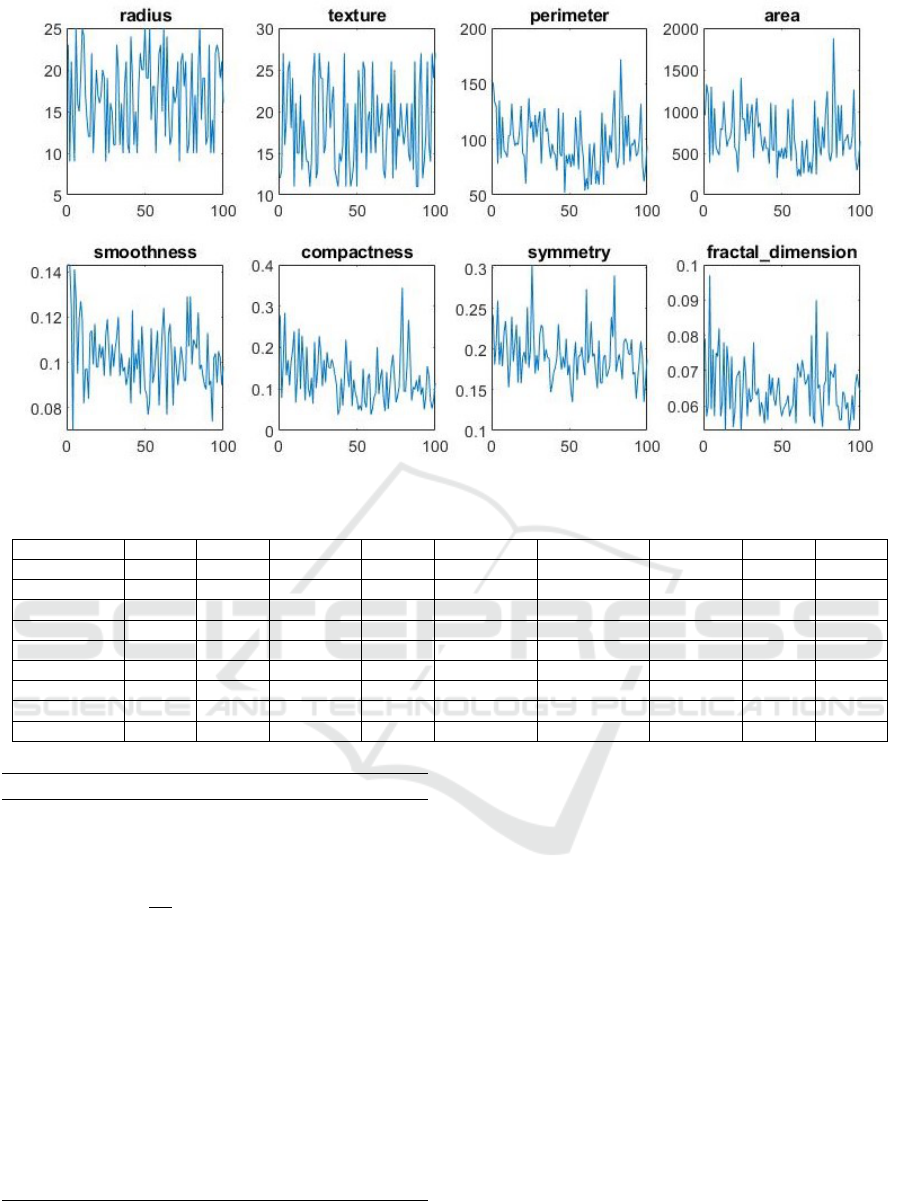
Figure 1: The clinical features evolution among the patients.
Table 2: Pearson Correlation Coefficient ρ
X,Y
among the features (including the class variable).
radius texture perimeter area smoothness compactness symmetry fractal class
radius 1.0000 0.1002 -0.2382 -0.2509 -0.1271 -0.1915 -0.0397 -0.0291 -0.1770
texture 0.1002 1.0000 -0.1135 -0.1137 0.1023 0.0324 0.0779 0.1392 0.0707
perimeter -0.2382 -0.1135 1.0000 0.9766 0.2694 0.5275 0.1955 -0.1954 0.6075
area -0.2509 -0.1137 0.9766 1.0000 0.2084 0.4249 0.1104 -0.2743 0.5624
smoothness -0.1271 0.1023 0.2694 0.2084 1.0000 0.4657 0.4242 0.3696 0.1976
compactness -0.1915 0.0324 0.5275 0.4249 0.4657 1.0000 0.6811 0.6480 0.5122
symmetry -0.0397 0.0779 0.1955 0.1104 0.4242 0.6811 1.0000 0.5686 0.2330
fractal -0.0291 0.1392 -0.1954 -0.2743 0.3696 0.6480 0.5686 1.0000 0.0082
class -0.1770 0.0707 0.6075 0.5624 0.1976 0.5122 0.2330 0.0082 1.0000
Algorithm 1: SMOTE.
Input: T (number of minority class samples, N (%
ratio of synthetic minority samples for class bal-
ancing), K (number of nearest neighbours);
Choose randomly a subset S of the minority class
data of size S =
N
100
T (synthetic minority class sam-
ples) such the classes are uniformly distributed;
for all s
i
∈ S do
(1) Find the K nearest neighbours.;
(2) Calculate the distance d
i,k
between the one
randomly selected NN among K and the sample
s
i
.;
(3) The new synthetic sample is generated as
s
n
= s
i
+ rand(0 − 1)d
i,k
(rand(0 − 1) generates
a random number between 0 and 1).;
end for
Repeat steps number 2–3 until the desired proportion
of minority class is met.
2.3 Machine Learning Models and
Performance Metrics
The assessment of ML models was conducted in
WEKA (WEK, ), free software which contains tools
for data pre-processing, classification, regression,
clustering, visualization, etc. The experiments were
performed on a computer system with the follow-
ing specifications: Apple MacBook Pro 13.3”, Retina
Display (M2/ 16GB RAM/ 256GB SSD). As for the
ML methodology, we applied ensemble techniques
(Sagi and Rokach, 2018) that combine multiple mod-
els to make predictions rather than individual ones.
From the family of ensemble techniques, the follow-
ing methods were considered:
1. Bagging (Ngo et al., 2022) – It creates a differ-
ent training subset from sample training data with
replacement and the final output is based on ma-
jority voting.
2. AdaBoost (Ying et al., 2013) – An Adaptive
Machine Learning Models for Prostate Cancer Identification
423

Boosting method combines weak learners into
strong ones by creating sequential models such
that the final model has the highest accuracy.
3. Stacking (Pavlyshenko, 2018) - It trains different
base learners on the same data and combines their
predictions using a meta-classifier that is trained
with the outcomes of the base models to learn the
class label.
4. Voting (Mushtaq et al., 2022) - It trains different
base learners on the same data and finds the final
prediction by applying soft voting. The soft vot-
ing scheme classifies input data by averaging the
probabilities of all the predictions made by differ-
ent classifiers. The winning class is the one with
the highest average probability.
5. Random Forest (RF) (Palimkar et al., 2022) - It se-
lects a random subset of data records and a subset
of features for constructing each decision tree. In-
dividual decision trees are built for each sample,
generate output and the final decision is derived
based on majority voting.
6. Rotation Forest (RotF) (Rodriguez et al., 2006)
- It is an ensemble classification method similar
to Random Forests. Data rotation is a key pro-
cessing step in RotF and is performed internally
prior to training the base classifiers (trees are com-
monly used) using Principal Component Analysis
(PCA). Therefore, base classifiers can divide the
decision space into the feature axes and directions
generated after the rotation. This feature makes
it much more powerful than other traditional en-
semble techniques.
Comparing bagging, boosting and stacking tech-
niques, each one fulfils a different purpose. Bag-
ging reduces the overfitting or variance of the model
while boosting reduces underfitting or bias. Finally,
stacking increases predictive accuracy. The benefit
of stacking is that it can harness the capabilities of
a range of well-performing models on a classifica-
tion task and obtain better predictions than any sin-
gle model in the ensemble. Here, the Bagging, Ad-
aBoost and RotF methods considered RF as a base
classifier. Stacking and Voting exploited as base clas-
sifiers the RF and Naive Bayes (NB) (Leung et al.,
2007) and, especially Stacking, as meta-classifier the
Logistic Regression (LR) (Maalouf, 2011).
To evaluate the ML models, we relied on metrics
(Hossin and Sulaiman, 2015) commonly used in the
ML field, namely accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score
and AUC. It should be noted that the ultimate value in
each metric was derived by averaging the outcomes
of both classes from all folds. The definition of these
metrics was based on the confusion matrix consisting
of the elements true-positive (Tp), true-negative (Tn),
false-positive (Fp) and false-negative (Fn). Hence, the
aforementioned metrics were computed as follows:
Accuracy =
Tn + Tp
Tn + Fn + Tp + Fp
,
Precision =
Tp
Tp + Fp
, Recall =
Tp
Tp + Fn
,
F1 − score = 2
Precision × Recall
Precision + Recall
.
In addition to the above metrics, in the assessment
of ensemble techniques the AUC metric was used.
The values of this metric should vary between 0 and 1
and show the models’ ability to discriminate the sam-
ples into “Benign” and “Malignant” classes, respec-
tively. The closer to 1 the higher the models’ sepa-
ration capacity. In the worst case, when AUC ≈ 0.5,
the model has no capacity to distinguish between the
“Benign” class and the “Malignant” class. Finally, the
AUC ROC curve is used to depict the performance of
the ensemble classification models. This curve plots
the True Positive Rate - TPR (or Recall) in terms of
False Positive Rate - FPR defined as
Fp
Fp+Tn
for differ-
ent cut-off points.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this section, we analyse the results acquired by
experimenting with the ensemble models RF, RotF,
Stacking, Bagging, Voting and AdaBoost trained to
classify a patient as “Benign” or “Malignant” and
thus, predict the type of prostate cancer. Also, a short
description of related works for prostate cancer iden-
tification is presented.
3.1 Ensemble Models Results
Focusing on Table 3, the selected ensemble models
were compared in terms of accuracy, precision, re-
call, f1-score and AUC. Also, in the context of our
analysis, the selected models were evaluated before
and after the application of class balancing using the
SMOTE technique. As the outcomes revealed, the use
of SMOTE for the models’ training increased their
predictive performance. RotF (after SMOTE) was the
dominant model indicating an accuracy, precision, re-
call, and f1-score of 86.3% and an AUC of 92.4%.
The voting scheme noted the second proximal accu-
racy, precision, recall, and f1-score of 86.1% and an
AUC equal to 90.7%. The rest models noted lower
performance than RotF but proximal to each other.
In Figure 2, the ROC curves are depicted. Com-
paring the behaviour of the selected models, it seemed
KDIR 2023 - 15th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
424
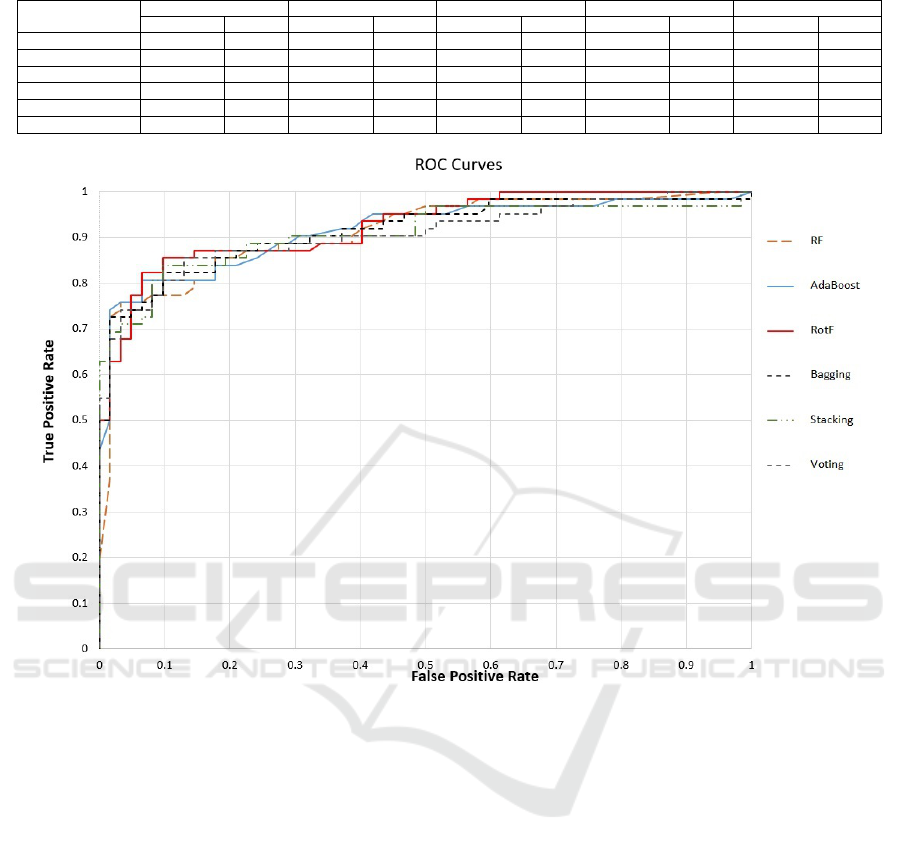
Table 3: Experimental Results without and with applying class balancing using SMOTE.
Ensemble Models
Accuracy - % Precision Recall F1 Score AUC
No SMOTE SMOTE No SMOTE SMOTE No SMOTE SMOTE No SMOTE SMOTE No SMOTE SMOTE
RF 82 83.1 0.820 0.831 0.820 0.831 0.820 0.831 0.882 0.912
RotF 85 86.3 0.850 0.863 0.850 0.863 0.850 0.863 0.887 0.924
Stacking 82 83.9 0.820 0.839 0.820 0.839 0.820 0.839 0.899 0.909
Bagging 82 83.1 0.820 0.831 0.820 0.831 0.820 0.831 0.895 0.915
Voting 85 86.1 0.850 0.861 0.850 0.861 0.850 0.861 0.888 0.907
AdaBoost 82 82.5 0.820 0.825 0.820 0.825 0.820 0.825 0.885 0.914
Figure 2: ROC Curves of ML models.
again that RotF was the classifier that indicated the
lowest classification error. This curve and the corre-
sponding AUC values showed that RotF with the se-
lected bio-makers (namely, features) had the highest
predictive ability to discriminate “Malignant” from
“Benign” patients.
3.2 Results on Related Works for
Prostate Cancer Prediction
In (Alam et al., 2020), a modified LR classifier is pro-
posed and implemented on patients who are suscepti-
ble to prostate cancer, achieving accuracy, sensitivity
and specificity equal to 96.86%, 95.50% and 98.39%,
respectively. Moreover, in (Wen et al., 2018), the
authors compared and evaluated four ML models,
namely Artificial Neural Network (ANN), NB, Sup-
port Vector Machine (SVM) and Decision Tree (DT),
for the prediction of prostate cancer survivability. The
results showed that ANN had the best predictive abil-
ity with an accuracy of 85.64%.
Similarly in (Wang et al., 2018), the authors exper-
imented with ML models SVM, Least Squares SVM,
ANN, and RF, to detect prostate cancer cases us-
ing the available biopsy information. ANN achieved
the highest accuracy of 0.9527 and an AUC value of
0.9755. RF outperformed the other three models in
classifying benign, significant, and insignificant cases
of prostate cancer, with an accuracy of 0.9741 and an
f1-score of 0.8290.
Huljanah et al. (Huljanah et al., 2019) experi-
mented with RF to detect prostate cancer. Feature
selection and the use of 85% of the data for the mod-
els’ training reached the best accuracy and precision
of 100%. Finally, in (Laabidi and Aissaoui, 2020),
the authors experimented with the same dataset as
the present research paper keeping the same features.
They applied scaling and no scaling techniques to the
dataset, and proposed the Recurrent Neural Network
(RNN) model, as it achieved better results. Specifi-
Machine Learning Models for Prostate Cancer Identification
425

cally, the RNN model without (with) scaling achieved
accuracy, AUC, f1-score, precision, and recall equal
to 81% (81.3%), 0.866 (0.866), 0.809 (0.802), 0.798
(0.802) and 0.810 (0.813). Comparing the outcomes
without scaling with the ones derived from the current
study, it was observed that our proposed model, i.e.
RotF, presented constantly more stable performance
than RNN in all metrics.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Prostate cancer is the most common health condition
in elderly men (with limited occurrence in men un-
der 40 years old) and the second leading cause of
death after lung cancer. Early diagnosis plays a con-
tributing role in prevention. In this research paper, we
based on a publicly available dataset, which provides
morphological descriptions in order to discriminate
the type of prostate tumour and facilitate the identi-
fication process. We applied the SMOTE technique
for training ensemble ML models, namely, Stacking,
Bagging, Voting, AdaBoost, Rotation Forest and Ran-
dom Forest on uniform distribution class data to cat-
egorize patients based on tumour type as benign or
malignant. The models were evaluated and compared
in accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score and AUC. The
RotF prevailed over the other models, achieving an
accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score of 86.3%, and
an AUC equal to 92.4% after SMOTE with 10-fold
cross-validation. Finally, we aim to investigate an al-
ternative methodology for prostate cancer detection
by applying Deep Learning models and techniques to
data generated from tumour X-rays.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was funded by the European Union and
Greece (Partnership Agreement for the Development
Framework 2014-2020) under the Regional Opera-
tional Programme Ionian Islands 2014-2020, project
title: “Indirect costs for project “Smart digital ap-
plications and tools for the effective promotion and
enhancement of the Ionian Islands bio-diversity” ”,
project number: 5034557.
REFERENCES
Prostate cancer dataset. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/
sajidsaifi/prostate-cancer. (accessed on 23 July 2023).
Weka. https://www.weka.io/. (accessed on 23 July 2023).
Alam, M., Tahernezhadi, M., Vege, H. K., Rajesh, P., et al.
(2020). A machine learning classification technique
for predicting prostate cancer. In 2020 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Electro Information Technology
(EIT), pages 228–232. IEEE.
Alexiou, S., Dritsas, E., Kocsis, O., Moustakas, K., and
Fakotakis, N. (2021). An approach for personalized
continuous glucose prediction with regression trees.
In 2021 6th South-East Europe Design Automation,
Computer Engineering, Computer Networks and So-
cial Media Conference (SEEDA-CECNSM), pages 1–
6. IEEE.
Bechis, S. K., Carroll, P. R., and Cooperberg, M. R. (2011).
Impact of age at diagnosis on prostate cancer treat-
ment and survival. Journal of Clinical Oncology,
29(2):235.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., and Kegelmeyer,
W. P. (2002). Smote: synthetic minority over-
sampling technique. Journal of artificial intelligence
research, 16:321–357.
Descotes, J.-L. (2019). Diagnosis of prostate cancer. Asian
journal of urology, 6(2):129–136.
Dritsas, E., Alexiou, S., Konstantoulas, I., and Moustakas,
K. (2022a). Short-term glucose prediction based on
oral glucose tolerance test values. In HEALTHINF,
pages 249–255.
Dritsas, E., Alexiou, S., and Moustakas, K. (2022b). Car-
diovascular disease risk prediction with supervised
machine learning techniques. In ICT4AWE, pages
315–321.
Dritsas, E., Alexiou, S., and Moustakas, K. (2022c). Copd
severity prediction in elderly with ml techniques. In
Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on
PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environ-
ments, pages 185–189.
Dritsas, E., Alexiou, S., and Moustakas, K. (2022d). Effi-
cient data-driven machine learning models for hyper-
tension risk prediction. In 2022 International Confer-
ence on INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Appli-
cations (INISTA), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Dritsas, E., Alexiou, S., and Moustakas, K. (2022e).
Metabolic syndrome risk forecasting on elderly with
ml techniques. In International Conference on Learn-
ing and Intelligent Optimization, pages 460–466.
Springer.
Dritsas, E., Fazakis, N., Kocsis, O., Fakotakis, N., and
Moustakas, K. (2021a). Long-term hypertension risk
prediction with ml techniques in elsa database. In
Learning and Intelligent Optimization: 15th Interna-
tional Conference, LION 15, Athens, Greece, June 20–
25, 2021, Revised Selected Papers 15, pages 113–120.
Springer.
Dritsas, E., Fazakis, N., Kocsis, O., Moustakas, K., and
Fakotakis, N. (2021b). Optimal team pairing of elder
office employees with machine learning on synthetic
data. In 2021 12th International Conference on Infor-
mation, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA),
pages 1–4. IEEE.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2022a). Data-driven machine-
learning methods for diabetes risk prediction. Sensors,
22(14):5304.
KDIR 2023 - 15th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
426

Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2022b). Lung cancer risk pre-
diction with machine learning models. Big Data and
Cognitive Computing, 6(4):139.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2022c). Machine learning meth-
ods for hypercholesterolemia long-term risk predic-
tion. Sensors, 22(14):5365.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2022d). Machine learning tech-
niques for chronic kidney disease risk prediction. Big
Data and Cognitive Computing, 6(3):98.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2022e). Stroke risk pre-
diction with machine learning techniques. Sensors,
22(13):4670.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2022f). Supervised machine
learning models to identify early-stage symptoms of
sars-cov-2. Sensors, 23(1):40.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2023a). Efficient data-driven
machine learning models for cardiovascular diseases
risk prediction. Sensors, 23(3):1161.
Dritsas, E. and Trigka, M. (2023b). Supervised machine
learning models for liver disease risk prediction. Com-
puters, 12(1):19.
Dritsas, E., Trigka, M., and Mylonas, P. (2023). Ensemble
machine learning models for breast cancer identifica-
tion. In IFIP International Conference on Artificial
Intelligence Applications and Innovations, pages 303–
311. Springer.
Fazakis, N., Dritsas, E., Kocsis, O., Fakotakis, N., and
Moustakas, K. (2021a). Long-term cholesterol risk
prediction using machine learning techniques in elsa
database. In IJCCI, pages 445–450.
Fazakis, N., Kocsis, O., Dritsas, E., Alexiou, S., Fakotakis,
N., and Moustakas, K. (2021b). Machine learning
tools for long-term type 2 diabetes risk prediction.
IEEE Access, 9:103737–103757.
Gandaglia, G., Leni, R., Bray, F., Fleshner, N., Freed-
land, S. J., Kibel, A., Stattin, P., Van Poppel, H., and
La Vecchia, C. (2021). Epidemiology and preven-
tion of prostate cancer. European urology oncology,
4(6):877–892.
Hossin, M. and Sulaiman, M. N. (2015). A review on eval-
uation metrics for data classification evaluations. In-
ternational journal of data mining & knowledge man-
agement process, 5(2):1.
Huljanah, M., Rustam, Z., Utama, S., and Siswantining, T.
(2019). Feature selection using random forest classi-
fier for predicting prostate cancer. In IOP Conference
Series: Materials Science and Engineering, volume
546, page 052031. IOP Publishing.
Konstantoulas, I., Dritsas, E., and Moustakas, K. (2022).
Sleep quality evaluation in rich information data. In
2022 13th International Conference on Information,
Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), pages 1–
4. IEEE.
Konstantoulas, I., Kocsis, O., Dritsas, E., Fakotakis, N., and
Moustakas, K. (2021). Sleep quality monitoring with
human assisted corrections. In IJCCI, pages 435–444.
Laabidi, A. and Aissaoui, M. (2020). Performance analysis
of machine learning classifiers for predicting diabetes
and prostate cancer. In 2020 1st international confer-
ence on innovative research in applied science, engi-
neering and technology (IRASET), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Leitzmann, M. F. and Rohrmann, S. (2012). Risk factors
for the onset of prostatic cancer: age, location, and
behavioral correlates. Clinical epidemiology, pages
1–11.
Leung, K. M. et al. (2007). Naive bayesian classifier.
Polytechnic University Department of Computer Sci-
ence/Finance and Risk Engineering, 2007:123–156.
Liu, Y., Mu, Y., Chen, K., Li, Y., and Guo, J. (2020).
Daily activity feature selection in smart homes based
on pearson correlation coefficient. Neural Processing
Letters, 51:1771–1787.
Maalouf, M. (2011). Logistic regression in data analysis:
an overview. International Journal of Data Analysis
Techniques and Strategies, 3(3):281–299.
Matsushita, M., Fujita, K., and Nonomura, N. (2020). In-
fluence of diet and nutrition on prostate cancer. Inter-
national journal of molecular sciences, 21(4):1447.
Mottet, N., Bellmunt, J., Briers, E., Van den Bergh, R.,
Bolla, M., Van Casteren, N., Cornford, P., Culine,
S., Joniau, S., Lam, T., et al. (2015). Guidelines on
prostate cancer. European Association of Urology,
56:e137.
Mushtaq, Z., Ramzan, M. F., Ali, S., Baseer, S., Samad,
A., and Husnain, M. (2022). Voting classification-
based diabetes mellitus prediction using hypertuned
machine-learning techniques. Mobile Information
Systems, 2022:1–16.
Ngo, G., Beard, R., and Chandra, R. (2022). Evolution-
ary bagging for ensemble learning. Neurocomputing,
510:1–14.
Palimkar, P., Shaw, R. N., and Ghosh, A. (2022). Machine
learning technique to prognosis diabetes disease: Ran-
dom forest classifier approach. In Advanced Com-
puting and Intelligent Technologies: Proceedings of
ICACIT 2021, pages 219–244. Springer.
Pavlyshenko, B. (2018). Using stacking approaches for ma-
chine learning models. In 2018 IEEE Second Interna-
tional Conference on Data Stream Mining & Process-
ing (DSMP), pages 255–258. IEEE.
Perdana, N. R., Mochtar, C. A., Umbas, R., and Hamid,
A. R. A. (2017). The risk factors of prostate cancer
and its prevention: a literature review. Acta medica
indonesiana, 48(3):228–238.
Pernar, C. H., Ebot, E. M., Wilson, K. M., and Mucci,
L. A. (2018). The epidemiology of prostate cancer.
Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, page
a030361.
Rawla, P. (2019). Epidemiology of prostate cancer. World
journal of oncology, 10(2):63.
Rodriguez, J. J., Kuncheva, L. I., and Alonso, C. J. (2006).
Rotation forest: A new classifier ensemble method.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 28(10):1619–1630.
Sagi, O. and Rokach, L. (2018). Ensemble learning: A sur-
vey. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining
and Knowledge Discovery, 8(4):e1249.
Machine Learning Models for Prostate Cancer Identification
427

Trigka, M. and Dritsas, E. (2023a). Long-term coronary
artery disease risk prediction with machine learning
models. Sensors, 23(3):1193.
Trigka, M. and Dritsas, E. (2023b). Predicting the occur-
rence of metabolic syndrome using machine learning
models. Computation, 11(9):170.
Verze, P., Cai, T., and Lorenzetti, S. (2016). The role of the
prostate in male fertility, health and disease. Nature
Reviews Urology, 13(7):379–386.
Wang, G., Teoh, J. Y.-C., and Choi, K.-S. (2018). Diag-
nosis of prostate cancer in a chinese population by
using machine learning methods. In 2018 40th An-
nual International Conference of the IEEE Engineer-
ing in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pages
1–4. IEEE.
Wen, H., Li, S., Li, W., Li, J., and Yin, C. (2018). Com-
parision of four machine learning techniques for the
prediction of prostate cancer survivability. In 2018
15th International Computer Conference on Wavelet
Active Media Technology and Information Processing
(ICCWAMTIP), pages 112–116. IEEE.
Ying, C., Qi-Guang, M., Jia-Chen, L., and Lin, G. (2013).
Advance and prospects of adaboost algorithm. Acta
Automatica Sinica, 39(6):745–758.
KDIR 2023 - 15th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
428
