
CNN-HMM Model for Real Time DGA Categorization
Aimen Mahmood
1
, Haider Abbas
2 a
and Faisal Amjad
1 b
1
National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
2
KTH-Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden
Keywords:
Domain Generation Algorithms, Domain Fluxing, Classification of DGA, Word-List DGA, Pseudo Random
DGA, Convolution Neural Network.
Abstract:
To remotely control the target machine, hackers manage to establish a connection between victim and their
Command and Control server(C2). In order to hide their C2 they generate domain names algorithmically.
Such algorithms are called Domain Generation algorithms(DGA). These algorithmically generated domain
names are either gibberish as the characters are generated and concatenated randomly, or pure dictionary
words or the combination of the two. This paper presents an algorithm that classifies the DGA running on
a compromised system either as gibberish, dictionary oriented or the mixed one, in real time. The proposed
algorithm consists of two distinct modules i) Network forensics to detect the DGA ii) Classification of the
DGA using the combination of Hidden Markov Model and Convolution Neural Network in real time. The
algorithm is trained and tested against more than 0.21 million samples taken from more than 50 different
DGAs. The algorithm gives as good as 99% accuracy for all types of DGAs. In addition it can detect zero day
DGA as well as multiple DGAs running on a system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays the organizations are opting the paper-
less technology to support the green environment, but
making the data more vulnerable to the cyber attacks.
On the contrary, adversaries are becoming more ac-
tive by producing sophisticated malicious attacks.
The most damaging attacks like credential stealing,
ransomware, banking trojans and many more are con-
ducted through a malicious remote server called Com-
mand and Control(C2) servers. In such attacks, the
compromised system try to establish a remote con-
nection with a C2, which then remotely controls the
infected system.
Malware is an unwelcome software which enters
into the victim system suspiciously. Normally the IP
address or the domain name of C2 is hard-coded in
the malicious binary file, inturn can be blocked eas-
ily. However, to keep their C2 alive and active, bad
actors have opted a sophisticated technique called do-
main fluxing in which the domain names are gener-
ated dynamically by in-cooperating ”Domain Gener-
ation Algorithm” (DGA) (Vormayr et al., 2017). Such
domain names are random in nature as they are based
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2437-4870
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4912-6168
on a seed value. If the seed value is known, then the
security analysts can predict the future domain names
and block them in advance.Alternatively adversaries
put all their effort to use such a seed that also changes
dynamically.
Figure1 shows the complete process of DGA.
Same DGA algorithm, with the same seed, executes
at both ends ie attacker as well as infected system.
Usually date/ time is used as a seed value, which is
taken either from an online source or through the http
response. In the simplest case malware generates the
alphabets/digits randomly and concatenate them into
a second level domain name(SLD) of a fixed length,
defined in the algorithm. Once being fully generated
then top level domains (TLD), which are predefined,
are concatenated with SLD to make a fully qualified
domain name(FQDN). Usually it generates a huge list
of domain names but only few of them are registered,
with a shorter time to live(TTL). The victim system
sends the DNS queries to the DNS server for all those
domain names. If the domain name is not found in
DNS server, it is forwarded to the root name server
as depicted in figure 1. In case of un registered do-
main names, Non existent domain name(NX domain),
a prominent characteristic of DGA, is returned as a
response. However if a rendezvous point is achieved
822
Mahmood, A., Abbas, H. and Amjad, F.
CNN-HMM Model for Real Time DGA Categorization.
DOI: 10.5220/0012136800003555
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2023), pages 822-829
ISBN: 978-989-758-666-8; ISSN: 2184-7711
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
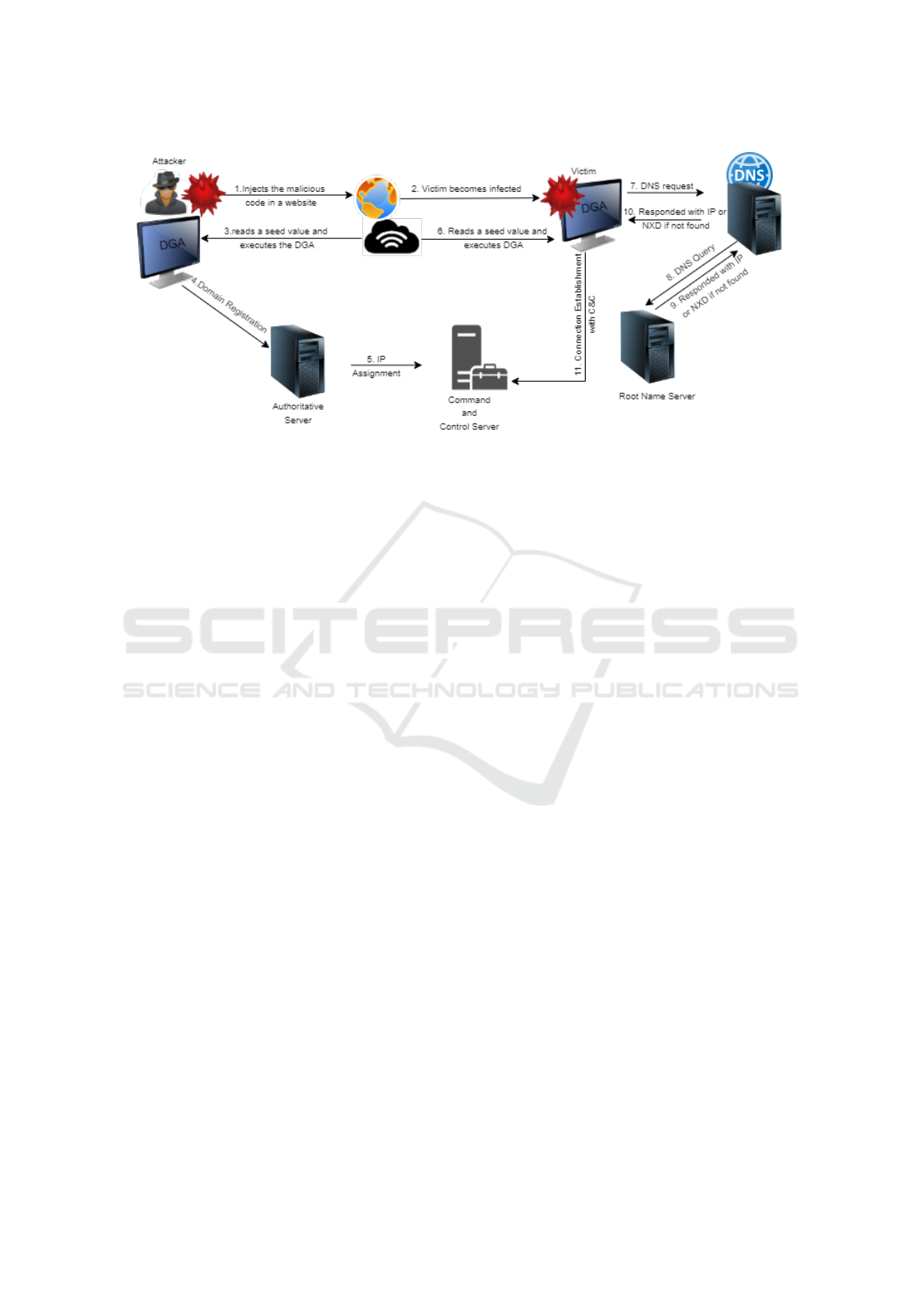
Figure 1: Overview of Domain Generation Algorithm.
the IP address is returned to the victim system, thus
establishing the connection.
Here, as characters and digits are generated and
concatenated randomly thus leading to a gibberish do-
main names(R-DGA), another lead indicator of DGA.
Most of the researchers have used them in their detec-
tion systems. Being easily detectable, so now mali-
cious authors are using dictionary words in the do-
main names(W-DGA), thus making them harder to
detect.
DGAs are incorporated in various types of mal-
ware including banking Trojans(Oppenheim et al.,
2017), adware, malware for IoT (Antonakakis et al.,
2017),(Vinayakumar et al., 2020), Botnets(Wang
et al., 2017), malware for supply chains (Labs,
2017) etc. Over the last decade, banks have be-
come the soft target for the banking Trojans(Atzeni
et al., 2020). These Trojans steal the credentials of
the customers and may also empty their accounts.
Emotet(Bromium, 2019), a banking Trajan, first seen
in 2014, is still active and becomes the one of the nas-
tier Trojans due its polymorphic nature(Technologies,
2020) and it incorporates DGA. Till date up to 50000
domain names have been used by it. Mirai is another
malware which has targeted IoT(Antonakakis et al.,
2017) and its variants are still active.
Malware with domain fluxing are ordinarily de-
tected on the basis of their DNS behavior and the
lexical features of SLD . In this paper we are pre-
senting an algorithm to detect DGA by monitoring
the DNS response followed by hybrid model of Hid-
den Markov Model (HMM) and Convolution Neural
Network (CNN) to categorize the given SLD into R-
DGA, W-DGA or the mixture of both. Our contribu-
tions towards this paper are listed as under:
• It presents an algorithm which detects a DGA by
using live Network forensics.
• The algorithm extracts the domain name from the
DNS query and tokenize it using Hidden Markov
model, an extension of probabilistic model, into
its constituent words or subwords if exists any.
• The extracted subwords/words alongwith their
probabilities are then used for feature engineer-
ing. Multiple features, extracted from subwords
are fed into CNN for classification.
• We have tested the algorithm for more than 56
different DGAs having the accuracy greater than
99%.
The paper is organized in 5 sections. Section II gives
the literature review, section III explains the proposed
framework. Section IV briefly analyzes the results
and performance. Finally the paper is concluded in
section V.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
DGA based malware are more sophisticated and dan-
gerous as their C2 remain untraceable due to the ran-
domness inherited by their SLDs. Taxonomy of such
SLD depend on a seed which can be dynamic in na-
ture. Various techniques have been proposed so far to
detect and classify these DGAs in real time or in close
to real time. Zaho et al., based on semantic features
of SLD, developed a DGA detection system(Zhao
et al., 2019). These semantic features include entropy,
length of the SLD, ratio of vowels, consonants, dig-
its etc. Malicious Domain names are detected on the
basis of N-gram and then are tested against the Alexa
dataset (Internet, 2018).
CNN-HMM Model for Real Time DGA Categorization
823
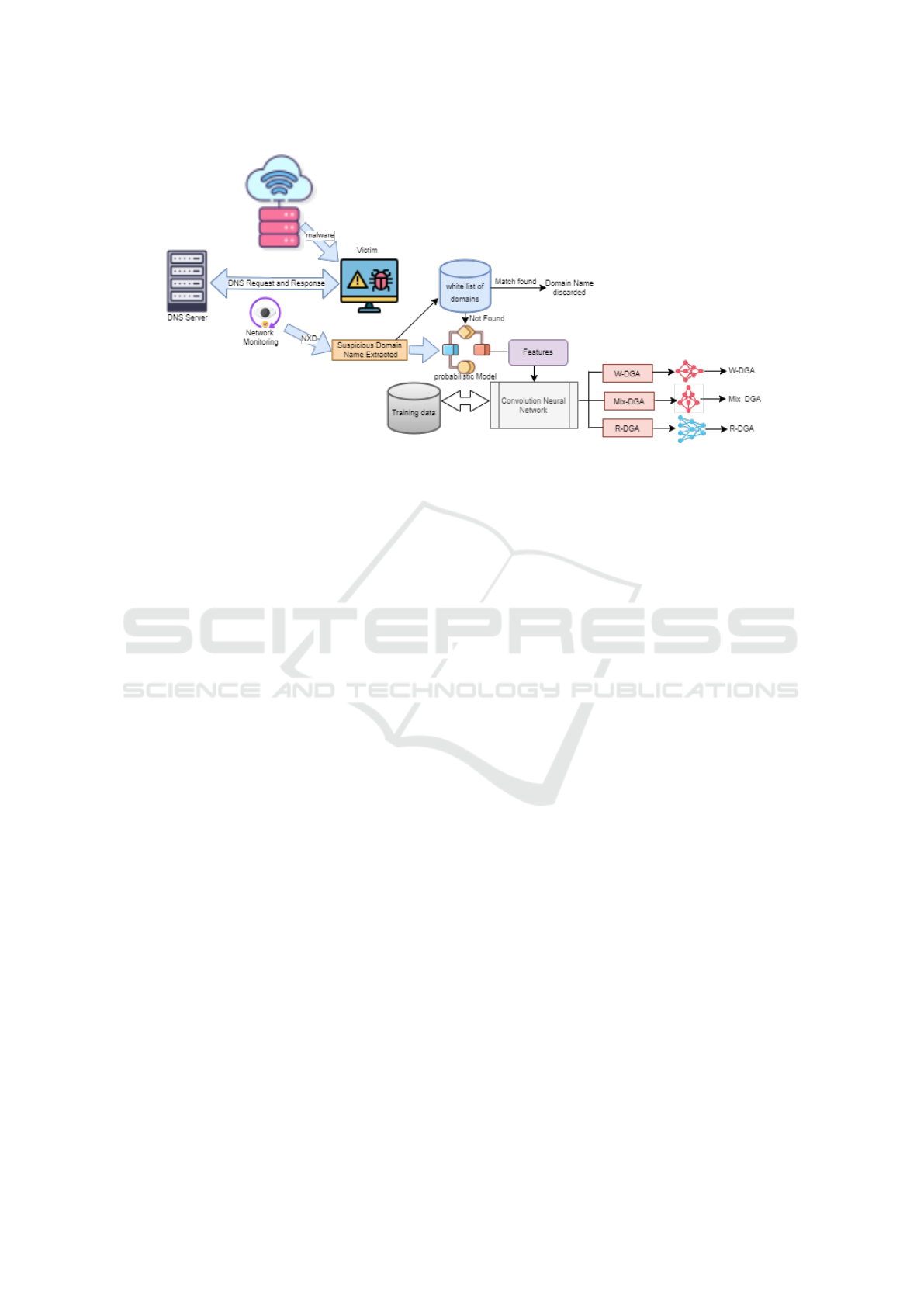
Figure 2: Overview of DGA Detection Algorithm.
DGAs are usually deployed for Bot network. All
the bots generate the DNS requests for the same do-
main names within a small time interval. The de-
tection algorithm tries to identify a pattern among all
these DNS queries, as they may inherit some similar-
ity(Wang et al., 2017). Although the detection accu-
racy in real time is high, but the approach is not suit-
able for the single system.Using the same approach
Erquiaga et al. (Erquiaga et al., 2016) considered the
behavioral models of DNS during a specific time win-
dow to detect DGAs.
Grill et al. (Grill et al., 2015) based their system
on NetFlow data, combination of a source IP and port
and a destination IP address and port, time stamps,
byte counters and packet counters. S. Tian et al. (Tian
et al., 2016) used mobile web traffic for DGA detec-
tion. The detection was based on textual features, sta-
tistical features and DNS traffic. The textual and se-
mantic features are actually humanly crafted features,
so the detection systems, based on these features, may
perform adversely for a zero day attack. And also a
minor change in the DGA algorithm will be effective
in bypassing such detection systems.
Researchers have deployed machine learning
algorithms using the above mentioned features.
These include deep neural networks, random for-
est(Yan et al., 2020), decision trees(Pereira et al.,
2018), clustering (Amini, 2008),(Bisio et al., 2017)
and (Pereira et al., 2018), support vector ma-
chines(SVM) (Wang et al., 2018), Recurrent Neu-
ral Networks(RNN), CNN(Hwang et al., 2020), Long
short term memory(LSTM)(Shahzad et al., 2021), au-
toencoders(Skansi, 2018). (Wang et al., 2018) has de-
ployed SVM to classify the DGA domain names from
benign domain names. The algorithm takes lexical
features like entropy, length of SLD, vowels, ratio of
consonants and the digits for classification. Although
the data set was small but the algorithm gave accu-
racy as good as 89%. F. Bisio et al. (Bisio et al.,
2017) analyzes the DNS traffic using K-means clus-
tering in a near-real-time in order to detect DGA.
(Xu et al., 2019) has developed a model based on N-
gram which works for both R-DGA and W-DGA. The
model gives more than 98% accuracy both on random
an as well as wordlist domain names. But they have
only tested on 16 different DGA malware. (Shahzad
et al., 2021) deployed LSTM but the detection was
focused on R-DGA only. CNN (Hwang et al., 2020)
based on linguistic features which worked well for R-
DGA only. Researchers have deployed deep neural
networks (Ren et al., 2020) but may only detect W-
DGA.
Although machine learning algorithms are best for
intelligent detection but their accuracy may suffer due
to imbalance of samples.(Liu et al., 2020) provided
a technique to handle imbalance sample set and thus
improved the accuracy. It is inferred from the litera-
ture that the above mentioned algorithms either focus
on R-DGA or on W-DGA but not on both and their
accuracy may suffer due to imbalanced training set.
In addition, there exists another DGA which is actu-
ally the mixture of both ie the domain names consists
of gibberish as well as dictionary words. It is inferred
from the above discussion that one machine learning
algorithm may work well for one category of DGA
but may suffer from another category. However, if
one is managed to classify them broadly into three ba-
sic classes and then deploy different machine learning
algorithms as per their class, accuracy will definitely
increase. So this research presents an algorithm to
classify between R-DGA, W-DGA and mixed DGA.
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
824

3 PROPOSED FRAMEWORK
Victim of a DGA based malware initiates the DNS re-
quests at a high rate. The response to most of these
DNS requests is NX domain, which is the key char-
acteristic of DGA malware, thus incorporating it in
the proposed algorithm. As shown in the figure 2 the
proposed algorithm has two main modules live net-
work monitoring and DGA classification which are
discussed below.
3.1 Live Network Monitoring
The main characteristic of DGA malware is their net-
work activity. Most commonly such malware checks
the availability of internet by sending UDP packets
to some renowned websites like google, yahoo, face-
book etc. In addition, sometimes they also need to
read their seeds form online sources, hard-codded in
their binary files. Once the FQDN is created, they
start sending the http requests for them. Most of such
domain names are non existent and DNS resolver
send NX domain response. To capture live DNS re-
sponse we are using wire-shark tool and incorporated
in Python. Every DNS response is captured, if its suc-
cess full the system ignores it, if its unsuccessful the
system go for packet inspection for error code.Error
code 3 means its NX domain. In addition to the er-
ror code it also gives the source port, destination port,
domain name for which the query name been initiated
and many more.
3.2 DGA Classification
SLD is extracted from FQDN which in turn is ex-
tracted from the unsuccessful DNS query response .
SLD, a sequence of alphabets, digits and special char-
acters (−, ) without spaces, is tokenize into its con-
stituent subwords via probabilistic model defined by
Peter Norvig (Norvig, 2009). The model works on
maximum likelihood estimation(MLE) which is de-
termined via Bayes theorem.
The proposed technique is based on a statisti-
cal language model of unigrams, alongwith their oc-
currence frequency. The dataset comprising of uni-
grams and their frequency is taken from Google Cor-
pus (Google, 2012). It contains almost 1 trillion to-
kens, but to keep the size manageable we only utilize
the tokens having the frequency greater than 10000.
Any token having the occurrence frequency less than
10000 is considered as unknown word. The un-
igrams are independent but their characters follow
a particular sequence in a particular domain name,
thus making a Bayesian network, an acyclic directed
graph. HMM being a sequential classifier and a tech-
nique to encode the Bayesian network, is deployed to
determine the probable word boundaries(Yan et al.,
2021)in a SLD. HMM consists of observable states,
Figure 3: HMM.
hidden states, initial probabilities, transition probabil-
ities and emission probabilities. Here, the observ-
able states are the positional characters in the do-
main name, and the hidden states are the probable
unigrams as shown in the figure 3. Here, in figure
3, the rightward arrow refers to the transition state
and downward arrow refers to the hidden states. For
example, if the given domain name is ’eatis’, then
the sample combinations are shown in the figure 3.
These sample sets include { ’e’,’a’,’t’,’i’,’s’ },{’ea’,
’tis’}, {’eati’,’s’},{’eat’,’i’,’s’}. Probabilities of each
set is determined using the relative frequency. Hidden
states or the unigrams in a particular set are indepen-
dent in nature, thus we can apply the chain rule as
depicted in equation 1.
Mathematical notation of the chain rule is:
P(C
1:n
) =
∏
k=1:n
P(C
k
) (1)
which is also known as Naive Bayesian Assumption.
The algorithm determines all the probable unique
sets of unigrams present in the SLD, compute
their probabilities through the chain rule equation(1)
and then using the Maximum Likelihood Estima-
tion(MLE), given in equation 2 determines the most
probable unigram boundaries within the SLD string.
P(C
1:n
) = argmax
i
P(c
i
) (2)
The unknown unigram must not have a zero prob-
ability but instead a lesser one as compared to the
known unigram. So it is calculated via equation 3.
Here, P depends on the length of unigram, so longer
the length smaller its probability.
P(unk) =
10
N ∗ 10
length
unk
(3)
Another challenge is to deploy an efficient algorithm
for determining the most probable segments or the
subwords. The most common and the easiest tech-
nique is brute force ie computing the all possible se-
quences and selecting the one with the highest prob-
ability, thus having the exponential time complexity.
CNN-HMM Model for Real Time DGA Categorization
825
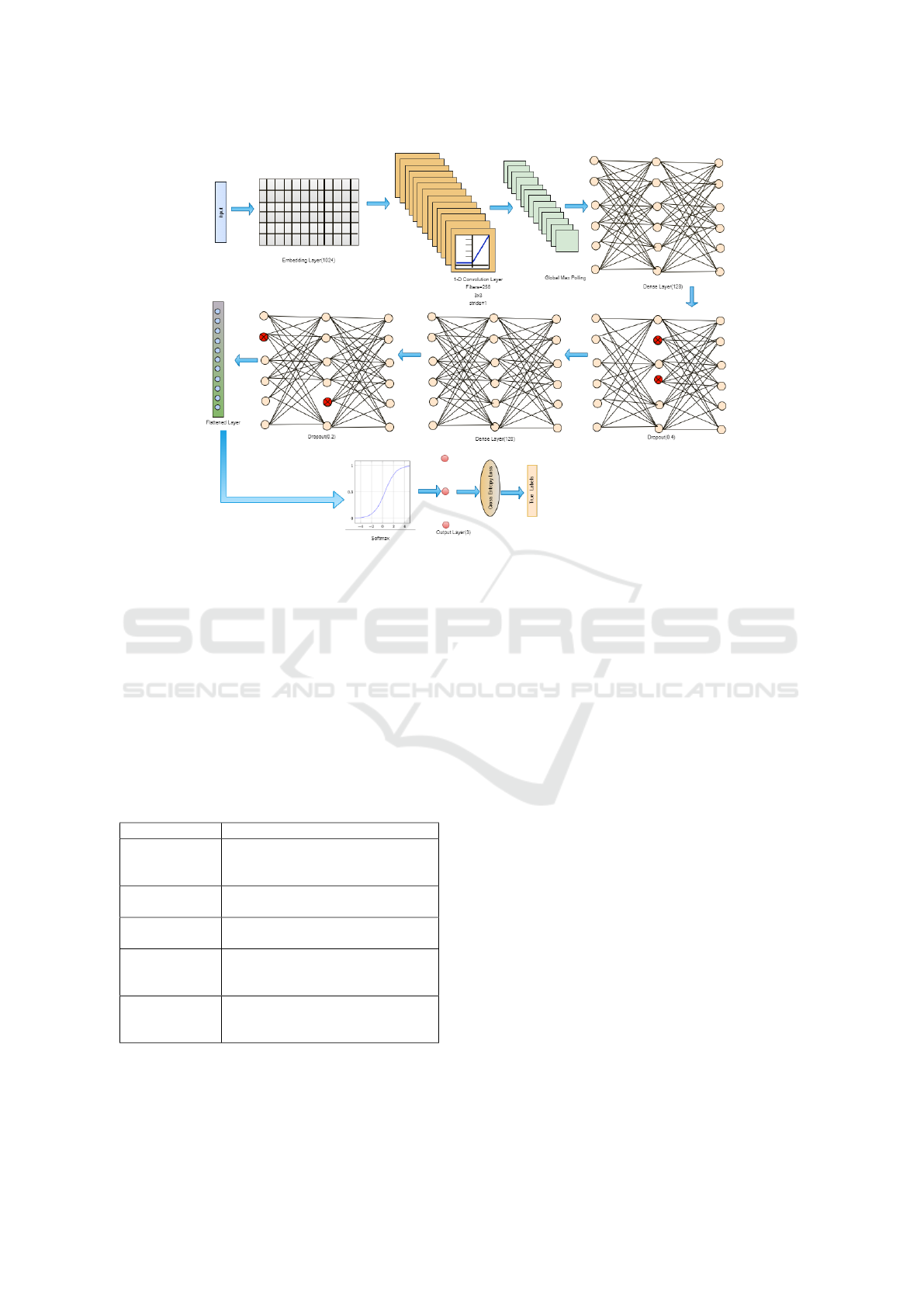
Figure 4: Machine Learning Framework.
To optimize the solution we have selected Viterbi al-
gorithm (Ciaperoni et al., 2022), a dynamic program-
ming technique. It reduces the time complexity by
avoid redundant calculations. Its time complexity is
linear in the length of the segment and quadratic in
the number of possible segments. This makes it much
more efficient than the brute force approach, espe-
cially for longer domain names with many possible
segments.
3.3 Machine Learning Framework
Table 1: List of Features.
Features Description
Probabilities
of segments
Domain name is divided into prob-
able segments based on their proba-
bilities
Length of seg-
ments
Segments having small lengths
have higher probabilities
Count of Seg-
ments
Total number of segments in a do-
main name
Ratio of digits W-DGA has either 0 or 1 digits
whereas R-DGA may have many
digits depending upon its algorithm
Count of spe-
cial Charatcers
Most of the samples belonging to
W-DGA and Mixed DGA have spe-
cial characters
The selected features, extracted from SLD, are
summarized in table 1. There are DGA like ’abcbot’
which generates gibberish SLD with only 1 seg-
ment. On the other hand, ’NGIOWEB’ gener-
ates word based SLD, having as many as 14 sub-
words, including the special characters. The spe-
cial characters are considered as a separate seg-
ment. However, digits, if exists any, may become
the part of segment depending upon the probabil-
ity. For example, consider a SLD ’9995bc0c’ gen-
erated by ’antavmu’ is a single segment having the
probability 9.75E-20 computed from the equation
3. However, ’7286a423a16a13886a2511c8afa8df65’
is another SLD, a R-DGA generated by bami-
tal. The algorithm divides it into 2 segments:
’7286a423a16a13886a2511c8’ and ’afa8df65’ having
probability 9.75E-36 and 9.75E-20 respectively. It is
evident from the above examples the probability de-
creases as the length of the segment increases. Now
consider a ’Bigviktor’, a W-DGA, it generates do-
main like ’holdthenprofessional’. The proposed al-
gorithm breaks it into ’hold’, ’then’, ’professional’
with 6.222E-5, 3.60E-4 and 1.2E-4 respective prob-
abilities. Usually, the maximum length of a SLD is
upto 64 characters and the maximum segments we
found in more than 0.1 million samples are 14. But to
handle a zero day DGA, the proposed algorithm has
a cushion for 30 segments. As shown in the table 1,
we are also considering the length of these segments.
So, for 30 segments, there are 30 lengths. Missing
segments and the lengths are considered are zero. In
addition, total number of segments in a SLD, ratio
of digits and special character is also included. All
these features are used in fully connected neural net-
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
826
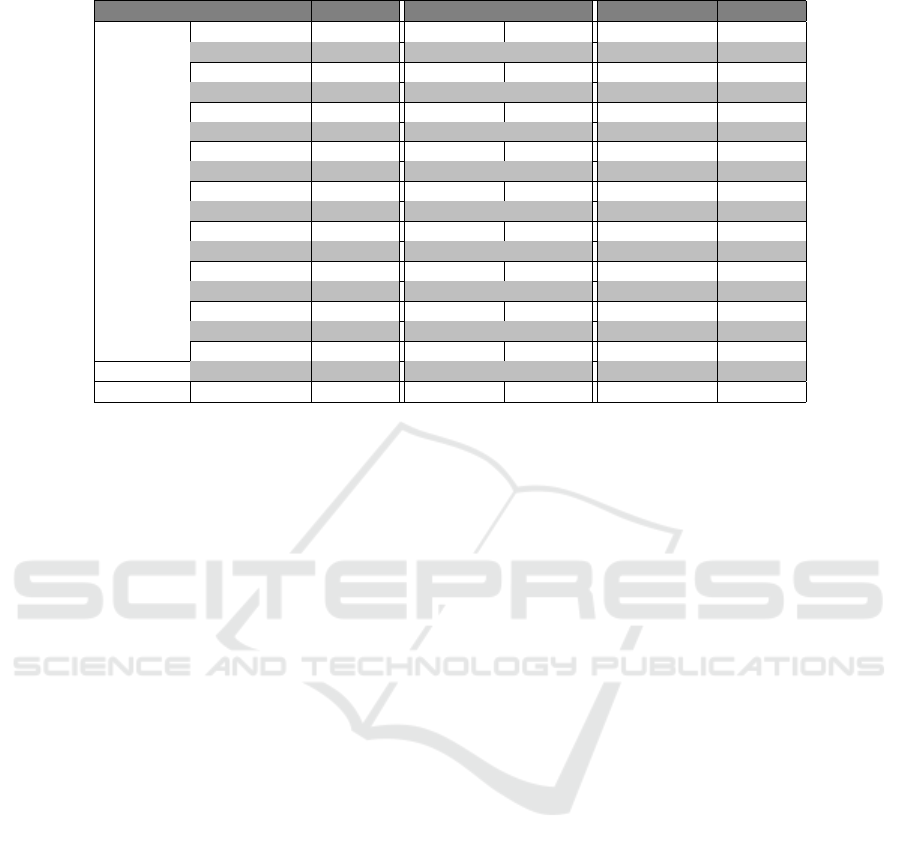
Table 2: Summary of Dataset.
Category DGA Samples DGA Samples DGA Samples
R-DGA
ABCBOT 27 ANTAVM 32 Bamital 104
Chinad 1000 Conficker 494 Cryptolocker 1000
Dicrypt 1000 Dmsniff 1000 Dyre 1000
Emotet 5952 Enviserve 491 Flubot 30000
Fobber 596 Gamevoer 12000 Gspy 100
Locky 1178 Nymaim 481 Padcrypt 2279
Necurs 40950 Qakbot 24804 Ramnit 20060
blackhole 180 ccleaner 30 cooperstealer 18
feodo 263 m0yv 63 madmax 530
monerominer 2495 murofet 8560 mydoom 10037
necro 2962 omexo 40 proslikefan 100
pykspa 7930 qadars 2200 Ranybus 13302
rovnix 4453 shifo 2541 shiotob 8004
simda 12383 symmi 4256 tempedreve 2733
tinba 13420 tinyuke 200 tofsee 20
tordwm 500 vawtrak 845 vidro 100
virut 9712 wauchos 5940 xshellghost 100
W-DGA Bigviktor 1007 Matsnu 903 Suppobox 2303
Mixed Ngioweb 5274 Banjori 7306 kfos 121
work (FCNN) and CNN. FCNN gave more than 92%,
whereas CNN gave more than 99% accuracy, so we
selected CNN for DGA classification. These results
prove the strength of the selected features as both ma-
chine learning algorithms gives accuracy greater than
90%.
Length of feature vector may vary with the length
of SLD. To normalize the feature set, zero padding
is introduced, thus generating a sparse matrix. This
sparse matrix becomes the input for a CNN. The se-
quential model of tensor flow is used and the arrange-
ment of layers with their dimensions are depicted in
figure 4. To convert the sparse matrix into a matrix
having real values, embedding layer is deployed. The
output of the embedding layer then becomes the input
of the 1D convolution layer. Convolution layer has
256 filters of size 3x3, having the stride=1. Maximum
Pooling layer is used here to select the features hav-
ing the maximum values. Then comes the dense layer
with 128 hidden units and relu activation function to
handle the non linearity. In order to avoid overfitting,
two dropout layers are added as shown in the figure
4. And the last dense layer has 3 hidden units hav-
ing the softmax activation function for the multi class
classification.
4 PERFORMANCE AND
RESULTS
The proposed algorithm is trained and tested on In-
tel(R) Core(TM) i7-1165G7 CPU @ 2.80 GHz 2.803
GHz and 16 GB RAM.The dataset comprising of dif-
ferent 57 DGA families as listed in table 2, is used for
training and testing. It is collected from Netlab (Net-
lab360, 2023), CIC dataset (for Cybersecurity (CIC),
2021) and kaggle (Kaggle, 2021) which are available
online. In addition, we also executed the DGA al-
gorithms which are available at github (Bader, 2023)
and tested our algorithm on them. In total we incorpo-
rated almost 0.27 million domain names for training
and testing. Almost 23% of the dataset is redundant,
which is discarded and the remaining 0.21 million is
used for training and testing. Out of 0.21 million do-
main names, 60% samples are selected randomly for
training and the remaining 40% are used for testing.
Training data is further divided into training and val-
idation in the ratio of 60:40 respectively. The model
is trained using 300 epochs and the its accuracy and
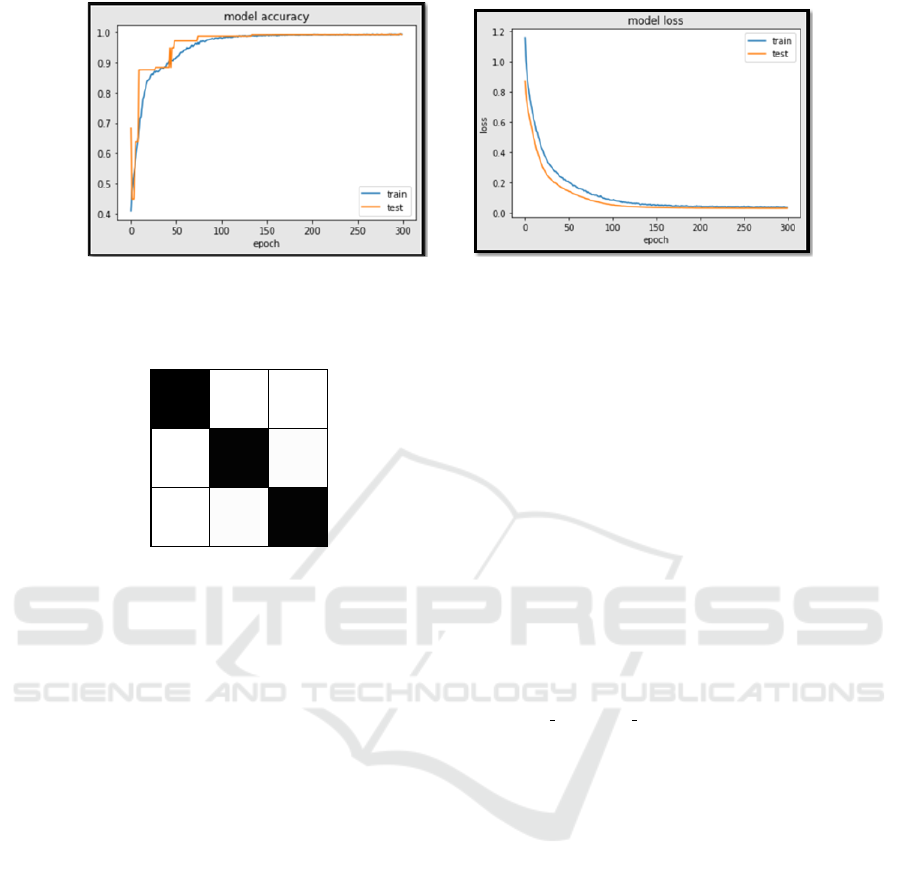
loss are shown in the figure 5 (a) and (b) respectively.
Accuracy graph 5(a) shows that the model keeps
on learning till 100 epoch and after that learning rate
becomes stable. On the other hand 5(b) shows that
loss decreases with the increase in number of epoch.
Also the confusion matrix for the test data is plotted
in the figure 6. The rows represents the true class and
the column represents the predicted class. Here, label
’0’,’1’ and ’2’ represents R-DGA, W-DGA and Mixed
DGA respectively. Confusion matrix shows that R-
DGA has 100% accuracy as compared to the rest of
the two. However, there are some missed classifica-
tion in case of W-DGA and Mixed DGA. Although
the overall accuracy is still greater than 99%.
After the training , then the complete system is
tested against the DGA based malware, which are ex-
ecuted in VMware with customized settings. When
the malware generates the DNS request, wireshark
traces it and looks for NX domain. In case of NX do-
main, the domain name is passed to the proposed al-
CNN-HMM Model for Real Time DGA Categorization
827
(a) Accuracy (b) Loss
Figure 5: Accuracy and Loss.
0
13203
100%
0
0%
15
0%
1
0
0%
1094
99%
32
1%
2
0
0%
0
15
1%
1
4617
99%
2
True Label
Predicted Label
Figure 6: Confusion Matrix.
gorithm which then breaks it into its constituent parts
and finally enters into machine learning framework
for classification.
To optimize the solution in terms of time complex-
ity and space complexity Viterbi algorithm(Cahyani
and Vindiyanto, 2019) is used as it reduces the time
complexity by using dynamic programming to avoid
redundant calculations and considering only the most
likely segment at each step.
5 CONCLUSION
DGAs are deployed to hide the malicious C2. DGAs
may generate gibberish domain names and the sophis-
ticated ones generate the dictionary oriented domain
names or the combination of both, thus difficult to de-
tect. Researchers have devised different techniques,
usually based on humanly crafted features, to detect
and classify such DGAs, but they are specific to one
class only. This research proposes an algorithm to dif-
ferentiate between the gibberish domain names, dic-
tionary oriented domain names and Mixed ones. Now
the researchers can deploy different machine learning
techniques to each of these categories for better accu-
racy.
REFERENCES
Amini, P. (2008). Kraken botnet infiltration. Available at
http://dvlabs.tippingpoint.com/blog/2008/04/28/krak
en-botnet-infiltrationdvlabs.tippingpoint.com.
Antonakakis, M., April, T., Bailey, M., Bernhard, M.,
Bursztein, E., Cochran, J., Durumeric, Z., Halderman,
J. A., Invernizzi, L., Kallitsis, M., et al. (2017). Un-
derstanding the mirai botnet. In 26th {USENIX} secu-
rity symposium ({USENIX} Security 17), pages 1093–
1110.
Atzeni, A., Diaz, F., Lopez, F., Marcelli, A., Sanchez, A.,
and Squillero, G. (2020). The rise of android banking
trojans. IEEE Potentials, 39(3):13–18.
Bader, J. (2023). Reverse engineering of domain generation
algorithms. Available at:https://github.com/baderj/do
main generation algorithms.
Bisio, F., Saeli, S., Lombardo, P., Bernardi, D., Perotti, A.,
and Massa, D. (2017). Real-time behavioral dga de-
tection through machine learning. In 2017 Interna-
tional Carnahan Conference on Security Technology
(ICCST), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Bromium (2019). Emotet:a technical analysis of the de-
structive, polymorphic malware. Available at https:
//www.bromium.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/B
romium-Emotet-Technical-Analysis-Report.pdf.
Cahyani, D. E. and Vindiyanto, M. J. (2019). Indonesian
part of speech tagging using hidden markov model–
ngram & viterbi. In 2019 4th International Confer-
ence on Information Technology, Information Systems
and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE), pages 353–
358. IEEE.
Ciaperoni, M., Gionis, A., Katsamanis, A., and Karras, P.
(2022). Sieve: A space-efficient algorithm for viterbi
decoding. In Proceedings of the 2022 International
Conference on Management of Data, pages 1136–
1145.
Erquiaga, M. J., Catania, C., and Garc
´
ıa, S. (2016). Detect-
ing dga malware traffic through behavioral models. In
2016 IEEE Biennial Congress of Argentina (ARGEN-
CON), pages 1–6. IEEE.
for Cybersecurity (CIC), C. I. (2021). Cic-bell-dns 2021
SECRYPT 2023 - 20th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
828

dataset. Availabe at : https://www.unb.ca/cic/dataset
s/dns-2021.html.
Google (2012). Corpus-n gram viewer. Available at: http:
//storage.googleapis.com/books/ngrams/books/datase
tsv2.html.
Grill, M., Nikolaev, I., Valeros, V., and Rehak, M. (2015).
Detecting dga malware using netflow. In 2015
IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated
Network Management (IM), pages 1304–1309. IEEE.
Hwang, C., Kim, H., Lee, H., and Lee, T. (2020). Effective
dga-domain detection and classification with textcnn
and additional features. Electronics, 9(7):1070.
Internet, A. (2018). Alexa dataset. Available at https://ww
w.alexa.com/topsites.
Kaggle (2021). Kaggle:domain generation algorithm
dataset. Available at:https://www.kaggle.com/dat
asets/gtkcyber/dga-dataset.
Labs, K. (2017). Shadowpad: Popular server management
software hit in supply chain attack. Available at https:
//media.kasperskycontenthub.com/wp-content/uploa
ds/sites/43/2017/08/07172148/ShadowPad\ technic
al\ description\ PDF.pdf.
Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Fan, X., and Dong, C. (2020).
Detection of algorithmically generated domain names
using the recurrent convolutional neural network with
spatial pyramid pooling. Entropy, 22(9):1058.
Netlab360 (Accessed: May 19, 2023). Network security
research lab at 360. https://data.netlab.360.com/dga/.
Norvig, P. (2009). Natural Language Corpus
Data:Beautiful Data, pages 219–242. O’Reilly
Media.
Oppenheim, M., Zuk, K., Meir, M., and Kessem, L. (2017).
Qakbot banking trojan causes massive active directory
lockouts. Available at https://securityintelligence.com
/qakbot-banking-trojan-causes-massive-active-direc
tory-lockouts/.
Pereira, M., Coleman, S., Yu, B., DeCock, M., and Nasci-
mento, A. (2018). Dictionary extraction and detection
of algorithmically generated domain names in passive
dns traffic. In International Symposium on Research
in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses, pages 295–314.
Springer.
Ren, F., Jiang, Z., Wang, X., and Liu, J. (2020). A dga
domain names detection modeling method based on
integrating an attention mechanism and deep neural
network. Cybersecurity, 3(1):1–13.
Shahzad, H., Sattar, A. R., and Skandaraniyam, J. (2021).
Dga domain detection using deep learning. In 2021
IEEE 5th International Conference on Cryptography,
Security and Privacy (CSP), pages 139–143. IEEE.
Skansi, S. (2018). Autoencoders. In Introduction to Deep
Learning, pages 153–163. Springer.
Technologies, C. P. S. (2020). July‘s most wanted malware:
Emotet strikes again after five-month absence. Avail-
able at https://blog.checkpoint.com/2020/08/07/julys
-most-wanted-malware-emotet-strikes-again-after-f
ive-month-absence/.
Tian, S., Fang, C., Liu, J., and Lei, Z. (2016). Detecting ma-
licious domains by massive dns traffic data analysis.
In 2016 8th International Conference on Intelligent
Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC),
volume 1, pages 130–133. IEEE.
Vinayakumar, R., Alazab, M., Srinivasan, S., Pham, Q.-
V., Padannayil, S. B., and Simran, K. (2020). A
visualized botnet detection system based deep learn-
ing for the internet of things networks of smart
cities. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,
56:4436–4456.
Vormayr, G., Zseby, T., and Fabini, J. (2017). Botnet com-
munication patterns. IEEE Communications Surveys
Tutorials, 19(4):2768–2796.
Wang, T., Lin, H., Cheng, W., and Chen, C. (2017). Dbod:
Clustering and detecting dga-based botnets using dns
traffic analysis. Computers and Security, 64:1–15.
Wang, Z., Jia, Z., and Zhang, B. (2018). A detection scheme
for dga domain names based on svm. In Proceedings
of the 2018 international conference on Mathematics,
Modelling, Simulation and Algorithms (MMSA 2018).
Atlantis Press.
Xu, C., Shen, J., and Du, X. (2019). Detection method of
domain names generated by dgas based on semantic
representation and deep neural network. Computers&
Security, 85:77–88. https://www.sciencedirect.com/
science/article/pii/S0167404818312938.
Yan, F., Liu, J., Gu, L., and Chen, Z. (2020). A semi-
supervised learning scheme to detect unknown dga
domain names based on graph analysis. In 2020 IEEE
19th International Conference on Trust, Security and
Privacy in Computing and Communications (Trust-
Com), pages 1578–1583. IEEE.
Yan, X., Xiong, X., Cheng, X., Huang, Y., Zhu, H., and
Hu, F. (2021). Hmm-bimm: Hidden markov model-
based word segmentation via improved bi-directional
maximal matching algorithm. Computers & Electrical
Engineering, 94:107354.
Zhao, H., Chang, Z., Bao, G., and Zeng, X. (2019). Mali-
cious domain names detection algorithm based on n-
gram. Journal of Computer Networks and Communi-
cations, 2019.
CNN-HMM Model for Real Time DGA Categorization
829
