
The Rise of Remote Project Management - A New Norm?: A Survey on
IT Organizations in Bangladesh
Azaz Ahamed, Touseef Aziz Khan, Nafiz Sadman, Mahfuz Ibne Hannan,
Nujhat Nahar and Mahady Hasan
Independent University, Bangladesh
Keywords:
Change and Configuration Management, Formal Methods, People Management, Project Management,
Remote Work, Work From Home, Productivity, Health, Career Growth.
Abstract:
The rise of remote work has brought about a significant shift in the way software development projects are
managed. With teams spread out across different locations and time zones, project managers must adapt to
new challenges to ensure the success of their projects. These challenges include difficulties in communication,
coordination, and motivation. It is seen that project managers are using a range of tools and tactics, including
agile methodologies, online communication tools, and best practices for remote work, to address these issues.
Other strategies may be required to successfully handle remote software development projects as conventional
ones are not always sufficient. In this paper, an in-depth and exploratory survey has been conducted on a
sample size of 250 employees from various IT organizations in Bangladesh. The results are analyzed to
understand the benefits and challenges that come with the Work from Anywhere (WFX) approach to software
development projects. The survey data is compared and analyzed against an extensive list of research papers
in a similar field and categorized in three dimensions: tools and productivity, work-life balance, and career
growth. The results support a strong correlation between WFX with increased productivity and better health.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the 21st century, most of the developed and de-
veloping nations are connected via the high-speed
internet that spans the globe. Communication, col-
laboration, and connectivity have gradually become
the norm rather than an exception (Ozimek, 2020).
As many doors technology and IT have opened, it
is conservative to believe that they have come with
the added complexity that needs to be constantly han-
dled and managed. In today’s era, virtual collabora-
tion tools and technologies have transformed the tra-
ditional approach of project management and thus,
eliminated the need for physical meetings between
the project manager and the team. PMs can now
leverage digital communication tools like video con-
ferencing, project management software, and instant
messaging to keep in touch with their teams, track
progress, and resolve issues or discrepancies, even if
they are located at distant locations. Therefore, the
conventional method of face-to-face communication
has become less common, and the virtual approach
has emerged as an efficient alternative for effective
and timely project management. Moreover, the com-
plexity of modern projects is further amplified by the
presence of multiple company offices situated in di-
verse regions across the globe, necessitating a deli-
cate equilibrium between autonomy and engagement.
Start-up companies, in particular, frequently engage
freelance teams or remote individuals to capitalize
on cost reductions and minimize overhead expenses.
Also, the global COVID-19 pandemic has forced
many co-located workplaces to adopt a work-from-
home (WFH)/ work-from-anywhere (WFX) culture
to continue daily operations during the lockdowns,
and general health concerns (Carroll and Conboy,
2020). Problems regarding work-life balance and
mental health quickly arose as the modality of work
shifted to WFH. While WFH has certain benefits of
working from a safe place, lack of proper manage-
ment results in most organization employees becom-
ing fatigued as the line between office hours and per-
sonal time blurs.
As the COVID-19 pandemic drastically altered
the way organizations operate, more companies have
turned to remote work as a viable working arrange-
ment to sustain business continuity. ”Remote Work”
(RW) is an older terminology often used to describe
518
Ahamed, A., Khan, T., Sadman, N., Hannan, M., Nahar, N. and Hasan, M.
The Rise of Remote Project Management - A New Norm?: A Survey on IT Organizations in Bangladesh.
DOI: 10.5220/0012125300003538
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2023), pages 518-525
ISBN: 978-989-758-665-1; ISSN: 2184-2833
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

freelance contractual work. However, with the sud-
den shift to work-from-home (WFH) arrangements
prompted by the pandemic, the term ”WFH” has be-
come more widespread as it offers clarity and preci-
sion on what it entails. This term has become more
familiar to employees and employers, allowing easier
communication and understanding of work arrange-
ments. Indeed, WFH has gained widespread adoption
in most industries since it is convenient, has lower
overhead costs, and is less ambiguous.
All these issues and happenings have a com-
mon denominator which is work-from-home (WFH)/
work-from-anywhere (WFX) or remote work (RW).
Both terminologies are interchangeable and boil down
to the same conclusive effect: added complications
for project management. It is not the tools we need
to orchestrate or coordinate such projects but rather
the attitude and aptitude. Since the popularization
of project management in the 1950s, its role has ex-
panded with additional responsibilities every decade.
In recent years, due to the remote and global nature of
work, PMs have to be well-versed in technical skills
deemed per the role and robust soft skills. The sudden
influx of remote work adoption has already imposed
a big challenge for PMs to coordinate effectively with
teams and produce optimum output. Failure to ad-
dress the difference in nature of remote work often
results in inefficient output, miscommunication, and
even low team morale [8]. Newer strategies are re-
quired to efficiently manage projects which require
learning various tools, languages/dialects, and astute
observation.
In this research, we have conducted thorough sur-
veys among hundreds of employees from various IT
companies in Bangladesh. From the survey data, we
intend to learn about the current WFH/RW practices
or lack thereof, management of such practices, pro-
ductivity, personal well-being, and their comments
about this modus operandi.
Our contribution from the survey is:
• A concentrated survey questionnaire that con-
verges to establishing a correlation between work
from home with impact on productivity and health
of the employees.
• A categorized representation of the data that gen-
eralizes the overall status of the IT organization in
Bangladesh.
• Same categorization applied to literature to ac-
commodate a global view of WFH.
The paper is organized with the categorization of
the studied literature in Section II. We present the
methodology and construction of our survey in Sec-
tion III and the analysis of the outcome in Section
IV. We conclude with our limitations and future di-
rections in Section V.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Tools and Productivity
The paper (Carroll and Conboy, 2020) focuses on how
the Covid-19 pandemic has forced organizations into
adopting work from home and altering their work
patterns. A few organizations had to completely re-
think their business model and move to online ser-
vices. The paper suggests using Normalization Pro-
cess Theory, where the theoretical constructs such
as Coherence, Collective Action, Cognitive Partici-
pation, and Reflexive Monitoring are described, and
how these constructs can be implemented to aid re-
mote work practices. Since the effect of the pandemic
is long-term, organizations must come up with effec-
tive technology-driven practices for remote work to
increase productivity and normalize those work prac-
tices. When establishing online connectivity for re-
mote work, the remote workers need secure access to
business resources (Saline, 2021) which must be pro-
vided by the organizations. Making cloud optimiza-
tions and tools for performance monitoring, and pri-
oritizing cyber security, big data, analytics, and cloud
infrastructure are necessary as customers and remote
workers require online services. Monitoring and cen-
tralizing tools were advantageous for project man-
agers to track project progress and get efficient reports
(Shamim, 2022). The biggest problems with remote
work (Ozimek, 2020) were technological issues, such
as internet connectivity issues, home computers not
working properly and being unable to be fixed, and
not having the right equipment such as web cameras
and microphones or speakers. Around 40% of the em-
ployees (Schmidtner et al., 2021) strongly agreed that
their organizations had provided digital tools such as
notebooks, video conference systems, and cloud ser-
vices for their remote work, while 10% disagreed and
3% strongly disagreed. Organizations may decide
to stay with the new methods of doing remote work
since they are investing resources and costs in pro-
viding online services and technologies to employ-
ees (Brynjolfsson et al., 2020). Due to the bene-
fits outweighing the disadvantages, many companies
decided to go remote post-pandemic going forward,
while some adopted a hybrid model where they allow
employees to do 3 days of remote work every week.
The report (Jain and Suman, 2018) states that almost
40% of Global Software Development (GSD) projects
were unsuccessful in delivering the expected bene-
The Rise of Remote Project Management - A New Norm?: A Survey on IT Organizations in Bangladesh
519

fits due to challenges faced in communication, coor-
dination, and control processes due to geographical
and organizational distances. Most companies glob-
ally are less experienced in remote work (Shamim,
2022). Agile approaches have been very popular and
widespread among organizations (Schmidtner et al.,
2021) since it enable the ability to adapt to changes
and divide the project work into distinct iterations
(Wysocki, 2011). A hybrid project management ap-
proach combines methodologies and practices from
more than one project management approach. The
paper (Gemino et al., 2021) gives us insight into how
the hybrid approach can be beneficial, compared to
traditional and agile practices in project management.
The paper (Brynjolfsson et al., 2020) shows that the
pandemic has forced organizations to try out new ap-
proaches, some of which were unexpectedly efficient
or effective. Research has shown that a hybrid ap-
proach can provide substantial improvements within
the same budget, time, scope, and quality when com-
pared to traditional approaches (Willis, 1995), which
can be used in remote work to increase productivity.
2.2 Work-Life Balance
The report (Boland et al., 2020) discusses how the of-
fice and work life should be revisited and adjusted due
to the pandemic since it has made work from home
a necessity to continue business operations. Orga-
nizations had to reconstruct how work can be done
effectively in home environments where distractions
can happen due to family, work-life balance, and dif-
ficulty in communication with others through online
systems. Organizations had to make sure they pro-
vide platforms such as Microsoft Teams or Zoom
meeting calls with a good internet connection to em-
ployees so that they can communicate and get work
done (Schmidtner et al., 2021). Due to work being
done from home, interruptions from family and kids
were common when communicating with others on-
line, sometimes causing privacy issues such as leak-
ing information about family members to others in the
online meeting calls, and causing discomfort among
team members. Online communication required ex-
tra effort and concentration, which caused project ex-
haustion much quicker than before (Shamim, 2022).
The report (Alexander et al., 2021) shows that anxiety
is decreasing work performance, and job satisfaction,
and negatively affects colleagues during work. Ac-
cording to the survey data (Shamim, 2022), the major-
ity of the employees experienced burnout from work.
Employees prefer to have more flexibility, where they
want to have the freedom of working both from home
or in the office as they desire, depending on their
needs and workload. The online meetings took longer
than face-to-face, which were held in boardrooms be-
fore the pandemic, where time slots were limited and
well-defined. The paper (Allen Smith, 2021) dis-
cusses how the majority of employees are unwilling to
return to office workspaces due to having the comfort
of working from home. Survey results from (Bryn-
jolfsson et al., 2020) have shown younger worker
groups of 25-35 are converting and preferring to do
remote work more than older worker groups of age
65 or older. There is flexibility in working from home,
where employees can halt work and return later since
they are inside their homes at all times. There is still
a drawback, where some project managers put more
workload realizing that the employees are working in
their homes and might skip working properly, result-
ing in overwork and burnout (Willis, 1995). How-
ever, employees prefer to work from home regardless
of the disadvantages. There is also the issue of com-
muting which consumes time for employees, safety
issues, and drains energy, thus employees prefer to
work from home regardless of the disadvantages.
2.3 Career Growth / Organizational
Growth
The paper (Allen Smith, 2021) contains a survey of
500 participants, stating what remote employees miss
the most, which is the in-person conversations, a reg-
ular structure, lunches and happy hours with col-
leagues, and reduced interruptions by family mem-
bers and kids. Flexibility is the key since the major-
ity of employees say that they want to work remotely
three days a week or more during post-pandemic. Be-
ing flexible with the model and allowing employees
to work in a hybrid format will attract and retain tal-
ents as many employees are even willing to leave their
jobs to maintain working from home. The overall em-
ployability of graduates has decreased due to the pan-
demic (SHAHRIAR et al., 2021), mainly due to the
economic fall during the pandemic, and the lack of
holding meetings and interviews in person. The pan-
demic has slowed down the economy and foreign di-
rect investment has been reduced. The failure rate of
startups has also drastically been affected due to the
pandemic. The paper (Ozimek, 2020) shows a recent
survey from 2020 which estimates that the share of
remote workers in the U.S. has quadrupled to nearly
50% of the nation’s workforce. Key findings include
the rapid rise in remote work, where more than half of
the American workforce is working from home dur-
ing the pandemic. About 56% of hiring managers felt
that the shift to remote work has gone better than ex-
pected. Remote work has also opened up opportuni-
ICSOFT 2023 - 18th International Conference on Software Technologies
520

ties for independent professionals living overseas to
get hired and work with top companies and clients
around the world. Businesses need to consider the
corporate culture and employee trust when consider-
ing the return to growth strategies. According to the
authors (PMI, 2021) based on survey data, the career
opportunities for project management professionals
and software developers are the highest, due to the
largest and fastest growth in software development
jobs globally. Regional trends show that there is an
increasingly high demand for software development
and management jobs, especially in emerging devel-
oping countries. Survey results (Brynjolfsson et al.,
2020) show that there has been a rise in unemploy-
ment and employees being laid off during the pan-
demic. The pandemic has also lowered the intensity
of unemployed individuals’ search activity, as well as
the interest for organizations to hire new employees.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study aimed to gain insights into the practices,
challenges, and pain points associated with managing
software development projects for RW/WFX. We em-
ployed an exploratory research design to achieve this
objective and collected data through a dynamically
branching questionnaire. We designed the question-
naire in such a way that only relevant questions are
asked and kept participants engaged. The question-
naire was constructed using Google Forms and was
designed to elicit positive and negative sentiments.
Before finalizing the questionnaire, we conducted
a small pilot test with a test group to ensure that the
questions were relevant and would produce valuable
data. The final survey questionnaire comprised 26
questions divided into six sections, as shown in Figure
1:
1. Information
2. Work hours/Productivity
3. Tools for WFX/RW
4. Work-life balance
5. Career Growth
6. Health and Well-being
The survey was distributed to a sample of experienced
participants managing software development projects
for RW/WFX.
The data collected through the survey was ana-
lyzed using descriptive statistics to identify patterns
and trends in the responses. The study results provide
valuable insights into the current state of practices,
challenges, and pain points associated with manag-
ing software development projects for RW/WFX and
could be used to inform the development of strategies
to improve project management in this domain.
Overall, the methodology employed in this re-
search study is designed to provide a comprehensive
understanding of the practices, challenges, and pain
points associated with managing software develop-
ment projects for RW/WFX. Using a dynamic ques-
tionnaire and pilot test ensured that the data collected
was relevant and valuable, and the analysis of the data
using descriptive statistics provided insights into the
field’s current state.
After validating the questionnaire, we contacted
IT organizations based on our connections in Dhaka,
Bangladesh. We made a list of 15 such organiza-
tions and approached their CEOs, COOs, CTOs, and
HRs to seek permission to conduct the survey. We re-
quested them to distribute the Google Form hyperlink
to their public employee notification channels such as
Email, Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Discord. Out of
the 15 companies, 11 permitted us to conduct the sur-
vey, and we successfully reached over 500 employees
through these channels. Ultimately, 253 completed
the study and provided valuable data for this research.
All the survey responses from the Google Form
were recorded in a Google Sheet spreadsheet file. We
took special care in the Information section to reduce
spam by limiting one response per email and using
ReCaptcha. As multiple-choice items made up the
majority of the poll, we combined several of them to
look for potential connections and links. We divided
the six sections of the questions into three categories
for easier presentation and comprehension:
1. Tools and Productivity
2. Health and Work-Life Balance
3. Career/Organizational Growth
To combine, visualize, and analyze data, we used
Google Data Studio (formerly known as Looker Stu-
dio) and the charting features of Google Forms. In
the data analysis phase, we utilized Google Data Stu-
dio (Looker Studio) to analyze and visualize the col-
lected data. The software allows for the creation of
interactive charts, tables, and dashboards to represent
the data, which helps identify the responses’ patterns
and trends. The visualization features of the software
were particularly useful in interpreting the results and
understanding the insights of the data. Additionally,
the software allows for easy sharing of the data visu-
alizations and analysis with collaborators, which ben-
efits the research team. A thorough analysis of our
collected data is covered in our section on result anal-
ysis.
The Rise of Remote Project Management - A New Norm?: A Survey on IT Organizations in Bangladesh
521
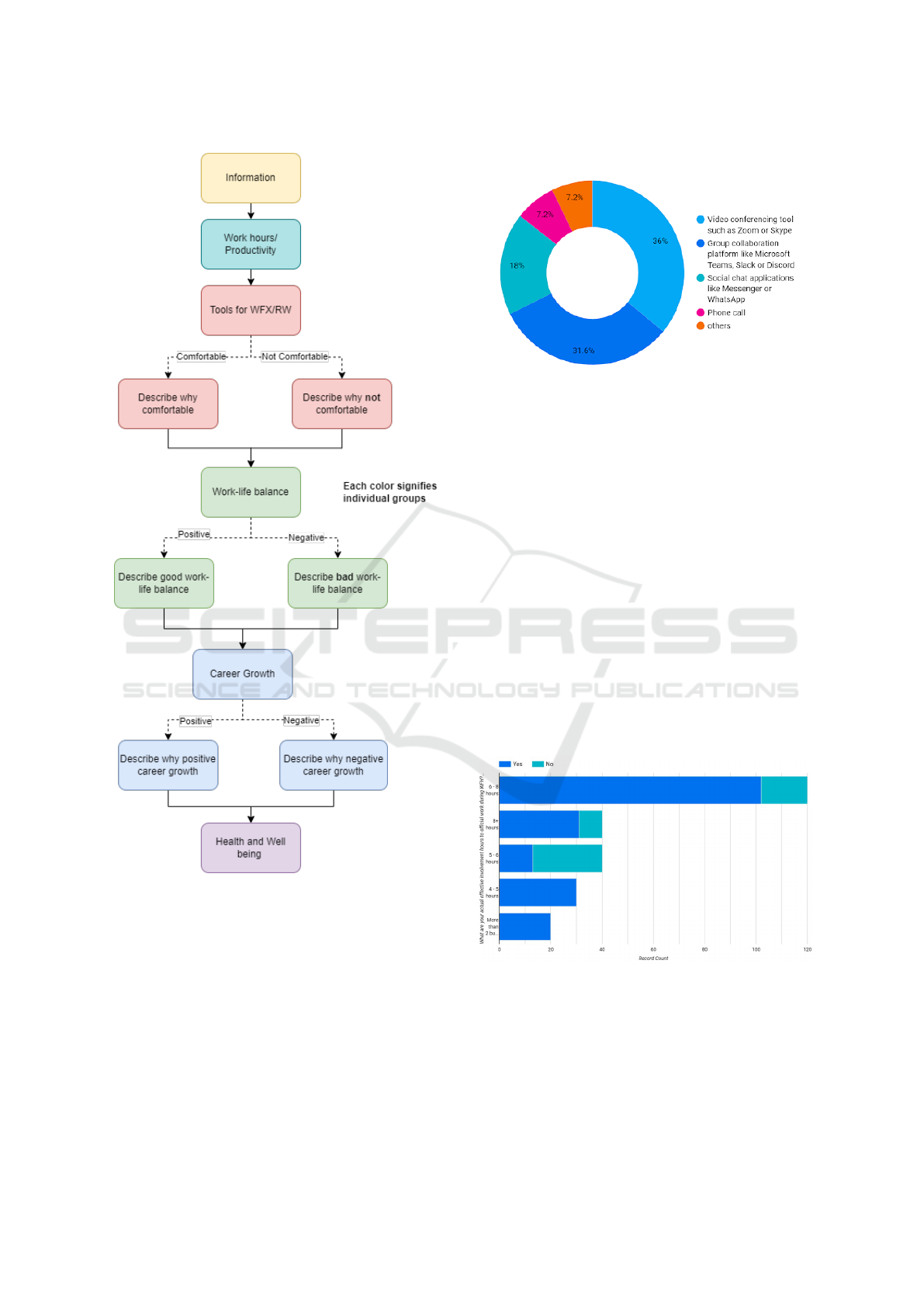
Figure 1: Survey Methodology.
4 RESULT ANALYSIS
Our survey produced some interesting insights and we
used the same categorization.
4.1 Tools and Productivity
We questioned our respondents on the productive
hours they put in during their office hours, and the
tools they used to communicate with the team or man-
agers when they are working from home.
Figure 2: Percentage of usage of tools used during WFX.
In Figure 2, we displayed results of the
tools/software used by participants and filtered them
by those who responded ”Yes” to the question, ”Do
you feel productive during WFH?”
Most respondents used a video communication
tool like Zoom or Skype and a project management
tool like Slack for text-based communication. Phone
calls were less preferred due to a lack of records.
This shows that specialized tools (e.g., Slack, Teams,
and Zoom) positively correlate to a productive WFH
environment because they enable security, record-
keeping, progress-tracking, and quick communica-
tion.
We also tried to investigate whether the respon-
dents felt more productive by working more hours or
less. Figure 3 tells us that 6-8 hours is the optimal
effective hours when they are most productive. Too
much (above 8 hours) and less (below 6 hours) re-
sulted in poor deliveries.
Figure 3: Relation with productivity and hours invested.
4.2 Career Growth
We inquired about the extent to which WFH pro-
motes self-development and career growth. Interest-
ingly, our analysis did not yield conclusive evidence
of career growth associated with WFH. Rather, the
ICSOFT 2023 - 18th International Conference on Software Technologies
522
results suggest the introduction of additional pres-
sures and some respondents reported going over-
time to complete tasks. Nevertheless, a subset of
respondents utilized their commute time to invest
in self-development by undertaking certified training
courses.
Figure 4: Career growth.
4.3 Work-Life Balance
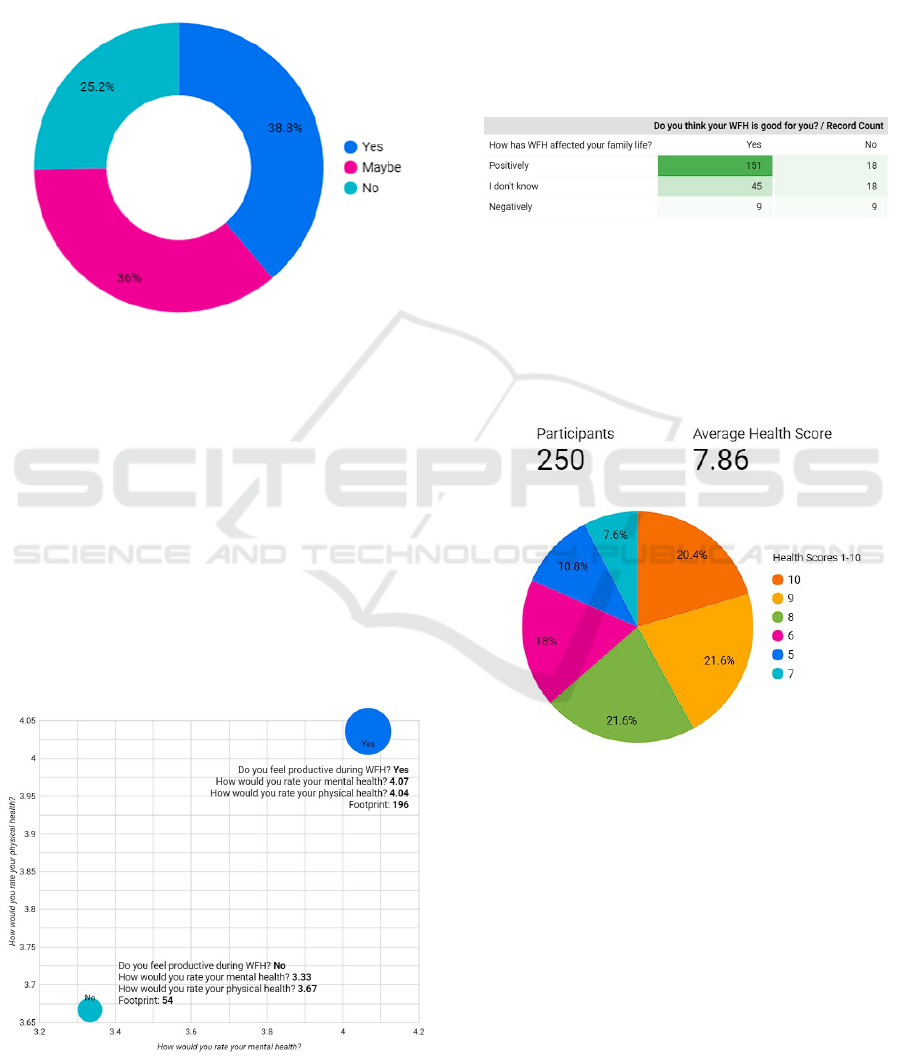
This portion of the result analysis explains the infor-
mation gathered and paints an accurate picture of the
work-life balance. If we look at Figure 5, 78.4% (196
footprints/data points) of the respondent believes they
feel productive during WFH, with an average mental
and physical health score of 4.07 and 4.04, respec-
tively. And the remaining 21.6% (54 footprints) think
they aren’t very productive, with average psycholog-
ical and physical health, respectively, coming in at
3.33 and 3.67. This confirms that higher overall health
results in feeling more productive.
Figure 5: Relation between productivity, mental and physi-
cal health.
According to Figure 6, most respondents believe
that WFH benefits them. One hundred fifty-one re-
sponded positively to WFH whose family lives had a
positive outlook. Subsequently, 45 respondents said
that the WFH was good for them and had a negli-
gible impact on their family life. Nine respondents
reported that the WFH was personally good and neg-
atively impacted their family life. Here we can see
that those respondents whose family lives were pos-
itively affected strongly believed WFH was good for
them and vice versa.
Figure 6: Work-from-home and family life.
As demonstrated in Fig. 7, we derived the health
score by adding the mental and physical health scores
for a total of 10 (5 for mental health + 5 for physical
health). Our sample size of 250 respondents yielded
an average health score of 7.86 out of 10, which signi-
fies a relatively healthy score while undergoing WFH.
Figure 7: Average health score and their distribution.
4.4 Discussion
The results of our study suggest that working from
home can positively impact work-life balance, partic-
ularly for IT professionals in Bangladesh. Spending
more time with their families and having more flex-
ible schedules allows them to feel more fulfilled and
satisfied with their work, leading to increased produc-
tivity.
However, it is essential to note that remote work
has its downsides, such as feelings of isolation and
disconnection from colleagues. To mitigate this,
we suggest organizations consider a hybrid working
The Rise of Remote Project Management - A New Norm?: A Survey on IT Organizations in Bangladesh
523

model, where employees can come to the office on
certain days and work from home for the rest of the
week. This would help employees to have a balance
between being in touch with their colleagues and also
having time for their families. Additionally, some par-
ticipants reported needing more career growth while
working remotely. This can be due to a lack of face-
to-face interaction with managers and difficulty prov-
ing their work. Therefore, managers must provide
regular feedback and hold regular meetings with em-
ployees to ensure their career growth is not hindered.
Overall, our research indicates that remote work-
ing has the potential to improve work-life balance and
productivity. Organizations must implement mea-
sures to reduce isolation and increase engagement to
ensure that remote working is sustainable in the long
run. Additionally, managers should ensure that em-
ployees are not experiencing stagnation in their career
growth while working remotely.
5 CONCLUSION
Our study focused on the effects of remote work on
work-life balance, productivity, and the use of spe-
cialized management tools in the context of IT orga-
nizations in Bangladesh. While our findings demon-
strate a positive correlation between remote work,
work-life balance, and productivity, it is important
to acknowledge the potential limitations of our study
related to generalizability to other regions/countries.
Further research is required to investigate the gener-
alizability of our findings to other sectors and regions.
The research also highlights areas for future work.
For instance, future questionnaires could focus on
more specific aspects, such as productivity, which is
a crucial concern for managers. Moreover, we ac-
knowledge the limitations of our study, particularly
in terms of data segmentation and the need for more
extensive data collection from more companies and
different types of projects. Additionally, we suggest
that future research should also consider distinguish-
ing the perspectives of managers and subordinates.
Despite the limitations, our study contributes to the
existing research on remote work and highlights the
positive impact of remote work on work-life balance
and productivity in the context of IT organizations
in Bangladesh. The use of specialized management
tools such as Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams ap-
pears to be beneficial for productivity.
REFERENCES
Alexander, A., De Smet, A., Langstaff, M., and Ravid, D.
(2021). What employees are saying about the future
of remote work. McKinsey & Company.
Allen Smith, J. (2021). Making the case for return to office.
Boland, B., De Smet, A., Palter, R., and Sanghvi, A. (2020).
Reimagining the office and work life after covid-19.
Brynjolfsson, E., Horton, J. J., Ozimek, A., Rock, D.,
Sharma, G., and TuYe, H.-Y. (2020). Covid-19 and
remote work: An early look at us data. Technical re-
port, National Bureau of Economic Research.
Carroll, N. and Conboy, K. (2020). Normalising the “new
normal”: Changing tech-driven work practices under
pandemic time pressure. International Journal of In-
formation Management, 55:102186.
Gemino, A., Horner Reich, B., and Serrador, P. M. (2021).
Agile, traditional, and hybrid approaches to project
success: is hybrid a poor second choice? Project Man-
agement Journal, 52(2):161–175.
Jain, R. and Suman, U. (2018). A project management
framework for global software development. ACM
SIGSOFT Software Engineering Notes, 43(1):1–10.
Ozimek, A. (2020). The future of remote work. Available
at SSRN 3638597.
PMI (2021). Talent gap: Ten-year employment trends,
costs, and global implications. Project Management
Institute.
Saline, S. (2021). Thriving in the new normal: How covid-
19 has affected alternative learners and their families
and implementing effective, creative therapeutic in-
terventions. Smith College Studies in Social Work,
91(1):1–28.
Schmidtner, M., Doering, C., and Timinger, H. (2021). Ag-
ile working during covid-19 pandemic. IEEE Engi-
neering Management Review, 49(2):18–32.
SHAHRIAR, M. S., ISLAM, K., ZAYED, N. M., HASAN,
K., and RAISA, T. S. (2021). The impact of covid-19
on bangladesh’s economy: A focus on graduate em-
ployability. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics
and Business, 8(3):1395–1403.
Shamim, M. M. I. (2022). The effects of covid-19 on project
management processes and practices. Central Asian
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Science, 3(7):221–
227.
Willis, B. E. (1995). Apm project-management body of
knowledge: the european view. International Journal
of Project Management, 13(2):95–98.
Wysocki, R. K. (2011). Effective project management: tra-
ditional, agile, extreme. John Wiley & Sons.
ICSOFT 2023 - 18th International Conference on Software Technologies
524
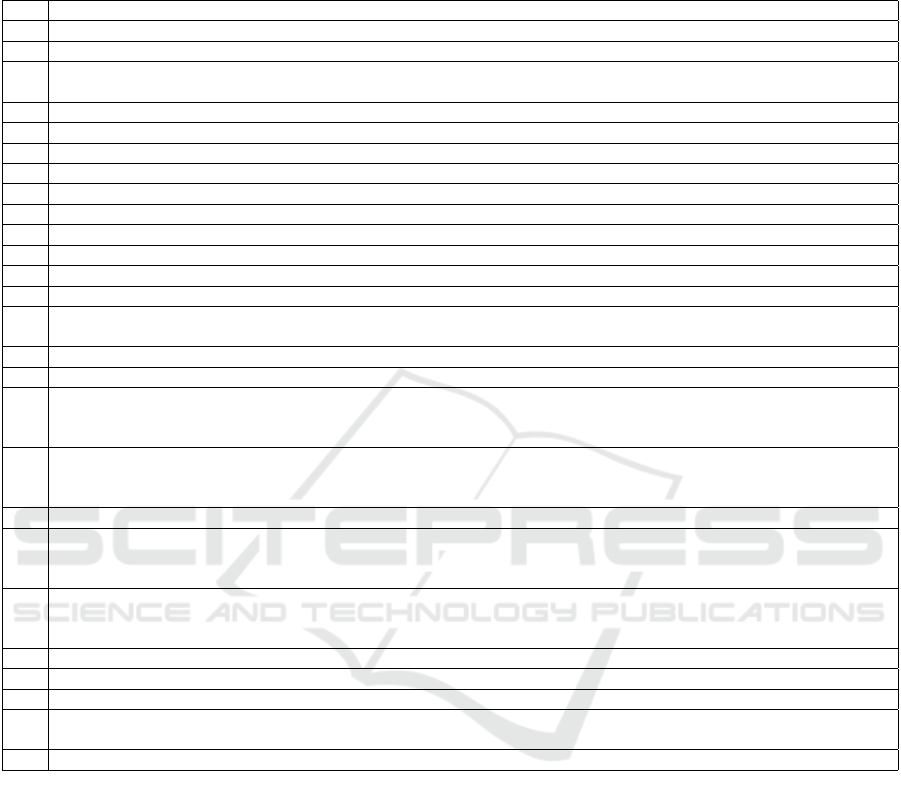
APPENDIX A: SURVEY
QUESTIONNAIRE
No. Questions
1 Working Hours?
2 What are your usual office hours during WFH? Let’s assume you work 8 hours a day. Pick one that closely matches you.
3
What are your actual involvement hours in official work during WFH? How long are
you expected to be involved in work each day?
4 How do you start your office from home?
5 Do you have an official setup at home like a dedicated desk table, working environment in the pc/laptop?
6 How do you usually report to your Manager during WFH?
7 How do you usually communicate with your subordinate/team members during WFH?
8 What level of comfort do you usually experience during WFH?
9 Comfort: This is optional but please remember that your responses have the potential to help a lot of people.
10 Discomfort: This is optional but please remember that your responses have the potential to help a lot of people.
11 How do you usually finish your office work every day during WFH?
12 Do you need to inform your Manager if you want to change your workstation during WFH?
13 Is there any company policy implemented in your company if anyone violates the rules of WFH?
14
Have your company/Manager forced/requested you to work during Government holidays or
non-office hours during WFH? If yes, then have they given you any extra compensation for this?
15 Were you fairly compensated?
16 How has WFH affected your family life?
17
Affected Positively: This is optional but please remember that your responses have the potential to
help a lot of people. Why do you think it did? Please be as brief or elaborate as you want.
We would love to hear from you.
18
Affected Negatively: This is optional but please remember that your responses have the potential to
help a lot of people. Why do you think it did? Please be as brief or elaborate as you want.
We would love to hear from you.
19 Do you think the WFH concept has a positive impact on career growth?
20
Positive Impact on Career: This is optional but please remember that your responses have the potential to
help a lot of people. Why do you think WFH had a positive impact on your career growth?
Please be as brief or elaborate as you want. We would love to hear from you.
21
Negative Impact on Career: This is optional but please remember that your responses have the potential to
help a lot of people. Why do you think WFH had a negative impact on your career growth?
Please be as brief or elaborate as you want. We would love to hear from you.
22 Do you think your organization’s WFH culture can be improved?
23 Do you think your WFH is good for you?
24 Do you feel productive during WFH?
25
How would you rate your mental health? 1 being very bad (chronic depression, anxiety, or panic attacks);
5 being very good (peaceful, calm, and in control)
26 How would you rate your physical health? 1 being very bad; 5 being very good
APPENDIX B: SURVEY
QUESTIONNAIRE (WITH
ANSWER OPTIONS)
Please visit the public URL for the complete survey ques-
tionnaire with answer options
The Rise of Remote Project Management - A New Norm?: A Survey on IT Organizations in Bangladesh
525
