
Designing an Agent-Based Model for a City-Level Simulation of
COVID-19 Spread in Cyprus
Philip Fayad
1a
, Stylianos Hadjipetrou
1b
, Georgios Leventis
1,3 c
, Dimitris Kavroudakis
2d
and Phaedon Kyriakidis
1,3 e
1
Department of Civil Engineering and Geomatics, Cyprus University of Technology, Limassol, Cyprus
2
Department of Geography, University of the Aegean, Mytilene, Greece
3
Eratosthenes Centre of Excellence, Limassol, Cyprus
phaedon.kyriakidis@cut.ac.cy
Keywords: ABM, Design, COVID-19, Spread, Spatial, Simulation, Cyprus.
Abstract: To date, several epidemiological agent-based models have been developed to study the spread of the highly
infectious coronavirus (SARS-COV) disease in different countries. However, no extensive effort has been
implemented for the Republic of Cyprus. In this research, we present the design framework of the EPIMO-
LCA agent-based model that respects the SEIR epidemiological model and attempts to simulate human
mobility to predict the spread of COVID-19 at a city-level of detail. More specifically, we fully describe the
three main model components (agents, environment and interactions) and explain all anticipated
functionalities, processes, input and output elements. The agent-based model envisaged is expected to
contribute to a better understanding of the interactions between intervention measures and disease spread for
the city of Larnaca, the Republic of Cyprus, and beyond.
1 INTRODUCTION
A pressing need for understanding the behaviour of
epidemiological diseases has emerged in light of the
recent COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) experience.
Having spread all over the world, leaving millions of
human losses behind, coronavirus 2 has posed
significant challenges to humankind at every level.
Cyprus was no exception, counting more than 1,500
deaths and 600,000 (>50% of the total population)
infections (World Health Organization, 2023). The
particularly high human-to-human inapparent
transmission rate in combination with the severe
implications that COVID-19 may have on human
health, and especially the vulnerable group of people,
have led to an urgent need of seeking ways to limit
the virus spread. Intermittent non-pharmaceutical
interventions (NPIs) have proven able to reduce the
infection spread rate (Buhat et al., 2020) but may, on
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1442-8361
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8808-3319
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2850-4342
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5782-3049
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4222-8567
the other hand, have significant impact on the
socioeconomic aspects of human life in the medium-
and long-term (Novakovic & Marshall, 2022). The
above highlight the importance of forming effective
policies and taking better-informed and timely
decisions in regard to prevention, control and
mitigation of COVID-like viruses spread (Cui et al.,
2006). In this context, radical advances on
epidemiological (disease spread) modelling have
marked the aftermath of the recent pandemic to
support scientists and decision makers in
understanding the underlying mechanisms driving the
spread of the infection.
Intricate relationships between social and physical
processes, including the transmission of infectious
diseases, have recently been at the focal point of
spatial sciences and geography. Indeed, modelling of
human-environment interactions enables insights into
the spatial dynamics of these relationships, leading to
218
Fayad, P., Hadjipetrou, S., Leventis, G., Kavroudakis, D. and Kyriakidis, P.
Designing an Agent-Based Model for a City-Level Simulation of COVID-19 Spread in Cyprus.
DOI: 10.5220/0012054000003546
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2023), pages 218-224
ISBN: 978-989-758-668-2; ISSN: 2184-2841
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
improved decision making and addressing of
complex challenges. Mathematical models,
representing simple or complex abstractions of
mobility and interactions among individuals and
populations, have been central to infectious disease
response and decision-making process (Bachar et al.,
2021; Hethcote, 1989, 2000; Kifle & Obsu, 2022;
Vytla et al., 2021). This is particularly useful in the
case of infectious diseases towards increasing our
understanding on the drivers of transmission (Crooks
& Hailegiorgis, 2014; Merler et al., 2015; Willem,
2015) and non-linear causal effects and providing the
ability to simulate future scenarios (Gomez et al.,
2021; Kerr et al., 2021; Kyriakidis et al., 2021;
Shastry et al., 2022; Silva et al., 2020). Among the
most widely used computational models, agent-based
models (ABMs) have become popular due to their
inherent ability to model and simulate mobility
transitions of autonomous agents within complex
systems (Mehdizadeh et al., 2022) based on a set of
behavioural rules guiding their interactions
(Bonabeau, 2002). This particular modelling
architecture is widely applied in fields where
simplifying complexity is crucial, like economics
(Heckbert et al., 2010), mobility (Loraamm, 2020)
and supply chain (Chen et al., 2013). Therefore, it is
only fitting that such modelling approach be utilised
in the field of epidemiology. In relative terms, agents
can be individuals, groups, organizations, or even
non-human entities able to interact with each other
and their environment in various ways, depending on
the specific model. Consequently, each agent can be
described by individual properties but also given a
certain status at each discrete time step, as described
in the following section. The bottom-up approach of
ABMs allows for the realistic simulation of
interactions among individuals both in space and time
which in turn could give insights to population-scale
patterns (Tracy et al., 2018) of the phenomenon under
study.
A plethora of ABMs, drawn from the extensive
data gathered for the needs of modelling COVID-19
transmission, has been developed during the last two
years. The majority is built upon dynamic equations
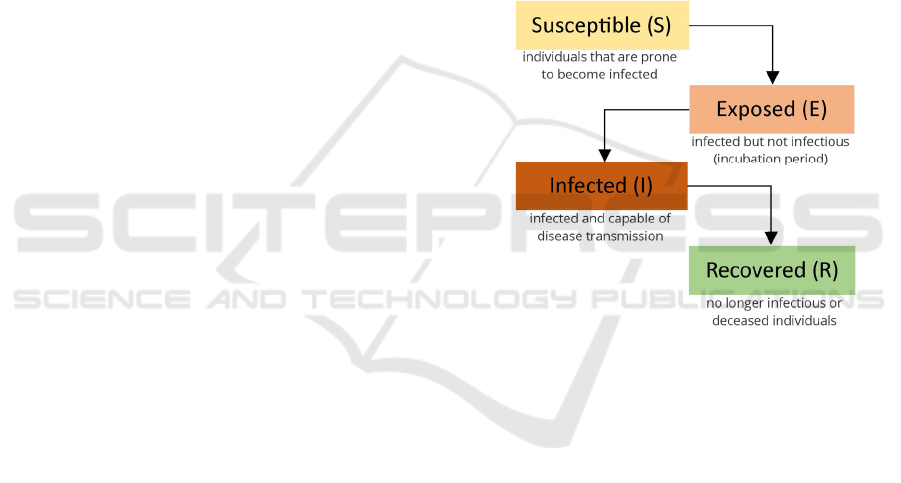
linking compartments; those being susceptible (S),
exposed (E), infected (I), and recovered (R). As the
letters S, E, I, R represent, the health status of a given
human population within a dynamic infectious
disease context, health experts and scientists should
always regard any pandemic situation within a tight
temporal context so as to accomplish its minimum
possible spread, while achieving better forecasts
(Yang et al., 2021) for the future.
Different variations of the so called SEIR model,
have been extensively used in an ABM context to
assess planned interventions used to combat COVID-
19
(Altun et al., 2021; Kim & Cho, 2022; Taghizadeh
& Mohammad-Djafari, 2022). A systematic review
on agent-based social simulation of Covid-19 is given
by Lorig et al. (2021) while Kong et al. (2022)
provide a scoping review of the compartmental
structures used in the dynamic models developed for
COVID-19 spread. Application examples include
Covasim (Kerr et al., 2021), an ABM model to project
COVID-19 dynamics and interventions, COVID-
ABS (Silva et al., 2020) developed in an attempt to
simulate health and economic effects of interventions
and CityCOVID (Ozik et al., 2021), incorporating
behavior and social interaction in a real-case scenario
in Chicago.
Figure 1: Diagram of a typical S.E.I.R Model.
In cases where the adoption of SEIR models is
needed to allow health stakeholders and officials to
extract concrete conclusions and make predictions,
proper model calibration is imperative in order to
understand both the static and dynamic nature of the
phenomenon under study. Towards that end, Ajbar et
al. (2021), answering to the critical -for such
understanding and for the model calibration as well-
inverse modelling problem, identified their model
parameters using real time data of Saudi Arabia and
subsequently used the computed values to analyse the
behavior of the model. Over time, SEIR models
showcased their advantages rendering them
important tools for policy makers and governments
when coupled with network-driven dynamics being
capable of predicting with high accuracy any
epidemic peaks taking into account external factors
such as the virus transmission over air (Liu et al.,
2020). Although, SEIR models might be considered
adequate for modelling and forecasting other
Designing an Agent-Based Model for a City-Level Simulation of COVID-19 Spread in Cyprus
219
diseases, as far as COVID-19 is concerned, Moein et
al. (2021) showed that a more complex approach that
takes into account mortality rates and hospital
capacity as well should also be considered when
attempting to make a pandemic forecasting feasible.
Building upon the need for a more complex
approach to COVID-19 modelling, the present study
introduces an ABM to simulate the spread of the
disease based on human mobility and evaluate the
impact of governmental countermeasures, with a
focus on the Republic of Cyprus as the study area. In
addition to simulating the distribution of future cases
and deaths, the model is designed to be able to predict
the possible outcomes after the implementation of
strong governmental countermeasures, thus, allowing
the evaluation of such actions in preventing COVID-
19 spread locally.
To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no similar
studies have been conducted for the particular region
of interest (Larnaca, Cyprus) that utilise agent-based
modelling to study the spread of COVID-19. Spatial
behavior is based on the Human Mobility Schedule
(HMS) and is designed to be incorporated to the
model through a questionnaire survey that represents
the human mobility of Cypriot citizens after each
iteration of the ABM simulations.
2 METHODOLOGY
To simulate the spread of COVID-19 using the agent-
based approach, we identify NetLogo software as the
most widely used open-source solution capable to
represent and analyse a model of this capacity. This
section describes the main logic of EPIMO-LCA
agent-based model and explains its functionalities,
processes, properties, input and output elements.
The Human Mobility Schedule (HMS) is a crucial
component of the model as it contains all the
necessary information regarding mobility behavior
(how and when the agents move based on age group)
on an hourly basis. The aim of the HMS is to describe
the main mobility activities of individuals in Cyprus
according to their age during a typical day. It is based
on the analysis of real data resulted from a two-part
questionnaire survey addressed to Cypriot citizens. In
the first part of the questionnaire, demographic
information (gender, age, region of residence and
occupation) as well as mobility characteristics (means
of transport, mobility type, frequency and distance)
are requested. The second part asks for the
completion of a mobility schedule indicating the
person's indicative location/activity per hour within a
typical day.
2.1 Agents
Based on their age, there are three principal types
(breeds) of agents in the EPIMO-LCA model. Each
bread describing a specific group of people, moves
differently according to the HMS: 1) Mostly-out
agents (age: 18-64) represent the group of people that
mainly move from-to their work office, 2) Students
(age: 6-24) represent the group of people that mainly
move from-to educational institutions and 3) Mostly-
at-home agents (age: 18+) represent the group of
people that stay mostly at home (unemployed, elderly
and work-from-home individuals).
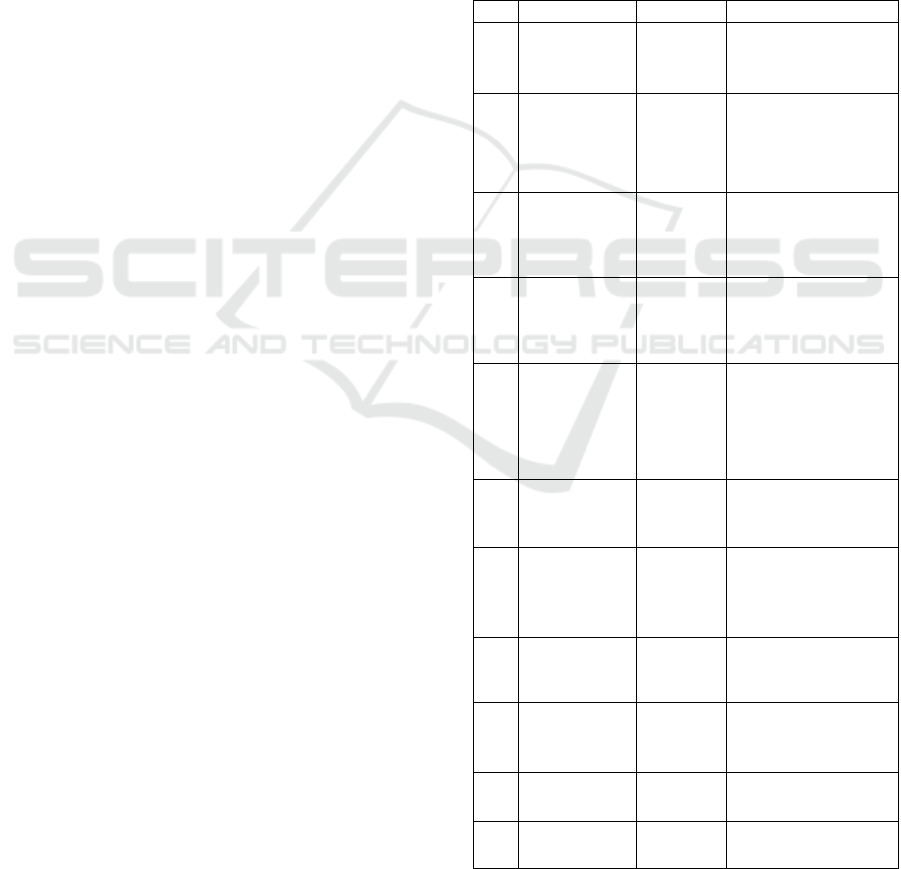
Table 1: Agent properties.
No Property Type Function
1 Age numeric
Initial setup of
population % by age
group
2
Chronic
disease
True/
False
Initial setup of
population % with
increased chance of
mortality
3 Mask wear
True/
False
Initial setup of
population % that
respect the mask-
use measure
4
Social
distance
True/
False
Initial setup of
population % that
respect the social
distance measure
5 Immune
True/
False
Initial setup of
population % that
are immune
(natural, vaccination
or medicine)
6 Healthy
True/
False
Initial setup of
population % that
are healthy
7 Infected
True/
False
Initial setup of
population %, and
later after being
exposed
8 Susceptible
True/
False
Agents that are in
close proximity with
an infected agent
9 Exposed
True/
False
Agents at high risk
to be infected
(incubation period)
10 Recovered
True/
False
After the pass of 14
days being infected
11 Deceased
True/
False
After being infected
and if at high risk
SIMULTECH 2023 - 13th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
220

Agents are defined by a set of eleven properties
(table 1). Properties 1 to 7 are set ahead of model
initialization (model parameters), while properties 6
to 11 are dynamic and change as the agents are
interacting with each other, describing the state of the
agent.
2.2 Actions and Behaviours
At the start of the simulation, agents are assigned one
of the 3 states (Healthy, Immune or Infected)
depending on the parameters initially set. After model
initialization, agents move using the road network
interacting with each other and gradually evolve to 4
more states (Susceptible, Exposed, Recovered,
Deceased). Depending on their state, agents behave
as follows. Healthy, Immune, Susceptible, Exposed
and Recovered agents continue to move based on
their breed and according to HMS. Immune and
Recovered agents stay in this state forever and cannot
transmit the virus nor get infected. Therefore, re-
infection is not possible. Infected agents can also
continue to move (according to HMS) or implement
the stay-at-home quarantine rule, depending on the
initial parameter set.
Moving progressively from one state to another,
there are five intermediate stages where agents evolve
1) from Healthy-to-Susceptible, after being in close
proximity and in contact with an infected agent, 2)
from Susceptible-to-Exposed, after in direct contact
with an Infected agent and if at high risk of infection
(no mask use, no social distancing, no immunity), 3)
from Exposed-to-Infected, after the pass of n days
(incubation period), 4) from Infected-to-Recovered,
after the pass of 14 days being infected and, lastly, 5)
from Infected-to-Deceased, after the pass of three
days and if at high risk of mortality (age group,
chronic disease).
2.3 Environment
Agents interact in a spatial environment using
the road network of the city of Larnaka, Cyprus. Each
time-step (tick) represents one hour of human
activity. Moreover, buildings are also mapped and
used as origin - destination for moving agents.
More specifically, these buildings correspond to high-
risk areas for virus transmission and are represented
as points (centroids) in space with different colours
based on building type (residential, offices, health
centers, educational institutions, shopping centers,
etc) and represented with various buffer sizes
depending on crowd capacity.
Having one of the highest car ownership rates in
the world (629+ cars per 1000 inhabitants), Cyprus'
residents rely heavily on private car commuting
(Obrien, 2022). Based on this fact, in our simulation
we don’t include any public transportation parameters
assuming all agents use private cars with an average
speed of 50km/h (speed limit in urban areas).
2.4 The Proposed ABM
Initially, the agents are randomly distributed in
residential buildings and as the model starts, they
begin to move (according to HMS) to other buildings.
As a result, while respecting each building crowd
capacity, agents are continuously gathering in closed
limited areas and interact with each other. Thus, the
virus begins to spread and emerge. The simulation
continues until all agents are either Healthy, Immune,
Infected, Deceased or Recovered. In our proposed
model, the simulation of COVID-19 spread adheres
to the following process (figure 2):
1. Agents are created according to setup
parameters (Initialization of the model).
2. Agents are assigned with a colour based on
their initial state (Healthy - green, Immune -
grey and Infected - red).
3. Agents are allocated randomly in space,
initially within residential areas while
respecting crowd capacity.
4. Healthy and Immune agents move according
to HMS. Infected agents also move
depending on preset rule (if 14-day home
quarantine parameter is disabled).
5. Non-immune and non-infected agents that
are in close proximity to infected agents turn
to yellow colour (susceptible).
6. Susceptible agents at low risk of infection
turn green colour (healthy).
7. Susceptible agents at high risk of infection
turn orange colour (exposed).
8. Exposed agents turn red colour (infected)
after n days (n*24 ticks).
9. Infected agents at high risk of mortality turn
black colour (deceased).
10. Infected agents at low risk turn blue colour
(recovered) after 14 days (336 ticks).
11. The Simulation stops when all agents are
either healthy, immune, infected, deceased
or recovered.
Designing an Agent-Based Model for a City-Level Simulation of COVID-19 Spread in Cyprus
221
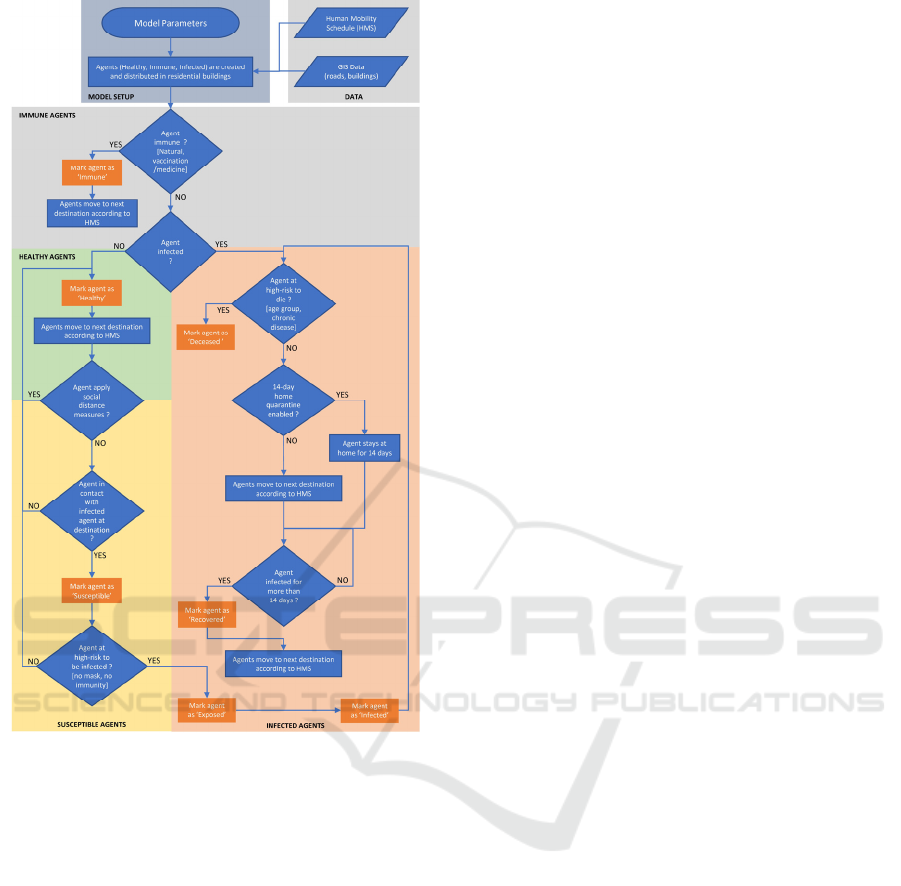
Figure 2: The EPIMO-LCA model flow chart.
Through NetLogo’s user interface, specific
demographic and epidemiological input parameters
can be easily adjusted and countermeasure policies
can be enabled or disabled (mask use, vaccination,
lockdown, etc.) in the simulation. More specifically,
the user using a slider can define the number of: a)
the total population size (ranging from 10-600), b)
people initially infected (% of total population), c)
immune people (% of total population), d) people
with chronic diseases (% of total population), e)
people in each age group (% of total population), f)
mortality rate, g) recovery rate, h) hospital
capacity/beds (ranging from 10-600), i) people that
adhere to social distancing (% of total population), j)
people vaccinated or on medication (% of total
population). Additionally, the user using a switch can
enable or disable important parameters regarding: k)
mandatory mask use, l) shops closure (entertainment,
restaurants, bars, shopping) and m) full lockdown
enforcement.
2.5 Data
All the required data are obtained from freely
available open repositories (OpenStreetMap and
National Open Data Portal of Cyprus - data.gov.cy)
and from local governmental authorities (Department
of Land and Surveys and Statistical Service of the
Republic of Cyprus). Additionally, the latest
CORINE Land Cover (CLC2018) product by the
Copernicus Land Monitoring Service is considered an
important dataset for the determination of land use
areas at an 100m spatial resolution using Sentinel-2
and Landsat-8 satellite data. All these data are
necessary for the development of the agent-based
model and additionally will be also used for the
purposes of data analysis and model validation.
2.6 Expected Results and Validation
The proposed ABM is expected to contribute to the
better understanding of the emergence and course of
the dangerous virus in the community while
considering the effects of important coping policies
as well as human mobility behaviours for the
simulation of the disease spread at a city-level. It aims
to help experts and decision makers to combat future
epidemic and pandemic events. By showcasing all the
critical statistics and graphs (number of healthy,
immune, susceptible, exposed, infected, recovered
and deceased people) in real time, the model aims to
be an efficient tool for the prediction of virus spread,
the evaluation of the important coping measures and
the estimation of the possible consequences.
To validate the effectiveness of the model, four
different case scenarios will be simulated for
comparison with real data. The case scenarios
concern specific key time periods (lockdown,
mandatory mask use, etc) during the COVID-19
(2020-2022) pandemic in Cyprus. For each
simulation, the coping policies as well as
demographic and epidemiological data will be
simulated using real data as input parameters.
Simulation results will be then compared with the
actual situation (real number of infections, people
immune, deaths, etc) that the Republic of Cyprus
experienced. In this way, we can evaluate the
effectiveness of the model.
3 CONCLUSIONS
Respecting the concept of the SEIR epidemiological
model, in this research we presented the design
framework of an ΑΒΜ for COVID-19. The "EPIMO-
SIMULTECH 2023 - 13th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
222

LCA" model is designed with the goal to simulate
human mobility behavior in order to predict future
outcomes (spatial distribution of cases and deaths) at
a city-level of detail, while also considering important
governmental countermeasures (like mandatory mask
use, lockdown enforcement, etc.). In our proposed
design we specified the types and properties of the
agents, their actions as well as the environment that
they will interact during the simulation. Additionally,
we identified the need for data concerning human
spatial mobility behavior as such data does not exist
for Cyprus. This is why we suggest the
implementation of a questionnaire survey. The results
of this survey will be analysed and lead to the
development of the HMS with the scope to be
integrated in the model as an immediate future step.
In this way we can produce a representative activity
schedule that describe the mobility of the Cypriot
citizens (per age group) during a typical day. Thus,
the HMS is a critical component as it defines the way
that the agents will move during the ΑΒΜ
simulations. After the actual development of the
model, the validation process will follow using real
data and specific case scenarios. Once the
methodology and all parameters are finalized, the
model can be expanded and parameterized for the rest
of the districts of Cyprus (Limassol, Nicosia, etc.).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The PhD study titled “Agent-based modelling and
simulation of human mobility in the context of
infectious disease spread”(epimogeo-covid.cut.ac.cy)
in the field of “Epidemiological Monitoring with the
use of Geoinformatics” is conducted at the
Department of Civil Engineering and Geomatics at
the Cyprus University of Technology. The PhD
research has received scholarship grants from the
State Scholarships Institution of Cyprus
(cyscholarships.gov.cy) and the Sylvia Ioannou
charitable foundation (sylviaioannoufoundation.org).
REFERENCES
Ajbar, A., Alqahtani, R. T., & Boumaza, M. (2021).
Dynamics of an SIR-Based COVID-19 Model With
Linear Incidence Rate, Nonlinear Removal Rate, and
Public Awareness. Frontiers in Physics, 9, 634251.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2021.634251
Altun, K., Altuntaş, S., & Derelı̇ , T. (2021). An interaction-
oriented multi-agent SIR model for the spread of
SARS-CoV-2. Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and
Statistics. https://doi.org/10.15672/hujms.751734
Bachar, M., Khamsi, M. A., & Bounkhel, M. (2021). A
mathematical model for the spread of COVID-19 and
control mechanisms in Saudi Arabia. Advances in
Difference Equations, 2021(1), 253. https://doi.org/10.
1186/s13662-021-03410-z
Bonabeau, E. (2002). Agent-based modeling: Methods and
techniques for simulating human systems. Proceedings
of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(suppl_3),
7280–7287. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.082080899
Buhat, C. A. H., Lutero, D. SM., Olave, Y. H., Torres, M.
C., & Rabajante, J. F. (2020). Transmission of
Respiratory Infectious Diseases between Neighboring
Cities using Agent-based Model and Compartmental
Model [Preprint]. Infectious Diseases (except
HIV/AIDS). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.24.20138
818
Chen, X., Ong, Y.-S., Tan, P.-S., Zhang, N., & Li, Z.
(2013). Agent-Based Modeling and Simulation for
Supply Chain Risk Management—A Survey of the
State-of-the-Art. 2013 IEEE International Conference
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1294–1299.
https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2013.224
Crooks, A. T., & Hailegiorgis, A. B. (2014). An agent-
based modeling approach applied to the spread of
cholera. Environmental Modelling & Software, 62,
164–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.08.
027
Cui, J., Takeuchi, Y., & Saito, Y. (2006). Spreading disease
with transport-related infection. Journal of Theoretical
Biology, 239(3), 376–390. https://doi.org/10.
1016/j.jtbi.2005.08.005
Gomez, J., Prieto, J., Leon, E., & Rodríguez, A. (2021).
INFEKTA—An agent-based model for transmission of
infectious diseases: The COVID-19 case in Bogotá,
Colombia. PLOS ONE, 16(2), e0245787. https://doi.
org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245787
Heckbert, S., Baynes, T., & Reeson, A. (2010). Agent-
based modeling in ecological economics: Agent-based
modeling in ecological economics. Annals of the New
York Academy of Sciences, 1185(1), 39–53.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05286.x
Hethcote, H. W. (1989). Three Basic Epidemiological
Models. In S. A. Levin, T. G. Hallam, & L. J. Gross
(Eds.), Applied Mathematical Ecology (Vol. 18, pp.
119–144). Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://
doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-61317-3_5
Hethcote, H. W. (2000). The Mathematics of Infectious
Diseases. SIAM Review, 42(4), 599–653.
https://doi.org/10.1137/S0036144500371907
Kerr, C. C., Stuart, R. M., Mistry, D., Abeysuriya, R. G.,
Rosenfeld, K., Hart, G. R., Núñez, R. C., Cohen, J. A.,
Selvaraj, P., Hagedorn, B., George, L., Jastrzębski, M.,
Izzo, A. S., Fowler, G., Palmer, A., Delport, D., Scott,
N., Kelly, S. L., Bennette, C. S., Klein, D. J. (2021).
Covasim: An agent-based model of COVID-19
dynamics and interventions. PLOS Computational
Biology, 17(7), e1009149. https://doi.org/10.1371/
journal.pcbi.1009149
Designing an Agent-Based Model for a City-Level Simulation of COVID-19 Spread in Cyprus
223

Kifle, Z. S., & Obsu, L. L. (2022). Mathematical modeling
for COVID-19 transmission dynamics: A case study in
Ethiopia. Results in Physics, 34, 105191.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105191
Kim, Y., & Cho, N. (2022). A Simulation Study on Spread
of Disease and Control Measures in Closed Population
Using ABM. Computation, 10(1), 2. https://doi.org/
10.3390/computation10010002
Kong, L., Duan, M., Shi, J., Hong, J., Chang, Z., & Zhang,
Z. (2022). Compartmental structures used in modeling
COVID-19: A scoping review. Infectious Diseases of
Poverty, 11(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-
022-01001-y
Kyriakidis, P., Kavroudakis, D., Fayad, P., Hadjipetrou, S.,
Leventis, G., & Papakonstantinou, A. (2021).
Promoting the adoption of agent-based modelling for
synergistic interventions and decision-making during
pandemic outbreaks. AGILE: GIScience Series, 2, 1–5.
https://doi.org/10.5194/agile-giss-2-44-2021
Liu, P., Beeler, P., & Chakrabarty, R. K. (2020). COVID-
19 Progression Timeline and Effectiveness of
Response-to-Spread Interventions across the United
States [Preprint]. Infectious Diseases (except
HIV/AIDS). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.17.20037
770
Loraamm, R. W. (2020). Incorporating behavior into
animal movement modeling: A constrained agent-based
model for estimating visit probabilities in space-time
prisms. International Journal of Geographical
Information Science, 34(8), 1607–1627.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2019.1658875
Lorig, F., Johansson, E., & Davidsson, P. (2021). Agent-
Based Social Simulation of the Covid-19 Pandemic: A
Systematic Review. Journal of Artificial Societies and
Social Simulation, 24(3), 5. https://doi.org/10.
18564/jasss.4601
Mehdizadeh, M., Nordfjaern, T., & Klöckner, C. A. (2022).
A systematic review of the agent-based
modelling/simulation paradigm in mobility transition.
Technological Forecasting and Social Change,
184, 122011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.
122011
Merler, S., Ajelli, M., Fumanelli, L., Gomes, M. F. C.,
Piontti, A. P. y, Rossi, L., Chao, D. L., Longini, I. M.,
Halloran, M. E., & Vespignani, A. (2015).
Spatiotemporal spread of the 2014 outbreak of Ebola
virus disease in Liberia and the effectiveness of non-
pharmaceutical interventions: A computational
modelling analysis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases,
15(2), 204–211. https://doi. org/10.1016/S1473-3099
(14)71074-6
Moein, S., Nickaeen, N., Roointan, A., Borhani, N.,
Heidary, Z., Javanmard, S. H., Ghaisari, J., & Gheisari,
Y. (2021). Inefficiency of SIR models in forecasting
COVID-19 epidemic: A case study of Isfahan.
Scientific Reports, 11(1), 4725. https://doi.org/10.1038/
s41598-021-84055-6
Novakovic, A., & Marshall, A. H. (2022). The CP‐ABM
approach for modelling COVID‐19 infection dynamics
and quantifying the effects of non‐pharmaceutical
interventions. Pattern Recognition, 130, 108790.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108790
Obrien, A. (2022). Infrastructure Solutions: How to make
public transport attractive (Infrastructure Solutions).
European Investment bank.
Ozik, J., Wozniak, J. M., Collier, N., Macal, C. M., &
Binois, M. (2021). A population data-driven workflow
for COVID-19 modeling and learning. The
International Journal of High Performance Computing
Applications, 35(5), 483–499. https://doi.org/10.1177/
10943420211035164
Shastry, V., Reeves, D. C., Willems, N., & Rai, V. (2022).
Policy and behavioral response to shock events: An
agent-based model of the effectiveness and equity of
policy design features. PLOS ONE, 17(1), e0262172.
https:// doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262172
Silva, P. C. L., Batista, P. V. C., Lima, H. S., Alves, M. A.,
Guimarães, F. G., & Silva, R. C. P. (2020). COVID-
ABS: An agent-based model of COVID-19 epidemic to
simulate health and economic effects of social
distancing interventions. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals,
139, 110088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.
110088
Taghizadeh, E., & Mohammad-Djafari, A. (2022). SEIR
Modeling, Simulation, Parameter Estimation, and Their
Application for COVID-19 Epidemic Prediction.
MaxEnt 2022, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/
psf2022005018
Tracy, M., Cerdá, M., & Keyes, K. M. (2018). Agent-Based
Modeling in Public Health: Current Applications and
Future Directions. Annual Review of Public Health,
39(1), 77–94. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-
publhealth-040617-014317
Vytla, V., Ramakuri, S. K., Peddi, A., Kalyan Srinivas, K.,
& Nithish Ragav, N. (2021). Mathematical Models for
Predicting Covid-19 Pandemic: A Review. Journal of
Physics: Conference Series, 1797(1), 012009.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1797/1/012009
Willem, L. (2015). Agent-based models for infectious
disease transmission exploration, estimation &
computational efficiency.
World Health Organization. (2023). WHO Coronavirus
(COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int
Yang, W., Zhang, D., Peng, L., Zhuge, C., & Hong, L.
(2021). Rational evaluation of various epidemic models
based on the COVID-19 data of China. Epidemics,
37, 100501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epidem.2021.
100501.
SIMULTECH 2023 - 13th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
224
