
Feedback in Online Mathematics Tutoring
Antonín Jančařík
1a
, Jakub Michal
1b
and Jarmila Novotná
1,2 c
1
Faculty of Education, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
2
CeDS, Université Bordeaux, France
Keywords: Online Tutoring, Feedback, Mathematics, Algebra, Geometry, Chatbot.
Abstract: The goal of this paper is to present issues related to assessment and feedback in the framework of online
mathematics tutoring implemented with the help of a chatbot using Artificial intelligence (AI) (Jančařík et al.,
2022). The presented project aims to create a teaching course that is intended to help the pupil in independent
preparation for the national entrance exams in mathematics for upper secondary schools in the Czech
Republic. The course takes the form of a chatbot with which a pupil can communicate in a web browser
environment or the Telegram communication application designed for all common operating systems
(Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, ...). The chatbot also includes a communication module using
artificial intelligence that can communicate with the pupil beyond the scope of the designed course. The
following two questions are addressed in the part of the research that is presented in this paper. The first
question is what form of feedback is effective in the given environment and most reflect the nature of tutoring.
The second question is how the chosen procedures must be modified for the different areas of mathematics
the course focuses on. The paper presents an implementation within the area of algebra and geometry.
1 INTRODUCTION
The use of technology in the teaching of mathematics
is a relatively new area of interest for mathematicians
and educators, not only in the area of mathematics.
Drijvers et al. (2010) summarize the stages of
development in the years 1960 to 1990. Already from
1942, there was a significant development in
computing technologies, but only in the late 1960s,
the focus of mathematicians and mathematics
educators turned their attention to the effects of
computing on the content of school-level and
university-level mathematics (Fey, 1984). One of the
main goals of the use of technology is to promote a
more active form of student learning.
Technology has also affected the teaching of
mathematics, and in the 1980s, theoretical
frameworks were developed in which the use of
technological tools in education was investigated.
Drijvers et al. (2010) draw attention to the
Tutor/Tool/Tutees (Taylor, 1980) and White
Box/Black Box (Buchberger, 1990) frameworks,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3331-2396
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3522-8411
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5306-2315
among others. In the mode Tutor, the technology
presents the materials which the student answers and
the technology evaluates their answers. The mode
Tool has a similar focus but requires less
programming than the mode Tutor. The mode Tutee
was described by Taylor as follows: “To use the
computer as tutee is to tutor the computer; for that,
the student or teacher doing the tutoring must learn to
program, to talk to the computer in a language it
understands” (Taylor, 1980, p. 4).
The use of ICT in education continues to be at the
centre of interest of mathematics educators
(Verschaffel et al., 2019; Hardman, 2019, Phuong et
al., 2022). Lagrange et al. (2001) present a survey of
literature about the educational uses of ICT in
mathematics education up to 2001. Gissel et al.
(2019) published a critical review of various meta-
studies about the impact of ICT use on students’
learning. Much attention is paid to the use of
Artificial Intelligence in education. This is also the
focus of this article, which focuses on questions
related to evaluation and feedback in the framework
of online mathematics tutoring implemented with the
374
Jan
ˇ
ca
ˇ
rík, A., Michal, J. and Novotná, J.
Feedback in Online Mathematics Tutoring.
DOI: 10.5220/0012017500003470
In Proceedings of the 15th Inter national Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 1, pages 374-381
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

help of a chatbot with the use of AI. The aim is to
develop a system of structurally homogenous courses
with a focus on the nationwide entrance examination
for Czech secondary schools where the AI would
support the learners' experience by answering pupils'
questions related or non-related to a given topic.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This section is discussed in two parts. Firstly the
definition of tutoring and related research is
described; secondly, the section talks about artificial
intelligence in education.
2.1 Tutoring
The term tutoring in this paper refers to tutoring in a
school subject which is taught in addition to
mainstream schooling. Tutoring is a worldwide
phenomenon that has been paid attention to especially
in recent decades (Hille et al., 2016; Bray & Silova,
2006). Its main focus is on the “core” subjects, i.e.
language and mathematics (Mischo & Haag, 2002).
Tutoring in mathematics, albeit in various forms, can
be found in the vast majority of countries (Song,
2013). Even though there are several different forms
of tutoring, the prevailing form is the form of private
supplementary tutoring, i.e. paid tutoring focusing on
content from school lessons or preparation for
entrance exams (Novotná, 2019). As this is a paid
activity, private supplementary tutoring is not
available to all students to the same extent.
Differences in family socioeconomic status are
further exacerbated by a system in which students
who are tutored achieve better results (Safarzyńska,
2013). Tutoring used to be typically carried out face-
to-face when a pupil or a group of students came to
see the tutor, or the tutor came to see the students.
Online tutoring expanded during the covid-19
pandemic. The fact that there is no direct contact
between the tutor and the student opens up space for
the automation of activities. Some studies show the
effectiveness of providing online tutoring (e.g. Beal
et al. (2007)). Artificial intelligence can contribute to
an increase in the frequency of use of online tutoring
and can partly or even completely replace the tutor.
The tutor can be replaced in the selection of the study
trajectory, in the evaluation of results, as well as in
communication with the student (Shahbazi & Byun,
2022). These changes aim to improve the quality and
accessibility of tutoring forms and thereby reduce the
impact of socioeconomic background on a student’s
performance and achievement (Alhossaini &
Aloqeely, 2021). That's why systems like the one
described here, which will use the latest technologies,
including AI, to deliver free education content to all
learners, have a big role to play.
2.2 AI in Education
The Research into the use of AI in education focuses
on the following four areas (Zawacki-Richter et al.,
2019):
1. Profiling and prediction;
2. Assessment and evaluation;
3. Adaptive systems and personalization;
4. Intelligent tutoring systems.
The here presented research focuses only on one
of the forms of using artificial intelligence, namely on
its use in the creation of an intelligent tutoring system,
i.e. a system in which one-to-one personal tutoring
takes place, where the tutor’s role is fully or partially
taken over by a computer system – artificial
intelligence. Despite the significant progress in the
development of artificial intelligence in recent years,
the difference between AI and a live tutor is still
evident. However, research conducted with the first
such systems shows that some students may find it
much easier to communicate with AI than with a
teacher or a tutor (Kim et al., 2020). In another study
(E. Park et al., 2011), when educating participants on
a certain topic, a robot tutor that provided positive
feedback was perceived as attractive and acceptable.
As part of Attard’s (2021) research, it was found that
when using an AI chatbot in the explanation of the
mathematics, 73% of the users enjoyed making use of
the chatbot, and the same percentage of respondents
also expressed a desire to use the chatbot again in the
future. In all, these studies support the review of
research showing that social robots in educational
settings have positive effects on student learning
(Belpaeme et al., 2018). In sum, although not always
the case, most research on robots in education has
shown promising ways that can facilitate effective
learning experiences.
AI instruction may provide an effective means for
delivering instruction when current events prohibit
face-to-face human interaction. Although the first
results show the great potential of using AI in
tutoring, research in this area is at the very beginning
and many questions are still open. One of the most
important issues is the design of an appropriate
structure for the course and the form of providing
feedback.
Tutoring differs from school education in many
ways. Thus, assessment and feedback must be
Feedback in Online Mathematics Tutoring
375
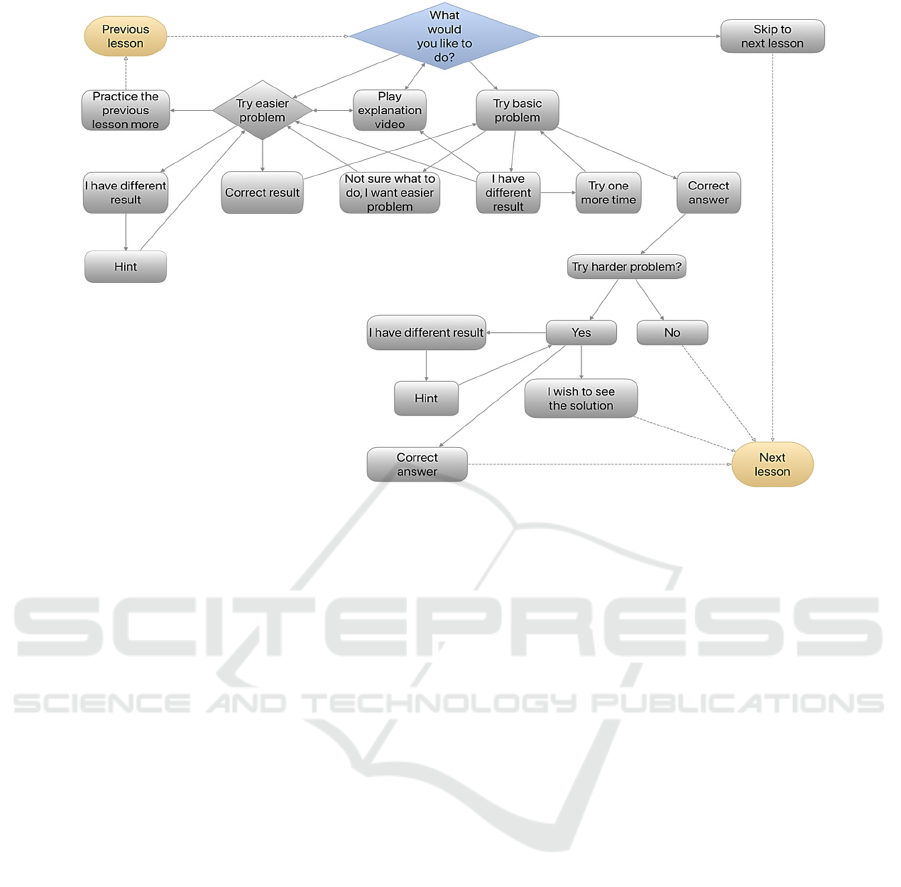
Figure 1: Options the user can choose from at each step.
adapted to these differences. Summative assessment,
which is often used in schools, does not seem
appropriate in the context of tutoring. Based on an
analysis of the effects of summative assessment
(Harlen et al., 2002), two reasons can be given why it
is advisable not to rely merely on summative
assessment in tutoring. The first reason is that
summative assessment motivates only some students
and increases the gap between higher and lower-
achieving students. By tutoring, however, we want to
reduce the differences between higher and lower-
achieving students (without reducing the
performance of high achievers). The second reason is
that summative assessment motivates students
towards performance goals rather than towards
learning goals, as required for continuing learning
(Harlen et al., 2002). The goal of tutoring should not
only be to achieve short-term results but to prepare
for continuous learning. The aim of assessment
should therefore not be an evaluation of achieved
goals, but rather the level of mastery of the needed
knowledge, procedures and skills. Fiori et al. (2004)
work with the term process-oriented assessment and
state that by assessing students’ problem-solving
processes rather than products alone, we may provide
them with more formative feedback as compared with
the other techniques. We consider the provision of
this kind of feedback to be essential for effective
tutoring. Roa (2006) states that when using ICT in
education it is important to utilize both formative and
summative evaluation. On the one hand, it is
important to determine not only the tools that allow
for the learning of a particular subject area but those
that allow for the correct feedback. Sadler (Sadler,
1998) points out that the quality of feedback is a
crucial issue.
In the paper, we focus on the use of AI for two
purposes. One of them is its independent use by
students as a tool for self-checking the correctness of
the solution or as an aid to finding a possible way to
the right results. We classify this as used in the Tutee
role (Taylor, 1980). The system can also be used by a
teacher who wants to introduce students to some
procedures that they do not know yet or do not know
how to use. This is the mode of the Tutor (Taylor,
1980).
Petty (2002) states the following motivational
reasons from a survey among students:
• The things I am learning are useful to me;
• The qualification I will get is good for me;
• I usually have good results in my studies and
this success boosts my self-confidence;
• If I study well, it will be appreciated by my
teacher or my classmates;
• If I don't study, there will be unpleasant (and
quite immediate) consequences;
• The things I am learning are interesting and
make me curious to learn more;
• The teaching is fun.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
376
3 RESULTS
The goal of our research is to design an online course
that will help students to prepare on their own for the
national entrance exams from mathematics for upper
secondary schools in the Czech Republic. The course
covers the following four areas: Number and
Arithmetic Operations, Dependencies, Relations and
Work with Data, Geometry in Plane and Space, and
Non-Standard Application Problems.
The course takes the form of a chatbot and can be
run in a web browser or the Telegram communication
application designed for all common operating
systems. Due to the need to implement the course into
the Telegram environment, the user interface consists
exclusively of elements suitable for touch phones and
tablets. Thus, the user communicates with the chatbot
mainly using selection fields or text fields. The
chatbot's response is typically verbal, with an image,
a gif, an URL link, or another decision-making level
with a selection from the pre-offered response fields.
Thanks to the integration of artificial intelligence, the
student can even drop the discussed topic and ask
questions to which the chatbot responds. This AI
system can also supply relevant information pupils
might need to solve the task. For example AI
responds pupil when he or she asks about
reconnecting to the course and starting over.
Questions and answers of a pupil are continuously
reflected upon and new functions are added (such as
searching for relevant information on wikipedia or
other databases of educational resources). AI is being
trained on questions and reactions of pupils’.
The aim of the course is not to test the student, but
to improve their abilities in and understanding of the
given areas. That is why we decided to implement the
course in a form where students do not get the usually
presented choice of answers of which only one is
correct and the others are wrong. Instead, we decided
to use a form where only one answer is given and this
answer is correct. The other options allow the student
to ask for advice or to give up on the solution. It is
thus up to the student to solve the task and then
answer whether they have reached the desired result.
We expect a higher level of motivation from this form
(Petty, 2002) when the student does not feel that he is
being tested and is not penalized for choosing the
wrong answer or for asking for advice. If the student
selects that they need advice, the chatbot will show
them a detailed solution to the given task, or a
procedure that can be used for the solution of the task
after some minor modification. For each topic,
questions are graded according to difficulty, allowing
the student to skip an easy task if they feel confident
in the area. Moreover, after solving a standard task, it
is up to the student to decide whether they want to try
to solve a difficult task. While working in the course,
the student is also allowed to play a video with an
explanation that will link them to YouTube or another
video server. Since our goal is to find out whether a
student has improved in the area after completing the
course and how they worked with the multiple-choice
format without distractors, their progress is recorded
anonymously. Among other things, the time between
displaying a question and selecting an answer or the
performance on a pre-test and post-test is monitored.
The student has the opportunity to generate topics for
the course based on the results of the pre-test. They
do not have to go through all the areas if they for
example only have problems in algebra.
Figure 2: Chatbot environment for Algebraic expressions
topic.
A more detailed functioning of the chatbot is
illustrated in Figure 1, which shows what options the
student chooses from at each step. Specific examples
of the use of algebraic identities and unit conversions
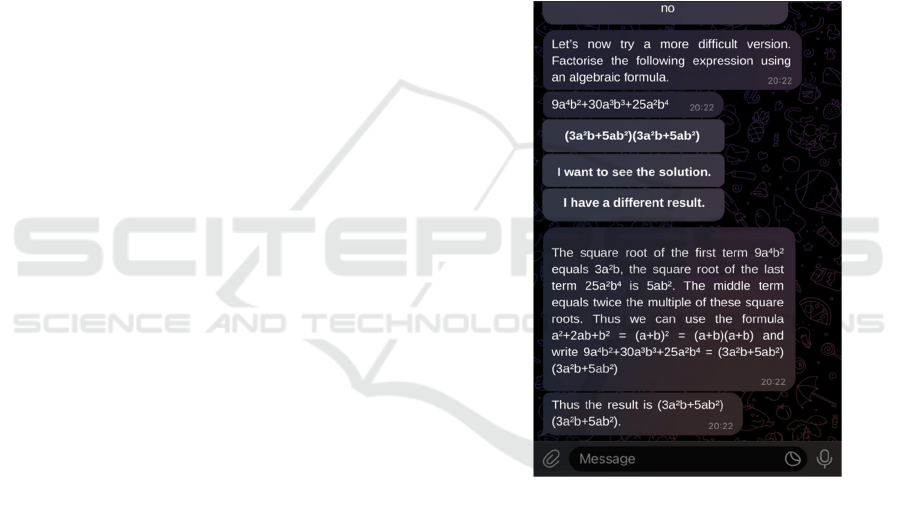
are shown in Figures 2 and 3. In Figure 2, the
student’s task is to factorise an algebraic expression
using the formula for the square of the sum. As the
student did not know what to do, they selected the
option “I want to see the solution”. Through this, the
student got access to an in-detail explained solution
to the problem. In Figure 3, the student’s task is to
convert units of length. The student chose the correct
answer, and in response, the chatbot commended the
Feedback in Online Mathematics Tutoring
377
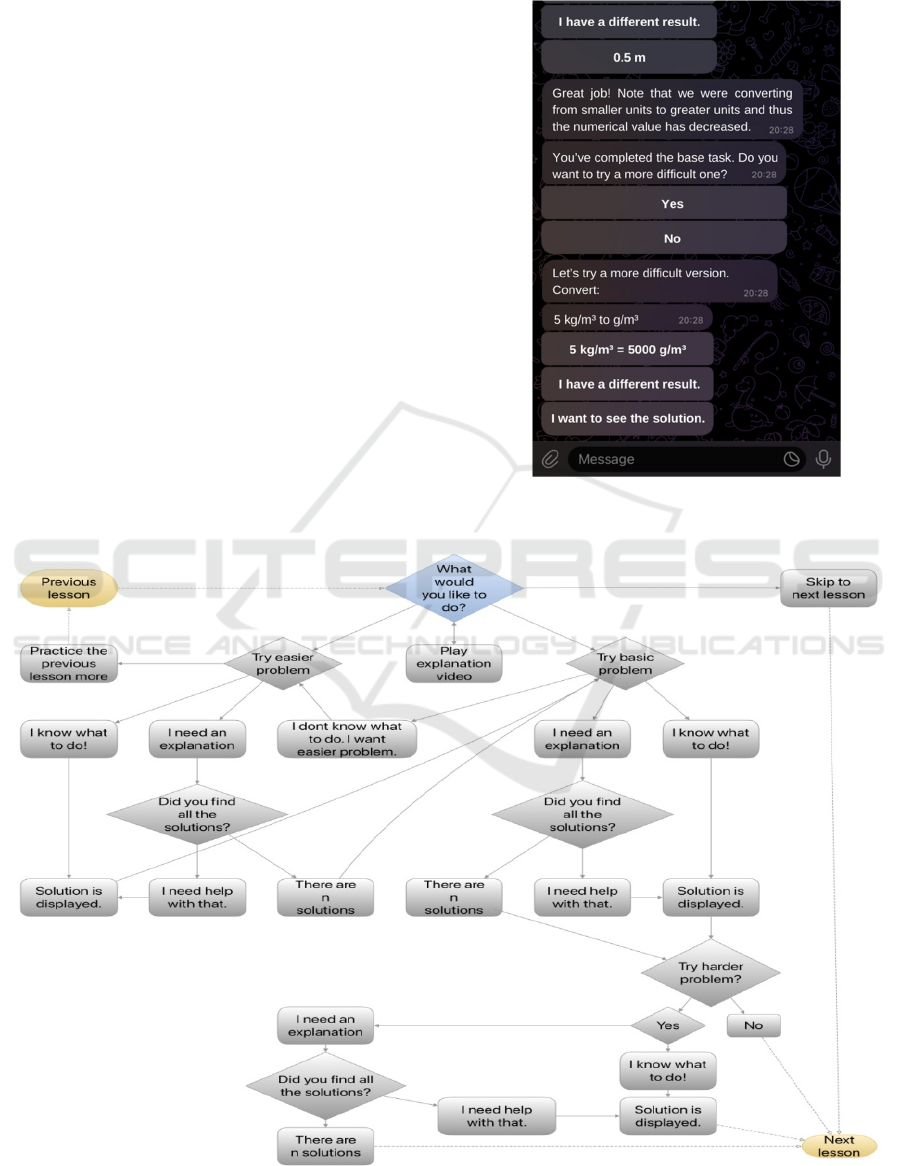
student as well as gave them useful tips on what to
look out for when converting.
The fundamental question addressed in our
research was whether this principle can be applied in
all areas of mathematics that the course focuses on.
Our original intention was to apply a uniform scheme
across all topics so that the student could get used to
the homogeneity of the environment and could work
in it effectively. However, this turned out to be
impossible, as different areas of mathematics require
different ways of presentation. While, for example, in
algebra, it is possible to offer an answer in the form
of an algebraic expression, there is no such possibility
in the field of geometry. Not only is it not possible to
express the solution with a one-line verbal answer,
but also a solution in the form of a picture may not be
sufficient for the student to understand. The
nonlinearity of the answer in the form of a picture
combined with the fact that the construction can
usually be done in many ways means that we have to
approach it differently than to offer one correct
answer. While displaying the correct solution in
arithmetic and algebra allows the student to check
their understanding of the procedure and helps to
eliminate numerical errors, in geometry showing one
solution may confuse the student, especially if the
student proceeded differently or found a different
solution.
Figure 3: Chatbot environment for Unit conversions.
Figure 4: Options the user can choose from at each step in the field of construction tasks.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
378
In the case of algebraic problems, the chosen
procedure was implemented in such a way that the
student was shown the correct answer together with
the assignment. The implementation of the entire
procedure can be found in Figure 1. In the case of
construction tasks, the correct answer cannot be given
immediately for the above reasons. This was solved
by giving the student the choice between the options
“I need an explanation” and “I know how to do it”.
This means that the second option is different from
how it works in the previous areas as there is no
visible solution or advice on how to proceed directly
on the button.
Figure 5: Chatbot environment for geometry.
Figure 4 shows how the chatbot works in the field
of construction tasks. Having asked for an
explanation, the student is offered a detailed verbal
answer, an animation (gif) showing the step-by-step
construction in a graphical software, a stationary
image of the solution, or a link to a video explaining
the phenomenon/construction/validity of a critical
step. The student’s task is then to determine whether
the problem has more than one solution. Having
clicked on the option “I know how to do it”, the
student is shown only a stationary image of one of the
solutions. The student is then asked if they have found
other solutions. They can choose from the options
“Yes, the task has n solutions (congruent solutions are
taken as 1)”, where n is dynamic, depending on the
task, and the option “I need advice on the number of
solutions”. Selecting the latter option means the
student is shown a detailed solution as if they selected
the option “I need an explanation” in the very
beginning. Examples of construction problems are in
Figures 5 and 6.
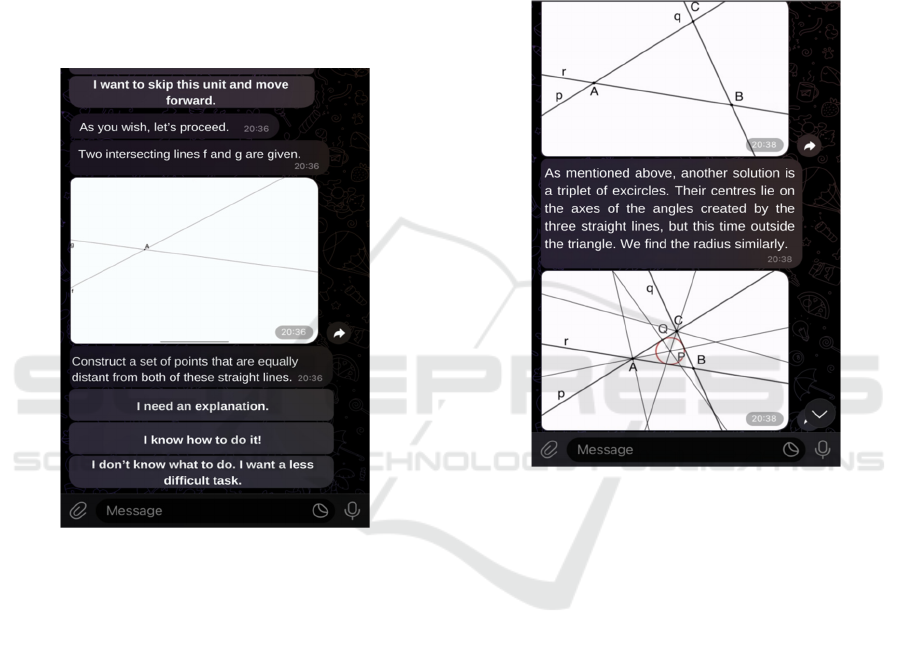
Figure 5 shows the assignment that the student
gets having chosen the difficulty of the task they want
to solve. This is described in words, sometimes it is
supplemented with an illustrative picture. Figure 6
shows an explanation of another problem is
displayed, where the student first sees the described
animation and then a picture of the solution. A set of
other solutions to the problem are also discussed here.
Figure 6: Offered solution of geometry task.
For each of the areas, at the end of the unit, the
student is offered links to other tasks or units of a
similar type created by teachers and uploaded to the
Ema.cz server. The tasks that are recommended to
students have been evaluated by the authors of the
paper in terms of quality and only the most suitable
ones have been selected. The course thus primarily
helps the student identify which areas they still need
to practice, it offers tasks and explanations but also
other resources where the student can improve or
practice their knowledge.
Before making the course available to students, we
plan to add links to interactive applets created in
GeoGebra (https://www.geogebra.org/, accesed on
15
th
March 2023) that will allow the student to
construct in a graphical software environment with a
limited palette of tools (circle, line, line segment,
compass, intersection, ...) and the software will
automatically evaluate the correctness of the solution,
similar to the Euclidea application (https://www.
euclidea.xyz/, accesed on 15
th
March 2023).
Feedback in Online Mathematics Tutoring
379

4 DISCUSSION & CONCLUSIONS
Our research confirms that it is necessary to proceed
differently in different areas of mathematics. In the
paper, this is documented in two different areas of
school mathematics – algebraic problems and
construction problems in geometry.
Petty (2002) states that anything that surprises,
arouses curiosity or anticipation or provokes thought
helps to motivate students. Pupils can be encouraged
to take an active approach to learning, among other
things, by presenting them with activities in which
they will correct and check their work (either on their
own or with each other), by making them study at
least some topics on their own from books and by
using inquiry-based approach and by allowing them
to experiment actively.
As we have shown in the paper, the use of a
chatbot meets these recommendations and can be
considered a suitable tool for fostering understanding
in problem-solving in mathematics. In further
research, we plan to focus on the use of the chatbot in
other areas of school mathematics, and on examining
the relationship between teachers and pupils to it.
Attention should also be paid to the introduction of
AI tools in teacher education.
The tutoring system is about to be tested with
pupils during the spring of 2023. Their feedback as
well as data from their answers (the time it took for
them to click the right answer) will be collected and
analyzed to further improve the system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was funded by the Technology Agency
of the Czech Republic, grant number TAČR N.
TL05000236 – AI assistant for pupils and teachers.
REFERENCES
Alhossaini, M., & Aloqeely, M. (2021, December). Causal
Analysis of On-line Math Tutoring Impact on Low-
income High School Students Using Bayesian Logistic
and Beta Regressions. In 2021 IEEE Symposium Series
on Computational Intelligence (SSCI) (pp. 1-10). IEEE.
Attard, A. E. (2021) AI assisted pedagogical chatbot
(Bachelor's thesis, University of Malta).
Beal, C. R., Walles, R., Arroyo, I., & Woolf, B. P. (2007).
On-line tutoring for math achievement testing: A
controlled evaluation. Journal of Interactive Online
Learning, 6(1), 43-55.
Bray, M., & Silova, I. (2006). The private tutoring
phenomenon: International patterns and perspectives.
In I. Silova, V. Būdienė, & M. Bray (Eds.). Education
in a hidden marketplace: Monitoring of private tutoring.
Overview and country reports (pp. 27–40). New York:
Open Society Institute. DOI: 10.1080/030579206010
24974.
Belpaeme, T., Kennedy, J., Ramachandran, A., Scassellati,
B., & Tanaka, F. (2018). Social robots for education: A
review. Science Robotics, 3(21), eaat5954.
https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.aat5954
Buchberger, B. (1990). Should students learn integration
rules? SIGSAM Bulletin, 24(1), 10–17.
Drijvers, P., Kieran, C. and Mariotti, M.A., with Ainley, J.,
Andresen, M., Cheung Chan, Y., Dana-Picard, T.,
Gueudet, G., Kidron, I., Leung, A. and Meagher, M.
(2010). Integrating Technology into Mathematics
Education: Theoretical Perspectives. In C. Hoyles and
J.-B. Langrange (Eds.), Mathematics Education and
Technology-Rethinking the Terrain (pp. 89-132).
Springer Science + Business Media. DOI 10.1007/978-
1-4419-0146-0_7
Fey, J.T. (Ed.) (1984). Computing and Mathematics: The
Impact on Secondary School Curricula. College Park:
The University of Maryland.
Fiori, N., Boaler, J., Cleare, N., DiBrienza, J., & Sengupta,
T. (2004). What discussions teach us about
mathematical understanding: exploring and assessing
students’ mathematical work in classrooms? In D. E.
McDougall & J. A. Ross (Eds.), Proceedings of the
twenty-sixth annual meeting of the North American
Chapter of the International Group for the Psychology
of Mathematics Education, 2, 491-498. Toronto:
OISE/UT.
Gissel, S. T., Ramos Artuso, A., & Køhrsen, L. (2019).
Does the use of ICT in education promote student
learning?.
https://iartemblog.wordpress.com/conferences/odense/
Hardman, J. (2019). Towards a pedagogical model of
teaching with ICTs for mathematics attainment in
primary school: A review of studies 2008–2018.
Heliyon, 5(5), e01726.
Harlen, W., Crick, R. D., Broadfoot, P., Daugherty, R.,
Gardner, J., James, M., & Stobart, G. (2002). A
systematic review of the impact of summative
assessment and tests on students’ motivation for
learning.
Hille, von A., Spieß, K., & Staneva, M. (2016). Immer mehr
Schülerinnen und Schüler nehmen Nachhilfe,
besonders in Haushalten mit mittleren Einkommen.
DIW Wochenbericht, 83(6), 111–120. DOI:
10.5684/soep.v30
Jančařík, A., Novotná, J., Michal, J. (2022) Artificial
Intelligence Assistant for Mathematics Education. In:
P. Fotaris, Panagiotis, Blake, A (Eds.),. Proceedings of
the 21st European Conference on e-Learning - ECEL
2022 (pp. 143-148). 1. Reading. ISBN 978-1-914587-
56-6. ISSN 2048-8637
Kim, J., Merrill, K., Xu, K. and Sellnow, D. D. (2020) My
teacher is a machine: Understanding students’
perceptions of AI teaching assistants in online
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
380

education. International Journal of Human–Computer
Interaction, Vol 36, No. 20, pp 1902-1911.
Lagrange JB, Artigue M, Laborde C, Trouche L. (2001). A
meta study on IC technologies in education. Towards a
multidimensional framework to tackle their integration.
In PME CONFERENCE 2001 (Vol. 1, pp. 1-111).
Mischo, C. & Haag, L. (2002). Expansion and effectiveness
of private tutoring. European Journal of Psychology of
Education, 17(3), 263–273, DOI: 10.1007/BF03173
536.
Novotná, G. (2019). Pupils' perception of their understand-
ing in mathematics and its connection to private
supplementary tutoring. Proceedings of CERME 11.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348579569
Petty, G. (2002). Moderní vyučování. Praha, Portál. ISBN
80-7178-681-0. Translated from Petty, G. Teaching
Today, Cheltenham: Stanley Thornes Ltd.
Robová, J., & Moravcová, V. (2019). Vývoj
matematického vzdělávání v České republice po roce
1989. Scientia in educatione, 10(3), 143-162.
Roa, H.B., Nariño, A. (2006). A model for teaching
mathematics via problem-solving supported by
technology. In: C. Hoyles, Lagrange, J./b/, Son, Le H.
& Sinclaire, N. (Eds.), Proceedings of the Seventeenth
ICMI Study Conference (pp. 66-73).
Sadler, D. R. (1998). Formative assessment: revisiting the
territory. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy
& Practice, 5(1), 77-84.
Safarzyńska, K. (2013). Socio-economic determinants of
demand for private tutoring. European Sociological
Review, 29(2), 139-154
Shahbazi, Z. and Byun, Y-Ch.(2022). Agent-Based
Recommendation in E-Learning Environment Using
Knowledge Discovery and Machine Learning
Approaches. Mathematics 2022, 10(7), 1192;
https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071192
Song, K. O., Park, H. J., & Sang, K. A. (2013). A cross-
national analysis of the student-and school-level factors
affecting the demand for private tutoring. Asia Pacific
Education Review, 14(2), 125-139.
Taylor, R. (Ed.) (1980). The Computer in the School: Tutor,
Tool, Tutee. New York: Teachers College Press.
Trinh Thi Phuong, T., Nguyen Danh, N., Tuyet Thi Le, T.,
Nguyen Phuong, T., Nguyen Thi Thanh, T., & Le Minh,
C. (2022). Research on the application of ICT in
Mathematics education: Bibliometric analysis of
scientific bibliography from the Scopus database.
Cogent Education, 9(1), 2084956.
Verschaffel, L., Depaepe, F., & Mevarech, Z. (2019).
Learning Mathematics in metacognitively oriented
ICT-Based learning environments: A systematic review
of the literature. Education Research International,
2019.
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V.I., Bond, M., and
Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research
on artificial intelligence applications in higher
education – where are the educators? International
Journal of Educational Technology in Higher
Education, 2-27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-
0171-0
Feedback in Online Mathematics Tutoring
381
