Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words
Takuro Hada
1,2 a
, Yuichi Sei
1,3 b
, Yasuyuki Tahara
1 c
and Akihiko Ohsuga
2 d
1
The University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo, Japan
2
First Organized Crime Countermeasures Division, Organized Crime Department, Criminal Investigation Bureau,
National Police Agency, Japan
3
JST PRESTO, Saitama, Japan
Keywords:
Dark Jargon, Compound Word, Microblog, Twitter, Word Embedding, Word2Vec.
Abstract:
Recently, drug trafficking on microblogs has increased and become a social problem. While cyber patrols are
being conducted to combat such crimes, those who post messages that lead to crimes continue to communicate
skillfully using so-called “dark jargon,” a term that conceals their criminal intentions, to avoid using keywords
(“drug,” ”marijuana,” etc.) of the target of monitoring. Evading detection by the eyes of monitoring, they con-
tinue to communicate with each other skillfully. Even if the monitors learn these dark jargons, they become
obsolete over time as they become more common, and new dark jargons emerge. We have proposed a method
for detecting dark jargons with criminal intent based on differences in the usage of words in posts and have
achieved a certain level of success. In this study, by using similar words, we propose a method for detecting
compound-type dark jargons that combines two or more words, which have been difficult to detect using exist-
ing methods. To confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted a detection experiment with
compound words and a detection experiment with dark jargons. As a result, we confirmed that the proposed
method enabled to detect compound-type dark jargons that could not be detected by existing methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid spread of social media, the number of
cybercrime has increased. A news article based on
a United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime report
noted increases in online drug trafficking via Face-
book, Twitter, and Instagram (Wongcha-um and Al-
lard, 2020). The Special Narcotics Control Law also
applies to social media postings that use dark jargons,
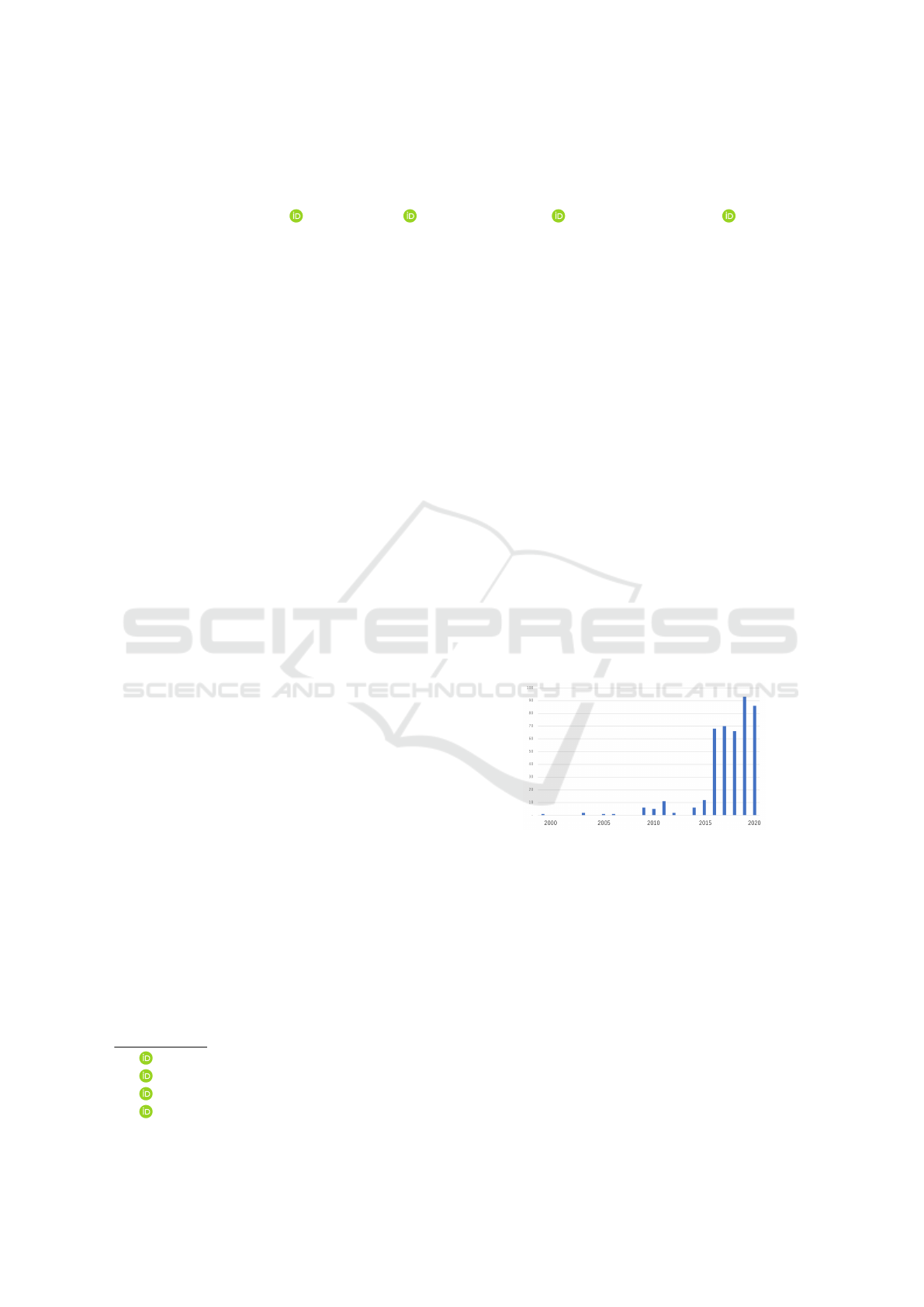
and as shown in Figure 1, the number of arrests has
dramatically increased in recent years.
Posters who aim to drug trafficking are wary of
having their posts deleted by cyber patrols, the po-
lice, or social media operators, having their accounts
frozen, or being arrested by the police. Therefore,
they tend to avoid words directly related to crimes
(“marijuana,” ”methamphetamine,” etc.) and use dark
jargons, as depicted in Figure 2, to conduct drug traf-
ficking only with those who know the meaning of the
dark jargons.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2853-9211
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2552-6717
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1939-4455
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6717-7028
Figure 1: Number of arrests for violation of the Narcotics
Control Law (stirring up and instigation) based on data from
the Ministry of Justice (MOJ, 2021).
Dark jargons are commonly used in the drug trade,
for example, “ganja,” “grass,” “weed,” and “joint” for
marijuana and “es,” “shabu,” “ice,” and “crystal” for
methamphetamine in Japanese. Even if these dark
jargons are regularly detected by keyword searches,
the effect tends to be limited. This is because, as
a characteristic of dark jargons, when they are gen-
erally recognized, new dark jargons are created to
avoid surveillance, or the meaning of a dark jargon
is given to a common word that has not been used be-
fore (Yuan et al., 2018). For example, in Japan, for
marijuana, the terms “grass,” “weed,” and “joint” are
Hada, T., Sei, Y., Tahara, Y. and Ohsuga, A.
Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words.
DOI: 10.5220/0011918800003393
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2023) - Volume 1, pages 427-437
ISBN: 978-989-758-623-1; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
427
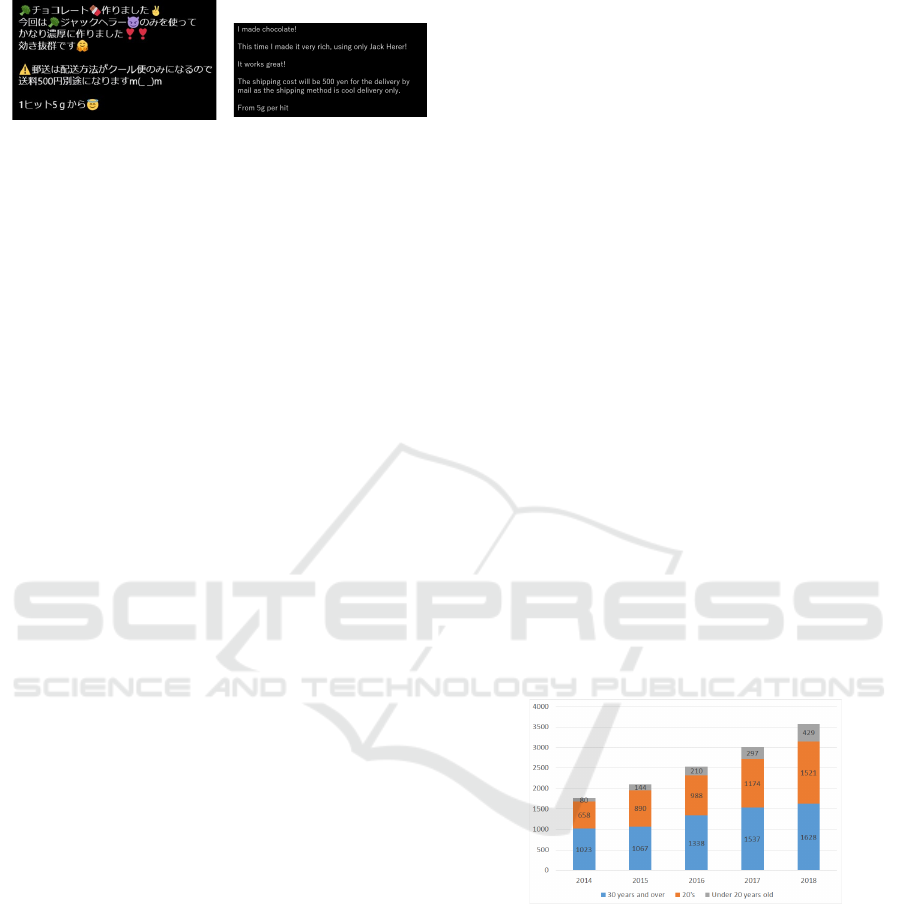
(a) Writing in Japanese (Ex-
ample).
(b) Translation of (a).
Figure 2: Example sentences with dark jargons from Twit-
ter.
used, and for methamphetamine, “ice” and “crystal”
are used. As a result, the monitors must continually
keep track of new dark jargons and add them to the list
of targets for detection, which places a heavy burden
on them. Therefore, to support cyber patrols to pre-
vent crimes such as drug trafficking, we aim to detect
posts that induce crimes, including dark jargons.
We have previously proposed a method for de-
tecting crime-inducing dark jargons by similar words
based on the hypothesis that similar related words
(hereafter “Related word”) appear around the words
used in illicit transactions.
Here, we focused on Twitter and classified tweets
related to dark jargons into four types:(Hada et al.,
2021)
1. Tweets that feature only known dark jargons (and
words directly related to crime).
2. Tweets containing only unknown dark jargons.
3. Tweets featuring a mixture of known dark jar-
gons (and words directly related to crime) and un-
known dark jargons.
4. Tweets that feature neither known nor unknown
dark jargons.
Moreover, we purposed to detect unknown dark
jargons based on the known dark jargons (and words
directly related to crime), assuming that the tweets in
(3) exist. Specifically, we used a corpus of tweets tar-
geting (1) and (3) above (hereinafter the “Bad Cor-
pus”) and a corpus of tweets targeting (4) above (here-
inafter the “Good Corpus”).
We then proposed a method that focuses on the
difference in similarity of the same word in two
groups of tweets by classifying them into the above
two corpora (Good Corpus, Bad Corpus).
Using our method, we succeeded in detecting un-
known dark jargons (Hada et al., 2021), (Hada et al.,
2022). However, our method has a problem in that it
cannot detect dark jargons that are compound words
combining two or more words. In this study, we call
words that are both compound words and dark jargons
“compound-type dark jargons.”
The ability to detect compound-type dark jargons
is very significant because it will expand the range of
dark jargons that can be detected using our method.
Therefore, this study proposes a method for detecting
compound-type dark jargons based on similar words
and conducts dark jargon detection experiments in
conjunction with existing dark jargon detection meth-
ods.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 de-
scribes the background of this study. Section 3 de-
scribes the methodology proposed in this study. Sec-
tion 4 describes the experimental setup and the results
of the experiments, and Section 5 describes the dark
jargon detection experiments using existing methods
based on the results of Section 4. In Section 6, we dis-
cuss the proposed method through experiments. Fi-
nally, Section 7 presents the conclusion of this study.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Increase in the Number of Crimes
Involving Drug Trafficking
In Japan, there have been many cases related to drug
trafficking using microblogs such as Twitter, which
have become a social problem. For example, Fig-
ure 3 shows the number of arrests for marijuana of-
fenses by age group. As shown in the figure, the num-
ber of arrests increases every year, particularly among
teenagers and those in their 20s.
Figure 3: Based on the number of arrests for marijuana of-
fenses by age group (data from the National Police Agency
(NPA, 2018)).
Therefore, this study focuses on Twitter because
of its large number of users, its accessibility to an un-
specified number of people, its environment in which
illegal transactions are likely to occur, and the ten-
dency to use dark jargons in such transactions.
2.2 Dark Jargon
Dark jargon is defined as a special word that is used
only within a specific society or group. The target of
this study is words used in crime, particularly those
NLPinAI 2023 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
428
related to drug trafficking, that evade the attention of
police and others.
We targeted the following dark jargon types.
1. The name of the object itself that constitutes a
criminal act.
• Words with High Recognition.
For example, “marijuana” and “LSD” fall un-
der this category. Since these words are gen-
erally recognized and do not have the effect
of making people hide their transactions, they
were classified as “related word” rather than
“dark jargon”.
• Words with Low Recognition.
Since the target word itself is not generally rec-
ognized, even if it is used as it is, only a specific
group of people will understand it.
For example, the types of cannabis “White
Kush,” “White Widow,” and “Gorilla Glue” fall
into this category.
2. Not the name of the criminal offense itself
• Diversion (camouflage).
Words used to camouflage commonly used
words by giving them a cryptic meaning fall
under this category. For example, as words re-
lated to drug trafficking, there are ”vegetable”
and ”grass” for marijuana, and ”ice” and ”crys-
tal” for methamphetamine.
• Coined words.
Words intentionally coined for illegal transac-
tions fall under this category. For example,
in Japan, words related to drug trafficking in-
clude “hashishi” and “pot” for marijuana, and
“shabu” and “gankoro” for methamphetamine.
2.3 Changes of Dark Jargon
Words gradually change in meaning over time, with
dark jargons used in crime changing as their meaning
becomes more generally recognized. Words gradually
change their meanings over time (Mihalcea and Nas-
tase, 2012), (Wijaya and Yeniterzi, 2011), and among
them, dark jargons used in crime change when their
meaning is generally recognized (Yuan et al., 2018).
Therefore, we prepared actual tweet data for the
years 2016 and 2020 to explore the situation with
respect to social media and conducted two studies
(Hada et al., 2022). The first was to investigate the oc-
currence rate of dark jargons, and we found that words
that were barely detected as dark jargons in the 2016
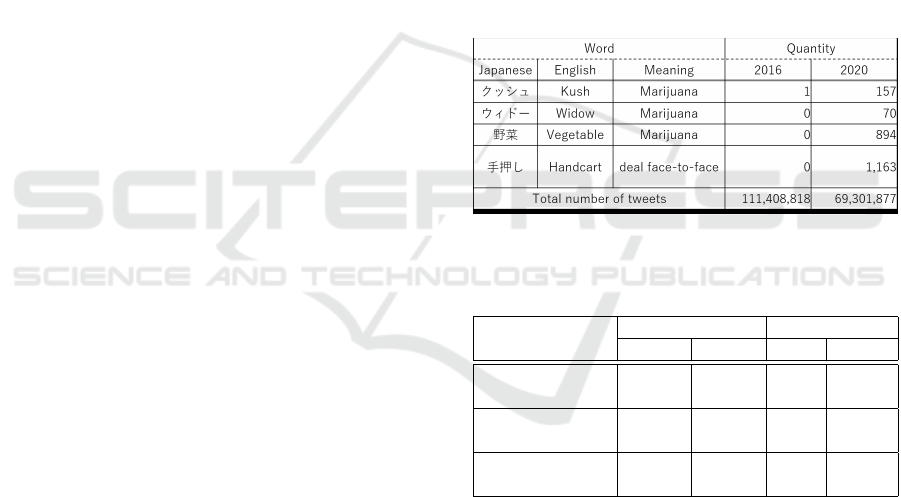
tweet data appeared in the 2020 tweet data, see Table
1. Second, we examined the extent to which com-
monly used dark jargons such as “vegetable (mean-
ing marijuana)” and “handcart (meaning direct sales)”
were used as dark jargons in 2016 and 2020, respec-
tively, and found that in the range of tweets collected,
neither “handcart” nor “vegetable”were dark jargons
in 2016 (Table 2).
In the range of tweets collected, the percentage of
tweets in which the meaning of handcart or vegetable
was defined as dark jargon was 0% in 2016, whereas,
in 2020, the percentage was 81.8% for handcart and
2.5% for vegetable, due to their several occurrences
in the general meaning; however, the percentage of
words that had never been used as dark jargons by
that time was 0.3%. In 2020, however, words that
have never been used as dark jargons will be used with
the meaning of a dark jargon. The results show that
words that were not used as dark jargons at all before
are being used as dark jargons in 2020.
Table 1: Difference in the number of tweets in which
each word appeared as dark jargons between the two
years(2016,2020).
Table 2: Difference in the percentage of tweets in which
each word was used as dark jargons between the two
years(2016,2020).
Vegetable Handcart
2016 2020 2016 2020
Number of 37,931 35,490 290 1,472
detections
Number used as 0 894 0 1,163
dark jargons
Percentage of s 0% 2.5% 0% 81.8%
dark jargon
2.4 Compound Word
The compound word is defined as two or more orig-
inally independent words combined to form a new
word with a new meaning and function. Examples
of compound words are “hon·bako (book box)” and
“yama·zakura” (mountain cherry blossom). (“·” de-
notes the concatenation of words.)
Alternatively, as examples of compound-type
dark jargons, we have identified “lemon·skunk,”
“gorilla·glue,” and “white·widow” as dark jargons for
marijuana in the tweets we have confirmed thus far.
The dark jargon detection method proposed by
Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words
429

Hada et al. (Hada et al., 2021), (Hada et al., 2022)
relied on a word segmentation unit. Thus we had the
problem that words that were originally compound
words could not be detected in their correct forms
if they were word segmented. For example, for the
words mentioned earlier, the words “lemon” “skunk,”
”gorilla” “glue,” and”white” “widow,” respectively,
were separated by single-word phrases, and although
“gorilla” could be detected, the word “gorilla·glue”
could not be detected.
One possible countermeasure to prevent
compound-type dark jargons from being sepa-
rated by phrases during segmentation is to adjust the
segmentation unit, but as segmentation is based on
an internal dictionary, words that do not exist in the
internal dictionary are not segmented into compound
units.
Because there are many coined words and words
with low recognition among those used as dark jar-
gons, they are typically not registered in segmen-
tation dictionaries and are unlikely to be automat-
ically added to the dictionary. Even if recognized
compound-type dark jargons are registered in the dic-
tionary, it is required human hand to catch up with
the latest changing dark jargons. Furthermore, when
a common word such as “lemon” is included in a
clause, for example, “lemon skunk,” the clause is con-
sidered separated from the rest of the sentence. If we
can register compound clauses in the dictionary in ad-
vance, we can expect to detect compound clauses us-
ing existing methods.
3 RELATED WORKS
Several studies have been reported on the detection of
dark jargons on Web sites such as BBS (Lee et al.,
2007) (Ohnishi and Tajima, 2013). There have also
been several reports on dark jargon detection for
platforms other than websites and BBS. For exam-
ple, Yuan et al. proposed a method for automati-
cally identifying dark jargons from the Dark Web,
as marijuana is exchanged under the names of pop-
corn and blueberries and child pornography under the
name of cheese pizza on the Dark Web(Yuan et al.,
2018). In doing so, since a single corpus by Word2vec
(Mikolov et al., 2013a) cannot detect cryptic terms,
multiple corpora are prepared and cryptic terms are
detected based on semantic discrepancies between
terms that appear in two different corpora. However,
the aforementioned study targets cryptic terms on the
Dark Web, but does not target short, context-free mi-
croblogs that are widely used by young people in gen-
eral. Regarding Chinese, Zhao et al. focus on dark
jargons used for cybercrime in the underground mar-
ket in China and implement dark jargon detection us-
ing unsupervised learning (Zhao et al., 2016). They
concluded that the combination of “CBOW + Neg-
ative Sampling” is the optimal setting for Word2vec
and is about 20% higher than the LDA approach.
However, according to the aforementioned authors,
it is still described as a first-stage study (Yuan et al.,
2018). Alternatively, A study of dark jargon detection
for Japanese has been reported for ID-Exchange BBS
as a platform (Satoshi ABIKO and SAKUTA, 2018).
Abiko et al. classified harmfulness using text classi-
fication (supervised learning) for ID-Exchange BBS
with short sentences and no context. However, they
note that it is difficult to deal with camouflaged dark
jargons such as “vegetable” and “ice”.
For Twitter, the subject of this study, research
has been conducted with the goal of reducing crime
(O’Day and Calix, 2013), (Kansara et al., 2016).
Among them, research has also been conducted on
detecting offensive or illegal words (Xiang et al.,
2012),(Wiedemann et al., 2018), (Hakimi Parizi et al.,
2019). Aoki et al.’s method detects uncommon us-
age by using the word vector of the word of interest
and its surrounding words to evaluate the degree to
which the surrounding words of the word of interest
differ from the surrounding words in the case of com-
mon usage(Aoki et al., 2017) . Aoki et al.’s method
requires prior recognition of the dark jargons and the
preparation of sentences in which the dark jargons ap-
pear. However, since dark jargons are characterized
by their ability to evade surveillance and be known
only to certain people, it is very labor intensive to
keep track of new dark jargons. In other words, the
biggest difference between our method and Aoki et
al.’s is that Aoki et al.’s research does not find new un-
known dark jargons, while our method detects words
that are used similarly from similar words of a word,
and it can discover unknown dark jargons that even
we do not recognize. As for Aoki et al.’s method, we
believe that our method can find new dark jargons and
recognize them as dark jargons and that our method is
essential for the effective use of Aoki et al.’s method.
Regarding the detection of dark jargons, it would
be difficult to apply the dark jargon detection meth-
ods used on the web and bulletin boards directly to
microblogs such as Twitter. This is because the fol-
lowing characteristics of microblogs have been de-
scribed(Dela Rosa and Ellen, 2009).
• Short character length.
Microblogs comprise as little as a single word to
less than a paragraph at most. For Twitter, there is
a limit of 140 characters per post.
• Informal and unstructured formats.
NLPinAI 2023 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
430

Microblogs contain slang, misspellings, and ab-
breviations.
An analysis of tweets related to dark jargons on
Twitter revealed that not only do many short sen-
tences appear, but tweets used for criminal transac-
tions, among others, are often even more disembod-
ied sentences because they attempt to conceal the
criminal intent. Therefore, it is considered difficult
to conduct analysis and machine learning using sen-
tence entailment. Alternatively, in order to conclude
a transaction in the shortest possible exchange, it is
necessary to include necessary information in a sin-
gle post, such as the target of the transaction, loca-
tion, amount, quality, etc. Therefore, we found a ten-
dency for crime-related words to appear around dark
jargons, which we defined as related words. There-
fore, we thought that we could effectively find dark
jargons and similar words used in criminal transac-
tions by using word-distributed expressions, taking
advantage of the tendency of crime-related words to
appear around dark jargons in tweets related to trans-
actions. Note that Word2vec was used in this study
as the word variance representation, and although
several studies using Word2vec and cosine similar-
ity have been reported recently, there are no exam-
ples of using it to detect unknown dark jargons(Yao
et al., 2021),(Huang et al., 2021). Therefore, we be-
lieve that detecting unknown dark jargons in short
sentences targeting Twitter is very significant because
it is expected to prevent crimes before they occur and
to deter crimes through early detection. Therefore,
we detect unknown dark jargons by using known dark
jargons as clues and focusing on their similar words.
4 ON THE DETECTION OF
COMPOUND-TYPE DARK
JARGONS
4.1 Approach to Detect Compound
Words
Existing methods (Hada et al., 2021), (Hada et al.,
2022) detect dark jargons based on segmented words,
and thus compound-type dark jargons consisting of
words separated by phrases are difficult to detect.
Therefore, the detection of compound words is
a challenge for us. For example, one word “green
crack,” which is used as a cloaking word for mar-
ijuana, is separated into “green” and “crack” when
Japanese segmentation processing is performed.
Because compound words, particularly
compound-type dark jargons, are assumed to
occur more frequently in the same context, i.e., such
words are considered strongly related to each other,
we hypothesized that words separated by compound
phrases would appear at the top of each other as
similar words.
Therefore, we constructed a word distribution
model for the Bad corpus with a window size of
2, which is smaller than the setting used to con-
struct word distribution models for dark jargon detec-
tion and examined the similarity between the words
“green” and “crack” for the word “green crack.” The
top similarity word for “green” was “crack,” whereas
the top similarity word for “crack” was “green,” indi-
cating that the two words are similar.
From this result, we hypothesized that it would be
possible to automatically detect compound words by
detecting words that match the top similar words in
both words.
Therefore, we propose the following method for
detecting compound words.
1. Search for the top i similar words of α. (S (α)
1st
. . . S (α)
ith
)
(“S (α)” denotes sequence of similar words of α.)
2. Next, similar words of each of S (α)
1st
. . . S (α)
ith
are searched respectively.
(S (S (α)
1st
)
1st
. . . S (S (α)
1st
)
ith
, S (S (α)
2nd
)
1st
. . .
S (S (α)
2nd
)
ith
, S (S (α)
ith
)
1st
. . . S (S (α)
ith
)
ith
)
3. And if α = S (S (α)
ith
)
ith
, then the words “α ·
S (α)
ith
” and “S (α)
ith
· α” are created as candidate
compound words.
4. We compare these words with the original bad
corpus, check the number of occurrences in the
original bad corpus, and consider the words that
exceed a certain number of occurrences to be
compound words.
In this paper, words that are close to each other in
the distributed representation model are considered as
“similar words” even if they have different meanings.
4.2 Process of Registering Compound
Words
The following process was used to detect compound
words.
1. Word search among the top 5 (i = 1. . .5) similar
words
• Word distributed expression model for com-
pound word detection was constructed using
Word2Vec (Mikolov et al., 2013a) by splitting
tweets in the Bad corpus.
Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words
431

• The words in the constructed word-distributed
representation model are extracted and listed to
create a word group A.
• For each word α
j
(j = 1. . .n) in the listed
word group A, retrieve the top 5 similar words.
(S (α
j
)
1st
. . . S (α
j
)
5th
)
• For each of the retrieved words
(S (α
j
)
1st
. . . S (α
j
)
5th
), the top 5 similar
words (S (S (α
j
)
1st
)
1st
. . . S (S (α
j
)
5th
)
5th
) are
also searched.
• Match α
j
against each of S (S (α
j
)
ith
)
ith
to de-
termine if they match.
• If α
j
= S (S (α
j
)
ith
)
ith
, swap the two words to
create two compound word candidates(“α
j
·
S (S (α
j
)
ith
)
ith
)” and “S (S (α
j
)
ith
)
ith
· α
j
”).
2. Match all created “α
j
· S (S (α
j
)
ith
)
ith
” and
“S (S (α
j
)
ith
)
ith
· α
j
” against the Bad corpus one
by one, and count the number of occurrences of
each word.
3. Only words with X or more occurrences (X is
specified separately) are added to the internal
dictionary for word segmentation as compound
words.
4.3 Considerations for Improving
Accuracy
To suppress the detection of unnecessary words and
improve the detection accuracy of dark jargons, we
verified several functions and added the following
three effective functions to the proposed method in
Section 4.2 (no functions added described as “pro-
posed method w/0 added func”).
4.3.1 Comparison with the Good Corpus
To avoid a risk of decrease rate of detecting
compound-type dark jargons by detecting general
compound words, we searched for similar words of
the same word α between the two corpora (Good and
Bad corpora) and considered that words α in which
the same word appeared did not appear in the con-
text as dark jargon. Therefore, we also searched for
similar words in the Good corpus when searching for
similar words, and if the word appeared in the top 20,
we stopped a process of registering compound words.
4.3.2 Filtering by Morphological Analysis
Because most of the compound-type dark jargons
consisted mainly of nouns, part-of-speech classifi-
cation was performed before combining compound
words, allowing only nouns to be extracted.
4.3.3 Deletion of Words in the Dictionary
Among the words detected as candidates for com-
pound words, single words were also detected. Words
that were already registered in the dictionary for word
segmentation were excluded from the candidate com-
pound words.
5 EXPERIMENT (COMPOUND
WORDS DETECTION)
5.1 Summary
Experiments were conducted to verify compound
word detection using the proposed method.
5.2 Experimental Process (Compound
Words Detection)
5.2.1 Data Collection
Using the Twitter API, we collected Twitter data
for approximately one year (from 2019/07/19 to
2020/07/27), of which only the text data were used.
Then, based on the keywords related to drug dark jar-
gons, we extracted a list of accounts tweeting about
drug trafficking using dark jargons. Then, using the
list as a key, we again collected Tweets during the
same period and created a corpus (hereinafter the
“Bad Corpus”).
5.2.2 Preprocessing
Words that were irrelevant for dark jargon detection
were removed in advance. The deleted items are as
follows.
1. URL
2. newline characters
3. Words frequently appearing on Twitter
(e.g., “RT,” “Favorite,” etc.)
5.2.3 Creating Corpora
The following two corpora were prepared.
1. Bad corpus
See section 5.2.1.
2. Good corpus
As a general corpus, we chose to use a large-
scale tweet corpus and used a large-scale Japanese
social media + Web corpus created by Hotlink
Corporation (Shogo Matsuno and Sakaki, 2019).
NLPinAI 2023 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
432

Note that the Good corpus is used in the additional
feature Section 4.3 of the proposed method.
5.2.4 Morphological Analysis
Japanese sentence structure is not separated by
spaces, etc. Therefore, morphological analysis pro-
cessing and segmentation are essential before word
distribution processing. Segmentation is the process
of dividing sentences into word units based on an
internal dictionary of words. This allows for the
word-by-word segmentation of sentences. The prob-
lem here is how to divide sentences appropriately.
Because Twitter is microblog and it is characterized
by short sentences, many new words and slang, and
many sentences that are intentionally cut off, which
may result in incorrect segmentation. In addition, be-
cause the target words of this study are dark jargon,
some of the words may be close to coined words and
thus need to be correctly segmented.
Thus, SUDACHI(Takaoka et al., 2018) was cho-
sen as the morphological analyzer for the following
two reasons.
1. The internal dictionary is updated regularly, and it
is maintained to correspond to new words as much
as possible.
2. The viewpoint of availability to select the word
segmentation unit for new words.
5.2.5 Adding Compound Words to the User
Dictionary for Word Segmentation
The following process was repeated 10 times on the
preprocessed Bad corpus.
1. Segmentation
The prepared corpus is split into separate words
using SUDACHI (Takaoka et al., 2018).
2. Building a word distribution model
Word2Vec was used to perform the modeling. The
parameters of Word2Vec for compound word de-
tection are presented in Table3.
3. Detecting compound words from the corpus
Table 3: Parameters of Word2Vec for compound word de-
tection.
Parameter Value
Size 300
Min-Count 3
Window Size 2
Negative 20
Methods Skip-Gram
(Mikolov et al., 2013b)
From the constructed distributed word representa-
tion model, a set of words registered in the model
is extracted, and the compound word detection al-
gorithm described in Section 5.2.1 is applied to
each word to create compound word candidates.
4. Checking the number of occurrences
Pick up words that appear two or more times in
the original corpus before segmentation.
5. Register words in SUDACHI’s (Takaoka et al.,
2018) user dictionary
Registering a word in the user dictionary allows
the compound word to be segmented as a single
phrase.
5.3 Experimental Conditions
In addition to the proposed method, comparative
evaluations were performed using the following two
methods.
For the experiment, a baseline method was devel-
oped for comparative evaluation.
5.3.1 Baseline Condition
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method,
we used the baseline condition in which all bi-grams
were obtained for sentences after segmentation (here-
inafter the “baseline method”). Because the proposed
method also prepares candidate compound words
with their front and rear parts swapped, we also pre-
pared candidate compound words with their front
and rear parts swapped for the above words. When
the proposed method was used to create compound
word candidates from the Bad corpus, 686,561 words
were created, and when the threshold for the num-
ber of occurrences was set to twice when referring to
the Bad corpus before preprocessing, 105,266 words
were created, which is a huge number compared with
other conditions. Therefore, we relaxed the thresh-
old for the frequency of occurrence from twice to 14
times or more and selected 14,218 words as the num-
ber of target words.
5.3.2 Detection of Related Words
Generally, transactions require information such as
“the object of the transaction,” “something descriptive
of the object of the transaction (e.g., high quality),”
“time,” “place,” “transaction method,” “transaction
amount,” “amount of money,” and so on. As words to
express these information, dark jargons can occur if a
common understanding arises among those who con-
duct transactions. However, in situations where there
are no words established as dark jargons yet, common
Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words
433
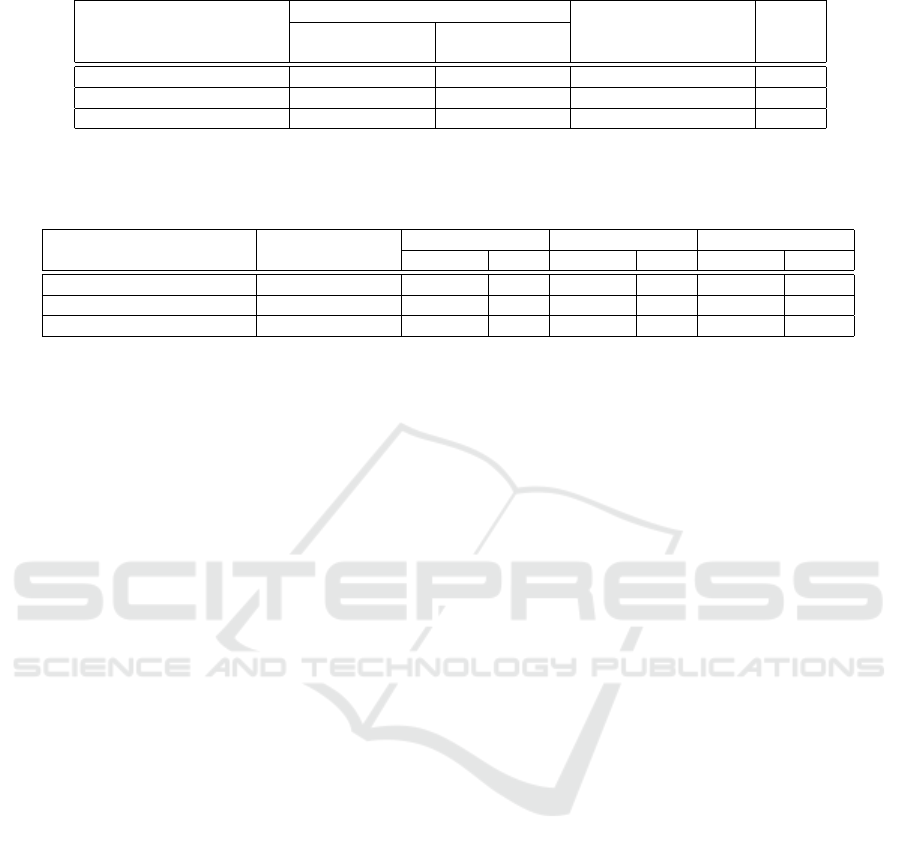
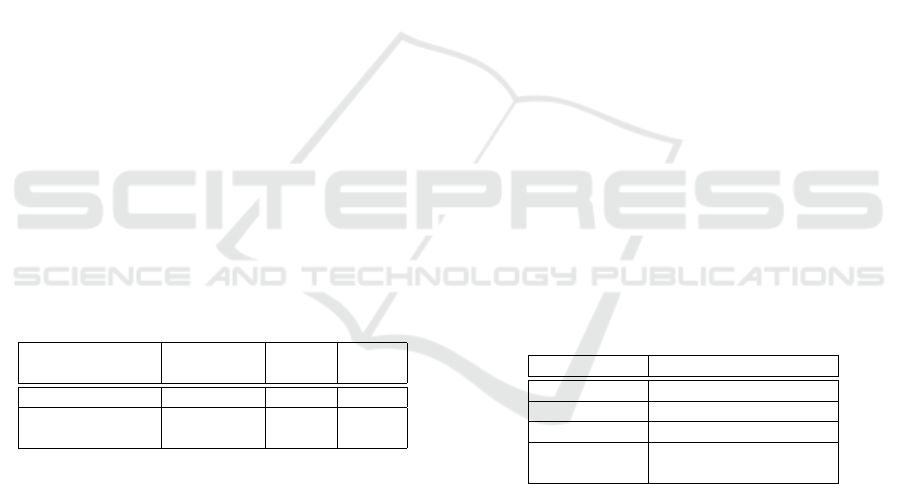
Table 4: Classification of compound word candidates.
Compound word candidates True compound words Rate
b
Method (Before applying (After applying
threshold filter) threshold filter)
Proposed 61,731
a
295
a
264
a
89.5%
Proposed w/o Added Func 101,573
a
521
a
308
a
59.1%
Baseline 686,561 14,218 388 2.73%
a
Total of 10 trials of the process in section 5.2
b
Number of True compound words/Number of candidate compound words
Table 5: Percentage of compound-type dark jargons under each condition.
Method Quantity of Dark Jargons Related Words SUM
Compound word Quantity Rate Quantity Rate Quantity Rate
Proposed 264 19 6.4% 23 7.8% 42 14.2%
Proposed w/o Added Func 308 25 4.8% 24 4.6% 49 9.4%
Baseline 388 30 0.2% 102 0.7% 132 0.9%
words are used to avoid misunderstandings among
each other. As words to express this information,
dark jargons can occur if a common understanding
arises among those who conduct transactions. How-
ever, in situations where there are no words estab-
lished as dark jargons yet, common words are used
to avoid misunderstandings among each other. There-
fore, even if one tries to conduct a transaction cleverly
using a dark jargons without being aware of the inten-
tion, it is considered necessary to include at least three
pieces of information: “object of the transaction,” “lo-
cation (e.g., in Tokyo),” and “amount of money. Fur-
thermore, in order to realize a speedy exchange while
evading surveillance,
it is necessary to include “transaction method
(hand delivery, mail, etc.)” and “something descrip-
tive of the transaction object (high quality, etc.)” in
the text.
We defined these words as related words, which
do not constitute dark jargons by themselves, but tend
to appear together with the dark jargons.
The words were classified into the following cate-
gories.
1. “Dark Jargon”
Words defined in Section2.2.Words judged to
have a meaning different from their original
meaning.
2. “Related word”
Although these words could not be categorized as
codewords, they tended to appear alongside code-
words and were judged as rarely appearing in gen-
eral tweets (e.g., “stock” and “price”).
3. “Unrelated word”
Words that do not meet the criteria of the previous
two categories.
5.4 Results
The three methods detected candidate compound
words and classified them into two categories: com-
pound or not. Words identified as compound words
were further classified as either dark jargons or re-
lated words. The results of the compound word de-
tection are presented in Table 4. The number of oc-
currences of compound word candidates (Section 4.2
3) was set to X =2 for the proposed method and the
proposed method (w/o added func) and X =14 for the
baseline.
Table 4 shows that the proposed method signif-
icantly outperforms the baseline in terms of com-
pound word detection accuracy. Furthermore, when
comparing the proposed method with the proposed
method without func, the proposed method outper-
forms the”proposed method without added function-
ality” by 30.1%.
The results for the compound-type dark jargons
that appeared in the compound words are presented
in Table 5.
The experimental results show that there is a sig-
nificant difference between the proposed method and
the baseline method in terms of the detection rate
of compound-type dark jargons, with the proposed
method without added func, the proposed method,
and the baseline method detecting 9.4%, 14.2%, and
0.9% of the compound words that contain dark jar-
gons and related words, respectively.
5.5 Consideration (Compound Words
Detection Experiment)
Tables 4 and 5 show that the proposed method signif-
icantly outperformed the baseline in detecting com-
NLPinAI 2023 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
434
pound words, indicating that the proposed method is
an effective method for compound word detection.
Furthermore, the proposed filter function was
30.1% more effective than the”proposed method
without added func,” demonstrating that the filter
function was effective in detecting compound words.
We also analyzed whether our method, which fo-
cuses on similar words, is an effective method for de-
tecting compound words from the perspective of de-
tecting proper nouns. This is because we thought that
the proper nouns of compound words are more likely
to be detected by the proposed method as they ap-
pear more frequently in the same word and thus are
more related to each other than to other words. Ta-
ble 6 shows that proper nouns accounted for approx-
imately half of the compound words detected by the
proposed method, at 48.5%. This indicates that the
proposed method is effective in detecting compound
words based on similar words, focusing on the degree
of word relatedness because proper nouns appeared
at a high frequency among the detected compound
words. Additionally, the proposed method with the
added functionality was the most accurate, so it can be
said that the added functionality worked effectively.
Among the parameters of Word2Vec, four types
of parameter values (1, 2, 3, and 4) are prepared
for“Window Size,” which sets the maximum distance
between the current and predicted words within a sen-
tence. Because of the experiments, the best result was
obtained with Window Size = 2; thus, we adopted
Window Size = 2 as the parameter this time.
Table 6: Number and percentage of proper nouns.
Method Compound Proper Rate
Word Noun
Proposed 264 128 48.5%
Proposed 308 112 36.4%
w/o Added Func
6 EXPERIMENT (DARK
JARGONS DETECTION)
6.1 Outline of Experiment
Using a set of words in a corpus, we experimented
to detect dark jargons and compound-type dark jar-
gons, which have not been detected by existing meth-
ods. We expected that compound-type dark jargons
would be detected by registering them in the dictio-
nary and then executing the program of the existing
method (Hada et al., 2021). Specifically, we prepared
18 of 21,210 words as a word list for collation and
aimed at detecting dark jargons.
6.2 Experimental Environment
Because the proposed method with added functions
was the most accurate in the compound word detec-
tion experiment, a compound word dictionary was
created using the proposed method.
6.3 Experimental Process (Dark Jargon
Detection)
6.3.1 Creation of the User Dictionary for Word
Segmentation
Compound words were added to the dictionary for
word segmentation, and the process described in sec-
tion 4.2 was repeated 10 times to create a compound
word dictionary to enable word segmentation in units
of compound words.
6.3.2 Creating Corpora
The process described in Section 5.2.1, Section 5.2.2,
Section 5.2.3, and Section 5.2.4 was followed until
the corpus was created.
6.3.3 Word Distributed Expression Processing
After the morphological analysis process, Word2Vec
was used to process the word distribution. The pa-
rameters were set as follows (Table 7).
Table 7: Parameter of Word2Vec.
Parameter Value
Size 300
Min-Count 3
Window Size 4
Methods Skip-Gram
(Mikolov et al., 2013b)
6.3.4 Execution of the Proposed System
As input to the system, a word list was created by ex-
tracting words that commonly occur in both corpora
and words that only occur in the Bad corpus from the
word distribution model. The number of words that
commonly occur in both corpora was 19,068, and the
number of words that only occur in the bad corpus
was 2,152.
6.4 Results
Because of the experiment, 115 words were detected
as candidates for dark jargons, and the classification
Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words
435
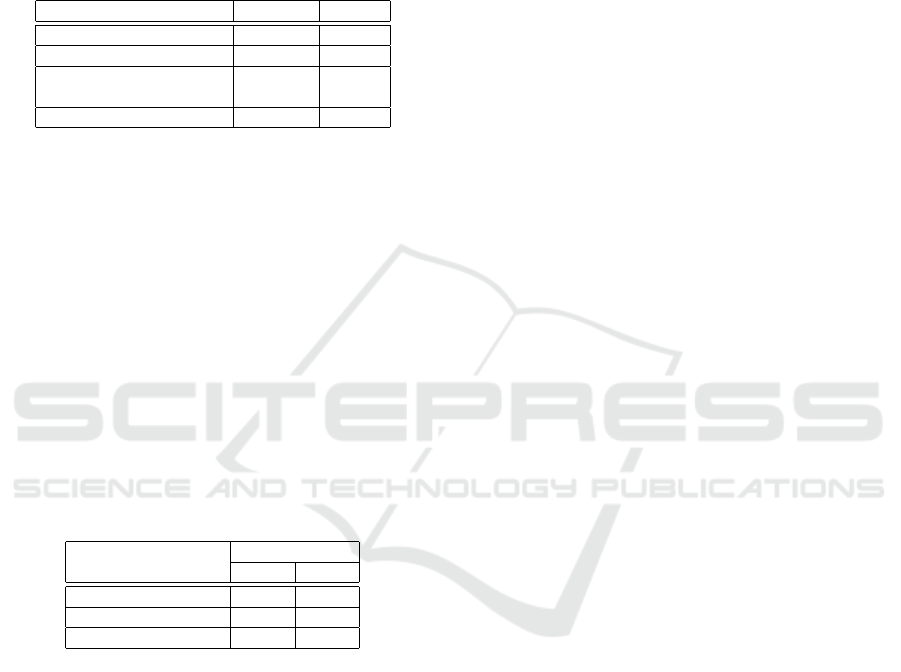
results are presented in Table 8. We could also iden-
tify compound-type dark jargons detected by the pro-
posed method, which could not be detected by ex-
isting methods. For example, 10 compound words
such as “pineapple chunk,” “jack-heller,” and “blue
dream,” which refer to marijuana, were included in
the classified words.
Table 8: Classification results.
Classification Quantity Rate
Dark jargons 74 64.3%
Related Words 20 17.4%
Part of Compound-Type 14 12.2%
dark jargons
Unrelated 7 6.1%
In terms of precision, we compared our method,
the baseline, and the existing method(Hada et al.,
2022) by separating the case for including a part of
the compound-type dark jargons in true and the case
for not including it, see Table 9. The results showed
that the proposed method performed better than both
of the baseline and existing methods.
Furthermore, regarding the difference in accuracy
between our method and the existing method, our
method was 0.095 points more accurate when a part of
the compound-type dark jargons was not included in
true. When a part of the compound-type dark jargons
were included in true, the difference between the two
methods widened further, with the proposed method
being 0.152 points more accurate.
Table 9: Comparison of precision.
Evaluation Method Precision
a b
Proposal method 0.765 0.643
the existing method 0.613 0.548
Baseline method 0.057 0.052
a) Include “Part of Compound-Type dark jargons” in true
b) Do not include “Part of Compound-Type dark jargons” in true
7 CONSIDERATION
In this experiment, those classified as ”a part of com-
pound word-type secret words” in Table 8 were clas-
sified as false positives. These were words that were
used for malicious purposes, but when the original
sentence was divided into spaces, a segment was cut
off, and part of it was detected. Therefore, the part
of the word alone did not have any meaning as a dark
jargon. For example, “big” (“big · bats,” “big · bat,”
etc. were identified) and “super” (“super · lemon ·
haze,” “super · lemon · skunk,” etc. were identified).
These words were not detected as compound words
by the proposed method based on similar words, be-
cause they appeared more frequently with other com-
mon words. For example, “super” and the top sim-
ilar words were unrelated to dark jargons. There-
fore, a method for detecting compound words that
include words with a high frequency of occurrence
with common words is a challenge for future study.
Additionally, we will continue to study other words
such as “doctor” (“Dr. · Greenspoon” and “Dr. · Ja-
maica” were identified), which could not be detected
as compound-type dark jargons because a clause of
compound-type dark jargon appeared as dark jargon.
8 CONCLUSIONS
To support cyber patrol, we proposed a method for
detecting detect compound-type dark jargons, which
has been a limitation of existing methods, and con-
ducted dark jargon detection experiments after cre-
ating a compound word dictionary, aiming to detect
dark jargons and compound-type dark jargons. The
experimental results showed that the precision and ac-
curacy of the proposed method were improved com-
pared with existing methods and that the proposed
method could detect 10 compound-type dark jargons
that had not been detected by existing methods. These
findings indicate that the combination of the proposed
method and existing methods for compound word de-
tection can be expected to provide efficient automatic
detection of dark jargons.
REFERENCES
Aoki, T., Sasano, R., Takamura, H., and Okumura, M.
(2017). Distinguishing Japanese non-standard us-
ages from standard ones. In Proceedings of the 2017
Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Lan-
guage Processing, pages 2323–2328, Copenhagen,
Denmark. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Dela Rosa, K. and Ellen, J. (2009). Text classification
methodologies applied to micro-text in military chat.
pages 710–714.
Hada, T., Sei, Y., Tahara, Y., and Ohsuga, A. (2021). Code-
word detection, focusing on differences in similar
words between two corpora of microblogs. Annals of
Emerging Technologies in Computing (AETiC), Print
ISSN: 2516-0281, Online ISSN: 2516-029X,, Vol. 5,
No. 2:1–7.
Hada, T., Sei, Y., Tahara, Y., and Ohsuga, A. (2022). Code-
words detection in microblogs focusing on differences
in word use between two corpora. The transactions
of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan. C, A
publication of Electronics, Information and Systems
Society, 142(2):177–189.
NLPinAI 2023 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
436

Hakimi Parizi, A., King, M., and Cook, P. (2019). UNBNLP
at SemEval-2019 task 5 and 6: Using language mod-
els to detect hate speech and offensive language. In
Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on
Semantic Evaluation, pages 514–518, Minneapolis,
Minnesota, USA. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Huang, L., Liu, F., and Zhang, Y. (2021). Overlapping
community discovery for identifying key research
themes. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Manage-
ment, 68(5):1321–1333.
Kansara, C., Gupta, R., Joshi, S. D., and Patil, S. (2016).
Crime mitigation at twitter using big data analytics
and risk modelling. In 2016 International Conference
on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering
(ICRAIE), pages 1–5.
Lee, W., Lee, S. S., Chung, S., and An, D. (2007). Harmful
contents classification using the harmful word filtering
and svm. In Shi, Y., van Albada, G. D., Dongarra, J.,
and Sloot, P. M. A., editors, Computational Science –
ICCS 2007, pages 18–25, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Mihalcea, R. and Nastase, V. (2012). Word epoch disam-
biguation: Finding how words change over time. In
Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short
Papers), pages 259–263, Jeju Island, Korea. Associa-
tion for Computational Linguistics.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and Dean, J. (2013a).
Efficient estimation of word representations in vector
space. In Bengio, Y. and LeCun, Y., editors, 1st In-
ternational Conference on Learning Representations,
ICLR 2013, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA, May 2-4, 2013,
Workshop Track Proceedings.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and
Dean, J. (2013b). Distributed representations of
words and phrases and their compositionality. CoRR,
abs/1310.4546.
MOJ, M. o. J. (2021). White paper on crime
2021. https://hakusyo1.moj.go.jp/jp/68/nfm/n68
2 4
2 2 3.html#h4-2-2-3.
NPA, N. P. A. (2018). Organized crime situation in 2018.
https://www.npa.go.jp/sosikihanzai/kikakubunseki/
sotaikikaku04/h30.sotaijousei.pdf(2020/11/25).
O’Day, D. and Calix, R. (2013). Text message corpus: Ap-
plying natural language processing to mobile device
forensics. pages 1–6.
Ohnishi, H. and Tajima, K. (2013). Discovering new jar-
gons based on skew of word appearance distribution.
DBSJ Journal, 12(1):49–54.
Satoshi ABIKO, Dai HASEGAWA, M. P. K. N. and
SAKUTA, H. (2018). Method for estimation of harm-
fulness of id-exchange bbs based on lexical jargoniza-
tions. Journal of Information Systems Society of
Japan, 13(2):41–58.
Shogo Matsuno, S. M. and Sakaki, T. (2019). Constructing
of the word embedding model by japanese large scale
sns + web corpus. The 33rd Annual Conference of
the Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence, 2019,
JSAI2019:4Rin113–4Rin113.
Takaoka, K., Hisamoto, S., Kawahara, N., Sakamoto, M.,
Uchida, Y., and Matsumoto, Y. (2018). Sudachi: a
Japanese tokenizer for business. In Proceedings of
the Eleventh International Conference on Language
Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki,
Japan. European Language Resources Association
(ELRA).
Wiedemann, G., Ruppert, E., Jindal, R., and Biemann, C.
(2018). Transfer learning from LDA to bilstm-cnn
for offensive language detection in twitter. CoRR,
abs/1811.02906.
Wijaya, D. and Yeniterzi, R. (2011). Understanding seman-
tic change of words over centuries.
Wongcha-um, P. and Allard, T. (2020). Asia-Pacific
drug trade thrives amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-asia-crime-
drugs/asia-pacific-drug-trade-thrives-amid-the-
covid-19-pandemic-idUSKBN22R0E0.
Xiang, G., Fan, B., Wang, L., Hong, J., and Rose, C. (2012).
Detecting offensive tweets via topical feature discov-
ery over a large scale twitter corpus. pages 1980–
1984.
Yao, K., Wang, H., Li, Y., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., and
de Albuquerque, V. H. C. (2021). A group discov-
ery method based on collaborative filtering and knowl-
edge graph for iot scenarios. IEEE Transactions on
Computational Social Systems, pages 1–12.
Yuan, K., Lu, H., Liao, X., and Wang, X. (2018). Reading
thieves’ cant: Automatically identifying and under-
standing dark jargons from cybercrime marketplaces.
In 27th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Secu-
rity 18). USENIX Association.
Zhao, K., Zhang, Y., Xing, C., Li, W., and Chen, H. (2016).
Chinese underground market jargon analysis based on
unsupervised learning. In 2016 IEEE Conference on
Intelligence and Security Informatics (ISI), pages 97–
102.
Detection of Compound-Type Dark Jargons Using Similar Words
437
