
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training
Games Using Roguelite Genre
B
´
er
´
enice Lemoine
a
, Pierre Laforcade
b
and S
´
ebastien George
c
LIUM Computer Science Laboratory, Le Mans Universit
´
e, Laval, France
Keywords:
Analysis, Serious Game, Declarative Knowledge, Training, Roguelite, Gameplay.
Abstract:
The training of declarative knowledge requires repetition and adaptation to learners’ needs. Learning games
for training purposes should then offer a wide range of adapted and varied game situations where facts are
questioned. Furthermore, answering these questions may involve many gameplays that keep the learner-
players engaged and motivated to practice again and again. This article presents and justifies how the Roguelite
game genre is well-adapted to tackle these challenges. It also proposes an analysis framework to support
pluridisciplinary teams of teachers and game developers in identifying the key orientations for designing such
training games. This framework is composed of questions to consider during the preliminary design of the
training game. We have identified and used this proposition in a specific research context about multiplication
tables training. The article illustrates the first results obtained which led to our first playable prototype. Finally,
we outlined the major drawbacks of our first game design (i.e., first analysis), which brought us to carry out a
second analysis through our proposed framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Explicit knowledge of facts, such as multiplication ta-
bles, historical dates or geographical information, are
known as declarative knowledge. Repetition is a nec-
essary task to encourage the memorization, general-
ization, and retention of declarative knowledge (Kim
et al., 2013; Roediger and Pyc, 2012). However,
repetitive or redundant serious games as well as the
ones presenting an imbalanced challenge relative to
the skills of the players can be boring for the play-
ers (Streicher and Smeddinck, 2016). Therefore, to
reduce the feeling of repetition, serious games target-
ing declarative knowledge should offer a wide variety
of adapted learning game activities.
Most of existing serious games for the training
of multiplication tables only present questions to an-
swer, surrounded by game elements that do not im-
pact the gameplay. Such training games do not pro-
pose long-term engaging activities. Poor gameplay
could quickly bore students and reduce their engage-
ment to practice (i.e., motivation, frequency, and du-
ration of sessions, etc.). It therefore seems important
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7608-3223
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8498-2731
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0812-0712
to allocate as much importance to gameplay as to ed-
ucational content when designing learning game ac-
tivities (Marty and Carron, 2011).
This article proposes to highlight a specific game
genre, Roguelites. Indeed, this genre is based on sev-
eral design principles, of which we propose to dis-
cuss their compliance with the requirements for effi-
cient and adapted training of declarative knowledge.
Our proposal is presented in the form of an analysis
framework in order to help the design of Roguelite-
oriented training games. This framework involves a
set of practical steps to be followed in each iteration
of a prototyping-based design approach. The aim is
to focus on design needs, from two dimensions (i.e.,
training and game), such as: technology (i.e., some
information needed for the game engine/generation
algorithm), game-gameplay (i.e., how the main game
mechanics of the Roguelite genre work), and game
structure (i.e., the game rules). To illustrate our pro-
posal, we present and discuss the application of this
analysis framework during two design iterations of
the same research context: the AdapTABLES project.
Test-based learning represents, in cognitive psy-
chology, the idea that the process of retrieving (i.e.,
remembering) concepts or facts increases their long-
term retention. Whilst tests are mainly used as sum-
mative assessment tools, they can also be formative.
276
Lemoine, B., Laforcade, P. and George, S.
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre.
DOI: 10.5220/0011840200003470
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2023) - Volume 2, pages 276-287
ISBN: 978-989-758-641-5; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
One way to implement test-based learning is through
repeated retrieval (i.e., retrieval practice). Research
has shown that this method can improve long-term
retention (Brame and Biel, 2015; Roediger and Pyc,
2012). Moreover, research also suggests that the ben-
efits of test-based learning are not linked to a specific
type of retrieval practice (i.e., various test formats en-
hance learning) (Brame and Biel, 2015). In this paper,
training involves providing the learner with various
forms of questions repeatedly, which is a form of re-
trieval practice.
The structure of this paper is as follows. Section 2
introduces our research context, including our AdapT-
ABLES project and its specific declarative knowledge
about multiplication tables. In addition, it presents the
video game Roguelite genre and discusses consider-
ing Roguelites as a suitable genre for designing train-
ing games. Section 3 is dedicated to the proposition of
a two-dimensional analysis framework (gaming and
training dimensions). This proposal has been applied
twice in the context of our project. Section 4 is then
devoted to the presentation of these two applications,
as well as the feedback gathered from the evaluation
of a prototype in line with the first analysis.
2 RESEARCH CONTEXT
The AdapTABLES project aims to design and de-
velop a serious game dedicated to the individual train-
ing of multiplication tables.
From a teacher perspective, the training game to
design will be adapted, prior to its use, to reflect how
teachers consider the training: source facts, difficulty,
progress... This training structure can be set up for
the entire classroom’s students, for a group, or for in-
dividuals having specific needs. From a student per-
spective, the training game will follow the learners’
progress, proposing facts according to their previous
training sessions and results. From a player perspec-
tive, the training game will offer game levels that take
into account their preferences. From a game perspec-
tive, a same training task should be tackled through
different gameplays with different game elements. Fi-
nally, at runtime, the training game will have to gen-
erate varied training game activities, adapted, both
in terms of gameplay and educational content, to the
teachers and learners-players perspectives.
We followed an iterative co-design and prototyp-
ing approach, involving teachers and didacticians of
mathematics, and game experts during the design and
evaluation phases. At first, two initial steps were nec-
essary: 1) specifying the knowledge to be trained, and
2) choosing a type of game that suits the training of
declarative knowledge. These contextual elements are
necessary to start designing at a high level the main
key concepts and rules of the training game.
2.1 Declarative Knowledge Training
We started an exploratory research (Laforcade et al.,
2022) with the help of a user group composed of
teachers and mathematics experts. The objective was
to specify the adaptations to take into account when
considering the training of multiplication tables from
a teacher perspective: what to consider (source and
targets of the adaptations) and how to realize these
adaptations. The main two results are: a model of
the training organization into training paths, and the
specification of 5 detailed training tasks.
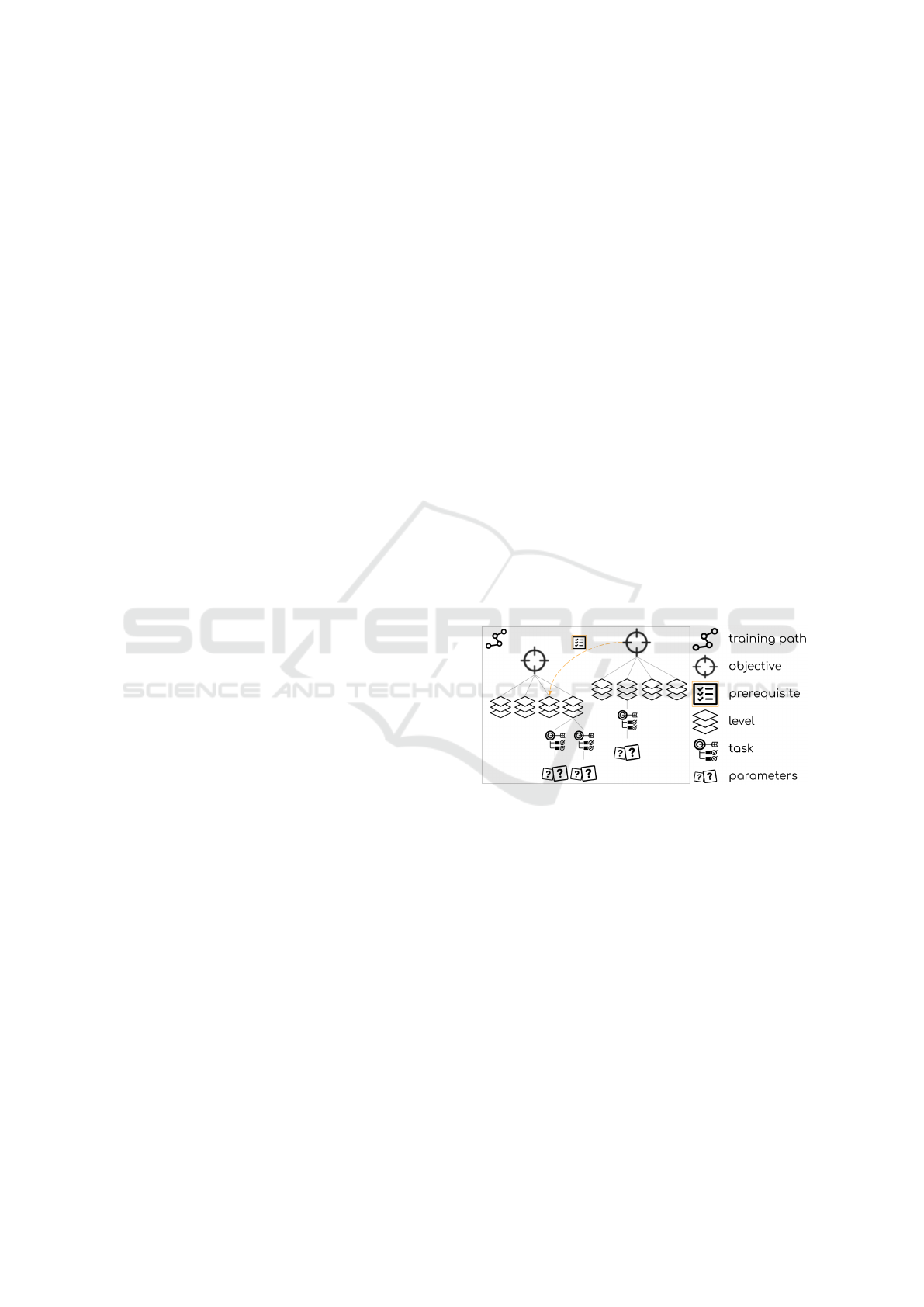
A training path, see Figure 1, is represented by a
set of objectives ordered by prerequisite relationships.
An objective (e.g., “Work on the table 2”) is broken
down into progressive levels of difficulty. Each level
is itself broken down into training tasks (e.g., “Level
1: Completion 1 with search for the result, Identifi-
cation by choice of the correct facts”). A task is de-
fined by its type and parameters. The levels’ achieve-
ments are considered from both a percent of encoun-
tered facts and a percent of achievement to reach.
Figure 1: Knowledge Structure.
Five types of tasks have been identified with the
teachers: Completion 1, i.e., complete an incomplete
fact that has one missing element (e.g., 3×? = 15,
15 =? × 5, 3 × 5 = ?); Completion 2, i.e., com-
plete an incomplete fact that has two missing ele-
ments (e.g., ?×? = 15 with a set of given choices
[3, 6, 5, 10], ? × 5 = ? or 3×? = ? also with sets of
given choices); Reconstruction, i.e., replace, in the
correct order, all important elements of a fact (e.g.,
?×? = ? with a set of given choices [3, 6, 5, 10, 15]);
Identification, i.e., identify the correctness or incor-
rectness of one or several facts (e.g., 3 × 5 = 15, true
or false?); Membership Identification, i.e., identify
the elements that share or do not share a given prop-
erty (e.g., [3, 5, 9, 14, 21] which are results of table 3?).
Considering the training tasks, their specification
led us to define several parameters whose values de-
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre
277

pend on teachers’ opinion and preferences to choose
and set-up these tasks for each {objective, level} pair.
For example, the parameters for the Completion 1 task
are presented in Table 1: the targeted tables, the mul-
tiplicand position, the result position, the interval (i.e.,
min/max) of the multiplier, the elements to search, the
order of the questions, the modality of response, and
the maximum response time.
As we are following a prototyping design ap-
proach, the design is carried out step by step. There-
fore, each new iteration takes into account a little
more information than the previous one. This article
presents the first two iterations of our design, which
does not yet include the full knowledge structuring
presented. The first prototypes aim at a parameteriza-
tion approach, i.e., teachers have to give the parameter
values (cf. Table 1) for each learner inside the game.
2.2 RogueLite Genre
Roguelike and Roguelite are video games genres
growing in popularity this last decade. They stem
from the game that pioneered this type of gameplay:
Rogue (Toy et al., 1980). Rogue was a turn-based
dungeon crawler game where you have to fight your
way through levels of a dungeon, picking up items
and defeating enemies along the way. The Berlin In-
terpretation (Harris, 2020) defined 8 high-value fac-
tors for Roguelikes, which includes:
• Random environment generation: different room
layouts with randomized locations for enemies
and items each time you play. This is usually re-
alized with procedural generations, not total ran-
domness, to avoid unwinnable situations.
• Permanent death: when the avatar die, all progress
is lost and the player must start over from the be-
ginning. No progress is carried over across runs.
Most of Roguelikes games fall to respect all 8 key
aspects, like the turn-based gameplay with movement
on a grid. As a result, people started considering
these games as “roguelike-like” or “roguelite”. For
now, Roguelite genre is used in relation to Roguelike
games, proposing a macro-level objective by carry-
ing over some items and progression after each
attempt. Some well-known commercial Roguelites
games are: Hades, Enter the Gungeon, The bind-
ing of Isaac, Rogue Legacy and Deadcells. They
propose different kind of gameplay, game styles and
lore as well as different features and permanent el-
ements to reach the game cross-run objective (e.g.,
weapons, currencies, upgrades, etc.). For example,
some collectible resources can persist between deaths
and players can use them to unlock permanent up-
grades and increase their chance of success.
Failure is a key-part of Roguelites. When players
start, the new mechanics, traps, difficult enemies and
bosses, or the various features that they need to learn,
will lead them to fail and/or die many times before
they win their first complete run. While losing over
and over again may not sound fun, Roguelikes typi-
cally have fast restart times and will quickly get play-
ers back into the action. Through playing more runs,
players begin to understand the underlying mechanics
and get further.
Figure 2: Roguelite Training Game Flow.
The game flow (i.e., temporal representation of
game sessions) of Roguelite oriented games can be
different from one game to another. This article con-
siders the game flow presented in Figure 2 where a
play session is a temporal session that begin when the
player starts the game and that ends when he/she stops
it. It is composed of complete or incomplete runs.
A run is a succession of game levels, played without
dying, with increasing difficulty. There are two con-
ditions for stopping the run: the end of the game is
reached or the avatar died. A game level is gener-
ally a level of a dungeon (or something similar) that
is composed of interconnected rooms or areas.
2.3 Adequacy of Declarative Knowledge
Training with RogueLite Genre
Replayability is at the heart of the Roguelite genre,
which is designed to keep players interested while re-
lying on a repetitive mechanic (i.e., permanent death).
In addition, the random environment generation fea-
ture offers a wide variety of dungeons (i.e., each gen-
erated dungeon level is different in terms of rooms,
room succession and elements). The procedurally
generated maps will always provide a different expe-
rience with each play through. Finally, the progress
feature allows for the storage of player data. All these
features are necessary elements in our research con-
text. Repetition to retain declarative knowledge, gen-
eration of varied activities to limit the impact of rep-
etition, and progression to keep track of the learner’s
progress and preferences in order to adapt the activi-
ties. Therefore, Roguelite seems to be a suitable genre
for declarative knowledge training, where the training
game activities generated are dungeon levels.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
278
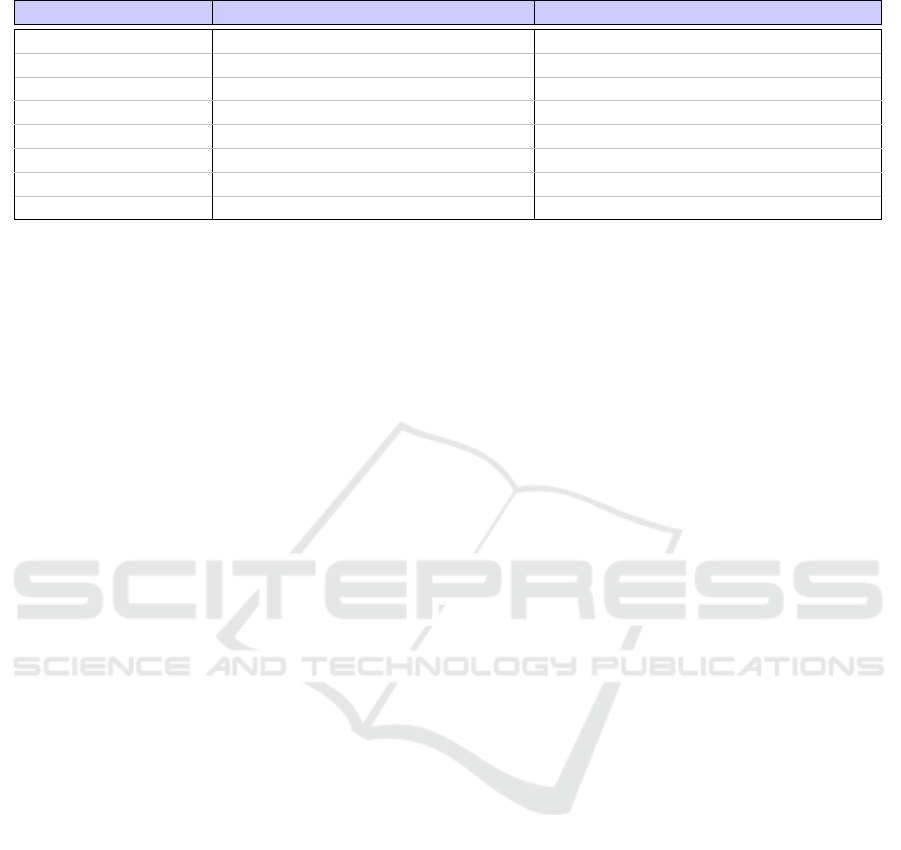
Table 1: Examples of parameters for the ”Completion 1” training task.
Adaptable element Possible Values Some Examples
Targeted Table(s) From 1 to 12
Multiplicand Position Left ∨ Right
1 × 2, 1 × 3, 1 × 4.. ∨ 2 × 1, 3 × 1, 4 × 1..
Result Position Left ∨ Right 1 × 2 = 2 ∨ 2 = 1 × 2
Multiplier Interval Integer Min/Max in [1, 12] [1, 5] ∨ [5, 10] ∨ [1, 12]
Element to search Result ∨ Multiplicand ∨ Operand
1 × ? = 2 ∨ ? × 2 = 2 ∨ 1 × 2 = ?
Questions Order Ascending ⊕ Descending ⊕ Random
Response Modality Choice between propositions ∨ Input
Max Response Time Time in seconds
2.4 Targeted Adaptations
Our general context is about the adaptation of the gen-
erated game and learning activities. This adaptation
needs then to be characterized from both game and
learning perspective. Adaptation is often character-
ized by three concepts: the source (i.e., to what do
we adapt?), the target (i.e., what is adapted?) and the
pathways (i.e., what methods are used to adapt the tar-
get to the source?) (Vandewaetere et al., 2011).
Foremost, in our context, the adaptation targets
generated dungeon and their elements (i.e., what is
adapted). Therefore, it takes place during the gen-
eration of an activity (i.e., when it is adapted). In
the spectrum of adaptation defined by (Oppermann
and Rashev, 1997), our targeted adaptation can be po-
sitioned in-between adaptivity and adaptability, as it
uses user’s data previously collected to automatically
generate an activity that is adapted to her/him.
In the literature, the gaming adaptations are
mostly based on players/personalities profiles (Ton-
dello et al., 2016; Nacke et al., 2014; Goldberg, 1990)
or players characteristics, such as age and genre. In
our context, adaptation from a game perspective seeks
to take into account player preferences to choose the
game elements (i.e., source). The main idea is to
represent preferences as game elements that can be
activated/deactivated by the player. From the learn-
ing perspective, our intention is to use knowledge of
the learner (e.g., actual level, previous mistakes) from
his/her learning path (source) to adapt the dungeons’
difficulty in terms of educational content.
Since the adaptation is an integral part of the gen-
eration, in our context, this article does not dissociate
them (i.e., the generation criterion includes adapta-
tion, see Section 3).
2.5 Research Question
Many questions need to be answered when design-
ing a Roguelite oriented game for training declara-
tive knowledge. What is generated? How and when
does the avatar die? What are the consequences?
What varies? What indicates a progression? And
so on. Furthermore, these questions need to be an-
swered from both an educational and a game perspec-
tive. Moreover, in a prototyping design approach, the
answers may change from one prototype to another.
Therefore, our research question is: How can the de-
sign of Roguelite-oriented learning be facilitated in
a prototyping design approach? Our proposal is an
analysis framework that helps designers ask the right
questions and make their choices explicit during each
design iteration.
3 ANALYSIS FRAMEWORK FOR
A ROGUELITE LEARNING
GAME
Firstly, it is important to keep in mind that we are de-
signing a game. Therefore, although the design tends
to focus on learning, the game aspect must not be ne-
glected. To this extent, the proposed framework aims
to provide a means of analyzing the design needs of
Roguelite-oriented learning games by specifying both
dimensions through specific criteria.
The first step in designing a Roguelite is the spec-
ification of game mechanisms, such as generation
(e.g., what is generated? How?), permanent death
(e.g., when does one die?), as well as progression
(e.g., what elements are kept?). Hence, the genera-
tion mechanism involves the specification of the vari-
ety mechanism, e.g., which elements should the gen-
eration vary? In a game, as in learning, an essential
notion is that of difficulty progression, e.g., how does
one increase difficulty? When? In our context, the
5 mechanisms (Generation, Death/Hurt, Variety,
Progress, and Difficulty) are criteria for analyzing
needs that must be specified from both points of view.
Each criterion consists of a series of questions that re-
late to the same mechanism. Each question should be
answered in order to clarify the design needs of the
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre
279
learning game. The questions per criterion are:
1) Generation
Q1. Which elements are generated?
Q2. When are they generated?
Q3. On what basis are they generated? (i.e., sources
of generation)
2) Death/Hurt
Q4. When can the avatar get injured or die?
Q5. What are the consequences of being injured?
Being killed?
Q6. Where can the avatar be injured or killed?
3) Variety
Q7. Which elements vary?
Q8. How do the elements vary? (i.e., are the varia-
tions initiated by player action? Are they ran-
dom? Is it a mixture of both? Are they based
on heuristics?)
4) Progress
Q9. What is retained/preserved in-between each
death? (i.e., what elements?)
5) Difficulty
Q10. What are the elements that increase or decrease
the difficulty?
Q11. How is the difficulty progression designed?
(i.e., if several elements have an impact on the
difficulty, in what order do they occur?)
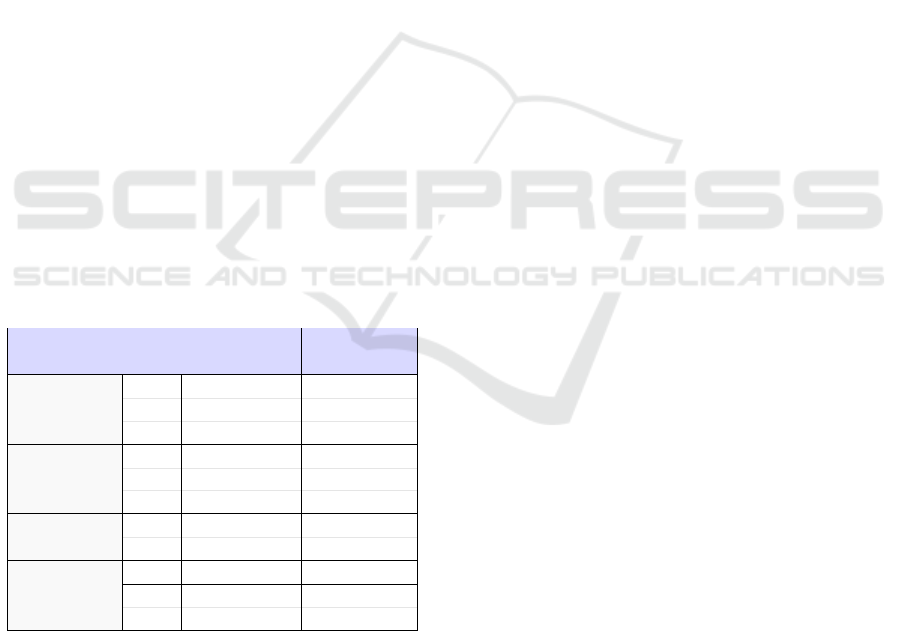
Table 2: Grid for Design Needs Analysis.
Educational Game
Criteria
Perspective Perspective
Q1
Q2Generation
Q3
Q4
Q5Death/Hurt
Q6
Q7
Variety
Q8
Progress Q9
Q10
Difficulty
Q11
The table 2 presents a structure to be completed
for the needs analysis. Each row represents a criterion
and is divided into X sub-rows (i.e., one sub-row per
question). Each column represents a dimension (i.e.,
a column for the game dimension, another for the ed-
ucational dimension). If both dimensions have some
common information, it can be precised by merging
both related cells. The proposed framework is inde-
pendent of the learning field and is suitable for the de-
sign of any learning game based on Roguelite genre.
The following section presents the application in the
context of the AdapTABLES project.
4 FRAMEWORK APPLICATION:
AdapTABLES PROJECT
This section is broken down into four subsections:
subsection 4.1 details the analysis for the design of the
first prototype; subsection 4.2 describes the current
prototype; subsection 4.3 presents the feedbacks (col-
lected informally in real-life conditions) on the proto-
type); subsection 4.4 specifies the design needs anal-
ysis for the next prototype, and subsection 4.5 dis-
cusses the proposition.
4.1 First Analysis
The initial step in our iterative process was to carry
out the design needs analysis for the first prototype.
The initial scope was to put aside the knowledge
structure by focusing on one task only (Completion
1 for multiplication tables) that will be manually set
up into the game (persistent information through dif-
ferent training sessions). Table 3 presents an overview
of the first design needs analysis.
Generation. The generated element (Q1) is a dun-
geon level and its elements (i.e., rooms, rooms or-
der, rooms elements, elements positions and values).
Each room has a type between question room and no-
question room. A question room is associated to a
task (i.e., the training task defined by the teacher and
set-up before playing). A no-question room is a fun
room where enemies, traps, and only game elements
are present. The presence of purely gaming rooms in-
tends to avoid giving the learners-players the impres-
sion that they are simply answering a disguised ques-
tionnaire. Following the game flow presented in Fig-
ure 2, a dungeon is generated when (Q2) the player
asks for a new game level.
As mentioned in Section 2.4, our game adapta-
tions target players’ preferences. To identify the pref-
erences, we first looked at the existing Roguelites and
found out that many of them offer a mechanism for
purchasing items (e.g., equipments, upgrades, skills).
Then, by working with game designers, we identified
three kinds of preferences: 1) Content, 2) Rules and
3) Visuals & Audio (Q3). Content preferences are
additional objects present while playing or elements
that change the structure of the activity if activated.
For example, an extra life or a dungeon mode (linear
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
280

or labyrinthine) are content preferences. Rules prefer-
ences are elements that impact the players, the avatar
or the NPCs (Non-Player Characters) behaviors. For
example, increasing the enemies speed or adding a
game goal (e.g., completing an activity without mis-
takes earns +10 coins) are rules preferences.
From the game dimension, the generation is based
on (Q3) these three types of preferences (e.g., if a
player bought and activated the labyrinthine mode,
the generation algorithm takes it into account). To
keep track of learners’ in game progress, the generator
also takes into account the last level number and state:
if the previous level was #5 and was successful, then
the next level is #6; in case of death, the next level is
reset to #1. Level number affects the dungeon length,
the quantity of rooms with questions, and the dun-
geon effects (levels greater than #4 are in dark mode).
In the educational dimension, many tasks parameters
can change depending on the level of the learners (cf.
Section 2). Therefore, all learners have their own set-
up for the task Completion 1 (or a shared one) de-
fined by the teachers. These parameters values are
used to produce relevant questioned facts associated
to the rooms-with-questions (Q3). Previous encoun-
tered questioned facts and results are used to avoid
answering again a successful questioned fact.
It is worth notice that both game and train-
ing dimensions can sometimes conflict. For exam-
ple, if a learner-player has bought and activated the
‘labyrinthine’ mode and if the task setup requires the
learner to meet the questioned facts in an ascendant or
descendant order. In these cases, our recommendation
is to consider the training dimension as a priority.
Death/Hurt. In both cases, when the avatar is injured
(Q5), it loses a life, and when there is no life left, it
dies. The player (through the avatar) gets hurt (Q4)
when touching a foe, falling into a pit (game dimen-
sion) or when answering incorrectly to a question (ed-
ucational dimension). It also happens when the time
is over (preliminary set in the task parameters). An-
swering a question incorrectly or running out of time
can only be done in a question room (Q6), while hit-
ting the wrong enemy or falling into a pit can be done
in both types of rooms.
Variety. In terms of game variety, different elements
can be chosen by the generation algorithm. In the
context of Roguelite, the variations are mainly based
on the types of objects, their position, the shape of
objects and dungeons, and the number of elements
present (Q7). Therefore, the decorative objects po-
sitions as well as the rooms shapes are chosen “ran-
domly” (Q8) (i.e., the coherence is kept, e.g., the el-
ements are not outside the room or the avatar can ac-
cess the necessary elements). The gameplay repre-
sents the concrete way in which the learner performs
the task. Therefore, having only one form of game-
play per task can quickly lead to a sense of redun-
dancy. One way to avoid this sense is to vary the
gameplay. To that extent, 4 gameplays were identified
(Q7) for the Completion 1 task type: open the chest
wearing the correct answer, pass through the door that
has the correct answer, touch the foe wearing the cor-
rect answer, or type down the correct answer.
From the learning dimension, the facts to be
worked on are different, until each fact has at least
been seen once (Q7). Moreover, depending on the pa-
rameters (cf. Table 3), the facts shapes (e.g., missing
element, position of the equal, etc.) vary (Q8). Some
degree of randomness is always involved in the varia-
tion of elements. However, this randomness is limited
by the preferences of the game, the educational con-
straints (i.e., the teachers’ choices) as well as by the
choices made earlier (i.e., elements already selected
by the algorithm).
Progress. In order to take into account players’ pref-
erences, our main idea is to use a purchase mecha-
nism (i.e., commonly used in Roguelites) where play-
ers can buy items and then activate/deactivate them
as they wish. Therefore, progression from the game
viewpoint can be seen through the elements bought
and the number of coins (Q9). Some Roguelites only
keeps progression when the level/dungeons are fin-
ished (i.e., the avatar did not die). Therefore, the coins
are only gained if the player finishes a dungeon com-
pletely. These coins are collected through the dun-
geon journey (randomly appear when opening a cor-
rect chest) or win at the end according to the activated
rules (for example, +10 if ending the dungeon level
without any mathematics error). Training progression
can be seen at the end of a dungeon (when reaching
the end or dying) with statistics presenting the mis-
takes made, the correct answers given, and what is
left to work on. All the results are persistent across
the runs.
Difficulty. From the game dimension, difficulty in-
creases during a run by increasing the number of
rooms-with-question (i.e., 5 rooms first, then 7, then
9, then 11, etc.) (Q10). The total number of rooms
may still vary according to the generation process
that can randomly includes rooms without question
along with the dungeon structure (tortuous but lin-
ear or labyrinthine) (Q11). After 5 levels played,
without losing, a harder level is proposed where the
player is in the dark, a torch only illuminates the
avatar (Q10). The educational difficulty increases in
accordance with the parameters defined by the teach-
ers, but while these parameters are not changed, the
questioned facts will always concern this setup (Q11).
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre
281

These choices are mainly debatable, and intends to
define a first version of the game’s difficulty progres-
sion, which is bound to evolve.
4.2 First Prototype
The prototype has been developed using the Unity
game engine, as a 2D game with C# scripts. It is
exported and deployed as a Web platform WebGL
build. The game uses an HTTP REST API (developed
in .Net Core) to persist data in a NoSQL MongoDB
database. In addition, a teacher dashboard is available
as a web application (developed in .NET with Blazor).
It allows teachers to monitor for their students: the
current settings for the multiplication parameters, cur-
rent achievement progress for the considered multi-
plication facts, current elements that has been bought.
Currently, only a French version playable with both a
gamepad or a keyboard is available.
Figure 3 shows 6 screenshots of the prototype.
The screen 3a represents part of the current ‘hub’
area with four accessible elements: statistics (“Stats
Generales”), progress (“Progression”), educational
settings (“Reglages”) and lastly the purchase panel
(“Achats”, i.e., game preferences). This ‘hub’ area
is where the player starts a run and goes back after he
died. It offers players a peaceful space where they can
check their progress or manage collectibles (purchase,
activation/deactivation). Screen 3b is an extract from
the educational settings panel (cf. Table 1). Screen 3c
is an extract from the item purchase panel. An ex-
ample of each of the currently implemented game-
plays present in the dungeon levels (i.e., choosing the
correct foe, the correct door, and the correct chest)
is illustrated in the Screens 3g, 3e, 3f. Finally, the
Screen 3h presents an example of a room where the
player has to type down his/her answer.
4.3 Experiment Feedback
The design of the prototype went through 3 iterations
where it was tested in real conditions and then im-
proved according to the feedback from teachers and
students (i.e., played in classroom by students su-
pervised by their teacher). Some empirical feedback
were about ergonomics concerns (keyboard versus
gamepad), playability experience, replayability incli-
nation, motivation to play and train the tables, etc.
The rest of the information collected were related
to the overall design, based on our previous analysis
choices, stated in the previous section. With regard
to the death/injury criterion, several problems have
been identified. Firstly, children sometimes make un-
intentional choices due to the current ‘touch’-oriented
interactions that do not require the use of a button
or key. Even if this gameplay problem is related
to ergonomics, it can lead to a feeling of unfairness
from the reward/punishment system. Secondly, some
rooms have randomly positioned foes very close to
the avatar’s entry area: swept along by the momen-
tum, children can lose hearts without having time to
avoid them. Similarly, some room-with-question also
embed holes to avoid. Teachers have pointed out to us
that these game elements can disturb children when
they should focus on the question.
Considering the variety criterion, children appre-
ciated the three gameplays for choosing an answer
(door, chest, and foe). This prototype offered 3 dif-
ferent room structures for each game, however it does
not vary enough. The gameplay about touching the
correct foe has been considered confusing by both
children and teachers. In some rooms, foes were to
be avoided, while in others the players must lead their
avatar to touch the foe with the answer they choose.
This is counter-intuitive, and teachers consider that
identifying a correct answer should not be associated
with a negative action (here, killing the foes). The
prototype also proposes several rooms-with-question
that require to directly type down the correct answer
on the keyboard. According to the correctness or not
of the answer, the right door or chest opens, or all foes
die. Any incorrect answer leads to open an empty
chest, open a door towards a dead end, or having no
effect on the touched foe, but in all three cases, in-
juring the avatar. These situations were initially de-
signed to vary the mode of response while providing
similar room content, but were ultimately confusing.
As far as the progression perspective is concerned,
we failed to provide a balanced way of collecting
coins. Only chest-oriented gameplays (choose or
write modality) can randomly contain ’+1’ or ’+3’
coins (or a ‘heart’/life). Some purchased and acti-
vated rules may provide other ways to earn coins,
but early successful dungeon levels may not result in
any coins being earned. Moreover, the first purchased
items are mainly those of the content category (extra
hearts), preferred to rules. In addition, some teachers
were not convinced about leaving learners free to buy
and activate rules that push them to act faster, stress-
ing them to answer quickly.
As mentioned earlier, the generation process may
disable some activated rules that do not conform to the
current configuration of the Completion 1 task. This
can lead to feelings of confusion when discovering the
generated dungeon levels.
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
282
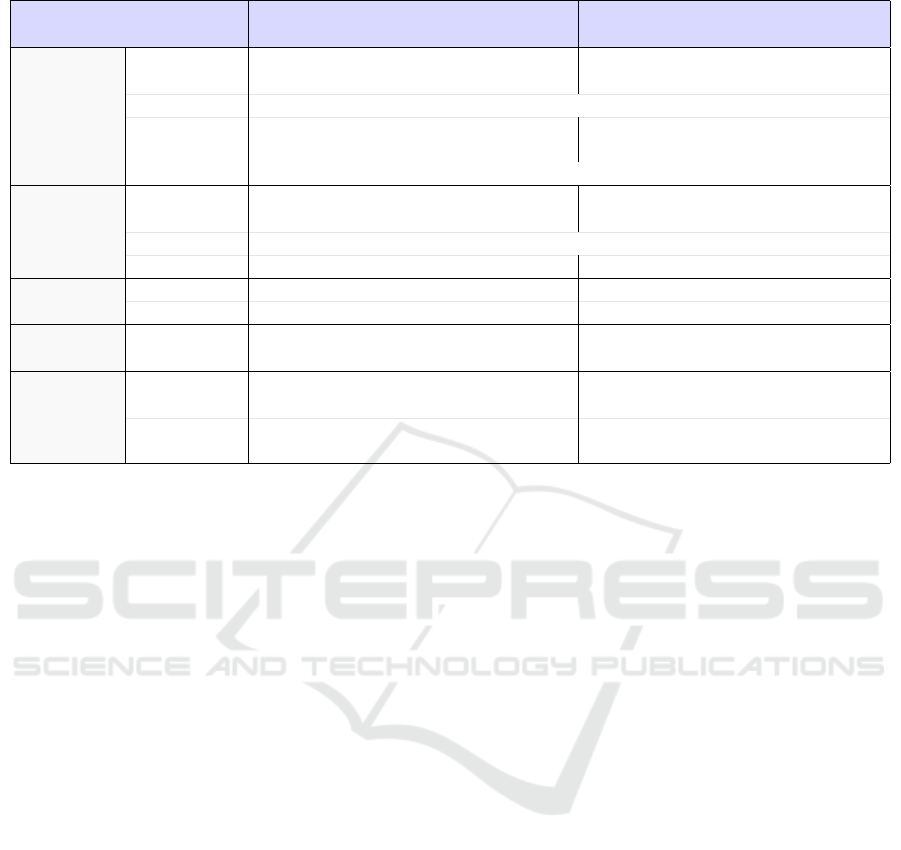
Table 3: Design Needs of the prototype #1.
Educational Game
Criteria
Perspective Perspective
Q1: What?
One task and one questioned fact per
Dungeon + rooms + entry + exit
room-with-question
Q2: When? When a new game level is required
Generation
Q3: Based
”Completion 1” set-up Previous level number and state
Current progress among possible facts Activated game elements or rules
on?
Task parameters have priority on activated game elements if conflict
Q4: What? Incorrect answers or time out
Being touched by foes, falling
into holes
Q5: When? Injuring causes heart lost, no more hearts causes death
Death/Hurt
Q6: Where? Question rooms Any room with foes or holes
Q7: What? Facts Rooms with gameplay and content
Variety
Q8: How? Progress and past results Random
Q9: What?
Success or failure on met Coins collected during successful
Progress
questioned facts game levels + purchased elements
Q10: What? Questioned facts
Dungeon level length
+ dark mode
Difficulty
Q11: How? In relation with the task parameters
According to previous level number
and state
4.4 Second Analysis
This second analysis was conducted for the design
of the next multiplication tables training prototype.
Based on teachers’ and learners’ feedback, we worked
with game designers to identify solutions and further
directions, both from a game and training dimension.
As with the functional scope of the first prototype,
the knowledge structure is still not taken into account,
although all 5 task types are considered. The proto-
type will make it possible to manually parameterize
the current training configuration for any children ac-
cording to their individual progress (correspondence
of a {objective, level} pair) of a learner’s training
path, cf. Figure 1).
Generation. The generated element (Q1) is still a
dungeon level composed of organized room of two
types: room without question, and room with one
question associated to one of the types of task in-
volved according to the training setup. Each room is
composed of various interactive elements. This dun-
geon level is generated when (Q2) the player requests
a new game level, from the hub-room (to start a new
run) or after the debriefing screens following a suc-
cessful dungeon level. From the game dimension, the
generation continues to take into account the last level
number and state (Q3) as well as the purchased and
activated features. However, the purchasable (activat-
able) elements have changed. These elements are ex-
plained in the following categories. From an educa-
tional dimension, each generation considers the cur-
rent configuration of the learner for all types of tasks
involved (from 1 to 5), and takes into account the pre-
vious questioned facts and the previous results.
Death/Hurt. The player still gets hurt (Q4) when
touching a foe, falling into a pit (game dimension),
when answering incorrectly to a question or lacking
of time (educational dimension). The main difference
is that the question rooms will no longer have traps
and game elements that can hurt the avatar other than
those related to the question to be answered (Q6).
Getting injured in a question room will always be
caused by a wrong answer or a time-out. The con-
sequences of an injury are not changed (Q5), it leads
to the loss of a life, or death.
Variety. In the first prototype, the different types of
rooms merged game elements and gameplays. In or-
der to propose more varieties of rooms (Q7), we con-
sider a new approach (see. the conceptual class dia-
gram in Figure 4). On one hand, the types of tasks
are mapped to different gameplay types according to
the current tasks parameters. Every type of game-
play requires a quantified number of elements having
the specified ability. On the other hand, the types of
rooms describe some positions accepting different el-
ements having a given ability. By extension, different
types of game elements are associated to the abilities
they can manage.
Combined, these elements will drive the genera-
tion of rooms and their built-in elements (Q8). As a
result, the purchase mechanic now consists of players
choosing items that will, if equipped (i.e., activated),
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre
283

(a) Prototype’s hub (b) Training settings panel
(c) Gaming settings panel (d) A no-question room
(e) Door Gameplay (f) Chest Gameplay
(g) Foe Gameplay (h) Answer entry
Figure 3: Screenshots of the current prototype features (text in French).
unlock new types of gameplays that can occur in cer-
tain rooms if they are consistent with the task associ-
ated to the room. By providing variants of game ele-
ments that share these abilities, game developers will
increase the possibilities for variations. Let’s take as
an example the “boxing gloves” item, that allow the
destruction of every “destroyable” elements (i.e., hav-
ing an ability). Several elements can have “destroy-
able” as an ability: walls, pots, statues, rocks, etc. If
the avatar is equipped with this item, it is possible to
create multiple variants of gameplays. The mecha-
nism remains the same, but the elements vary (e.g.,
destroy the wall, break the rock).
Progress. Equipment items are definitely purchased
across runs. The coin mechanism is retained, but will
be adjusted so the learners will earn one coin per cor-
rect answer. Questioned facts encountered and asso-
ciated results are also saved beyond death. Therefore,
the progression can be observed through: the equip-
ments available, the number of coins, and fact results,
i.e., available outside a game level (Q9).
Difficulty. The educational difficulty is maintained
as in the first prototype, i.e., according to the param-
eters of the tasks supervised by the teachers (Q11).
From a gameplay point of view, the progression ac-
cording to the length of the dungeons is kept, but a
new gameplay mechanism is added: the curses (Q10).
The game progression will be structured in different
minimum thresholds, unlocking curses that may or
may not occur during the dungeon level to be gen-
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
284
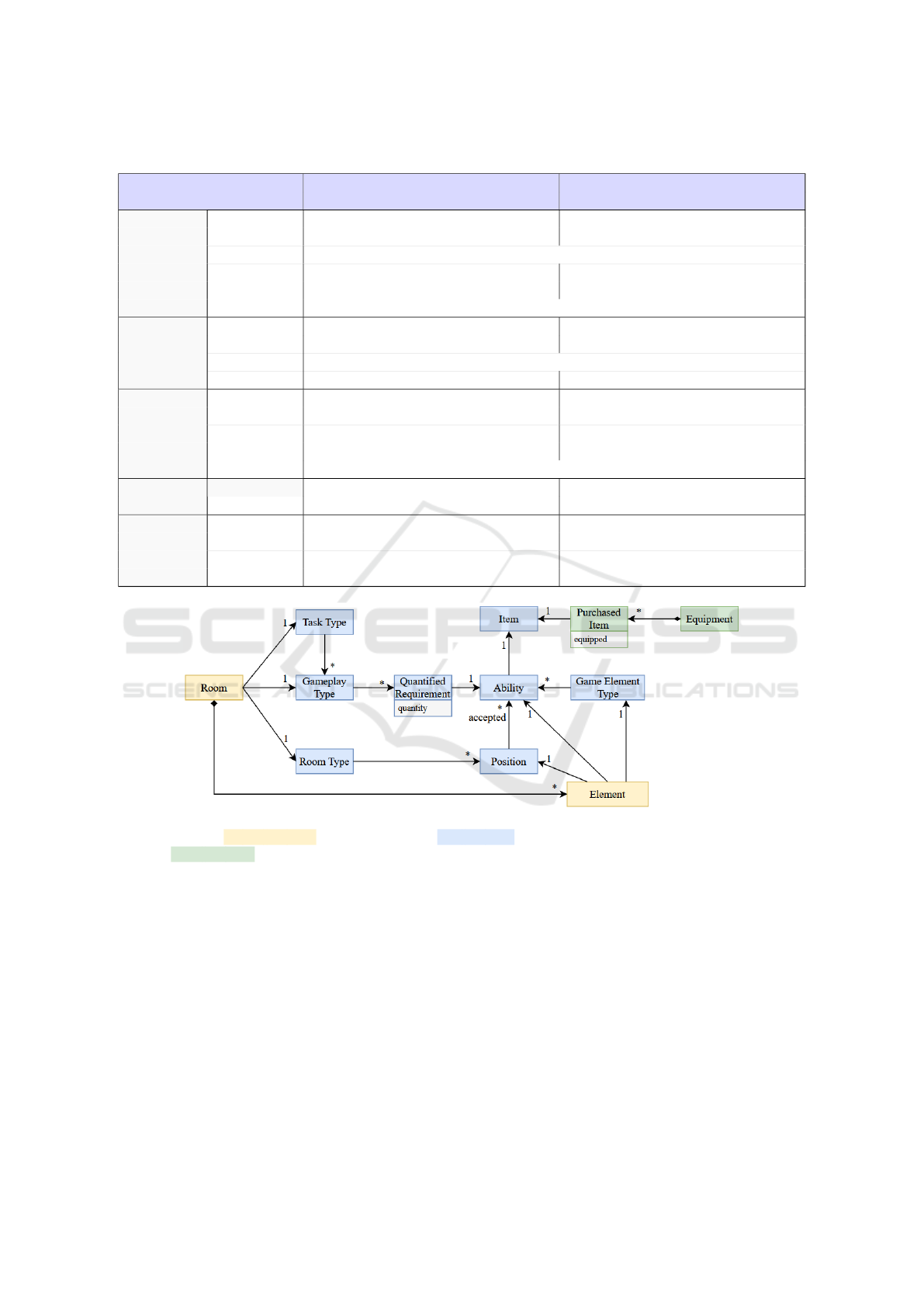
Table 4: Design Needs of the Future Prototype (Bold describes changes from the first analysis).
Educational Game
Criteria
Perspective Perspective
Q1: What?
One task and one questioned fact
Dungeon structure + rooms
per room-with-question
Q2: When? When a new game level is required
Generation
Q3: Based
All tasks set-up Previous level number and state
Current progress among possible facts Equipped items
on?
Task parameters have priority on activated game elements if conflict
Q4: When? Incorrect answers or time out
Being touched by foes, falling
into holes
Q5: What? Injuring causes heart lost, no more hearts causes death
Death/Hurt
Q6: Where? Question rooms Only rooms with no question
Q7: What? Facts
Different types of rooms, types of
gameplays, types of elements
Variety
Q8: How?
Progress and past results
Based on the available equipments,
gameplays, elements,
and in relation to the tasks ⇐⇒ gameplays mappings
Q9: What?
Success or failure on met Coins collected during successful
Progress
questioned facts game levels + purchased items
Q10: What? Questioned facts
Dungeon level length
+ curses
Difficulty
Q11: How? In relation with the task parameters
According to previous level number
and state
Figure 4: Conceptual class diagram illustrating the domain elements and relationships involved in considering a wide variety
of question pieces. Yellow concepts are to be generated; blue concepts are specifications of the game and didactic elements
available; green concepts concern each learner-player.
erated (Q11). For example, if we consider thresholds
every 3 dungeon levels, the generation of level #10
may involve at worst 3 curses, or 0 with luck.
4.5 Discussion
The first advantage of the framework is the trace-
ability of design choices. Indeed, at each itera-
tion, the choices are explained and then summarized.
This traceability facilitates the evolution of the design
without the risk of involuntarily going backwards. On
the other hand, the visual synthesis (cf. Table 2)
makes it possible to check that none of the dimensions
has been neglected (i.e., presence of an empty box in
case of neglect). In a prototyping approach, iterations
are essential to fix certain settings. However, it would
seem that the use of such a framework (i.e., allowing
traceability as well as visual verification of the non-
neglect of a dimension) could reduce the number of
iterations required. Finally, this tool provides a sup-
port that can be understood by all stakeholders of the
design process.
However, the proposed framework takes into ac-
count a rather precise context: training or retrieval
practice (i.e., a form of test-based learning) in the con-
text of the Roguelite video game genre. Moreover,
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre
285

the criteria used are those that we consider essential.
Consequently, other criteria might be considered es-
sential by other researchers or game designers. In
particular, some criteria depending on the application
domains might be interesting to add.
5 RELATED WORK
The literature includes many frameworks and meth-
ods for games, serious games, game-based scenario
design. However, many of them are mainly oriented
towards and used for the analysis of already existing
games (Junior and Silva, 2021).
(De Freitas and Jarvis, 2006) proposed a four-
dimensional learner-centered framework (Represen-
tation, Context, Pedagogy, Learner) to help design
game-based learning scenarios. This approach is at
a high level of design, which does not facilitate the
transition from educational content to concrete game
elements. (Winn, 2009) introduced the DPE frame-
work, an extension of the Mechanics, Dynamics, Aes-
thetics (MDA) framework (Hunicke et al., 2004) for
serious games. This framework is broken down into
three categories (design, play, experience; i.e., the de-
signer designs the game, the player plays the game,
which results in player’s experience), each described
by four criteria: Learning, Narrative, Gameplay, User
Experience. (Schell, 2008) proposed a method con-
sisting of a series of questions on different aspects to
be taken into account for the design of the game. This
method is more generic than ours (i.e., at a higher
design level) because it does not focus on a specific
type of knowledge or game genre. (Amory, 2007)
described GOM II, a framework for the design of
educational games extended from the Game Object
Model (GOM). This framework considers that an ed-
ucational game is composed of a set of elements de-
scribed by abstract and concrete interfaces (based on
the Object-Oriented paradigm). This work is theo-
retical and focuses on the general design of games
rather than their concrete implementation. (Arnab
et al., 2015) proposed the LM-GM framework that en-
ables the association of Learning Mechanics to Game
Mechanics through the use of Serious Game Mechan-
ics (SGM; “design decision that concretely realizes
the transition of a learning practice/goal into a me-
chanical element of gameplay for the sole purpose of
play and fun”). Nevertheless, this framework is more
oriented towards the analysis of games than towards
their design. (Carvalho et al., 2015) presented a con-
ceptual model, called ASTMG, based on activity the-
ory, which seeks to provide a better understanding of
the relationships between the serious games elements
and learning objectives/goals. This framework is also
more oriented towards game analysis.
Many other framework and methodologies ex-
ists (Yusoff et al., 2009; Barbosa et al., 2014; Marne
et al., 2012; Kiili, 2005; Silva, 2019). Some works
offer methods that are closer to some general game
genre (i.e., adventure games, story oriented games
for (De Lope et al., 2017)). However, these works are
mainly generic (i.e., they are not specific to a type of
knowledge or a game genre). Therefore, being in the
specific context of the Roguelite genre, none of the
existing works met our requirements. Nevertheless,
these frameworks are not incompatible and can be
used together. As examples: the framework proposed
by (Schell, 2008) could be used to describe the gen-
eral design of the game; the ASTMG (Carvalho et al.,
2015) could be used to verify the coherency of each
prototype. In short, the current frameworks that share
our goal of assisting the design of learning games deal
with different pedagogical objectives, different types
of knowledge, different game genres. They do not aim
to assist design in situations where the game genre is
already identified because of its relevance to a specific
learning objective. Our analysis framework is dedi-
cated to Roguelite games for declarative knowledge
retention: a very specific scope. Nevertheless, multi-
disciplinary teams also require specific frameworks to
guide them deeper in the design of relevant, adapted,
and balanced learning games.
6 CONCLUSION
This article 1) presented Roguelite as a suitable
game genre for declarative knowledge training, and
2) introduced a design needs analysis framework
for Roguelite-oriented learning game. The proposed
framework gives a very first insight into the mecha-
nism and choices that benefits both to the game and
training dimension. The main idea is to allow a two-
dimensional design between the play and learning di-
mensions. This design aims at a separate description
of the dimensions while allowing the verification (and
maintenance) of both dimensions’ conformity.
This framework was used in a prototyping design
approach in the context of the AdapTABLES project.
This project aims at creating a game for multiplica-
tion tables training. This article presents the applica-
tion of the framework over two iterations: 1) the first
iteration led to the current existing prototype, 2) the
second iteration presents the design requirements of
the future prototype.
In the future, we would like to apply this frame-
work to other fields of application than mathemat-
CSEDU 2023 - 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
286

ics. Currently, we are working on its application to
history-geography facts (e.g., historical dates, coun-
tries of the European Union).
REFERENCES
Amory, A. (2007). Game object model version II: A theo-
retical framework for educational game development.
Educational Technology Research and Development,
55(1):51–77.
Arnab, S., Lim, T., Carvalho, M. B., Bellotti, F., de Freitas,
S., Louchart, S., Suttie, N., Berta, R., and De Gloria,
A. (2015). Mapping learning and game mechanics for
serious games analysis: Mapping learning and game
mechanics. British Journal of Educational Technol-
ogy, 46(2):391–411.
Barbosa, A. F. S., Pereira, P. N. M., Dias, J. A. F. F., and
Silva, F. G. M. (2014). A New Methodology of Design
and Development of Serious Games. International
Journal of Computer Games Technology, 2014:1–8.
Brame, C. J. and Biel, R. (2015). Test-Enhanced Learning:
The Potential for Testing to Promote Greater Learning
in Undergraduate Science Courses. CBE—Life Sci-
ences Education, 14(2).
Carvalho, M. B., Bellotti, F., Berta, R., De Gloria, A.,
Sedano, C. I., Hauge, J. B., Hu, J., and Rauterberg,
M. (2015). An activity theory-based model for serious
games analysis and conceptual design. Computers &
Education, 87:166–181.
De Freitas, S. and Jarvis, S. (2006). A Framework for devel-
oping serious games to meet learner needs. Interser-
vice/Industry Training, Simulation & Education Con-
ference, I/ITSEC.
De Lope, R. P., Medina-Medina, N., Soldado, R. M., Gar-
cia, A. M., and Gutierrez-Vela, F. L. (2017). Design-
ing educational games: Key elements and method-
ological approach. In 9th International Conference
on Virtual Worlds and Games for Serious Applications
(VS-Games), pages 63–70, Athens, Greece. IEEE.
Goldberg, L. R. (1990). An alternative” description of per-
sonality”: The big-five factor structure. Journal of
personality and social psychology, 59(6):1216–1229.
Harris, J. (2020). The Berlin Interpretation. In Exploring
Roguelike Games, pages 37–43. CRC Press.
Hunicke, R., LeBlanc, M., and Zubek, R. (2004). MDA: A
formal approach to game design and game research.
In Proceedings of the AAAI Workshop on Challenges
in Game AI, volume 4. San Jose, CA.
Junior, R. and Silva, F. (2021). Redefining the MDA Frame-
work—The Pursuit of a Game Design Ontology. In-
formation, 12(10).
Kiili, K. (2005). Digital game-based learning: Towards an
experiential gaming model. The Internet and Higher
Education, 8(1):13–24.
Kim, J. W., Ritter, F. E., and Koubek, R. J. (2013). An inte-
grated theory for improved skill acquisition and reten-
tion in the three stages of learning. Theoretical Issues
in Ergonomics Science, 14(1):22–37.
Laforcade, P., Mottier, E., Jolivet, S., and Lemoine, B.
(2022). Expressing adaptations to take into account
in generator-based exercisers: An exploratory study
about multiplication facts. In 14th International Con-
ference CSEDU, Online Streaming, France.
Marne, B., Wisdom, J., Huynh-Kim-Bang, B., and Labat,
J.-M. (2012). The Six Facets of Serious Game De-
sign: A Methodology Enhanced by Our Design Pat-
tern Library. In 21st Century Learning for 21st Cen-
tury Skills, volume 7563, pages 208–221. Springer,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Marty, J.-C. and Carron, T. (2011). Hints for improving
motivation in game-based learning environments. In
Handbook of Research on Improving Learning and
Motivation through Educational Games: Multidisci-
plinary Approaches, pages 530–549. IGI Global.
Nacke, L. E., Bateman, C., and Mandryk, R. L. (2014).
BrainHex: A neurobiological gamer typology survey.
Entertainment Computing, 5(1):55–62.
Oppermann, R. and Rashev, R. (1997). Adaptability and
adaptivity in learning systems. Knowledge transfer,
2:173–179.
Roediger, H. L. and Pyc, M. A. (2012). Inexpensive
techniques to improve education: Applying cognitive
psychology to enhance educational practice. Jour-
nal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition,
1(4):242–248.
Schell, J. (2008). The Art of Game Design: A Book of
Lenses. CRC press.
Silva, F. G. M. (2019). Practical Methodology for the
Design of Educational Serious Games. Information,
11(1):14.
Streicher, A. and Smeddinck, J. D. (2016). Personalized and
Adaptive Serious Games. In D
¨
orner, R., G
¨
obel, S.,
Kickmeier-Rust, M., Masuch, M., and Zweig, K., ed-
itors, Entertainment Computing and Serious Games,
volume 9970, pages 332–377. Springer International
Publishing, Cham.
Tondello, G. F., Wehbe, R. R., Diamond, L., Busch, M.,
Marczewski, A., and Nacke, L. E. (2016). The Gamifi-
cation User Types Hexad Scale. In Proceedings of the
Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction
in Play, pages 229–243, Austin Texas USA. ACM.
Toy, M., Wichman, G., Arnold, K., and Lane, J. (1980).
Rogue [digital game].
Vandewaetere, M., Desmet, P., and Clarebout, G. (2011).
The contribution of learner characteristics in the de-
velopment of computer-based adaptive learning envi-
ronments. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(1):118–
130.
Winn, B. (2009). Handbook of Research on Effective Elec-
tronic Gaming in Education:. IGI Global.
Yusoff, A., Crowder, R., Gilbert, L., and Wills, G. (2009).
A Conceptual Framework for Serious Games. In 9th
IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learn-
ing Technologies, pages 21–23, Riga, Latvia.
An Analysis Framework for Designing Declarative Knowledge Training Games Using Roguelite Genre
287
