
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data
Poisoning Attacks
Israt Jahan Mouri
a
, Muhammad Ridowan
b
and Muhammad Abdullah Adnan
c
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), Dhaka, Bangladesh
Keywords:
Support Vector Machine, Poisoning Attack, Outlier Detection, Federated Learning.
Abstract:
Federated Support Vector Machine (F-SVM) is a technology that enables distributed edge devices to collec-
tively learn a common SVM model without sharing data samples. Instead, edge devices submit local updates
to the global machine, which are then aggregated and sent back to edge devices. Due to the distributed nature
of federated learning, edge devices are vulnerable to poisoning attacks, especially during training. Attack-
ers in adversarial edge devices can poison the dataset to hamper the global machine’s accuracy. This study
investigates the impact of data poisoning attacks on federated SVM classifiers. In particular, we adopt two
widespread data poisoning attacks for SVM named label flipping and optimal poisoning attacks for F-SVM
and evaluate their impact on the MNIST and CIFAR10 datasets. We measure the impact of these poisoning
attacks on the precision of global training. Results show that 33% of adversarial edge devices can reduce
accuracy up to 30%. Furthermore, we also investigate some basic defense strategies against poisoning attacks
on federated SVM.
1 INTRODUCTION
Federated Learning is a promising solution that en-
ables numerous decentralized edge devices to jointly
build a common prediction model while maintain-
ing all of the training data on the edge device. The
edge devices train the model using their data and then
send it to the global machine, which combines the
models to generate the global model. Though ini-
tially designed for Deep Neural Networks, federated
learning concepts are currently being investigated for
other machine learning models, such as Support Vec-
tor Machine (SVM). In Federated Support Vector Ma-
chine (F-SVM) frameworks (Kabir and Adnan, 2019;
Zhang and Zhu, 2017), edge devices create local hy-
perplanes utilizing their data and only share them with
the global machine. The global hyperplane is then
created by combining the local hyperplanes on the
global machine.
However, edge devices are susceptible to poison-
ing attacks due to the distributed nature of federated
learning. Data poisoning attacks introduce poisoned
data into the training dataset and disrupt the machine
learning training process, endangering the model’s in-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0160-4212
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5964-675X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3219-9053
tegrity. This attack modifies the learned classifier and
compromises the model’s ability to generate accurate
predictions. As a result, the accuracy of the classi-
fier is reduced, and the model may categorize mali-
cious instances into desirable classes (e.g., labeling
spam e-mails as safe). Numerous studies (Doku and
Rawat, 2021; Shejwalkar et al., 2022; Tolpegin et al.,
2020; Sun et al., 2021) have examined the effects of
poisoning attacks on federated deep neural networks
and federated convolutional neural networks. How-
ever, none of the research investigated the effects of
poisoning attacks on F-SVM.
Another type of attack in a federated system is
where adversarial edge devices may attack the local
model to be trained instead of training data. This
strategy is more effective than the data poisoning at-
tack, according to research (Bagdasaryan et al., 2020;
Bhagoji et al., 2019; Fang et al., 2020). However, to
launch a model poisoning attack, the attackers need
access to the edge device’s learning process, which is
difficult to achieve in practice. For example, a virus
or malicious user can poison the dataset but can not
change the model or training process. Therefore, al-
though model poisoning attacks are an important re-
search topic, it is not the focus of this research.
This study investigates the impact of two popu-
lar data poisoning attacks on SVM classifiers, namely
24
Mouri, I., Ridowan, M. and Adnan, M.
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data Poisoning Attacks.
DOI: 10.5220/0011825800003488
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2023), pages 24-33
ISBN: 978-989-758-650-7; ISSN: 2184-5042
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

(1) label flipping attack, and (2) optimum poisoning
attack (Biggio et al., 2012; Xiao et al., 2015; Demon-
tis et al., 2019). Our contributions can be summarized
as,
• We develop a framework for the collaboration of
multiple clients, including both adversarial and
non-adversarial, in a Federated Support Vector
Machine (SVM) training process.
• We evaluated the effectiveness of this framework
by implementing and evaluating two attack strate-
gies: label flipping and optimum poisoning. We
also assessed the impact of varying numbers of
adversarial edge devices on the accuracy of the
Federated SVM for the MNIST and CIFAR10
datasets.
• Finally, we tested three outlier detection algo-
rithms as basic defense mechanisms to determine
their efficacy.
We measured the negative impact of adversarial
edge devices on global F-SVM accuracy. One ad-
versarial edge device, for instance, can decrease the
overall performance by 2%. If 33% of edge devices
are adversarial, accuracy is reduced by 30%. All our
programs are open-source and written in Python on
Google’s Colab Notebook platform.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. Sec-
tion 2 provides a summary of the related works. An
outline of the foundational ideas employed in this re-
search is given in Section 3. An F-SVM with poi-
soning attacks is then briefly described in Section 4.
The effects of poisoning attacks are detailed in Sec-
tion 5. The discussion of various defense strategies
against poisoning attacks in F-SVM is presented in
Section 6. Finally, we conclude in Section 7.
2 RELATED WORKS
Google introduced the concept of federated learning
(Kone
ˇ
cn
`
y et al., 2016a; Kone
ˇ
cn
`
y et al., 2016b) for
the first time in 2016. After that, several researchers
(Kabir and Adnan, 2019; Zhang and Zhu, 2017)
began implementing federated learning concepts for
privacy-enabled SVMs. F-SVM is utilized for vari-
ous purposes, including the detection of Android mal-
ware (Hsu et al., 2020), and wireless networks (Wang
et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2020), amongst many others.
However, data poisoning attacks remain a significant
concern for any federated learning system (Mu
˜
noz-
Gonz
´
alez et al., 2017). Several researchers (Sun et al.,
2021; Fang et al., 2020) discussed poison attacks and
defense against them for federated deep neural net-
works.
2.1 Data Poisoning Attacks
Data poisoning attacks remains one of the major
threat for any machine learning systems (Zhu et al.,
2022; Bovenzi et al., 2022; Radford et al., 2018;
Pitropakis et al., 2019; Ding et al., 2021; Anisetti
et al., 2022). This attack does not create any suspi-
cious data points. Rather it works by altering the ex-
isting data points (Biggio et al., 2011; Paudice et al.,
2019). Data poisoning attacks can be targeted (mis-
classifying positive data points) or untargeted (accu-
racy reduction). Our focus is on untargeted accuracy
reduction of Federated SVM. Currently, there are two
major types of data poisoning attacks for untargeted
accuracy reduction in SVM:
Label Flipping Attack: A label-flipping attack
(Barreno et al., 2010; Paudice et al., 2018) is an at-
tack in which an attacker creates poisonous samples
by altering the labels of specific training samples.
(Barreno et al., 2010) demonstrate that label-flipping
attacks increase both false positives and false nega-
tives. (Paudice et al., 2019) outlined their effects on
SVM and also discussed the defense mechanisms.
Optimal Poisoning Attack: (Biggio et al., 2012)
demonstrated poisoning attacks against SVM for the
first time using the MNIST dataset. The authors pro-
posed an algorithm to compute optimal poisonous
points using gradient descent and then injected these
custom-designed poisonous points into the training
data. They demonstrated that incorporating these poi-
sonous points into subsequent training significantly
affects accuracy. Consequently, further studies (Xiao
et al., 2015; Mei and Zhu, 2015; Jagielski et al., 2018;
Biggio and Roli, 2018; Mu
˜
noz-Gonz
´
alez et al., 2017)
improved the generation of poisonous points by uti-
lizing additional datasets.
Most poisoning attack researches against feder-
ated learning system target deep neural networks or
logistic regressions. However, our research indicates
that the non-federated SVM data poisoning attacks
are adaptable to F-SVM. In particular, in this re-
search, we demonstrate that existing poisonous point
generation algorithms can be applied to F-SVM also.
2.2 Defense Against Poisoning Attacks
Numerous defense strategies against data poisoning
attacks on SVM rely on data pre-filtering, in which
poisoned samples are detected, filtered out, and then
cleaned datasets are used to retrain the model. (Dalvi
et al., 2004) presented a formal framework and algo-
rithms for outlier detection where the authors viewed
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data Poisoning Attacks
25
classification as a game between the classifier and
the adversary. Then they produced an optimal naive
Bayes classifier based on the adversary’s optimal
strategy. (Zhou et al., 2012) introduced an adver-
sarial SVM (AD-SVM) model, which incorporated
additional constraint conditions to the binary SVM
optimization problem to thwart an adversary’s poi-
soning attacks. (Laishram and Phoha, 2016) intro-
duced an algorithm named Curie that identifies the
poisoned data points and filters them out. (Steinhardt
et al., 2017) introduced a framework for detecting out-
liers that filters the poisonous points from the training
data. Later, (Paudice et al., 2018) demonstrated that
the adversarial examples generated by poisonous at-
tack strategies are very distinct from genuine points
because detectability constraints are not considered
when crafting the attack. Finally, they proposed a
defense strategy against poisoning attacks based on a
distance-based outlier detector using a small number
of trusted data points.
All of the previously mentioned defense strategies
are inapplicable to F-SVM because all defense mech-
anisms rely on pre-filtering data. If an edge device is
adversarial and crafts poisoning attacks on purpose,
it will not participate in data pre-filtering. Since the
global machine lacks access to the local dataset, pre-
filtering of data is also impossible in the global ma-
chine. We also discuss some defense strategies to mit-
igate the effects of data poisoning attacks on F-SVM.
3 PRELIMINARIES
3.1 Support Vector Machine
In support vector machine (SVM), the training dataset
with N data points is defined as (⃗x
i
,y
i
) where i =
1,2,...,N. Here, the input data point ⃗x
i
is a p dimen-
sional real vector. Their corresponding data label is
y
i
∈ 0 .. .k represents k classes. Next, the SVM algo-
rithm finds the hyperplane with the maximum sepa-
rate margin. The margin is defined by (⃗w,b) where ⃗w
is a p dimensional real vector representing the normal
to the hyperplane and
b
|⃗w|
is the distance between the
hyperplane and the origin along ⃗w.
3.2 Federated Learning
A federated learning system consists of two entities,
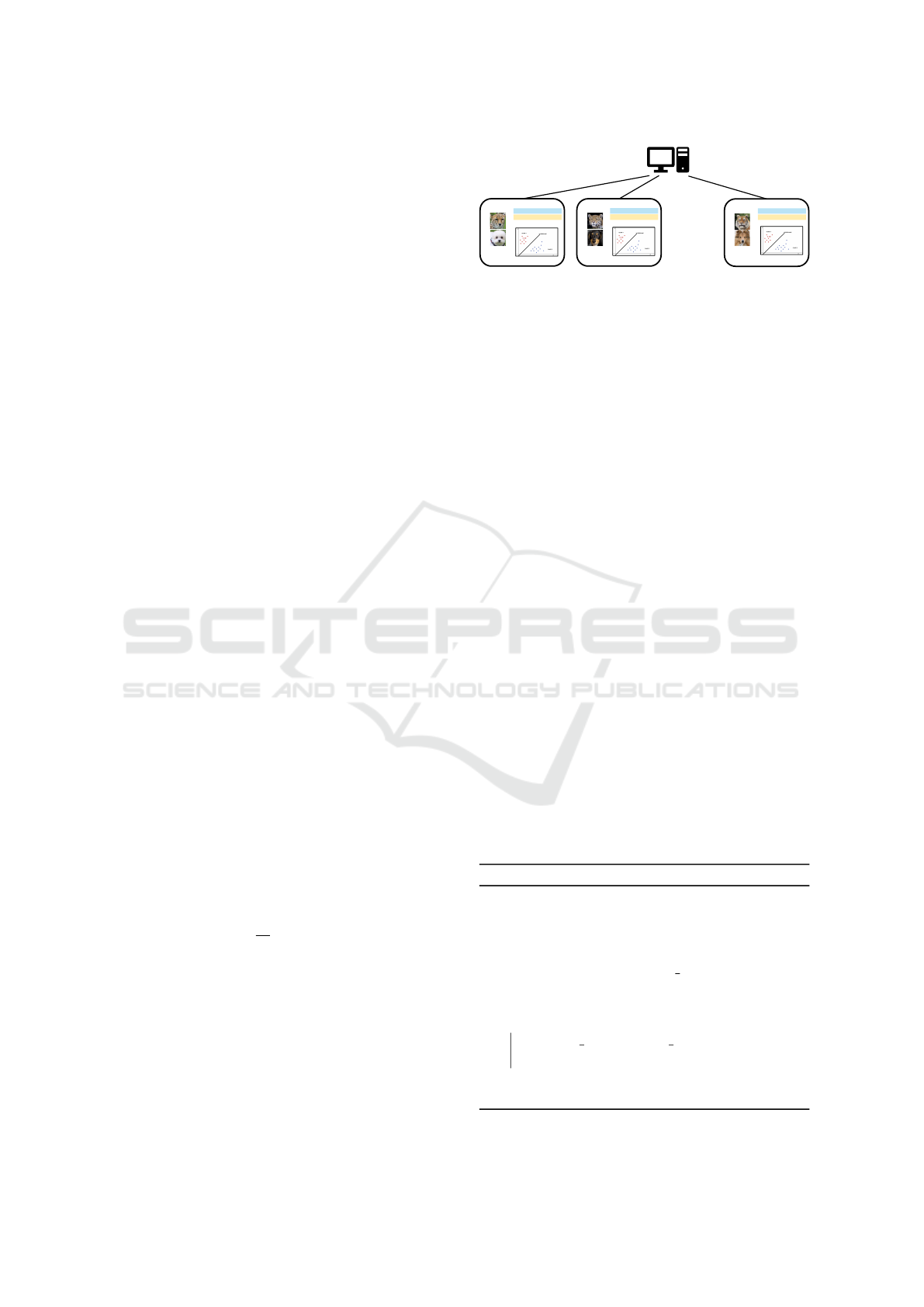
as presented in Fig. 1.
1. Edge Devices: S numbers of geo-distributed inde-
pendent edge devices are collaborating to train a
machine learning model. All edge devices have
local SVMs
local SVMs
local SVMs
local SVMs
local SVMs
local SVMs
EdgeDevice1
EdgeDeviceS
EdgeDevice2
GlobalMachine
…….
Figure 1: A Federated Learning System.
confidential data; therefore, they will not share
data during the training. They will train a model
using their local data. Only the trained models
will be sent to the global machine.
2. Global Machine: Global machine is a centralized
server coordinating global training. The global
machine does not have direct access to training
data. However, it will combine training models
from edge devices to compute a globally trained
model. The global machine will also ensure the
correctness and security of global training data.
4 OUR FRAMEWORK FOR
POISONING ATTACK OF
F-SVM
4.1 System Description
The federated system is based upon (Kabir and Ad-
nan, 2019)’s distributed SVM. Although the authors
describe the model as a privacy-preserving distributed
SVM, they integrated federated learning ideas to
make D-SVM privacy-preserving. There are S edge
devices, each having dataset X
j
where j = 1,. .. ,S.
For each data point (⃗x, y) ∈ X
j
, ⃗x is a p-dimensional
vector with y being one of the label from the k class
labels. Each edge device trains its SVM with it’s
Algorithm 1: Local SVM Training.
Data: dataset X
j
for j
th
edge device where
j ∈ 1 . . . S
Result: Local Hyperplane Set H
j
Run SVM on the dataset X
j
;
generate k support vectors s vectors for k
classes ;
H
j
←− [] ;
foreach i ∈ 0 . . . k do
w, b ←− s vectors[i].w, s vectors[i].b ;
add w||b to H
j
;
end
return H
j
;
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
26

dataset. The training is a standard multi-class SVM
model training which generate the hyperplane set
H
j
= H
j1
,H
j2
,. .. ,H
jk
for all the k classes. An in-
dividual hyperplane is represented as a vector H
ji
=
⃗w||b. Each edge device sends its own hyperplane set
H
j
to the global machine. Algorithm 1 shows the pro-
cess.
The whole hyperplane set in global machine is
H = H
1
,H
2
,. .. ,H
S
. Global machine combines all the
hyperplane sets in H to generate global hyperplane set
H
global
. This process consists of two parts,
1. Clustering: For each class i = 0 . . . k, global ma-
chine uses k-means clustering on all the hyper-
planes for label i (H
1i
,H
2i
,. .. ,H
ji
). The initial
hyperplane for label i is the cluster’s centroid and
denoted by H
initial
i
.
2. Convergence: Convergence is a multi round pro-
cess. In each round, for each j
th
edge device ( j ∈
1. .. S ) and for each class i ∈ 0. .. k, H
ji
is set as
the average between H
ji
and H
initial
i
. Afterward,
each H
initial
i
is recomputed using k-means clus-
tering on the new hyperplanes for all i ∈ 0 .. .k.
This process continues unless all hyperplanes for i
(H
1i
,H
2i
,. .. ,H
ji
) becomes the same. After which,
H
initial
i
is declared as final result H
global
i
for class
label i. Algorithm 2 denotes the full steps.
Algorithm 2: Global Machine Clustering and
Convergence.
Data: Class i where i ∈ 0 .. .k, Hyperplane
set H = H
1
,H
2
,..., H
S
Result: Global Trained Hyperplane H
global
i
hSets ←− H
ji
|i ∈ 1 . . . S ;
isU pdated ←− True ;
while isU pdated do
isU pdated ←− False ;
Compute H
initial
i
as KMeans cluster
centers of hSets ;
foreach l ∈ 1 . . . length(hSets) do
if H
initial
i
!= hSets[l] then
hSets[l] ←−
H
initial
i
+hSets[l]
2
;
isU pdated ←− True ;
end
end
end
return H
global
i
←− H
initial
i
;
4.2 Problem Definition and Threat
Model
In our framework, the global machine is a trusted en-
tity. Therefore, we do not consider any malicious
activity in global SVM generation. Global accuracy
only hampers if the poisonous models are sent from
edge devices. Attackers have access to some of the
edge devices. In this subsection, we present the at-
tackers’ goals, capabilities, background knowledge,
and strategies of attackers.
4.2.1 Attacker’s Goal
We consider that an attacker’s goal is to manipulate
the global model such that it has a low accuracy rate
due to misclassifications for all testing examples.
4.2.2 Attacker’s Capability & Background
Knowledge
We assume the attacker knows about the full F-SVM
training methods and has access to some edge de-
vices. They have full access to the local training
dataset in each adversarial edge device. Attacker can
manipulate these before the actual training start. They
can run any computation on the local dataset includ-
ing running mock training. However, they only have
full access to the dataset X
j
but cannot modify the
training process or trained hyperplane set H
j
. The at-
tack’s target is to generate poisonous data points us-
ing X
j
and generate a poisonous dataset that will be
used in training. The poisonous dataset will generate
a poisonous hyperplane set H
adv
j
.
One crucial assumption is that the adversary can-
not compromise or does not know anything about the
global machine’s code, data, or other edge devices hy-
perplanes used to generate the global model. More
importantly, it does not have access to any other edge
devices’ local models, training data, or submitted up-
dates, regardless of whether they are adversarial or
not. Each attacker works independently.
4.3 Data Poisoning Attacks on F-SVM
These attacks are described from the perspective of
an individual attacker. An attacker in j
th
devices cre-
ates a poisonous dataset X
adv
j
from the device’s local
dataset X
j
. The procedures are described below.
4.3.1 Label Flipping Attack
In adversarial edge devices, the attackers change the
labels of the training dataset and then train the SVM
classifier with that dataset. Specifically,
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data Poisoning Attacks
27

X
adv
j
= {(x, (y + 1) mod k)|(x,y) ∈ X
j
}
That is the entire dataset X
j
is replaced with X
adv
j
.
4.3.2 Optimal Poisoning Attack
Optimal poisoning attack, as described in (Biggio
et al., 2012; Xiao et al., 2015; Mei and Zhu, 2015),
is a gradient-based method by which an attacker can
construct a data point that significantly reduces the
accuracy of the SVM. They assumed,
• The adversary is aware of the learning algorithm
and can extract data from the underlying data dis-
tribution to create a validation dataset D
val
.
• The attacker is aware of the training data used
by the learner and could substitute a training set
D
train
drawn from the same distribution.
To make these assumptions compatible with our
attacker capabilities, as discussed in 4.2.2, we split X
j
evenly to D
train
and D
val
. Then the optimal poisonous
point generation algorithm in the optimal poisoning
attack is used to create a poisonous point. The pro-
cess is repeated to create multiple poisonous points,
which are collected to generate X
adv
j
. (Biggio et al.,
2012) combines X
adv
j
and D
train
to create the train-
ing dataset in the original attack description. How-
ever, our experiments indicate that only using X
adv
j
to
generate the hyperplane set H
j
has a more significant
impact on global F-SVM accuracy. These steps are
specified in Algorithm 3.
It can be easily understood that the more poi-
sonous points in X
adv
j
, the more it should impact
global F-SVM accuracy. However, the process of
generating poisonous points is very computationally
expensive. A reasonable value for the number of poi-
sonous points np = |X
adv
j
| should at least make the
trained hyperplane set reflect the attack’s direction.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULT
5.1 Implementation of the F-SVM
We choose a modified version of (Kabir and Adnan,
2019)’s distributed SVM for a simple reference F-
SVM. Although the authors describe the model as a
privacy-preserving distributed SVM, they integrated
federated learning ideas to make D-SVM privacy-
preserving. For the experiment, we have taken 15
edge devices. We have used SVC class of Scikit-learn
(Sklearn) (Pedregosa et al., 2011) library for the SVM
classifier. In this experiment, only the linear kernel
is considered, and the regularization parameter of the
Algorithm 3: Local Poisonous SVM Training.
Data: dataset X
j
for j
th
edge device where
j ∈ 1 . . . S, and Attack type attack type
Result: Local Hyperplane Set H
j
if attack type = label f lip then
X
adv
j
←− {(x, (y + 1) mod k)|(x,y) ∈ X
j
};
end
else
Divide dataset x
j
into D
train
and D
val
evenly;
Determine np as the number of poisonous
points to generate X
adv
j
←−
np
S
i=1
optimal point gen(D
train
,D
val
)
end
Run SVM on the data set X
adv
j
;
generate k support vectors s
vectors for k
classes ;
H
j
←− [] ;
foreach i ∈ 0 . . . k do
w, b ←− s vectors[i].w, s vectors[i].b ;
add w||b to H
j
;
end
return H
j
;
SVM is fixed to C = 1. We have only considered bi-
nary classification for our experiment because most
research on poisoning data generation only consid-
ered binary SVM classifiers. Although, the attack
ideas can be researched for multi-class SVM.
In the following section, we first demonstrate the
effect of the poisoning attacks on the accuracy of
an F-SVM using classical MNIST handwritten digit
recognition dataset and CIFAR10 datasets. The ac-
curacy of the test dataset without any poisoning at-
tack is 91.3% in MNIST dataset and 75% in CIFR-
10 dataset. We use the Google colab platform’s note-
books to write our programs using python. Our pro-
gram is open-source
1
.
5.2 Dataset
MNIST Dataset. The MNIST database (Modi-
fied National Institute of Standards and Technology
database (LeCun, 1998)) contains 60,000 samples for
training and 10,000 samples for testing. The digits in
this dataset have been size-normalized and centered
in a fixed-size image. Each digit is represented as a
feature vector representing a 28*28 grayscaled image,
where each one of the 784 features represents the rel-
1
https://github.com/pkse-searcher/fsvm-pois-attack-d
efense
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
28

ative pixel intensity on a scale between [0, 255]. We
normalize each feature to be in the range of [0, 1].
Although the complete dataset involves ten different
digits, we consider the experiment of distinguishing
between digits 5 and 9, which is a binary classification
problem. Each edge device received 100 random sam-
ples with 1000 different samples for accuracy testing.
CIFAR-10 Dataset. The CIFAR-10 dataset (Cana-
dian Institute For Advanced Research (Krizhevsky
et al., 2009)) is a collection of 32*32 sized 60000
RGB images of 10 different classes (6000 color im-
ages per class). Although the complete dataset in-
volves several different images, we consider the ex-
periment of distinguishing between the images of air-
planes and automobiles. The image dimension is
3*1024 for RGB images with integer values rang-
ing [0-255]. We convert the images into fractional
grayscale in the range [0-1], reducing the dimension
to 1024. Each edge device gets 100 randomly selected
data with 1000 separate images for accuracy testing.
5.3 Simulation of Label Flipping Attack
on F-SVM and Results
We simulate the effect of label poisoning attacks
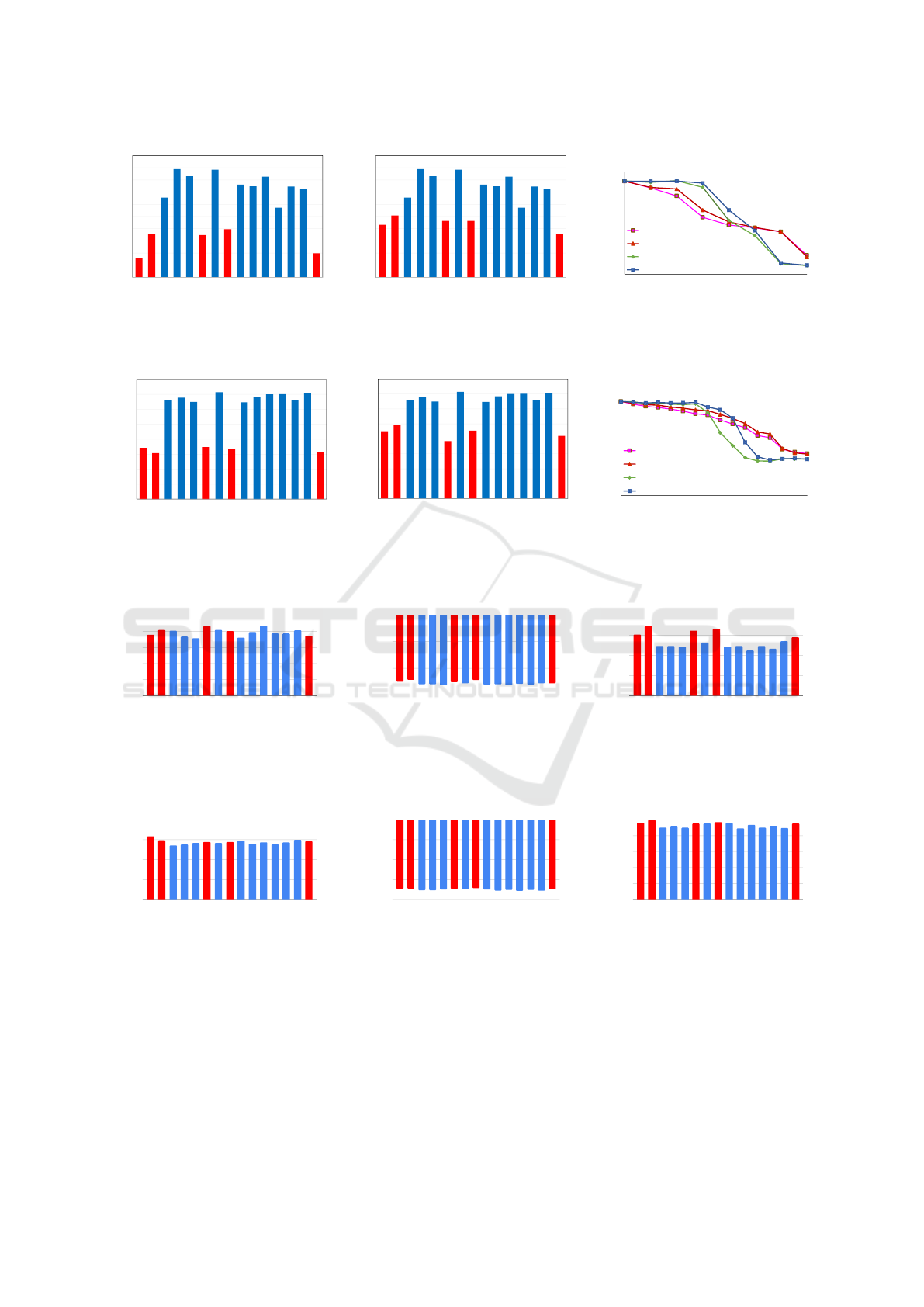
for the MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets. Fig. 2 and
Fig. 3 illustrate the impact of label-flipping attacks on
both edge devices and global F-SVM accuracy. Ac-
cording to these figures, the accuracy of adversarial
edge devices is significantly lower than that of non-
adversarial edge devices. The accuracy of edge de-
vices is depicted in Fig. 2-(a) and Fig. 3-(a). Fig. 2-
(c) and Fig. 3-(c) illustrate this attack’s impact on
the global F-SVM. We can see from the figures that
when only a small number of edge devices are ad-
versarial, the impact of the label-flipping attack on
global accuracy is negligible. That is because the
F-SVM algorithm, like SVM, is quite noise-resistant
(Suykens et al., 2002). Therefore, label-flipping at-
tacks are ineffective against a small number of ad-
versarial devices. Additionally, the convergence algo-
rithm appears more robust against label-flipping at-
tacks than clustering alone. However, for both the
MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets, Fig. 2-(c) and Fig. 3-
(c) demonstrate that global accuracy decreases signif-
icantly when one-third of the edge devices are adver-
sarial.
5.4 Simulation of Optimal Poisoning
Attack on F-SVM and Results
We simulate optimal poisoning attacks using SecML
(Melis et al., 2019), an open-source Python library
for the security evaluation of Machine Learning (ML)
algorithms. To simulate an optimal poisoning attack
in an edge device, we generate 10 optimal poisonous
points and use them as the training dataset. Our exper-
iments show that for a binary SVM classifier, a rea-
sonable value for the number of poison points should
be at least 10. More than 10 points do not signifi-
cantly decrease the accuracy. The effect of an optimal
poisoning attack on the edge devices’ accuracy is de-
picted in Fig. 2-(b) and Fig. 3-(b). According to these
figures, the accuracy of adversarial edge devices is
significantly lower than that of non-adversarial edge
devices.
From Fig. 2-(a, b) and Fig. 3-(a, b), we can see that
the more advanced optimal poisoning attack’s impact
on local SVM accuracy is less than that of the label-
flipping attack, which should not have been the case.
This is because the optimal poisoning attack gener-
ates poison points to be added to a training dataset to
introduce ambiguity. These poisonous points are not
intended to be used directly to train the SVM. How-
ever, experiments find that using them directly as the
training dataset significantly impacts global F-SVM
accuracy.
Fig. 2-(c) and Fig. 3-(c) represents the effect of
poisoning attacks on global F-SVM accuracy. When
no edge device is adversarial, global accuracy is al-
most 90% for the MNIST dataset and 70% for the
CIFAR-10 dataset. However, the accuracy decreases
as the number of adversarial edge devices increases.
Even a small percentage of adversarial devices can
significantly decrease global F-SVM accuracy in the
optimal poisoning attack. The impact of this attack is
significantly more harmful than the label-flipping at-
tack for a lower number of adversarial edge devices.
From the figures, we can observe that the presence
of one-third of adversarial devices decreases accuracy
by nearly 30% in MNIST dataset. However, when
more than half of the edge devices in both datasets are
adversarial, which is impractical, the label-flipping at-
tack is more effective than the optimal poisoning at-
tack.
6 DEFENSE STRATEGIES
From the experiments, we observe that, poisonous hy-
perplanes are somewhat different from non-poisonous
hyperplanes. Therefore, we evaluate three popular
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data Poisoning Attacks
29
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
AccuracyofLocalMachine
LocalMachine
(a)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
AccuracyofLocalMachine
LocalMachine
(b)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 1 3 5 7 9 11 15
AfterClustering(Optimal)
After Convergence(Optimal)
AfterClustering(Fliping)
AfterConvergence(Fliping)
Numberofadv.LocalMachines
AccuracyofGlobalMachine
(c)
Figure 2: Effect of (a) Label flipping attack, and (b) Optimum poisoning attack on edge devices for MNIST dataset. In this
experiment, edge devices 0, 1, 5, 7, 14 are adversarial. Effect of both poisoning attacks on global accuracy is presented in (c).
Red columns represent adversarial local machine and blue columns represent non-adversarial local machine.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
AccuracyofLocalMachine
LocalMachine
(a)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
AccuracyofLocalMachine
LocalMachine
(b)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
AfterClustering(Optimal)
After Convergence(Optimal)
AfterClustering(Fliping)
AfterConvergence(Fliping)
Numberofadv.LocalMachines
AccuracyofGlobalMachine
(c)
Figure 3: Effect of (a) Label flipping attack, and (b) Optimum poisoning attack on edge devices for CIFAR-10 dataset. In this
experiment, edge devices 0, 1, 5, 7, 14 are adversarial. Effect of both poisoning attacks on global accuracy is presented in (c).
Red columns represent adversarial local machine and blue columns represent non-adversarial local machine.
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Label Flipping Attack, MNIST, kNN
(a)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
-3000
-2000
-1000
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Label Flipping Attack, MNIST, Histogram
(b)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0
200
400
600
800
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Label Flipping Attack, MNIST, Copula
(c)
Figure 4: Adversarial edge device (0,1,5,7,14) detection for label flipping attack on MNIST dataset using (a) K-Nearest
Neighbor(K-NN), (b) Histogram, and (c) Copula based outlier detection algorithm. Red columns represent adversarial local
machine and blue columns represent non-adversarial local machine.
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Label Flipping Attack, CIFAR-10, KNN
(a)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
-4000
-3000
-2000
-1000
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Label Flipping Attack, CIFAR-10, Histogram
(b)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0
250
500
750
1000
1250
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Label Flipping Attack, CIFAR-10, Copula
(c)
Figure 5: Adversarial edge device (0,1,5,7,14) detection for label flipping attack on CIFAR-10 dataset using (a) K-Nearest
Neighbor(K-NN), (b) Histogram, and (c) Copula based outlier detection algorithm. Red columns represent adversarial local
machine and blue columns represent non-adversarial local machine.
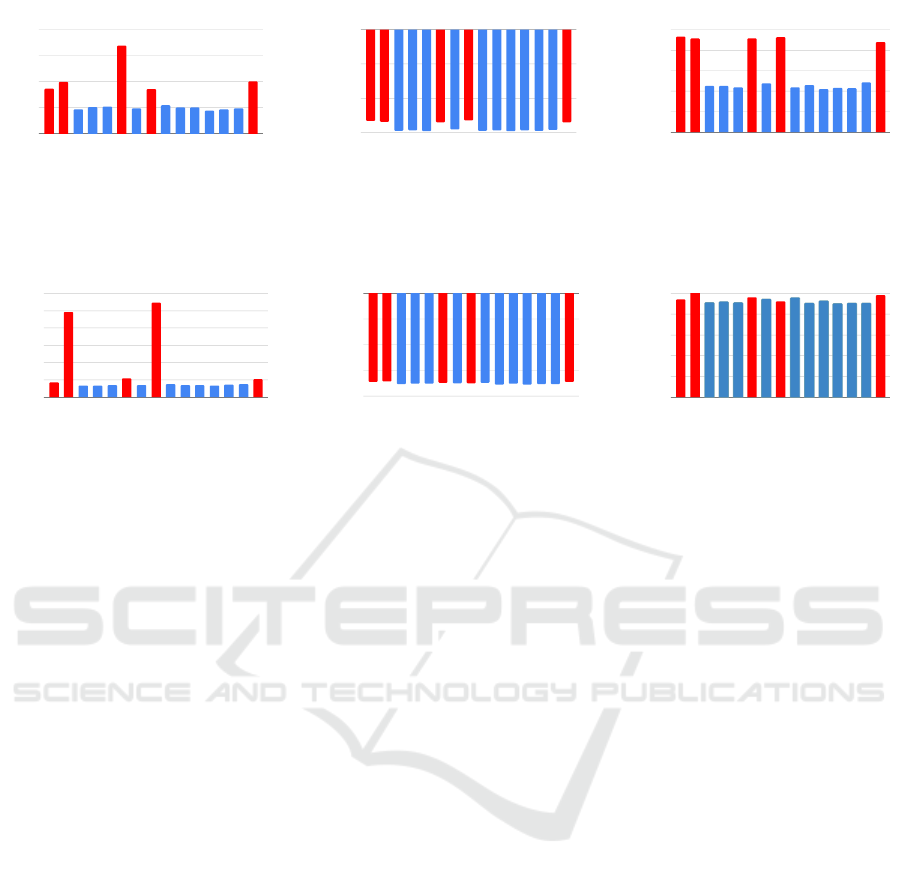
unsupervised outlier detection algorithms to deter-
mine if the attacks are easily detectable. These are:
1. K-Nearest Neighbor(K-NN) Algorithm (Ra-
maswamy et al., 2000),
2. Histogram Based Outlier Detection (Goldstein
and Dengel, 2012),
3. Copula Based Outlier Detection (Li et al., 2020).
We have used PyOD (Zhao et al., 2019) toolkit to
implement outlier detection algorithms. We applied
outlier detection algorithms on the whole hyperplane
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
30
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0
1
2
3
4
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Optimal Poisoning Attack, MNIST, KNN
(a)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
-6000
-4000
-2000
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Optimal Poisoning Attack, MNIST, Histogram
(b)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0
250
500
750
1000
1250
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Optimum Poisoning Attack, MNIST, Copula
(c)
Figure 6: Adversarial edge device (0,1,5,7,14) detection for optimal poisoning attack on MNIST dataset using (a) K-Nearest
Neighbor(K-NN), (b) Histogram, and (c) Copula based outlier detection algorithm. Red columns represent adversarial local
machine and blue columns represent non-adversarial local machine.
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Optimum Poisoning Attack, CIFAR-10, KNN
(a)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
-4000
-3000
-2000
-1000
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Optimum Poisoning Attack, CIFAR-10, Histogram
(b)
Local Machine
Outlier Score
0
250
500
750
1000
1250
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Optimum Poisoning Attack, CIFAR-10, Copula
(c)
Figure 7: Adversarial edge device (0,1,5,7,14) detection for optimal poisoning attack on CIFAR-10 dataset using (a) K-Nearest
Neighbor(K-NN), (b) Histogram, and (c) Copula based outlier detection algorithm. Red columns represent adversarial local
machine and blue columns represent non-adversarial local machine.
set in the global machine, H = H
1
,H
2
,. .. ,H
S
, without
any preprocessing and compared the outlier scores.
Fig. 4, 5, 6, 7 illustrate the results of outlier detection
algorithms. In all these experiments, we assume that
edge devices 0, 1, 5, 7, and 14 are adversarial. The
red color bars in the graphs indicate the outlier score
of these adversarial devices.
From these experiments, we observe that, label-
flipping attacks are nearly undetectable by K-NN and
Histogram-based outlier detectors. Copula-based out-
lier detector can somewhat detect label-flipping at-
tacks in the MNIST dataset but not in the CIFAR-
10 dataset. Therefore, label-flipping attacks appear
to be more resilient to naive outlier detectors. How-
ever, optimal poisoning attacks in the MNIST dataset
are detectable by all the outlier detectors. All the
detectors have higher outlier score for poisonous hy-
perplanes than the non-poisonous hyperplanes. How-
ever, only the K-NN algorithm performs satisfactorily
detecting this attack in the CIFAR-10 dataset. The
histogram-based detector misses the attack entirely in
the CIFAR-10 dataset.
The results are somewhat consistent with a pre-
vious research by (Paudice et al., 2018) where the
authors show to detect optimal poisoned points using
outlier detectors. A naive outlier detector with filter-
ing like (Paudice et al., 2018) can be a optimum de-
fense strategy. However, more research is needed to
optimize outlier detectors to detect poisonous hyper-
planes effectively.
Another defense mechanism is to keep some test-
ing data in the global machine and test the edge de-
vices accuracy on that training dataset. The local
SVM updates that significantly impact the error rate
for these testing data will be rejected (Fang et al.,
2020). Byzantine-robust federated averaging system
such as Krum (Blanchard et al., 2017), Trimmed
mean (Yin et al., 2018), and others can also be used
to provide some protection for loss of small accuracy.
We can also consider the defenses of other federated
learning algorithms like FLTrust (Cao et al., 2020) for
F-SVM.
7 CONCLUSIONS
F-SVM is a technology that enables distributed edge
devices to collectively learn a common SVM model
without sharing data samples. However, edge devices
are susceptible to poisoning attacks due to the dis-
tributed nature of federated learning. In federated set-
tings, attackers like viruses can gain access to edge
devices and poison the dataset. Dataset poisoning is
much easier than controlling the training process or
impersonating edge devices to the global server. This
paper examines the effect of data poisoning attacks on
global F-SVM accuracy. We ported two heavily re-
searched data poisoning attacks of SVM to federated
settings and checked their impact.
Experiments demonstrate that while label-flipping
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data Poisoning Attacks
31

attacks have a relatively insignificant effect on global
accuracy, optimal poisoning attacks can severely
hamper global F-SVM accuracy. However, the de-
fense mechanism of existing poisoning attacks will
not work in a federated setting. We tested some
naive outlier detectors to detect the attacks and ob-
served mixed results. Given the prevalence of fed-
erated learning, the poisoning attacks should be re-
garded as a significant threat. Therefore, any prac-
tical federated SVM system should at least employ
bare minimum defense mechanisms, such as anomaly
detection. Additionally, more robust defense mecha-
nisms need to be developed for Federate SVM.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been carried out in the department of
Computer Science and Engineering, Bangladesh Uni-
versity of Engineering and Technology (BUET). The
authors gratefully acknowledge the support and facil-
ities provided by BUET.
REFERENCES
Anisetti, M., Ardagna, C. A., Balestrucci, A., Bena, N.,
Damiani, E., and Yeun, C. Y. (2022). On the robust-
ness of ensemble-based machine learning against data
poisoning.
Bagdasaryan, E., Veit, A., Hua, Y., Estrin, D., and
Shmatikov, V. (2020). How to backdoor federated
learning. In International Conference on Artificial In-
telligence and Statistics, pages 2938–2948. PMLR.
Barreno, M., Nelson, B., Joseph, A. D., and Tygar, J. D.
(2010). The security of machine learning. Machine
Learning, 81(2):121–148.
Bhagoji, A. N., Chakraborty, S., Mittal, P., and Calo, S.
(2019). Analyzing federated learning through an ad-
versarial lens. In International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, pages 634–643. PMLR.
Biggio, B., Nelson, B., and Laskov, P. (2011). Support
vector machines under adversarial label noise. In
Asian conference on machine learning, pages 97–112.
PMLR.
Biggio, B., Nelson, B., and Laskov, P. (2012). Poison-
ing attacks against support vector machines. page
1467–1474.
Biggio, B. and Roli, F. (2018). Wild patterns: Ten years
after the rise of adversarial machine learning. Pattern
Recognition, 84:317–331.
Blanchard, P., El Mhamdi, E. M., Guerraoui, R., and
Stainer, J. (2017). Machine learning with adversaries:
Byzantine tolerant gradient descent. Advances in Neu-
ral Information Processing Systems, 30.
Bovenzi, G., Foggia, A., Santella, S., Testa, A., Persico,
V., and Pescap
´
e, A. (2022). Data poisoning attacks
against autoencoder-based anomaly detection models:
a robustness analysis. In ICC 2022 - IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Communications, pages 5427–
5432.
Cao, X., Fang, M., Liu, J., and Gong, N. Z. (2020). Fltrust:
Byzantine-robust federated learning via trust boot-
strapping. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.13995.
Chen, M., Yang, Z., Saad, W., Yin, C., Poor, H. V., and
Cui, S. (2020). A joint learning and communications
framework for federated learning over wireless net-
works. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communica-
tions, 20(1):269–283.
Dalvi, N., Domingos, P., Sanghai, S., and Verma, D. (2004).
Adversarial classification. In Proceedings of the tenth
ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowl-
edge discovery and data mining, pages 99–108.
Demontis, A., Melis, M., Pintor, M., Jagielski, M., Biggio,
B., Oprea, A., Nita-Rotaru, C., and Roli, F. (2019).
Why do adversarial attacks transfer? explaining trans-
ferability of evasion and poisoning attacks. In 28th
{USENIX} Security Symposium ({USENIX} Security
19), pages 321–338.
Ding, H., Yang, F., and Huang, J. (2021). Defending svms
against poisoning attacks: the hardness and dbscan
approach. In de Campos, C. and Maathuis, M. H.,
editors, Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh Conference
on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, volume 161
of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pages
268–278. PMLR.
Doku, R. and Rawat, D. B. (2021). Mitigating data poi-
soning attacks on a federated learning-edge comput-
ing network. In 2021 IEEE 18th Annual Consumer
Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC),
pages 1–6. IEEE.
Fang, M., Cao, X., Jia, J., and Gong, N. (2020). Local
model poisoning attacks to {Byzantine-Robust} fed-
erated learning. In 29th USENIX Security Symposium
(USENIX Security 20), pages 1605–1622.
Goldstein, M. and Dengel, A. (2012). Histogram-based
outlier score (hbos): A fast unsupervised anomaly de-
tection algorithm. KI-2012: Poster and Demo Track,
pages 59–63.
Hsu, R.-H., Wang, Y.-C., Fan, C.-I., Sun, B., Ban, T.,
Takahashi, T., Wu, T.-W., and Kao, S.-W. (2020). A
privacy-preserving federated learning system for an-
droid malware detection based on edge computing. In
2020 15th Asia Joint Conference on Information Se-
curity (AsiaJCIS), pages 128–136. IEEE.
Jagielski, M., Oprea, A., Biggio, B., Liu, C., Nita-Rotaru,
C., and Li, B. (2018). Manipulating machine learning:
Poisoning attacks and countermeasures for regression
learning. In 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and
Privacy (SP), pages 19–35. IEEE.
Kabir, T. and Adnan, M. A. (2019). A scalable algorithm for
multi-class support vector machine on geo-distributed
datasets. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on
Big Data (Big Data), pages 637–642. IEEE.
Kone
ˇ
cn
`
y, J., McMahan, H. B., Ramage, D., and Richt
´
arik,
P. (2016a). Federated optimization: Distributed ma-
chine learning for on-device intelligence. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1610.02527.
CLOSER 2023 - 13th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
32

Kone
ˇ
cn
`
y, J., McMahan, H. B., Yu, F. X., Richt
´
arik, P.,
Suresh, A. T., and Bacon, D. (2016b). Federated
learning: Strategies for improving communication ef-
ficiency. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.05492.
Krizhevsky, A., Hinton, G., et al. (2009). Learning multiple
layers of features from tiny images.
Laishram, R. and Phoha, V. V. (2016). Curie: A method for
protecting svm classifier from poisoning attack. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1606.01584.
LeCun, Y. (1998). The mnist database of handwritten digits.
http://yann. lecun. com/exdb/mnist/.
Li, Z., Zhao, Y., Botta, N., Ionescu, C., and Hu, X. (2020).
Copod: copula-based outlier detection. In 2020 IEEE
International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM),
pages 1118–1123. IEEE.
Mei, S. and Zhu, X. (2015). Using machine teaching to
identify optimal training-set attacks on machine learn-
ers. In Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial
Intelligence.
Melis, M., Demontis, A., Pintor, M., Sotgiu, A., and Big-
gio, B. (2019). secml: A python library for secure
and explainable machine learning. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1912.10013.
Mu
˜
noz-Gonz
´
alez, L., Biggio, B., Demontis, A., Paudice,
A., Wongrassamee, V., Lupu, E. C., and Roli, F.
(2017). Towards poisoning of deep learning algo-
rithms with back-gradient optimization. In Proceed-
ings of the 10th ACM workshop on artificial intelli-
gence and security, pages 27–38.
Paudice, A., Mu
˜
noz-Gonz
´
alez, L., Gyorgy, A., and Lupu,
E. C. (2018). Detection of adversarial training exam-
ples in poisoning attacks through anomaly detection.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.03041.
Paudice, A., Mu
˜
noz-Gonz
´
alez, L., and Lupu, E. C. (2019).
Label sanitization against label flipping poisoning at-
tacks. In Alzate, C., Monreale, A., Assem, H., Bifet,
A., Buda, T. S., Caglayan, B., Drury, B., Garc
´
ıa-
Mart
´
ın, E., Gavald
`
a, R., Koprinska, I., Kramer, S.,
Lavesson, N., Madden, M., Molloy, I., Nicolae, M.-I.,
and Sinn, M., editors, ECML PKDD 2018 Workshops,
pages 5–15, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos,
A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and
Duchesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
Pitropakis, N., Panaousis, E., Giannetsos, T., Anastasiadis,
E., and Loukas, G. (2019). A taxonomy and survey of
attacks against machine learning. Computer Science
Review, 34:100199.
Radford, B. J., Apolonio, L. M., Trias, A. J., and Simpson,
J. A. (2018). Network traffic anomaly detection using
recurrent neural networks. CoRR, abs/1803.10769.
Ramaswamy, S., Rastogi, R., and Shim, K. (2000). Efficient
algorithms for mining outliers from large data sets. In
Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD international
conference on Management of data, pages 427–438.
Shejwalkar, V., Houmansadr, A., Kairouz, P., and Ramage,
D. (2022). Back to the drawing board: A critical eval-
uation of poisoning attacks on production federated
learning. In IEEE Symposium on Security and Pri-
vacy.
Steinhardt, J., Koh, P. W., and Liang, P. (2017). Certified
defenses for data poisoning attacks. In Proceedings of
the 31st International Conference on Neural Informa-
tion Processing Systems, pages 3520–3532.
Sun, G., Cong, Y., Dong, J., Wang, Q., Lyu, L., and Liu, J.
(2021). Data poisoning attacks on federated machine
learning. IEEE Internet of Things Journal.
Suykens, J. A., De Brabanter, J., Lukas, L., and Vandewalle,
J. (2002). Weighted least squares support vector ma-
chines: robustness and sparse approximation. Neuro-
computing, 48(1-4):85–105.
Tolpegin, V., Truex, S., Gursoy, M. E., and Liu, L. (2020).
Data poisoning attacks against federated learning sys-
tems. In European Symposium on Research in Com-
puter Security, pages 480–501. Springer.
Wang, S., Chen, M., Saad, W., and Yin, C. (2020). Fed-
erated learning for energy-efficient task computing in
wireless networks. In ICC 2020-2020 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Communications (ICC), pages
1–6. IEEE.
Xiao, H., Biggio, B., Brown, G., Fumera, G., Eckert, C.,
and Roli, F. (2015). Is feature selection secure against
training data poisoning? In international conference
on machine learning, pages 1689–1698. PMLR.
Yin, D., Chen, Y., Kannan, R., and Bartlett, P. (2018).
Byzantine-robust distributed learning: Towards opti-
mal statistical rates. In International Conference on
Machine Learning, pages 5650–5659. PMLR.
Zhang, R. and Zhu, Q. (2017). A game-theoretic defense
against data poisoning attacks in distributed support
vector machines. In 2017 IEEE 56th Annual Confer-
ence on Decision and Control (CDC), pages 4582–
4587. IEEE.
Zhao, Y., Nasrullah, Z., and Li, Z. (2019). Pyod: A python
toolbox for scalable outlier detection. Journal of Ma-
chine Learning Research, 20(96):1–7.
Zhou, Y., Kantarcioglu, M., Thuraisingham, B., and Xi, B.
(2012). Adversarial support vector machine learning.
In Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD interna-
tional conference on Knowledge discovery and data
mining, pages 1059–1067.
Zhu, Y., Cui, L., Ding, Z., Li, L., Liu, Y., and Hao, Z.
(2022). Black box attack and network intrusion de-
tection using machine learning for malicious traffic.
Computers & Security, 123:102922.
Towards Poisoning of Federated Support Vector Machines with Data Poisoning Attacks
33
