
Development of A Self-Directed Learning Model in Entrepreneurship
Courses to Develop Problem-Solving Ability Among Students
Sumanti
1a
, Yesmira Syamra
2b
, Zahara
3c
, Desri Nora
4d
and Mira Chairani
3e
1
Geography Education, Al-Muslim University, Almuslim street, Aceh, Indonesia
2
Economic Education, UPGRISBA, Gunung Pangilun Street, Padang, Indonesia
3
Economic Education, Al-Muslim University, Almuslim Street, Aceh, Indonesia
4
Sociology Education, Universitas Negeri Padang, Prof. Dr. Hamka Street, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Entrepreneurship, Learning Model, Self-Directed Learning, Problem-Solving.
Abstract: According to preliminary research conducted at Al-Muslim University's Geography Study Program, there are
numerous issues with Entrepreneurship education, including the poor development of problem-solving skills
in student entrepreneurship courses. Participation in learning activities has not increased due to problem-
solving student activities. There are insufficient learning materials, and the paradigms used in education do
not enable students to develop their knowledge. Based on these conditions, this type of study is considered
Research and Development (R&D). The employed model of development is the Plomp Model (2013). The
stages of development are as follows: preliminary/initial research, product design, and assessment/evaluation.
The validity and usability of product design are measured via formative evaluation, including self-evaluation
and one-on-one. A summative evaluation is conducted at the assessment stage to establish the product's
effectiveness. In addition to conversation, observation, interviews, questionnaires, and learning achievement
exams, focus group discussions were used to obtain research data (FGD). The gathered information was
examined using descriptive and inferential statistics.
1 INTRODUCTION
National Education seeks to explore and develop the
potential and skills of students for them to become
people who have faith, are devoted to God Almighty,
have a noble character, are healthy, knowledgeable,
capable of creative, and independent, as well as
democratic and responsible citizens. (Ministry of
National Education, 2003). In line with the 21
st
-
century educational framework, students must have
skills and abilities, namely the ability to communicate
well (communicative), be creative (creativity), the
ability to work with other parties (collaborative), and
have high creativity (BSNP, 2010). The realization of
these hopes is manifested in the form of the K22
curriculum or what is known as the Independent
Campus Learning Curriculum (MBKM). Freedom to
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5292-346X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2655-885X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1712-2931
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-7183-1085
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4343-854X
learn. The independent campus is a government
policy to encourage students to master various
knowledge that can be useful for entering the world
of work.
Learning activities are not material-intensive but
essential. Students can take credits outside the study
program at other tertiary or higher education
institutions in the independent learning program. The
aim is to gain experience or new knowledge in
developing students' insights. One of the activities
outside of higher education is entrepreneurial
activities. The competency achievements of
independent learning independent campuses in this
entrepreneurship course are producing goods and
services and formulating policy objectives and
strategies in entrepreneurship. It is a critical learning
system based on analysis, reasoning, and
224
Sumanti, ., Syamra, Y., Zahara, ., Nora, D. and Chairani, M.
Development of A Self-Directed Learning Model in Entrepreneurship Courses to Develop Problem-Solving Ability Among Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0012198900003738
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Innovation in Education (ICoIE 4 2022) - Digital Era Education After the Pandemic, pages 224-229
ISBN: 978-989-758-669-9; ISSN: 2975-9676
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

interpretation, not memorization, to achieve the
curriculum's and educational goals' expectations. It
aims to change the way students think. That is, they
always desire to find out and make observations.
Students are also directed to formulate problems, not
only solve problems. Learners are trained to sharpen
their reasoning power by thinking analytically. So the
Geography Study Program sets entrepreneurship
courses with a weight of 2 credits. The expected
learning outcomes are that students can interpret the
role of entrepreneurs in the country and apply the
skills that an entrepreneur must have to develop
entrepreneurial attitudes and profiles that become a
true entrepreneur (Indonesian National Qualification-
Based Curriculum, 2020).
However, based on searches on Geography study
programs, especially fifth semester (V) students in
entrepreneurship courses, students attending lectures
is still like lecturing pulpit. Students silently listen as
if only the lecturer is the only source of learning, so
learning is monotonous and boring. Students are only
passive. Inactive, unable to think critically. In
response to the facts and phenomena above, it is
necessary to find learning solutions, namely changing
learning models and strategies. One of the learning
models considered appropriate is the Self-Directed
Learning (SDL) learning model. This learning model
is innovative. This SDL mode provides opportunities
for students to create and diagnose, formulate
learning objectives, select and implement learning
strategies, and evaluate learning outcomes (Pluskwik
et al., 2018; Ramadhan & Jalinus, 2021; Scroccaro &
Rossi, 2021; Silamut & Petsangsri, 2020). As for the
syntax or steps of the SDL model, there are three
kinds: planning, students planning learning locations,
and times when students feel comfortable.
Furthermore, students determine the learning
components and determine achievement targets. Then
the next step is to monitor. Namely, students observe
learning so that learning activities will be more
meaningful and then carry out evaluations. The Self
Directed Learning model ignores religious or
religious values in students according to national
education goals (Beach, 2017; LaTour & Noel, 2021;
Silamut & Petsangsri, 2020). So this model only
emphasizes knowledge alone. Religion. The model
developed is called Insert Self-Directed Learning
(ISDL). This study aims to develop a self-directed
learning model that is valid, practical, and effective in
the Entrepreneurship course at the teaching and
educational faculty of the geography study program.
The philosophical foundation used in the Insert
Self Directed Learning (ISDL) Learning model is the
educational philosophy that Ki Hajar Dewantara put
forward. This philosophy is a convergence of the
philosophy of progressivism regarding the natural
ability of students to overcome the problems they face
by providing the broadest possible freedom of
thought (Wichadee, 2011). Meanwhile, the learning
theory used relies on constructivist learning theory,
which reveals that knowledge is the result of human
constructs, meaning that here students, through their
interactions with objects, the environment,
phenomena, and experiences, will construct
knowledge (Jonassen et al., 1995; Joyce et al., 2015).
Learning is processed and where activities
originate or are transformed through training
procedures (whether in the laboratory or a natural
environment). Good learning embraces learning
without boundaries (Joyce et al., 2015; Kurniati et al.,
2020; Pateliya, 2013; Szmidt & Majewska-
Owczarek, 2020). To embrace diverse students, you
have to use a suitable model. The model can be a
guideline explaining what the teacher must do to help
students achieve learning goals (Schiering et al.,
2012). The Learning Model is a framework of
reference for learning that is carried out based on
patterns that have been systematically designed. So
that learning is carried out effectively and efficiently
(Mousoulides, 2011).
Learning Model Self Directed Learning (SDL) is
a learning process that is carried out based on one's
desires and initiative. Essentially, this model is
independent learning (Beach, 2017; Deng et al., 2022;
Mamun et al., 2020; Ramadhan & Jalinus, 2021).In
line with the opinion above, the direct instruction
learning model is specifically designed to support
student learning related to well-structured declarative
and procedural knowledge that can be taught with a
gradual pattern of activities step by step. The Self-
Directed Learning model will increase students'
problem-solving abilities. Problem-solving ability is
a thought or ability to find a solution or way out of a
problem or problem with very mature and reasonable
considerations. (Koh et al., 2010).
2 METHOD
This study involves both research and development
(Research and Development). This research has
generated a learning model titled Insert Self-Directed
Learning (SDL). This learning paradigm enhances
students' capacity to solve valid, practical, and
efficient problems. The development design
employed is Plomp, which comprises many stages: 1)
preliminary study, 2) prototype phase, and 3)
evaluation stage. (Plomp, 2013). Data analysis was
Development of A Self-Directed Learning Model in Entrepreneurship Courses to Develop Problem-Solving Ability Among Students
225

carried out in a qualitative and quantitative
descriptive manner. The test of the model's validity
uses experts' opinions (judgment experts). The
validators/experts were asked for their opinions about
the models and products being developed. The
validation developed includes constructing validity
and content validity. The practicality test of the model
is determined from the results of assessments by
observers and practitioners. Practicality regarding the
product's ease of use and understanding in learning.
In order to determine the validity and applicability
of the results provided by the validator, practitioner,
or assessor, an intraclass correlation test was
conducted with the SPSS program's Intraclass
Correlation Coefficient (ICC). An analysis of the
effectiveness of the Insert Self-directed Learning
learning model was derived from a problem-solving
ability test and a learning achievement test
administered to students in entrepreneurship courses.
The evaluation uses a rubric that is evaluated from
three perspectives: 1) identifying what is known
about a problem; 2) formulating the problem,
followed by determining the best approach and being
able to interpret the problem; and 3) solving the
problem analytically and methodically. Exam
questions are in essay format. The product's
effectiveness was evaluated using a t-test. This
study's participants were fifth-semester students in
unit C of the geography study program. The trial
group was randomly selected from the entire research
subject population. This study's participants were
fifth-semester students from five classes. They
gathered information through observation,
interviews, and focus group discussions (FGD).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This research was carried out referring to the
development of Plomp, which includes:1)
Preliminary research (preliminary research);2)
Prototype Phase (Prototyping phase); 3) Assessment
stage (Plomp & Nienke, 2013; Van den Akker, 2006).
The results of the study are as follows:
3.1 Preliminary Research
In the needs analysis stage, the importance of the self-
directed learning (SDL) model is analyzed in
entrepreneurial learning. Needs analysis includes a)
problem analysis during learning activities. b)
curriculum analysis. The curriculum analysis that is
carried out is the application of the curriculum, the
scope of material and learning methods, and the goals
and strategies for achieving this are carried out to
know the problems in the field. This data is intended
as a basis for the development of learning models.
Based on preliminary research results, it was found
that entrepreneurship learning was carried out in the
form of pulpit lectures, and monotonous learning was
still rote. No lecturers in the learning process use the
self-directed learning model because it takes a long
time and disrupts the previously prepared lesson
plans. From a curriculum point of view, when viewed
from the scope of the material, it is generally in the
form of a collection of theories and concepts so that
learning cannot make students think analytically. The
critical and reasoning power of students is weak. Seen
from the lecturers generally do not prepare learning
tools properly, such as semester learning plans (RPS)
media and other learning resources. At the same time,
the analysis of students (students) reveals a feeling of
boredom when attending entrepreneurship lectures
because learning is monotonous and does not involve
students actively in the learning process. A design or
learning model is prepared as a book based on
searches and information obtained from lecturers,
students, and related parties. The self-directed
learning model book is designed to contain four parts,
namely: first, the rational model contains the critical
background and urgency of developing the self-
directed learning model; secondly, supporting
theories contain learning theories put forward by
several experts, the third model component contains
philosophical and theoretical foundations model, and
the fourth implementation of the problem-based self-
directed learning model contains the syntax of the
social system and the principle of reaction to
instructional impact and accompanying impact.
Learning components according to the existing
problems
Insert Self Directed Learning learning is based on
the results of preliminary research conducted and
studies of learning theories and learning models
equipped with syntax where the syntax is one part of
the learning model that contains references to models
in actions or activities that are arranged based on clear
stages of the entire activity. Moreover, the stages are
carried out by the teacher in learning. The results of
these studies can be guidelines for compiling the
syntax of the developed model. The syntax of the
model is designed to pay attention to how to invite
students to be actively involved and feel directly as
part of the learning process. The model syntax was
developed from the Self-directed Learning model
proposed by. Song & Hill as for the syntax of the
Insert Self Directed Learning (ISDL) learning model.
(1) the activity starts before the students read the
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
226
Asmaul husnah together, (2) the lecturer divides the
student groups consisting of 3-4 students to make
plans about the desired learning components, (4)
students carry out learning in a place where preferred.
(5) students with their groups carry out the discussion.
To identify learning activities (6), further class
meetings are held, and the teacher gives feedback and
evaluates learning to know how far students have
mastered the learning components that have been
implemented.
Table 1: Theory Analysis Results in the Development of
Investigation-Based Learning Models.
No
Theory, Concept, and
Material
Role
1 Model Construct By
Joyce & Well (1992,
2000), Personal,
Benny A (2011),
Rusman(2012), Kemp
et al. (1994)
For the preparation of
model components
(syntax, reaction
principles, social
systems, model impacts,
and model support
systems
2 Model development by
Chandra 2014 and
Pum
p
s
(
2013
)
Guide to model
development stages
3 Philosophy of learning
(constructivist theory)
initiated by Mark
Baldwin
The basic concepts of
developing knowledge
underlie model
development and
b
uildin
g
model s
y
ntax
4 theoretical basis
Cognitive learning
theory-
Constructivism
Problem-Solving
Theory
Learning model Self-
directed Learning
Santrock (2010), Slavin
(2011)
Gredler (2011), Suparno
(1997)
Jonassen (1997), Kapur
(2015)
Carin (1997) Cindy &
hamello
David Johnson &
Johnson
Richard I. Arend (2008)
5 perspective(learning
theories: Educational
Perspective) by Dale H
(2012), Learning and
Learning by Dimyati
(2009), E-Learning
theory. Hartley
[Hartley, 2001and
Communications
Hovland in Mulyana
(2007:68)Darmansyah
(
2011
)
To construct self-
directed learning
(ISDL), insert model
syntax.
6 The cooperative
learning model by
Robert E. Slavin
(2008), active learning
b
y Mel Silberman
For reference
comparison of model
development
No
Theory, Concept, and
Material
Role
(2002), and CTL by
Elaine Jhonson (2010),
7 Analysis of
Approaches, Methods,
Strategies, and
Learning Models by
(Iru & La Ode 2012).
Designing Effective
Instruction by Kemp et
al. (1994)
Teaching and Learning
Interaction and
Motivation by
Sardiman (2011)
(
Russman, 2012
)
.
To devise social
systems, reaction
principles, and impact
models
3.2 Prototype Stage
The development of the self-directed learning model
is based on the Self-directed Learning model
proposed in the model book consisting of several
structures as shown below.
The structure is contained in the model book.
Table 2: Model’s Book Component.
Model Boo
k
Foreword
List of contents
Introduction
Rational Learning Model Self-Directed Learning
Philosophical Foundation and theoretical models
Implementation of models
Model syntax
Social system
Reaction system
Instructional impact
Companion impact
Supporting products
References
Author Profile
3.3 Product Validation
The results of product validation carried out by five
experts/validators showed that the insert self-directed
learning (SDl) model proved valid, as data processing
results showed that the result was > 3.20. The model
book's scoreIntraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC)
amounted to 0.885.
Development of A Self-Directed Learning Model in Entrepreneurship Courses to Develop Problem-Solving Ability Among Students
227
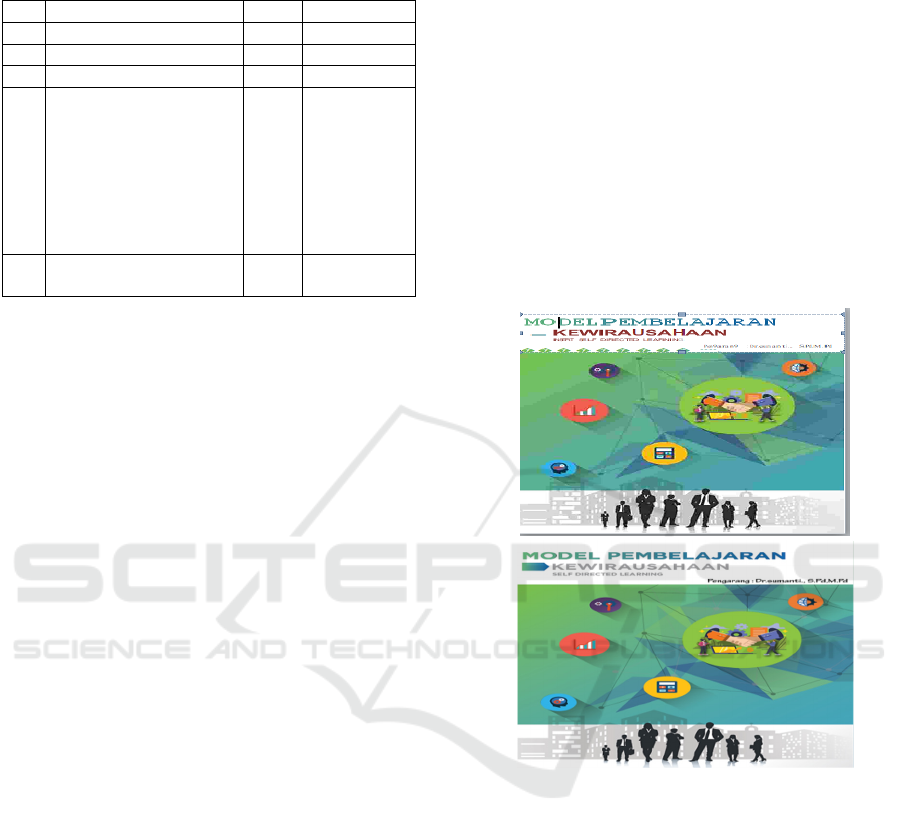
Table 3: Summary of Book Validation Results Insert Self-
Directed Learning Model.
No Assessment Aspect
K
Categor
y
1 Book Construct 0.85 Very vali
d
2 Rational Model 0.87 Very vali
d
3 Su
pp
ortin
g
Theor
y
0.82 Ver
y
vali
d
4 Model Structure Self-
Directed Learning
a. Syntax
b. Social system
c. Reaction Principle
d. Support System
e. Instructional and
Accompaniment Impact
0.79
0.84
0.87
0.89
0.89
0.87
Valid
Very valid
Very valid
Very valid
Very valid
Very valid
5 Model Implementation
in Learning
0.89 Very valid
Source: Processed Primary Data
The model book was valid and could be continued
at other stages. However, there were several essential
suggestions from the validator for improving the
model book, especially the use of grammatical words,
letters, and coloring and the structure of the model.
Then the next step is product revision in the form of
a model book.
3.4 Practicality
3.4.1 Practicality of the Self-Directed
Learning Insert Learning Model in the
Entrepreneurship Course to Improve
Geography Problem-Solving Skills
Al-Muslim University's analysis of implementing the
learning model Insert Self-Directed Learning in
entrepreneurship courses. Data collected from three
observers showed that the average score for all
aspects was 4.75. Thus, implementing the learning
model Self Directed Learning in entrepreneurship
courses to enhance problem-solving skills is
conducted in particular categories. The intraclass
correlation test for the model implementation yields a
value of 0.186. It indicates a slight correlation
between assessors in determining the feasibility of the
model, i.e., the value of the learning model itself.
Experts/validators have provided well-executed
Directed Learning in Entrepreneurship courses to
enhance problem-solving skills. There is only enough
correlation between validators to determine the
practicability of the model. Observer observation
revealed that using learning models, Self-Directed
Learning in Entrepreneurship courses to enhance
problem-solving skills, and using teacher books and
student books in the learning process conforms to the
established criteria in terms of practicality.
3.4.2 Stage Focus Group Discussion (Focus
Group Discussion/ FGD)
The results of the Focus Group Discussion included
critiques and recommendations from FGD U
participants. Participants in the FGD suggested using
grammar and spelling consistent with Indonesian
spelling. As with student textbooks, the front cover
must be revised, but the images used in model
textbooks already support the description. The results
of this FGD indicate that the problem-based learning
model, supported by Facebook, teacher's books, and
student books, is reasonable and practicable. The
results of product revisions are known as prototype
products.
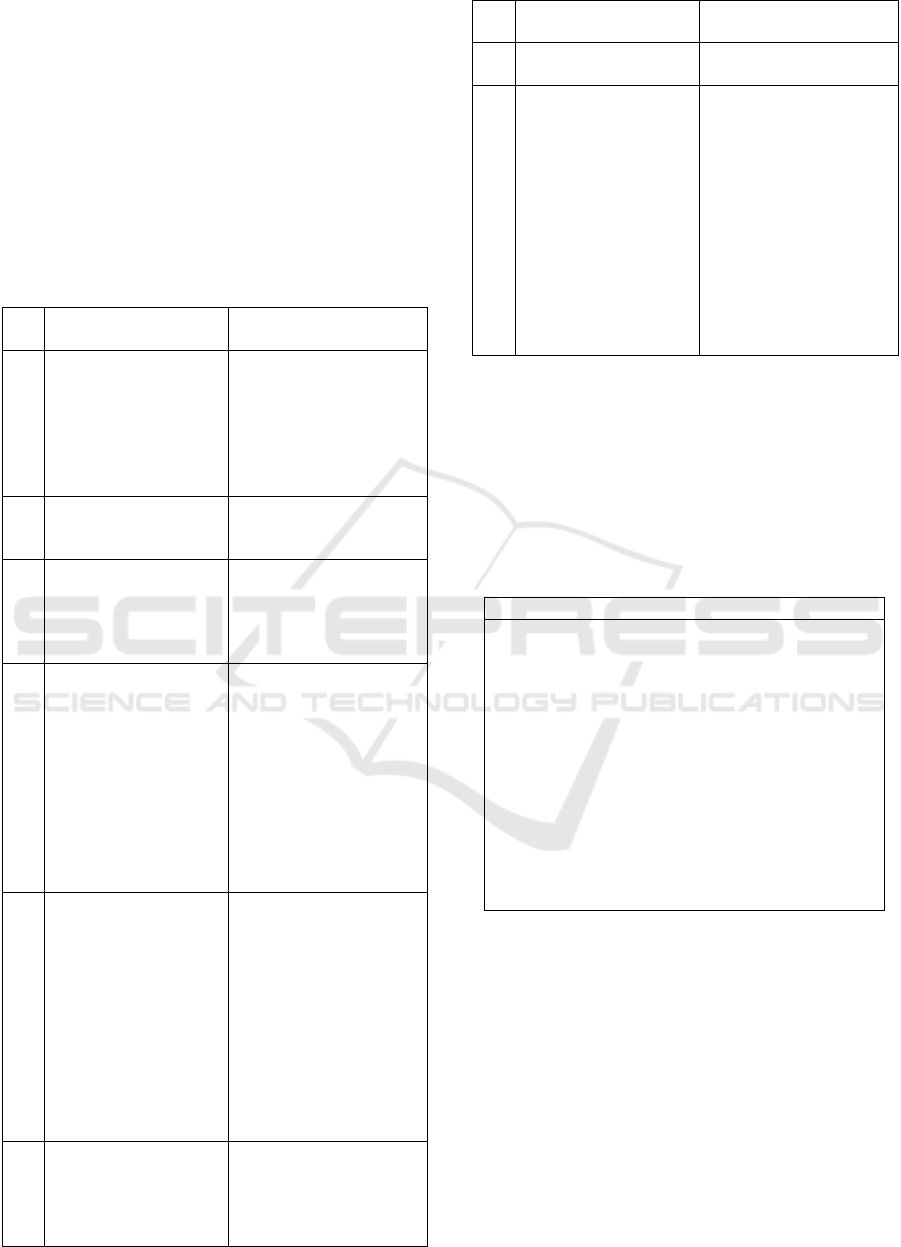
Figure 1: Model Book Cover before and after Revision.
3.4.3 Effectiveness Test
Effectiveness in terms of development, activity,
observation sheets, and the development of
entrepreneurial problem-solving skills is obtained
through learning achievement tests in the form of
assessment essays carried out from the learning
rubric. Using t-test analysis obtained a significance
level of 0.01.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of field research regarding the
development of the Self-Directed Learning model,
ICoIE 4 2022 - The Fourth International Conference on Innovation in Education
228

the Insert Self Directed Learning model using the
development steps proposed by Plump are as follows.
1. The Insert Self Directed Learning model book,
after being validated by experts consisting of
discussion experts, material experts, and design
experts, is declared valid and suitable for use.
2. Based on the assessment of observers,
practitioners, and users, the Self-Directed
Learning book states that the model book is
convenient because learning is carried out well
without any obstacles, and students enjoy the
process of learning.
3. When observing the learning activities, learning
motivation, and problem-solving abilities, data
was obtained on students' problem-solving
abilities development, as evidenced by very
satisfying learning outcomes.
4. The self-directed learning model was developed
and called Insert Self Directed Learning (ISDL)
so that lecturers can apply it in entrepreneurship
courses because this ISDl learning model has been
proven to be valid, practical, and effective in the
learning process, and students can use this model
and make a reference in subsequent research.
The development of the self-directed learning model
has produced a product or Novelty in the form of a
valid, practical, and influential Insert Self Directed
Learning (ISDL) model book for students in
Entrepreneurship courses.
REFERENCES
Beach, P. (2017). Self-directed online learning: A
theoretical model for understanding elementary
teachers’ online learning experiences. Teaching and
Teacher Education, 61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.
2016.10.007
Deng, C., Wang, Y., Qin, C., Fu, Y., & Lu, W. (2022). Self-
directed online machine learning for topology
optimization. Nature Communications, 13(1). https://
doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27713-7
Jonassen, D., Davidson, M., Collins, M., Campbell, J., &
Haag, B. B. (1995). Constructivism and Computer-
Mediated Communication in Distance Education.
American Journal of Distance Education, 9(2), 7–26.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08923649509526885
Joyce, B., Weil, M., & Calhoun, E. (2015). Models of
Teaching (9th Edition). Pearson. https://doi.org/10.
4324/9780429398117-5
Koh, J. H. L., Herring, S. C., & Hew, K. F. (2010). Project-
based learning and student knowledge construction
during asynchronous online discussion. Internet and
Higher Education, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.iheduc.2010.09.003
Kurniati, E., Jufrizal, & Jufri. (2020). Communicative
Games in Teaching English at Elementary Schools in
Jambi. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.200306.009
LaTour, K. A., & Noel, H. N. (2021). Self-Directed
Learning Online: An Opportunity to Binge. Journal of
Marketing Education, 43(2). https://doi.org/10.117
7/0273475320987295
Mamun, M. A. Al, Lawrie, G., & Wright, T. (2020).
Instructional design of scaffolded online learning
modules for self-directed and inquiry-based learning
environments. Computers and Education, 144. https://
doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103695
Mousoulides, E. &. (2011). Models and Modeling:
Cognitive Tools for Scientific Enquiry. Springer.
Pateliya, Y. P. (2013). An Introduction to Modern Models
of Teaching. International Journal for Research in
Education (IJRE), 2(2).
Plomp & Nienke. (2013). Introduction to Educational
Design Research: An Introduction. Educational Design
Research.
Plomp, T. (2013). Educational Design Research: A
Introduction. In Educational Design Research.
Pluskwik, E., Leung, E., & Lillesve, A. (2018). The
growing entrepreneurial mindset in interdisciplinary
student engineers: Experiences of a project-based
engineering program. ASEE Annual Conference and
Exposition, Conference Proceedings, 2018-June.
https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2--30565
Ramadhan, A. A., & Jalinus, N. (2021). The Development
of E-Module Based on Learning Models of Self
Directed Learning in Welding Subject. JURNAL
PENDIDIKAN TEKNOLOGI KEJURUAN, 4(2).
https://doi.org/10.24036/jptk.v4i2.16923
Schiering, M. S., Bogner, D., & Buli-holmberg, J. (2012).
Teaching and learning: a model for academic and social
cognition. In Choice Reviews Online (Vol. 49, Issue
06). https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.49-3394
Scroccaro, A., & Rossi, A. (2021). Start-up lab: A
springboard for university entrepreneurship and
students’ start-ups. Proceedings of the European
Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship,
ECIE. https://doi.org/10.34190/EIE.21.229
Silamut, A. acha, & Petsangsri, S. (2020). Self-directed
learning with knowledge management model to
enhance digital literacy abilities. Education and
Information Technologies, 25(6). https://doi.org/10.
1007/s10639-020-10187-3
Szmidt, K. J., & Majewska-Owczarek, A. (2020).
Theoretical Models of Teaching Creativity-Critical
Review. Creativity, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.2478/ctra-
2020-0004
Van den Akker, J. (2006). Educational Design Research.
Educational Design Research. https://doi.org/10.
4324/9780203088364
Wichadee, S. (2011). Developing The Self-Directed
Learning Instructional Model To Enhance English
Reading Ability And Self-Directed Learning Of
Undergraduate Students. Journal of College Teaching
& Learning (TLC), 8(12). https://doi.org/1
0.19030/tlc.v8i12.6620
Development of A Self-Directed Learning Model in Entrepreneurship Courses to Develop Problem-Solving Ability Among Students
229
