
Research on Spatial Agglomeration and Development Strategy of
Feed Enterprises Based on GIS Geographic Data Mining
Defa Li
*a
and Changfen Shao
b
Chongqing Tourism Vocational College, Zhoubai Street, Qianjiang District, Chongqing, China
Keywords: Teed Enterprises, Data Mining, Industrial Agglomeration, Spatial Distribution.
Abstract: Enterprise agglomeration is an important indicator of industrial scale development. Studying the spatial
agglomeration level and regional differences of feed enterprises can provide reference for the development
and spatial layout of feed industry. Based on the spatial distribution data of feed enterprises, ArcGIS spatial
analysis technology was used to study the spatial agglomeration and distribution of feed enterprises in China.
The results showed that: (1) The spatial agglomeration of feed enterprises in China was obvious and had a
certain spatial agglomeration effect. (2) The spatial distribution of China 's feed enterprises has the typical
characteristics of ' Hu Huanyong Line ', showing a dense southeast and sparse northwest; (3) China has
formed a number of feed enterprises gathering center, and the trend of industrial cluster development is
becoming increasingly evident; (4) The regional differences of China 's feed enterprises are large, and the
level of industrial agglomeration needs to be improved. Therefore, it is of great significance to achieve
optimal allocation of resources and optimize the structure of feed industry by strengthening the regional
division of labor and cooperation and playing the leading role of feed enterprise cluster.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Industrial agglomeration is an important
phenomenon in the process of economic
development and industrialization, which refers to
the mechanism of a certain number of enterprises in
the same industry to gather in a designated
geographical area to seek agglomeration benefits,
which is a geographical phenomenon in the process
of the evolution of an industry into an advantageous
industry, which plays an important role in promoting
the development of spatial agglomeration of regional
economic entities and achieving economies of scale,
and has become the model choice for promoting
economic development in many regions (Wang
2019). Based on the analysis of the level and process
of industrial agglomeration, the relevant research
results take market size, transportation conditions,
policy support, economic level, resource endowment
and urbanization level as the main factors affecting
industrial agglomeration (GAO 2022, MA 2021). In
terms of the benefit evaluation of industrial
agglomeration, some scholars have studied the role
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7781-0843
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4572-6011
and impact of the agglomeration effect of different
industries on socio-economic development and
industrial layout optimization (LI 2021, LIU 2021);
In terms of measuring the level of industrial
agglomeration, some scholars used methods such as
industry concentration, location entropy index,
spatial Gini coefficient, and Moran index to measure
the agglomeration level of relevant industries
(YE
2022). There are also relevant research results from
the perspective of industrial agglomeration, the
countermeasures and measures for the development
of dairy industry and logistics industry
agglomeration and the construction of overseas
industrial agglomeration areas are demonstrated and
analyzed (LI 2016); At the same time, based on
different research scopes and regional differences,
relevant scholars have conducted empirical research
on the characteristics of industrial agglomeration
and the impact of industrial agglomeration on
economic growth (GUO 2021, LUO 2021). In
summary, industrial agglomeration is a spatial
agglomeration of various resource elements formed
within a certain geographical range under the action
of different influencing factors, which plays an
important role in promoting regional social and
economic development.
244
Li, D. and Shao, C.
Research on Spatial Agglomeration and Development Strategy of Feed Enterprises Based on GIS Geographic Data Mining.
DOI: 10.5220/0012072800003624
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2022), pages 244-249
ISBN: 978-989-758-658-3
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Based on the provincial panel data of feed
enterprises, this paper measures the agglomeration
level of feed enterprises from the perspective of
industrial agglomeration development, analyzes the
spatial agglomeration level and spatial distribution
characteristics of feed enterprises, aims to simulate
the development stage and temporal and spatial
evolution characteristics of feed industry, so as to
obtain the level division of spatial agglomeration
development of the national feed industry, and
provide a scientific basis for optimizing the spatial
layout of feed industry, promoting the large-scale
development of feed industry and realizing the
optimal allocation of feed industry resources.
2 RESEARCH MATERIALS AND
METHODS
2.1 Research Materials
The national basic geographic data required for the
study came from the Resource and Environmental
Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/) of
the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the data of
China's provincial administrative boundaries in
2015, which was edited and operated based on
ArcGIS 10.2, and used as the basic map data for
kernel density spatial analysis.
The feed enterprise data comes from the official
website (https://www.tianyancha.com/), and the
directory of feed enterprises with a registered capital
of more than 20 million yuan in each province (city)
in the livestock breeding industry as of April 8, 2022
is obtained, including the enterprise name, registered
capital, date of establishment, number of insured
persons, registered address, business scope and other
characteristic data, and a total of 4,775 feed
enterprises were obtained after screening. ArcGIS
10.2 spatial analysis software was used to spatialize
the obtained feed enterprises according to the
address, and spatially matched with the national
vector map to obtain the point data of the spatial
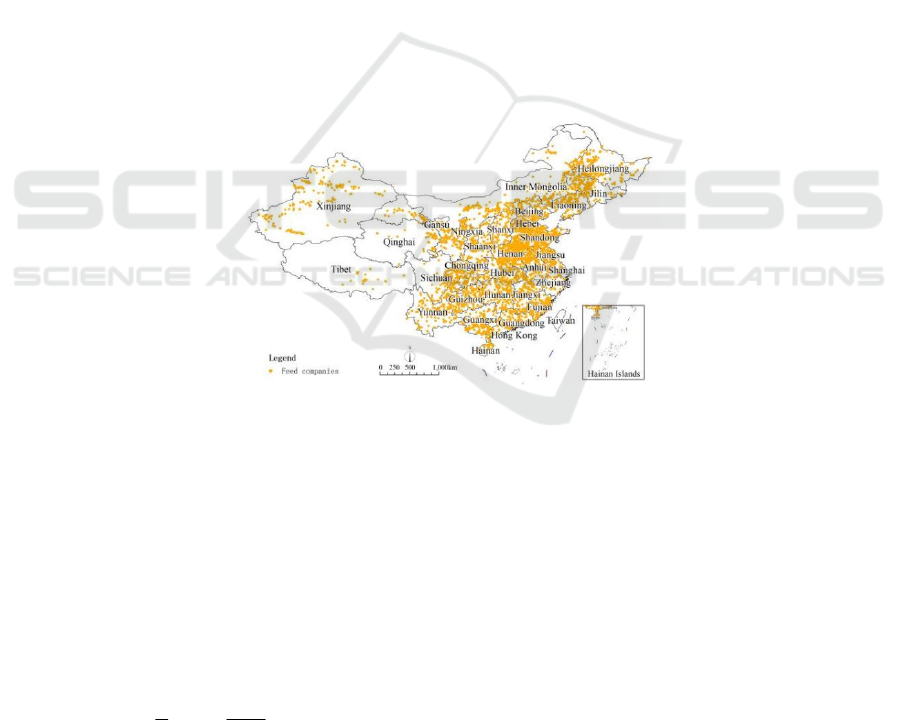
distribution of feed enterprises (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Feed enterprise spatial point.
2.2 Research Methods
Kernel density estimation (KDE) is a commonly
used spatial analysis method to study the degree of
distribution aggregation of spatial points, which can
convert point features distributed in a geographical
area into density polygons (Yin 2022), which is used
to describe the distribution density and change trend
of geographical events in regional space
(FANG
2013), so as to calculate the following formula
(WANG 2022):
=
−
=
n
i
i
nh
n
)
h
xx
K((x)F
1
1
(1)
In equation (1), Fn(x) represents the kernel
density value, K represents the kernel density
equation, h represents the radius of the search range,
n represents the number of sample points in the
search range, x-xi is the estimated point, and the
distance from x to the sample point xi. In this paper,
the kernel density analysis method was used to
analyze the spatial agglomeration degree and
distribution characteristics of feed enterprises in 30
provinces (cities) in China with the help of ArcGIS
10.2.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Spatial Distribution Characteristics
of Feed Enterprises in China
According to the spatial distribution and
visualization results of feed enterprises (Figure 2),
Research on Spatial Agglomeration and Development Strategy of Feed Enterprises Based on GIS Geographic Data Mining
245
since 1987, the distribution of feed enterprises with
registered capital of more than 20 million yuan has
obvious spatial differentiation characteristics, the
main distribution areas are concentrated in Henan,
Shandong, Inner Mongolia, followed by Hebei,
Heilongjiang, Guizhou and Xinjiang, generally
showing the characteristics of more north and south
and less economically underdeveloped areas than
more economically developed areas, and the
concentrated distribution areas of feed enterprises
are mostly large agricultural planting provinces or
animal husbandry provinces. To a certain extent, it
shows that the geographical environment, economic
conditions, agricultural planting, animal husbandry
and other factors have a certain impact on the
development and spatial layout of feed enterprises.
Figure 2: Spatial distribution of feed enterprises.
3.2 Spatial Evolution and
Agglomeration Characteristics of
Chinese Feed Enterprises
Based on the spatial distribution data of feed
enterprises, use the ArcGIS10.2 spatial analysis
module to analyze the kernel density of feed
enterprises in China from 1984 to 2005, 2006 to
2015, and 2016 to 2022, and obtain the kernel
density of feed enterprises in three different time
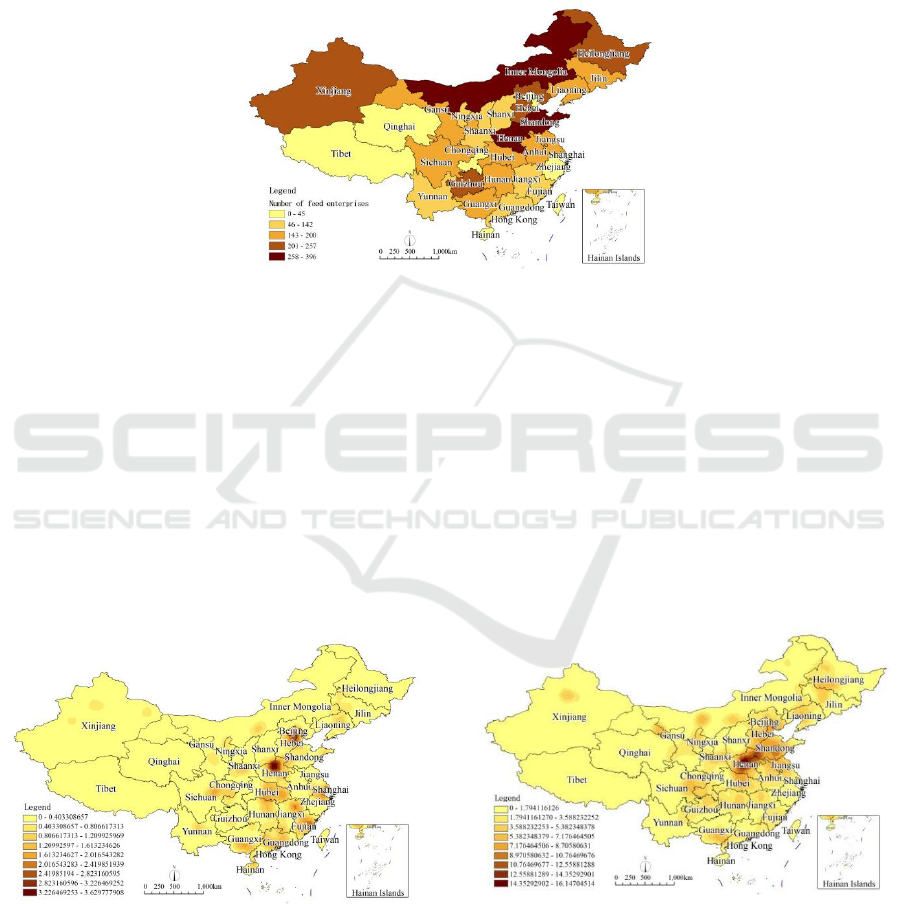
periods Distribution map (Fig. 3a-c), the generated
kernel density distribution map mainly reflects the
density changes and hot spots of feed enterprises.
Figure 3(a): 1984-2005 the kernel density distribution of
feed enterprises.
It can be seen from Figure 3(a) that the density
distribution of feed enterprises in China from 1984
to 2005 was dominated by “dot-like” and adjacent
provinces were relatively independent, and a
continuous planar layout had not yet been formed.
However, in Beijing-Tianjin -Hebei-Henan-Hubei-
Hunan (Jiangxi)-Guangdong (Fujian) has shown a
trend of continuous spatial development. The highest
density value during this period was 3.656, which
respectively formed the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei high-
density area and the high-density area in Henan
Province with Beijing as the core, as well as two
sub-high-density areas in Fujian Province and
Shanghai, and Tibet Autonomous Region and
Qinghai Province. In low-density areas, feed
enterprises present a distribution trend of multiple
agglomeration centers.
Figure 3(b): 2006—2015 the kernel density distribution of
feed enterprises.
It can be seen from Figure 3(b) that from 2006 to
2015, China's feed enterprises had an obvious "band-
shaped" distribution feature, and had similar
characteristics with the "Hu Huanyong Line". The
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
246
distribution density of feed enterprises in
southeastern China was generally higher than that in
northwest China. The adjacent provinces in the
southeast region are connected in series to form a
belt-like layout, forming the Heilongjiang-Jilin-
Liaoning-Tianjin-Hebei-Shandong-Henan-Hubei
feed enterprise agglomeration development belt. The
highest density value in this period is 16.208,
forming A high-density agglomeration area centered
on Henan Province. Compared with 1984-2005, the
distribution density of feed enterprises in first-tier
provinces and cities such as Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei,
Shanghai and Fujian Province is lower, indicating
that the proportion of feed industry in the national
economy in economically developed areas has
gradually declined, and it has become an area where
feed enterprises have moved out; Tibet The
Autonomous Region and Qinghai Province still
maintain a low distribution density, which to a
certain extent shows that ecological environment
protection is still the main task of local social and
economic development; the distribution density of
feed enterprises in other provinces has increased to a
certain extent, compared with the previous period It
has been expanded outwards, and the overall
distribution situation of "one center and multiple
points" has been shown.
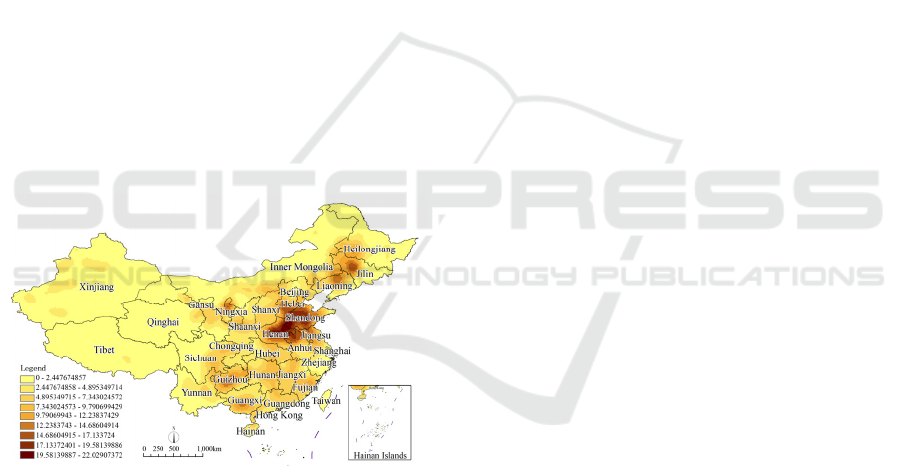
Figure 3(c): 2016—2022 the kernel density distribution of
feed enterprises.
It can be seen from Figure 3(c) that the spatial
distribution of China's feed enterprises from 2016 to
2022 has formed a "plane shape", and continues the
characteristics of denseness in the southeast and
sparseness in the northwest. Developed and formed
four major agglomeration areas of Northeast,
Northwest, Southwest and Henan-Shandong-Hebei
(Henan, Shandong, Hebei), among which the core
density value of the Henan-Shandong-Hebei group
is 22.061, which is the highest in the region, and has
become a national feed enterprise agglomeration
highland. During this period, feed enterprises in
Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong Province and other
provinces and cities maintained a low distribution
density, and became areas where feed enterprises
moved out; different from the previous period, the
distribution density of feed enterprises in Tibet
Autonomous Region and Qinghai Province showed
an increasing trend , indicating that the development
of feed enterprises has expanded unprecedentedly; at
the same time, the spatial distribution of feed
enterprises in other provinces has also further
expanded, and the density value of the distribution
has been greatly increased, forming a regional
agglomeration center, showing a multi-regional
integrated development trend.
4 SPATIAL DEVELOPMENT
STRATEGY OF FEED
ENTERPRISES IN CHINA
4.1 Optimize and Adjust the Industrial
Structure and Promote the Optimal
Allocation of Resources
From the perspective of the development status and
characteristics of the feed industry, the development
of China's feed industry is in a period of
transformation and development, and the large-scale
benefits generated by feed industry agglomeration
have a positive effect on promoting the development
of the national economy. In the face of the problems
of the overall competitive advantage of China's feed
enterprises is not obvious, the degree of
specialization is not high, etc., it is necessary for all
departments to carry out structural reform from the
supply side, adjust and optimize the spatial layout of
feed enterprises, promote the optimal allocation of
feed resources and the development of feed industry
clusters, improve the overall competitiveness of feed
enterprises, and drive the integrated and coordinated
development of upstream and downstream
industries, so as to form a new economic
development highland and promote the sustainable
development of regional economy.
4.2 Build a Cluster of Key Feed
Enterprises and Play a Leading
Role in Demonstration
From the perspective of industrial clusters and
coordinated regional development, the country
focuses on building four feed enterprise clusters in
Liaojihei (Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang), Shaanxi-
Research on Spatial Agglomeration and Development Strategy of Feed Enterprises Based on GIS Geographic Data Mining
247

Gansu-Ningxia (Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia),
Guiguichuan (Guangxi, Guizhou, Sichuan) and
Yuluji (Henan, Shandong, Hebei), giving full play to
the demonstration role of the four feed enterprise
clusters, promoting and driving the coordinated
development of surrounding areas, strengthening
regional resource sharing and the circulation of
production factors, and promoting the high-quality
development of regional feed industry.
4.3 The Two Sides Will Strengthen
Regional Division of Labor and
Cooperation to Achieve
Complementary Regional
Advantages
From the perspective of regional differentiated
development, regions with high agglomeration
levels of feed enterprises should increase policy
support and capital investment to develop the feed
industry as a pillar industry; Areas with a high level
of feed enterprise agglomeration can improve the
regional competitive advantage of the feed industry
by improving infrastructure construction, increasing
industrial innovation, and strengthening the division
of labor and cooperation between regions;
Economically developed areas should increase
scientific and technological investment in feed
enterprises and develop technology-intensive and
knowledge-intensive feed industries; The
development of feed industry in ecologically
protected areas should adhere to the ecological
bottom line, develop green or pollution-free feed
enterprises, and achieve the goal of coordinated
development of development and protection.
5 CONCLUSION AND OUTLOOK
5.1 Main Conclusions
Based on ArcGIS spatial analysis technology, this
paper uses kernel density estimation and statistical
analysis to study the spatial agglomeration of feed
enterprises in China, analyzes the development
process of China's feed industry and its spatial
distribution characteristics, and obtains the
following main conclusions:
(1) Combined with the actual development of
China's feed processing industry and the distribution
characteristics of the registration sequence of feed
enterprises with a registered capital of more than 20
million, the development process of feed industry
can be divided into four stages: start-up period
(1974-1983), development period (1984-2005),
mature period (2006-2015), and transition period
(2016-2022), China's feed processing industry
generally presents the characteristics of late start and
rapid development, slow development in the early
stage, and mainly policy-oriented. In the later stage,
it grew rapidly, mainly based on market
mechanisms, and actively responded to the call of
national policies at all stages to promote regional
national economic growth.
(2) From the overall temporal and spatial
evolution and spatial distribution characteristics of
feed enterprise layout, it can be seen that the
development and layout of feed enterprises are
affected by relevant factors such as geographical
environment, economic conditions, related
industries, regional policies, etc., and the overall
spatial agglomeration phenomenon of Chinese feed
enterprises is significant, and the agglomeration area
is mainly concentrated in the southeast region, and
the spatial agglomeration phenomenon becomes
more obvious with the passage of time, showing that
Henan, Shandong, Jilin, Guizhou, Ningxia and other
places as the agglomeration center spreads to the
peripheral areas, forming a "point-line-surface" The
evolution of the spatial distribution of feed
enterprises.
(3) The spatial agglomeration phenomenon of
China's feed enterprises is obvious, but the level of
spatial agglomeration is not high, and there is a lack
of competitive advantage in the industrial
composition, and the degree of clustering and
specialization of feed enterprises need to be
improved. At the same time, the regional difference
in the spatial agglomeration level of feed enterprises
is obvious, and there is a lack of high-level industrial
agglomeration areas, and the three regions of
Guangxi, Liaoning and Shandong have comparative
advantages over other regions, and the level of feed
enterprise clustering and specialization is relatively
high, becoming a national feed industry
development highland.
5.2 Research Outlook
Limited to the limitations of research materials and
methods, there are still the following shortcomings:
first, the analysis of the development stage of the
feed industry is mainly based on the changes in the
number of feed enterprises, without considering the
industrial output value, scientific and technological
innovation, policy environment and other variables,
and multiple variables can be introduced for multi-
PMBDA 2022 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
248

variable comprehensive analysis in the future, so as
to more accurately divide its development stage;
Secondly, the spatial agglomeration of feed
enterprises is affected by the comprehensive effect
of a variety of influencing factors, limited by data
acquisition, and cannot comprehensively consider
multiple factors, so the next research will conduct
spatial superposition analysis from many aspects
such as the number of enterprises, enterprise scale,
industrial output value, operating income, etc., and
comprehensively reflect the agglomeration level and
spatial distribution characteristics of feed
enterprises. Finally, the research method of spatial
agglomeration of feed enterprises in this paper is not
perfect, which will affect the change of spatial
agglomeration level of feed industry, and new feed
enterprise clusters will appear with the development
of feed industry, so further research on the
agglomeration level of feed enterprises and its
development changes needs to be further studied.
FUND
2022 Chongqing Municipal Education Commission
Science and Technology Research Program
(KJQN202204608, KJQN201904605); 2022
Chongqing Tourism Vocational College Research
Project (XJ2202)
REFERENCES
FANG Zhongquan (2013). Spatial agglomeration
characteristics and influencing factors of Guangzhou
exhibition enterprises. J. Acta Geographica Sinica,
68(04): 464-476.
GAO Chenyu, TANG Shuangshuang (2022). Research on
agglomeration level and influencing factors of
advanced manufacturing industry in Jiangsu Province.
J. Modern City Research, (02): 104-111.
GUO Weijun, HUANG Fanhua (2021). The impact of
high-tech industrial agglomeration on the quality of
economic growth: An empirical study based on
China's provincial panel data. J. Exploration of
Economic Issues, (03): 150-164.
LI Rong, ZHANG Jixin (2021). Research on the influence
of innovative industrial clusters on the agglomeration
effect of national high-tech zones. J. Research of
Technology Economics and Management, (08): 114-
118.
LIU Daobo, QI Fanfan (2021). The influence effect of
circulation industry agglomeration on farmers' income
increase:Based on the analysis of congestion effect
and agglomeration effect. J. Journal of Business
Economics, (11): 21-23.
LI Li (2016). Research on influencing factors and
development countermeasures of China's logistics
industry agglomeration. J. Reform and Strategy,
32(08): 97-100.
LUO Fuzhou, ZHAO Jia (2021). The impact of resource
industry agglomeration on the economic growth of
resource-based cities: An empirical study based on
night lighting data. J. Resources Development and
Market, 37(04): 429-434.
MA Xuefeng, TAN Jiaxin, HUANG Jun (2021). Research
on regional tourism industry agglomeration process
and its influencing factors: A case study of Xiangxi
region. J. Tourism Journal, 36(09): 13-27.
Wang Xiaoran (2019). Research on the impact of high-
tech industry agglomeration on economic growth in
Beijing. D. Capital University of Economics and
Business.
WANG Zheng, ZHANG Yun (2022). Analysis of spatial
distribution characteristics of village toponymic
cultural landscape in Yuxi City based on GIS. J. Green
Science and Technology, 24(02): 196-201.
YE Qianlin, LIU Haiyu, ZHU Wenxing (2022).
Measurement and influencing factors of regional
cultural and creative industry agglomeration. J.
Statistics and Decision, 38(04): 84-87.
Yin Zhangcai, Kang Ziqiang (2022). Research progress of
kernel density estimation supported by temporal
geography. J. Progress in Geography, 41(01): 64-72.
Research on Spatial Agglomeration and Development Strategy of Feed Enterprises Based on GIS Geographic Data Mining
249
