
The Application and Implementations of Cryptocurrency in NFT
Hongxi Li
1,*
and Jiayuan Li
2,†
1
Beijing Normal University (Zhuhai), Zhuhai 519087, China
2
Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, 611756, China
†
These authors contributed equally
Keywords: Cryptocurrency, Blockchain, NTF, Web3.0.
Abstract: Contemporarily, world is shifting from traditional wallets to digital wallets, i.e., software-based programs that
could securely store user payment information. Since the launch of the first Bitcoin software in 2009, the
cryptocurrency market has expanded rapidly and is increasingly recognized. At the same time, NTF will usher
in rapid growth in 2021. Nowadays, there is a strong intersection between cryptocurrency market participants
and NFT market participants, and the application of cryptocurrencies in NTF has gradually become a research
hotspot. The core of modern finance is to realize simple and efficient value transfer. Web3 based on block-
chain technology is the evolution of digital infrastructure, which improves the efficiency of value transfer and
will create greater development space for financial and other services. This article deeply analyzes the core
of the NFT algorithm, lists the common applications of Crypto in recent years, and then takes the pet store
demo created by imitating the NTF platform as an example, uses the truffle development framework to de-
velop a decentralized dApp project, and creates exclusive and irreplaceable NFTs for pets, then use Web3JS
to connect metamask to create a cryptocurrency wallet for transactions. From the perspective of the dog rescue
community, explore the current application of cryptocurrency in NTF, analyze the limitations of current ap-
plications, and predict the future development trend of cryptocurrency.
1 INTRODUCTION
The blockchain industry has experienced rapid devel-
opment and changes in recent years: from budding in
2017, smart contracts in 2018, to DeFi in 2020, and
in 2021, NFT is undoubtedly the hottest topic. NFT
made its debut in 2015. In 2017, the first pixel avatar
project called CryptoPunks was launched. Six months
later, the NTF project Cryptokitty quickly became
popular, and then people started a zoo on the
Ethereum blockchain, and virtual rabbits and virtual
dogs were launched one after another. In 2021, NTF
will usher in rapid growth. According to statista (Sta-
tista, 2022), the total sales involving a non-fungible
token in gaming, art, sports and other segments has
grown from $36.77 million in 2018 to $13,981.9 in
2021.
Cryptocurrencies are as popular as NFT, but dif-
ferent from NFT as NFTs cannot be traded or re-
placed with each other. Beyond that, NFTs have an
odd relationship with cryptocurrencies. When the
NFT market was small, its price action relied on the
crypto market, but as they matured, they kept break-
ing away. Before the advent of cryptocurrencies,
there have been many people trying to create crypto-
currencies, and most of them are mainly facing the
problem of double spending. They must ensure that
digital assets can only be used once in order to pre-
vent copying and counterfeiting of digital assets. Ten
years ago, Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper,
which introduced the powerful functions of the
Bitcoin blockchain network, and Bitcoin entered our
society as the first cryptocurrency vision (Nakamoto,
2008). On July 30, 2015, the Ethereum network was
officially launched. As the second-largest cryptocur-
rency by market capitalization, Ethereum brings
smart contracts and decentralized finance to the world
of cryptocurrency. These achievements consent
Ethereum to build an entire ecosystem on its block-
chain, while hosting its own native currency: ether,
ETH. A token is also a cryptocurrency that does not
have its own specialized blockchain, but uses the
blockchain of other crypto assets. Since then, the
cryptocurrency world has never stopped. The rise of
cryptocurrencies has also made them more and more
recognized and used. Today, Central Bank Digital
Li, H. and Li, J.
The Application and Implementations of Cryptocurrency in NFT.
DOI: 10.5220/0012035800003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 511-516
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
511

Currencies (CBDCs) are being created and compa-
nies are showing incremental interest in investing in
cryptocurrencies and blockchain. Clearly, such
events will fuel the rapid expansion of the cryptocur-
rency market.
Recently, the usage of cryptocurrencies in NTF
has gradually become a hot research object. The fol-
lowing are some case studies. The first example is
about DeFi, where DeFi platforms provide users with
a way to borrow, save or trade cryptocurrencies with-
out manual transfers and arbitration in the event of
disputes. GameFi brings finance into new territory,
where playing and creating in virtual worlds is a via-
ble way to invest, make money, and contribute to pop
culture. If NFT games make various items in the
game have their own value, then DeFi provides a way
to let these values enter the hands of players (Park,
2022). In addition, encryption has been applied to the
media sector, with WhatsApp in Dubai allowing users
to display NFTs on their profiles and creating a mar-
ketplace for users to buy and sell digital artwork and
collectibles. (Shin, 2022). Cryptocurrencies and
NFTs have also been applied to tax policy. Indonesia
uses a regulated research method to analyze how
cryptocurrencies and digital assets (NFTs) should be
taxed at low or high rates. Tax policy for digital assets
(Sitompul, 2022). Besides, crypto tokens can be used
to fund wildlife conservation as a supplemental
source of income, which can be catalyzed by the de-
velopment of crypto-wildlife non-fungible tokens
(NFTs) that can prove to be scarce, unique and pro-
grammable digital wildlife Collection assets
(Mofokeng, 2018). Finally, the application of crypto-
currency technology in the fields of physical exercise,
physical activity, sports and active aging, as a way of
assigning unique or non-fungible items to specific us-
ers, introduced so-called non-fungible tokens (NFTs),
which were then used Cryptocurrencies serve as in-
centives for users (Lopez-Barreiro, 2022).
Nowadays, there is a strong intersection between
cryptocurrency market participants and NFT market
participants. This is partly because, one needs to use
cryptocurrencies as a means of payment to buy NFTs.
The application of cryptocurrencies in the NFT mar-
ket is getting more and more attention, and it is enter-
ing a rising stage, which requires a lot of research to
improve. Therefore, this article deeply analyzes the
core of the NFT algorithm, and lists the common ap-
plications of Crypto in recent years. Subsequently,
this study takes the demo of the pet store as an exam-
ple to create an exclusive non-fungible token (NFT)
for pets, and deeply explore the role of cryptocur-
rency in improving the dog rescue community. Fi-
nally, we analyze the limitations of the current appli-
cation and look forward to the future trend of crypto-
currencies and NFTs.
2 DESCRIPTION OF CRYPTOS
AND NFTS
A cryptocurrency is a virtual or digital asset that uses
cryptography to secure transactions, which works on
the blockchain. A blockchain is a digital ledger that
records all cryptocurrency transactions. This infor-
mation is stored in decentralized databases spread
across a global computer network. This decentraliza-
tion ensure the safety of transactions based on cryp-
tocurrencies. Since there is no central point of control,
cryptocurrencies are resistant to fraud and hacking.
Blockchain technology is also transparent, which
means that everyone on the network can see all trans-
actions.
Unlike cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens are
unique digital assets that represent real-world items
such as videos, trading cards, photos, and music,
which managed in a digital ledger and bought and
sold without cash. Almost any digital asset can be cre-
ated and purchased as an NFT, e.g., in-game digital
characters, digital artwork, or virtual real estate. NFT
assigns a hash value to digital assets by minting coins
on the blockchain, which is permanently stored on the
blockchain. Based on the irreversibility and openness
and transparency of the blockchain, digital works can
be truly unique, which means that digital assets can-
not be exchanged or replaced with each other.
The position of NFT in the blockchain technology
stack is probably like this: the bottom layer is the
blockchain, the middle layer is the virtual machine
EVM, and the top is the smart contract. Primarily, the
blockchain mainly provides infrastructure, such as
consensus algorithms, P2P networks, etc. (Donet,
2014). The blockchain itself is a decentralized distrib-
uted ledger, and the hash encryption algorithm it uses
has preimage resistance and sub-preimage resistance.
The NFT issued on the blockchain itself is a transac-
tion confirmed on the chain, then once the transaction
is confirmed to form a block and join the main chain,
it cannot be maliciously tampered with that has a
unique identifier. Looking further up, it is the virtual
machine EVM. EVM is the abbreviation of
"Ethereum Virtual Machine" (Hirai, 2017). The exist-
ence of EVM is to allow the written smart contract
code to be parsed and run in the public chain environ-
ment. Finally, there are smart contracts. A smart con-
tract is a piece of code that is triggered and executed
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
512

when two parties trade on blockchain assets. It real-
izes the automatic processing of traditional contracts
in the form of computer instructions. The essence of
NFT is actually a non-fungible digital asset token cre-
ated, maintained and executed by smart contracts.
Based on this contract, creating NFTs usually
needs to follow a certain protocol. The commonly
used protocols are ERC721, ERC1155 and ERC998.
These protocols define a set of interface methods and
events, and writing a smart contract only needs to im-
plement these methods and events, which is an NFT
smart contract.
3 APPLICATIONS
Cryptoassets have come a long way since the advent
of Bitcoin. Encrypted digital assets can be used for
various forms of asset registration, inventory, trans-
action media, etc., and even affect the financial, eco-
nomic and currency transaction systems of countries
and regions. More and more countries and enterprises
have begun to put "blockchain and encrypted digital
assets" into actual business models, and their applica-
tion has also achieved remarkable results. Below are
three applications of cryptoassets that demonstrate
how far the fintech revolution is taking place.
The first case is digital cash. As network fees be-
gan to rise, forcing numerous merchants to drop their
support for BTC, a growing number of Bitcoin Core
supporters began to advocate for a store of value
(SoV) narrative rather than a medium of exchange.
The main purpose behind cryptocurrencies is that an-
yone can send and receive money through a decen-
tralized P2P network. This can act as a digital version
of cash. Cryptocurrencies allow anyone to transfer
funds directly to another person, entity or organiza-
tion while always maintaining control over their
funds. It removes the constraints of traditional finance
and enables access to financial services for many un-
banked and underbanked users around the world. The
characteristics of cryptocurrency make it efficient and
convenient enough to be widely used, but it also
comes with huge security risks. The disadvantage of
cryptocurrencies is that they do not have the authority
to be responsible for all the problems that arise in all
transactions, and money laundering crimes also occur
frequently, which is a challenge to how to utilize
cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology in the
current era of globalization (Amsyar, 2020).
The second example is collateral. Crypto lending
is a novel financial tool to obtain the cash one needs
quickly, as crypto-backed loans allow borrowers to
use their crypto assets as collateral to get fiat or stab-
lecoin loans. It means allowing borrowers to access
funds without selling their crypto assets and use cash
to achieve more goals and leverage greater leverage
before repaying the recovered crypto assets. Lending
services such as Maker, Compound, and Instadapp
are now flourishing on the Ethereum network, and
many countries have gradually begun to implement
adjustments to relevant legal treaties. For example,
the United States and Ontario have specific theoreti-
cal and regulatory guidance for using cryptocurren-
cies for secured loans (Menard, 2019).
The third application is collection. As with physi-
cal collectibles, chasing fashion is fairly common in
the world of collectibles, and the same is true in the
world of digital collectibles. The crypto community
has been exploring digital collectibles for years, and
Tondello et al. have found that utility, enjoyment, in-
vestment, self-expression, and memory are the most
common reasons to value digital collectibles. Espe-
cially for reasons such as investment or collection,
methods to verify the authenticity of digital collecti-
ble objects are becoming more and more important
(Toshendra, 2020). Terra Virtua (beta) is a mobile,
PC, and web-based digital collectibles platform and
ecosystem for AR and VR. They are not the first dig-
ital collectibles platform to use DLT or NFTs, but the
way they uniquely combine collectible, trading, fa-
natical and commodity elements with a unique cyber-
space makes them potentially the global standard for
digital collectibles.
4 DEMO IN NFTS
This section focuses on the implementation of crypto-
currency in NFTs. It describes why this demo was cre-
ated, how to imitate a current existing platform and
what technologies and tools were used for it. It will
provide a step-by-step explanation of the entire pro-
cess.
4.1 Front-End
This demo provided was written on MacOS. VSCode
was used as the main development tool. The demo
was also utilizing one of the famous front-end frames
called Vue. Besides, Web3 JS is used to connect
Metamask which can simulate cryptocurrency trad-
ing. Ganache is used to provide virtual accounts. To
begin with, there are amounts of NFTs platforms over
the Internet. BlueArk is one of the most famous plat-
forms in the world. It provides a platform for the
owner and the buyer. A buyer can purchase whatever
they want and use USDT to trade with the owner.
The Application and Implementations of Cryptocurrency in NFT
513
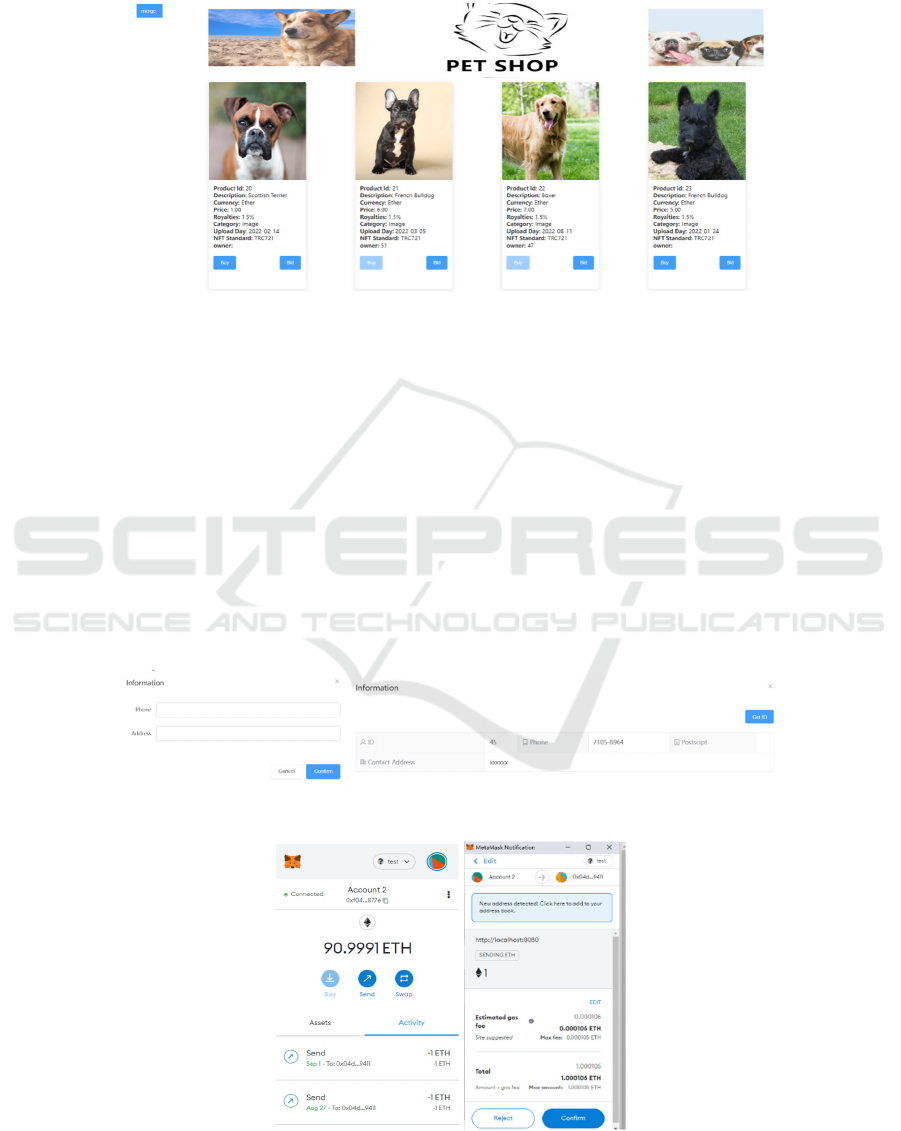
Thus, the demo stimulate BlueArk and cryptocur-
rency can be seen how to work in a trade. The demo
mainly used Vue. As shown in Fig. 1, this is the main
page of the website. There are four buttons on the
leftside menu which includes user registration, ac-
count, update log and connect to metamask.
Figure 1: Main page of the demo website. [Owner-draw].
Seen from a single subplot in the main page. It has
a lot of information, including product ID, descrip-
tion, currency, price, royalties, category, upload day,
NFT standard and owner if any. It stipulates which
cryptocurrency the buyer requires to use for trade.
Once a buyer purchases an item, there is a buyer ID
displayed in “owner” and the “buy” button will turn
unavailable. Each transaction needs 24 hours to be
confirmed. If no other buyer wants the same item, the
NFT will belong to the buyer 24 hours later. Other-
wise, if there are more than 2 buyers who want to pur-
chase the same item, they can bid for each other. The
one bid the highest will have the opportunity to pur-
chase it. A new buyer who first comes to the website
needs to register an account (seen the left panel in Fig.
2). On this platform, privacy is the most important
thing. The buyer only requires to write down a phone
number and address for registration. Also, an ID
which is require to buy items will be given to the
buyer (as depicted in the right panel of Fig. 2). This
ID is random generation, and it is very safety. Others
buyer don’t know who buy a NFT but just an ID num-
ber. There is a price in each pet’s item card. A buyer
can select an item which one loves and pays for it.
Initially, the buyer needs to connect the metamask
and then choose an account.
Figure 2: The use registration (left panel) and information (right panel). [Owner-draw].
Figure 3: Transaction test. [Owner-draw].
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
514

When connection is done, the buyer can check the
bill as exhibited in Fig. 3. Afterwards, the buyer needs
to pay corresponding price which is displayed in the
bill. The total price includes basic price, estimated gas
fee and royalties. When the buyer pays the bill, the
platform will confirm this transaction. Afterwards, a
picture will be sent to buyer’s account. In conclusion,
the demo stimulates one of the most famous NFT
platforms and shows the whole process of how cryp-
tocurrency works in NFTs.
4.2 Metamask and Interacting with the
Demo
Metamask is a cryptocurrency wallet for interacting
with Ethereum blockchain. It allows users to access
their Ethereum wallets through a browser extension
or mobile app to interact with DApps. In this demo,
metamask is used as a cryptocurrency wallet. It pro-
vides ether which buyer can utilize it to purchase
NFTs.
4.3 Web3JS
Web3.js is a collection of libraries that allow you to
interact with a local or remote ethereum node using
HTTP, IPC or WebSocket (Panda, 2021). In this
demo, Web3Js are used to connect websites and meta-
mask. When a buyer wants to use metamask to buy
NFTs, Web3Js allow buyers to access their wallet so
that they can pay the cryptocurrency.
5 LIMITATIONS & PROSPECTS
Although NFTs are evolving swiftly nowadays, there
are still many problems we need to confront. In detail,
the most serious problem is poor liquidity. Firstly,
most buyers do not realize what NFTs are. Consumers
need to spend more time understanding NFTs assets
before making purchasing decisions. Secondly, most
mainstream NFTs collections have high prices and
low accessibility, resulting in a small user base. Last,
NFTs lack practicality. So far, most experiments
around NFTs have focused on the artwork and col-
lectibles categories. Owing to the limited scope, we
have yet to see unique and innovative applications
outside of PFP. To generate superior liquidity, the
product or asset itself needs to have sufficient utility
to produce strong demand. With strong demand, as-
sets are easier to sell and turn into liquid assets, such
as cash. Furthermore, it will cause many problems.
Lower trading liquidity means that users cannot read-
ily swap one asset for another, and it creates greater
slippage, leading to severe price deviations. Moreo-
ver, low trading volume and exchange demand for il-
liquid assets leads to asymmetric pricing and market
information, and opaque information leads to slug-
gish market activity and difficult asset valuations.
For cryptocurrency, it trades at a glacial pace and
it also has no transparency and security. In a block-
chain, if a 1MB block is generated every 10 minutes
and each transaction requires 250B to store data, the
calculation shows that 1MB can only store 4194
transactions, divided by the time, which is a maxi-
mum of 7 transactions per second. Obviously, this
speed is not sufficient to satisfy normal transaction
demand. Besides, the lack of information and under-
standing about cryptocurrency transactions makes it
hard for governments to regulate tax revenue. This
also creates a lot of criminal activity and problems for
investors. In addition, there is a lot of uncertainty due
to fears of exchanges being hacked. Moreover, it has
high volatility. The value of cryptocurrencies fluctu-
ates. Investor confidence has been compromised,
with some having difficulty determining how much
cryptocurrency they actually own.
Currently, NFTs are highly concentrated on ava-
tars and game assets, and the lack of utility hinders
mass adoption, thus inhibiting the demand for NFTs.
Envisioning a world where NFTs become ubiquitous
and unprecedented products or commodities through
the adoption of NFTs and blockchain technology is
seen as a new asset class. It is a long way off to
achieve this dream. The following advice may be
adopted in the future. Firstly, NFTs need to be divided
into different categories with different risk and re-
ward characteristics. All asset classes in traditional fi-
nance have their own risk and return profiles, and are
given risk ratings by specialized agencies. Nonethe-
less, the risk ratings given by third-party rating agen-
cies are not entirely reliable, because the financial in-
struments issued by these centralized intermediaries
frequently have assets wrapped in layers, and the
opaque process makes it difficult to correctly assess
risks. While blockchain technology facilitates trans-
parency in financial instruments, for institutions or in-
vestors, adoption of blockchain technology can en-
hance the health of financial markets and optimize
risk-reward profiles. Secondly, a risk profile of buyer
can be established. Credit assessment in the crypto
space is still in its early stages, and it is anticipated
that the field will mature when firms have clearer user
profiles. Users’ on-chain data can then be tied to user
identities to evaluate buyer’s creditworthiness and
recommend assets that match their risk profile.
The Application and Implementations of Cryptocurrency in NFT
515

6 CONCLUSION
In summary, this paper investigates cryptocurrency in
NFTs with an illustration demo. Specifically, it fo-
cuses on how cryptocurrency works in NFTs. Ac-
cording to the analysis, a demo was built to imitate
the existing NFT platform. The demo has a vast ma-
jority of functions including user registration and
NFT purchase. The website generally uses Vue as the
framework. And it also uses Web3JS to connect meta-
mask, which is a cryptocurrency wallet. Thus, it can
cost a certain amount of cryptocurrency when buyer
purchases NFTs. Moreover, it also provides a bid
function to tackle a solution which more than two
people want to buy the same NFT. It can raise the
price and the highest bidder will have the opportunity
to purchase the NFT. However, NFT is not popular
nowadays since it’s safe and slow speed of transac-
tion. The lack of oversight may lead to fraud and it
may cause people to lose their money. In addition,
NFT are not commonly used due to cryptocurrency’s
low transaction speed. Nevertheless, it will become
popular since technology improvement. With the pro-
gress of technology, people will gradually accept this
form. Overall, these results provide a guideline for
how cryptocurrency has a better use in NFTs.
REFERENCES
Amsyar, I., Christopher, E., Dithi, A., et al.: The Challenge
of Cryptocurrency in the Era of the Digital Revolution:
A Review of Systematic Literature. Aptisi Transactions
on Technopreneurship (ATT), 2(2): 153-159 (2020).
Donet, J. A., Pérez-Sola, C., Herrera-Joancomartí, J.: The
bitcoin P2P network. International conference on finan-
cial cryptography and data security. Springer, Berlin,
Heidelberg, 87-102 (2014).
Hirai, Y.: Defining the ethereum virtual machine for inter-
active theorem provers. International Conference on Fi-
nancial Cryptography and Data Security. Springer,
Cham, 520-535 (2017).
Lopez-Barreiro, J., Alvarez-Sabucedo, L., Garcia-Soidan,
J. L., et al.: Use of Blockchain Technology in the Do-
main of Physical Exercise, Physical Activity, Sport, and
Active Ageing: A Systematic Review. International
Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
19(13): 8129 (2022).
Menard, X. F.: Cryptocurrency: Collateral for Secured
Transactions?. Banking & Finance Law Review, 34(3):
347-386 (2019).
Mofokeng, N., Fatima, T.: Future tourism trends: Utilizing
non-fungible tokens to aid wildlife conservation. Afri-
can Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 7(4):
1-20 (2018).
Nakamoto, S.: Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash sys-
tem. Decentralized Business Review, 21260 (2008).
Panda, S. K., Satapathy, S. C. An investigation into smart
contract deployment on ethereum platform using Web3.
js and solidity using blockchain. Data Engineering and
Intelligent Computing. Springer, Singapore, 549-561
(2021).
Park, A., Kietzmann, J., Pitt, L. Dabirian, A.: The Evolution
of Nonfungible Tokens: Complexity and Novelty of
NFT Use-Cases. IN IT Professional, vol. 24, no. 1, pp.
9-14, 1 Jan.-(2022)
Statista.: Total sales involving a non-fungible token (NFT)
in gaming, art, sports and other segments from 2018 to
2021”, <https://www.statista.com/statis-
tics/1221400/nft-sales-revenue-by-segment/> (2022).
Shin, D., Rice, J.: Cryptocurrency: A Panacea for Economic
Growth and Sustainability? A Critical Review of
Crypto Innovation. Telematics and Informatics, 101830
(2022).
Sitompul, A. D.: Imposition of Tax Law on Cryptocurren-
cies and NFT in Indonesia. Pancasila and Law Review,
3(1): 43-54 (2022).
Toshendra, K. S.: Key Challenges for Blockchain Adoption
In 2020. <https://www.blockchain-council.org/block-
chain/5-key-challenges-forblockchain-adoption-in-
2020/> (2020)
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
516
