Research on the Impact of Executive Shareholding Ratio on
Profitability of GEM Listed Companies
Xiaoqi Xin
a
Beijing Jiaotong University, China
Keywords: GEM Listed Companies, Shareholding Ratio of Senior Executives, Profitability.
Abstract: The GEM is an integral part of China's multi-level asset market, which is characterized by high growth,
high innovation, small scale, and high risk. In addition, senior executives may affect the company's
operation and management activities, and may seek private interests and damage the company's interests.
Therefore, shareholding by senior executives has become a common incentive method for companies, but
corporate governance issues such as principal-agent issues and senior executives' moral hazard have
followed. Therefore, at present, domestic and foreign scholars have taken executive stock ownership as a
core topic of company research. Based on the above background, analyze the impact of executive stock
ownership on profitability of GEM listed companies, and draw a conclusion.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8589-6720
1 INTRODUCTION
China's basic economic system is a socialist market
economic system with public ownership as the
mainstay, multiple ownership systems developing
together, distribution according to work as the
mainstay, and multiple distribution modes
coexisting. In this context, the company occupies an
important position in the market, and there are many
problems in the company, in the process of company
development, the need to continuously improve the
company's operating efficiency, the need to
maximize the value of the company's shareholders,
some scholars in the study of the company found the
problem of principality, executives as the company's
agents, in the company has an indispensable
position, is the company's operation and investment
decision executor, but they may seek private
interests and hinder the company's long-term
development of behavior. As a result, equity
incentives came into being and became a common
means to prevent such phenomena. Senior
management's shareholding and shareholders'
interests converge, and whether the company can
achieve rapid development has also become a
concern of executives.
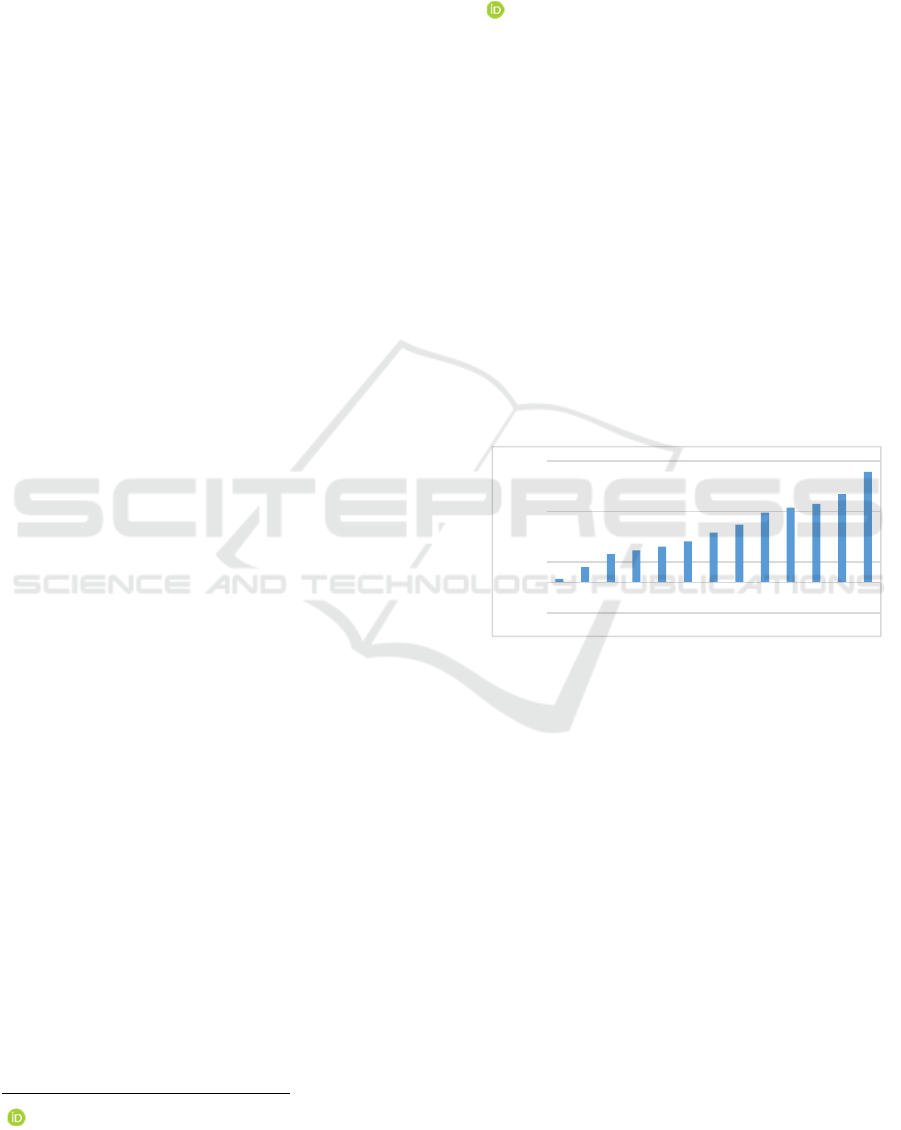
Figure1: Number of GEM listed companies.
The number of listed companies in China's GEM
market has exceeded 1,000 so far, and it has tended
to mature. As of August 2022, the total market
capitalization reached 12 trillion yuan. GEM market
for entrepreneurial companies, small and
medium-sized companies and high-tech companies
that do not meet the listing conditions of the main
board to provide financing and development
channels, has an important complementary role to
the main board market, but also plays a key role in
the entire securities and even asset market, and
GEM listed companies have the characteristics of
general executive shareholding and relatively
concentrated equity, in this context, the company
pays more attention to whether the proportion of
executive shareholding has an impact on the
-300
200
700
1200
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
2021
174
Xin, X.
Research on the Impact of Executive Shareholding Ratio on Profitability of GEM Listed Companies.
DOI: 10.5220/0012027600003620
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering (ICEMME 2022), pages 174-179
ISBN: 978-989-758-636-1
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

company's profitability and how to affect it.
Therefore, this article takes GEM listed companies
as the background to explore the impact of executive
shareholding on the company's profitability.
As the GEM market becomes more and more
mature, how to effectively manage the company
according to its own characteristics, give full play to
its advantages as a supplement to the main board
market, let the investees who need to invest stand
firm, on the basis of the main board, increase the
company's financing methods, solve the capital
problems of small and medium-sized companies, and
increase investment opportunities, is a problem that
the market needs to pay attention to now, which is
conducive to the comprehensive development of
China's economic market. At present, few scholars
have studied the relationship between executive
shareholding ratio and profitability in detail, and few
have used GEM listed companies as a sample to
explore. It is of certain practical significance to
explore the relationship between corporate
profitability and executive shareholding ratio: first,
to clarify the impact of executive shareholding ratio
of GEM listed companies on profitability, and
second, the research conclusion provides certain
references for GEM listed companies that plan to
implement equity incentives.
2 RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS AND
DESIGN
2.1 Research Hypothesis
Based on the principal-agent theory, two-factor
theory and stakeholder theory, the company has
information asymmetry, different responsibilities of
owners and operators, resulting in agency conflicts,
according to the research results of many domestic
and foreign scholars on the issue of principal-agent,
giving executives a certain number of company
shares can effectively alleviate the agency conflict
problem of owners and operators, so that the
interests of executives and shareholders are unified
and converge, Xu Cheng (2020) research believes
that if the senior executives in the company hold
shares, Then to a certain extent, the interests of
shareholders can be safeguarded and the company's
governance can be improved, so executive
shareholding is conducive to improving the
company's profitability. Wu Gaobo and Du Yanping
(2021) studied Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share
companies from 2014 to 2018 and concluded that
executive shareholding is positively correlated with
the cost of equity capital, and certain equity
incentives can weaken the cost of capital effect of
accrued earnings management. Giving executives a
certain amount of company equity represents the
affirmation of their past work and operation, which
can allow them to maximize their self-worth,
maximize work efficiency, and promote the
development of the company. As an effective
incentive mechanism, executive shareholding meets
people's most basic needs and promotes the growth
of the company, thereby affecting the ability to
operate. Similarly, after holding shares in the
company, executives have a certain shareholder role,
give priority to themselves when making corporate
investment decisions, and prefer higher-income
business methods and strategies, and at this time, the
interests of executives and other stakeholders
converge, which will increase the return related to
investors' investment assets, increase the value of
the company, and enhance the company's
competitiveness and development ability.
As the decision-makers of the company's
investment and operation, executives will work more
actively for the company's profits in order to increase
the market value of the shares held, use all the
company's existing resources for profit, and work
harder to improve the ability of investors to generate
income from the funds invested in the company. Tian
Guoshuang and Qi Yingnan (2018) analyzed 245
companies from 2012 to 2016, and believe that the
increase in the proportion of executive shareholding
will increase the company's economic efficiency. Wei
Wenjun and Shi Huaqian (2017) analyzed A-share
companies and believe that executive shareholding
positively affects financial performance. Wang
Xiaoning and Zhou Meiling (2016) study empirical
data in the real estate industry to demonstrate the
positive correlation between executive shareholding
and company performance. Li ed al. (2007) studies
that from 1992 to 2000, listed companies proposed
that executive shareholding helped to improve
corporate performance, and that companies with a
high proportion of shares had about 2% higher
operating capacity and profitability than companies
with a low proportion of shares. Wang Xiufen and
Xu Xiaopeng (2017) analyzed A-share enterprises
from 2011 to 2015 and demonstrated that executive
shareholding can improve operational profitability.
Most scholars believe that executive shareholding
can effectively make executives pay more attention
to the company's performance, effectively improve
the company's performance, and the company's
executives holding a certain number of company
Research on the Impact of Executive Shareholding Ratio on Profitability of GEM Listed Companies
175

shares can protect the interests of shareholders to a
certain extent, suppress the problem of principality,
and improve corporate governance. As the operator
of the company, the executive has a good
understanding of the company's asset information,
and the company gives a part of the shares to the
executive, which will allow the executive to make
better use of the existing information to make
decisions to maximize the value of the company,
maximize the efficiency of asset operation, and
improve the overall profitability of the company
using all assets. Similarly, senior executives'
shareholding can enable them to obtain the rights of
shareholders, participate in major decisions of the
company, have a strong sense of belonging to the
company, pay more attention to the interests of the
company, make various business decisions that will
be closer to the requirements of the company's
interests, make behaviors that use power for personal
gain to harm the interests of the company, and the
risk appetite of company executives for investment,
projects, etc. will converge with the company's
shareholders, and the use of the company's assets will
be more effective. Therefore, the hypothesis is
proposed:
H1: There is a positive correlation between
executive shareholding and profitability.
2.2 Research Design
2.2.1 Sample Selection
The data in this paper comes from the Guotai An
database, which is sorted out by Excel and tested by
Stata to test the model. Taking the five-year data of
GEM listed companies from 2017 to 2021 as the
research sample, in order to draw a more accurate
conclusion, ST, *ST listed companies and financial
industry companies are excluded from the sample
selection, and the company should continue to
operate in the five years from 2017 to 2021 and have
been listed in 2017, and the data is complete and
complete to ensure the consistency of the sample. In
the end, a total of 2810 sample data from 562
sample companies were obtained after screening.
2.2.2 Variable Selection
Interpreted variable: profitability
Referring to the research of Liang Yuanni (2020),
Chen Yaomeng (2021) and others, the return on
equity reflects the company's net profit income,
which can enable managers and investors to decide
whether to expand the scale of operation or
investment, and capital profitability is the ability of
the company owner to benefit from investing capital
management; Return on total assets can reflect the
company's ability to use and manage total assets,
and asset profitability is the company's ability to
return on operating assets; Operating profit margin
reflects the company's operating efficiency,
operating profitability is the company's financial
operation ability, so the return on net assets, return
on total assets, operating profit margin as the
indicator to measure profitability.
Explanatory variable: Shareholding ratio
of senior executives
The shareholding ratio of senior executives is an
important indicator to measure the degree of senior
management's shareholding. The shares held by the
executives in this article are the company's current
shares, and if one person wears multiple positions,
the number of shares is not double-counted.
The relevant variables and definitions involved
in this article are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Variable definitions and descriptions.
Var Symbol definition
Interpreted
variable
Return on
equit
y
ROE Net profit/net assets*100%
Return on
total assets
RTA
(Total profit+interest expense)/Total
average assets*100%
Operating
profit margin
OPM Operating profit/revenue*100%
Explanatory
variable
Shareholding
ratio of senior
executives
ESR
Total shares held by senior executives/total
shares of the company*100%
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
176

control variable
company size SIZE
Natural logarithm of total assets at the end
of the year
Shareholding
ratio of the
largest
shareholder
FIRST
Number of shares held by the largest
shareholder/total number of shares*100%
leverage LEV
Total liabilities at the end of the year/total
assets at the end of the year *100%
2.2.3 Model
To verify that the hypothesis is correct, the following
multiple linear regression model is established:
𝑅𝑂𝐸\𝑅𝑇𝐴\𝑂𝑃𝑀 𝛼 𝛽𝐸𝑆𝑅 𝛾
𝑆𝐼𝑍𝐸
𝛾
𝐹𝐼𝑅𝑆𝑇 𝛾
𝐿𝐸𝑉 𝜀
Among them, the meaning of each variable is
shown in Table 1, 𝛼 is the constant term, 𝛽, 𝛾
1
,
𝛾
2
, 𝛾
3
are the model regression coefficients, 𝜀 are
the model random error terms.
3 EMPIRICAL RESULTS AND
ANALYSIS
3.1 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
In order to obtain a preliminary understanding of the
executive shareholding ratio, profitability and
control variables of the sample companies,
descriptive statistics were used for analysis. The
specific results are shown in Table 2:
Table 2: Descriptive statistical analysis.
V
a
r
N Max Min Mean St
d
ROE 2810 0.311 -0.613 0.096 0.501
RTA 2810 0.361 -0.609 0.080 0.509
OPM 2810 0.459 -9.032 0.055 5.332
ESR 2810 0.648 0 0.276 0.011
SIZE 2810
24.54
4
19.29
0
21.39
1
0.794
FIRST 2810 0.624 0.056 0.249 0.008
LEV 2810 1.037 0.021 0.302 0.166
The average return on net assets is 0.096, and the
profitability of net assets is strong; The difference
between the maximum value and the minimum value
of the return on total assets is large, with the average
value of 0.080. The level of input and output is
strong, and the assets are well used; The minimum
value of operating profit margin is -9.032, and the
average value is 0.055, indicating that some sample
companies have excessive losses, but the overall
development potential is fair and the profitability is
strong.
The shareholding ratio of senior executives
reached 64.8% at the highest level. The value of
some sample companies was 0, with an average of
27.6%, indicating that the index value of the whole
market was high, indicating that the equity incentive
of GEM listed companies was widely implemented
and successfully implemented.
As can be seen from Table 2, the difference in
the size of the company is small; the average
shareholding ratio of the largest shareholder is
24.9%, and the equity is relatively concentrated;
Under normal circumstances, the asset-liability ratio
of companies with a good asset structure should not
exceed 50%, as can be seen from Table 2, the
maximum is 1.016 higher than the minimum, and
the gap in financial risks is large, but the average
value is 30.2%, indicating that the overall risk is at a
reasonable level.
3.2 Regression Analysis
Table 3: Regression analysis results.
Va
r
ROE RTA OPM
ESR
0.180
**
(
2.480
)
0.185
**
(
2.500
)
0.196
**
(
3.914
)
SIZE
0.227
**
(
2.746
)
0.239
**
(
2.492
)
0.163
**
(
5.592
)
FIRST
-0.322
**
(
-3.340
)
-0.338
**
(
-3.440
)
-0.246
**
(
-2.573
)
LEV
0.156
**
(
2.326
)
0.208
**
(
2.726
)
0.215
**
(
3.821
)
R
2
0.097 0.101 0.044
Ad
j
ust R
2
0.087 0.091 0.033
F 9.850
**
10.250
**
4.170
*
N 2810 2810 2810
Note: ** indicates a significant correlation at the 0.01
level (bilateral) and * indicates a significant correlation at
the 0.05 level (bilateral).
Adjust R
2
is a comprehensive measure of how well a
regression model fits. Table 3 shows that the model
Research on the Impact of Executive Shareholding Ratio on Profitability of GEM Listed Companies
177

fit is average, but it is significant at 1% and 5%
levels F and the model is usable.
The executive shareholding ratio and return on
net assets coefficient is 0.180, the growth of this
indicator will pull up the return on net assets, that is,
the proportion of executive shareholding positively
affects the profitability of capital, and the executive
shareholding ratio and total return on assets
coefficient is 0.185, indicating that the growth of
executive shareholding ratio will increase the return
on total assets, that is, the proportion of executive
shareholding positively affects asset profitability,
and the executive shareholding ratio and operating
profit margin coefficient are 0.196, indicating that
the growth of executive shareholding ratio will
increase the operating profit margin, that is, the
proportion of executive shareholding positively
affects operating profitability, assuming that H1 is
verified.
The results show that the shareholding ratio of
senior executives of GEM listed companies is
positively correlated with capital, assets and
operating profitability. After the executives hold the
company's shares, they have a certain shareholder
role, take into account their own benefits when
making company operation decisions, will adopt
higher returns, relatively stable investment strategies
and business methods, the company's value will rise,
similarly, their own interests will gradually be
consistent with the interests of the company and
investors, and the risk appetite of company
executives for investment and projects will also
converge with the company's shareholders, which
will increase the return on investors' investment
assets and increase the return on investment. It can
also effectively improve the ability of investors to
generate income on the funds invested in the
company, thereby improving the profitability of
assets. On the other hand, the company grants
executives a certain amount of equity, which is to
affirm their past work performance, and mobilize
their work enthusiasm, it also strengthen their
growth needs, and maximize work efficiency, so that
it can enable them to prove their excellent
management ability through the company's operating
efficiency, and at the same time realize self-worth,
and promote the growth and development of the
company, so that the company's operating profit
margin can be improved and profitability enhanced.
4 RESEARCH CONCLUSIONS
AND RECMMENDATIONS
This paper uses 2810 sets of data from 562 listed
companies in China's GEM market from 2017 to
2021 as research samples, first reviews and
summarizes relevant domestic and foreign research
results and theories, and then analyzes each variable,
on this basis, uses multiple regression models to
carry out empirical analysis of the three research
hypotheses proposed, and concludes: (1) capital
profitability will increase with the increase of
executive shareholding; (2) asset profitability will
increase with the increase of executive shareholding;
(3) Operating profitability will increase with the
increase of executive shareholding.
Based on the previous analysis and conclusions,
the following recommendations are made:
Reasonably formulate an equity incentive
system
The shareholders of the company will strengthen
the supervision of senior executives or give equity
so that senior executives do not make business
decisions that harm the interests of the company, and
the interests of senior executives are consistent, and
the equity incentive system can make the interests of
the two converge and solve the problem of agency
conflict, so executive shareholding has become a
common incentive method for many companies.
According to the research of this paper, executive
shareholding has been a very common phenomenon
in the GEM board, and positively affects the
profitability of the company, so it is necessary to
reasonably formulate the executive incentive
system, conduct regular assessment of the executive
behavior and management level, and establish a
long-term incentive and short-term incentive
combined executive salary and remuneration
system, when the long-term remuneration directly
obtained by the executive and the benefits obtained
through encroachment on the company's interests
tend to be at the same time, the constraint of moral
hazard can play a role again, and the behavior of
operators harming the interests of the company can
be effectively avoided. It ensures a high degree of
unity of interests between managers and
shareholders.
Rationalization of the equity distribution
of the company
GEM listed companies are special in nature,
many are family businesses, and the operator is also
the chairman of the board, the person who holds the
largest share of the company, and the direct
decision-maker of the company. The company's
ICEMME 2022 - The International Conference on Economic Management and Model Engineering
178

equity is too concentrated and easy to listen to the
decision-making of the person with the highest
shares, does not absorb the opinions of other
shareholders, resulting in losses to the company, and
the largest shareholding ratio is too high is not
conducive to mutual restraint and balance between
shareholders, and is not conducive to the
improvement of the company's profitability.
Therefore, for GEM listed companies, scientific
methods should be adopted to correctly guide the
largest shareholder to transfer part of its equity to
other shareholders, or the company should absorb
more investors, reduce the shareholding ratio, and
rationalize the equity distribution, so as to promote
the company to solve problems efficiently, it also
make economic decisions more effective, and
improve the company's profitability. At the same
time, the company should establish a structure of
mutual restraint among shareholders, maintain a
moderate level of shareholding of the largest
shareholder of the company, and further optimize the
ownership structure.
REFERENCES
Cai Hui. Executive Equity Incentives, Institutional
Investor Shareholding and Corporate Performance[J].
Finance and Accounting Letters, 2020(03): 59-62.
Chen Yaomeng. Enterprise Profitability Analysis——A
Case Study of "Huawei"[J]. Statistics and
Management, 2021, 36(04): 87-93.
Cheng Ziqi, HUANG Yue, WANG Jinting. Research on
the impact of management shareholding on enterprise
value of GEM listed companies[J]. Contemporary
Economics, 2017(12): 102-105.
Liang Yuanni. Analysis of profitability of listed companies
based on analytic hierarchy method——A case study
of Zhuhai Gree Electric Co., Ltd.[J]. Quality and
Market, 2020(22): 48-50.
Li D, Moshirian F, Nguyen P, et al. Managerial ownership
and firm performance: Evidence from China's
privatizations[J]. Research in International Business
and Finance, 2007, 21(3): 396-413.
Tian Guoshuang, Qi Yingnan. Does Equity Incentive
Really Have an Impact on Company
Performance——Based on the Data of A-share Listed
Companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen in China[J].
Friends of Accounting, 2018(17): 44-50.
Wang Xiaoning, Zhou Meiling. Research on the
Correlation between Executive Remuneration and
Corporate Performance in Real Estate
Industry——Based on a Comparative Analysis of
State-Owned and Non-State-Owned Companies[J].
Friends of Accounting, 2016(24): 64-70.
Wang Xiufen, XU Xiaopeng. Executive equity incentive,
operational risk and corporate performance[J]. Friends
of Accounting, 2017(10): 84-89.
Wei Wenjun, SHI Huaqian. Senior Executives' Stock
Ownership, Investment Behavior and Financial
Performance[J]. Finance and Accounting Letters,
2017(32): 23-26.
Wu Gaobo, Du Yanping. Accrued earnings management,
executive shareholding and cost of equity capital[J].
Finance and Accounting Newsletter, 2021(08): 40-43.
Xu Cheng. Analysis of Equity Structure and Corporate
Performance of Listed Companies[J]. Journal of
Financial Management Research, 2020(08): 35-40.
Research on the Impact of Executive Shareholding Ratio on Profitability of GEM Listed Companies
179
