
Creative Economic Sustainability in Digital Transformation and
Government Policy Instability in the Society Era 4.0
Hardi Fardiansyah
Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Creative Economy Sustainability, Digital Transformation, Government Policy Instability.
Abstract: Economic resilience is a dynamic situation of the nation's economic life and resilience that contains the ability
to develop national strength when facing and overcoming all threats, obstacles, disturbances, challenges both
from abroad or within the country either directly or indirectly to ensure the economy of the state of the
Republic of Indonesia derived from Pancasila and the 1945 Constitution. Digital transformation is currently
one of the important agendas regarding Indonesian economy, which is Indonesia's creative economy, the
demand for transformation is a top priority for companies, to be more agile in a market which changing
rapidly. Those changes are a result of fundamental, disruptive and dynamic transformation. This research uses
empirical and qualitative method, and or a combination of both. The results of creative industry research have
contributed to economic development. However, it’s still had many issues, especially regarding human
resources, which has an impact on competitive advantage, based on the concept of competitive advantage,
having local resources and support for protection policies from the government, also domestic and foreign
markets. In order to gain a sustainable competitive advantage, digital transformation, collaboration and
cooperation from all parties involved in the entrepreneurial ecosystem in each creative industry area are
needed.
1 BACKGROUND
The creative economy sector in Indonesia provides a
significant economic contribution. The development
of the creative economy in Indonesia is supported by
the Presidential Instruction of the Republic of
Indonesia Number 6 of 2009. This industry consists
of: Advertising (creation and production of
advertisements), architecture (city planning,
landscaping, etc.), arts, crafts, design (interior,
exterior) , graphics), fashion (styling), video, film &
photography, interactive games, music, performing
arts, publishing & printing, computer services &
software, television & radio, research &
development. (Meira,2013) The creative industry is
an industry based on creativity and innovation
utilizing natural resources and the environment. This
creativity and innovation added value to the product
and has a positive impact on the economy and social
life of the community. In accordance with the West
Java Provincial Government Regional plan as stated
in the West Java Regional Medium-term
Development Plan (RPJMD) 2013 – 2018, Chapter
VI-4 (Source: West Java Regional Medium-term
Development Plan (RPJMD) 2013 – 2018, Chapter
VI-4), stated that one of the strategies in the industrial
sector is to increase industrial competitiveness, with
the following policy directions:
1. Increasing small and medium-sized industrial
business units and inter-industry partnerships;
2. Increased production and quality of leading
industries (agro-industry, creative industry and
information and communication technology
industry).
With this, the creative industry becomes the main
focuses of the regional government's industrial sector
program. According to Hesmondhalgh and Pratt in
Maryunani, Salfitrie Roos and Mirzanti, Isti
Raafaldini, (Issenberg, 2011) the creative industry
began with the commercialization of cultural
production in the nineteenth century, and from the
early 20th century onwards then increased in
advanced industrial societies. One of the first
literatures on the creative industries was Adorno and
Horkheimer, who developed the notion of the 'culture
industry', which was intended to draw attention to the
commodity of art. In the mid-20th century, the growth
of the “culture industry” increased. (Hoffman, 2000)
332
Fardiansyah, H.
Creative Economic Sustainability in Digital Transformation and Government Policy Instability in the Society Era 4.0.
DOI: 10.5220/0012005700003582
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP) UTA â
˘
A
´
Z45 Jakarta (ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022), pages 332-340
ISBN: 978-989-758-654-5; ISSN: 2828-853X
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

The term creative industries then began to be used by
researchers to describe those sectors of the British
economy where science and creativity gain economic
and social value to goods and services.
In its development, the creative industry is
considered as one of the most promising economic
activities in developed countries, having an
environment that has the potential to contribute to job
availability. Furthermore, another role of creative
industries in research and policy making is the
performance of economic innovation. Later, this
innovation becomes one of the sources of strength for
competitive advantage. Local Competitive
Advantage Porter stated that the factor of comparative
advantage has been outweighed by technological
advances. However, each region still has a special
advantage factor which is not only based on low
production costs, but more than that, is the existence
of innovation. Therefore, each region is expected to
have the ability to innovate how to produce products
or services in order to be superior products with great
competencies that describe the unique potential of
each region. (Yun, 2017:1-11)
Regions that have reached the core competency
stage have four attributes:
1. The ability to provide access to a wider
variety of markets
2. The ability to make a significant contribution
to customer opinions regarding the benefits
of goods and services offered.
3. The ability to produce superior goods and
services that are difficult to imitate and create
entry barriers for other regions to provide
similar services.
4. The ability to perform complex coordination
of various technologies and skills.
Local Economic Development (LED) emerged as
a new strategy in regional development. In this
concept, communities determine what and how their
own future will be, identify local potentials
(resources), and think about what kind of economic
activities will be developed according to local
potentials and characteristics. According to Blakele,
the main goal of local economic development is to
create and increase the number and types of jobs that
are adapted to the skills and expertise of the local
community. The more job opportunities for local
workers develop, the more the welfare of the
community will increase. An increase in the welfare
of the community is an indication that the region is
experiencing development.
Each region has a pattern of economic growth that
is different from other regions. Therefore, the first
step of planning the economic development is to
recognize the economic, social and physical
characteristics of the region itself, including its
interactions with other regions. Thus, every region
will have different economic development strategies.
On the other hand, the plan of regional economic
development strategies, both in the short and long
term, an understanding of the theory of regional
economic growth, which is summarized from a study
of patterns of economic growth from various regions,
is a factor that is sufficient to determine the quality of
the region economic development plan.
MSMEs/SMEs who have inadequate knowledge
and experience with digital models in carrying out
their business activities have a great potential when
experiencing a crisis during the COVID-19
pandemic. In contrast with large or established
businesses that have experience knowledge and
access to digital models which made them respond to
changes relatively quickly, MSMEs/SMEs must
adopt digital models then continue to carry out digital
transformation into their business activities in order
to remain stable. Digital transformation can also be
carried out as one of the anticipations to have
sustainable business activities after the COVID-19
pandemic, namely the new normal era.
Based on a report from the World Economic
Forum, during the COVID-19 pandemic the use of
digital models experienced a significant increase.
Internet usage increased by 70%, the use of
application-based communication increased by 2
times and the daily use of video streaming services
increased by 20 times. Below are some factors in the
era of digital transformation. (Kurjakovic; Masuda;
Kohda, 2017)
1. In the era of digital transformation, the
business sector is expected to be able to adapt
to changes that occur and adjust its business
strategy in order to maintain its competitive
advantage
2. Changes in the business sector that constantly
occurs pose challenges for MSMEs/SMEs to
harmonize information technology with their
business processes.
3. In digital transformation, business owners do
not only use technology to increase efficiency
in running a business, but can also explore
existing potentials through digital innovation.
According to Article 3 of Law Number 20 of 2008
concerning Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
(MSMEs) (Republic Of Indonesia Law Number 20,
2008:Article 3) the objective of Micro, Small, and
Medium Enterprises shall be engendering and
developing their businesses in the context of building
the national economy based on equitable economic
Creative Economic Sustainability in Digital Transformation and Government Policy Instability in the Society Era 4.0
333

democracy. One of the objectives of empowering
MSMEs based on Article 5 letter (c) of Law Number
20 of 2008 concerning Micro, (Republic Of Indonesia
Law Number 20, 2008:Article 5) Small and Medium
Enterprises is to improving the role of Micro, Small,
and Medium Enterprises in regional development,
creating job opportunities, even distribution,
economic growth, and alleviation of people from
poverty. Meanwhile, digital transformation, also
known as digitization, has changed the way people
communicate and interact with their environment.
(Simon; Fischbach; Schoder, 2017)
Digital transformation is defined as a company's
initiative to use new capabilities by leveraging digital
technology to change an organization's strategy and
operations. Digital transformation is a new concept
that looks different for every company, digital
transformation is closely related to: (Berghaus and
Back, 2016)
1. The use and alignment of digital technology
within a company,
2. Make organizational alteration,
3. Enable activity
4. Create and capture new opportunities and
valuesopportunities and values.
According to Garzoni et al, the four-level
approaches to digital transformation are digital
awareness, digital needs, digital collaboration, and
digital transformation. Meanwhile, according to
Bautista et al, digital transformation is divided into 4
stages, namely analysis, execution, optimization and
big data. (Nasiri; Ukko; Saunila; Rantala, 2020) The
main goal of digital transformation is to redesign the
organization's business through the introduction of
digital technology, achieving benefits such as
increased productivity, reduced costs and innovation.
Successful and consistent digital transformation
requires not only investments in IT artifacts and
infrastructure (e.g. hardware, software, networks,
etc.), but also in strategic, intellectual, structural,
formal and informal, social and cultural dimensions.
(Li,2020)
Despite the high demand from the industry for a
digital transformation approach, most companies are
not satisfied with their current activities regarding
digital transformation. Digital transformation among
MSMEs ensue the four stages of the digital
technology initiation process, changes in functions
and processes, the management of the resulting skill
gap, and strategic shifts, which are also driven by
managerial cognition, social capital development,
human resource development, and organizational
capacity development. The needs of MSMEs in the
digital transformation processes are varied thus the
content privatization is needed through company size,
sector, and MSMEs, the speed of digital
transformation is actually determined by consumer
demands, the key factor to support SMEs to take
advantage of technological opportunities in
connection with digitalization is the adaptation of
high concepts with demands company specific.
(Jeansson and Bredmar, 2019)
Industry 4.0 and the digital transformation had
major challenges for companies and employees.
Digitalization requires radical changes both in terms
of strategy and in terms of culture within the
company. However, according to Ericson,
implementing digital transformation does not
necessarily require more disruptive and radical
changes in organizational culture and leadership.
Changes, adaptations and innovative business models
that do not involve large investments in new
technologies seem to be quite common among SMEs.
While digitalization can offer great opportunities for
SMEs to enter new markets, the path of digital
transformation remains unclear, and manufacturing
SMEs face major barriers to digital services. (Graf;
Peter; Grivas, 2019)
2 PROBLEM FORMULATION
1. How is Creative Economy Sustainability as an
Alternative Solution to Improve National
Competitiveness in the Digital Age?
2. How the Government Prevents Creative
Economy Instability and Digital
Transformation in Indonesia?
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The problems that have been formulated above will
be answered or solved using an empirical juridical
approach. The juridical approach (law is seen as a
norm or das sollen), this research uses legal materials
(both written law and unwritten law or both primary
and secondary legal materials). Empirical approach
(law as a social, cultural reality or das sein), because
this research uses primary data obtained from the
field research. Thus, the empirical juridical approach
in this study is intended to analyze the problem by
combining legal materials (which are secondary data)
with primary data obtained in the field. Thus, the
empirical juridical approach in this study is intended
to analyze the problem by combining legal materials
(which are secondary data) with primary data
obtained in the field, namely about the sustainability
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
334

of the creative economy in digital transformation,
which is engaged in industry and has a large, small,
or medium scale.
4 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
4.1 People's Economic Theory
A Background
There are 4 (four) reasons why the people's economy
needs to be used as a new paradigm and a main
strategy for Indonesia's economic development. The
four reasons referred to are:
1. Characteristics of Indonesia
The success of South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore,
Brazil, imitated the concept of economic
development carried out by Western European and
American countries, in fact for other developing
countries, which applied the concept that gave
different results. By relying on foreign loan funds to
finance development, investment from abroad,
strengthening the export substitution industry, for two
to three decades it has succeeded in encouraging a
fairly high growth of national output and providing
ample employment opportunities for the people. Even
though Indonesia was once dubbed as one of the eight
countries in Asia as the Asian Miracle or a magical
Asian country, due to its fairly steady economic
growth rate for three decades, it turned out to be very
vulnerable when faced with supply shocks. The Bath
currency crisis in Thailand, in fact, quickly brought
Indonesia into a serious economic crisis and in a very
short time, the Indonesian economy collapsed.
This fact shows us that the concepts and strategies of
economic development that are successfully
implemented in one country will not necessarily be
successful if applied in other countries. Harrod-
Domar's growth theory, Rostow's growth theory,
David Romer's growth theory, Solow's growth
theory, are built from the structure of the community
of economic actors that is different from the
economic structure of Indonesian society. Each
theory is always built with certain assumptions,
which not all countries have assumed conditions.
That is why, to build a strong, stable and just
Indonesian economy, it is not possible to use existing
generic theories. We must formulate our own concept
of economic development which is in accordance
with the political demands of the people, the demands
of our constitution, and in accordance with our
objective conditions and subjective situation.
2. Constitutional Demand
Although the formulation of our constitution
concerning the economic order that should be built is
not clear enough and a bit hard to explain and even
can be interpreted in various ways (a kind of
pendulum clock economy, depending on the owner’s
ideological beliefs); however from historical analysis
actually the meaning is quite clear. (Republic Of
Indonesia Constitution, 1945:Article 27 & 33) The
spirit of the economic system of business which
money based on kinship is an economic system that
provides opportunities for all people to participate as
economic actors. The economic order that should be
built is not a monopoly, monopsony or oligopoly
economic system. The economic system demanded
by the constitution is an economic system that
provides opportunities for all people or citizens to
own assets in the national economy. The national
economic system is an economic system that clearly
distinguishes which goods and services must be
produced by the government and which goods and
services must be produced by the private sector or the
non-government sector. Regarding the form of
economic institutions, although in the explanation of
article 33 it is interpreted as a form of cooperative, but
must adapt to the development of society and the
environment.
3. Empirical Facts
Rupiah against the dollar, apparently did not paralyze
the national economy. That due to the economic
crisis, the prices of basic necessities have soared,
inflation has barely been controlled, exports have
decreased (especially exports of manufactured
products), imports of capital goods have decreased,
production of manufactured goods have decreased,
unemployment has increased. However, all of this did
not have a serious impact on the people's economy,
whose source of income is not from selling labour.
Many businesses that are engaged in or owned by
the people, whose products do not use imported
materials, have almost no significant shocks. Another
fact is that when investment was zero percent, and
there was even a decrease in capital, it turned out that
the Indonesian economy was able to grow 3.4 percent
in 1999. This all proves that the Indonesian economy
will be strong if the economic actors are carried out
by as many citizens as possible.
4. Failure of Economic Development
The economic development that we have carried out
for more than 32 years, from one aspect, has indeed
shown quite good results. Even though during that
period, we faced 2 economic crises (namely the
Pertamina debt crisis and the crisis due to the drop in
Creative Economic Sustainability in Digital Transformation and Government Policy Instability in the Society Era 4.0
335

oil prices), however the average national economic
growth is still above 7 percent per-year. Per capita
income or GDP also increased sharply from 60 US
dollars in 1970 to 1400 US dollars in 1995. The
volume and value of oil and non-oil exports also
increased sharply. But on another aspect, we must
also recognize that the number of poverty is
increasing (SUSENAS) the income gap between
population groups and between regions is getting
wider, the amount and ratio of debt to GDP has also
increased sharply, as well as the transfer of ownership
of economic assets from the people to a small group
of citizens.
Although we have implemented various poverty
alleviation programs, we have launched 8
equalization pathways, but in fact all of them have not
been able to solve these problems. Therefore, what
we really need now is not a poverty alleviation
program, but to reformulate a development strategy
that is suitable for Indonesia. If the present economic
development strategy is correct, then all development
programs are the same as poverty alleviation
program.
B Sustainability Theory
Sustainable development aims to improve people's welfare,
to meet human needs and aspirations. Sustainable
development is essentially aimed at seeking equal
distribution of development between generations, both now
and in the future. According to KLH development (which
is basically more economically oriented) sustainability can
be measured based on three criteria, namely: (Djajaningrat,
2001)
1. There is no waste of use of natural resources or
depletion of natural resources;
2. No pollution and other environmental impacts;
3. The activities must be able to increase useable
resources
In line with the above concept, Sutamihardja stated that the
sustainable development targets include efforts to realize
the occurrence of: (Susmihardja,2004)
1. Equitable distribution of the benefits of
intergenerational development results
(intergenerational equity) which means that the use
of natural resources for the sake of growth needs to
pay attention to reasonable limits in the control of
ecosystems or environmental systems and is directed
at replaceable natural resources and emphasizes the
lowest possible exploitation of resources
irreplaceable nature.
2. Safeguarding of the preservation natural resources
and the environment and preventing ecosystem
disturbances in order to ensure a good quality of life
for future generations.
3. The use and management of natural resources is
solely for the sake of pursuing economic growth
regarding equitable distribution of sustainable use of
natural resources between generations.
4. Maintaining sustainable people (society) welfare
both in the present and in the future (inter temporal).
5. Maintaining the benefits of development or
management of natural resources and the
environment that have long-term or sustainable
impacts between generations. Also, maintaining the
quality of human life between generations in
accordance with their habitat or replaceable
resources.
From Fauzi’s economic point of view, there are at least
three main reasons why economic development must be
sustainable. (Fauzi, 2004)
1. First, concerns moral reasons. The current
generation enjoys goods and services produced from
natural resources and the environment, so it is
morally necessary to pay attention to the availability
of these natural resources for future generations. The
moral obligation includes not extracting natural
resources to the point of damaging the environment,
which could deprive future generation opportunities
to utilize the same advantages.
2. Second, regarding ecological reasons, for example,
biological diversity has a very high ecological value,
therefore economic activities should not be directed
at the use of natural resources and the environment
alone, which in the end can threaten ecological
functions.
3. Third, economy is the reason to pay attention to the
sustainability aspect. The reason from the economic
side is still in debate because it is not known whether
or not economic activity has met the sustainability
criteria, as we know, that the sustainable economic
dimension itself is quite complex, the sustainability
aspect from the economic side often only limited to
the measurement of intergenerational welfare
maximization.
According to Sutamihardja, in the concept of sustainable
development, policy collisions may occur between the need
to explore natural resources to fight poverty and the need to
prevent environmental degradation also need to be avoided.
Sustainable development also requires the fulfillment of
basic needs for the community and providing broad
opportunities for community members to pursue the ideals
of a better life without compromising future generations.
The development of the concept of sustainable
development needs to consider socially and culturally
reasonable needs, disseminate values that create different
consumption standards within the limits of the
environment's capabilities, and naturally everyone is able to
aspire to it. However, there is a tendency that the fulfilment
of these needs will depend on the need to realize economic
growth or production needs at a maximum scale.
Sustainable development clearly requires economic growth
where the main needs cannot be consistent with economic
growth, as long as the content of growth reflects the
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
336

principles of sustainability. However, the reality is that high
production activity can occur simultaneously with
widespread poverty. This condition can harm the
environment. So sustainable development requires people's
needs by increasing their production potential and at the
same time ensuring equal opportunities for everyone. How
can this be done? The government certainly needs a policy
realistic strategy that can be implemented with an
appropriate control system. Exploitation of natural
resources is recommended preferably on replaceable
natural resources so that the ecosystem or environmental
system can be maintained. (Heal, 1998)
5 RESULTS OF ANALYSIS AND
DISCUSSION
5.1 Creative Economy Sustainability as
an Alternative Solution to Improve
National Competitiveness in the
Digital Era?
As a new talent, the creative economy is expected to
be able to leverage competitiveness. Its existence
requires recognition that must be realized through
various regulations/policies and joint actions between
regulators, mediators, facilitators, implementors,
actors, and even other beneficiaries.
From a managerial perspective, a sense of urgency
perspective, there are 5 (five) creative economy
development agendas that have been identified as
requirement which need complete arrangement and
management. The five agendas are: (Buhler, 1999:14)
1. Mapping of operational constraints;
2. Breakthrough efforts;
3. Commitment and action;
4. Public awareness; and
5. The importance of database
The term creative economy developed from the
concept of creativity-based capital that could
potentially increase economic growth in an area.
According to President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono
in Agung Pasca Suseno, "The creative economy is the
fourth wave of economy which is a continuation of
the third wave of economy with an orientation
towards creativity, culture, and cultural and
environmental heritage". Jo Foord (Foord, 2008)
stated that there must be an integration between
public institutions and private sector with corporate
growth and social causes that are increasingly popular
at the city regarding the development of the creative
economy.
Promotional activities and support for the
development of creative industries require strategic
planning. At the same time, the growth of creative
industry employment began to be erratic in the
centers of cities thus it need wider and greater
economic knowledge to overcome them. Economy
creative based on the book titled The Development of
Indonesia Economy Creative 2025: Indonesia
Economy Creative Plan in 2009-2015, published by
the Ministry of Trade of the Republic of Indonesia is
a new economic era that intensifies information and
creativity by relying on ideas and stock of knowledge
from its human resources as the main production
factor in its economic activities. In other words, the
main concern of the creative economy is on the
human capital factor.
Science (knowledge) in the modern economy
plays the most important role. A society that
develops, is advanced in civilization and has good
welfare is a society that has a good foundation of
economic knowledge. This is absolutely necessary,
especially in Indonesia, whose economy is still
developing. Quoting from the Creative Economy
Blueprint 2025, the creative economy is an act to add
value (economic, social, cultural, environmental)
based on ideas born from the creativity of human
resources (creative people) and the implementation of
science, including cultural heritage and technology.
Creativity is not limited to works based on art and
culture, but can also be based on science and
technology, engineering and telecommunications.
There are 3 main things that form the basis of the
creative economy, including creativity, innovation
and invention.
a. Creativity
Can be described as a capacity or ability to produce
or create something unique, fresh, and generally
accepted. It can also generate new or practical ideas
as a solution to a problem, or do something different
from the existing one (thinking out of the box).
Someone who has creativity and can maximize that
ability, can create and produce something useful for
themselves and others
b. Innovation
A transformation of ideas based on creativity by
utilizing existing inventions to produce a product or
process better than the original, added value, and its
usefulness. As an example of innovation, look at
some of the innovations in Youtube videos with the
keyword "lifehack". The video shows how an original
product is then innovated and can produce something
of higher selling value and more useful.
c. Invention
This term emphasizes creating something that has
never existed before and can be recognized as a work
Creative Economic Sustainability in Digital Transformation and Government Policy Instability in the Society Era 4.0
337
that has a unique function or has never been known
before. Making applications based on Android and
iOS is also one example of inventions based on
technology and information that greatly facilitates
humans in carrying out their daily activities.
The term Creative Economy has been widely
discussed since John Howkins, wrote the book
"Creative Economy, How People Make Money from
Ideas". Howkins states the Creative Economy as an
economic activity in which its inputs and outputs are
ideas. In short, the essence of creativity is an idea. So
it is conceivable that only with the ideas, someone
who is creative can earn a relatively high income. The
economic condition expected by Indonesia is a
sustainable economy and also has several sectors as
pillars and supports for economic activity in
Indonesia.
Sustainability in question is the ability to adapt to new
geographical conditions and economic challenges,
which ultimately results in sustainable growth. High
growth is reflected in the competence of individuals
in creating innovation. Creative Economy in which
there are creative industries have high bargaining
power in a sustainable economy because individuals
have creative basic which they can use to create
innovations. In Indonesia, what is meant by
contribution to the economy are as follows: First,
contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
According to data from the Central Statistics Agency
(BPS) this industry in Indonesia contributed 7.28% to
GDP in 2008 and 7.8% to GDP on average from 2002
to 2008. The creative industry's contribution to GDP
mostly came from fashion (3.7%) and handicrafts
(1.9%). Second, job creation, data from BPS shows
that the creative industry in Indonesia absorbed
7,686,410 workers in 2008 and an average of
7,391,642 workers employment from 2002 to 2008.
On average from 2002 to 2008, the creative industry
absorbed 7.7% of the total workforce in the industry.
With such a large percentage, the creative industry is
the fifth largest industry that absorbs labour after the
agriculture, livestock, forestry, and fisheries
industries; trade, hotel and restaurant; community
services; and processing services. (Department Of
Trade Republic Of Indonesia)
5.2 The Government Prevents Creative
Economy Instability and Digital
Transformation in Indonesia
Indonesia is one of the countries that has the greatest
economic performance. In 2015 Indonesia recorded
growth in gross domestic product (GDP) 4.79%
higher than global economic growth which was
estimated to only reach 2.4%. This positive climate is
certainly the right moment for the government to
strengthen the foundation of the economy, especially
in the real sector. One of the real sectors that has
become a priority is the creative economy. The
government is optimistic that it will become the
backbone of the Indonesian economy. In contrast to
other sectors that are highly dependent on the
exploitation of natural resources, the strength of the
creative economy relies more on the superiority of
human resources. (Burhanuddin, 2008)
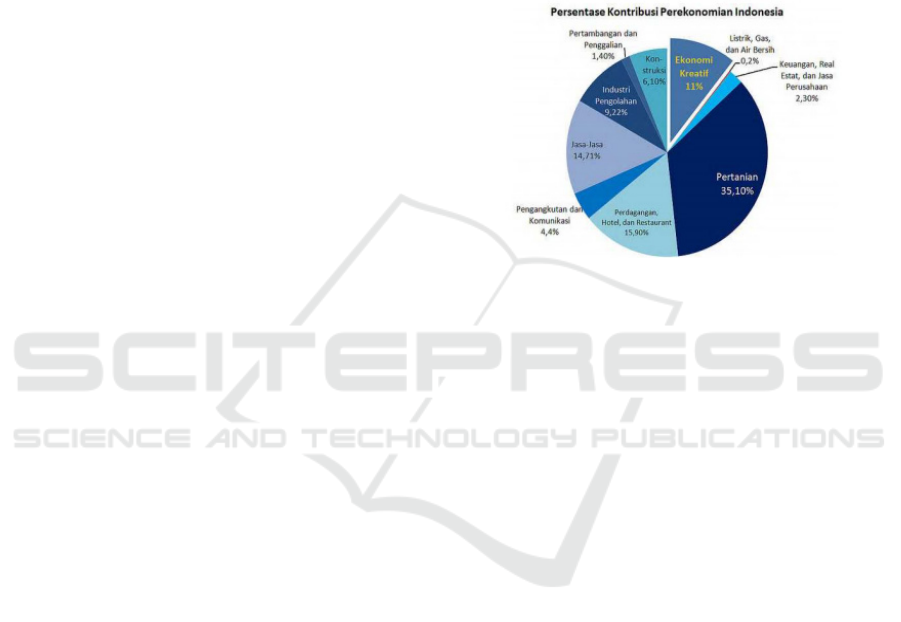
Diagram 1: Presentase Kontribusi Perekonomian Indonesia.
The creative industry in Indonesia has made a good
contribution to petrify the national economy. This can
be seen from the increasing number of creative
industries in Indonesia. So that it can make a very
good contribution to national economic growth. The
creative economic system is believed to be able to be
a solution in overcoming these problems, as well as
an alternative in facing global economic challenges
that will shift the existing economic system.
Indonesia, which is rich in culture and has a large
population, has enormous potential in developing the
creative economy. (Suwartawan and Purbadharmaja,
2017).
The development of the creative economy has
developed into a phenomenon in facing the
developments and challenges of globalization. The
information technology factor makes the
development of the creative economy more rapid, so
that the creative economy becomes an answer to the
challenges in the welfare of the community, besides
that the creative economy can reduce the
unemployment rate. (Fahrudin, 2008) The creative
economy will provide added value both to the
production process and to human resources so that the
creative economy system is believed to be able to
answer the challenges of various problems that exist
today. The development of science and technology
has been able to change the perspective, mindset, and
pattern of human life and is able to encourage the
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
338

creation of inventions which hinder the scarcity of
goods and services. (Saksono, 2012:93) Through
continuous innovation, research, development,
products and services are created according to
consumers want and need. Creative economy
development can increase business income. Revenue
is the amount of money that craftsmen receive from
selling products to customers. Income is one indicator
to measure the level of prosperity and welfare of the
community so that the size of economic income
reflects economic progress. (Azizah and Muhfiatun,
2017:66)
The government efforts in preventing the
instability of the creative economy and digital
transformation are:
1. Labour sector: the most constraining obstacle
is the absence of workers, this is further
exacerbated by the low quality and undiscipline
workers, as well as the poor management
system
2. Production process sector: the most
constraining obstacles is the poor
implementation management system which
includes operations and production,
governance, technology maintenance, and
innovation, in addition to the low quality of
human resources, which is reflected in the low
awareness of workers regarding safety and
quality.
3. Facilities sector: the most constraining obstacle
is the complexity of the bureaucratic process in
obtaining permits and assistance. Another
factor is the ignorance and inability of creative
economy human resources (owners) to make a
correct and good financial reports, general
infrastructure that is far from expectations.
4. Business competition sector: the most
constraining obstacle is the instability of raw
material prices and selling prices as well as the
number of craftsmen, another factor is the
insensitivity of creative economy actors to the
latest information and global competition.
6 CONCLUSION
1. Sustainability of the creative economy of
digital transformation is a concept in the new
economic era that intensifies information and
creativity by relying on ideas and knowledge
from human resources (HR) as the main
production factor in economic activity.
Therefore, ideas are an important factor in the
development of the creative economy. The
creative economy can affect the economy in
Indonesia because human resources in
Indonesia always have new ideas. Thus that the
creative economy sector experiences economic
growth which can be seen from the Gross
Domestic Product or GDP. Creative economy
has no effect on economic growth.
2. Based on the discussion above, it can be
concluded that the development of information
and communication technology contributes and
encourages the growth of the creative
economy, which can be used as a solution for
the welfare of the community because the
creative economy system provides added value
both to the industry itself or to its human
resources.
7 SUGGESTION
1. There are still obstacles to developing creative
economy such as lack of fund, skilled
personnel, and lack of fund assistance from the
local government. Therefore, for cases in
several regions, it is an assignment for us to
solve problems more serious and need
cooperation from all parties, both the
community, the government and the private
sector in developing the creative economy so
that their products have innovative value and
high competitiveness also are useful for
improving more stable economic growth.
2. The existence of the creative economy has a
positive impact in reducing the unemployment
rate and will ultimately increase the level of the
economy.
REFERENCES
A. Berghaus, S., & Back, “Stages in Digital Business
Transformation: Results of an Empirical Maturity
Study.” 10th Mediterranean Conference on Information
Systems. Cyprus., 2016.
A. Javaid, S. Kurjakovic, H. Masuda, and Y. Kohda,
“Enabling digital transformation in SMEs by
combining enterprise ontologies and service
blueprinting,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including
Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes
Bioinformatics), vol. 10371 LNCS, pp. 224–233, 2017,
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319- 61240-9_21.
Abdullah, Burhanuddin. 2008. Ekonomi Islam. Jakata: PT.
Raja Grafindo Persada
Buhler, P. (1999). Managing in the 90‘s:Training 90‘s
style: An Organizational Requirement. National
Research Bureau 60 (14)
Creative Economic Sustainability in Digital Transformation and Government Policy Instability in the Society Era 4.0
339

D. Simon, K. Fischbach, and D. Schoder, “An exploration
of enterprise architecture research,” Commun. Assoc.
Inf. Syst., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 1–71, 2013, doi:
10.17705/1cais.03201.
Djajadinigrat, 2001 Untuk Generasi Masa Depan:
“Pemikiran, Tantangan dan Permasalah Lingkungan”,
ITB.
Departemen Perdagangan RepublikIndonesia:
Pengembangan Ekonomi Kreatif Indonesia 2025:
Rencana Pengembangan Ekonomi Kreatif Indonesia
2009-2015, Deperdag RI, 2009
Fahrudin, Adi. 2008. Pemberdayaan Partisipasi &
Penguatan Kapasitas Masyarakat. Bandung:
Humaniora.
F. Li, “The digital transformation of business models in the
creative industries: A holistic framework and emerging
trends,” Technovation, vol. 92–93, no. November, pp.
1–10, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.technovation.2017.12.004.
Fauzi.A. 2004, Ekonomi Sumber Daya Alam dan
Lingkungan, Teori dan Aplikasi, Gramedia Pustaka
Utama, Jakarta
Genisa Meira, Tity Soegiarty, Bandi Sobandi. (2013). Kain
Tenun Ikat Dengan Bahan Sutera Alam (Analisis
Deskriptif Oranamen Kain Tenun Ikat dengan Bahan
Sutera Alam di Kampung Tenun Panawuan Kabupaten
Garut). Kriya Tenun dan Tekstil, Volume 1, Nomor 3,
Oktober 2013
Isenberg, Daniel. (2011). The Entrepreneurship Ecosystem
Strategy As A New Paradigm For Economy Policy:
Principles For Cultivating Entrepreneurship. Babson
Entrepreneurship Ecosystem, Babson College, Babson
Park: MA
Hoffman, Nicole P. (2000). An Examination of the
"Sustainable Competitive Advantage" Concept: Past,
Present, and Future. Academy of Marketing Science
Review volume 2000 no. 4
Herie Saksono, ―Ekonomi Kreatif : Talenta Baru Pemicu
Daya Saing Daerah,‖ Jurnal Bina Praja Vol. 4 No. 2
(Juni 2012): 93.
Heal, G.1998 Valuing the Future: Economic Theory and
Sustainability. Columbia University Press.New York
Howkins, John. 2001. Creative Economy: How People
Make Money from Ideas. London: Pinguin Global.
Komang Suwartawan dan Purbadharmaja, ―Pengaruh
Modal dan Bahan Baku Terhadap Pendapatan Melalui
Pengerajin Patung Kayu di Kecamatan Sukawati
Kabupaten Gianyar,‖ Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan
Universitas Udayana Vol. 6 No. 9 (September 2017):
1633.
JinHyo Joseph Yun, et al. (2017). Growth of a platform
business model as an entrepreneurial ecosystem and its
effects on regional development, European 10
AdBispreneur: Jurnal Pemikiran dan Penelitian
Administrasi Bisnis dan Kewirausahaan Vol. 3, No. 1,
April 2018, DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24198/adbispreneur.v3i1.16083, hal
1-11 Planning Studies, 25:5, 805-826, DOI:
10.1080/09654313.2017.1282082
J. Jeansson and K. Bredmar, “Digital Transformation of
SMEs : Capturing Complexity,” 32nd Bled
eConference Humaniz. Technol. a Sustain. Soc. BLED
2019 - Conf. Proc., 2019, doi: 10.18690/978-961-286-
280-0.28.
Jo Foord, 2008, Strategies for creative industries: an
international review, Creative Industries Journal
Volume 1 Number 2 Cities Institute, London
Metropolitan University.
M. Nasiri, J. Ukko, M. Saunila, and T. Rantala, “Managing
the digital supply chain: The role of smart
technologies,” Technovation, vol. 96–97, no. March, p.
102121, 2020, doi:
10.1016/j.technovation.2020.102121.
M. Graf, M. Peter, and S. Gatziu-Grivas, Foster Strategic
Orientation in the Digital Age. Springer International
Publishing, 2019.
Siti Nur Azizah dan Muhfiatun, ―Pengembangan Ekonomi
Kreatif Berbasis Kearifan Lokal Pandanus Handicraft
dalam Menghadapi Pasar Modern Perspektif Ekonomi
Syariah,‖ Jurnal Aplikasi Ilmu-ilmu Agama Vol. 17 No.
2 (2017): 66.
Sutamihardja, 2004 Perubahan Lingkungan Global;
Program Studi Pengelolaan Sumber Daya Alam dan
Lingkungan Sekolah Pascasarjana; IPB
Undang-Undang Dasar 1945
Undang-Undang Nomor 20 Tahun 2008 tentang Usaha
Mikro, Kecil dan Menengah bahwa Usaha Mikro, Kecil
dan Menengah (UMKM)
ISCP UTA’45 Jakarta 2022 - International Seminar and Call for Paper Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta
340
