
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19
Yan Wang
1
and Yunlang Xie
2
1
School of Accounting, Research Center for Accounting and Economic Development of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao
Greater Bay Area, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies, Guangzhou, China
2
School of Accounting, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies, Guangzhou, China
Keywords: Innovation, CSR, COVID-19, Corporate Competitiveness.
Abstract: In 2020, COVID-19 spread all over the world, seriously threatening human life and health and severely
impacting economic development. Chinese pharmaceutical state-owned enterprise (SOE) Da An Gene
quickly developed new products and helped meet huge demands for protective supplies. Its “R&D innovation
and corporate social responsibility (CSR)” interactive mechanism formed in the course of long-term
innovation and capital accumulation enabled it to seize opportunities brought by the epidemic. This study
explores the path of how innovative SOEs created value through interaction of R&D innovation and CSR
with case study against the background of COVID-19, and whether reform of state-owned capital regulatory
system to inject market vitality into SOEs can effectively transform the interaction mechanism of R&D
innovation and CSR into sustainable core corporate competitiveness.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Organization for Economic Co-
operation and Development (OECD) in 2020, the
wide spread of COVID-19 is considered one of the
biggest public health security incidents in the
contemporary era. In addition to public health, it has
produced catastrophic impacts on the economy. Due
to their weak financial capabilities, micro and small
enterprises have halted production or closed down on
a large scale (
Bartik A et al., 2020). Enterprises need
to find a survival mechanism in crises (
Champion D,
1999
). In the context of sudden disasters such as
COVID-19, companies with the ability to innovate
and launch innovative products can more quickly
adapt to rapidly changing external environment
(
Amore M D, 2015). However, they need to undergo
a long technological R&D cycle and consume a lot of
human and financial resources, so most of them give
priority to reducing costs (
Bushee B J, 1998). On the
other hand, studies have shown that companies that
continue to focus on product innovation can
accumulate R&D skills and innovation resources,
who are more likely to survive crises than those
adopting a cost-cutting strategy (
Amore M D, 2015).
Therefore, companies need to lay stress on
accumulating innovation capital and cultivating
innovative talents in the boom times, so as to quickly
adapt to changes when major crises come and
withstand the impacts of huge external shocks. On the
other hand, COVID-19 has highlighted the
importance of CSR. CSR can not only reduce
companies’ production and labor cost (
Berman S L
et al., 1999
), affect the recruitment, retention and
motivation of employees (
Aguilera R V et al., 2007),
but also improve customer satisfaction and corporate
reputation, thereby affect customers’ loyalty and
purchase intention (
Lee S et al., 2020). During
economic crises, companies actively fulfill their
social responsibilities for the purpose of gaining the
trust of stakeholders and the public (
Popkova E et al.,
2021
), which helps them effectively coordinate the
relationship with stakeholders and thus survive
difficulties (
He H et al., 2020).
Under socialist market economy system, China’s
state sectors are the most important force for funding
and conducting innovative research, who provide
SOEs with stable talents, capital, knowledge, and
technical resources so that they can continue to work
on R&D and effectively commercialize patents and
R&D results (
Cao X et al., 2020). SOEs enjoy more
resources from government departments than private
enterprises, but should assume more CSR, especially
during difficult times such as economic crises or
natural accidents (
Zhu Q et al., 2016). However,
there are some problems in their development, such
Wang, Y. and Xie, Y.
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19.
DOI: 10.5220/0011954200003536
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment (ISWEE 2022), pages 175-186
ISBN: 978-989-758-639-2; ISSN: 2975-9439
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
175

as imperfect supervision mechanism, which lead to
their limited development and insufficient vitality. In
respond, the state proposed to continue to deepen the
reform of the state-owned assets management system,
and impose more supervision on specialized state-
owned capital investment and operating companies,
so as to release the management power of SOEs,
stimulate their vitality, realize the maintenance and
appreciation of state-owned assets, and ensure their
role as main players in the market.
Da An Gene Co., Ltd. of Sun Yat-sen University
(hereinafter referred to as “Da An Gene”) is a state-
owned listed pharmaceutical company that draws
support from Sun Yat-sen University in terms of
scientific research. Since its establishment in 1991, it
has been focusing on R&D innovation. The company
has rich innovation resources and practical
experience, and adheres to fulfilling social
responsibilities based on product innovation. At the
outbreak of COVID-19 in early 2020, it quickly
seized market opportunities with its competitive
advantages in R&D innovation and CSR, and became
one of the first pharmaceutical companies to develop
and produce COVID-19 detection kits. In September
of the same year, its largest shareholder transferred its
equity to State-owned Assets Supervision and
Administration Commission of the State Council, and
the company began to receive assistance from
Guangzhou Finance Holdings for capital operations,
which put the company into more active market
competitions. Therefore, Da An Gene is a typical case
for studying the role of interaction between R&D
innovation and CSR in improving enterprises’ core
competitiveness, helping them resist the impacts of
COVID-19, increasing the value of state-owned
assets, and exploring potential development
opportunities brought by the reform of regulatory
model after transferring state-owned assets and the
path of corporate value creation after introducing
supervision of state-owned assets.
Although existing research points out the
importance of R&D innovation and CSR to the
development of enterprises, and that in most cases,
the fulfillment of CSR can promote R&D innovation,
there are few literatures on the mechanism of the
interaction and mutual promotion of R&D innovation
and CSR. This study focuses on the interaction
between “R&D innovation and CSR” among SOEs,
and adopts single case study with Da An Gene as a
typical case to discuss the path and mechanism for
innovative SOEs to create value through the
interaction between R&D innovation and CSR, and
explores whether competitive advantages of the
interaction mechanism can maintain and contribute to
the growth of corporate value in the market
environment of changed state-owned capital
operation and supervision model. Specifically, it
concludes “enterprises can accumulate R&D skills
and innovation resources if they continue to focus on
R&D and innovation”, that “enterprises can earn
social trust by fulfilling social responsibilities”, that
“R&D innovation and CSR interact and complement
with each other”, and that “reform of the state-owned
capital management system guarantees the long-term
and stable operation of interaction mechanism
between R&D innovation and CSR” based on case
study. By single case analysis, this study explores the
mutual promotion of R&D innovation and CSR in
innovative SOEs against the background of COVID-
19, enriches related theories, builds the path of
creating corporate value through an interaction
mechanism between R&D innovation and CSR, and
discusses whether Da An Gene’s interaction
mechanism can translate into its continuous core
competitiveness, which provides reference for the
development of other SOEs that implement a new
model of supervising state-owned assets.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The literature review is as follows.
2.1 Influencing Factors and Mode of
Innovation
R&D innovation is an important driving force for
social and economic development, as well as an
important factor for the sustainable development of
enterprises. In the past two decades, more scholars at
home and abroad began to study its role in
enterprises. In related literature, influencing factors
on it are divided into external factors and internal
factors. External factors mainly include national
policy (
Gu Y and Zhang L, 2017), competitive
environment (
Lunn J, 1986), etc., while internal
factors mainly include enterprise scale (
Chen C T et
al., 2004
), equity incentive (Chang X et al., 2015),
employee compensation and benefits (
Li J et al.,
2020
), and managerial personality (Shen H et al.,
2020
), which either promote or inhibit enterprise
R&D innovation. However, the most important
determinant in corporate R&D is capital. Companies
raise capital mainly through equity financing (
Huang
Y et al., 2014
) and debt financing (Anderson et al.,
1999
). In China, government subsidy is also an
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
176
important source for companies to promote R&D
innovation (
Czarnitzki D and Licht G, 2006).
Main modes of R&D innovation are internal
R&D, external R&D and collaborative innovation
(
Arvanitis S, 2012). Enterprises would adopt
different modes in R&D innovation. Relevant studies
have shown that main determinants in the choice of
innovation modes are corporate size and dedicated
system (
Hull C E and Covin J G, 2009). From the
perspective of enterprise scale, small companies are
more likely to choose internal R&D or external R&D
alone, while large ones tend to choose both internal
R&D and external R&D (
Fritsch M et al., 2001 and
Veugelers R et al., 1999
). After controlling the
variable of scale effect, when dedicated system is
strong, companies tend to conduct independent
external R&D; when internal information is more
important for R&D, they tend to conduct both internal
and external R&D (
Veugelers R et al., 1999). When
companies develop to a certain extent, collaborative
innovation can also improve their innovation
performance (
Wang C and Hu Q, 2020). Each
innovation mode can promote the development of
enterprises to a certain extent, but enterprises should
appropriately balance R&D activities under multiple
modes (
Denicolai S et al., 2016).
2.2 Relationship Between Innovation
and CSR
After analyzing 817 papers related to “research and
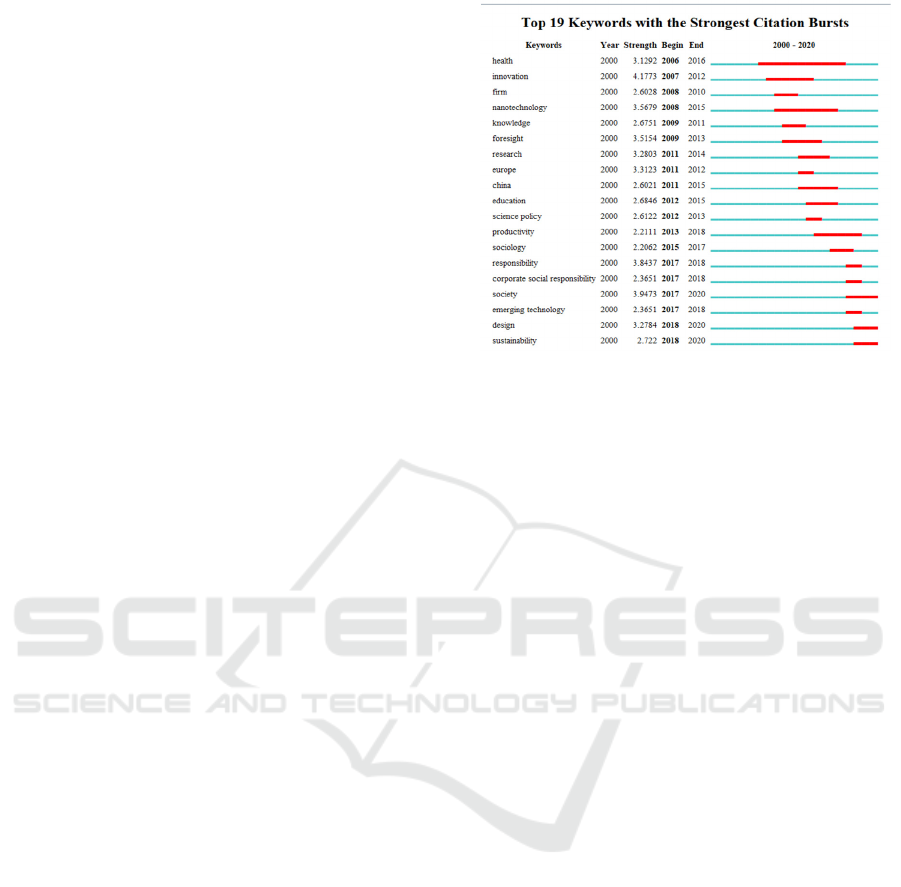
innovation” in the past 20 years (as shown in Figure
1.) with CiteSpace, we see that topics related to
corporate R&D and innovation and the fulfillment of
CSR have increasingly aroused the attention of
scholars in the last two years (
Luo X and Du S,
2015
). CSR mainly includes economic responsibility,
environmental responsibility and social responsibility
(
Yu W and Zheng Y, 2020), but no consensus has
been reached on the relationship between innovation
and the three kinds of CSR. Although some studies
point out companies will squeeze innovation
resources and inhibit innovation when fulfilling CSR
(
Mithani M A, 2017), that additional costs required
for performing CSR such as charity donations are
prone to cause agency conflicts (
Bethel J E et al.,
1993
), and that companies need to bear certain tax
risks in this regard (
Davis A K et al., 2015), but most
studies reveal the fulfillment of CSR exerts positive
effects on R&D innovation.
Figure 1. Keywords for innovation with strongest citation
bursts.
Bereskin believe that by setting up incentives for
employees and fulfilling economic responsibilities
related to employees, companies can improve
employee stability and innovation efficiency, and
inject vitality into R&D innovation (
Bereskin F L et
al., 2016 and Liu B et al., 2020
). Investing in
stakeholders such as shareholders and creditors
contributes to the sustainability of corporate profits
and financial support for continuous innovation
(
Choi J and Wang H, 2009). Miles and Covin point
out that environmental awareness enables enterprises
to carry out product innovation, solve social
problems, and improve business performance through
cost savings and market benefits (
Dionisio M et al.,
2020
). Voluntary charity activities and other social
activities can help enterprises not only solve social
problems and gain reputation, but also obtain more
external information to accumulate capital for future
innovation (
Holmes S and Smart P, 2009). In short,
companies that continue to perform CSR can win
social recognition, form a good industrial
responsibility atmosphere, and improve innovation
performance (
Bereskin F L et al., 2016 and Ko K-C
et al., 2020
).
Existing research points out R&D innovation and
CSR are important to the development of enterprises,
and that most activities for fulfilling CSR can
promote corporate R&D innovation, but there is no
study on whether the transfer of corporate holdings of
SOEs under the background of state-owned capital
reform can inject vitality into enterprise development,
and the mechanism of interaction and mutual
promotion of R&D innovation and CSR. This article
explores the role of R&D innovation activities and
CSR fulfillment in the development of SOEs against
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19
177

COVID-19 and China’s deepened SOE system
reform.
Figure 2. Framework of interaction between innovation and
CSR.
Based on review and summary of existing
research, this study builds an analytical framework
for interaction between R&D innovation and CSR in
promoting the sustainable development of SOEs in
the context of state-owned capital reform and
COVID-19, as shown in Figure 2. Enterprises gain
economic and product benefits through R&D
innovation, which is conducive for them to perform
CSR (in a broad sense). In turn, by performing CSR,
they win social trust and obtain more innovative
resources for R&D innovation. Under the background
of reform of state-owned capital management system
and COVID-19, the interaction between R&D
innovation and CSR facilitates the value creation of
SOEs, increases the value of state-owned assets, and
improves the core competitiveness of SOEs. This
study focuses on the process of R&D innovation of
SOEs, explores the mutual interaction and influence
of CSR performance and R&D innovation in the
context of COVID-19, and predicts that the reform of
state-owned assets supervision system will promote
this interaction mechanism to create value for SOEs.
3 EMPIRICAL METHODOLOGY
This part includes the empirical methodology as
follows.
3.1 Sample
This article follows the principle of typicality in case
selection and sets out the criteria for selecting case
company as follows (
Patton M Q, 1987). (1) The
company should have been focusing on R&D
innovation for a long time, embrace matured
innovation practice, and actively fulfill CSR, which is
the basis for exploring the path of mutual interaction
between R&D innovation and CSR. (2) It should be a
leader in the industry and perform well in COVID-19,
which make it a representative typical case. (3) It
should be east to obtain data about the company,
including public information to guarantees
availability and comprehensiveness, which is
conducive to the smooth progress of this study.
Following the above criteria, this study identified
Da An Gene as the sample enterprise. First of all, Da
An Gene is one of the state-owned university-run
enterprises that was founded early, has relatively
complete managerial mechanism, and embraces
excellent performance. It is also the first listed high-
tech enterprise run by
a university in Guangdong. As
a pharmaceutical company relying on the strong
scientific research strength of Sun Yat-sen
University, it has been emphasizing scientific and
technological R&D since its establishment, and has
achieved excellent results in vitro molecular
diagnostics. The company adopts diverse innovation
modes, including independent R&D, collaborative
innovation and technology introduction. As a state-
holding company, Da An Gene comprehensively
fulfills CSR. Secondly, the company performed
outstandingly in the fight against COVID-19. When
COVID-19 broke out in China, it quickly developed
nucleic acid detection kit (based on fluorescence
PCR) with ensured quality and producing capacity,
and earned a large number of domestic and foreign
orders, which brought it surging profits and better
development. In the meanwhile, Da An Gene has
accelerated its pace of market-oriented reform.
Guangzhou Finance Holdings will soon become its
state-owned asset investment and operation company,
thus realize modern governance of Da An Gene and
promote its sustainable development. Last but not
least, Da An Gene has been listed, so it is easier to
collect data in an all-round manner. Therefore, the
company is a very representative research case.
3.2 Data
To ensure the rigor of case study and improve the
reliability and validity of this study, we collected data
with triangulation. The data are mainly primary and
secondary data. Primary data include materials
collected from semi-structured interviews,
questionnaire, and field surveys, while secondary
data mainly consist of public information such as
assembly materials, minutes and reports of meetings,
publicity materials, and public information retrieved
via the Internet. They help us gain an in-depth
understanding of the entire process of Da An Gene’s
technological innovation, CSR fulfillment and state-
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
178
owned asset regulatory reform. Diversified sources of
data ensure the integrity and richness of information.
Table 1 shows details of sources of data about the case
company.
Table 1. Access to data about case company.
Type Sources Access
Primary
data
Financial manager
of Da An Gene
Semi-structured
interviews (sound
recorded)
Department head of
Guangzhou Finance
Holdings
Semi-structured
interviews (sound
recorded)
Secondar
y data
Assembly materials
Assembly materials,
product information,
annual reports
Publicity materials
Brochures, press
releases
Other public
information
Company website,
public information
retrieved via Internet
tools such as
browsers and
databases
Field investigation and interview of case company
were conducted by 7 team members. Before that, we
prepared the outline for survey of case company and
its controlling shareholder Guangzhou Finance
Holdings, trained team members, and divided work
among members to ensure smooth interview. During
interviews, 2 people asked and answered questions, 3
made notes, and 2 recorded to ensure data accuracy.
After that, recorded interviews were transcribed in a
timely manner to avoid memory deviation.
3.3 Measures
This paper adopts single case study to discuss mutual
promotion of R&D innovation and CSR by
longitudinal case analysis. In addition, it hopes to
build a mechanism and path for the interaction
between R&D innovation and CSR. Grounded
Theory is a method of establishing a substantive
theory from the bottom up, which generalizes original
data to form theoretical system (
Jantunen S and
Gause D C, 2014
), being suitable for constructing a
deductive path and consistent with expectations of
this paper.
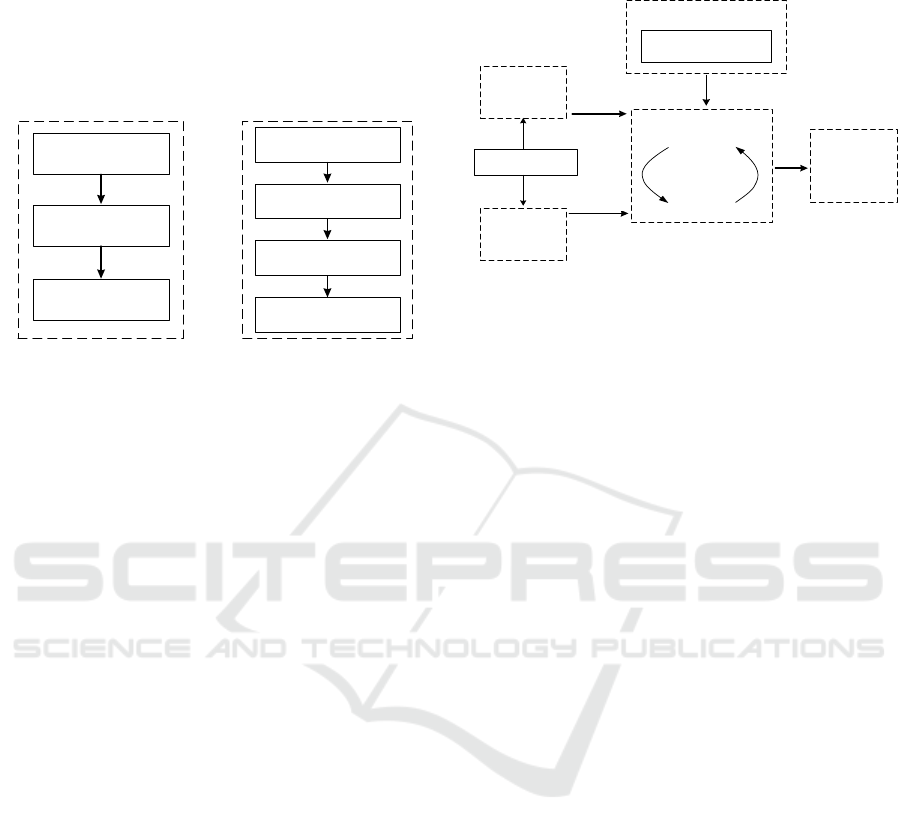
Grounded Theory mainly includes three
processes: open coding, axial coding and selective
coding, as shown in Figure 3. Open coding refers to
the process of decomposing, refining, and
categorizing data acquired. We decomposed original
data item by item, labeled and conceptualized them,
refined them into initial categories (subcategories),
and completed open coding based on expert opinions;
then conducted axial coding, namely to further
generalize subcategories, analyze the nature of each
subcategory and the connection relationship among
them, and summarize interconnected independent
subcategories into fundamental categories; and
finally integrated main category codes into core
categories through selective coding. Throughout the
process, we interpreted data as objectively as
possible, and repeatedly compared coding results
with materials to ensure that the obtained categories
are saturated.
Figure 3. Grounded theory coding process.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this part, the results and discussions will be
presented.
4.1 Framework of Innovation-CSR
interaction
The framework of innovation-CSR interaction.
4.1.1 Innovation
Innovation is an important cornerstone in enterprises’
long-term development. In the 1990s, traditional PCR
technology could not meet the needs of clinical
diagnosis. Based on access to a large amount of
foreign information, Da An Gene’s scientific and
technical personnel decisively worked on
fluorescence PCR technology in developing next
generation PCR products, which won support from
the Ministry of Health and the National Science and
Technology Commission, and was included as a key
research project for “Ninth Five-Year Plan” on
biotechnology. Da An Gene still focuses on the R&D
of PCR genetic testing kits now. It has played an
important role in several major epidemic disease
outbreaks in China, which mainly owes to its
emphasis on R&D innovation for more than 20 years.
The important events in its innovation and
development are shown in Table 2.
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19
179
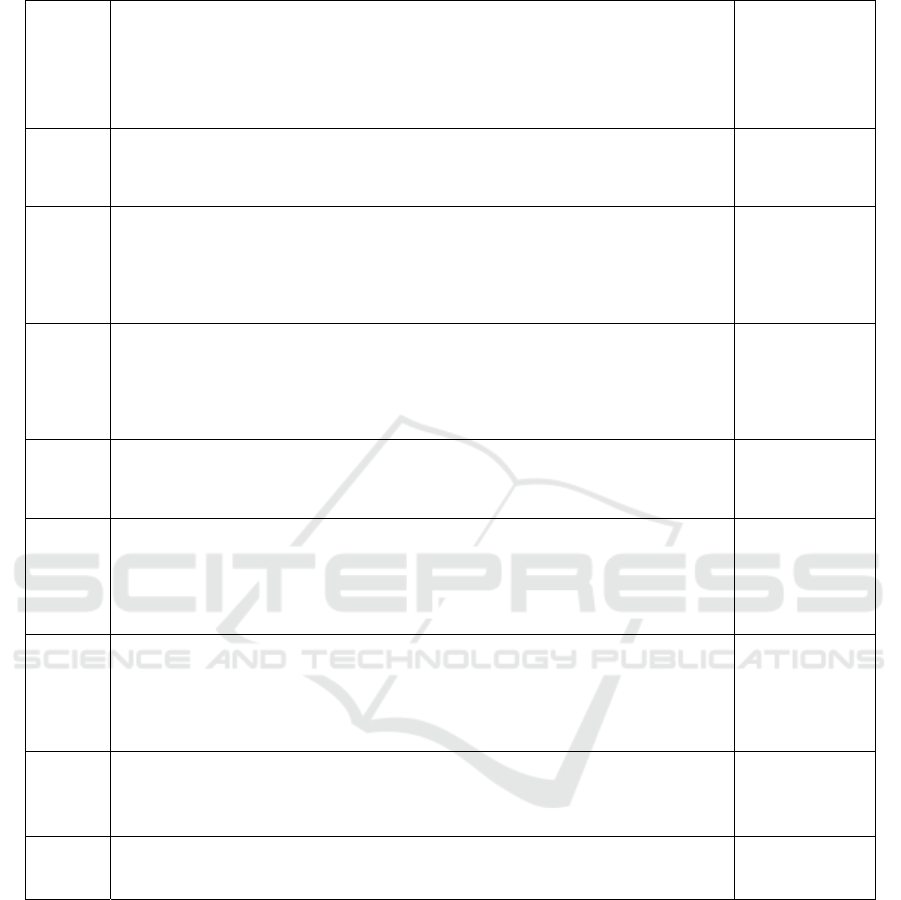
Table 2. Important innovation events in the development of Da An Gene.
Events
Innovation
capital
accumulation
(Fundamental
category)
1996
Independently developed fluorescence quantitative PCR detection technology,
achieving technical breakthrough in this regard in China.
Intellectual
capital
1999
Completed property rights restructuring with the new mechanism and funds of the
People’s Government of Guangzhou Municipality, realized equity diversification,
introduced capitals, and thus commercialized its innovative products.
Financial capital
2004
Got listed on the SME board of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange, became the first
listed university-run company in Guangdong, and realized the combination of
intellectual capital and financial capital.
Financial capital
2005
Applied for testing and calibration laboratory with China National Accreditation
Board for Laboratories (CNAL) and was accredited.
Intellectual
capital
2007
Acquired Zhongshan Biotech and obtained multiple immune diagnostic reagents,
which were powerful supplements to its existing nucleic acid products and
enriched its product lines.
Intellectual
capital
2008
Purchased land and prepared to build Foshan Medical Devices Company as its
equipment production base to strengthen its R&D ability, which will specialize in
the research, development and production of life science analytical instruments.
Intellectual
capital
2009
Passed the Dn An Gene’s Incentive Plan for the First Batch of Stock Option
(Draft), which injected vitality into its continuous innovation and development.
Intellectual
capital
2011
till now
Established a professional big health incubator to focus on creating a “no wall”
resource sharing platform for the big health industry and promote collaborative
innovation amon
g
enter
p
rises.
Intellectual
capital
In the early days of its establishment, Da An Gene
achieved independent innovation and breakthrough in
fluorescence quantitative PCR detection technology
relying on government subsidies and intellectual
capital, embraced growth to some extent, but did not
have the strength for industrial development. It
launched capital increase and restructuring in 1999,
successfully got listed in 2004, and established a
perfect capital entry and exit mechanism, which
brought it external financing and helped it further
enhance R&D and innovation. In the meanwhile, the
company strengthened its innovation capabilities and
improved market competitiveness through
technology introduction, mergers and acquisitions. In
2011, it began to create a big health ecosystem,
aiming to help entrepreneurs and SMEs, raise the
success rate of entrepreneurship, and promote the
collaborative innovation and development of
enterprises.
Accumulation of innovation capital over the past
two decades has enabled Da An Gene to quickly adapt
to crises brought by the outbreak of COVID-19 in
2020 and seize development opportunities. The
epidemic resulted in surging demands for test kits in
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
180
China, to which Da An Gene quickly responded and
developed 2019-nCoV nucleic acid test kit on January
20. On January 28, the test kit was approved by the
National Medical Products Administration and
available on the market in large quantities.
Based on above case analysis, we put forward the
following research propositions:
Proposition 1: Enterprises that continue to focus
on R&D innovation can accumulate R&D skills and
innovation resources, and quickly adapt to changes
when sudden crises such as COVID-19 come, when
R&D skills and innovation resources will become
their core competitiveness.
CSR
R&D
Innovation
Product
innovation
Social trust
innovative capital
promote
Figure 4. Framework of innovation-CSR interaction.
4.1.2 Corporate Social Responsibility
As a high-tech biomedical company, Da An Gene
actively fulfills its social responsibilities in a
professional spirit. The process of its R&D and
innovative development mentioned above shows that
its innovative products in each stage have been
promoting the development of fluorescence PCR
gene detection in China. At first, it invented
fluorescence PCR technology, which solved false
positives and non-quantitative detection caused by
the contamination of gene amplification products in
traditional PCR technology. During the SARS
epidemic in 2003, the H1N1 influenza in 2009 and the
COVID-19 epidemic in 2020, it quickly launched test
kits, made important contributions to preventing the
further spread of diseases, and protected the health of
the public.
Adhering to the mission of “reach the source of
life and secure the foundation of health”, Da An Gene
fully fulfills its CSR to ensure people’s health. During
the Spring Festival of 2020, its R&D team still
worked in the laboratory and finally developed test
kits, thereby seizing the huge market opportunity of
domestic and foreign demand for protective medical
products. During the critical period of COVID-19, the
R&D team developed in vitro testing reagents and
related instruments, ensured production capacity, and
secured product quality. This shows that Da An Gene
responded to problems occurred in the course of
social development through innovative ways, has
achieved profitability and sustainable development,
and won social trust and respect.
On the basis of above analysis, we propose the
following proposition:
Proposition 2: By fulfilling CSR, enterprises can
win trust from the society, effectively coordinate the
relationship with various stakeholders, obtain more
external resources, and better survive crises.
4.1.3 Innovation and CSR
Above-mentioned analyses reveal that continuous
R&D innovation can help companies accumulate
innovation resources, and that actively fulfilling CSR
can help them win social trust and obtain social
resources, but is there an interaction between them
and how does it work if there is? Exploring the issue
will help us better understand the mechanism of
interaction between R&D innovation and CSR.
After summarizing original data about Da An
Gene during the epidemic, we refined 18 concepts,
further compared and analyzed them, and finally
divided them into 8 subcategories and 5 core
categories, as shown in Table 3.
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19
181
Table 3. Coding of Da An Gene during the fight against COVID-19.
Primary data Conceptualization Subcategory
Fundamental
category
In the face of sudden outbreak of COVID-19 across
the country, almost all designated hospitals were in
short supply of nucleic acid detection kits.
A1 domestic
demand (a1)
AA1 market
demand (A1, A2)
Impacts of
COVID-19
Beginning in late February, overseas markets showed
great demands for detection kits.
A2 international
demand (a2)
As the epidemic continued to spread globally,
formalities of applying for CE certification became
simpler and the threshold was continuously lowered.
A3 low
certification
threshold (a3)
AA2 industry
status (A3, A4)
On March 25, Spanish newspaper El Pais reported
that a batch of rapid detection kits purchased from
China were inaccurate.
A4 some
companies only
pursued profits
(
a4
)
Starting from March 29, Chinese companies must
obtain relevant qualifications from the National
Medical Products Administration while exporting
protective products against COVID-19.
A5 Chinese
policies tightened
(a5)
AA3 related
policies (A5, A6,
A7)
The threshold set by the country did not affect export
of medical supplies, as there is huge demand. This is
a good news for compliant manufacturers.
A6 favorable
policies (a6)
The State Council stipulated that in addition to
people, objects should be included for COVID-19
testing.
A7 expanded
detection range
(a7)
On January 24, President Xi Jinping clearly put
forward the requirement of scientific prevention and
targeted policy implementation, and emphasized
resolutely winning the battle against the epidemic.
A8 science and
technology-based
anti-epidemic
measures (a8)
AA4 response to
the epidemic in
China (A8, A9,
A10)
Fight against
COVID-19
Beginning on February 2, under the guidance of the
Central Steering Group, Wuhan launched dragnet
investigation, centralized treatment, and thorough
investigation.
A9 strengthened
COVID-19
screening (a9)
Rapid spread of the epidemic was contained. The
epidemic was generally stable across the country
except Hubei.
A10 China made
progress in
epidemic
prevention and
control
(
a10
)
China consolidated and deepened the results of
epidemic prevention and control, promptly deal with
outbreak in clusters, resumed work and production in
an orderly manner, and cared for overseas Chinese
citizens.
A11 Epidemic
prevention and
control abroad
(a11)
AA5 response to
the epidemic in
foreign countries
(A11)
After the outbreak of COVID-19, Da An Gene
quickly launched 2019-nCoV nucleic acid detection
kit (based on fluorescence PCR).
A12 independent
innovation (a12)
AA6 R&D
innovation (A12)
R&D
innovation
The company’s nucleic acid detection technology
enabled timely prevention, control, diagnosis and
treatment of the epidemic.
A13 product
function (a13)
AA7 products and
services (A13,
A14, A15)
CSR
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
182
After successfully developing the test kit, the
company quickly put it into production, providing a
large amount of “ammunition” support for the “fight”
against the epidemic.
A14 guaranteed
production
capacity (a14)
The company has its own fluorescence quantitative
PCR instrument, nucleic acid extraction instrument
and molecular hybridization instrument, but also sells
imported fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument
and nucleic acid extraction instrument to meet
demands in different scenarios.
A15 instrument
R&D (a15)
The company witnessed CNY 2.133 billion of
revenue in the first half of 2020, an increase of
313.63% year-on-year with a gross profit margin of
67.41%.
A16 profits
surged (a16)
AA8 capital
inflow (A16, A17,
A18)
Corporate
sustainable
development
From January 2 to July 31, the company’s stock price
rose from CNY 10.45/share to CNY 43.34/share, an
increase of 314.83%.
A17 stock price
rose (a17)
The joining of Guangzhou Finance Holdings brought
it government endorsements and enabled it to obtain
more social capitals, which promoted its R&D
innovation.
A18 new
milestone in
development
(a18)
Through data analysis, we found that there is a
story line at different stages of Da An Gene’s
development: internal factor (accumulated innovation
capital) and external factors (shock by COVID-19,
response to it) → action strategy (R&D innovation,
CSR) → result (sustainable development).
Under the impact of the epidemic (external
factor), market demand increased dramatically,
bringing opportunities to companies. Whether
companies can seize the opportunities depends
mainly on if they can produce normally and have
certain technical strength. As shown in the history of
its R&D innovation, Da An Gene laid the foundation
for subsequent R&D innovation (internal factor) by
accumulating innovation capital in the early days.
During the Spring Festival when COVID-19 broke
out, Da An Gene persisted in protecting people’s
health and safety. Its R&D personnel remained at
their post, actively responded China’s policy against
the epidemic, and soon developed nucleic acid
detection kits (R&D innovation), which were
produced in sufficient capacity with guaranteed
quality. In doing so, it not only contributed to the
prevention and control of the epidemic (CSR), bu also
made a lot of profits and embraced raised stock price
(corporate sustainable development).
While enjoying economic benefits brought about
by epidemic prevention and control, Da An Gene also
further promoted market-oriented reform. On
December 21, 2020, Sun Yat-sen University, the
shareholder of Guangzhou Zhongda Holding Co.,
Ltd., and Guangzhou Finance Holdings completed
changes in equity, which changed the status of Da An
Gene who did not have goals of strategic growth as a
university-run enterprise. Therefore, this equity
transfer was a new milestone in the development of
Da An Gene (corporate sustainable development).
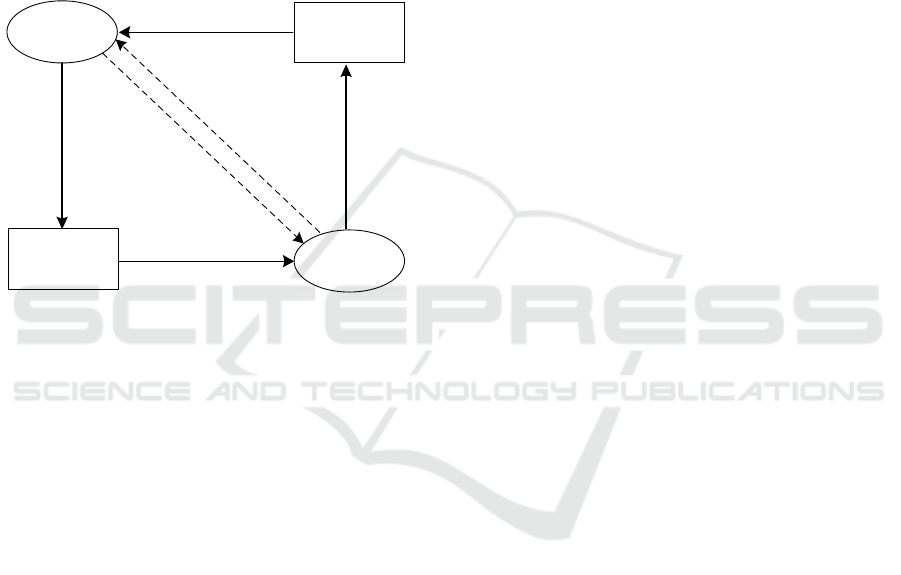
The Figure 4 is a simple diagram of the mechanism
of interaction between R&D innovation and CSR.
By above analysis, we put forward another
proposition:
Proposition 3: R&D innovation promotes
pharmaceutical companies to solve social problems.
By actively performing CSR, companies win social
trust and embrace inflow of social capitals, which
further promote their innovation and development,
form a mechanism of interaction between R&D
innovation and CSR, and thus help them seize
opportunities and achieve rapid development in times
of crisis.
4.2 Innovation-CSR and Institutional
Background
Universities do not place goals of strategic growth
performance on their enterprises, which makes it
difficult for such enterprises to have long-term
development impetus. Therefore, the performance of
listed university-run companies is not ideal. In recent
years, China accelerated the reform of separation of
SOEs and state-owned assets, implemented separated
operation of SOEs and state-owned assets, and
transferred to capital management from assets
management. In 2020, Sun Yat-sen University, the
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19
183
actual controller of Da An Gene, signed the
Agreement on Transfer of State-owned Property
Rights with Guangzhou Finance Holdings,
transferring its 100% equity of Guangzhou Zhongda
Holding (including 16.63% of equity of Da An Gene)
to Guangzhou Finance Holdings for free, as shown in
Figure 5.
Guangzhou Municipal
Government
Guangzhou International
Holding Group Co., Ltd.
Guangzhou Zhongda
Holding Co., Ltd.
Da An Gene Co., Ltd. of
Sun Yat-Sen University
Guangzhou Zhongda
Holding Co., Ltd.
Sun Yat-sen University
Da An Gene Co., Ltd. of
Sun Yat-Sen University
100%
16.63%
16.63%
100%
100%
»
Figure 5. Changes in Da an Gene’s Actual Controller.
After the equity transfer, Da An Gene’s direct
controller is Guangzhou Zhongda Holding, actual
controller is changed to Guangzhou Finance
Holdings, and ultimate controller is Guangzhou
Municipal Government. This brings government
endorsements to the company and helps it gain more
social capitals. Stable flow of capitals is also
conducive to its continuous R&D innovation and
guarantees the interaction between R&D innovation
and CSR. In addition, Guangzhou Finance Holdings’
capital operation capabilities can help the company
maintain a leading position in the biomedical
industry, promote integration of resources in the
pharmaceutical industry, bring new milestones for its
development, and maintain its sustainable future
development.
There, we propose the following proposition:
Proposition 4: Under the institutional background
of reform of state-owned assets management system,
Da An Gene embraced stronger capital operation
ability, which guarantees its long-term and stable
interaction between R&D innovation and CSR.
Above analyses show that external environmental
impacts promote companies to adopt the strategy of
launching R&D innovation and fulfilling CSR at the
same time. Accumulation of innovation capital is an
important internal support for companies to quickly
complete R&D. “R&D innovation and CSR” can be
transformed into their core competitive advantages in
crises like COVID-19 and help them secure further
development, as shown in Figure 6. Da An Gene
completed equity transfer in 2020. In the future, its
actual controller Guangzhou Finance Holdings may
continue to maintain this core competitiveness
through capital operation and market value
management.
support
Outbreak
response
Epidemic
impact
Sustainable
development
promote
Results
External factors
Behavioral strategies
Internal factors
Innovation capital
accumulation
promote
CSR
Innovation
Reformation
Figure 6. Selective decoding graph.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study explores the mechanism of interaction
between “R&D innovation and CSR” and the path of
how the reform of state-owned capital regulatory
system creates value for enterprises with Da An Gene
as a representative case.
First, enterprises should emphasize accumulating
innovative resources during boom times, and
maintain social trust by actively fulfilling their CSR.
Second, pharmaceutical companies solve social
problems through innovation. Actively performing
CSR is conducive for them to win the trust of the
public. Inflow of social capitals to companies further
promotes their innovation and development,
facilitates interaction between R&D innovation and
CSR, and helps them tide over crises. Third, in the
context of the transformation of state-owned assets
supervision mode, the mechanism of interaction
between R&D innovation and CSR and capital
operation help enterprises form core competitive
advantages.
6 LIMITATIONS
Although single case study has unique advantages for
constructing theories in this paper, the conclusions
drawn need to be treated with caution. A
representative company whose development was
promoted by interaction between R&D innovation
and CSR under the impact of COVID-19 was
analyzed, but due to limitations of the case, research
conclusions are not universally applicable. That is,
the promotive relationship between R&D innovation
and CSR shown in this study may not be the only
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
184

possibility. In the future, the validity of research
conclusions can be tested and expanded by empirical
research or other methods.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First of all, the first author is grateful for being the
chief expert in the 2021 National Major Project
(ongoing) “Research on Mechanism Innovation and
Practice Path of Deepening Mixed Ownership
Reform (21ZDA039)” of the National Office of
Philosophy and Social Sciences and the authors
thanks for the support from this project. Secondly,
The authors thank the grant from the Chinese
National Social Science Fund Granted Project of
China (Grant: 20VSZ006); Thirdly, the authors
appreciate the support from the project of “The
Research on Comprehensively Promoting Urban
Digital Transformation in Guangzhou
(2022GZZK06)” of the 14th Five-Year Plan for the
Development of Guangzhou Philosophy and Social
Sciences in 2022, and thank to the support of the 2022
project "ESG (environment, social and governance)
Report on the impact of the Certified Public
Accountants industry". Moreover, the authors also
want to give the appreciation to the support of these
two projects: the 2022 Industry research project of the
Guangdong Institute of Certified Public Accountants
"Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
Accounting Firms to Promote ESG Information
Disclosure" and the 2023 Guangdong Institute of
Certified Public Accountants industry research
project (ongoing) "Comprehensive Evaluation of
Public Accountants".
REFERENCES
Bartik A, Bertrand M, Cullen Z, Glaeser E L, Luca M and
Stanton C (2020) How are small businesses adjusting
to covid-19? Early evidence from a survey HKS Faculty
Research Working Paper Series RWP 20-012
Champion D (1999) The asian crisis - the price of
undermanagement Harvard. Bus. Rev. 77 14-5
Amore M D (2015) Companies learning to innovate in
recessions Res. Policy. 44 1574-83; Archibugi D,
Filippetti A and Frenz M (2013) Economic crisis and
innovation: Is destruction prevailing over
accumulation Res. Policy. 42 303-14
Bushee B J (1998) The influence of institutional investors
on myopic R&D investment behavior Account. Rev. 73
305-33; Orsenigo L and Malerba F (2000) Knowledge,
innovative activities and industrial evolution Ind. Corp.
Change. 9 289-313
Berman S L, Wicks A C, Kotha S and Jones T M (1999)
Does stakeholder orientation matter? The relationship
between stakeholder management models and firm
financial performance Acad. Manage. J. 42 488-506
Aguilera R V, Rupp D E, Williams C A and Ganapathi J
(2007) Putting the s back in corporate social
responsibility: A multilevel theory of social change in
organizations Acad. Manage. Rev. 32 836-63
Lee S, Han H, Radic A and Tariq B (2020) Corporate social
responsibility (CSR) as a customer satisfaction and
retention strategy in the chain restaurant sector J.
Hosp. Tour. Manag. 45 348-58; Pivato S, Misani N and
Tencati A (2008) The impact of corporate social
responsibility on consumer trust: The case of organic
food Bus. Ethics. 17 3-12
Popkova E, DeLo P and Sergi B S (2021) Corporate social
responsibility amid social distancing during the
COVID-19 crisis: BRICS vs. OECD countries Res. Int.
Bus. Financ. 55 101315
He H and Harris L (2020) The impact of Covid-19 pandemic
on corporate social responsibility and marketing
philosophy J. Bus. Res. 116 176-182.
Cao X, Cumming D and Zhou S (2020) State ownership
and corporate innovative efficiency Emerg. Mark. Rev.
44 100699; Cumming D, Rui O and Wu Y (2016)
Political instability, access to private debt, and
innovation investment in China Emerg. Mark. Rev. 29
68-81
Zhu Q, Liu J and Lai K-h (2016) Corporate social
responsibility practices and performance improvement
among Chinese national state-owned enterprises Int. J.
Prod. Econ. 171 417-26
Gu Y and Zhang L (2017) The impact of the Sarbanes-
Oxley Act on corporate innovation J. Econ. Bus. 90 17-
30
Lunn J (1986) An empirical analysis of process and product
patenting: A simultaneous equation framework J. Ind.
Econ. 34 319–30
Chen C T, Chien C F, Lin M H and Wang J T (2004) Using
DEA to evaluate R&D performance of the computers
and peripherals firms in Taiwan Int. J. Bus. 9 261-288;
Scherer F M (1965) Firm size, market structure,
opportunity, and the output of patented inventions Am.
Econ. Rev. 55 1097-125
Chang X, Fu K, Low A and Zhang W (2015) Non-executive
employee stock options and corporate innovation J.
Financ. Econ. 115 168-88
Li J, Shan Y, Tian G and Hao X (2020) Labor cost,
government intervention, and corporate
innovation: Evidence from China J. Corp. Financ. 64
101668
Shen H, Lan F, Xiong H, Lv J and Jian J (2020) Does top
management team’s academic experience promote
corporate innovation? Evidence from China Econ.
Model. 89 464-75
Huang Y, Lam F Y and Wei K C (2014) The Q-Theory
explanation for the external financing effect: New
evidence J. Bank. Financ. 49 69–81
Anderson M H and Prezas A P (1999) Intangible
investment, debt financing and managerial incentives J.
Innovation and CSR on Chinese SOEs: Adapting to COVID-19
185

Econ. Bus. 51 3-19; Mann W (2018) Creditor rights
and innovation: Evidence from patent collateral J.
Financ. Econ. 130 25-47
Czarnitzki D and Licht G (2006) Additionality of public
R&D grants in a transition economy: The case of
Eastern Germany Econ. Transit. 14 101-31
Arvanitis S (2012) How do different motives for R&D
cooperation affect firm performance? - an analysis
based on Swiss micro data J. Evol. Econ. 22 981-1007
Hull C E and Covin J G (2009) Learning capability,
technological parity, and innovation mode use J. Prod.
Innovat. Manag. 27 97-114
Fritsch M and Lukas R (2001) Who cooperates on R&D?
Res. Policy. 30 297-312
Veugelers R and Cassiman B (1999) Make and buy in
innovation strategies: Evidence from Belgian
manufacturing firms Res. Policy. 28 63-80
Wang C and Hu Q (2020) Knowledge sharing in supply
chain networks: Effects of collaborative innovation
activities and capability on innovation performance
Technovation. 94-95 102010
Denicolai S, Ramirez M and Tidd J (2016) Overcoming the
false dichotomy between internal r&d and external
knowledge acquisition: Absorptive capacity dynamics
over time Technol. Forecast. Soc. 104 57-65
Luo X and Du S (2015) Exploring the relationship between
corporate social responsibility and firm innovation
Market. Lett. 26 703-14
Yu W and Zheng Y (2020) The disclosure of corporate
social responsibility reports and sales performance in
China Account. Financ. 60 1239-70
Mithani M A (2017) Innovation and CSR - do they go well
together Long. Range. Plann. 50 699-711
Bethel J E and Liebeskind J (1993) The effects of ownership
structure on corporate restructuring Strategic. Manage.
J. 14 15-31
Davis A K, Guenther D A, Krull L K and Williams B M
(2015) Do socially responsible firms pay more taxes
Account. Rev. 91 47-68
Bereskin F L, Campbell T L and Hsu P-H (2016) Corporate
philanthropy, research networks, and collaborative
innovation Financ. Manage. 45 175-206
Liu B, Sun P-Y and Zeng Y (2020) Employee-related
corporate social responsibilities and corporate
innovation: Evidence from China Int. Rev. Econ.
Financ. 70 357-72
Choi J and Wang H 2009 Stakeholder relations and the
persistence of corporate financial performance
Strategic. Manage. J. 30 895-907
Dionisio M and De Vargas E R (2020) Corporate social
innovation: A systematic literature review Int. Bus.
Rev. 29 101641; McWilliams A and Siegel D (2001)
Corporate social responsibility: A theory of the firm
perspective Acad. Manage. Rev. 26 117-27; Miles M P
and Covin J G (2000) Environmental marketing: A
source of reputational, competitive, and financial
advantage J. Bus. Ethics. 23 299-311
Holmes S and Smart P (2009) Exploring open innovation
practice in firm-nonprofit engagements: A corporate
social responsibility perspective R&D Manage. 39 394-
409
Ko K-C, Nie J, Ran R and Gu Y (2020) Corporate social
responsibility, social identity, and innovation
performance in China Pac-Basin. Financ. J. 63 101-415
Patton M Q (1987) How to use qualitative methods in
evaluation (California: Sage Publications)
Jantunen S and Gause D C (2014) Using a grounded theory
approach for exploring software product management
challenges J. Syst. Software. 95 32-51
ISWEE 2022 - International Symposium on Water, Ecology and Environment
186
