
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical
and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered
by Artificial Intelligence
Xingang Shen
a
, Liming Peng
b
, Guiyang Jin
*c
, Aiguo Jin
d
and Jianwei Shen
e
Intelligent Equipment Research Institute, Ningbo Polytechnic, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
1300415814@qq.com,
544860629@qq.com
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Empowerment, New Computer Technology, Integration Project, Mechanical and
Electrical Major, Curriculum System, The Vocational Ability of The Post.
Abstract: Nowadays, the correspondence between the professional curriculum system and the talent training objectives
is not close enough, talent training lacks effective project support. Therefore, with the help of new modern
computer technology such as artificial intelligence, intelligent and personalized management software system
is designed for training mechanical and electrical professionals. Through developing professional integration
projects covering professional knowledge and vocational ability of the post and adapting to teaching and
practice, training program formulation, teaching process implementation, and teaching result assessment are
organically integrated into the professional curriculum system, which not only effectively supports the
realization of the talent training objective, but also makes the learning goals of students clearer, the teaching
contents of teachers to be more carrier-based, and the curriculum to be coherent and systemic. Moreover, the
curriculum system turns into an organic whole, and curriculum management and assessment get more
intelligent, efficient, and accurate. The introduction of professional integration projects empowered by
artificial intelligence can overcome the shortcomings of the discipline system in the traditional professional
teaching model. If the advantages of modern computer information technology can be fully used to exert the
systematic and complete advantages of the discipline system and emerge with the practice and teaching of the
integration project, professional talents training objective will be effectively supported to realize the “top-
down” design and implementation of professional talent training and improve the quality of talent training
due to the supplementation between theory and practice.
1 INTRODUCTION
Talent training according to professional
classification is an ordinary way of modern higher
education, and professional education is to shape and
develop the vocational ability of the post and
comprehensive quality of people in a certain field.
The school sets up majors according to the needs of
social and industrial development, formulates
professional talent training objectives, develops a
professional curriculum system, and decomposes the
knowledge and skills required by vocational posts
into different courses. Through implementing the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4346-0405
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0515-7042
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6359-0851
curriculum system, students will finally have the
vocational ability to meet the needs of vocational
posts and the needs of enterprises for talents.
Therefore, when training talents, the market demand
must be focused to establish clear goals. The
construction of a professional curriculum system,
teachers’ teaching, students’ learning knowledge, and
training skills should be carried out around the
training objectives.
From the current situation, the specialty has
described the objective of talent training when
developing talent training programs and has
established a talent training curriculum system with a
logical relationship. However, the logical progression
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7544-3223
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0552-3447
496
Shen, X., Peng, L., Jin, G., Jin, A. and Shen, J.
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered by Artificial Intelligence.
DOI: 10.5220/0011914400003613
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education (NMDME 2022), pages 496-505
ISBN: 978-989-758-630-9
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

of these courses is limited to the accumulation and
transmission of knowledge, as well as a certain
increase in vocational ability. It can not
systematically shape students’ vocational ability,
because there is no effective and consistent teaching
project support in the specific implementation
process of the curriculum system, and there is no
organic connection between courses. Most of the
different courses are the personal behavior of
teachers, and there is no project to take charge of the
talent training in the whole process. In addition, there
is also a lack of specific standards for talent training,
and the assessment of professional courses and
vocational abilities is devoid of standards and basis.
As a result, an objective and fair assessment of the
quality of professional talent training cannot be made.
In addition, problems occurring in talent training
cannot be fed back to the talent training program,
which is also the reason why the State Council issued
the National Vocational Education Reform
Implementation Plan in 2019 to implement the pilot
1+X certificate system.
With the development of society and industry
towards lean optimization, the professional
counterpart rate and employment quality of students’
employment have become more important indicators
to measure the quality of professional talent training
compared with the employment rate of professional
students that were paid more attention to before. The
training quality of professional talents and the
professional counterpart rate after employment are
positively correlated. In other words, only premium
talent training quality can ensure a high employment
counterpart rate. On the contrary, poor talent training
quality inevitably leads to a low professional
counterpart rate. In addition, the current talent
training system is short of a customized, intelligent,
efficient, and accurate information management
system in the whole process in terms of talent training
plan formulation, teaching process implementation,
and teaching result assessment, which makes each
teaching link seriously disconnected and profoundly
restricts the upgrading of the talent training system
and the quality of talent training.
2 TRADITIONAL TEACHING
MODEL AND EFFECT
Taking the compulsory course “Fundamentals of
Mechanical Design” for mechanical and electrical
majors as an example, the teaching model and effect
of the traditional knowledge architecture course are
illustrated in this paper. This course is an important
professional course for mechanical and electrical
majors, mainly teaching various basic concepts,
knowledge, commonly used components, mechanical
structures, and design methods used in mechanical
design. The traditional course materials and teaching
models are conceived and arranged according to the
knowledge system structure (as shown in the block
diagram in Figure 1). How can students acquire the
practical ability of “mechanical design”? According
to the knowledge points taught in the course
Fundamentals of Mechanical Design, it is difficult
for students to obtain design ability, because
knowledge is scattered in the teaching process, and
mechanical design is an application of
comprehensive ability. Therefore, the general
practice is to design the curriculum twice or so in the
professional curriculum system, and the practice
project adopted is the well-known reducer design
(from the design of primary to secondary gear
reducers, etc.). The reducer is a typical project case
suitable for mechanical design, which can cover loads
of mechanical design knowledge. However, this
project has been a routine design process without too
much change, from which students can gain little
training in creative thinking and ability. Moreover, a
big problem of this project is that it can only stay on
the drawings. Due to the complexity of the
component structure and the particularity of the
processing technology (casting, gear processing) and
other problems, it is difficult to turn the design results
into real works and present them in front of students.
At the same time, for electromechanical majors, the
project also lacks the application of knowledge and
skills related to electrical control.
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered by
Artificial Intelligence
497
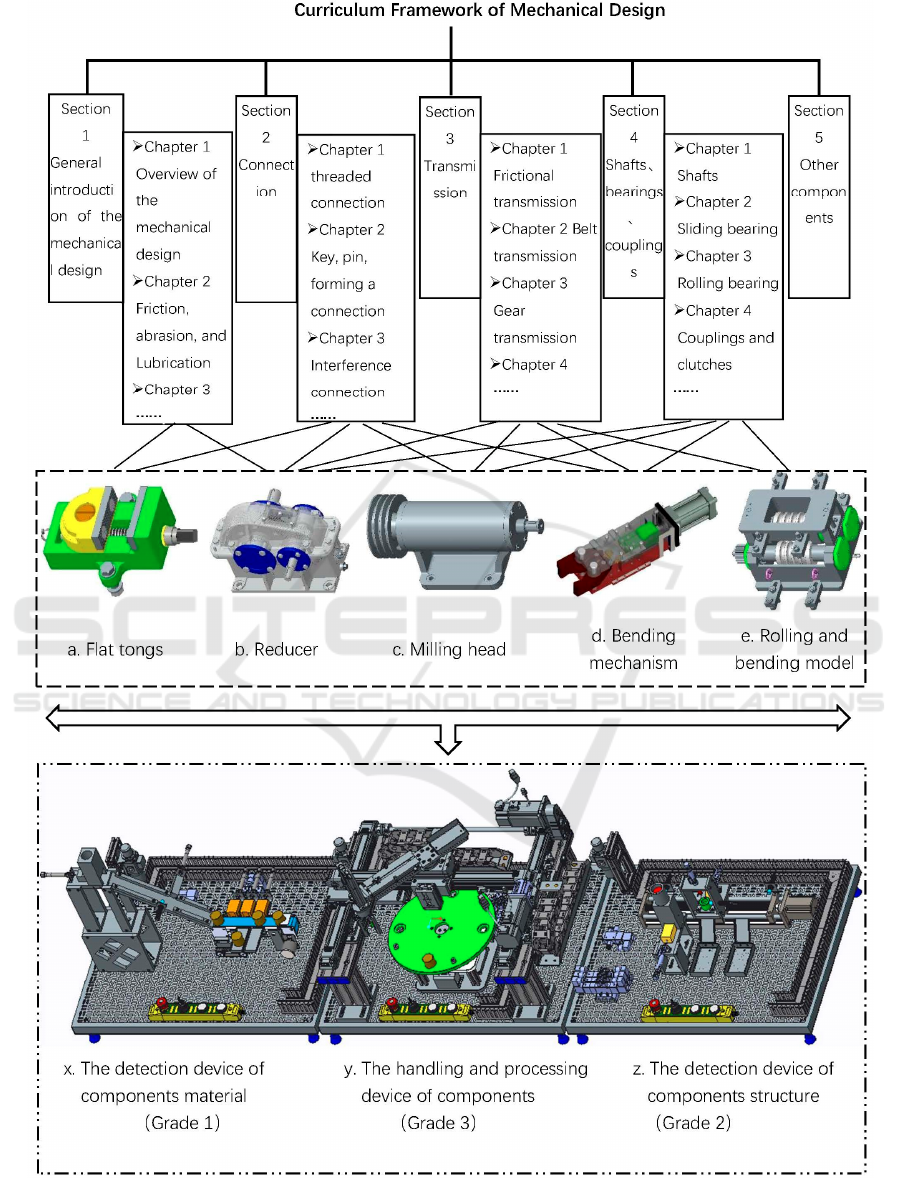
Figure 1: Project teaching reform of curriculum system
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
498

3 PROJECT REFORM OF
CURRICULUM AND
CURRICULUM SYSTEM
To improve the quality of professional talent training,
higher vocational education has been continuously
reformed for more than 20 years. As an important
field of teaching reform in higher vocational
education, project teaching presents the main
exploration direction and effective way to reform the
teaching of the discipline system in higher vocational
education. Over the years, much literature has
summarized the reform and effect of project teaching
of the curriculum. For example, Zhang Anfu put
forward the transformation from the indoctrinated
CPE teaching logic to the project PTI teaching
method (Zhang 2019, Yao 2020, Ding 2019, Wu
2015, Yu 2015). Duan Yongkang proposed that
“project teaching has played an important role in
improving the quality of higher vocational education,
but there are some constraints when implementing the
project, such as higher requirements for teachers’
ability and inadequate allocation of resources,” and
suggested to “build a teaching coordination
mechanism” (Yan 2018). The author of this paper also
deeply believes that. Some literature also further
proposed to “develop a penetrating project teaching
system to improve students’ comprehensive
application ability and innovative consciousness
towards knowledge” (Duan 2019).
To improve the teaching quality and effect, the
projected reform of the course is carried out in the
process of teaching reform. In the teaching field of
mechanical and electrical specialty, the so-called
teaching project should refer to some teaching
carriers with independent and complete functions,
which should be defined from the function of the
carrier, rather than the knowledge system. Therefore,
the first stage of the teaching project reform is to
develop some teaching carriers suitable for
mechanical design as teaching projects, such as the
design of flat tongs, reducers, milling cutter heads,
etc. (as shown in the dashed frame of Figure 1),
integrating the original knowledge points of the
mechanical design course into these projects. By
implementing these projects, knowledge is acquired
and curriculum skills are trained. This projected
curriculum reform has made great strides and
progress compared with the teaching model based on
the knowledge system. However, these projects are
called “granular” teaching projects because they are
decentralized and not systematic although some
knowledge of the curriculum is covered.
To further improve the teaching effect, several
comprehensive projects (as shown in the double
dotted line frame of Figure 1) are developed as the
carrier, and the curriculum in the professional
curriculum system is decomposed into these projects
so that the training objectives of professional
knowledge and skills are realized through
implementing the projects. In this way, many
“granulation” projects in the original different
courses can be unified into a professional integration
project to implement the mechanical design in the
whole process, components processing and
manufacturing, electrical control system design,
mechanical and electrical installation, and
adjustment. In this process, the knowledge system in
the course is no longer the main content of teaching,
but the content of learning to complete the project.
Knowledge can be acquired through implementing
the project, rather than taking project training to
acquire knowledge. The active and passive
relationship of teaching has been transformed,
realizing the “project” design and implementation of
the curriculum system.
4 CLOSED-LOOP MODEL OF
TALENT TRAINING
In this paper, it is proposed to construct a closed-loop
control model for professional talent training based
on artificial intelligence empowerment (as shown in
Figure 2), which mainly includes two aspects. One is
to systematically design and develop integration
projects that run through the professional talent
training in the whole process according to the
objectives of professional talent training. Through
these projects, the courses in the professional
curriculum system are organically connected. When
implementing talent training, guided by ability and
achievements, the quality of professional teaching is
evaluated and guaranteed through the “X certificate”
to achieve closed-loop control of the quality of
professional talent training. The other is to customize
or research and develop the management system of
professional talent training empowered by artificial
intelligence in the whole process, providing
intelligent, efficient, and accurate technical support in
curriculum system design, teaching process
implementation, training system effect assessment,
and other links, and serving the entire professional
talent training system.
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered by
Artificial Intelligence
499
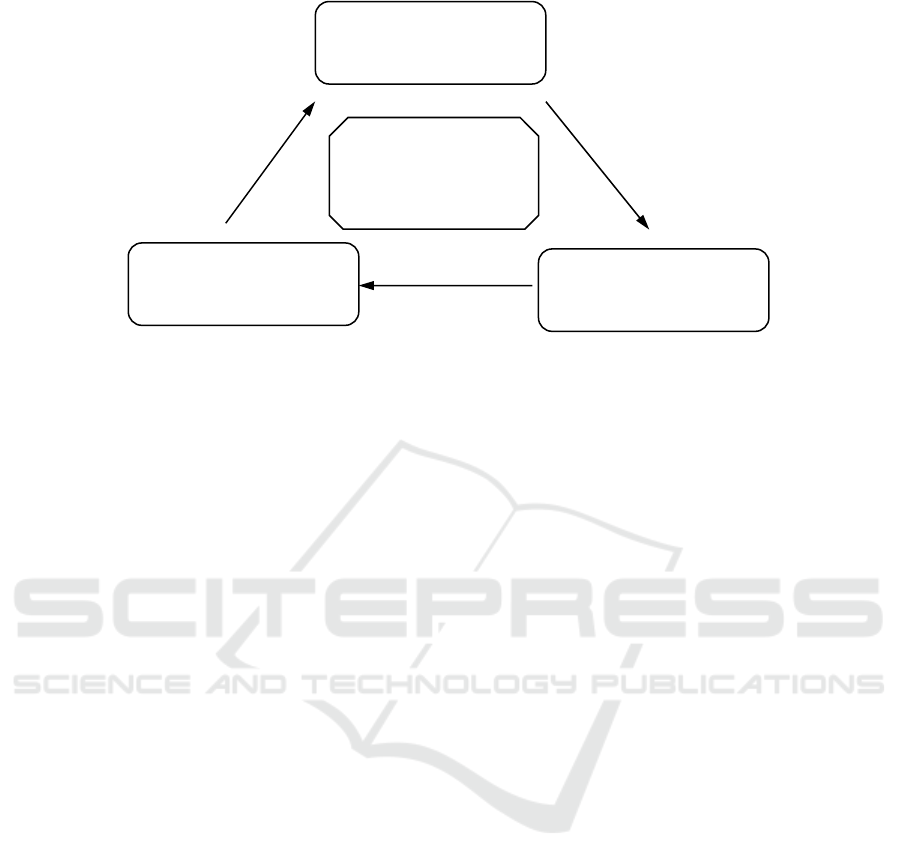
Figure 2: Closed-loop model of talent training empowered by artificial intelligence
In the closed-loop control model shown in Figure
2, the design module, implementation module, and
evaluation module at the time
1+t are
)(
t
XD
,
)(
t
XI , )(
t
XE respectively. The closed-loop
control model can be expressed as follows:
(
)
)()()()()
1
(
t
XE
t
XI
t
XD
t
XF
t
XY •=
+
(1)
)
1
()()
1
(
+
+=
+
t
XY
t
XF
t
XF
(2)
)(
t
XF refers to the input transformation
function. It can be seen from the above formula that
Formula 1 represents the output obtained
t
X
at the
current time
t as input through the closed-loop
model at the time
1+t
. Formula 2 represents the
feedback module. By introducing the system output
feedback at a time
1+t
, the output of the entire
closed-loop model is optimized.
As for the management system of professional
talent training empowered by artificial intelligence in
the whole process in Figure 2, its main responsibility
is to serve the implementation of the design module
)(
t
XD
, implementation module,
)(
t
XI
and
evaluation module
)(
t
XE
, which are realized by
three artificial intelligence ( AI ) models respectively.
For the design module
)(
t
XD
, by introducing the
professional curriculum settings of other schools and
the professional curriculum settings and teaching
evaluation of one’s school, the professional
curriculum training system can be automatically
recommended with the help of the artificial
intelligence algorithm. The formula is as follows:
),(
1
D
O
D
t
D
t
YYAIModel1Y =
+
(3)
Among them,
D
t
Y
1+
,
D
t
Y
, a n d
D
O
Y
respectively
refer to the professional talent training curriculum
system optimized by the AI model, the professional
talent training curriculum system of the school before
the optimization, and the professional talent training
system of corresponding majors of other schools.
For the implementation module
)(
t
XI , AI
empowerment mainly completes the intelligent
arrangement of course progress, phased effect
evaluation, etc. Its formulaic description is as
follows:
),(2,
11
I
t
I
t
I
t
I
t
ZYAIModelZY =
++
(4)
Among them,
I
t
Y
and
I
t
Z
respectively refer to
the schedule of professional talent training courses
and the phased effect evaluation plan before
optimization in the school.
I
t
Y
1+
and
I
t
Z
1+
represent
the optimized schedule of the professional talent
training courses and the phased effect evaluation plan
in the school. For the evaluation module
)(
t
XE , AI
empowerment, mainly for the student-centered multi-
dimensional talent training effect evaluation,
evaluates the training effect of professional talents in
the school, including innovation ability, engineering
practice ability, critique ability, enterprise
adaptability, and so on. Its formulaic expression is as
Design
(Curriculum system inte
g
ratin
g
integrated projects)
Evaluation
(X certificate evaluation of the
independent third-party)
Implementation
(Teaching oriented by
achievement and ability)
The management system
of professional training
empowered by AI in the
whole proces
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
500
follows:
)(3
1
E
t
E
t
YAIModelY =
+
(5)
Among them,
E
t
Y
refers to the effect evaluation
data of the professional talent training system before
optimization in the school, and
E
t
Y
1+
r e p r e s e n t s t h e
multi-dimensional effect evaluation results of the
professional talent training after AI optimization in
the school.
5 VOCATIONAL POST AND
CURRICULUM SYSTEM
CONSTRUCTION
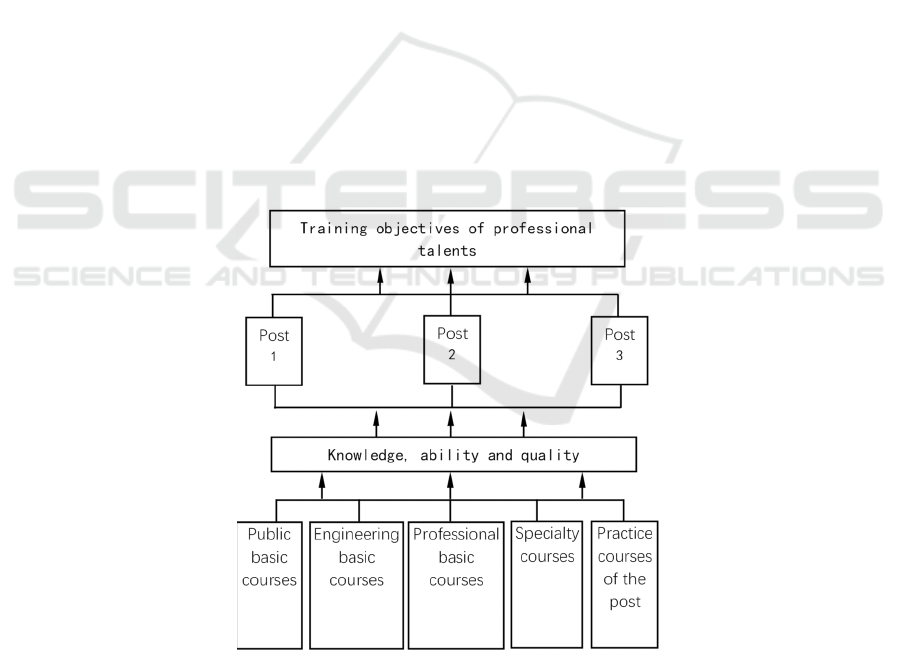
The typical vocational posts corresponding to the
major and the vocational ability of the post are the
basis for formulating the professional curriculum
system, and also the direct embodiment of the
training objectives of professional talents. Therefore,
the professional curriculum system is the core to
support the training objectives of professional talents
(as shown in Figure 3). In the article “Reconstruction
of electromechanical curriculum system based on the
international engineering education professional
certification standards”, the author summarized the
methods and processes of constructing the
electromechanical curriculum system in detail.
According to such methods and processes, the author
constructed a disciplinary curriculum system
structure with logical relations. The curriculum
system structure is complete and logical. Evaluated
from the normative and scientific aspects, the
professional curriculum system built in the way the
author proposed has made much more progress than
that constructed by the traditional way. However,
from the perspective of the implementation process,
there are still problems as described in Section “one”.
There is only a logical relationship between functions
and knowledge among the courses in the curriculum
system, lacking cohesion and coherence in skills
training and promotion. There is no unified common
goal between courses as a teaching guide. Therefore,
to strengthen the logical connection between courses,
the curriculum system and courses must be integrated
to serve the training objectives of professional talents
through the professional integration project, so that
the integration project can become the link
connecting courses and the information center of
professional talents training (as shown in Figure 4).
Figure 3: Professional curriculum system supporting talent training objectives
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered by
Artificial Intelligence
501
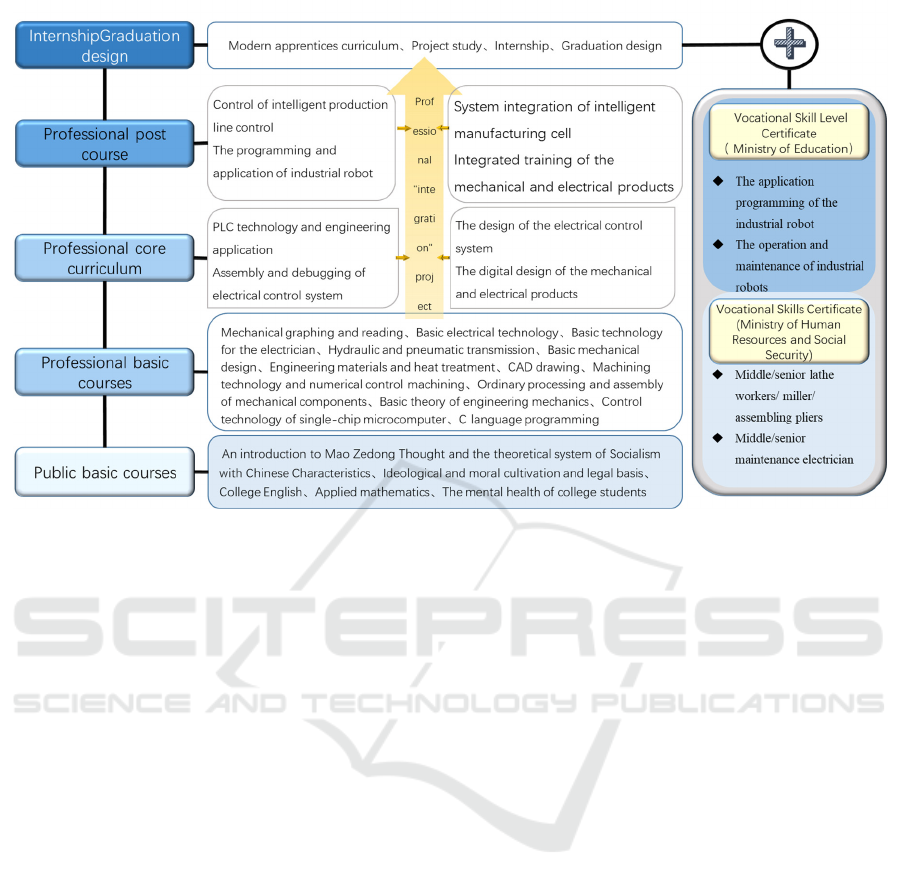
Figure 4: Curriculum system architecture of electromechanical specialty
6 IMPLEMENTATION OF THE
INTEGRATION PROJECT OF
THE PROFESSIONAL
CURRICULUM SYSTEM
The integrated teaching project refers to a
comprehensive teaching project that can guide
professional knowledge and professional skills,
including electromechanical specialty. The integrated
project should cover the knowledge and skills of
mechanical graphing and reading, mechanical design
(including CAD, digital design of electromechanical
products), machining technology and numerical
control machining, the design of hydraulic or
pneumatic transmission system, the design of
electrical control system, PLC technology, and
engineering application, the installation and
debugging of the electrical control system, intelligent
equipment application, and other aspects. By
developing several integrated teaching devices that
can cover the professional knowledge and
professional skills of electromechanical specialty,
and running the integrated project through the talent
training of electromechanical specialty in the whole
process, the courses in the professional curriculum
system will be organically connected, so that the
course is no longer an independent one, but a
necessary link to complete the project. Each course in
the curriculum system is to complete a specific
function in the whole project. All courses aim to
complete several specific projects (as shown in
Figure 5). Students gradually form corresponding
vocational abilities through various stages of the
course. Finally, Students can complete the whole
project and form specific teaching works, so that
teachers’ teaching and students’ learning can be more
targeted.
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
502
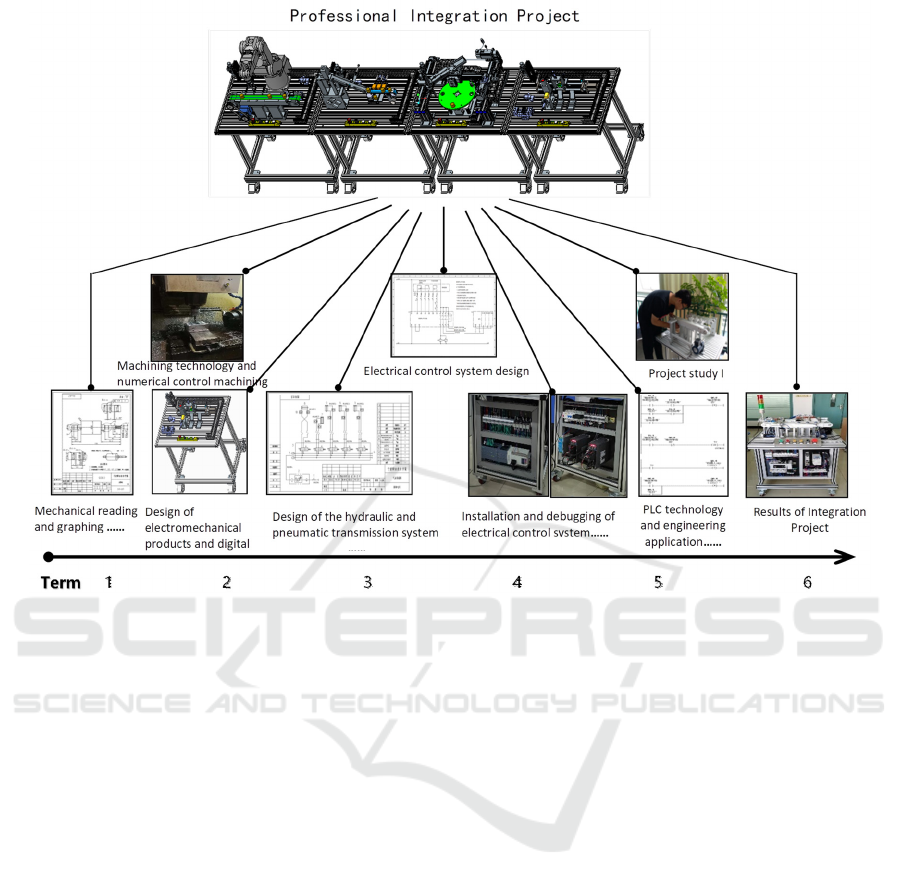
Figure 1: Professional integration project and curriculum system
7 CONDITIONS FOR
IMPLEMENTING
INTEGRATION PROJECTS
7.1 The Development of the Project
The primary condition for implementing the
professional integration project is to develop several
projects that can cover the core knowledge and skills
of the profession, and form a complete teaching kit of
the integration project, from which the teaching
materials of each course in the professional
curriculum system can be obtained. Organized by
professional teachers, the materials can become the
project carrier of the curriculum teaching. On one
hand, taking the mechanical and electrical specialty
as an example, according to the professional
characteristics, the integration project must be able to
cover the knowledge and skills of mechanical,
electrical, liquid (gas), control technology, and other
aspects. On the other hand, the integration project
should be a comprehensive project suitable for
teaching rather than directly gaining from the actual
project of the enterprise. Since the actual project
completely from the enterprise is ever-changing, with
complex project processes and high development
costs, and the students lack the process cognition and
accumulation of the enterprise project, the actual
project completely from the enterprise cannot be
transformed into actual products and are difficult to
implement in the school. Therefore, the integration
project must be suitable for professional teaching.
The project can come from the enterprise, but it must
be sorted, optimized, and refined.
7.2 The Configuration of Teachers
Another important condition for carrying out
professional integration teaching is that the teaching
team with rich practical experience must be able to
integrate knowledge and skills into the
implementation process of the project, and can
quickly solve the problems proposed by students
when completing the project, which is a test for
professional teachers. On the one hand, the teaching
content should be transformed into actual results and
works, which can avoid the disconnection between
theory and practice. On the other hand, through
implementing professional integration projects, the
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered by
Artificial Intelligence
503
professional skills of professional teachers will also
be greatly improved.
7.3 The Complement of Funds
The curriculum and curriculum system is transformed
and implemented with project orientation, which
ultimately aims to complete the actual product.
Therefore, consumables cost is a real problem that
must be considered. Taking the Z device shown in
Figure 1 as an example, the cost of main components
such as mechanical components, electrical control
cabinets (including S7 1200 PLC), and pneumatic
components is about 75 thousand (The cost details are
shown in Table 1.), which is completed by a project
team composed of three students. Therefore, the
average cost per student's shoulder is 25 thousand
yuan. If the secondary or multiple uses of electrical
control components, pneumatic components, and
other components in the original device are
considered, the cost can be controlled within one
thousand yuan per person. Therefore, doing actual
projects will not greatly increase the cost of teaching.
In addition, the project transformation and
implementation of the curriculum and curriculum
system also involve the management system for the
professional talent training empowered by artificial
intelligence in the whole process. There are two
solutions. One is to develop a set of management
systems with complete intellectual property rights for
intelligent and professional talent training in the
whole process in the form of curriculum design or
graduation design. The other is to entrust an IT
company to develop a set of management systems
empowered by artificial intelligence in the whole
process of professional talent training. The system is
about 100,000-150,000 yuan. It is worth noting that
the system can be applied to the management of each
different professional talent training in the whole
process in the whole school, and the cost averagely
shouldered by each student is also acceptable.
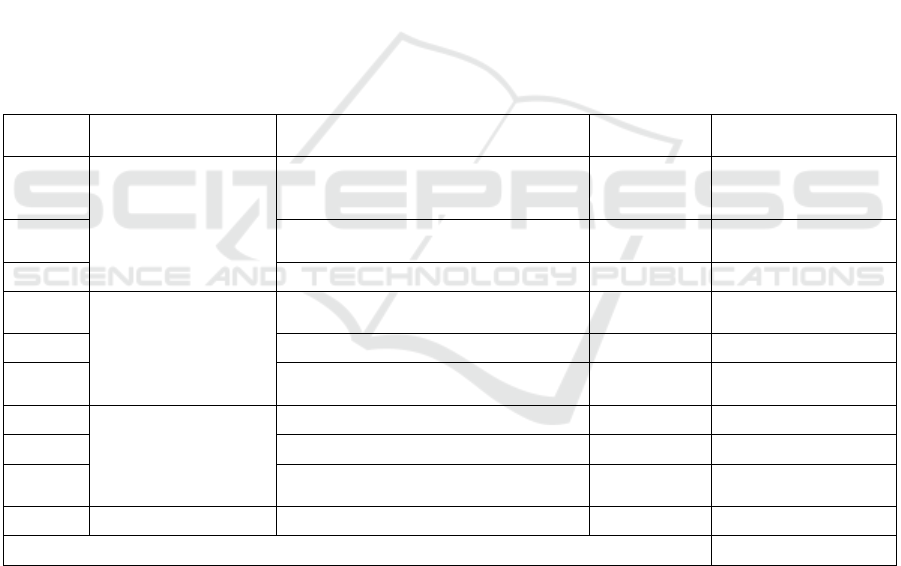
Table 1: The project cost of the device Z (Figure 1)
Number
Major categories of
the components
Details of spare components Amount
Cost
(ten thousand yuan)
1
Mechanical
components
machining fitting
One batch
(20)
0.01
( only material cost
concerned
)
2
Heat treatment on components
( blackening )
One batch
(20)
0.01
3 Grid of 304 stainless steel 1 piece 0.045
4
Electrical components
Screw module ( including stepper
motor
)
1 piece 0.04
5 S7 1200 and I/O extended module 1 piece 0.4
6
Electric control cabinet and low-voltage
electrical components, etc
1 set 0.1
7
Pneumatic
components
Pneumatic cylinder 3 pieces 0.015
8 Reversing valve 4 pieces 0.02
9
Gas source processor and other
p
neumatic accessories
1 set 0.015
10 Others Accessories 1 set 0.1
Total 0.755
8 CONCLUSION
The integration project transformation of the
professional curriculum system aims to connect and
integrate the courses teaching professional
knowledge and training ability for students in the
curriculum system through integration projects.
Through the management system of professional
talent training in the whole process, the talent training
is empowered from the beginning to the end,
supplementing the shortcomings of systematic ability
while giving full play to the systematic advantage of
knowledge in the curriculum system. The dispersed
“granular” ability training is changed to “continuous”
and “systematic” ability training, integrating theory
and practice teaching, and forming the talent training
model of “integration project leading, ability and
NMDME 2022 - The International Conference on New Media Development and Modernized Education
504

result guiding”. From the practice of
electromechanical specialty for about 3 years, the
effect is remarkable. The engineering practice ability
of the students has been significantly improved, with
a shorter cycle of adapting to professional posts. The
students are welcomed by enterprises, and the
professional counterpart rate of students has been
significantly promoted. In the future, this model will
be integrated with the “X” vocational skill level
certificate which is vigorously promoted and
continuously improved by China, realizing the third-
party assessment of teaching quality. The training
quality of higher vocational education professionals
in China will be significantly improved. On this basis,
the exploration and practice of the specialty in the
training model of innovative talents, the cultivation of
the professional skills, engineering expertise, and
literacy of the students will be paid attention to.
Meanwhile, more attention will be paid to training the
creative thinking and innovation ability of the
students. Students will be truly cultivated into
compound high-skilled talents with sustainable
development potential.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to express appreciation for the
financial supports from the second batch of teaching
reform project of higher education in Zhejiang
province during the “13th Five-Year-
Plan”(No.JG20190718); Zhejiang Province "13th
Five-Year-Plan" Provincial Industry University
Cooperation Collaborative Education Project(Office
of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Education
〔2021〕.No.7 );Ningbo “2025 S&T Megaprojects”
(No.2020Z072); 2021-2022 National Machinery
Industry Vocational Education Research Project
(No.JXHYZX202129); Special Research Project on
Education and Teaching Reform of Ningbo
Polytechnic in 2021(No.jg20210094).
REFERENCES
Ding Changtao & Lv Yuanjun. (2019). Research on
Curriculum System of Mechatronics Technology
Specialty Based on “Sydney Agreement” .J. Vocational
Education Research, 07,77-81.
Duan Yongkang. (2019). Discussion on Teaching
Coordination Mechanism in Higher Vocational
Colleges Based on “Project System” Teaching.J. Higher
Education Forum. 01, 65-68.
Wu Qi. (2015). Teaching Design and Practice of Project
Course in Higher Vocational Education.J. Chinese
Vocational and Technical Education. 35, 41-45.
Yan Jing. (2018). Talent Training Model Reform of Project
Teaching and Engineering Education.J. Journal of
Yangtze University (Social Science Edition). 41
(04),120-124.
Yao Jia, Huang Quanyou & Zeng Yicong.(2020). Research
and Practice of Penetrating Project Teaching System in
Mechanical and Electrical Specialty.J. Experimental
Technology and Management. 37(02),223-225.
Yu Hanqi, Xie Naijun & Wu Jingqiu, et.al.
(2015).Exploration and Practice of Engineering
Education Training Model under the Construction of
Project Teaching and Training System.J. Journal of
Nanjing Institute of Technology (Social Science
Edition).15(03),81-84.
Zhang Anfu. (2019) .Project Teaching: an Effective Method
to Improve the Quality of Engineering Talents
Training.J. Research in Higher Education of
Engineering. 03, 166-169.
Exploration and Practice of the Talent Training Model of Mechanical and Electrical Majors Based on the Integration Project Empowered by
Artificial Intelligence
505
