
Application of New Media Technology in Safety Warning Education
to Reduce the Incidence of Unsafe Behaviors Based on Pearson
Correlation Coefficient
Xiuhua Li*, Jianying Su*, Chenyu Yan, Yuanwei Li, Xiaolin Fu and Man Liu
State Grid of China Technology College, Jinan, China
Keywords: New Media Technology, Big Data, Safety Warning Education, New Employee Training, Pearson Correlation
Coefficient.
Abstract: With the popularization of the Internet, big data analysis has been widely applied to today's education. In the
study, the correlation between the incidence of unsafe behavior and the usage of new media in warning edu-
cation were evaluated, by retrieving big data from the large-scale new employee training of Enterprise S for
Pearson Correlation Coefficient analysis. Based on the correlation analysis, the "Three New" model of new
media safety education was constructed and implemented to arouse trainees' active participation in warning
education and raise their alert coverage of the consequences of unsafe behavior. The study shows that making
full use of new media technology to carry out safety education effectively reduces the incidence of unsafe
behavior.
1 INTRODUCTION
To promote the strategy of "cultivating talents to
strengthen the enterprise" in the new era, most large
enterprises conduct comprehensive centralized train-
ing for new employees (Su, 2010). On the whole, new
employees are active in thinking but poor in safety
awareness, and some of them are even "safety illit-
erate" (Zhang, 2004). Then the process of new em-
ployee training is dotted with trainees' unsafe behav-
iors in violation of training disciplines, healthy life-
style, or ethical principles with potential risks, such
as alcohol drinking, staying up late or making inap-
propriate remarks on the Internet. Some of these even
lead to sudden illness, negative network public opin-
ion or other safety incidents, seriously affecting the
training’s stability and the new employees’ healthy
growth.
As an indicator of unsafe behavior density propor-
tional to safety incidents, the incidence of unsafe be-
havior refers to the ratio between the number of un-
safe behaviors and the total number of trainees within
a specific training period. With the purpose of im-
proving the safety literacy of new employees, Enter-
prise S, a large state-owned enterprise in China, put
forward the requirement to reduce the incidence of
unsafe behavior in the new-employee training to less
than 2%,referring to the all-time best level. How-
ever, according to safety inspection data for the first
training phase of 2021 (from January to March), the
average monthly incidence of unsafe behaviors was
3.12%.
As to how to lower the incidence of unsafe behav-
ior, comprehensive research has been conducted from
the aspects of innovating safety education, perfecting
a safety management system and strengthening safety
behavior supervision (Zhang, 2003; Ouyang, 2019;
Wang, 2020). Particularly, with the development of
new media technology, much research has been car-
ried out from the perspective of applying new media
to improve safety warning education, which generally
refers to safety case education by warning people
against conducting unsafe behavior with the punish-
ment consequences of unsafe behavior cases. As Li
Yina pointed out, new media which appear in people's
cognitive world through video, animation and other
forms, is of great significance in safety warning edu-
cation (Li, 2020). Li Lu further asserted that making
full use of new media platforms will maximize the ef-
fectiveness of safety warning education (Deng 2019).
From the perspective of applying new media to
improve safety warning education, the study takes
trainees from Enterprise S’ 5 phases of new employee
training classes in 2021 as research objects. Based on
Li, X., Su, J., Yan, C., Li, Y., Fu, X. and Liu, M.
Application of New Media Technology in Safety Warning Education to Reduce the Incidence of Unsafe Behaviors Based on Pearson Correlation Coefficient.
DOI: 10.5220/0011741400003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 479-484
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
479
Pearson Correlation Coefficient between new media
usage in warning education and the incidence of un-
safe behaviors, the “Three New" model of warning
education was constructed and implemented by up-
dating the new media courseware covering unsafe be-
havior cases related to new-employee training, build-
ing the new media platform for warning education
based on mobile Internet, and constructing the long-
term new media mechanism warning education. The
implementation results of the "Three New" model of
warning education show that making full use of new
media to enhance the effect of warning education suc-
cessfully lowers the incidence of unsafe behavior in
new employ training.
2 CORRELATIONAL ANALYSIS
BETWEEN THE NEW MEDIA
USAGE IN WARNING
EDUCATION AND THE
INCIDENCE OF UNSAFE
BEHAVIOR
Data about the new media usage in warning education
and the incidence of unsafe behavior were obtained
through questionnaire surveys and interviews, and
their correlation was analyzed based on Pearson Cor-
relation Coefficient.
2.1 Investigation Into the Causes of
Trainees' Unsafe Behavior
An online questionnaire was designed to investigate
the causes of unsafe behaviors among 176 trainees
who conducted unsafe behaviors in the second phase
of 2021 training. According to the result, 68% of them
were not aware of the consequences of unsafe behav-
ior. Then, 50 of them were randomly selected for in-
terviews about their participation in warning educa-
tion. 86.7% of them stated that they were not im-
pressed by the warning education. They stated the
reason as follows: currently, the warning education is
primarily the speech statement of the head teacher,
which cannot attract their attention. On the contrary,
they are more willing to embrace the new media-
based interactive education model. Based on the in-
vestigation, it can be concluded that compared with
the expectations of the trainees, new media usage in
warning education is not sufficient.
2.2 Investigation Into the New Media
Usage in Warning Education
In this research, the new media usage refers to the ra-
tio between the actual numbers of new media ele-
ments utilized and the numbers that can be used in
warning education, including the numbers of new me-
dia courseware forms, new media platforms, new me-
dia tweets, etc.. According to data from warning edu-
cation, the overall new media usage in warning edu-
cation for the first phase of training is summarized as
follows.
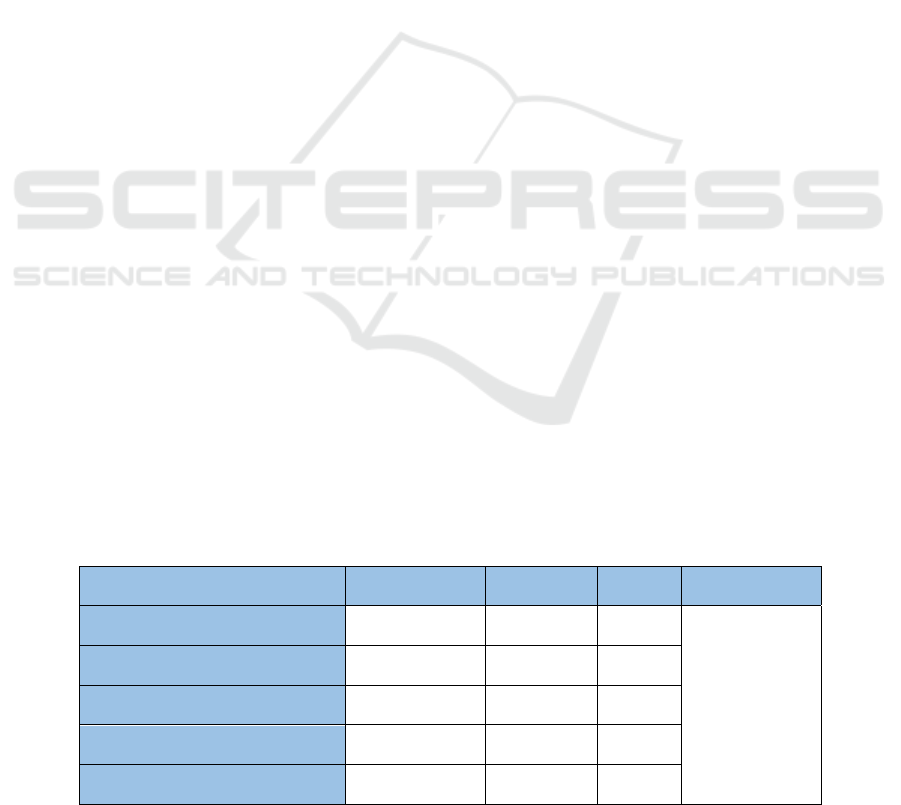
As shown Table 1, the average new media usage
in general warning education is 33%, which implies
big space for increasing new media usage in warning
education.
2.3 Correlation Analysis of The New
Media Usage in Warning Education
and The Incidence of Trainees'
Unsafe Behavior
To further analyze the correlation between new media
usage in warning education and the incidence of train-
ees’ unsafe behavior, we took 93 new staff training
classes as samples, and counted new media usage and
unsafe behavior incidence for each class.
Table 1: Statistical table of new media usage in safety warning education (Original).
Items Capable Use Actual use Usage Average Usage
Forms of new media courseware 3 1 33%
33%
Types of unsafe behavior covered 12 4 33%
New media platforms 4 1 25%
New media tweets 8 4 50%
New media-based activities 8 2 25%
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
480
2.3.1 Statistics of
The
New Media Usage in
Warning Education, Trainees’ Active
Participation and Trainees’ Alert
Coverage of Unsafe Behaviors Types
Based on work records, we first counted the different
new media usages in warning education in all class,
which were divided into 13 grades, ranging from 28
to 78%. By referring to the class work records, we
computed trainees’ active participation by "number of
active participants/number of all trainees " for each
class. Last, with the following question: "Among the
following unsafe behaviors, please select the types
that you think are likely to cause a security incident",
we conducted a survey among trainees to compute
trainees’ alert coverage of unsafe behaviors. The re-
sults are shown in the following table.
As shown in Table 2, trainees’ active participation
and alert coverage of unsafe behavior types are posi-
tively correlated to the new media usage in warning
education.
2.3.2 Correlation Coefficient Between New
Media Usage in Warning Education
and the Incidence of Unsafe Behavior
Combined with the safety inspection data, we counted
the average incidence of unsafe behavior. Pearson
Correlation Coefficient Calculator was used to calcu-
late the correlation coefficient between the new media
usage in warning education and the incidence of train-
ees' unsafe behavior for each group, as shown in
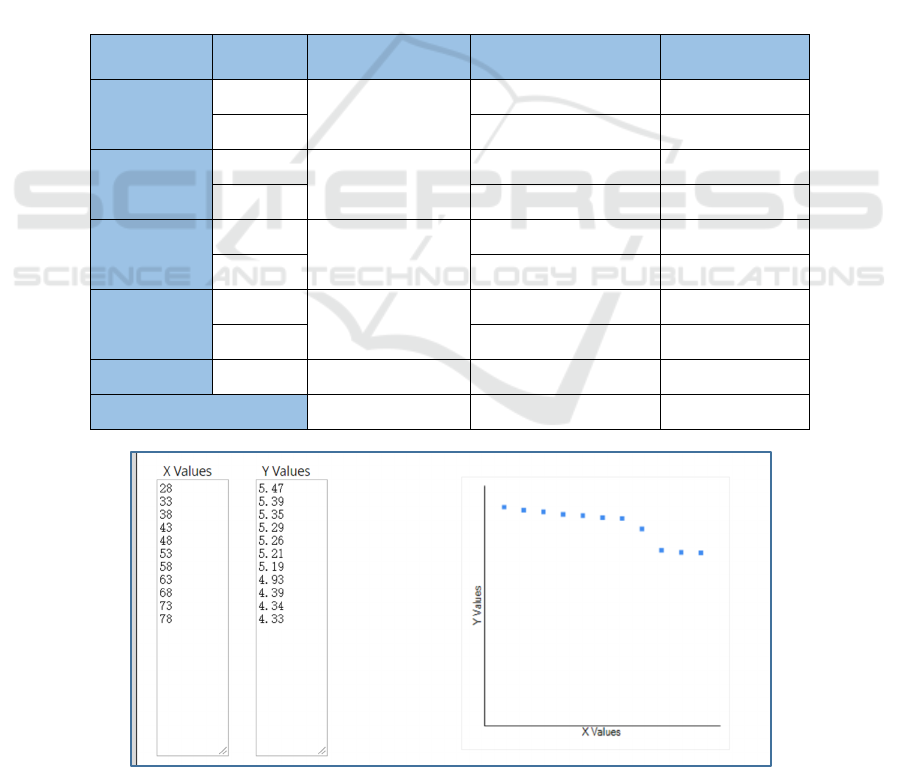
Fig.1.
Referring to Table of Critical Values: Pearson Cor-
relation, when the N-2=11 and the significance
Table 2: New media usage, trainees’ active participation and alert coverage (Original).
Group Class
New Media Usage
(%)
Active participation
(%)
Alert coverage
(%)
Group
Class1
28
19 15
Class5 19 16
Group2
Class6
33
25 34
Class51 26 36
…Group5
Class68
48
39 43
Class74 38 42
…Group11
Class88
68
61 77
Class90 62 77
…Group13 Class93 78 63 79
Average 41 39 43
Figure 1: Correlation coefficient between the new media usage and the unsafe behavior incidence (Pearson Correlation
Coefficient Calculator).
Application of New Media Technology in Safety Warning Education to Reduce the Incidence of Unsafe Behaviors Based on Pearson
Correlation Coefficient
481

level a=0.05, |R|>0.553 indicates a strongly negative
correlation of X and Y. According to Fig.1, |R| is
0.977 and R2 is 95.5%, suggesting that the new media
usage in warning education is strongly, negatively
correlated with unsafe behavior incidence for each
group. Moreover, as shown in the XY scatter plot, the
unsafe behavior incidence is no longer clearly
reduced when the new media usage rises above 68%.
3 CONSTRUCTING AND
IMPLEMENTING THE "THREE
NEW" MODEL OF NEW MEDIA
WARNING EDUCATION
Based on the above analysis, we set the goal as new
media usage above 70%. And trainees’ alert coverage
of types of unsafe behavior above 80%. Guided by the
new media communication theory of "experience is
king" [8], we make full use of new media to conduct
warning education by constructing and implementing
the "Three New" model. This model consists of
updating new media courseware covering unsafe
behavior cases, conducting new media education
activities based on the mobile Internet platform and
constructing the long-term mechanism of new media
warning education, with the focus on raising trainees'
alert coverage of unsafe behavior types.
3.1 Updating The New Media
Courseware Covering Unsafe
Behavior Cases
We created and updated new media courseware
which covers the main types of unsafe behaviors
cases in the new staff training for warning education
to arouse the trainees' high alert to the consequences
of unsafe behaviors.
First, we collected typical cases of unsafe
behavior during the training and dynamically added
recently occurring unsafe behaviors of new type.
With sensitive information removed and warning
significance highlighted, we conducted a compilation
of cases covering all types of major unsafe behavior
in new employee training such as floating smoking,
alcohol drinking, nonstandard electricity
consumption, rumor spreading, staying up late, etc.
With the cases as the material, we further produced
new media courseware for warning education in the
living way of micro video, which was presented in the
weekly safety-themed class meeting to show the
severe consequences of unsafe behaviors. In this way,
warning education was conducted with the latest
vivid cases to arouse the trainees' awareness of the
consequences of unsafe behavior.
3.2 Conducting New Media Activities
Based on Mobile Internet Platform
Supported by mobile Internet platform, we carried out
warning education activities with the theme of
"Building the foundation of safety” by combining "
Everyone protects safety" lecture sharing with " Safe
Campus Corridor" micro works competition.
First, we attracted more trainees to participate in
the activities by investigating their expectations and
issuing activity notices online. Then, the class
meetings with the theme of "Everyone protects
safety" were held offline and relevant tweets were
posted online to involve all trainees in warning
education. On this basis, trainees were organized to
participate in "Safe Campus Micro Corridor"
competition by creating micro works with their
understanding of safety. The outstanding micro works
were broadcast on mobile Internet platforms such as
Palm Academy APP and the official Wechat account.
With the widespread dissemination of micro works,
we have created a new trend of warning education
with multi-directional interaction based on new
media.
3.3 Constructing The Long-Term
Mechanism of New Media Warning
Education
We built a long-term mechanism of new media
warning education by compiling the operating
instructions, improving the public opinion monitoring
mechanism and optimizing the evaluation system.
First, we compiled the operating instructions and
solidified the organization standards for new media
warning education. At the same time, we established
the information supervision mechanism to strengthen
the detection of communication. On the one hand, we
set up a team that was responsible for reviewing the
warning education courseware or micro-works to
ensure the safety of information release; On the other
hand, we made positive responses to guide public
opinions, creating a positive and healthy warning
education environment. Then, we made full use of
new media to optimize the evaluation system by
constructing an objective assessing mechanism,
smoothing interactive feedback channels and
improving the education methods according to
trainees’ feedback so as to achieve the long-term
development of warning education.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
482
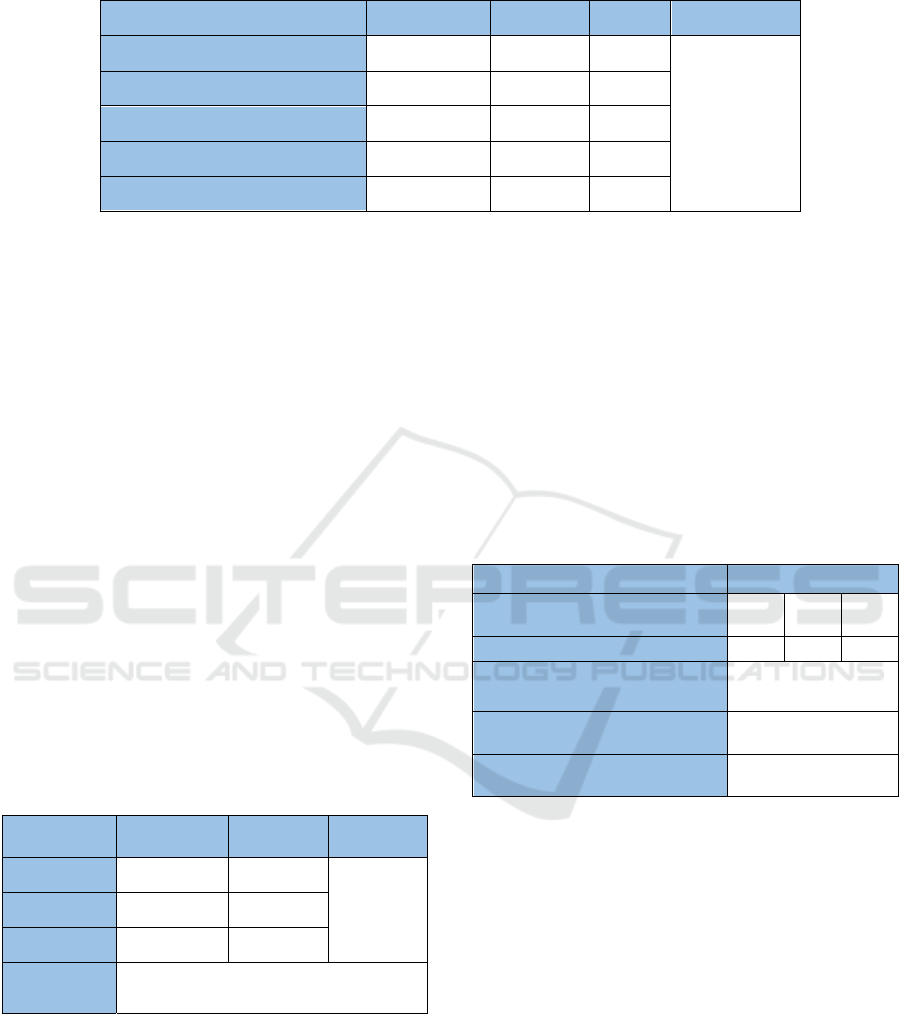
Table 3: The new media usage in unified safety warning education (Original).
Items Capable Use Actual use Usage Average Usage
Forms of new media courseware 3 3 100%
90%
Types of unsafe behavior covered 12 12 100%
New media platforms 4 4 100%
New media tweets 12 12 100%
New media based activities 12 6 50%
4 RESULTS OF CONDUCTING
“THREE NEW” MODEL OF
WARNING EDUCATION
The first round implementation of “Three New”
model of warning education was completed at the end
of August 2021. Based on safety inspection data, we
calculated new media usage in warning education,
trainees’ active participation and the incidence of
trainees’ unsafe behaviors from June to August 2021
as follows.
4.1 The New Media Usage in Warning
Education
We made statistics on the new media usage in unified
warning education and in each class through
retrieving new media data, as shown in the following
tables.
Table 4: The average new media usage for each class
warning education (Original).
Number
New media
usage
Number of
Classes
Number of
all classes
1 87% 3
87
2 92% 65
3 97% 19
Average new
media usage
(85%×3+90%×65+95%×19)÷87=90.9%
From the above tables, it can be concluded that new
media usage in unified warning education has
increased to 90%, and the average new media usage
in warning education of each class has reached
90.9%, which are all above the target value of 70%.
4.2 The Trainees’ Alert Coverage of
Unsafe Behavior Types
An online questionnaire survey was conducted
among 3521 trainees, and 3389 pieces of data were
obtained. According to the survey, after the
implementation, trainees’ alert coverage of unsafe
behaviors’ consequences was counted as shown in
Table 5:
Table 5: Statistical table of trainees’ alert coverage of
unsafe behavior types (Original).
Items Numbers
Types of unsafe behaviors that
are alerted to
11 12 13
Trainees who are alert 156 1023 2210
Average Types of unsafe
behaviors that are alerted to
(156×11+1023×12+2
210×13)÷3389=12.6
Types of unsafe behaviors that
exist
13
Alert coverage of types of unsafe
b
ehaviors
12.6÷13=96.9%
As displayed in the above table, trainees’ alert
coverage of types of unsafe behavior was 96.9%,
which was higher than the target value of 90%.
4.3 The Incidence of Unsafe Behavior
The “Three New” Model of New media warning
education ran for three months from September to
November 2021. On December, 2021, according to
the three months of normalized safety inspection data,
we calculated the incidence of trainees’ unsafe
behaviors from September to November 2021 as
follows:
Application of New Media Technology in Safety Warning Education to Reduce the Incidence of Unsafe Behaviors Based on Pearson
Correlation Coefficient
483
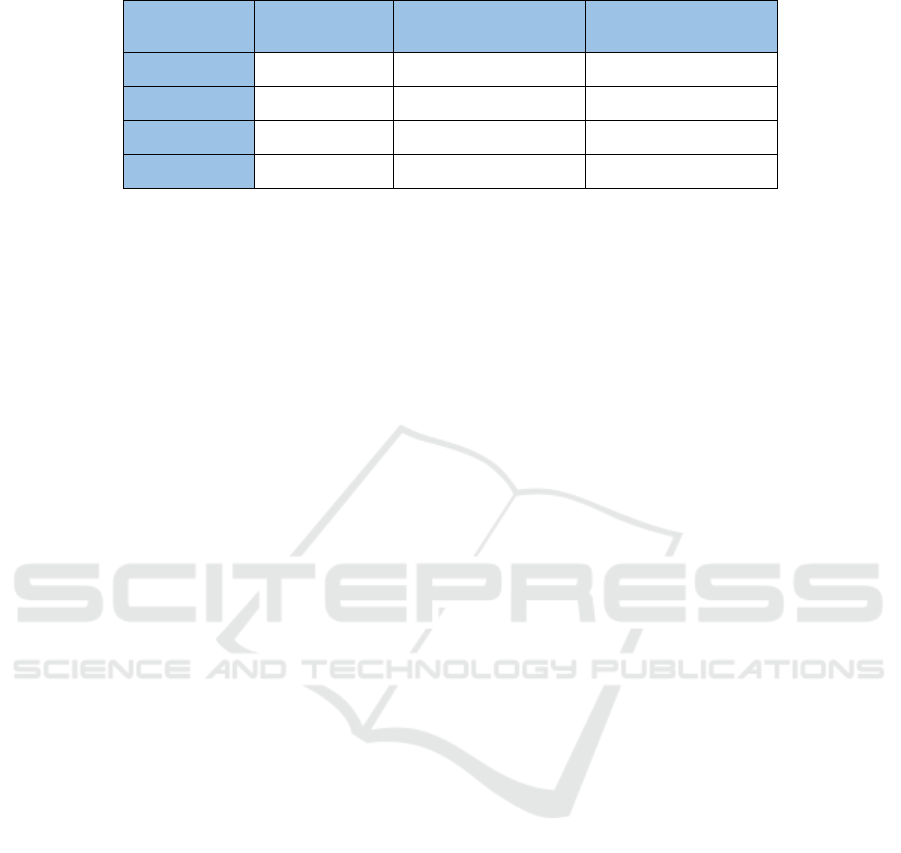
Table 6: Trainees’ incidence of unsafe behaviors from September to November 2021(Original).
Month
Number of
Trainees
Number of unsafe
behaviors
Incidence of unsafe
behavior
September 3697 70 1.88%
October 3697 69 1.86%
November 3342 62 1.85%
Average 3579 67 1.87%
As shown in the above table, after implementing
the “Three New” model, the incidence of unsafe
behaviors of trainees decreased from 3.12% to 1.87%,
achieving the goal of reducing the incidence of unsafe
behaviors to less than 2%.
In summary, the effect examination suggests after
implementing the "Three New" model of warning
education, trainees' alert coverage of unsafe behavior
types and the incidence of unsafe behavior conducted
by trainees all achieved the target values.
5 CONCLUSION
The Three New Model of new media safety warning
education has been applied to educating more than
20,000 trainees in the centralized new employee
training classes by Enterprise S, leading the trainees
to continuously strengthen their safety awareness and
reduce their unsafe behaviors. In the long run, with
the improvement of trainees' safety literacy, trainees
will reduce the probability of production safety
incidents caused by weak consciousness of safety at
work, thereby reducing the economic losses and
improving the social credibility of the enterprise.
REFERENCES
Deng Yongtao. "Experience is King ": the innovation path
of new media for government affairs in the era of
integrated media – taking "Guangdong Affairs" as an
Example [J]. Media, 2019 (20): 2019.20.017.48-49. (in
Chinese)
Li Yina. The importance of new media in the safety warning
education for oil workers [J]. Corporate Culture,
2021(3): 121-122. (in Chinese)
Li Lu. Innovating the warning education based on network
information platform [J]. New Generation, 2020,
25(19):192. (in Chinese)
Ouyang Yongqiang, Zhou Wei, Hua Xia. The institutional
construction and legal subject synergism for education
tourism safety in foreign primary and second schools.
[J]. Education Science, 2019,35(4):59-63. (in Chinese)
Su Li. Attaching great importance to new employee
management to provide qualified talent team for
realizing the strategy of "Cultivating Talents to
Strengthen the Enterprise" [J]. Coastal Enterprises and
Technology, 2010(12): 74-75,73. (in Chinese)
Wang Shuai, Li Yanbing, et al. Design of safety inspection
and behavior improvement system [J]. Industrial Safety
and Environmental Protection,2020,46(10):53-57. (in
Chinese)
Zhang Xueqing, Gao Jing. Current situation and
countermeasures of pre-job safety education for new
employees [J]. Safety, Health and Environment, 2004,
4(12): 39-40. (in Chinese)
Zhang Chuanbin, Strengthening safety education and
raising legal awareness [J]. Journal of Guangxi
University (philosophy and social sciences
edition),2003,25:27-28. (in Chinese)
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
484
