
Exploration of Digital Asset Application: A Blockchain-Enabled
Media Copyright Organizing Solution Based on Cloud Computing
Yunjing Zhang
1,
* and Zhexu Zhang
2
1
Postdoctoral Research Fellow of Beijing E-Hualu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
2
Senior Solution Engineer of Beijing E-Hualu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
Keywords: Digital Asset Application, Media Copyright Trading, Blockchain.
Abstract: The media industry has been impacted by big data. Digital assets, as an important asset, with the combination
of cultural and economic attributes, owned by media companies, which is of great significance to explore its
innovative application. In this paper, we design a media copyright trading based on online-offline hybrid
model. Specifically, the online media asset hosting operation platform, is divided into two parts, MAM and
trading section. MAM is the foundation of the platform, and digital assets needs to be guaranteed through
MAM before the transaction. MAM stores certificates through block chain, to realize media digital data copy
right confirmation. Based on the premise of the separation of ownership and usufruct, the transaction plate
realizes the realization of the usufruct of media assets hosted on the media asset trusteeship operation platform
through "Block trading" and "Live trading" assets transactions. In addition, by giving full play to the charac-
teristics of media resources and extending the digital assets transaction scenarios offline, which can effectively
maximize the transaction value. It is expected that this paper can provide an effective path of digital assets
application for the media industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
At present, the theoretical understanding of digital as-
sets lags behind its application practice, and on the
whole, there are widespread disputes over big data's
confirmation of rights, transaction pricing and capi-
talization in all kinds of industries. This forms a po-
tential hidden danger to the sustained and healthy de-
velopment of big data's industry and digital economy,
as well as the media industry, cultural industry and
other related fields rooted in digital assets.
This paper focuses on digital assets, through the
construction of a blockchain-enabled media copy-
right organizing solution based on cloud computing,
to explore the digital assets' right determination,
transaction, digital application path, hoping to pro-
vide reference for the exploration of big data in cer-
tain industries and related fields.
2 THE DEFINITION OF DIGITAL
ASSETS AND THE
IMPORTANCE OF ITS
COPYRIGHT TRADING
2.1 The Definition of Digital Assets
How to define digital assets? "A digital asset is any
item of text or media that has been formatted into a
binary source that includes the right to use it. " (Van,
2006), "Digital asset is an ownership with any kind of
data in binary form stored in your computer or over
the internet in a cloud somewhere." (Toygar, 2013),
"Any digital form of information stored in computers,
smart phones, digital media or clouds. " (Warwick-
Ching, 2012), however, these definitions are based on
format, without considerations of the content of digi-
tal assets.
Generally speaking, digital assets mainly refers to
video, audio, text, pictures and other media content
data generated by media companies in the process of
business production, as well as channel big data and
Zhang, Y. and Zhang, Z.
Exploration of Digital Asset Application: A Blockchain-Enabled Media Copyright Organizing Solution Based on Cloud Computing.
DOI: 10.5220/0011740400003607
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology (ICPDI 2022), pages 469-474
ISBN: 978-989-758-620-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
469

advertising resource big data. In addition, the appli-
cation of big data collection technology, the collec-
tion of user terminal data, interactive data, behavior
data and other derivative data. From the perspective
of asset attributes, on the one hand, digital assets is
not only the content asset of media companies, but
also the core asset, with high cultural value; on the
other hand, these "sleeping" assets are often sealed in
inventory, lack of effective scene applications, and its
potential commercial value needs to be further ex-
plored.
Looking at the typical characteristics of digital as-
sets for media, it is mainly based on original and con-
tained data, with obvious characteristics such as un-
structured, fragmented, massive disorder, high reuse
value, strong spillover effect and so on.
2.2 The Importance of Copyright
Trading for Digital Assets
Copyright is the core of the value chain of media in-
dustry. In essence, the digital asset belongs to copy-
right industry. Media is the carrier of content assets,
which is the form of expression of media. With the
rapid development of modernization, industrializa-
tion and informatization of the media industry, the
traditional broadcasting channels owned by the radio
and television media are no longer scarce resources,
and the development of the media industry is gradu-
ally encountering a bottleneck. (Li, 2014) For media
industry, in addition to channel resources, a large
number of content resources accumulated for many
years should be their most valuable core assets. How
to transform the advantages of content resources into
industrial advantages and maximize the copyright
value and economic interests of content resources is a
realistic problem to be solved urgently. It is of great
significance to solve the problem of copyright use of
media assets inventory content resources, to make
these precious content materials really move, to pro-
mote the industrial development of media assets, and
to increase the value of content assets through the
market.
Large media companies are working on their dig-
ital work-digitizing historical newspapers, valuable
documentary videos, audio materials, and even TV
dramas, variety shows, stage dramas, etc., so that peo-
ple can access them on the Internet. For example,
China Central Television has more than 1 million
hours of collection resources, of which nearly 700000
hours have been digitized (Sun, 2018); for example,
BBC's ambitious Digital Media Initiative (DMI)
spent £100millon, but cancelled the project because
of high costs, poor internal management, and inability
to explain the value of digital media assets (Steve
Hewlett). It is noteworthy that some local regional
media companies have been digitizing rapidly and ef-
fectively.
The Weekly Challenger, as a local newspaper in
Saint Petersburg, Florida, United States, established
in 1967, successfully realized digital through a spe-
cial legislative appropriation from the State of Florida
(García-Perdomo, 2021). Palopo Pos, a local media in
Luwu Regency, Sulawesi Selatan, Indonesia (Amir,
2022) and a newspaper library in Kerala, Malaysia
(Sreekala, 2019) have successfully realized digital by
the help of local authorities or companies’ funds.
Compared with large media companies, they have rel-
atively less media resources and lower costs, so they
can digitize faster. However, in the era of integrated
media, they face the same cost challenges in the future
as the volume of data storage continues to increase.
3 DESIGN OF
BLOCKCHAIN-ENABLED
MEDIA COPYRIGHT
ORGANIZING SOLUTION
BASED ON CLOUD
COMPUTING
For media asset management, the traditional way is to
store it and manage it through the platform. However,
with the rise of social media, the attention of local re-
gional media companies is decreasing, and the cost of
maintaining media assets is also increasing. There-
fore, it is necessary to make use of the value of media
assets through a series of combination methods, such
as technology and business, to reduce the cost of me-
dia asset management, and even become a new source
of income.
3.1 Traditional Media Assets Rights
Management in Regional Media
Company
Local regional media companies, different from
trans-regional media, even some multinational media
groups such as CNN, BBC, FOX, TASS and CGTN,
pays more attention to local news, activities and other
content related to the life of local residents. Although
it does not perform well in the media content variety,
compared with multinational media groups, its con-
tent is more accurate (Selina, 2018), and compared
with social media, it can reflect objective facts more
timely and comprehensively (Limaye, 2020). Local
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
470

regional media companies output includes local news,
especially breaking news, daily news, local variety
shows, films, documentaries, event records and so on.
With the expansion of data scale, especially the im-
provement of video definition, the cost of preserving
and managing these data assets increases gradually
over time, thus it is necessary to manage these valua-
ble local media data assets while managing them, in
order to give these assets effective and profitable pro-
tection, instead of increasing the pressure of financial
cost simply.
However, most Media Asset Management plat-
form (MAM) only focuses on (Veynberg, 2019) the
management of media assets, that is, digital assets
metadata governance, including a series of processes
such as the formation of data associations. At present,
there are some forward-looking researches, such as
FINA's MAM database (Kaliszewska, 2021), not only
does it have effective tools and multi-dimensional
metadata structures, but also detailed analysis of the
unique characteristics of audiovisual collections. Pay-
ing attention to the analysis of the content of media
assets is undoubtedly based on the establishment of
content-based transactions. Therefore, it is necessary
to design a platform that supports the trading of media
assets based on MAM function.
However, the copyright issue is a major difficulty
in media asset trading process, especially the context
of social platforms, while copyright is the restriction
of copying, whereas the ethos of social networking is
the promotion of sharing (Bosher, 2019). Informing
in its user agreement is useless because very few peo-
ple will read it, and most copyright infringement is
untraceable. Using block chain for certificate storage
and tracking combined with crawler technology is a
feasible way (Zhou, 2019), but it is a better way to
plan media property transactions through online plat-
forms or offline scenarios.
3.2 Integration of Digital Asset Hosting
Operation Plan Base on Online and
Offline
In the article, the online media asset hosting operation
platform, is divided into two parts, MAM and trading
section. MAM is the foundation of the media asset
hosting operation platform, carrying the responsibil-
ity of data governance and ownership determination.
Not only does MAM distinguishes data by format, but
also the semantic attributes of entities, including par-
ticipants, organizations, location, events, and time.
Among them, participants are not limited to the au-
thor of media, but also includes the main characters
in media, such as the protagonist of the play, the party
of the news and so on. Similarly, the other four ele-
ments, such as organizations, containing not only the
file metadata, but also the analysis of the content.
Meanwhile, the platform will complete the data min-
ing of media assets through data cleaning, association
and other steps, and ensure media data transmission
and data security through point-to-point transmission.
Media assets needs to be guaranteed through
MAM before the transaction. In view of the two prob-
lems, the difficulties of media assets tracing and the
unclearness of commercial value, MAM stores certif-
icates through block chain, and embeds copyright in-
formation and embedded coding in metadata to real-
ize media digital data copy right confirmation, build-
ing foundations for subsequent copy right evidence
obtaining. MAM crawls the embedded code in the
whole network and compares it with copyright con-
firmation to realize the media resource copy tracking.
Currently, a phenomenon exists that media assets
is in the hands of individuals, including editors, jour-
nalists, directors, and other staff. On the one hand,
this has caused economic losses to local-regional me-
dia companies-you can't force the staff to take out the
media assets that the company does not know exists.
On the other hand, hiding these media assets is a
waste of society, and people will no longer see or hear
the history behind these media assets. At the same
time, there are many phenomena of illegal use of me-
dia assets to develop derivative products or services
without permission, which cannot be completely
solved by crawler search and tracking, and it is diffi-
cult to obtain evidence and safeguard rights in court.
NFT has caught public attention since 2021, with
bright market expectations and variable collections
from videos, pictures, art masterpieces, even games.
Considering the difficulties to protect copyrights, and
the current situation that NFT could be seen as eco-
nomic bubbles because of lacking actual dependents.
Therefore, it is necessary by applying blockchain
technology, based on NFT tokens, through digital as-
sets dividends to enable stakeholders to have the op-
portunity to obtain benefits in a legitimate form. As-
sets owners and local-regional media companies can
achieve permanent accounts that cannot be tampered
with through the number of NFT holdings on the basis
of reaching an agreed dividend ratio. Through plat-
form access, developers, such as YouTube's organiz-
ers, can meet their needs and get their corresponding
income from buyers. Simultaneously, consumers can
also buy NFT through the platform, so as to get a cer-
tain income of digital assets to participate in divi-
dends, so as to make NFT produce value, rather than
simple speculation. In addition, by accessing the ju-
dicial chain of the court, the platform can upload the.
Exploration of Digital Asset Application: A Blockchain-Enabled Media Copyright Organizing Solution Based on Cloud Computing
471
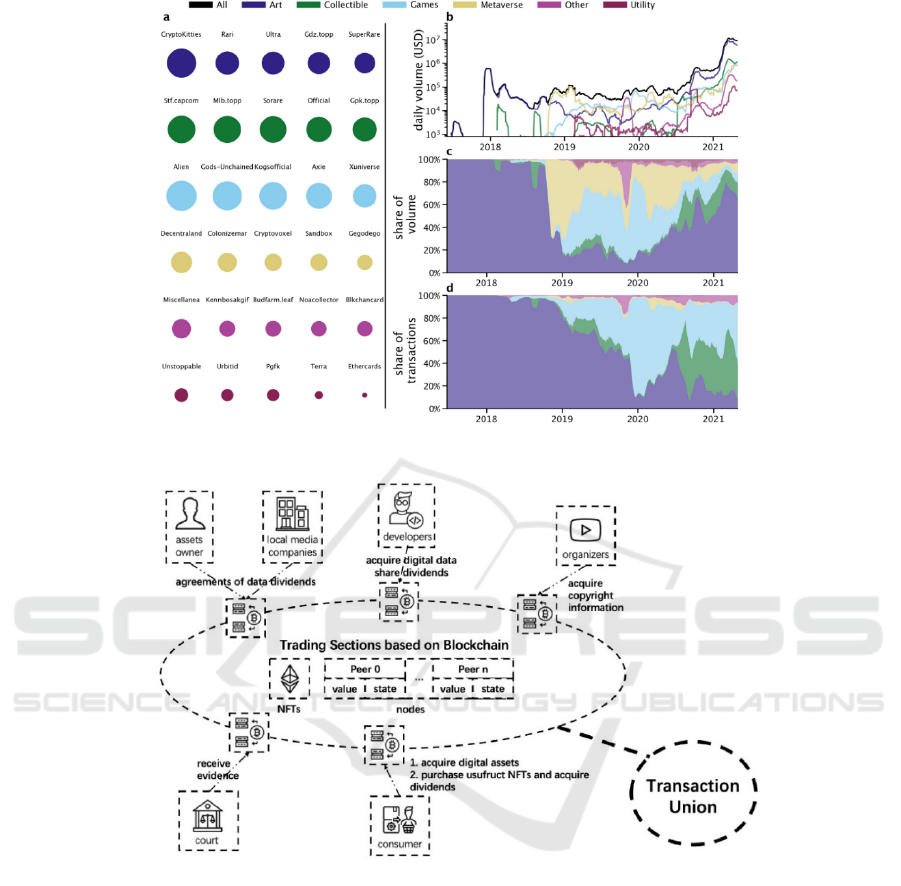
Figure 1: NFT market description (Nadini, 2021).
Figure 2: Trading Sections based on Blockchain (Photo credit: Original).
evidence directly to the court as material evidence.
Finally, through the interconnection of multiple plat-
forms, we can achieve transaction union and form a
decentralized and untampered local-regional media
companies blockchain platform, so as to improve the-
liquidity of media assets and increase more value.
Based on the premise of the separation of owner-
ship and usufruct, the transaction plate realizes the re-
alization of the usufruct of media assets hosted on the
media asset trusteeship operation platform through
"Block trading" and "Live trading" assets transac-
tions. "Block trading" refers to the one-time sales of
media assets through the platform API interface to
operators, including professional trading platforms or
databases, such as Springer Link CNKI, or large com-
prehensive media such as BBC, social networking
sites such as YouTube, according to a certain theme,
pricing according to Digital Assets Valuation Model
(Song, 2010). MAM's trading section records the start
and end times of each transaction, so that the user is
notified of the termination of the contract at the end
and the new contract can be renewed.
"Live trading" digital asset transactions are based
on the consumer side, providing services to provide
media resources directly to consumers. One way to
open data is to sell directly, such as "Birthday Daily"-
- selling the electronic media resources to consumers
in the form of "birth-date newspapers", based on
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
472
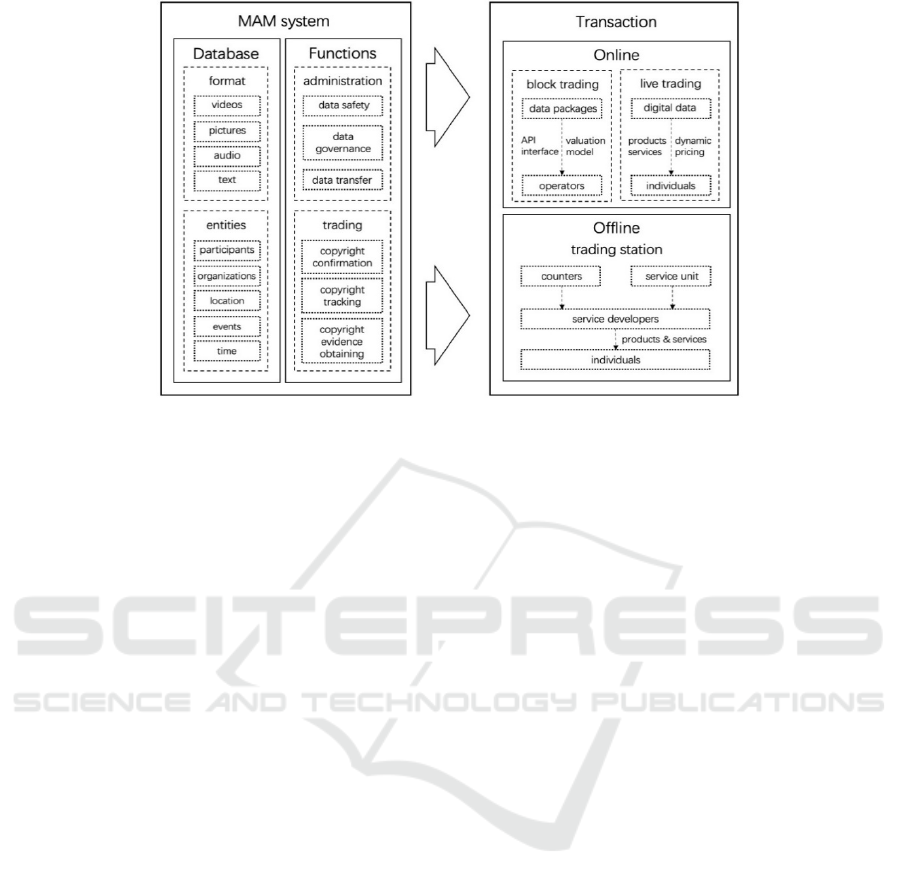
Figure 3: Media Copyright Trading based on Online-Offline Hybrid Model (Photo credit: Original).
MAM's participants' face recognition data, extracting
the characters in specific media resources, etc. In ad-
dition to the direct pricing of similar referring prod-
ucts, auction bidding is adopted for popular media re-
sources and derivative products, and the final pur-
chasers can get the NFT tokens of media resources
and derivative products.
Traditionally, asset trusteeship only relies on
online platform, by using website or applications, los-
ing opportunities of extending to make money on
scale. However, the high-input city-level hall of com-
pared with, fully considering that the “trading station”
of the media resource application is more cost-effec-
tive, which can be deployed in shopping malls, librar-
ies, cinemas and other places that are fully related to
the content of media resources. It includes temporary,
mobile automatic interactive equipment, or spot with
personnel to promote the platform. These will be li-
censed to local service developers, such as film pro-
moters, event planners, curators, etc., helping local-
regional media companies develop its unique local
advantages over large media groups
4 CONCLUSION: RETHINKING
ON THE APPLICATION OF
DIGITAL ASSETS
Specifically, the online and offline integrated digital
assets copyright trading application has important in-
novative value, which effectively solves the business
"inertia" of "re-broadcasting over copyright". It pro-
vides a clear path of fine authorization and online-of-
fline integration, which is helpful to solve the di-
lemma of transaction channels in the market-oriented
development and utilization of digital media copy-
right resources. As a kind of identifiable intangible
assets, radio and television media assets are the pre-
cious wealth with the most development potential.
Only through the realization of the value of media as-
sets and the reorganization of the trading platform and
local-regional media companies’ organizational
structure, can we maximize its potential market value
in the face of huge media content assets, achieve ex-
tensive economic benefits, and maintain and increase
the value of valuable assets.
Generally, digital assets, as an important part of
big data in cultural area, which is a small step in the
application and exploration of digital assets, could
help to improve advance of the media industry. As
media industry is different from other industries, dig-
ital assets is also significantly different from data in
other industries. In addition to economic benefits, the
important cultural value, historical value and social
value of culture itself are also worthy of attention.
Technology serves the business, and it is expected
that this article can bring some different practical
paths and theoretical sublimation in the field of "big
data + culture".
REFERENCES
Amir M F F, Kadir A R, Lasise S. MEDIA BUSINESS
STRATEGY: CASE STUDY OF PALOPO POS
NEWSPAPER [J]. Hasanuddin Journal of Applied
Exploration of Digital Asset Application: A Blockchain-Enabled Media Copyright Organizing Solution Based on Cloud Computing
473

Business and Entrepreneurship, 2022, 5(1): 51-62.
BBC's Digital Media Initiative failed because of more than
poor oversight, Steve Hewlett
Bosher H, Yeşiloğlu S. An analysis of the fundamental ten-
sions between copyright and social media: The legal im-
plications of sharing images on Instagram[J]. Interna-
tional Review of Law, Computers & Technology, 2019,
33(2): 164-186.
García-Perdomo V. Re-digitizing television news: The re-
lationship between TV, online media and audiences[J].
Digital journalism, 2021, 9(2): 136-154.
Kaliszewska J. Narration in digital archiving: Functional
design in FINA’s media asset management digital cata-
logue [J]. Journal of Digital Media Management, 2021,
9(3): 224-231.
Li Lingshu. Prerequisite for industrialized media content
development: copyright clarity[J]. CHINA RADIO &
TV ACADEMIC JOURNAL,2014(1):80.
Limaye R J, Sauer M, Ali J, et al. Building trust while in-
fluencing online COVID-19 content in the social media
world[J]. The Lancet Digital Health, 2020, 2(6): e277-
e278.
Nadini M, Alessandretti L, Di Giacinto F, et al. Mapping
the NFT revolution: market trends, trade networks, and
visual features[J]. Scientific reports, 2021, 11(1): 1-11.
P. Song and X. Wang, "Analysis on Value Chain Model of
the Media Business Based on Digital Asset Manage-
ment," 2010 International Conference on Management
and Service Science, 2010, pp. 1-4, doi:
10.1109/ICMSS.2010.5575344.
Sun Chao. A Preliminary Study on the Operation and Man-
agement of Diversified Value of Media Assets of Bei-
jing Radio [J]. CHINA RADIO & TV ACADEMIC
JOURNAL, 2018(2):90.
Sreekala P K, Baby M D. Digital Archiving and Access to
Print Media Resources: A Study among Leading Mala-
yalam Newspaper Libraries in Kerala [J]. Asian Journal
of Information Science & Technology (AJIST), 2019,
9(3).
Selina D. The Role of Regional Television in the Life of a
Megacity[J]. Journal of Media Critiques, 2018, 4(14):
255-260.
Toygar A, Rohm Jr C E, Zhu J. A new asset type: digital
assets [J]. Journal of International Technology and In-
formation Management, 2013, 22(4): 7.
Van Niekerk, A. J. (2006). The Strategic Management of
Media Assets; a Methodological Approach. Allied
Academies, New Orleans Congress.
Veynberg R R, Titov V A. Business Processes of Managing
Media Assets: Technology and Practice of Implementa-
tion MAM-Class Systems [J]. Advanced Science Let-
ters, 2019, 25(1): 66-69.
Warwick-Ching, L. (2012). Who really owns your digital
assets? http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/2bd0b814-13b3-
11e2-9ac6-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2IBfFoNiO
Zhou X, Liu L, Ren J, et al. Application of Blockchain
Technology in Copyright Protection of Digital Media
Assets [J]. 2019.
ICPDI 2022 - International Conference on Public Management, Digital Economy and Internet Technology
474
