
The Role of a Marketing Research Sub-System (MRSS) in Problem
Solving: Matoke Micro-processing Project Case Study
Dorothy Nduku Hodson
University of Dar es Salaam Business School, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
Keywords: Marketing Research, System, New Product, Development.
Abstract: Marketing as a customer centered discipline is challenged to make contributions to global problems. Information on
providing healthy food is one such challenge. Marketing research is tasked with this important role of information
provision. The study uses desk research methodology, reviewing literature to explore how the marketing research
information subsystem (MRSS) can be utilized to provide this information. The Matoke micro-processing project
aims to produce affordable banana flour and pieces to urban consumers. Findings are that while marketing research is
recognized, some challenges in practical application exist. For the Matoke micro-processing project, the specific
information sought is identified as stage six of new product development. This has specific information requirements
that identified models can be adapted to provide. The suggested model would be integrated into the marketing
research system, resident in the product system with specific new product development tasks. Ultimately, it would
provide highly customized reports, specific to the project stage. Further areas to consider are supporting projects with
research workers and optimizing the new product development process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Marketing is customer centric, as pointed out by
management lead-thinker Peter Drucker ‘. the whole
business…from the customer’s point of view.’ (Kotler,
1984). The 1970s presented many challenges in
economic crises, yet opportunities in technology
positioned marketing for an important role in’ launching
a new era of economic activity and raising living
standards’. The current global environment has
significantly more severe economic crises, presenting an
urgent need to accelerate optimization or actualization of
technology benefits. It is not clear if marketing and
marketing research with this specific role met the earlier
global brief, but it is clear now that urgent and effective
solutions are required. This study aims to explore and
present a working proposition for the role of marketing
research in solving current important global problems.
According to the Consultative Group on
Agricultural Research (CGIAR), through the Roots,
Tubers and Bananas (RTB) - program opportunities
for breakthrough research and development were
created. Operating between 2012 to 2021, acquiring
significant financing of $750mn and with over 200
partners in Africa - it is considered a model for
successful collaborative research (Thiele et al,
2022). Research outputs included specific
technologies and innovation such as value addition
and processing. The economic importance of RTBs
is value addition and employment in rural areas,
especially for women. These crops are crucial for
Africa Food Security and include cassava, banana,
plantain, potato, sweet potato and yam. For
consumers, RTBs are vital sources of calories but
have received little investment in research and
development. Program challenges were in low
productivity, diseases, poor storage systems, limited
processing and value addition. Success in R & D
was recorded, for example in food processing with
cassava flour mixed with wheat flour to create
composite flour. Bananas and plantains are grown in
101 countries, production trends indicate high
growth and a contribution of 27.7% to total value in
the RTB category. RTBs represent 25 to 57% of
total food in some countries, global supply and
demand is mostly in Africa with smaller volumes in
Asia and Latin America (Thiele et al 2022).
14
Hodson, D.
The Role of a Marketing Research Sub-System (MRSS) in Problem Solving: Matoke Micro-processing Project Case Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0011601300003581
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Finance, Information Technology and Management (ICFITM 2022), pages 14-21
ISBN: 978-989-758-628-6
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
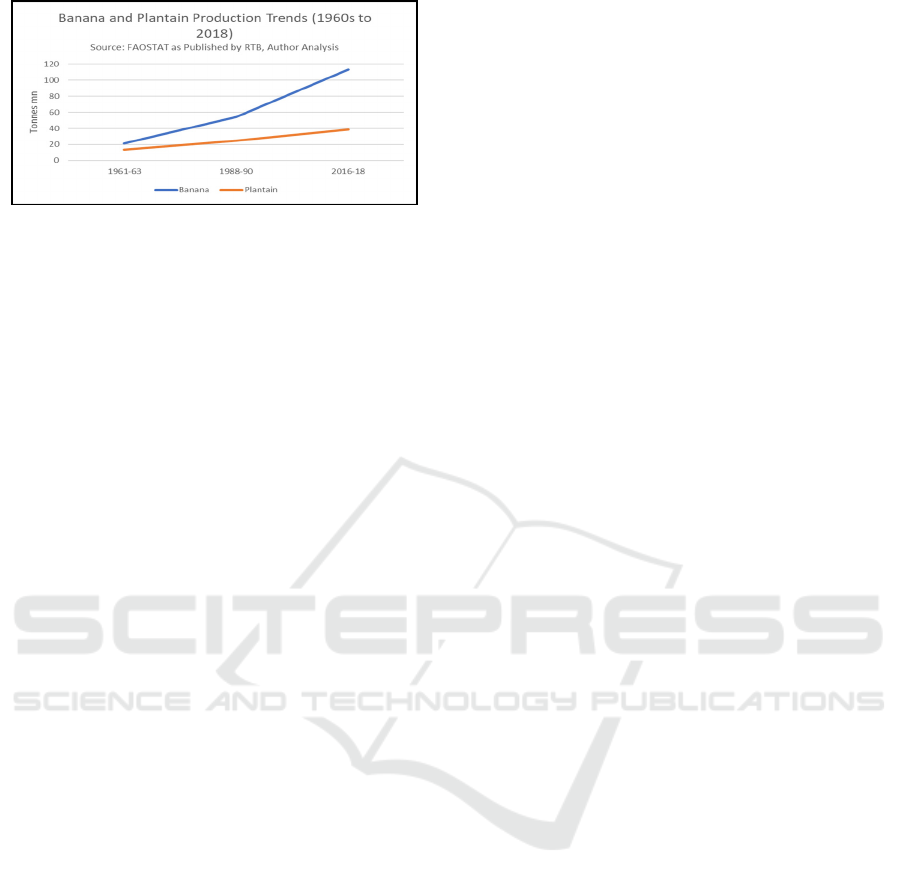
(Source: Thiele et al, 2000, Author Analysis)
Figure 1: Banana and Plantain Trends.
On a smaller, more focused scale The Matoke Micro
processing project is a business concept utilizing a
cottage method of preparing Matoke flour and pieces
for household consumption, storage, consumer and
retails sales. Current value addition to Matoke, (raw
uncooked plantain/ banana) is boiled and mashed,
stewed and chipped (banana crisps). It’s both trendy
and traditional, used as a staple food and also as a
snack. Why add value to bananas? To provide an
affordable and convenient food staple (Hodson,
2018).
2 PROBLEM
Large scale food R & D projects present challenges,
demonstrated by the CGIAR RTB program. Stated
was that extensive transformation of current
processing technology was required to provide these
food crops to urban consumers (Thiele et al, 2022).
In terms of research priorities, banana and plantain
are favorable for poverty reduction although cassava
and potato have higher priority. RTB presented
innovation clusters as opportunities for postharvest
innovation, however no specific banana or plantain
research was selected. The clusters present specific
attributes for value addition. For the RTB program,
the innovation model linked products to the market,
research outcomes and development. (Author note:
bioengineered RTBs or GMO food products
referenced in this and other sections are not
promotion of GMO products in view of current
African regulatory protocols, or lack there-of in this
crop area).
In the African context, a study examining
marketing research practice in Tanzania determined
most Small and Medium sized enterprises (SMEs) in
manufacturing carried out mostly unstructured
marketing research. Further, the study established
empirically there was no significant relationship
between marketing research and business
performance. 66.5% of surveyed SMEs do not
utilize structured marketing research. SMEs that
utilized structured marketing research reported some
positive growth in profits and sales. 69% perceived
marketing research as an important activity. As a
function, marketing research was considered
important for competitive responses in exploiting
opportunities in trade and investment and also seen
to enhance SME growth. The paper postures that
despite tangible benefits strategically – marketing
research has not demonstrated adequate value to
SMEs. Also, existing theory does not accurately
predict how SMEs act. The study recommendations
include a more systematic and coordinated approach
to the application of marketing research strategies
and resources This is the study gap (Nyamanza,
2021).
Within the EAC region, a study report from
Tanzania and Uganda examined the market research
function and identified marketing and selling as
specific problems - namely; limited information on
markets of operations; few market assessments and
analysis due to knowledge and skills gap; few
products and services, limited identification of
opportunities for diversification; inadequate linkages
in agri-food chain; limited feedback to processors
and producers (Dietz et al, 2000) This is a broad
based research problem that the study research
questions will seek to further refine and clarify.
2.1 Working Proposition and Research
Questions (RQs)
Working proposition:
Marketing Research Subsystems have an important
role in project problem solving.
Research questions:
RQ1: What are the marketing research problems in
the Matoke Micro-Processing Project?
RQ2: What marketing research subsystem model
can be developed to address these problems?
RQ3: What is the overall role of the marketing
research subsystem for the project?
2.2 Paper Research Methodology
The research methodology is desk research using
literature review, case study and modelling. Current
thought on context specific studies, such as localized
case studies in producing and obtaining acceptance
are considered and addressed. Context-specific
refers to the limited generalizability to other contexts
and other findings. This can be unique content
and/or limited generalizability of findings.
The Role of a Marketing Research Sub-System (MRSS) in Problem Solving: Matoke Micro-processing Project Case Study
15

Typically, marketing pursues a scientific approach
hence proposition, hypothesis, findings. Overall, the
study pursues this, with a working proposition and
research questions. Context specific studies can add
value in three ways: higher validity (accuracy &
precision) to specific context, higher importance to
specific context; and higher creativity and
innovation in this area. To broaden generalizability
the paper looks at global research, across industries,
utilizing established texts, widely used journals and
standard accepted modeling. The study adds
accuracy, importance and creativity to the specific
context by immersing in industry-rich publications
in, using an in-depth case specific project, materials
documented, reviewed and published over five (5)
years and adaptive modelling to address case
problem. (Stremerch et al, 2022)
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Working Proposition
Marketing research is defined as ‘identification,
collection, analysis and dissemination’. Further,
as ‘a process with opportunities and problems,
actions’. The activities involve ‘information,
methods, data collection, results, findings and
implications/communications’ (Malhotra, 1996).
Implicit in this definition is that marketing research
aims to identify opportunities and problems, then
propose solutions. This is a process utilizing
information resources. Important is communication
of the solution. The importance of research and its
role is therefore as a problem-solving process. Other
definitions of marketing research include ‘search for
knowledge’ or ‘scientific and systematic search for
pertinent information on a specific topic’ and
‘academic process of defining and redefining
problems, formulating hypothesis or suggested
solutions, collecting and evaluating data, making
deductions and reaching conclusions, carefully
testing conclusions to ensure a fit to the
hypothesis/suggested solution’. (Kothari & Garg,
2004). There is a differentiation between market
research and marketing research (CIM, 1994).
Marketing research refers to ‘all elements of the
marketing mix (price, product/service, promotion
etc.’. Market research is in markets (sizes, segments,
trends, market shares). According to Daniel et al
(2021) marketing research is 'providing information
for marketing decision-making'. Also, market
research focuses on markets, marketing research
aligns with marketing processes. Projects are
pre-defined sets of activities with specific
objectives, fixed resources and a time frame.
Due to their nature, marketing research
requirements would inherently be different.
Therefore, marketing research for projects
should be: set to achieve specific project
objectives; designed to utilize allocated project
resources; implemented within project stipulated
time frame.
3.2 RQI: Marketing Research Problems
Sustainability - a popular term is mostly used in
reference to the environment. Marketing
sustainability is concerned with customers and
businesses, creating socially responsible marketing
and practiced in different sectors, including public,
private and non-governmental.
Sousa et al (2003) discuss the role of value
design of for marketing sustainability. Their
marketing definition is ‘assessing information needs,
implementing a research process and communicating
findings, while also useful in monitoring the firm
performance.’ Most researchers insist high
performing businesses use marketing research,
generated internally rather than externally. It is pre-
emptive and practical, not responsive. (Sousa et al,
2003). The importance of sustainability to both
marketing research and products/services outputs is
stated, while clarity of the research process is also
important.
Aligned with this classification of research by
Malhotra, (1996) two main categories are presented:
problem solving research involving segmentation
and correcting marketing principles; and problem
identification research, concerned with market
potential. The above problem is analyzed to
determine classification, approach and focus. The
relevant problem is few products and services with
limited identification of diversification
opportunities. An MRSS that is problem solving in
nature and can; first, identify products and service
options; second, identify diversification
opportunities is therefore the study focus.
For the Matoke Micro-processing project, the
basis of projections as per a conference paper from a
Tanzanian national perspective consider sales value
of app $2600/hectare; gross margins of 50%; retail
margins of 400%. The projects’ current key goal is
development, launch and commercialization of
Matoke flour and pieces, creating a sustained project
for micro-processing, training and sale of end-
consumer products: Project short term objectives are
to secure start-up capital of $3900; set up a pilot
ICFITM 2022 - SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON FINANCE, INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
16
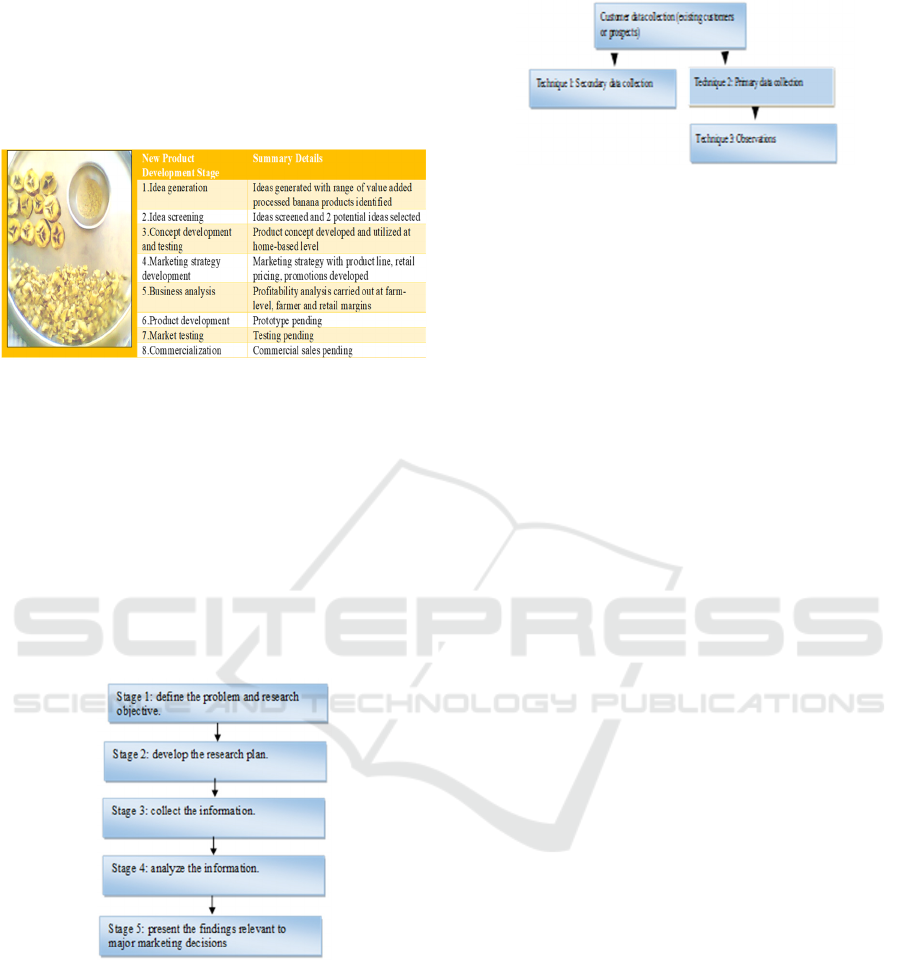
project; maintain positive project cash flows. Longer
term financial objectives are: achieve payback
within 11 months; achieve a 20% net margin
(Hodson, 2018)
Table 1: NPD Process-Project Stage (Source: Hodson,2018).
3.3 RQ2: Marketing Research
Subsystems
A theory is ‘interrelated concepts that explain facts’,
while a model is a ‘system representation and can be
descriptive, explanative or simulation. (Cooper &
Schindler, 2000). The study examines two
theoretical models. Kotler (2000) defines Marketing
Research System as ‘the systematic design,
collection, analysis and reporting of data and
findings relevant to specific marketing situations
facing the company’.
Figure 2: MRSS Model 1 (Source: Kotler, 2000).
Basandra (1999) defines market research subsystem
as describing firm’s marketing transactions. Types
of data are either on customers or prospects, both
primary and secondary sources, collected by the firm
or other parties.
Figure 3: MRSS Model 2 (Source: Basandra, 2000).
3.4 RQ3: Role of MRSS
Possible generic roles of marketing research, subject
to adjustment for project purposes are: first,
rationale (or why) for example to provide
information. This could be strategic direction (CIM,
1994) due to widening gaps between organizations
and customers caused by complex competition,
technology change, changing consumer markets and
higher marketing costs. This could also be for a
specific purpose. (CIM, 2000). The researcher is
required to set clear objectives then follow a specific
research process: second, for a purpose based on
structure within MKIS of storing specific studies on
marketing problems, opportunities and effectiveness.
It must interact with other MKIS subsystems (CIM,
1994); thirdly, for a purpose based on systematic
process, for example to answer questions by
applying the procedure. This could be to understand
a phenomenon, describe characteristics, to determine
frequency of an occurrence, test the hypothesis of
causal relationships (Kothari & Carg, 2004). In
summary, the overall MRSS role could be to provide
information, to store information or to implement
research.
4 MAIN FINDINGS
4.1 Working Proposition
The problem-solving importance to projects can be
seen by considering a similar product type – sweet
potato. This done in a Ugandan study examining its
health role and impact of processing. Modern
lifestyles have led to an increased consumption of
unhealthy foods and incidence of Non-
Communicable Diseases (NCD): These include:
stroke, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory
conditions, metabolic conditions and diabetes,
chronic respiratory diseases, chronic kidney
diseases, cancer. These are projected to increase
during 2000 to 2030 globally, from 60% to 70% and
in Low Income Countries, from 27% to 50%. Food
The Role of a Marketing Research Sub-System (MRSS) in Problem Solving: Matoke Micro-processing Project Case Study
17

based approaches are seen as 'cheaper and more
sustainable' than medications in treating NCDs.
Sweet potato is well suited due to its combined
features of high starch in cereals, vitamins and
peptides in fruits and high vitamin and minerals in
vegetables. Overall, it is high in nutritional value, an
important starch staple that is also drought
resistance. It can therefore be used for food and
nutrition security. Further studies on the effect of
food preparation and processing on sweet potato and
access to bio-compounds are suggested. In this case,
MRSS determines a health benefit that can
potentially be delivered, pending research on food
alteration by processing. It therefore provides
important preliminary health information (Amagloh
et al, 2021).
For the Matoke micro-processing project, the
following possible MRSS roles have been
identified. The first role could be to provide
information. This may be in two ways – in strategic
direction to provide a convenient, tasty, affordable
starch food staple product. This could also be
through stating specific objectives in line with the
key goals of development, launch and
commercialization of Matoke flour and pieces.
Second, an MRSS could store marketing data on
problems, opportunities and effectiveness: problems
are inadequate food starch staples; opportunities are
in processing available food products; effectiveness
is in successful launch of the food product. Thirdly,
the project MRSS could answer specific questions
by applying the research procedure. What model
MRSS is required and how can it be used to achieve
project objectives?
4.2 RQ1: MRSS Problems
The research question implies, priority is required in
defining the problem domain. An example is a study
that sought to evaluate food prescriptions as an
intervention (Little et al, 2021). Food prescriptions
are specific interventions for food insecure (FI)
patients at risk of health related diseases. There are
interventions to subsidize or provide healthy foods.
‘Food as medicine’ is an approach gaining
popularity in North America aiming to improve
'access, affordability, convenience and desirability of
safe and healthy foods, including whole grains, fruits
and vegetables. The global context is that
suboptimal diets account for 18% of deaths and 10%
of disability adjusted lifestyles (DALYs) as reported
by the Global Study on Disease Burden Study
(2016). Poor diets are low in whole grains, fruits and
vegetables. Diet behavior and consumption result
from varying factors, among which are 'affordability
and pricing, vendor and product features'. The
research methodology reviewed abstracts and
manuscripts, determining food prescriptions are
promising interventions in improving fruit and
vegetable consumption and reducing food insecurity.
However overall health impact in these studies was
seen as weak. A barrier to implementation was 'poor
quality produce at participating retailers'. More
studies are recommended to further investigate
health impact of the programs (Little et al, 2021).
This implies that while information on interventions
was required, health impact was a priority for
providing adequate research.
The Matoke micro-processing project has
already identified the main problem domain as few
products and services and limited identification of
opportunities for diversification. In identifying
products and service options the following were
product/service options generated: Matoke generic
product type, Matoke product original form, Matoke
processed product forms, Matoke nutritional
analysis and Matoke value addition process. In
identifying diversification opportunities in product
(not market) diversification, the following options
and opportunities were identified: new product
characteristics, new product packaging, new product
pricing and new product placement.
4.3 RQ2: MRSS Models
Soltesz et al (2003) utilize a classic project
management system, whereby successful product
development is seen as a common challenge to both
technical and managerial teams. They state success
factors include: precision regulation and focus on
collaboration; knowledge management and
collaboration within units; defining project success
and utilizing lessons learnt or module information;
improving project processes and utilizing time better
and provide more valuable products to customers.
Project management is about risk and has an impact
on investment and production. Risks are generally
associated with reception of the product in the
market. In a survey design, utilizing a questionnaire
sent to one hundred and twelve (112) experts, a
specific section handled information for the future.
This dealt with three (3) areas: project feedback
meeting and collecting lessons learnt, lessons learnt
database, module database. Findings indicate a high
rating on clarification of project goals with more
importance given to project feedback than databases
(Soltesz, 2003). When applied to the current MRSS
study, projects require a management framework
ICFITM 2022 - SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON FINANCE, INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
18
with objectives and information is important. The
MRSS is therefore a good focus for project success
as it has both.
Further examination of newly developed
technology models is carried out to develop MRSS
systems specifications. In selecting information
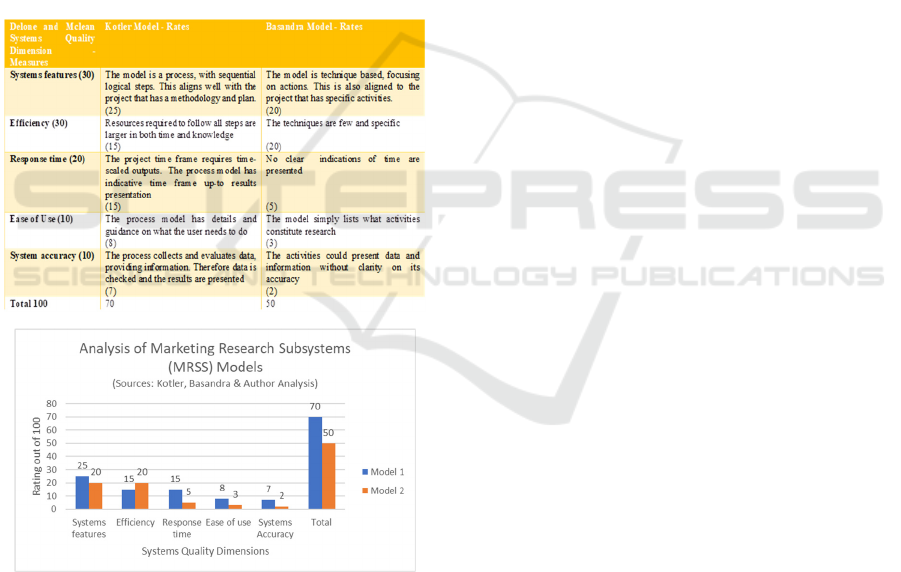
systems, several considerations can be made. Delone
and MacLean Information Systems Success Model
(2003) has dimensions with measures that can be
used in assessment. For the Matoke Micro-
processing project, based on project characteristics
and aligned with the study working propositions -
systems quality is an indicative dimension with the
following measures five (5) measures: systems
features, efficiency, response time, ease of use and
systems accuracy.
Table 2: Two MRSS model options analysis (Sources:
Delone & McLean, 2003 and Author analysis).
Figure 4: Results of Model suitability: (Source: Author).
4.4 RQ3: MRSS Role
Practically, this MRSS study examines research and
the roles assigned to it. In Africa’s biggest economy,
Nigeria – research in a leading growth sector of
SMEs indicates marketing research can provide
needed information and enable SME survival
(Daniel et al, 2021). The problem is that 80% of
SMEs did not have a business plan and most new
products were launched without an enquiry into
customer needs and wants. The role of marketing
research was therefore to assess and provide
information for sound marketing decisions.
Marketing research was seen as a transformational
function - changing the orientation of business 'from
producing what you can sell rather selling what you
produce' implying a market-oriented method of
doing business. An important role of research was to
monitor the environment and avert undue
risks/uncertainty. The specific research problems
identified were lack of proper identification of
research problems in industry. The study conclusion
with recommendations indicate marketing research
is important and should be conducted before and
after production. Its role can enhance and provide
better products and services for increased customer
satisfaction, profitability and sustainability (Daniel
et al, 2021).
For the MRSS study purpose, the overall roles is
to provide information on product/service and
diversification options. Specifically, information on
the current stage of product development is needed.
A complete Marketing Information system (MKIS)
review is a necessary starting point. NPD data and
information are stored in the NPD subsystem with
indicative features according to Kotler (2000) as:
organized to gather, generate and screen new
product ideas; carry out adequate research and
analysis before investing in new ideas; for adequate
product and market testing. At this point, it is
evident that an NPD subsystem is required. This can
only be identified and utilized by evaluating full
Marketing Information Systems (MKISs). For
simplicity and consistency, two MKIS models can
be examined from the same sources/authors. Kotler
(2000) presents an MKIS with MRSS as a core
processing subsystem with no NPD. However, there
is a report output for product decisions. Basandra
(1999) presents an MKIS with MRSS as an input
subsystem featuring a database for processing and
product system as outputs. Within this is a New
Product evaluation model that is quantitative,
presenting rational for introducing new products by
analyzing utilization of manufacturing and
marketing resources. Qualitatively assessing these
two models, neither can be well applied for project
purposes. Following the paper findings, the NPD
process can be adapted to give guidance on specific
research at product development stage. The result is
indicative model for a project MRSS.
The Role of a Marketing Research Sub-System (MRSS) in Problem Solving: Matoke Micro-processing Project Case Study
19
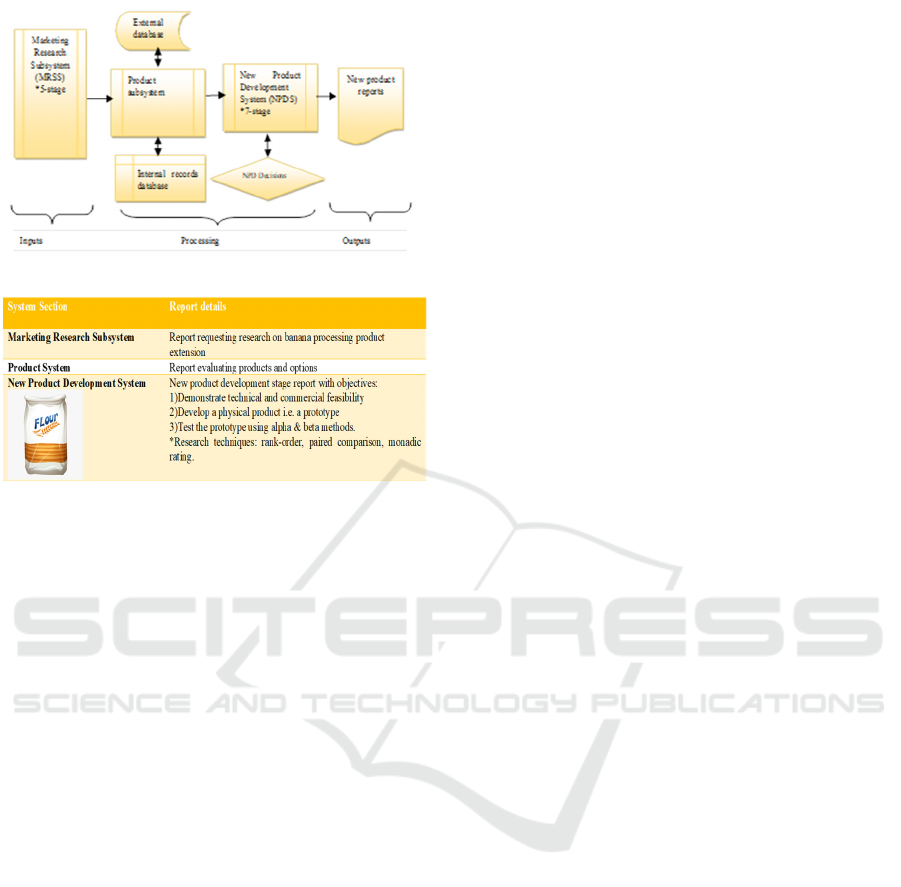
Figure 5: Integrated MRSS with NPD (Source:Author).
Figure 6: Sample Project Report (Source: Author).
5 CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS
AND RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 Conclusions
With regard to the working hypothesis, an MRSS
can be integrated or re-configured to have an
important role in project problem solving. 3 specific
roles could be; to provide information, to store
marketing data and to implement the research
process. The Matoke Micro-processing Project
identifies the most important role for an MRSS is to
provide information.
The Research Questions have been answered as
follows: In RQ1, research can be problem-solving or
problem identification. The Matoke Micro-
processing project is problem solving research,
related to product. For RQ2, two (2) MRSS models
are presented for review, a Kotler model with seven
(7) sequential processes, and a technique-based
model by Basandra with three (3) specific research
activities. Upon evaluation with the famous Delone
and McLean Information Success System model,
five (5) dimensions of systems quality relevant to
the project are reviewed namely; systems features,
efficiency, response time, ese of use and accuracy.
Model 1 scores 70/100, while Model 2 scores
50/100. RQ3 finds that in determining the role of
MRSS in providing information, an integrated
MRSS model can be developed with features of a
core MRSS subsystem, linked to a product system
with a New Product Development Subsystem
(NPDS). Linked to these are external and internal
databases with decision points and New Product
report outputs which are clear and
implementable. This will provide a complete
input, processing and output systems as per the
Information Systems concept.
5.2 Implications
In projects, a complete MRSS should be an
important consideration. The MRSS should have
clear research objectives aligned to overall project
objectives. Modelling MRSS is complex and
requires integration within the complete,
documented and functioning MKIS. The benefits of
an MRSS are derived from specification or
customization as projects tend to have complex
research needs. This supports MIS research that
suggests flexible systems are needed. The MRSS
requires high user knowledge of both project areas
and research as a function. These should be
considered in project teams structures.
5.3 Recommendations
A complete and documented NPD Subsystem would
be advantageous. This would complete all the
defined NPD process stages. The MRSS models can
be further assessed to ensure efficient integration
with emerging project specific needs.
REFERENCES
Amagloh. F. C et al. (2021). The potential of Sweet Potato
as functional food in Subsaharan Africa and its
Implications for Health: A Review. Molecules.
Basandra, K. S. (1999). Management Information Systems.
Wheeler Publishing.
Chartered Institute of Marketing (CIM). (1994).
Management Information for Marketing and Sales
(Study Text). BPP Publishing.
Chartered Institute of Marketing (CIM). (2000).
Management Information for Marketing Decisions
(workbook). BPP Publishing.
Cooper, D.S and Schindler, P. (2000). Business Research
Methods. MacCraw Hill. 7
th
Edition
Daniel, N. C. et al (2021). Research in Nigeria – A
Survival Strategy for SMEs in a Competitive
Environment. The Melting Pot Journals.
Delone, W. and Mclean, E (2003). The Delone and
McLean Model of Information Systems Success: A Ten
ICFITM 2022 - SECOND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON FINANCE, INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
20

Year Update. Journal of Information Management
Systems.
Dietz M. et al. (2000). Assessment of Small-Scale Food
Processing Sub-Sector in Tanzania and Uganda.
Technical Center for Agriculture and Rural
Cooperation - CTA (ACP-EU).
Hodson, N. D. (2018). Matoke Micro-processing Project -
ICTs for Development. 7
th
ICTIC Conference 2018.
Kothari C R and Garg Gaurav. (2004). Research
Methodology – Methods and Techniques (3rd Edition).
New Age International (P) Limited Publishers.
Kotler, Philp Prof.. (1984). Marketing Management –
Analysis, Planning and Control. Prentice-Hall. 5
th
Edition
Kotler, Philp Prof.(2000). Marketing Management –
Analysis, Planning and Control. Prentice Hall.
Millenium Edition
Little. M. Prof et al (2021). Promoting Healthy Food
Access and Nutrition in Primary Care: Scoping review
of Food Prescription Programs. American Journal of
Health Promotion.
Malhotra, N. (1996). Marketing Research – An Applied
Orientation. Prentice Hall. 2
nd
Edition
Nyamanza, U. B. Dr. (2021). The Importance of
Marketing Research Practices on The Performance of
Tanzanian Manufacturing SMEs. Journal of Economic
Finance and Management Studies.
Soltesz, L and Berenyi L. (2003). Success Factors in
Product Development Projects: Expert Opinions. IOP
Publishing.
Sousa, B. et al (2021). Challenges for Marketing Research
in the Concept of Sustainable Development.
International Journal of Marketing, Communication
and New Media (JMCNM).
Stremerch, S. et al., (2022). The Importance of Context
Specific Studies for Marketing. Journal of The
Academy of Marketing Science.
Thiele. G. et. al, (2022). Root, Tuber and Banana food
Systems innovations. value creation for inclusive
outcomes. Springer Imprint.
The Role of a Marketing Research Sub-System (MRSS) in Problem Solving: Matoke Micro-processing Project Case Study
21
