
Mechanism for Settlement of Environmental Crises in the Economy
Deshchi Musostova
1a
, Valentina Dzobelova
2b
and Varvara Markaryan
3c
1
Chechen State University, Grozny Named After A.A. Kadyrova, Grozny, Russian Federation
2
North-Ossetian State University Named After K.L. Khetagurov, Vladikavkaz, Russia
3
Krasnodar Branch of Financial University Under the Government of the Russian Federation, Krasnodar, Russia
Keywords: Ecology, ecological crisis, economy, settlement of ecological crises, green economy.
Abstract: The current ecological crisis threatens the possibility of sustainable development of human civilization. The
degradation and destruction of local ecosystems leads to the destabilization of the biosphere, the loss of its
unity and the potential to support vital environmental parameters. Overcoming the ecological crisis can be
carried out only through the formation of a fundamentally new, more harmonious model of interaction
between nature and man. Under these conditions, a comprehensive assessment of the environmental situation
and the development of a mechanism for resolving environmental crises in the economy are of great
importance.
1 INTRODUCTION
The adoption of the concept of sustainable
development implies the assumption by individual
states and regional integrations of obligations to
implement the principles of the "green" economy,
which involve the harmonization of economic, social
and environmental aspects of the development of
society. Meanwhile, as international environmental
studies show, over the past 50 years, mankind has
been steadily widening the gap between the demand
for environmental resources and the ability of nature
to satisfy it. At the same time, developed countries
leave the largest “ecological footprint”,
demonstrating a high level of consumption of
resources and end products.
The increase in environmental tension
necessitates the implementation of comprehensive
measures in order to ensure the environmental safety
of the individual, society and the state. In developed
foreign countries, these measures are implemented
through the implementation of comprehensive legal
and organizational regulation of the environmental
sphere, as well as toughening responsibility for
environmental offenses and creating threats to the
environment.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9258-6277
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7673-3559
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7335-0920
In Russia, topical environmental problems are
largely ignored, as evidenced by the ineffectiveness
of existing regulations, the use of outdated models of
interaction between society and nature, as well as the
low credibility of environmental organizations in the
country. The consequences of such an irresponsible
attitude to environmental issues are the gradual
depletion of natural resources, a high level of
pollution of territories, and the deterioration of public
health. Meanwhile, ensuring rational nature
management and environmental protection of
territories is an integral factor in the country's
sustainable development in the long term.
The ecological protection of the territory implies
a normal ecological situation, that is, the state of
safety of the natural environment and the vital
interests of a person from the possible negative
impact of economic and other activities, natural and
man-made emergencies, their consequences (Article
1 of the Federal Law of January 10, 2002 No. 7-FZ
"On Environmental Protection").
2 MAIN BODY
Environmental security is an integral element of the
national security of the state along with its military,
Musostova, D., Dzobelova, V. and Markaryan, V.
Mechanism for Settlement of Environmental Crises in the Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0011569800003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
253-257
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
253
political, economic, food, information and other types
of security. The system for ensuring environmental
safety at the national level involves a comprehensive
assessment of territories, the implementation of
continuous monitoring of their ecological state, as
well as the adoption of managerial decisions to
improve it.
The Russian Federation, as the world's largest
state in terms of territory, has a particularly
significant mission to maintain the ecological balance
on the planet. The scale of the country's natural,
industrial and intellectual potential also implies its
active participation in solving the global problems of
our time. Meanwhile, the sphere of ensuring
environmental protection in Russia is on the
periphery of the attention of both state bodies and the
population, which, combined with irrational nature
management, causes a significant deterioration of the
environment and entails a threat to human health.
At the present stage, Russia ranks 54th in the
ranking of countries in terms of environmental
pollution (NONEWS. https://nonews.co), yielding to
almost all developed countries, as well as many Latin
American countries. The country's most serious
environmental problems are deteriorating water
quality, air pollution, deforestation, soil degradation
and loss of biodiversity. Significant concerns are also
caused by the presence of radioactive contamination
and excessive volumes of unprocessed municipal
solid waste.
According to official sources, in 15% of the
country's territory, where most of the population is
concentrated, the quality of anthropogenic
ecosystems is recognized as unsatisfactory. This
leads to adverse consequences for public health, in
particular, an increase in the number of oncological
and acute respiratory diseases.
Of particular concern is the problem of air
pollution: the level of air pollution in Russian cities is
assessed as high, which leads to extremely adverse
consequences for human health. The indicators of the
emission of pollutants into the atmosphere are
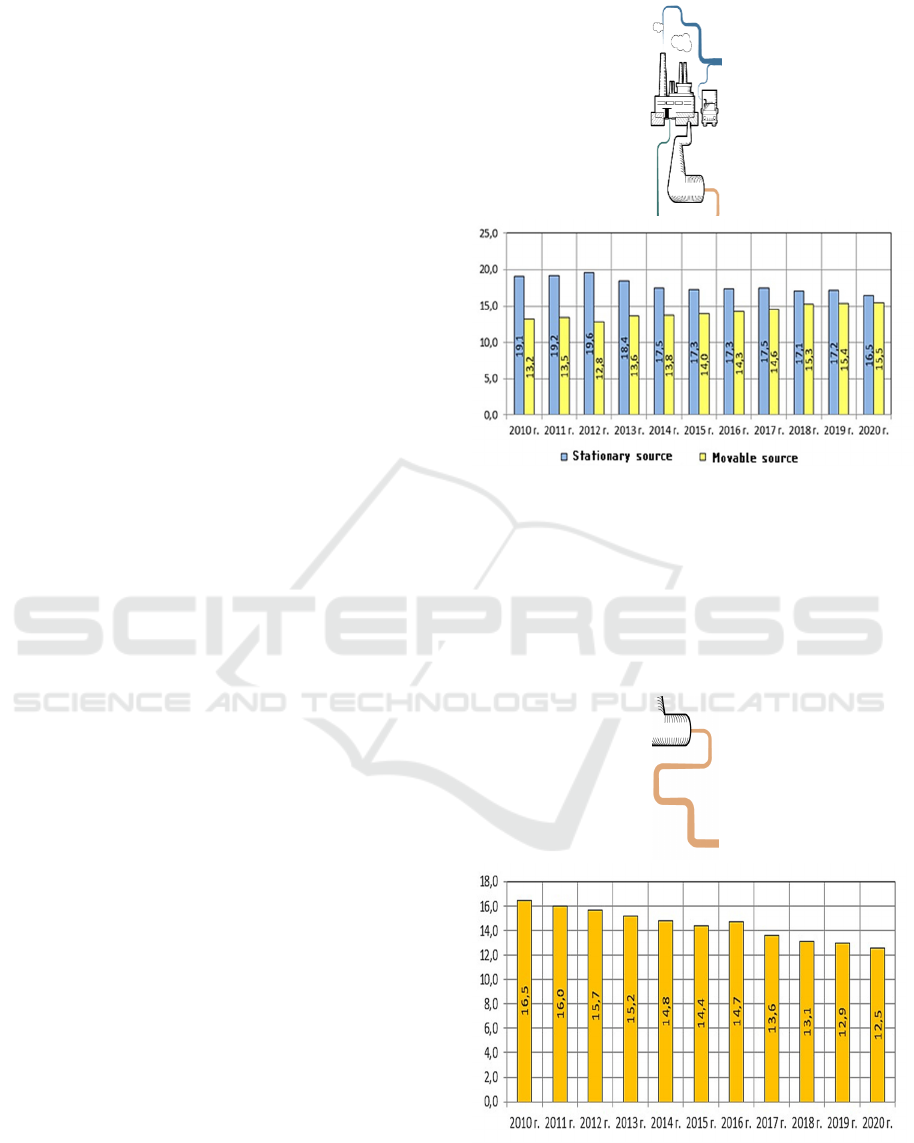
presented in Figure 1.
Thus, the volumes of emissions of pollutants into
the atmosphere in the last 10 years have actually
remained at the same level. At the same time,
emissions from stationary sources decreased by
13.7% over the study period due to environmental
measures and a general reduction in industrial
production. Emissions from mobile sources increased
by 17.4% due to a significant increase in motorization
in Russia.
Figure 1: Emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere,
million tons (Rosstat, https://rosstat.gov.ru/).
Serious scale is the pollution of the water basin of
the Russian Federation. An important factor in water
pollution is the widespread use of outdated and
inefficient treatment facilities. The dynamics of the
discharge of polluted wastewater in the Russian
Federation is clearly shown in Fig.2
Figure 2: Emission of polluted wastewater in the Russian
Federation, billion m3 (Rosstat, https://rosstat.gov.ru/).
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
254
Thus, the dynamics of polluted wastewater
discharges in the Russian Federation tends to
decrease: in the period from 2010 to 2020, their
volume decreased by 4 billion cubic meters, or 32%.
At the same time, today up to half of wastewater has
a high level of pollution, which exceeds European
standards by dozens of times and leads to a decrease
in environmental safety. The result of pollution of the
aquatic environment is the death of fish and the
emergence of infectious diseases among the
population (Dedul, 2018).
Solid waste from industrial production and
household waste pose a significant hazard. So, in
Moscow alone, more than 50 million tons of them are
formed annually - in the future they are exported to
the Moscow region and accumulate in landfills. The
territory of landfills cannot be used in the future,
chemicals located in landfills can get into
groundwater, and the number of landfills themselves
is already so large that at some point they will have to
be arranged farther from Moscow and other
megacities. The dynamics of production and
consumption waste generation in the Russian
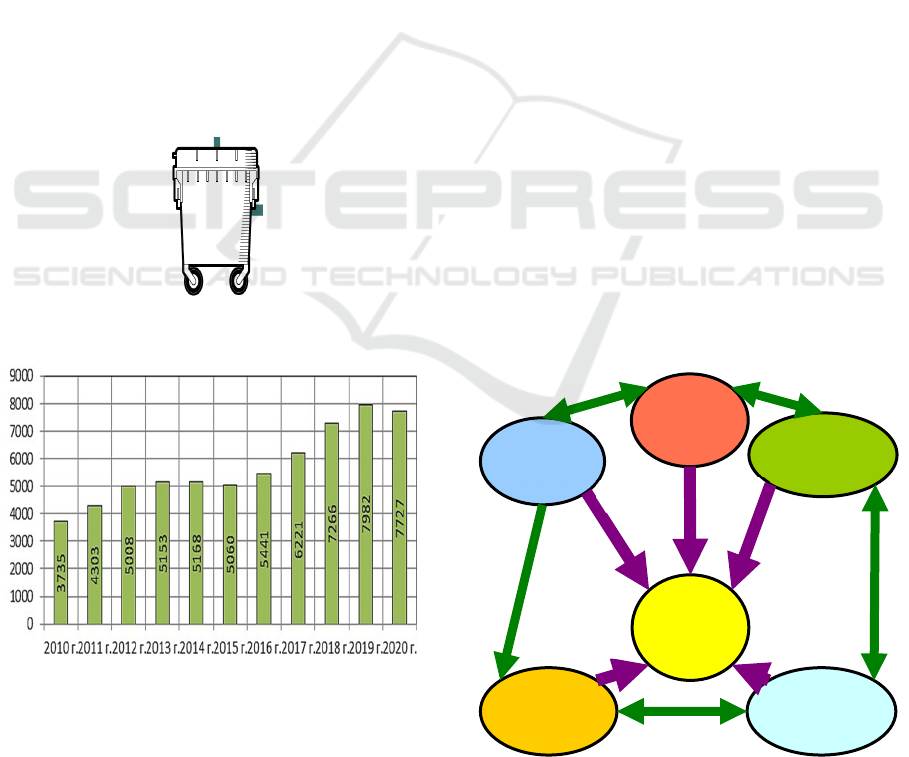
Federation is shown in Figure 3
Figure 3: Generation of production and consumption waste
in the Russian Federation, million tons (Rosstat,
https://rosstat.gov.ru/).
Thus, the volume of production and consumption
waste for the period from 2010 to 2020 more than
doubled. At the same time, the problem of dealing
with solid waste is not solved, and only 2-3% of
household waste is recycled, which is an extremely
low share. In countries with a high level of
environmental safety, about 60% of solid waste is
currently recycled. Also in Russia there is a problem
of radioactive contamination. Currently, Russia has
33 nuclear reactors operating at nuclear power plants,
and the Navy includes 50 ships that use nuclear
installations. Some nuclear power plants have either
reached the end of their service life or are
approaching this line, which increases the risk of
accidents and emergencies.
Another source of radioactive contamination are
enterprises that produce material for the creation of
nuclear weapons. For the needs of the military sector,
there are nuclear test sites, radioactive waste burial
sites, specialized laboratories and research institutes
that use fissile material in their work.
In recent decades, the ecological situation has
become more difficult due to uncontrolled
deforestation, which is observed in such regions as
Karelia, the Khabarovsk Territory, the Kostroma and
Arkhangelsk Regions.
In the energy sector, most of the electricity is still
produced by burning fuel on inefficient and outdated
equipment, which leads to harmful emissions into the
atmosphere. The transition to modern equipment
would reduce harmful emissions by 25%.
The operation of outdated power plants is fraught
with the risk of man-made disasters, which may be of
a radiation, chemical, electromagnetic or mechanical
nature. One of the serious problems is the unreliable
system of mining and transportation systems.
Figure 4: The impact of environmental factors on human
health (Shilov, 2020).
HUMAN
HEALTH
Changin
g of the
climate
Desertificati
on and land
degradation
Destruction
of the ozone
layer
Loss of
biodiversity
Deterioratio
n of fresh
water quality
Negative
im
p
act
UV
irradiation
Productivity of
agroecosystems
Degradation
of ecosystem
services
Quantity
and safety
of water
Mechanism for Settlement of Environmental Crises in the Economy
255
Environmental problems affect the health of the
population. Currently, doctors record an increase in
diseases of the endocrine system, respiratory organs,
the presence of such congenital diseases as
malformations and various forms of deformities is
noted.
Thus, an unfavorable environmental situation has
developed in Russia, caused by such factors as
outdated forms of energy production, lack of proper
control over harmful emissions into the atmosphere,
and irrational nature management. To solve the
problems that have arisen, it is necessary to create
measures to ensure environmental safety, both at the
federal and regional levels. The negative impact of
environmental problems on the health and quality of
life of the population indicates the need to find ways
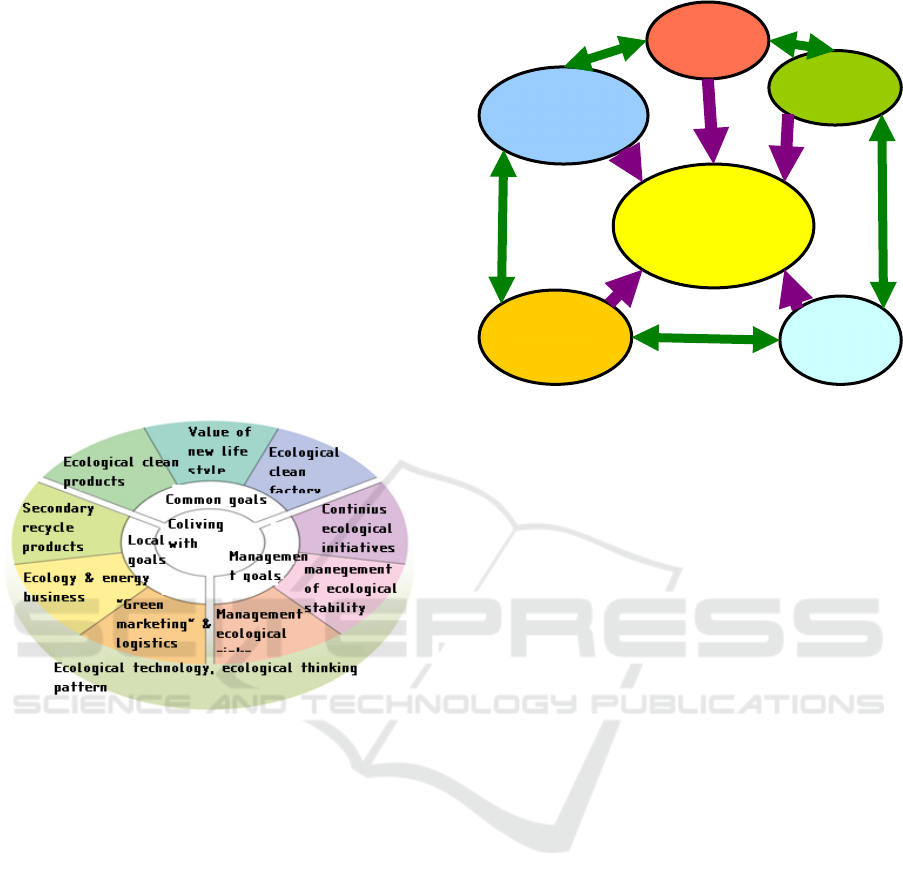
for a more optimal coexistence of man with the
environment (Fig. 5) (Alikaeva, 2019).
Figure 5: Coexistence of man with the environment.
The study of the actual state of the natural and
anthropogenic environment allows us to conclude
that there are significant threats to Russia's
environmental security. The environmental crisis in
the country is caused by irrational nature
management, the presence of numerous hazardous
industries, the lack of a separate waste collection
system and an inefficient system for controlling
emissions of pollutants and radioactive substances.
Countering these threats is one of the most significant
tasks facing the state, and its solution is based on the
development and implementation of large-scale
projects and measures to ensure environmental safety
at the federal, regional, municipal and industry levels.
The mechanism for resolving environmental
crises in the economy is based on the relationship of
various structural elements of ensuring
environmental security (Fig. 6) (Blumenfeld, 2018).
Figure 6: Elements of the system for ensuring
environmental safety and resolving environmental crises in
the economy.
The mechanism for the comprehensive settlement
of environmental crises is associated with the
transition to a "green" economy, which involves the
harmonization of economic, social and environmental
aspects of development. The methodological basis of
the social approach to the "green" economy was laid
by the concept of "sustainable development" formed
in the late 1970s, according to which the satisfaction
of the current needs of mankind should be carried out
without prejudice to future generations. According to
V.D. Kalner, the "green" economy is such a "model
of sustainable development, which proceeds from the
conditions of maintaining a balance between
economic and social requirements and maintaining
the state of the environment at a level necessary to
ensure the livelihoods of living people without
prejudice to the needs of future generations of
earthlings in the resources of the biosphere" (Kalner,
2019).
For the first time, the United Nations
Environment Program (UNEP) identified social
justice as an essential feature of a green economy. In
the report “Towards a Green Economy”, published
within the framework of this program, the “green”
economy is characterized as an economic activity that
is designed not only to reduce the risks of negative
impact on the environment, but also to increase the
welfare of the population, to ensure social justice
(UNEP Report? 2011).
In practice, the following tools are used to
implement these principles (Fig. 7).
ENVIRONMENTAL
CRISES
MANAGEMENT
MECHANISM
Legal
support
Institutional
support
Information and
methodological
support
Technical and
technological
support
Staffing
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
256
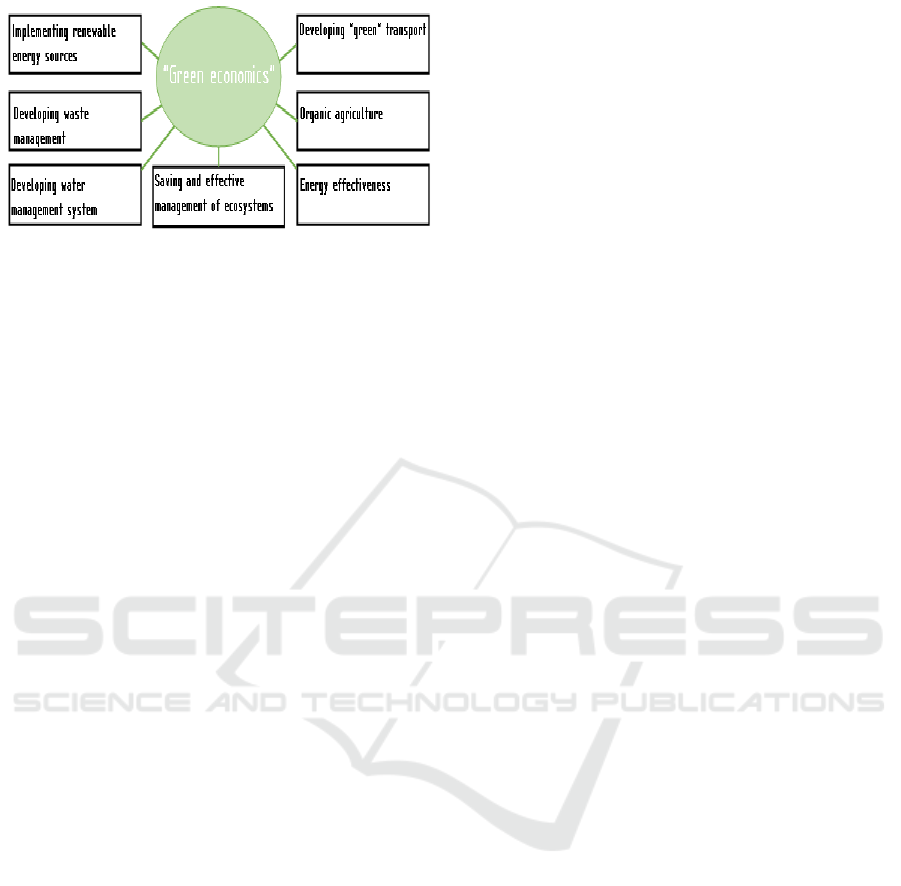
Figure 7: "Green" economy as a mechanism for resolving
environmental crises.
For a gradual transition to the principles of a green
economy, the state must take a number of key
measures to change the approach to the organization
of production and economic processes. First of all, we
are talking about reducing investment in industries
containing environmentally harmful technologies and
increasing tax rates for these industries. This
approach forces entrepreneurs to choose
environmentally friendly technologies.
3 CONCLUSION
On the part of the state, increased attention should be
directed to investing in and supporting "clean" energy
sources, agriculture and waste processing. The
transition to alternative energy sources should take
place not only at the industrial level, but also at the
household level. An important task is the introduction
of environmentally friendly technologies in the
extraction of natural resources, where resource-
intensive methods are actively used.
Thus, the "green" economy is a low-carbon,
resource-saving, energy-saving, cleaner and socially
fair economy, focused on improving the well-being
of society while reducing the burden on the
ecosystem. The listed components can be called
axiological, i.e. value level of the concept of "green"
economy. At the same time, the ontological aspect of
the studied model, which ensures its internal
movement and development, acquires the greatest
importance.
REFERENCES
Rating of countries by the level of environmental pollution.
NONEWS.
https://nonews.co/directory/lists/countries/pollution-
rating.
Shilov, I. A., 2020. Ecology. Yurayt. p. 76.
Kalner, V. D., Polozov, V. A., 2019. Green economy and
non-alternative natural resources. Kalvis. p. 19.
Towards a Green Economy: Pathways to Sustainable
Development and Poverty Eradication: UNEP Report.
Saint-Martin-Bellevue: UNEP, 2011. VI. p. 42.
Rosstat. https://rosstat.gov.ru/.
Alikaeva, M. V., Ksanaeva, M. B., 2019. Small business in
sustainable development economy of Russia. p. 67.
Blumenfeld, V., 2018. Big problems of small business.
Economics and life.
Dedul, A., 2018. Small business in Russia: Achievements,
problems, prospects. Federal newspaper. p. 84.
Mechanism for Settlement of Environmental Crises in the Economy
257
