
New Technologies in Production
Zelimkhan Musostov
1a
, Albina K. Berkaeva
2b
and Isa Basnukaev
3c
1
Chechen State University, Grozny Named After A.A. Kadyrova, Grozny, Russian Federation
2
North Ossetian State University Named After K.L. Khetagurova, Vladikavkaz, Russian Federation
3
Grozny State Oil Technical University Named After Academician M.D. Millionshchikova, Grozny, Russian Federation
Keywords: Ecology, green economy, green technologies, renewable sources, green production, eco-friendly production.
Annotation: The adoption of the concept of sustainable development implies the commitment by individual states and
regional integrations to harmonize the economic, social and environmental aspects of development. One of
the areas of such activity is the introduction of "green" technologies in various branches of economic activity.
This article discusses the problems and prospects for the development of "green" technologies in production.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the key areas of sustainable development of
modern civilization is the introduction of "green"
technologies - environmentally friendly technological
processes, production lines and logistics that provide
the most optimal parameters of resource saving,
energy efficiency and environmental safety in the
current conditions. The introduction of "green"
technologies in the manufacturing industries is based
on the appropriate mechanisms of state policy, which
involve stimulating innovations in the field of "green"
ecology and tougher penalties for environmental
offenses.
Developed countries are implementing "green"
technologies in all sectors of the economy and at all
stages of the product life cycle - from the design and
production of products to its processing and final
disposal.
With the introduction of environmental
technologies, success is achieved in reducing the
expenditure of resources and the increased use of by-
products arising from the organization of production
processes. For example, in the new millennium,
refrigerators consume 75% less electricity compared
to refrigerators produced in the 70s of the XX
century. At the same time, they have a lot of power.
These results were achieved through the use of new
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8166-3807
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0332-6378
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4174-1596
materials that provide increased insulation and the
development of more efficient cooling systems.
Compared to the 1970s, cargo ground transport
consumes 20% less fuel with an increase in carrying
capacity; in civil aviation, fuel savings amounted to
50%. In recent decades, due to the use of the latest
technologies, the efficiency of oil and gas production
has increased.
The most important direction in the
implementation of "green" technologies is the energy
industry, which has a direct impact on all existing
industries. The key areas in this area are increasing
energy efficiency and using renewable energy
sources.
Renewable energy sources are inexhaustible
resources. The main principle of renewable sources is
to obtain them from natural processes that are cyclical
in nature: radiation of sunlight, sea tides, wind,
geothermal energy of the earth. When using these
natural energy sources, it is possible to obtain energy
comparable to energy from burning oil, gas, coal and
their products. The use of natural resources does not
affect the energy balance of the planet and is the basis
of the "green economy", which leads to the active
development of renewable energy in European
countries, which have high hopes for it in the long
term. The role of renewable energy sources in solving
244
Musostov, Z., Berkaeva, A. and Basnukaev, I.
New Technologies in Production.
DOI: 10.5220/0011569300003524
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Methods, Models, Technologies for Sustainable Development (MMTGE 2022) - Agroclimatic Projects and Carbon Neutrality, pages
244-247
ISBN: 978-989-758-608-8
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
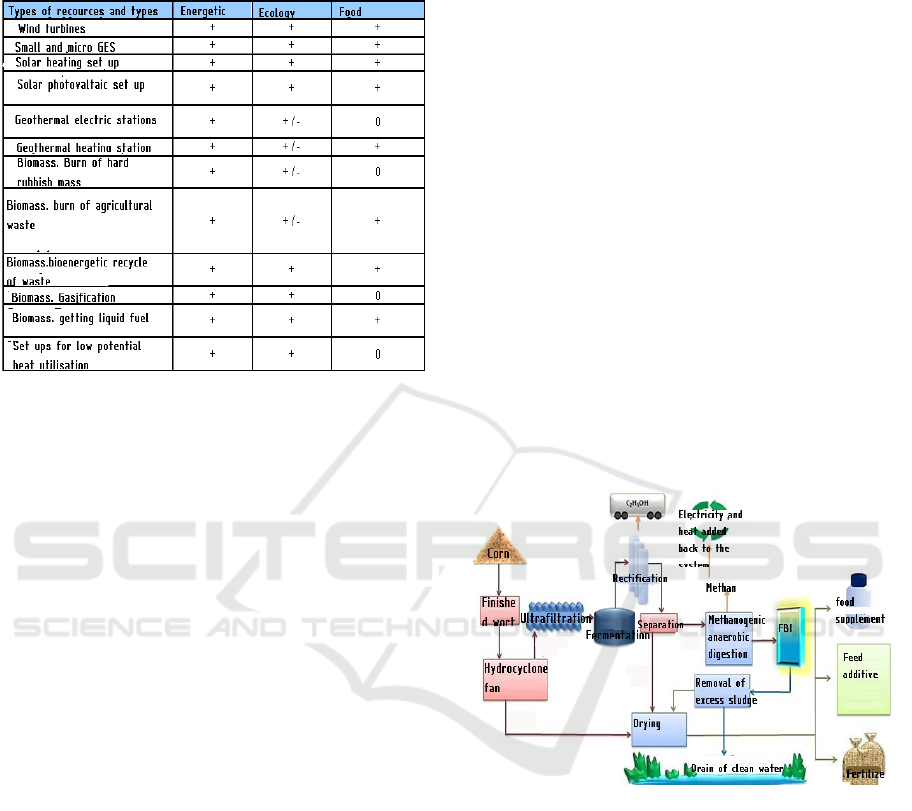
global civilizational problems is clearly presented in
Figure 1.
Figure 1: The role of renewable energy sources in solving
global problems (*Note. + positive impact, – negative
impact, 0 no impact.).
Obviously, renewable energy sources are
essential for the energy system that feeds the most
significant industries. Renewable sources also have
the advantage of being located close to energy supply
facilities, unlike traditional fuel and energy systems,
in which high costs are required to deliver energy to
enterprises. Further development of renewable
sources will improve the supply of remote regions,
reduce the intensity of traffic flows and ensure the
uniform development of production in the country.
Some of the renewable energy sources contain
components from which it is possible to obtain not
only energy products, but also elements used in the
chemical industry, metallurgy, road construction and
agriculture. These elements include oil shale, thermal
waters and bituminous rocks, which contain nickel,
lithium, sulfur, vanadium and other elements in
sufficient quantities (Vladimirov, 2020).
Another direction for the introduction of "green"
technologies in production activities is the
manufacture of non-toxic products that can be used in
a closed cycle: "production - disposal - new
production" (Kalner, 2018). An example of the
implementation of "green" technologies is the use of
only recyclable types of plastic in the production, as
well as the development and implementation of its
biodegradable counterparts.
Waste-free and low-waste production
technologies are also widely used. For example, in the
metallurgical industry, the problem of the formation
of solid, liquid and gaseous wastes is solved by
melting the metal in a liquid bath, which ensures the
preservation of solid and liquid emissions. Sulfur-
containing gases accumulate in a special tank and are
subsequently used to produce sulfur and sulfuric acid.
Powder metallurgy is recognized as a practically
waste-free technology, in which the utilization rate of
the feedstock reaches 99%. The wood processing
technology is actually waste-free, since the waste left
after the formation of furniture panels and lumber is
used for the industrial production of chips, sawdust,
pellets and fuel briquettes.
The introduction of "green" technologies in the
chemical and oil refining industries is based on the
active use of membranes for the separation of liquids
and gases, the production of biogas from organic
residues, the use of plasma, ultraviolet radiation and
electric pulse intensity to transform waste into useful
substances. In the mechanical engineering industry,
environmental developments should be directed to
the development of water recycling processes in order
to minimize their use and pollution. An example of
waste-free production technology is shown in figure
2 (Molchanova, 2019).
Figure 2: An example of a waste-free technology for the
production of ethyl alcohol.
The use of "green" technologies in production not
only improves the environment, but also reduces
costs, improves the efficiency of technological
processes, and ensures high competitiveness of
manufactured products. This causes significant
interest in such technologies not only from developed
countries, but also from rapidly developing
economies, such as China.
At present, there are about 2,000 research centers
and state-owned business incubators in China,
designed to ensure the development of
environmentally friendly technologies. At present,
China ranks among the top countries in the world in
New Technologies in Production
245

the number of patents in the field of wind power,
biofuel production and the sustainable use of coal.
Small businesses are of particular importance in the
implementation of scientific research and the
development of "green" technologies in production.
Small innovative enterprises (SIEs) are companies
that meet the national criteria for classifying small
businesses and specialize in the development and
implementation of science-intensive "green"
technologies, high-tech and innovative products.
2 MAIN BODY
In developed countries (EU countries, Japan, New
Zealand, Republic of Korea), the share of spending
on research and development in the field of "green"
technologies reaches 10-15% of the total state budget.
The most active developments are carried out in the
production of innovative biofuels, as well as in
technologies of high-temperature superconductors
and smart grids (Egorova, 2020). A significant
direction in the development of "green" technologies
is the fight against pollution. Thus, in Australia they
are actively working on technologies for purifying
water resources, in Germany all attention is focused
on air pollution, in Brazil, India and China,
technologies for the effective management of
municipal solid waste are of particular importance.
The most significant global environmental problems
include climate change, deterioration of fresh water
quality and reduction of biodiversity. It can be
assumed that the further development of "green"
technologies will be aimed at solving these problems.
Today, the most promising areas for the development
of "green" technologies are increasing the efficiency
and environmental friendliness of vehicles,
improving building materials, reducing the size of
gadgets while increasing their functionality, and
developing nanotechnologies and biotechnologies
aimed at cleaning the environment from pollution.
In the Russian Federation, "green technologies"
have an extremely low development, the total number
of Russian patents in this area is less than one percent.
The introduction of environmentally friendly
technologies could improve the situation with
environmental pollution, saving resources, increasing
efficiency in certain production areas. All these
factors are of great importance for our country.
A serious problem in the implementation of
"green technologies" is the development of a strategy
for its application and the organization of the
application of new processes. The transition to green
technologies requires a significant initial investment,
and research shows that this transition later provides
an increase in natural capital and, in general,
increases the level of GDP.
The approach to the use of "green technologies"
primarily depends on the policy of the state and the
ratio of costs for traditional and environmentally
friendly processes. A constraining factor in the
development of this area is the high cost of electric
vehicles, whose share in the automotive market in
Western Europe is no more than one percent.
Also, the spread of "green technologies" is
constrained by weak regulation by the state, a long
period of development and organization of the
process, the need to reorganize the energy and
transport infrastructure, the lack of qualified
specialists and management, and the unpreparedness
of business for fundamental changes in the approach
to technological processes. Despite these difficulties,
in many advanced countries the state builds its policy
taking into account the widespread use of "green
technologies" and takes measures aimed at shaping
environmental consciousness among citizens (Shilov,
2020).
So, at present, Russia has adopted and is
implementing the national project "Ecology" - one of
the 14 national projects operating in Russia for the
period from 2019 to 2024. This project was adopted
in pursuance of the Decree of the President of the
Russian Federation "On the national goals and
strategic objectives of the development of the Russian
Federation for the period up to 2024". The national
project "Ecology" includes 11 federal projects. The
structure of the national project "Ecology" is shown
in figure 3 (Murtazova, 2021).
Figure 3: The structure of the national project "Ecology".
MMTGE 2022 - I International Conference "Methods, models, technologies for sustainable development: agroclimatic projects and carbon
neutrality", Kadyrov Chechen State University Chechen Republic, Grozny, st. Sher
246

Thus, the national environmental development
project is being implemented in five areas: "Waste",
"Water", "Air", "Biodiversity", "Technologies".
The national project "Ecology" has six main
goals:
⎯ efficient management of production and
consumption waste, including the elimination
of all identified unauthorized dumps within the
boundaries of cities;
⎯ reduction of atmospheric air pollution in large
industrial centers;
⎯ improving the quality of drinking water for the
population;
⎯ environmental rehabilitation of water bodies,
including the Volga River, and the preservation
of unique water systems, including lakes Baikal
and Teletskoye;
⎯ conservation of biological diversity, including
through the creation of at least 24 new specially
protected natural areas;
⎯ ensuring the balance of disposal and
reproduction of forests in the ratio of 100%
(Gakaev, 2020).
The total funding is 4,041,000,000,000 rubles. Of
these, about 700 billion rubles are expected to be
attracted from the federal budget, 133 billion rubles
from regional budgets and the rest from
extrabudgetary sources. More than half of these funds
are expected to be used to finance the federal project
"Introduction of the best available technologies"
(Souter, 2019).
The second project in terms of funding is the
Clean Air project, the third is a project related to
improving the municipal waste management system.
3 CONCLUSION
The implementation of the national project "Ecology"
is closely connected with the development of "green"
technologies in Russia. The development of such
technologies has significant prospects: the country is
actively developing nuclear power, nano- and
biotechnologies, the production of laser equipment,
and information technologies. The growth of
investments in environmental innovations, the
creation of sustainable development institutions, and
the support of the innovation infrastructure in general
contribute to the introduction of "green" technologies
in Russian production.
During the coronavirus pandemic, technologies
related to air disinfection and biological safety were
noted among the new trends. Green technologies have
been extremely successful in the construction
industry. Thus, as part of the implementation of the
Skolkovo project, an exclusively “green” building
planning and design code is being implemented, the
LEED Silver level (that is, a certificate of leadership
in energy and environmental design) is mandatory for
all industrial and technological facilities being built.
Lakhta Center in St. Petersburg is also a modern
LEED-certified skyscraper. All the newest and
reconstructed MEGA-IKEA facilities comply with
the BREEAM environmental standard. Residential
quarter "European" in the city of Tyumen was
awarded the highest rating "excellent" according to
the BREEAM standard (RBC).
Gradually, environmentally friendly technologies
are being introduced in all sectors of the Russian
industry, however, for a full-fledged "green
transition" can only be implemented under conditions
of comprehensive interaction between the state and
business.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The article is written as part of the RFFI grant 20-310-
90063.
REFERENCES
Kalner, V. D., Polozov, V. A., 2019. Green economy and
non-alternative natural resources. p. 22.
RBC. The pandemic set new trends in green building: what
developers are implementing.
https://realty.rbc.ru/news/5fd3194a9a7947115ccf9d7a.
Shilov, I. A., 2020. Ecology. Yurayt. p. 78.
Murtazova, K. M.-S., 2021. Ecological and economic
assessment of sectoral agricultural technologies. 3(15).
pp. 68-71.
Gakaev, R. A., Bayrakov, I. A., Bagasheva, M. I., 2020.
Ecological foundations of the optimal structure of forest
landscapes in the Chechen Republic. Environmental
problems. Looking into the future. pp. 50-52.
Vladimirov, A. M., Imanov, F. A., 2019. Principles for
assessing the ecological flow of rivers. pp. 225-229
Molchanova, Ya. P., 2019. Hydrochemical indicators of the
state of the environment, p. 192.
Egorova, N. I., Mityakova, O. I., 2020. Environmental
Innovation and Sustainable Development. pp. 209-215.
Souter, MacLean, Okoh and Creech, 2019. ICTs. Internet
and Sustainable Development: Towards a new
paradigm. IISD, Winnipeg, Manitoba Canada.
New Technologies in Production
247
