
Analysis of Restaurant Tax Revenue in Medan City During Covid-19
Pandemic
Faisal Eriza and Afri Rizki Lubis
Program Study of Development Study, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Dr. A. Sofiyan no 01, Padang Bulan, Medan,
Indonesia
Keywords: Tax, Reveue, Restaurant, Covid-19, Pandemic.
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to determine the effects of the covid pandemic on restaurant tax revenue in
Medan. The method used is qualitative descriptive research for this study sought to describe a social
phenomenon that is describing the fact. This study uses primary data and secondary data relating to restaurant
tax revenue in Medan before and after the covid pandemic. Data collection techniques used in this research
include observation, documentation, and interviews. The result of this study indicates that the covid pandemic
affects a decline in restaurant tax revenue caused by decreases in restaurants income, due to business operation
hour restrictions and time rules for dine-in visitor regulations. Owing to a decline in restaurant tax revenue
and people’s weak purchasing power causes numerous restaurants permanently closed. The realisation of
restaurant Tax Revenue of 2020-2021 targets set by Taxes & Levies Management Board of Urban Terrain
doesn’t reach their target. Whereas in 2015-2019 the realisation consistently exceeds the targets.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tax is an essential thing in the journey of a nation.
Almost all countries in this world apply the rules or
scheme about tax imposition directly or indirectly. No
exception in Indonesia itself. Tax is the one of the
biggest income sector for Indonesia. The tax revenue
fund is allocated by government to fulfill the country
needs in general and to reach the society’s welfare
and prosperity. The more people pay taxes, the more
facilities and infrastructure are built (Pandiangan,
2008: 5). One kind of tax is Local Tax. Therefore,
Local Tax is prioritized because able to become the
one of region financial source to improve the
distribution and development of society’s welfare in
that region. The local tax capability that owned by
each region is an indicator of the local government
readiness in regional autonomy. Hence, something
that obtained from local tax are directed to increase
Locally Generated Revenue (LGR) or also known as
Original Local Government Revenue, so that region
autonomy can be well-executed, therefore to increase
the LGR, it also needed the contribution from many
sectors, one of them is from food industrial sector.
Food industrial or also known as restaurant is the
incredible sector. Restaurant industry is fulfilled by
potential, prospect, and growing fast along with the
times. Restaurant tax that managed by Taxes &
Levies Management Board of Urban Terrain
(BPPRD) of Medan City is one of the Local Tax that
contribute towards good impact to increase LGR
because more restaurants in Medan City.
However, in the beginning of March 2020,
Indonesia was started the against the Covid-19 virus
that enter to Indonesia. Certainly, when the first time
Corona Virus in Indonesia, it gives the impact
indirectly for Indonesian state especially in economic
aspect. The implementation of Large- scale social
restrictions (PSBB) rule by government had give the
large impact especially on the decline for society’s
economic activity especially in food industries. And
for the tax income data in Medan city itself also
decreased and did not reach the target in pandemic
era, and here are some of data on Medan city at the
time before and while the pandemic occurred.
Eriza, F. and Lubis, A.
Analysis of Restaurant Tax Revenue in Medan City During Covid-19 Pandemic.
DOI: 10.5220/0011541100003460
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Social and Political Development (ICOSOP 2022) - Human Security and Agile Government, pages 117-121
ISBN: 978-989-758-618-7; ISSN: 2975-8300
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
117
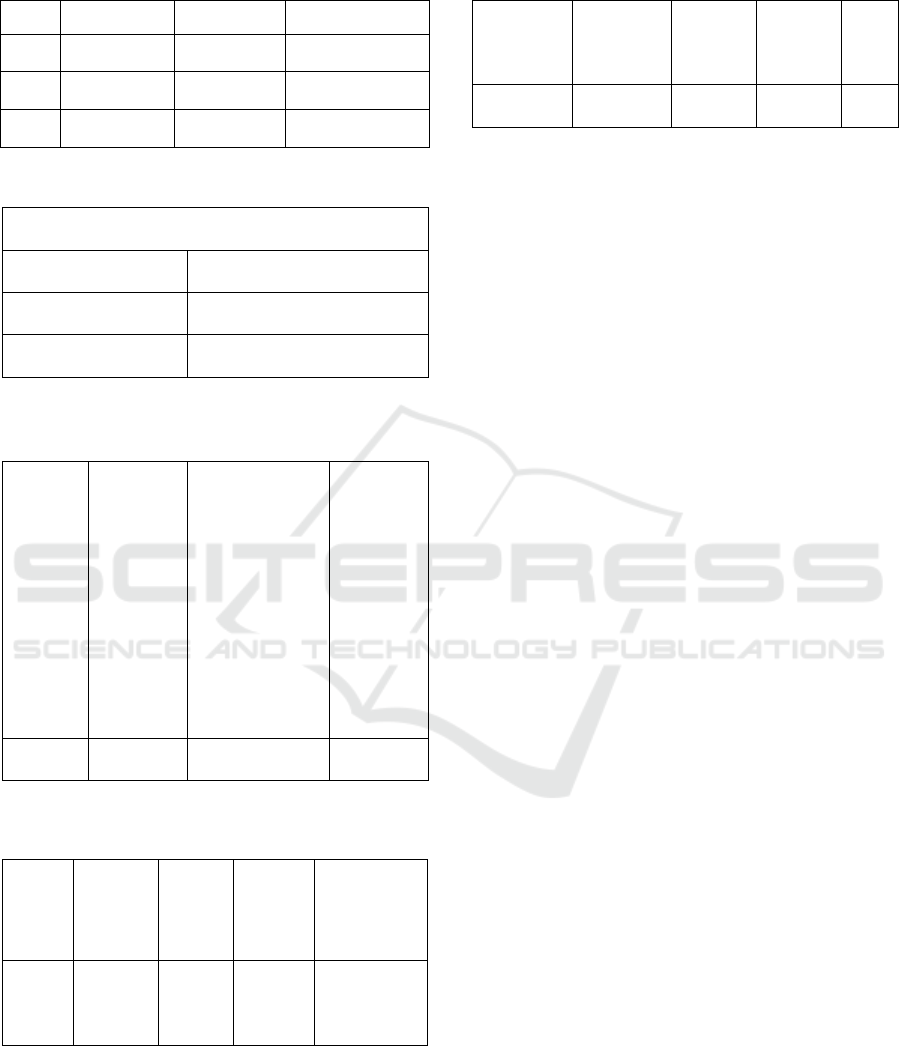
Table 1: Details of realization of medan city restaurant tax
in 2018-2020.
2018 2019 2020
Total 172.788.503.063
,71
209.883.937.063
,74
180.477.531.250,00
Target 170.000.000.000
,00
204.000.000.000
,00
180.000.000.000,00
Perce
ntage
101,64% 102,88% 76,93%
Table 2: Target and Realization of Tax.
Restaurant in 2021.
Table 3: Target Refocusing on Restaurant Tax.
Table 4: Reputation of Restaurant Taxpayer as of July 31,
2020.
Types
of
taxes
Active
taxpaye-r
Inactive
taxpayer
Incidental
taxpayer
Total
Restau
-rant
1629 697 557 2883
Table 5: Recapitulation of Restaurant Taxpayer as of July
31, 2020.
Types of
taxes
Active
taxpayer
Inactive
taxpayer
Incidental
taxpayer
Total
Restaurant 1894 697 559 3150
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Tax
Tax is public's dues to the State treasury based on the
law (which can be enforced) by not receiving
reciprocal services (counter-achievements), which
can be shown directly and used to pay general
expenses (Djojohardikusuma, 2006:1).
2.1.1 Regional Tax
Regional Tax is a mandatory contribution to the
region owed by an individual or entity that is coercive
under the law without receiving direct compensation
and is used for regional purposes for the greatest
prosperity of the people. Examples: Vehicle Tax,
Vehicle Transfer Fee, Surface Water Tax, Cigarette
Tax, Hotel Tax, Restaurant Tax, Entertainment Tax,
Advertising Tax, Street Lighting Tax, etc.
2.1.2 Restaurant Tax
Restaurant Tax is a tax on services provided by
restaurants, while restaurant is a facility providing
food and beverages with a fee, which also includes
restaurants, cafeterias, canteens, stalls, bars, and the
like, including catering / catering services (Marihot
Pahala Siahaan, 2010:15).
2.1.3 Restaurant Tax Subject and Taxpayer
According to Marihot Pahala (2010: 330), those who
are subject to the restaurant tax are individuals or
entities who buy food and or drinks from restaurants.
In simple terms, the tax subjects are consumers who
buy food and drinks in restaurants. Meanwhile, the
taxpayer is an individual or entity operating a
restaurant, namely an individual or entity in any form
within the company or work environment conducting
business in restaurant or dining sector.
Target for
restaurant
tax before
the end of
2020
Initial target of
restaurant tax at
the beginning of
p
andemic
(secondquarter of
2020)
Intial target
of
restaurant
tax at the
beginning
of
p
andemic
(secondqua
rter 0f
2020)
Restaurant 245.000.000.0
00,00
171.500.000.000,00 180.000.000.0
00,00
In 2021, as of May 31, 2021
Target 250.859.144.759,00
Realization 65.559.352.384,00
Percentage 26,13%
ICOSOP 2022 - International Conference on Social and Political Development 4
118

2.1.4 Restaurant Tax Collection Method
According to Tax Law article 8 (1) of the restaurant
tax imposition base is the amount of received
payment or properly received for restaurant. The
collection of restaurant tax can not be bought by the
entire stock that means the entire process of restaurant
tax collection activity are can not be handed over to
third parties. However, there is the probability of
cooperation with third parties in tax collection
process, such as the tax form printing, the delivery of
letters to taxpayer, or the collecting data of tax object
and tax subject. Some activities that can not be
collaborated with third parties are the activity of the
calculation of amount owed tax, the control of tax
deposition, and collecting taxes.
3 METHODS
This type of research used in this study is qualitative
by conducting data studies in descriptive or
descriptive form. This method of research attempts to
describe and interpret the objects in accordance with
reality. The descriptive method is implemented
because the data analysis is presented descriptively.
The study was conducted in Taxes & Levies
Management Board of Urban Terrain Medan. Medan
City Taxes & Levies Management Board of Urban
Terrain was selected as the research setting by
considering their tasked, collecting regional taxes on
provincial taxes, which include restaurant taxes.
To obtain the representative data, the key
informant and the main informant are necessarily
needed who comprehend and related to the problem
being studied as well as the additional informant who
can provide the information even though not directly
involved in studied social interactions.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Taxes & Levies Management Board
of Urban Terrain’s Profile
(BPPRD)
Before regarded as the Taxes & Levies Management
Board of Urban Terrain (BPPRD), it was known as
the Regional Revenue Service (DISPENDA). In the
beginning, DISPENDA of Medan City was the sub-
section of finance division that managed the revenue
and regional income. In this subsection, there are no
more sub-sections, because at this time, there were no
many taxpayers or levies that domiciled in Medan
City. With consideration of development and the rate
of population growth in Medan city, towards the
Regional Regulation, the financial sub-section was
changed into the revenue section. In the income
section, several sub-sections manage the tax revenue
and regional levies that are the obligations for
taxpayers or levies in Medan city area, which involve
21 sub-districts such as Medan city, Medan Area,
Medan Maimun, Medan Polonia, Medan Denai,
Medan Baru, Medan Amplas, Medan Barat, Medan
Johor, Medan Selayang, Medan Sunggal, etc.
4.2 Description of Main Duties and
Functions of Taxes & Levies
Management Board of Urban
Terrain (BPPRD)
The following are the forms of strategies or efforts
carried out by the One-Stop Integrated Investment
and Licensing Service Office Province North
Sumatra to increase investment in North Sumatra
Province based on the indicators:
According to the decision of the Mayor Medan
city, Number 27 Year 2017 about Main Duties and
Functions of Taxes & Levies Management Board of
Urban Terrain (BPPRD) of Medan city, towards this
decision what is meant by
1. The region is Medan city.
2. Regional Government is the administration of
government affairs by regional government and
Regional Houses of Representatives according
to the principle of autonomy and assistance
tasks with the principle of autonomy as wide as
possible in the system and principle of Unitary
State of the Republic of Indonesia (NKRI) as
referred to the 1945 Constitution of the Republic
of Indonesia.
3. Regional Government is the Mayoralty as the
administration element of Regional
Government that lead the implementation of the
Government affairs also the authority of
autonomous region.
4. The mayor is Mayor of Medan city.
5. Regional Secretary is the Regional Secretary of
Medan city.
6. Agency is the Taxes & Levies Management
Board of Urban Terrain (BPPRD) of Medan
city.
7. The Head of the Agency is the Head of the
Taxes & Levies Management Board of Urban
Terrain (BPPRD) of Medan city.
Analysis of Restaurant Tax Revenue in Medan City During Covid-19 Pandemic
119

8. Secretary is the Secretary of the Taxes & Levies
Management Board of Urban Terrain (BPPRD)
of Medan city.
9. State Civil Apparatus, herein after abbreviated
as ASN employees is the profession for the Civil
Servant and the government staff with work
agreements working for government agencies.
10. State Civil Apparatus Employees, herein after
abbreviated as ASN is the profession for the
Civil Servant and the government staff with
work agreements by the service supervisor and
assigned tasks in government position or
entrusted with other state duties and paid
according to the laws and regulations.
11. Civil Servant, herein after abbreviated as PNS
are Indonesian citizens who fulfill certain
requirements, are appointed as the ASN
employees on a permanent basis by staffing
officials to occupy government positions.
12. Government Affairs is the power of government
as the President obligation which its
implementation managed by the state ministry
and Regional Government administrators to
protect, serve, empower, and prosper the
community.
13. Regional Apparatus Work Unit, herein
abbreviated as SKPD is the regional apparatus
in the regional government as the budget or
goods user.
14. Regional Apparatus is the supporting element of
Mayor and DPRD in the administration of
government affairs as the region authority.
4.3 Data Presentation
In obtaining the necessary data to answer the research
problem, there are some steps that carried out by the
author, involve: First, the research begins with the
collection of various written documents. Second, the
author conducts the interview with some selected
informants to obtain the information with
comprehensive facts regarding to the problem
research. Informants in this research were four
peoples as the employees or staff in the Taxes &
Levies Management Board of Urban Terrain
(BPPRD) of Medan city.
The type of interview that chosen by the author is
systematic interview type, where before the interview
is starting, the first step is the author compiles the
asked questions list. The compiled questions clearly
related with the Effect of Pandemic Covid-19 Virus
on Restaurant Tax revenues in Medan city. However,
within the process itself, the author does not rule out
the emergence of new questions that can learn in-
depth the information from the informant.
In this interview, there are some question which
asked to the informants about the problem of
Pandemic Impact of Covid-19 towards Restaurant
Tax revenues in Medan city. The author only sorts
some informant as the main informants according to
their relevant field and position with the result that the
entire raised problems in this research could be
answered.
According to the research and observation results
that was conducted by the author, can be concluded
that: The impacts that occur because of pandemic
virus towards Restaurant Tax revenues in Medan city
is decrease because decreased restaurant’s income
and the restriction of visitors amount that cause the
absence of consumers at certain hours and the
decrease of consumers amount. Taxes & Levies
Management Board of Urban Terrain (BPPRD) of
Medan city has the annual tax target with different
nominal in every year. However, during the pandemic
Covid-19 era, Taxes & Levies Management Board of
Urban Terrain (BPPRD) of Medan city provide the
dispensation for restaurant because the decline of
public consumption so that causes many restaurants
are permanently close. Taxes & Levies Management
Board of Urban Terrain (BPPRD) of Medan city
provide the dispensation for many restaurants that
affected by pandemic era such as the tax delays for
several months.
From 2015-2019, the number of realizations
always exceeds the biggest target, especially in 2019.
From the year before pandemic era, taxpayers always
increase and during the pandemic era in 2021,
taxpayers continued to increase than 2020. There is
no difference in calculation of tax payment in
restaurant and Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises
(UMKM). The criteria of restaurant and UMKM that
must be taxed are if that restaurant has gross income
of IDR 9,000,000 each month. However, there is no
specific policy for UMKM to pay the tax before
pandemic era.
REFERENCES
Adityo Susilo, C. d. Maret 2020. Coronavirus Disease
2019: Tinjauan Literatur Terkini. Jurnal Penyakit
Dalam Indonesia Vol. 7 No. 1.
Edward, W. M. 2013. Efektivitas dan Kontribusi
Penerimaan Pajak Hotel dan Pajak Restoran Terhadap
Pendapatan Asli Daerah Kota Manado. E-Journal Vol.
1 No. 3: 871-881.
Handayani, R. T. 2020. Jurnal Ilmiah Permas: Jurnal
Ilmiah STIKES Kendal Vol. 10 No. 3, hal 373 - 380.
ICOSOP 2022 - International Conference on Social and Political Development 4
120

Ilyas, W. B. 2013. Hukum Pajak. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Nugraha, L. d. 2004. Analisis Efektivitas Pajak Hotel dan
Pajak Restoran dan Kontribusinya Terhadap
Pendapatan Asli Daerah diKota Bandung. Jurnal
Umum Administrasi Vol. 4: 1-10.
Salamah, B. &. 2020. Pengaruh Pandemi Covid Terhadap
Penerimaan Pajak di Negara Indonesia Pada Tahun
2020. Vol. 1, No. 2, hal 277-289.
Siregar, N. Y. 2021. Dampak Covid-19 Terhadap
Penerimaan Pajak Negara Pada Sektor UMKM di
Indonesia. Jurnal STIE IBMI Medan Vol. 3 No. 1.
Yusriani, d. 2020. Masa-Masa Covid 19 Mengenal dan
Penanganan dari Bebagai Perspektif Kesehatan.
Analysis of Restaurant Tax Revenue in Medan City During Covid-19 Pandemic
121
