
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists
and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New
Educational Paradigm
Olha Chyzhykova
1a
, Oksana Romanenko
1b
, Larysa Dzevytska
2c
and Olena Zotova-Sadylo
2d
1
Department of Foreign and Business Ukrainian Language, State University of Economics and Technology, 16, Medychna
Str., Kryvyi Rih, Ukraine
2
Department of Foreign Languages, Donetsk State University of Internal Affairs, 89, A. Lunin Ave., Mariupol, Ukraine
Keywords: Polycultural Competence, Multicultural Society, Foreign Languages Learning, New Educational Paradigm.
Abstract: The urgency of the problem of the formation of polycultural competence in Ukrainian higher educational
establishments is due primarily to the requirements of modern multicultural society according to higher
education system reforming. The given research is devoted to the problem of polycultural competence and its
paramount importance for future economists and lawyers as members of multicultural environment. The
works by Ukrainian and European scientists on above-mentioned issues are analyzed, the main directions of
covering the problem of polycultural competence are revealed. The components of polycultural competence
are described. The study of pluricultural competence development in distance learning of foreign languages
is given. In order to investigate the state of the problem researched the survey was conducted among the
lecturers and students of three higher educational non-linguistic universities. The authors came to the
conclusion that polycultural competence formation should be held by means of foreign languages learning.
Prerequisites for successful polycultural competence formation in future economists and lawyers by means
of foreign languages learning are found. The emphasis is placed on the importance of cultural background for
new generation of learners; the significance of using cross-cultural communication for professional purposes
is outlined. The ways of polycultural competence formation are described.
1 INTRODUCTION
Under the influence of numerous global social and
political as well as economic changes the great
interest to the culture of other peoples as a
determining condition for the realization of the
creative potential of the individual and the society as
a whole arose. Moreover, the forms of asserting the
identity of the nation and the foundation of the
nation's spiritual health, political and cultural
contacts, are being developed today in the terms of
specific cultural integration and political context. All
these factors have contributed to the development of
a new paradigm in education. Thus, the realities of
modern environment together with the new
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4432-9743
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5129-9135
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9093-7635
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9474-016X
requirements for future specialists’ training in higher
educational establishments demand a careful reset of
the aims, tasks and objectives of higher education, its
subordination to present-day norms and rules of the
existence of future citizens.
This study is particularly relevant in terms of the
new educational paradigm, the basic foundations of
which were formulated in the end of the 20th century
(Johnson et al., 1998). From the old educational
model, we moved to an absolutely new one,
according to which students build, develop and
transform the acquired knowledge, skills and abilities
independently, under the guidance of teachers. It is
difficult to deny the fact that the conditions of online
education have forced students to change completely
their attitude to education. Under these circumstances
468
Chyzhykova, O., Romanenko, O., Dzevytska, L. and Zotova-Sadylo, O.
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New Educational Paradigm.
DOI: 10.5220/0011365800003350
In Proceedings of the 5th International Scientific Congress Society of Ambient Intelligence (ISC SAI 2022) - Sustainable Development and Global Climate Change, pages 468-477
ISBN: 978-989-758-600-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

they began to acquire knowledge with even greater
desire, seeking and finding the most useful facts in the
great amount of information to which they have a free
and easy access today.
It should be noted that a new paradigm in
education is based on such principles of learning as:
learning, acquiring, transforming and expanding
knowledge independently, taking into account what
will be necessary for students in their further
activities, teachers making efforts to develop
students' competencies and talents; learning based on
strong cooperation of teachers and students in the
context of their common cooperative work, training
supported by the integrated application of theory and
research, which requires special teachers’ formation
and constant improvement of their teaching skills.
In a new educational paradigm modern generation
of learners should be well aware of the current laws
of life in a completely new, open and tolerant world,
in which communication and communication means
have taken their very important place in public life
and, accordingly, have created new laws and
regulations. The problem of intercultural
communication has recently become especially
important.
The specificity of intercultural interaction is
indisputably defined by external and internal factors
that are connected with the social, economic and legal
characteristics of any country and the conditions of its
polycultural environment. It is obvious that the
modern society should change the existing
stereotypes of intercultural interaction, and for this
purpose it is necessary to bring a targeted effort in the
field of modern education and specialists’ training. In
this regard, the system of higher education faces the
task of developing theoretical and methodological
principles and technologies of social and cultural
experience in order to develop the students’
intercultural interaction in a polycultural world.
In the frame of the globalization process, social
interaction has become an essential issue ensuring
interrelation of different cultures. The development of
polycultural competence that fosters intercultural
interaction provides intercultural dialogue between
members of diverse cultures. Polycultural
competence determines the ability of a person to
navigate in a multicultural society in various spheres
of social and professional life. It also determines a
complex of knowledge, affect and skills such as
language proficiency, knowledge of a specific
culture, intercultural experience and personal traits
including conscientiousness, extraversion, emotional
stability and emotional regulation, flexibility and self-
monitoring (Abbe, Gulick and Herman, 2007).
Moreover, in recent publications it is stated that
foreign language pedagogy should follow a global
approach thus linking its discourse with social
changes. In other words, this approach underlines the
necessity to respect and accept the Other, paying
special attention to positive polycultural values
(Awayed-Bishara, 2018). Thus, in the frame of our
research we will try to investigate the resent
publications on cross-cultural competence, define its
components, structure, and polyculural values in
terms of foreign language study of future economists
and lawyers; develop and implement innovative
teaching methods to ensure intercultural effectiveness
by means of foreign languages learning.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Analysis of Recent Studies and
Publications
The investigated phenomenon has been studied by
modern foreign and domestic researchers. Cultural
dialogue has received a wide reflection in scientific
essays of the 20th century. The most common
interpretation of the dialogue of cultures presents this
phenomenon as a process of interaction and influence
of different historical or modern cultures and certain
forms of their coexistence. With such interaction, the
phenomenon of cultural dialogue, cultural
cooperation and cultural mutual reflection is formed.
Consequently, a positive cultural dialogue is possible
under a number of conditions: equality of all cultures,
recognition of the right of each culture to be different
from others, respect for a foreign culture. M. Bakhtin
understood culture in three aspects: 1. as a form of
communication between people of different cultures
and a form of dialogue; 2. as a mechanism of self-
determination of personality, with its inherent
historicity and sociality; 3. as a form of acquisition,
perception of the world for the first time (Paksina,
2015).
Recognizing the urgency of the above-mentioned
phenomenon, the Ukrainian scientists have touched
on the problem of polycultural competence and the
related issues in their recent studies. Thus, the
formation, structure and essential characteristics of
polycultural competence have been explored by T.
Poyasok and O. Bespartochna (2019), V.
Romashenko (2017), N. Zamotaieva (2017) and
others.
The essence, structure and main aspects of
polycultural competence have been the subject of
research of such scientists as V. E. Benera and V.
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New
Educational Paradigm
469

Kashubskyi (2020). V. Olishevych (2019) researched
pedagogical technologies of the development of
future foreign language teachers’ polycultural
competence; F. Grin and K. Faniko (2012) studied
personal characteristics which provide success in a
polycultural society and ensure multicultural
effectiveness; L. Mukharlyamova and N. Konopleva
(2018) devoted their survey to the structure of
intercultural communicative competence while
learning foreign languages, paying special attention
to the linguistic and communicative components.
Peculiarities of multicultural environment, the
dialogue of cultures, cooperation and tolerant attitude
towards the other peoples have been explored by P.
Kendzor (2016).
In spite of numerous researches on polycultural
competence, its formation and structure, the problem
of forming polycultural competence in future
economists and lawyers in foreign languages learning
has not been studied properly yet. Therefore, at
present, there is an objective necessity to deepen and
supplement the methodological approaches to the
study of such phenomena of modern society as
polycultural education and polycultural competence.
The aim of the given research is to study theoretical
aspects of polycultural competence formation of
future economists and lawyers in foreign languages
learning, define the level of formation of the concept
of polycultural competence and polycultural
education among foreign language teachers and
students of economic and law specialties and reveal
the prerequisites and teaching methods of
polycultural competence formation by means of
foreign languages learning.
These processes should be conducted taking into
consideration the modern realities of the globalized
world and national identity. Therefore, the new vector
of pedagogical research of polycultural education in
the new paradigm of education provides, firstly, its
study in the context of modern information society;
secondly, by identifying it as a factor and means of
positive human development and creative
development of an individual, thirdly, regarding
polycultural education as a methodological principle
of the formation of Ukrainian civic and patriotic
identity.
2.2 Main Material Exposition
In scientific researches polycultural competence is
defined as dynamic integrative characteristic of the
level of professionalism of the future specialist; as a
significant feature of the level of cultural education
and self-awareness of a person; multicultural identity,
which is manifested in the ability to constructively
interact with representatives of other cultural groups;
as a multicomponent individual personal skill that is
the result of multicultural education and is based on
theoretical knowledge and true representation of the
diversity of the world; as an ability that is realized
through skills and behaviors ensuring interaction with
representatives of certain cultures on the basis of a
positive attitude to them, as well as through the desire
for intercultural interaction; as an ability that
promotes effective interethnic cooperation in modern
society (Benera and Kashubskyi, 2020); as a part of
future specialists’ professional competence; as a
dynamic personal entity that can be formed and
developed (Olishevych, 2019).
Among personality characteristics that provide
multicultural effectiveness and success researchers
mention such abilities as: cultural empathy, ability to
be open-minded, emotional and social aspects, such
as initiative and linguistic flexibility (Grin and
Faniko, 2012); linguistic components (the usage of
linguistic means in accordance to the communicative
situation), communicative components (the ability to
understand knowledge and values, psychological
aspects and identity characteristics of the culture
which may include activity, relevance, dynamism)
and cultural component (cultural literacy); general
and linguistic culture, socio-cultural and professional
components (Mukharlyamova and Konopleva, 2018);
creative abilities, erudition, curiosity, inspiration and
problem-solving skills (Zamotaieva, 2017). A model
of successful participation in a diverse world
comprises 20 competences merged into 4 groups:
values, skills, attitudes and knowledge and critical
understanding. Among learners’ competences
essential for successful participation in a culture of
democracy and effective cooperation in diverse
democratic societies Council of Europe focuses on
such skills as empathy, plurilingualism, adaptability,
critical thinking and ability to resolve conflicts;
ability to value cultural diversity, respect and
tolerance of cultural otherness etc. are underlined as
important integral components of the model
(European Council, 2016).
Therefore, we can identify polycultural
competence of students of economic and law
specialties as a complex dynamic integrative personal
formation that comprises knowledge and practical
abilities to apply these skills in professional situations
ensuring interaction with members of diverse cultures
and providing intercultural dialogue in a polycultural
society.
The structure of the polycultural competence
comprises such components as cognitive (the system
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
470

of polycultural knowledge which is the basis for a
person’s activity in a polycultural society);
motivational (the system of motivational and value
aspects: external and internal motives, interests,
needs and values, polycultural characteristics that
govern daily life and activity of the individual in a
polycultural society), activity-based (polycultural
skills and abilities, social norms and rules of how to
behave in a polycultural society, positive experience
of intercommunion with members of other cultures);
and personality-oriented components (successful
self-realization in professional activity) (Benera and
Kashubskyi, 2020).
Taking into consideration the results of the
domestic and foreign researches we offer the
following componential structure of future
economists and lawyers’ polycultural competence:
cognitive component (a system of polycultural
knowledge that helps to solve professional economic
and juridical issues in a polycultural society),
motivational component (interests, needs,
motivations, values that stimulate the development of
polycultural competence of a professional), practical
component (polycultural skills and abilities,
sufficient expertise of future economists and lawyers
which are essential to work efficiently in a
polycultural society); result-assessing and reflexive
components (assessment and self-assessment of the
obtained results with further elaboration and
improvement).
Among the most effective means of the
development of future specialists’ polycultural
competence during foreign language training can be
mentioned the following ones: usage of authentic
materials in the form of printed texts, videos, web
quests, podcasts and other interactive materials that
combine motivational materials that encourage
students to intercultural interaction, as well as
materials for acquaintance and working out of speech
material presented in situations (Olishevych, 2019).
For the formation of intercultural competence, the
authors offer to use such creative methods as video
tutorials, project work, learning situations,
educational speech situations, and problematic
situations, presentations that develop writing skills
and enhance communicative skills. The usage of
audio and video materials for the perception,
understanding and further discussion facilitates
cognitive abilities and develops learners’
communicative skills (Mukharlyamova and
Konopleva, 2018).
In the context of remote education because of
pandemic we should take into account the current
state of educational process which is implemented in
the distant form. We analyze the prospects for the
improvement of this form of education and its impact
on students’ pluricultural competence development.
Taking into account the results of modern
researches on distance learning (Trajanovic, Domazet
and Misic-Ilic, 2021), (Kolyada, Shapovalova, Guz
and Melkonyan, 2021) we have singled out the
challenges of learners’ pluricultural competence
development in the context of distance learning of
foreign languages as follows:
1. students’ motivation for distance learning
(economic and law students should be more
organized, ready to overcome some problems
connected with the development of communication
skills arising in the process of remote learning);
2. usage of online technologies, computer
proficiency of both students and teachers;
3. implementations of technology-mediated
interactions and provision of high level of interaction
in e-learning environment;
4. provision of peer interaction in the virtual
context;
5. psychological aspects (overcoming the
feeling of being isolated, lack of face-to-face
communication).
3 RESEARCH METHODS
In the frame of our exploration we tried to check the
level of awareness of lecturers and students in this
issue, to find out their attitude to polycultural
education and polycultural competence, to outline the
main directions of formation of multicultural
competence of students, define the directions of the
development of modern foreign language education
in the terms of polycultural society as well as to
determine the attitude of teachers and students to the
phenomenon of polycultural society and tolerance as
a whole.
3.1 Participants of the Research
The participants of the experiment were lecturers and
students of State University of Economics and
Technology (Kryvyi Rih), Dnipro State Agrarian and
Economic University and Donetsk State University of
Internal Affairs. In our exploration we used such
methods as interview, questionnaire, and tests.
3.2 Purpose of the Research
In the context of the subordination of Ukrainian
higher educational standards and norms to common
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New
Educational Paradigm
471
European standards, it is extremely important to
determine the attitude of foreign language teachers to
such concepts as "polycultural education" and
"polycultural competence". Therefore, the tasks of
the survey were considered as follows:
• to provide a definition of "polycultural
competence" from the point of view of foreign
languages learning process and its participants
both students of economic and law specialties
and teachers;
• identify the values of the modern polycultural
environment seen by both lecturers and
students;
• reveal the bases for the preparation of new
generation of learners for the life in a
polycultural environment;
• research the influence of foreign languages
learning on the formation of students’
polycultural competence;
• determine the motivational and value criteria
for the formation of a certain level of
polycultural competence;
• define the basic foundations of cultural
training, provide the definition of "culture";
• identify the importance of cross-cultural
communication;
• identify the components of "cross-cultural
social intelligence";
• research in what ways foreign languages
learning provides the formation of polycultural
competence.
3.3 Data Collection and Analysis
Both lecturers and students were asked to choose one
or more of the five answers, or to provide their own
answer in case of the absence of a suitable one.
Besides, teachers were asked to choose from the
options given the best tasks and exercises aimed at
developing a certain level of polycultural education.
It should be noted that the survey arose interest
from teachers and students’ sides, as polycultural
education is not considered to be a separate subject in
the preparation of bachelors, respectively, the
formation of polycultural competence of students
takes place more in the process of learning foreign
languages. Thus, while teaching foreign languages to
future economists and lawyers we mean not only
language education, but also deepening knowledge of
general culture and, respectively, polycultural
education.
According to the survey, students of economics
consider polycultural education in terms of its
usefulness for their future professional activities, as a
means of professional communication and a solid
way of facilitating cross-cultural communication with
foreign partners. Adhering to the idea that university
education, especially the first four years of
preparation for the bachelor's degree, is aimed at
providing general cultural training and acquaintance
with purely professional subjects, both teachers and
students recognize the importance of cultural and
multicultural education.
It is necessary to ensure that students are generally
aware of the importance of forming a general culture
in higher education institutions, and most of them
understand well how important is foreign languages
learning for the development of general culture. It is
a generally accepted fact that the study of foreign
languages is a perfect way of learning European
cultural values, general cultural competence
formation and polycultural competence too and thus
easily and successfully integrating into the European
space.
Let us now consider the results of the
questionnaire for lecturers. The total number of
respondents was 62 teachers from 6 departments and
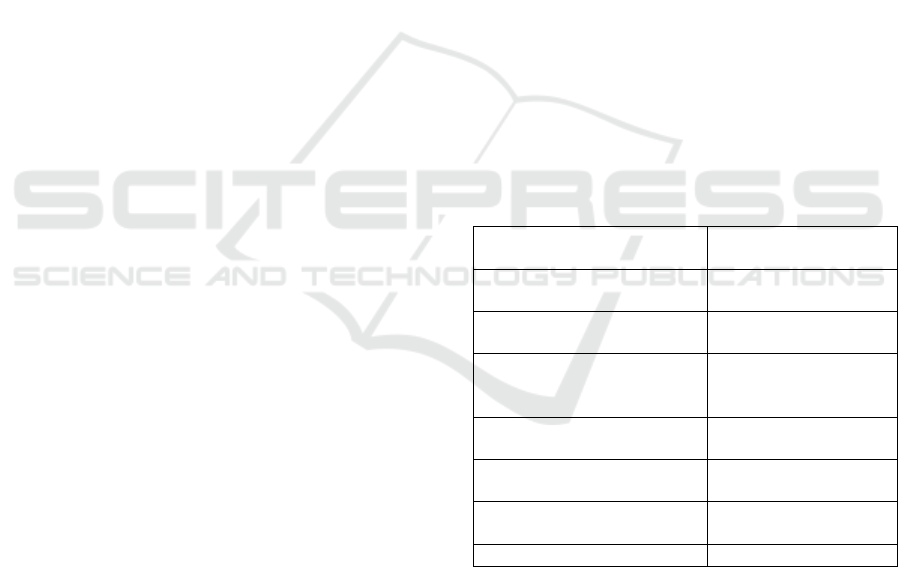
3 universities. The Table 1 below illustrates the
breakdown of lecturers and departments.
Table 1: Distribution of respondents (lecturers) by
departments.
Department Number of
respondents
Foreign Language
De
p
artment
12
Engineering Pedagogy
and Lan
g
ua
g
e Trainin
g
8
The Department of
Ukrainian Language
and Histor
y
11
The Department of
Philolo
gy
9
Department of
Information Technologies
10
Department of Finance,
Bankin
g
and Insurance
12
Total number 62
The first part of the questionnaire is aimed to find
out whether the lecturers are aware of the term
polycultural competence and its functional
peculiarities for teaching. The questions were: What
do you think polycultural competence is? And What
is the most significant element in polycultural
competence? The majority of those who responded to
this item reported that ability to make friends and
communicate in a friendly / sincere manner with
representatives of the different nations and cultures.
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
472
Only a small number of respondents 3% indicated
that they had not dealt with the term polycultural
competence. One of the reasons they mentioned was
lack of experience in communicating with people /
students of other cultures. Interestingly, 42 % of the
lecturers observed the important role and
effectiveness of culturally appropriate interaction or
cooperation in working environment, for example.
Most of technical professors appeared to
underestimate the role of foreign languages for the
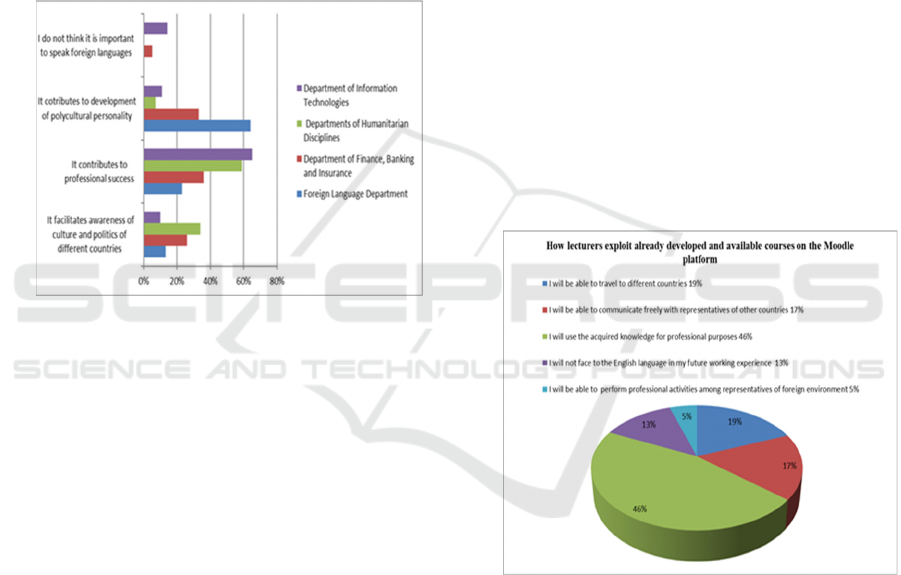
development of prospective specialists. Figure 1
compares the intercorrelations between professional
affiliation of the respondents and their awareness of
importance to speak foreign languages.
Figure 1: Foreign languages in the formation of
professional personality.
The single most striking observation to emerge
from the data comparison was that skills of speaking
foreign languages could be one of the fundamental
components of a prospective professional. From the
diagram, it can be seen that correlation between
educators who are conscious of the key role of foreign
languages (over 60%) and those who still do not pay
enough attention to polycultural education (8%) is
illustrative. We can presuppose that the reason is not
in lack of appropriate knowledge or necessary skills
but in a stubborn refusal to acknowledge progress and
globalization of labour market. To cope with present-
day conditions, namely limited number of academic
hours, the lecturers of foreign language departments
have to redesign and retail the standard programs of
the disciplines by adding special blocks/theme units
or develop the special courses which include the
elements for a full-fledged self-paced training on
polycultural skills of the students.
The majority of participants agreed with the
statement that fluency in one or more foreign
languages contributes to improvement the
polycultural competence (91%), in particular it
prepares the students to effective communication
within the chosen profession (59%) and allows us to
realize a person’s identity (25%), it facilitates our
incentives to be more tolerant in our relations with the
representatives of other nations and nationalities
(7%). The lecturers were required to choose three
options from offered and/or propose any others. The
most commonly chosen ones are represented above.
This once again emphasizes the pertinence of the
theme of our research.
Let us turn to the students’ survey. In total 134
students of Law, Law Enforcement Activity,
Economic and IT Faculties were interviewed. The
respondents noted the tend to get polycultural
knowledge at the university as a part of curriculum
because it is an important element of professional
success and an integral part of a concerned citizen
(61%). On the other hand, our respondents gave
priority to vocational and professional specific
knowledge (56%) and noted that polycultural
education could be an effective supplementary
component in future professional activity; 31%
respondents rate polycultural education first; 13%
suppose that polycultural education is not necessary
in our modern society.
Figure 2: Correlation between polycultural education,
learning of foreign languages and future professional
success.
We need to find out the correlation between polycultural
education, learning of foreign languages and future
professional success from the perspective of the students,
consequently they were offered the list of possible answers
and had to choose the most important ones. Some
interviewees argued that they would not face to the English
language in their future working experience (13%), while
others 87% were aware of English language proficiency.
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New
Educational Paradigm
473

4 RESULTS OF THE RESEARCH
The results of students’ interview have become really
meaningful to design the recommendations in terms
of polycultural education in the universities. It should
be noted that most of the respondents (72%) have
realized that they need much more practice to hone
foreign language skills and it will take time to become
skilled but at the same time 72% of those who were
interviewed indicated that they suffer from a lack of
practice in English.
Taken together, these results suggest that there is
a demand on polycultural education and students are
interested in improving the language proficiency, on
the one hand. On the other hand, there are not enough
courses which are narrowly focused on specifications
of polycultural competence.
Taking into account the results of the experiment
we have summarized special recommendations for
foreign language teachers and non-linguistic students
on polycultural competence formation of future
economists and lawyers: firstly, creation of a friendly
atmosphere at the foreign language lessons and while
performing extracurricular activities; secondly, it is
necessary to build a stable motivational basis for
foreign language learning and the development of the
polycultural competence components; thirdly, it is
useful to implement such types of activities as text-
based ones, problem-solving, task-based strategies,
innovative teaching methods and interactive
technologies (case studies, debates, simulations,
business games, problematic lectures); fourthly,
while distance learning it is useful to implement such
creative forms as project-based activities, video and
audio tutorials, problem-solving tasks, online
conferences; fifthly, providing necessary feedback,
and sixthly, ensuring assessment, self-assessment and
self-reflection.
5 CONCLUSIONS
According to the research made, we came to the
conclusion that polycultural competence can be
referred to the effective interaction in a particular
situation, taking into account cultural characteristics
and respecting customs and traditions of the
representatives of other cultures. The most important
prerequisites for living in a polycultural society as it
was found out are tolerance towards the
representatives of different cultures and the ability to
adapt to the multicultural society. The motivational
and value criteria for living in a polycultural
environment are considered to be the desire for cross-
cultural interaction and acceptance of other cultures’
values.
Therefore, cultural formation must be based on
people’s willingness to communicate in a
polycultural society. Considering this, one of the
problems in cross-cultural communication could be
misunderstanding between the representatives of
different cultures. So cross-cultural intelligence
which can be referred to the ability to interpret
correctly social interaction in the process of
intercultural communication must be a paramount
feature of new generation learners who will be in
nearest future the members of a polycultural society.
Mastering foreign languages without any doubt
effects the polycultural competence formation as
foreign languages learning aims to instill the
foundations of culture and civilization of the
countries the language being studied. Given the fact
that future economists and lawyers are more
interested in acquiring foreign languages knowledge
for better understanding their professional tasks and
using foreign languages for searching necessary
information and studying different new methods of
doing their jobs they it is hard to deny the usefulness
of polycultural competence to live and work in a
multicultural environment.
Based on the results of the experiment conducted
and on the long-term pedagogical experience in order
to form polycultural competence of future lawyers
and economists we suggest using text-based
activities, problem-solving, task-based strategies,
which ensure integration of polycultural context in
the content of the program material; integration of
classroom and extracurricular activities in the process
of formation and further development of future
economists and lawyers’ polycultural competence;
implementation of modern pedagogical technologies
and innovative teaching methods (case studies,
debates, simulations, business games, problematic
lectures) for mastering polycultural competence.
In the conditions of distance learning it is useful
to implement such creative forms and teaching
methods for the plurilingual competence
development of students of economic and law
specialties as project-based activities, video and audio
tutorials, problem-solving tasks, presentations and
educational communicative situations, participation
in online conferences. We believe that such types of
learners’ activities are not only appropriate and
suitable in case of distance learning, but also are
aimed to develop students’ collaborative learning
skills, creative abilities, flexibility, elaboration skills,
oral speech and writing skills, abilities to work with a
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
474

bulk of cultural and professionally oriented
information, socio-cultural skills etc.
The lecturers and students showed their interest
and attention towards the problem of polycultural
environment and admitted the importance of
polycultural education due to the fact of poilycultural
environment in which the graduates of higher
educational establishments will work in the nearest
future. The knowledge of foreign languages is
recognized as an important component for the
formation of cross-cultural social intelligence so
foreign languages learning must be aimed to the
certain level of polycultural competence formation.
Among the motivational and value criteria for the
formation of polycultural education the most
important one is the ability to use the acquired
knowledge for professional purposes.
REFERENCES
Johnson, D., Johnson, R., Holubec, E., 1998. Cooperation
in the classroom. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Awayed-Bishara, M., 2018. EFL discourse as cultural
practice. Journal of Multicultural Discourses, V. 13,
Issue 3, 243-258.
https://doi.org/10.1080/17447143.2017.1379528
Abbe, A., Gulick, L. Herman, J., 2007. Cross-Cultural
Competence in Army Leaders: A Conceptual and
Empirical Foundation. United States Army Research
Institute for the Behavioral and Social Sciences.
https://www.hsdl.org/?view&did=21358
Paksina, E., 2015. The concept of dialogue in the works of
M. Bakhtin and V. Bibler. Modern problems of science
and education, 1-2. https://science-
education.ru/ru/article/view?id=19949
Poyasok, T., Bespartochna, O., 2019. Forming polycultural
competence for future economists. Engineering and
Educational Technologies, 7 (1), 56–64.
https://doi.org/10.30929/2307-9770.2019.07.01.06
Romashenko, V., 2017. The problem of formation of
student’s sociocultural and multicultural competences
of philological course. Continuing Professional
Education: Theory and Practice, (3-4), 101–105.
https://doi.org/10.28925/1609-8595.2017(3-4)101105
Zamotaieva, N., 2017. Development of culture-forming
competence in humanities teachers of higher military
educational establishments: psycho-pedagogical
conditions. Continuing professional education: theory
and practice, 1-2, 50–56. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28925/1609-8595.2017(1-2)5056
Benera, V., Kashubskyi, V., 2020. Development of
polycultural competence in humanities teachers in
higher schools of the Republic of Poland. "Scientific
Bulletin" of Kremenets Regional Humanitarian and
Pedagogical Academy named after Taras Shevchenko,
12. https://doi.org/10.37835/2410-2075-2020-12-18
Olishevych, V., 2019. Realisation of the technology of
developing future foreign language teachers’
polycultural competence. Professionalism of the
teacher: theoretical and methodological aspects, 11,
233-243. https://doi.org/10.31865/2414-
9292.11.2019.197236
Grin, F., Faniko, K., 2012. Foreign language skills and
intercultural abilities: Operationalization with a large
population. Dans Management & Avenir, #55, 168 -
184.https://www.cairn.info/revue-management-et-
avenir-2012-5-page-168.htm
Mukharlyamova, L., Konopleva, N., 2018. Formation of the
Intercultural Communicative Competence of Students
in Process of Learning Foreign Languages. Journal of
History Culture and Art Research, 7(4):230-236.
DOI:10.7596/taksad.v7i4.1840
Kendzor, P., 2016. The role of the multicultural component
of teacher training in Ukraine. Didactica Pro… Revistă
de teorie şi practică educaţională, 4, 14–18.
http://www.prodidactica.md/revista/Revista_98.pdf
Competences for Democratic Culture: Living together as
equals in culturally diverse democratic societies.
Strasbourg: Council of Europe, 2016. 78p.
https://rm.coe.int/16806ccc07
Trajanovic, M., Domazet, D., Misic-Ilic, B., 2010. Distance
learning and foreign language teaching. Balkan
Conference in Informatics, 441-452.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/32231723_D
istance_learning_and_foreign_language_teaching
Kolyada, N., Shapovalova, L., Guz, Yu., Melkonyan, A.,
2021. Distance Learning of a Foreign Language –
Necessity or Future. International Journal of Emerging
Technologies in Learning, Vol 16, No 04. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v16i04.18299
APPENDIX
Questionnaire for Students
CHOOSE THE RIGHT, IN YOUR OPINION,
ANSWER. SEVERAL OPTIONS ARE POSSIBLE.
1)Do you think polycultural education is compulsory
for university graduates?
1. Yes, polycultural education is an integral part of
educating worthy members of society;
2. I think polycultural education is important, but not
paramount;
3. I do not think that polycultural education is more
important than vocational training;
4. It seems to me that polycultural education is not
needed in our society;
5. Own answer.
2)What does "a highly cultured person" mean?
1. An educated person;
2. A man armed with professional knowledge and
prepared for life in the modern world;
3. A highly educated, tolerant person;
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New
Educational Paradigm
475

4. A person who has knowledge of several foreign
languages;
5. Own answer.
3) Does polycultural education include the
knowledge of several foreign languages?
1. Yes, of course, the more languages we know, the
better we will live in a polycultural environment;
2. It is enough to know one foreign language and
understand your profession well;
3. The knowledge of the language does not mean
being a highly cultured person;
4. Tolerance is not nurtured by means of foreign
languages;
5. Own answer.
4) What is the purpose of learning foreign languages
in non-linguistic higher education institutions?
1. Learn to communicate with representatives of
foreign languages;
2. To teach cultural differences of representatives of
other countries and peoples for successful cross-
cultural communication;
3. To teach professional skills of foreign languages to
improve professional training;
4. To form a high level of culture, tolerance and
education of graduates by means of learning foreign
languages;
5. Own answer.
5) How will the knowledge of foreign languages help
you in the future?
1. I will be able to most effectively perform
professional activities among representatives of
foreign environment;
2. I will be able to easily find and process information
about my professional activities in order to use the
acquired knowledge for professional purposes;
3. I will be able to communicate freely with
representatives of other countries and nationalities;
4. I will be able to travel to different countries;
5. Own answer.
6) How is a certain level of polycultural education
formed in the study of foreign languages?
1. By means of studying the peculiarities of the
cultural life of the native speakers;
2. By means of communication with native speakers;
3. Studying the features of different economic
systems;
4. Conducting cross-cultural communication;
5. Own answer.
7) What tasks and exercises are aimed at developing
a certain level of polycultural education?
1. Working out texts concerning the cultural realities
of the countries under study;
2. Holding meetings with representatives of different
countries;
3. The acquaintance of the representatives of other
nations and nationalities with Ukrainian cultural
realities;
4. Study of cross-cultural communication;
5. Own answer.
8) Can you imagine living in a polycultural
environment without the formation of multicultural
education?
1. Higher education provides graduates with a certain
degree of tolerance for communication with
representatives of other cultures;
2. Yes, I believe that vocational education is more
important than polycultural education;
3. Life in our country excludes the possibility of
tolerance towards the representatives of other nations
and nationalities;
4. No, I can't imagine. I believe that modern
university graduates should have a certain level of
polycultural education;
5. Own answer.
9) How will polycultural education affect your future
career?
1. Such education will ensure a successful life in a
modern polycultural environment;
2. I will be more effective in my professional
activities in a multinational environment;
3. I think that polycultural education will not affect
purely professional activities;
4. It provides opportunities to communicate
effectively with people of different nations and
nationalities;
5. Own answer.
10) What means of forming polycultural education do
you consider the most effective?
1. Study of the cultural realities of the countries of the
studied languages;
2. Travel to the country of the language being studied;
3. Communicating with representatives of other
nations and nationalities, discussing their pressing
issues;
4. Awareness of their own identity, respect and
preservation of traditions and customs of the
Ukrainian people;
5. Own answer.
Questionnaire for Lecturers
CHOOSE THE RIGHT, IN YOUR OPINION,
ANSWER. SEVERAL OPTIONS ARE POSSIBLE.
1) What do you think polycultural competence is?
1. The ability to make friends with people from
different cultures;
2. An effective interaction in a particular situation,
taking into account cultural characteristics;
3. The knowledge of traditions and customs of
different peoples;
ISC SAI 2022 - V International Scientific Congress SOCIETY OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
476

4. The ability to speak several foreign languages;
5. Own answer.
2) What is the most significant element in
polycultural competence?
1. Awareness of cultural diversity;
2. Tolerance according to the representatives of
different cultures;
3. Mutual understanding and respect for all members
of society;
4. The ability to determine correct behavior in
different conditions of a multicultural society;
5. Own answer.
3) What do you think is the basis for preparing a
person for life in a polycultural society?
1. The study of the national characteristics of the
environment;
2. Study of socio-psychological characteristics of
members of society;
3. Understanding the value orientations of modern
society;
4. Understanding of professional functions and social
roles;
5. Own answer.
4) Do you think that learning several foreign
languages will allow students in the future:
1. pursue a policy of polylingualism in a multicultural
space;
2. navigate in the cultural relations of native and
foreign countries;
3. better perform their professional duties;
4. become a highly cultured person;
5. own answer.
5) What is the motivational and value criterion for the
formation of a certain level of polycultural
competence?
1. Awareness of socio-professional significance;
2. The interest towards other cultures;
3. The desire for cross-cultural interaction;
4. Acceptance of polycultural values;
5. Own answer.
6) Cultural formation is based on:
1. Social activity;
2. Willingness to work in another country;
3. Ability to gain our own socio-cultural experience,
4. Willingness to communicate in a polycultural
society;
5. Own answer.
7) What is the problem of cross-cultural
communication?
1. Misunderstanding of cultural issues;
2. Unemployment in society;
3. Different social roles of members of the society
given;
4. Poor knowledge of foreign languages;
5. Own answer.
8) What can be referred to cross-cultural social
intelligence?"?
1. The level of human intelligence;
2. Recognition and understanding of verbal and
nonverbal cues in different cultures;
3. Ability to correctly interpret social interaction in
the process of intercultural communication;
4. Achieving the necessary goals in the process of
intercultural interaction through understanding of
other cultures and their acceptance;
5. Own answer.
9) What is culture, in your opinion:
1. Internationalized subject of activity;
2. "Our culture" in full, it is the one in which the
individual grew up;
3. "Flawless" translator of "absorbed" previously
values;
4. Inexhaustible source of society’s cultural values;
5. Own answer.
10) Does mastering one or more foreign languages
affect the formation of polycultural competence?
1. Of course, yes. We become more tolerant in our
relations with the representatives of other nations and
nationalities;
2. Yes, it does. Because the more languages we know,
the more we are a human.
3. Knowledge of several foreign languages allows
you to realize your own identity;
4. Knowledge of foreign languages first of all
prepares for effective communication within the
chosen profession;
5. Own answer.
11) How is a certain level of polycultural education
formed in the study of foreign languages?
1. By means of studying the peculiarities of the
cultural life of native speakers;
2. By means of communication with foreign people;
3. The study of the features of different economic
systems;
4. Conducting cross-cultural communication;
5. Own answer.
12) What tasks and exercises are aimed at developing
a certain level of poycultural education?
1. Working out the texts concerning the cultural
realities of the countries under study;
2. Holding meetings with representatives of different
countries;
3. The acquaintance of representatives of other
nations and nationalities with Ukrainian cultural
realities;
4. Study of cross-cultural communication;
5. Own answer.
The Formation of Polycultural Competence of Future Economists and Lawyers in Foreign Languages Learning in the Context of New
Educational Paradigm
477
