
Renewal of Land Transfer Fee and Real Estate Tax in the Silver Age
of Real Estate: Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution and
Policy Design
Xinqiang Song
1
, Jiajia Ke
2
, Huami Yi
3
and Peng Zhang
4
1
Headmaster’s office, Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
2
School of Humanities and communication, Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, Guangzhou, Guangdong,
China
3
School of Culture Tourism and Geography, Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, Guangzhou, Guangdong,
China
4
School of Public Administration, Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Keywords: Land Transfer Fee, Real Estate Tax, Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution, Policy Design.
Abstract: Focusing on the current hot discussion on the collection of real estate tax and how to renew the land use term,
this paper discusses how to deal with the relationship between real estate tax and land transfer in the future.
Taking Guangzhou land market as the research object, by establishing an alternative analysis framework for
Guangzhou real estate tax and transfer fee, the total amount of existing urban residential buildings in
Guangzhou is estimated based on GIS technology, the effect of real estate tax and land transfer fee is
empirically analysed, and finally the process of government collecting real estate tax is simulated. Providing
theoretical analysis and policy design for the functional substitution between Guangzhou's future real estate
tax collection policy and transfer fee renewal policy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The golden age of real estate has passed which is
becoming the basic consensus of professionals. In
order to promote high-quality economic
development, we have to improve the ability to
prevent and resolve major risks. Therefore, the future
land financial transformation and the resolution of
local government debt risks urgently need the reform
of the national financial and tax system and
management system (Yang, et al, 2021, Zhang, et al,
2016). The legislation of real estate tax is imminent.
Can the real estate tax gradually replace the land
transfer fee? Can ordinary people no longer pay the
due land transfer fee under the condition of paying
real estate tax? These are hot topics at present, and
they are also hot issues related to the basic livelihood
and well-being of the people (An, 2015).
In recent years, real estate tax legislation is a hot
topic in the two sessions every year, and it is also a
hot spot in China's tax system reform, but there is no
specific timetable for its collection. At present, the
development trend of China's real estate is very
complex. On the one hand, the expiration and renewal
of commercial housing not only brings confusion to
residents, but also affects the real estate market; On
the other hand, the real estate tax to be introduced by
the state is also like a fog. How to deal with the
expiration and renewal of residential land use right
has always been a widely concerned problem by the
government and academia (Yi, et al, 2017, Zhang,
2021). At the same time, the real estate tax, which is
closely related to the real estate market and people's
life, has also attracted extensive social attention. On
the issue of land renewal upon expiration, although
the property law states "automatic renewal", there are
no specific legal provisions on the details such as how
long the renewal period is and whether the transfer
fee needs to be paid. Since the tax system reform in
1994, the land transfer fee has been placed under local
management, which has improved the land utilization
rate, but due to the unreasonable structure of local
fiscal revenue, the mode of relying on land sales to
obtain income to fill local fiscal revenue is
unsustainable. Therefore, the current institutional
problem is how to deal with the relationship between
1010
Song, X., Ke, J., Yi, H. and Zhang, P.
Renewal of Land Transfer Fee and Real Estate Tax in the Silver Age of Real Estate: Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution and Policy Design.
DOI: 10.5220/0011363000003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 1010-1017
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
real estate tax and land transfer fee, which is an urgent
problem to be discussed and solved.
2 GUANGZHOU REAL ESTATE
TAX POTENTIAL
ESTIMATION AND FUNCTION
SUBSTITUTION
2.1 Alternative Analysis Framework of
Real Estate Tax and Transfer Fee
The collection of real estate tax can not only maintain
the financial revenue of local governments, but also
take into account people's acceptance ability. This
study takes Guangzhou land market as the research
object to estimate the renewal land transfer fee under
the background of Guangzhou real estate tax in the
future. This study assumes that the transfer fee to be
paid for new land (including renewed land) in the
future will be reduced, and the reduction of land
transfer fee will reduce the financial revenue of local
government. In order to maintain the source of
government revenue, the total amount of land transfer
fee reduction and renewal add up to the total amount
of real estate tax collection every year (
Chen, et al,
2016
).
2.2 Empirical Calculation of Real
Estate Tax Collection
2.2.1 Using GIS Technology to Estimate the
Total Value of Existing Urban Housing
in Guangzhou.
The tax base of real estate tax is the value of
residential taxable area. To study the impact of
Guangzhou real estate tax on local finance, we should
consider the total value of urban housing in
Guangzhou. Since the housing information is not
disclosed to the public, the area of urban housing in
2021 is unknown. The total amount of urban housing
in 2021 is estimated by GIS technology. The
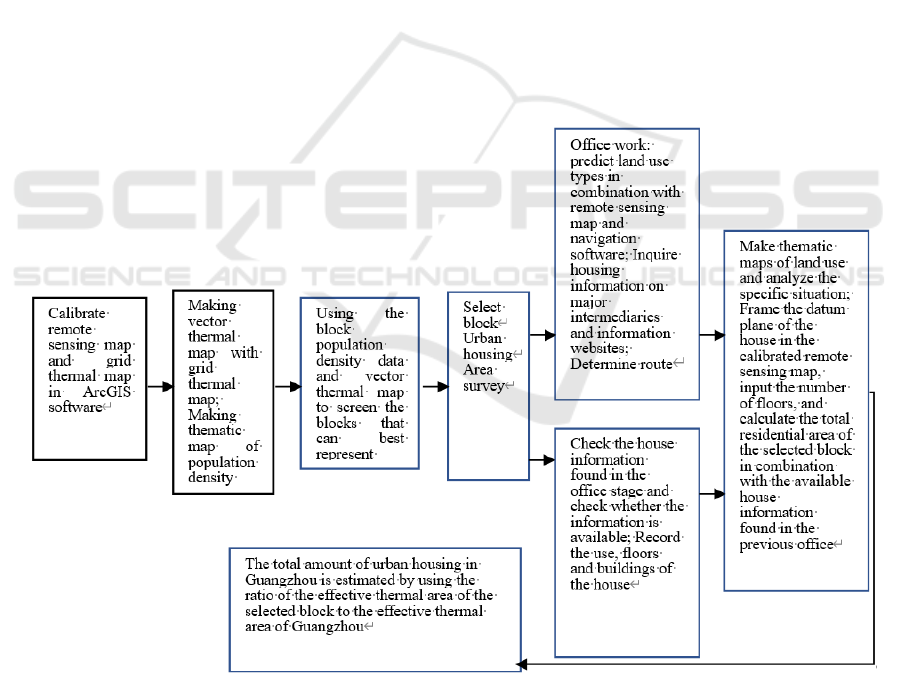
estimation process is shown in Figure 1.
Source: the author made his own according to the research results
Figure 1: Technical roadmap of GIS estimation.
Renewal of Land Transfer Fee and Real Estate Tax in the Silver Age of Real Estate: Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution and Policy
Design
1011
a) Selection of representative blocks
In order to estimate the total amount of urban
housing in Guangzhou more scientifically, block
population density data are selected. The blocks close
to the average population density are used as the
survey object, by comparing the block thermal scale
map with the thermal map of Guangzhou to ensure
that the selected blocks are more representative by
observing the availability (
Luo, et al, 2007).
Through the observation of block remote sensing
map and comparing the uniformity of land use type,
building density and residential distribution, we
found that the residential distribution of Tianyuan
street is relatively uniform, the area of urban villages
is small, and the average population density of
Guangzhou block is the smallest in the representative
area. Combined with the difficulty of field
investigation, Tianyuan street is preliminarily
selected as a representative block.
b) Estimation of urban residential area in
Tianyuan Street
In the internal business stage, the residential area
is counted from the existing data, and the availability
needs to be checked in the external business stage. To
estimate the residential area using GIS technology, it
is necessary to collect the number of
residential floors,
housing structure, supporting commercial building
floors and structures in the field stage, and give
corresponding symbols in the calculation process for
accumulation or elimination. To estimate the
residential area using GIS technology, it is necessary
to accurately deduct the building datum from the
remote sensing surface after calibration, and then
input the number of floors to calculate the calculation
results (see Table 1).
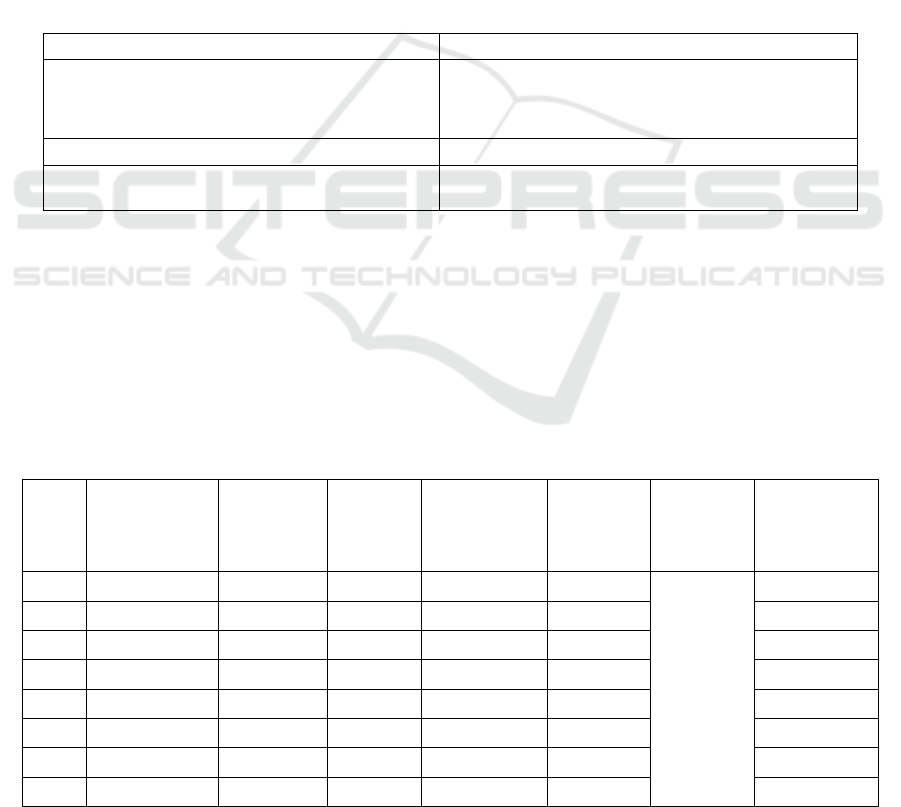
Table 1: Urban residential area of Tianyuan Street.
project Area (M2)
Calculate the urban residential area obtained from
Tianyuan street with ArcGIS (excluding the
statistical part of existing data)
1730355.057766
Statistics of urban residential area available 5725111.38
Estimated total urban housing area of Tianyuan
Street
7,455,466.437766
Source: the author calculated according to the research results
c) Estimation of total value of existing urban
housing in Guangzhou
The income method is adopted for the appraisal.
With reference to the rent data of China real estate
intermediary association, the annual net income =
monthly rent (yuan / month / ㎡) × 12. The rate of
return is determined by the rent level and selling
price. Since China only reformed welfare housing
distribution into monetary housing distribution in
1998, the service life of commercial housing land in
China is generally 70 years. In order to estimate the
house price in Guangzhou, the income life is set as 60
years in 2021, and so on in other years. The following
data and calculation results are obtained (see Table 2
and table 3).
Table 2: Estimation of the total value of existing urban housing in Guangzhou.
partic
ular
year
Annual rent
per square
meter in year
(yuan)
House price
(yuan / m2)
Rate of
return
Growth rate
of net income
over the
previous year
Years of
income
Annual
growth rate
of net
income
Appraisal
price (yuan /
m2)
2014 400.56
14762
2.71% 19.68% 67
5.55
10628
2015 411.36
16555
2.48% 2.7% 66 11919
2016 444.24
19208
2.31% 7.99% 65 13829
2017 486.24
18564
2.62% 9.45% 64 13366
2018 520.92
20016
2.6% 7.13% 63 14411
2019 616.56
22926
2.67% 18.35% 62 16506
2020 629.4
28578
2.2% 2.08% 61 20576
2021 645.24
32413
1.99% 2.51% 60 23454
Source: the author calculated according to the research results
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
1012
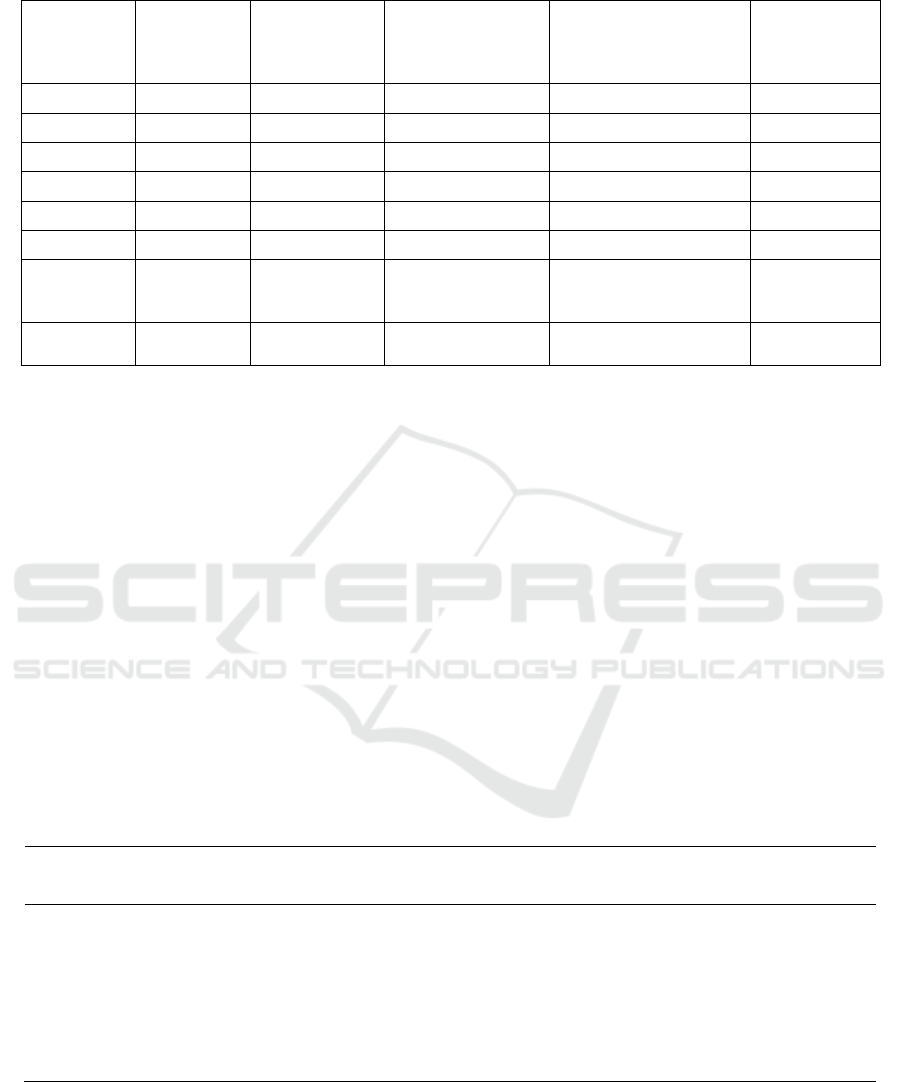
Table 3: Estimation of total population and housing.
particular
year
Proportion
of urban
population
(%)
Permanent
resident
population
(10000)
Per capita housing
area (M2)
Total urban residential
area (M2)
Appraisal
price (yuan /
m2)
2014 84.78 1275.96 21.89 234830509.2298 10628
2015 85.02 1283.39 22.46 245069634.7788 11919
2016 85.27 1292.68 22.73 250545570.0428 13829
2017 85.43 1308.05 23.32 260593331.218 13366
2018 85.53 1350.11 24 277139779.92 14411
2019 86.06 1404.35 25.42 307221953.662 16506
2020 86.14 1449.84 29.86 (latest
published sampling
data)
372919202.7536 20576
2021
(
estimated
)
86.6 1500 30 389734362.612 23454
Source: the author calculated according to the research results
2.2.2 Empirical Analysis on the Effect of
Real Estate Tax and Land Transfer
Fee
a) Empirical calculation of real estate tax levy
This paper uses the following formula to simulate
and calculate the real estate tax revenue of
Guangzhou after the collection of real estate tax:
𝑅
=𝑃
∗𝑇
∗𝑆
−𝑆
∗𝑁
∗4+𝑁
In essence, the above formula shows that the real
estate tax income is the difference between the total
urban residential value in Guangzhou and the
deductible residential value after the real estate tax is
levied. Among them, in order to evaluate the average
house price, it is calculated according to 72% of the
current price; For the real estate tax rate, this paper
selects 0.4%, 0.5% and 0.6% to study; It is the tax-free
area per capita. In the specific analysis, we divide it
into 20m²/ Person, 25m²/ Person, 30m²/ Three
scenarios are discussed. For the number of primary
and secondary school degrees in Guangzhou,
assuming that the student family of each degree is a
family of four, the total number of families with
houses in Guangzhou can be inferred through the
number of degrees 4 and the aging population, so as
to calculate the total reduced or exempted housing
value in Guangzhou. For the real estate tax rate,
referring to the real estate tax rate background
formulated by Chongqing and Shanghai, this paper
studies the real estate tax rate in three cases: 0.4%,
0.5% and 0.6%, and simulates the calculation results
(see Table 4).
Table 4: Income simulation calculation of real estate tax in Guangzhou.
particular
year
Number
of degrees
Aging population
Total urban
residential area
Assess average
house price
𝑇
=0.5%, 𝑆
=30
Real estate tax income at
2015 1381389 1184000 234830509.2 14762
17.82519084
2016 1373263 1264000 245069634.8 16555
25.24329468
2017 1406204 1330000 250545570.0 19208
28.97250868
2018 1432942 1406499 260593331.2 18564
31.03940816
2019 1453098 1475260 277139779.9 20016
42.15953895
2020 1474216 1546091 307221953.7 22926
69.27015554
2021 1234400 1618500 372919202.8 28578
181.3118054
Source: the author calculated according to the research results
Due to space constraints, only the tax rate is 0.5%
and the per capita tax-free area is 30m ²/ Real estate
tax income calculated by person time. In this paper,
based on the reduction area per capita, it is proposed
to be 20m² respectively, 25m², 30m² analysis on the
substitution effect of real estate income in Guangzhou
on land transfer fee in Guangzhou (see Table 5).
Renewal of Land Transfer Fee and Real Estate Tax in the Silver Age of Real Estate: Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution and Policy
Design
1013

Table 5: Estimation of substitution effect of real estate tax on land transfer fee under 0.5% real estate tax rate.
partic
ular
year
Land
transfer fee
(100 million
yuan)
Income from real estate tax (100 million yuan)
Reduced
area 20m ²
Substitution
effect (%)
Reduced
area 25m ²
Substitution
effect (%)
Reduced area
30m ²
Substitutio
n effect
(
%
)
2015 307.4 53.48 17.40% 35.65 11.60% 17.83 5.80%
2016 412.0 65.51 15.90% 45.38 11.01% 25.24 6.13%
2017 762.0 77.06 10.11% 53.02 6.96% 28.97 3.80%
2018 841.0 78.74 9.36% 54.89 6.53% 31.04 3.69%
2019 907.1 94.67 10.44% 68.42 7.54% 42.16 4.65%
2020 282.0 130.70 46.35% 99.98 35.46% 69.27 24.56%
2021 1173.0 248.76 21.21% 215.04 18.33% 181.31 15.46%
Source: the author calculated according to the research results
According to the statistical yearbook of land and
resources, the land transfer fee shows an increasing
trend as a whole. In 2016, due to the influence of
policy regulation, the land transfer fee in Guangzhou
was depressed. If it is included in the analysis, which
will affect the analysis effect, so it is excluded from
the analysis. See Table 6 for the average replacement
rate of different tax rates and different reduced areas
in 2016-2021.
Table 6: Estimation of average substitution rate of different tax rates and different reduced areas in 2016-2021.
Substitution effect (%)
Tax rate
(
%
)
0.40% 0.50% 0.60%
Reduced
area m ²
Reduced
area
20m ²
Reduced
area
25m²
Reduced
area
30m²
Reduced
area
20m²
Reduced
area
25m²
Reduced
area
30m²
Reduced
area
20m²
Reduced
area
25m²
Reduced
area
30m²
Average
substitution
effect
11.26 8.26 5.27 14.07 10.33 6.59 16.88 12.39 7.90
Source: the author calculated according to the research results
As can be seen from table 6, when the tax rate is
0.4%, the reduction area is 30m², the real estate tax
can averagely replace 5.27% of the land transfer fee;
When the tax rate is 0.6%, the reduced area is 20m²,
the real estate tax can averagely replace 16.88% of
the land transfer fee. The above analysis shows that
there are two extreme collection methods, while the
more moderate collection tax rate is 0.5% and the
reduction area is 25m². At this time, the average
replacement rate of real estate tax on land transfer fee
is 10.33%, and the effect is also more appropriate.
However, in the short term, when choosing the
appropriate collection rate, we also need to take into
account the actual situation of Guangzhou residents'
tax burden, tax collection technical conditions and
taxpayers' psychological expectations. Limited by
objective factors, the collection rate is generally less
than 100%. If the collection rate is too low, the effect
of real estate retention tax will be affected. Rural real
estate is not considered in the estimation of the
substitution effect of land transfer fee by real estate
tax. If rural real estate is included in the calculation
scope, the substitution effect is estimated to make up
for the lack of collection rate. Therefore, it is feasible
for real estate tax to replace land transfer fee.
b) Simulating the impact of real estate tax on local
fiscal revenue
Based on Guangzhou housing data, this paper
simulates and predicts the expected income of
Guangzhou personal housing real estate tax, and then
analyzes the impact of real estate tax on Guangzhou's
fiscal revenue.
Firstly, considering the sustainability of
government revenue and the acceptability of public
opinion, selecting the real estate tax rate is 0.5% and
the per capita tax-free area is 30m² to explore the
impact of real estate tax on Guangzhou’s fiscal
revenue. Based on the analysis of the substitution
effect of the former real estate tax on the land transfer
fee, the substitution effect is 6.59%; Secondly, select
the fiscal and tax data of Guangzhou from 2015 to
2021, and use the time series analysis method to make
an empirical analysis with the general budget revenue
(Y) as the explanatory variable and the real estate tax
revenue ( 𝑅
) as the explanatory variable. By
analyzing the impact of real estate tax reform on
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
1014
government revenue effect, a regression model is
constructed. The regression model is as follows:
LnY = β
+β
∗LnR
+ε
Among them, Y represents the general budget
revenue of Guangzhou, R
represents the real estate
tax revenue, β
represents the constant term,
β
represents the influence coefficient, and ε is the
residual term of the equation. In order to eliminate the
influence of heteroscedasticity on the regression
equation, logarithms are taken on both sides of the
regression equation of the model for linear regression
analysis.
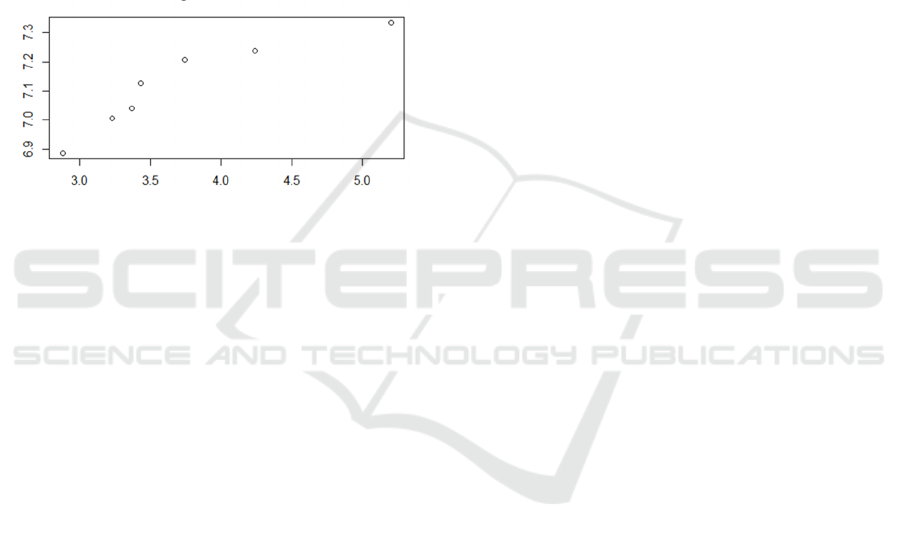
① The scatter diagram of the relationship
between real estate tax income and general budget
income is shown in Figure 2
(Abscissa: Real estate income, Ordinate: General budget
income)
Figure 2: scatter diagram of real estate tax income and
general budget income.
Source: the author calculated according to the research
results
According to figure 2, the logarithmic sample data
points fall near an approximate straight line,
indicating that there is a significant linear relationship
between real estate tax revenue and general budget
revenue. Because the sample points are not all on a
straight line, it shows that the relationship between
𝑅
andY is not completely linear, and there is an
interference term.
② Statistical analysis
Through Pearson correlation analysis (the
analysis process is omitted), the correlation
coefficient is 0.9225249 and the p value is 0.003077.
When the significance level is 0.01, the original
hypothesis is rejected and it is considered that there is
a significant linear correlation between real estate tax
income and general budget income after the
introduction of real estate tax. The determination
coefficient R
2
= 0.8511, the fitting degree of the
regression equation is good, which can explain the
variance of 85.11% of the dependent variable, and the
constant term and regression coefficient are
significant at the level of 0.01. The residual diagram
shows that all points are within 3 and there are no
abnormal values. It can be considered that the sample
data of this example is basically normal, and the
research assumptions of the theoretical model are
reasonable.
③ Analysis on the impact of levying real estate
tax on local fiscal revenue
Through modeling analysis, the regression
equation between general budget income and real
estate tax income is:
LnY = 6.43821 + 0.18293 ∗ LnR
As shown in the formula, there is a significant
positive correlation between the real estate tax
revenue and the general budget revenue, the
coefficient is 0.18293, and the elasticity is less than
1, indicating that the general budget revenue will
increase by less than the real estate tax revenue, that
is, for every 1% increase in the real estate tax revenue
after the introduction of the real estate tax, the general
budget revenue will increase by 0.18%, After the
introduction of real estate tax, the real estate tax
revenue plays an obvious role in stimulating the
financial revenue of Guangzhou.
3 RENEWAL OF LAND
TRANSFER FEE UNDER THE
BACKGROUND OF FUTURE
GUANGZHOU REAL ESTATE
TAX: POLICY SIMULATION
3.1 Policy Mix
In order to comply with the public opinion and make
the government revenue grow continuously and
steadily, according to the survey data and modeling
analysis, it is suggested to adopt the following policy
combination.
For the general population, 25m more than the per
capita tax-free housing² (refers to the housing
construction area, the same below) shall be calculated
according to the tax rate of 0.5% of the average
transaction price of new houses in the administrative
region in December of the previous year, and the tax
system of the current year shall be paid at the
beginning of the year, with no upper limit. Tax
payable = taxable area * average transaction price of
new houses in the administrative region where the
house is located in December of the previous year *
tax rate.
For retirees, set the age threshold. For example,
those who exceed the retirement age (generally 60
years old) only have one set of housing, which is tax-
Renewal of Land Transfer Fee and Real Estate Tax in the Silver Age of Real Estate: Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution and Policy
Design
1015

free no matter how large; If there is more than one set,
tax shall be paid from the second set. If more than one
suite is not self occupied and has income, it can bear
the tax and prevent others from attaching the house to
the tax-free quota for tax avoidance.
For retirees, set the age threshold. For example,
those who exceed the retirement age (generally 60
years old) only have one set of housing, which is tax-
free no matter how large; If there is more than one set,
tax shall be paid from the second set. If more than one
suite is not self occupied and has income, it can bear
the tax and prevent others from attaching the house to
the tax-free quota for tax avoidance. For the
unmarried young house buyers whose children of
Guangzhou families buy houses for the first time in
adulthood, if the house purchase area exceeds 100m²,
Considering the large area of tax payable, the
implementation of the registered residence
registration fee reduction 50m² for such people, non
registered residence registration can enjoy 35m² fee
reduction; If the area is less than 100m²/ The
registered residence of the city can enjoy 40m² fee
reduction. Non registered residence registration can
enjoy 25m² fee reduction. The registered residence of
singletons has more than 100m². The reduced area is
50m ². The area of tax exemption for those who hold
the residence permit for talent introduction in
Guangzhou is 50m². The self owned houses built by
farmers on the homestead are temporarily exempted
from real estate tax.
3.2 Using GIS Technology to Simulate
the Expropriation Process
Based on the above analysis, GIS technology is used
to simulate the process of government collecting real
estate tax. Based on the survey results, some
Tianyuan streets are selected as tax areas. The
housing types in this area include class I residence
(Villa) and class II residence, and have many factors
affecting house prices, such as location, greening,
education, commerce and so on. After learning the
housing location information, the corresponding
record carrier is established through GIS system to
realize the visualization of spatial relationship. The
10 housing information is assumed and the ownership
is Guangzhou registered residence. The income
method is adopted for the appraisal. GIS assisted
appraisal predefines and calculates the mathematical
model according to the selected appraisal method to
provide the reference price of real estate. The free
area is only for the first house of the owner, and the
free area is not allowed from the second house.
The tax rate policy of five grades of excess
accumulation system is implemented for the taxable
area. The tax rate of 0.7% is adopted for the taxable
area of class I residence of 50m² - 100m², and 1.1%
is adopted for the taxable area of class II residence of
more than 90m² and less than 120 m².
4 RESEARCH CONCLUSION
Taking GIS as the main research tool, this study
selects representative blocks by using the data of
block population density, economic development
level and income level. At the same time, the
replacement rate of real estate tax on land transfer fee
is calculated by different tax rates and exempted areas
based on the data of permanent population and the
number of primary and secondary school degrees.
Referring to the implementation methods of the
current two pilot cities of real estate tax, simulate the
policy rules and policy combination, and finally
simulate the real estate tax collection process (Fan, et
al, 2010).
In addition to legal principles and respecting
historical traditions, the renewal and supplementary
payment of land use right also needs to be based on
economic principles, the concept of social equity and
the specific practice of land system (Huang, 2018).
Based on the land price theory, from the perspective
of land policy and public policy, land taxation and
social equity, and from the perspective of realizing
social fairness and justice, reducing management
costs and conforming to economic laws, China
should abandon the policy orientation of continuing
to pay the transfer fee according to the real-time
market rent when the land expires, and amend
relevant laws in time to make the use right of
residential land long-term or even permanent, and
adopt appropriate land tax policies to return the land
value-added income to the state (Chen, et al, 2007,
Zhu, 2016). The recovery of land appreciation should
become the main value orientation of China's land
policy in the future. Therefore, the three policies of
differentiated low standard collection, consolidated
real estate tax and land appreciation are more
reasonable, especially land appreciation (Zhu, Fang,
2019).
No matter when the land use right expires, in the
real estate transaction link, the evaluation institution
entrusted by the government will calculate the land
appreciation and recover 30% - 60% of the
appreciation. If the appreciation is not increased,
there is no need to make up the payment. The
supplementary payment of similar land value-added
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
1016

tax is only collected when the property right is
transferred and expires. This method is different from
the function of real estate tax. It should reflect the
basic system of state ownership, and the price rise
should be returned to the public. The land value-
added tax paid during the period can be included in
the historical cost accounting and deducted when
making up the payment (Peng, 2016). In short, there
is no value-added tax (transfer fee).
REFERENCES
An Tifu., 2015. Legal basis and relevant policy suggestions
for real estate tax legislation. Research on local finance.
Chen Ping, Li Jianying, Zhuang Hailing., 2018. Prediction
of the impact of real estate tax reform on local fiscal
revenue -- simulation calculation based on Guangzhou
data. Tax research.
Chen Yulu, Zhao Ziwei, Guo Dongjun, Zou Dahai, Chen
Zhilong., 2021. Study on the correlation between urban
underground space and population distribution. Journal
of underground space and engineering.
Fan Zhongjun., 2010. Bayesian vector autoregressive
analysis method and its application. Mathematical
statistics and management.
Huang Xiaofang., 2018. The automatic renewal of house
property rights after 70 years lays the foundation for the
collection of real estate tax. Economic daily.
Luo Gang Hui, Wu Ci Fang, Zheng juan'er., 2007.
Influence of parcel area on residential land price. China
land science.
Peng Pei., 2016. Land development right and distribution
of land value-added income. Chinese issues and British
experience. Chinese and foreign law.
Yang Yuanyuan, Jia Pengfei, Gao jiechao., 2021. Choice of
long-term regulation paradigm of China's real estate:
real estate tax policy or macro Prudential policy.
Finance, trade and economy:
Yi Liqi, Zhou Ruiping., 2017. Analysis of settlement
change characteristics and influencing factors from the
perspective of Urban New Area Construction in recent
10 years. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University
(PHILOSOPHY AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
EDITION).
Zhang Ping, Ren Qiang, Hou Yilin., 2016. China's real
estate tax and the transformation of local public
finance. Journal of public management.
Zhang su., 2021. Research progress of tax base batch
evaluation in real estate tax reform. Special economic
zone.
Zhu Haifeng, Fang Xu., 2019. Research on land income
balance calculation method supported by GIS.
Computer and digital engineering.
Zhu Liyu., 2016. Analysis on the substitution effect of real
estate tax on land transfer fee in the "post land finance"
period--Taking Sichuan Province as an example.
Journal of Henan College of Finance and taxation.
Renewal of Land Transfer Fee and Real Estate Tax in the Silver Age of Real Estate: Potential Estimation, Functional Substitution and Policy
Design
1017
