
The Trade Potential and Trade Efficiency of the “One Belt, One
Road” Countries along the Border and Their Impact on China's
Foreign Direct Investment: Based on the Stochastic Frontier Gravity
Model
Yulanxin Wang
1
, Xinran Wang
2
, Junkai Guo
3
, Yiwen Jiang
4
and Qifei Ma
5
1
Department of Quantitative Economics, Jilin University, Jilin, China
2
Department of Finance, Jilin University, Jilin, China
3
Department of Economics, Jilin University, Jilin, China
4
Department of International Trading, Jilin University, Jilin, China
5
Department of Human Resource Management, Jilin University, Jilin, China
Keywords: Stochastic Frontier Gravity Model, OFDI, Trade Potential And Trade Efficiency.
Abstract: With the rapid development of big data economy, economic and trade cooperation between countries has been
better studied for better development. This paper uses the "one belt, one road" countries data from the
database, such as the world bank and other databases. And the paper is also to test the applicability of the
model and to prove that the stochastic frontier gravity model should be used for the study. “One belt, one
road” countries’ GDP and the degree of integrity have significant impact on China's OFDI.
1 INTRODUCTION
After the outbreak of the financial crisis, the
economies of various countries are gradually brewing
recovery, the international situation is still in a state
of instability, the phenomenon of development and
differentiation between countries due to the existence
of economic circles, the economic gap between
countries is gradually widening, and the more
backward countries are facing great challenges. Since
2019, the world has seen a new dilemma - the new
crown pneumonia epidemic. The world economic
growth rate has been at the lowest level since the 2008
financial crisis, trade between countries has slowed
down significantly due to the epidemic restrictions
and the economy has suffered a huge impact, but the
outflow of outward direct investment has increased
by 33.2% year-on-year after three consecutive years
of decline. The pace of China's opening up to the
outside world is still stable. And Chinese enterprises
are also constantly "going out". In 2019, China's
outward direct investment was US$1369.1, second
only to Japan's, and China's outbound investment
stock reached US$2.2 trillion, ranking third in the
world. Second only to the United States and the
Netherlands.
In today's context of both impetus and obstacles,
the joint construction of the "Belt and Road" can
conform to the current background of economic
globalization and uphold the spirit of China's
"opening up". In this context, the impact of the trade
potential and trade efficiency of countries along the
"Belt and Road" on China's outward direct
investment is studied, and then the policy
recommendations of China's outward direct
investment under the background of the "Belt and
Road" economic cooperation are given, which has a
significant impact on the development of China's
economy and trade. In the process of reading the
literature, I found that many scholars have research
directions related to the "Belt and Road", and some
scholars have carried out the research direction of
trade potential and trade efficiency on a certain
industry, based on the importance of trade and OFDI,
which has gradually been put on the agenda, coupled
with the inseparable link between trade and OFDI, so
this article discusses the literature on trade efficiency
and trade potential for OFDI.
In recent years, due to the continuous
advancement of the wave of economic globalization,
218
Wang, Y., Wang, X., Guo, J., Jiang, Y. and Ma, Q.
The Trade Potential and Trade Efficiency of the â
˘
AIJOne Belt, One Roadâ
˘
A
˙
I Countries along the Border and Their Impact on Chinaâ
˘
A
´
Zs Foreign Direct Investment: Based on the Stochastic
Frontier Gravity Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0011172100003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 218-226
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

many scholars have conducted research on the trade
potential and trade efficiency of the "Belt and Road"
countries. First of all, in the development trend of
trade efficiency and trade potential, scholars have
reached inconsistent conclusions. Through the study
of bilateral trade, he (Zhang, 2017) concluded that
trade efficiency is now low, and gave suggestions on
how to increase outward direct investment and sign
free trade zones; The paper was used (Li, 2018) by a
stochastic frontier model in the analysis and
calculation of trade efficiency and trade potential of
countries along the "Belt and Road" to conclude that
although trade efficiency is declining, there is an
overall upward trend; When calculating the trade
potential of countries along the "Belt and Road"
based on the stochastic frontier gravitational model,
it is believed (Quan, 2019, Gao, 2019) that neither
trade potential nor trade efficiency has reached a very
high level, and there is still a high room for
improvement. In the study on the development scope
of trade efficiency and trade potential, the paper was
used (Li, 2020, Ni, 2020) by the HT model to measure
the countries along the "Belt and Road", and
concluded that China's trade potential for Asian
countries is small, while its trade potential for Central
and Eastern European countries is large.
In terms of the selection of explanatory variables,
it is believed (Feng, 2019, CHEN, 2019) that some
economic indices, the total number of countries,
political systems, and preferential trade agreements
are important factors when influencing trade
efficiency and potential; Based on the study of
stochastic frontier gravitational models and trade
inefficiency models, it is concluded (Li, 2019, Lü,
2019) that signing free trade agreements and opening
Confucius Institutes is conducive to China and the
"Belt and Road" in improving financial freedom,
infrastructure construction, cultural exchanges, etc.
The improvement of trade efficiency in countries
along the Belt and Road; Based on the study of trade
potential based on the stochastic frontier gravitational
model, it is concluded (Zhang, 2020, Zhang, 2020,
Chen, 2020) that common language, trade freedom,
political stability, trade facilitation degree, and the
signing of free trade agreements can have a positive
impact on trade efficiency and potential; Based on the
stochastic frontier gravitational model, the study of
global trade efficiency and trade potential was carried
out (Chen, 2016, XIE, 2016, LIN, 2016), and the
study showed that trade input, trade concentration,
trade complementarity index positively correlated
trade efficiency and trade potential, and the degree of
trade diversification had a negative correlation with
it, but the impact of trade diversification, trade
concentration and trade complementarity index on
trade was not obvious; Based on the stochastic
frontier gravitational model and trade non-efficiency
model, it is concluded (Li, 2020, Zhang, 2020, Chen,
2020) that the scale of economic development of
countries and the import of final consumer goods by
participating countries have a positive effect on trade,
while differences in political systems and
geographical distance have a restraining effect on
trade; The paper was used (Li, 2021) by the stochastic
frontier gravitational model draw the conclusion that
the income level of countries along the "Belt and
Road" has a very obvious role in promoting trade
efficiency, and has a more obvious impact on trade
efficiency in terms of geographical location at the
same time. Trade freedom and tariff levels have a
positive effect on trade efficiency.
In the study (Yang, 2019) of influencing factors,
based on the stochastic frontier gravitational model
and trade inefficiency model, the income level,
population size, geographical distance and
landlocked countries restrictions between China and
the belt and road have a significant impact on trade
potential, trade inefficiency is the main reason for the
gap between the actual trade level and trade potential,
and helps to improve trade efficiency by narrowing
the gap between the democratic degree of
government, improving trade freedom and signing
regional trade agreements. The paper was used
(Zhang, 2017) by the study of stochastic frontier
gravitational model. It is concluded that there are still
major problems in trade facilitation and government
governance capacity of countries along the "Belt and
Road" that inhibit trade efficiency between countries.
In addition to enhancing the degree of convenience
and government capacity, China can promote the
negotiation of inter-state trade agreements and
increase of outward direct investment to improve
trade efficiency and trade potential; The paper (Li,
2021) was used by the stochastic frontier
gravitational model. It is concluded that the per capita
GDP, geographical distance, common border, WTO
organization, trade freedom and other factors of the
countries along the route have a greater impact on
trade potential and trade efficiency, while the
government integrity index, trade freedom, labor
scale, final consumption expenditure, and exchange
rate estimates have a significant effect on trade. The
innovation of its research is to conclude that tariff
levels are negatively correlated with trade and that the
role of financial freedom and OFDI in trade
efficiency is not a simple promotion, and this
indicator does not play a large role in China's trade
with countries along the route.
The Trade Potential and Trade Efficiency of the â
˘
AIJOne Belt, One Roadâ
˘
A
˙
I Countries along the Border and Their Impact on Chinaâ
˘
A
´
Zs
Foreign Direct Investment: Based on the Stochastic Frontier Gravity Model
219

Due to the increasingly close ties between
countries and the smooth operation of the strategy of
"Belt and Road" proposed by China today, the topic
of trade potential and trade efficiency has become
more and more hot, and many scholars have done
research in this regard. The study found (Tan, 2015,
Zhou, 2015) that the trade efficiency of countries
along the "Belt and Road" is improving, and there is
still a wide range of improvements in trade potential;
It is believed (Wang, 2016) that China's trade
efficiency with Iran, Kyrgyzstan, Ukraine, Russia and
other countries along the "Belt and Road" is relatively
high, and it is also at a high level in terms of trade
potential.
At the same time, it can also be found that
scholars' research on trade efficiency and trade
potential involves many different fields, including
agricultural products, manufacturing, cultural
products, and foreign exports. For example, the paper
was measured (Chen, 2018, Xie, 2018, Liu, 2018) by
the efficiency of cultural trade, etc., and used (Wang,
2019, CHEN, 2019, GAO, 2019) by complex
network analysis method and combined with
stochastic frontier models to study the topological
characteristics of the "Belt and Road" trade network
and its impact on China's import and export trade
efficiency.
In a study of OFDI related to the research topic of
this paper, it was argued (Zhang, 2017) that China's
OUTWARD direct investment with countries along
the "Belt and Road" will increase the volatility of the
inefficient value of trade due to the strong volatility
between China and the region itself. It was argued
(Li, 2021) that foreign investment in inter-country
trade dilutes the demand for import trade.
It is equally important to study the relationship
betwee trade and OFDI abroad. It was examined
(Amour, 2017, WU, 2017) by the implementation of
China's OFDI, surveying some theoretical and
empirical literature on the motivations and
determinants of CHINA's OFDI. In the past, most
scholars have argued that strategic behavior and
economic considerations seem to be the basic
motivations for China's OFDI, but in fact, the main
factors that determine the amount of Chinese FDI
include market size variables, labor market
conditions, institutional variables, macroeconomic
policy variables, and the global supply of FDI, as well
as GDP, market size, and trade freedom. The study
also points out that China's offline foreign direct
investment in the world is seeking markets and
resources. It was concluded (Suresh, 2014, Bulbul,
2014, Vivek, 2014) that over the past decade, outward
direct investment and economic growth have been
inextricably linked, but the causality has been
controversial. The article examines the multiple
causal relationships between China's outward direct
investment, economic growth, and foreign trade
between China and India. The article found that the
two countries presented opposite results in terms of
the causal relationship between FDI and GDP.
Foreign scholars not only study trade and OFDI on
the current situation, but also give corresponding
policy recommendations. The studies (Zhang, 2006)
show that OFDI can reduce poverty by promoting
economicgrowth and spreading growth. And OFDI is
also an important source of China's economic growth.
By leading programs and policies to improve the
investment environment in poor provinces,
government can reduce more poverty and attract
more OFDI; The study (Li, 2011, Jin, 2011) points
out that China is South Korea's largest exporter and
largest importer. In terms of economic dependence
and geographical location, South Korea cannot ignore
the importance of China, which should take into
account both countries, namely trade and investors,
while increasing the volume of outward direct
investment. By changing the way the economy
depends on, South Korea should also increase its
outward direct investment from China to keep trade
and investment balanced between the two countries.
The study notes (Makaranga, 2019) that the
relationship between OFDI and trade growth has long
been an area of concern for many policymakers,
economists and academics. This is because OFDI can
affect many macroeconomic factors in recipient
countries. OFDI is a resource bundle for economic
growth in developing countries, particularly in
Africa. As a result, most African countries have
expressed support by providing incentive policies to
foreign companies related to OFDI. The article also
draws false conclusions: the impact of FDI inflows on
economic growth will certainly increase, thus
achieving sustainable economic growth and
development.
In summary, there have been in-depth studies on
trade potential, trade efficiency and China's outward
foreign direct investment, but there are few studies on
China's outward direct investment from the
perspective of common trade potential and trade
efficiency, and there are few studies that combine
trade potential, trade efficiency and China's outward
direct investment in the context of the Belt and Road
Initiative. Based on this, on the basis of China's
analysis of the current situation of outward direct
investment in the "Belt and Road" countries, the
study empirically analyzes the trade potential of
countries along the "Belt and Road" from the
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
220
perspectives of GDP, population size, distance from
China, whether there is a common border,
government integrity, trade freedom, monetary
freedom, financial freedom, whether to sign a free
trade agreement, whether to join the WTO, etc.,
through the establishment of a random frontier
gravitational model.
2 ANALYSIS OF THE SITUATION
2.1 The Size of China's Outbound
Direct Investment
Current between countries are closely linked, is
undergoing dramatic changes, after the outbreak of
the financial crisis, the economy is gradually making
recovery, the international situation is still in a state
of flux, between countries due to the existence of the
economic circle, the phenomenon of the development
of differentiation, gradually widening economic gap
between countries, relatively backward countries
facing a great challenge. Since 2019, the world and a
new dilemma - COVID - 19 outbreak, the world's
economic growth to its lowest level since the
financial crisis in 2008, trade between countries
restricted by epidemic appeared significantly
slower.Economy suffered a huge impact.However,
foreign direct investment flow after falling for three
years rose 33.2%, China is still opening up steadily,
and Chinese companies are also going global. In
2019, China's outbound direct investment reached us
$1,369.1, second only to That of Japan. China's
outbound investment stock reached $2.2 trillion,
ranking third in the world. Only the United States and
the Netherlands.
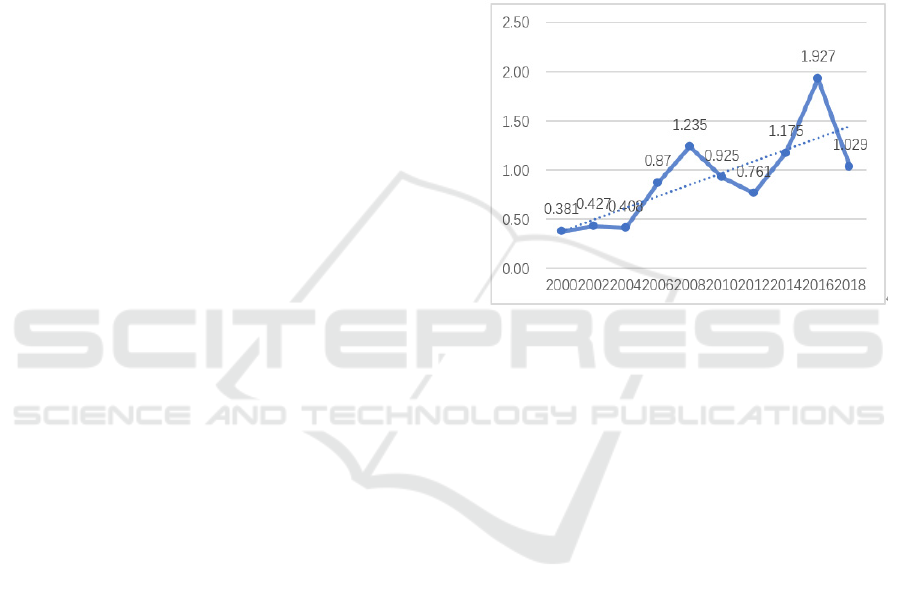
According to Figure 1, the proportion of net
outflow of OFDI in GDP was 0.381% at the
beginning of this century in 2000, and increased to
0.925% ten years later in 2010. Due to the impact of
Covid19 at the end of 2019, import and export trade
at home and abroad will have strong fluctuations, and
the scale of OFDI will also be greatly impacted.
However, before that, the data in 2018 had increased
to 1.029%. As can be seen from the trend line shown
in the figure, the proportion of China's net outflow of
OFDI in GDP showed an overall upward trend.
If only consider the relevant data of foreign direct
investment, although it can be seen that the
development trend, It can be easily affected by other
aspects. When GDP also maintains rapid rising trend,
the economic environment is optimistic and the
economy of every composition lead toward the
development of the whole .And we are through the
foreign direct investment outflows as a share of
GDP,Then we can know the relative changes of
foreign direct investment. If OFDI is compared to a
boat in the downstream, then the proportion data is
equivalent to the relative speed of the boat and the
current. Thus, it can be concluded that the importance
of OFDI for China's economy has been growing,
which is also the root of our research. Under the
current background of both driving forces and
obstacles, the Belt and Road Initiative can adapt to
the current background of economic globalization
and uphold the spirit of China's "opening-up".
Figure 1: Net outward direct investment outflow (share of
GDP).
2.2 OFDI between China and Other
Belt and Road Countries
In recent years, many developing and emerging
countries have undergone dramatic changes from
isolationist, import-substitution policies to open
market policies aimed at increasing outward direct
investment. Foreign investment plays an increasingly
important role in a country's economic growth, and
all countries begin to attach importance to foreign
investment and increase foreign investment, while
encouraging foreign investment in their own country.
The study of foreign direct investment is of great
significance and guiding role in the development of
economic globalization.
China has high hopes for trade with countries
along the belt and Road, and has set ambitious trade
growth targets with ASEAN, India and other
countries, and actively removed barriers to trade
development. On this basis, the paper studies the
trade potential and trade efficiency of countries along
the "Belt and Road", the factors influencing trade
potential and trade efficiency, and the actual impact
of trade potential and trade efficiency on China's
foreign investment. The study of these problems has
The Trade Potential and Trade Efficiency of the â
˘
AIJOne Belt, One Roadâ
˘
A
˙
I Countries along the Border and Their Impact on Chinaâ
˘
A
´
Zs
Foreign Direct Investment: Based on the Stochastic Frontier Gravity Model
221
important theoretical value and practical significance
for enriching and improving China's OFDI.As the
spread of COVID-19 has brought great uncertainties
to the economy, OFDI has changed greatly under the
influence of policies of various countries, so our data
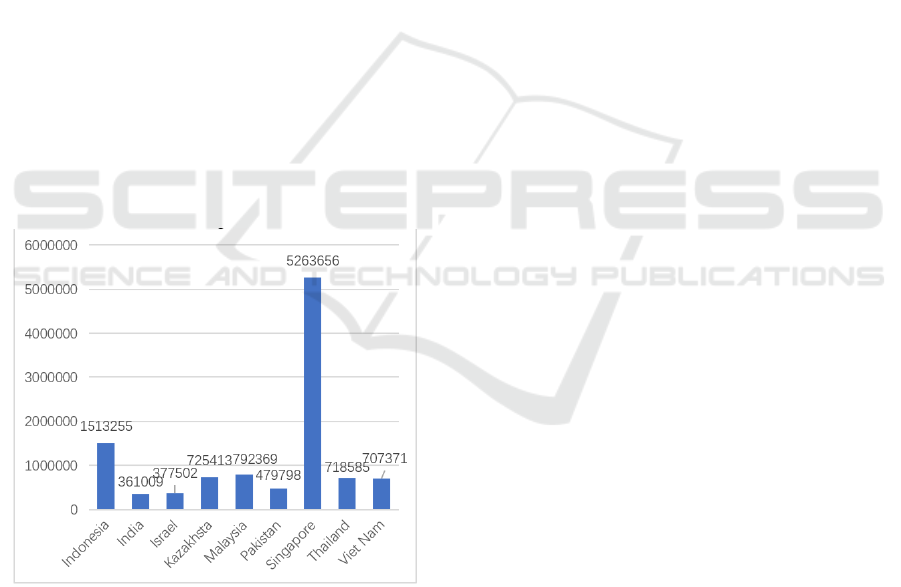
are mainly analyzed based on 2019. According to
figure 2 can see, in the year 2019, China's
"neighbourhood" net foreign investment up to
Singapore and other countries as much as $52.63656
billion, the second contact in foreign direct
investment in China is closely followed by Indonesia,
Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, kazakhstan, Pakistan,
Israel, India, etc., However, these countries are far
behind Singapore, but they have great potential for
future development. Therefore, China can provide
appropriate policy support to these countries in the
future construction of the "Belt and Road", so as to
facilitate the steady and efficient development of
regional economy.
While some countries are opposite bigger and the
Chineseon the net foreign investment is not high, the
reason may be that some political factors. In order to
better economic regional exchange in the future,
China also need to maintain good diplomatic image,
with other countries to establish friendly and close
relationship between foreign trade, promote the
development of health, coordination between
economy and effectively.
Figure2 China's Net Outbound Investment to Other
Countries (2019).
2.3 The Influence of Trade
Potential and Trade Efficiency on China's Foreign
Direct Investment
In the study of trade efficiency and trade potential,
it can be found that although they contain two
different aspects, there are still many similarities. The
total population, GDP, infrastructure construction,
logistics and transportation among countries will all
have an impact on trade efficiency. For trade
potential, in addition to some hard indicators,
"software", such as technology and experience, these
can also have a great impact. In general, some
countries that do not have hard indicators tend to have
the advantage of being a late mover. Therefore, in the
context of "One Belt and One Road", there are many
factors that need to be considered when studying
trade efficiency and trade potential. They are not only
the superficial positive correlation, but also some
other interfering factors.
Some of China's traditional industries have a
comparative advantage in the international market is
close to saturation. But with the incoming of the
economic globalization, the financial crisis is
emerging, which makes China's export growth have a
downward trend. The research of foreign direct
investment can effectively avoid the country setting
up for China of tariff and non-tariff barriers to
facilitate the export of China's domestic advantage
products, And in the information can be more
transparent and reduce the export process of trial and
error and blindness.
3 MODEL CONSTUCTION AND
DATA SOURCE
3.1 Theoretical Analysis
The purpose of the stochastic frontier gravity model
is to combine the stochastic frontier theory with the
gravity model to analyze the technical efficiency in
the production function. The model decomposes the
stochastic disturbance term into two parts: Trade non
efficiency and random error term.
The model form can be expressed as
( ) exp( ) exp( ), 0
it it it it it
Yfx
β
θ
μμ
=−≥,
(1)
or
Take logarithms on both sides and get
ln ln ( ) , 0
it it it it it
Yfx
β
θ
μμ
=+−≥,
(2)
In formula (2): 𝑌
refers to the investment
amount of China to country i in period t. 𝑥
is the
main factor affecting the actual investment amount,
generally natural factors, such as economic scale,
population, distance, etc; 𝛽 is the parameter to be
estimated of the explanatory variable; 𝜃
is a
random disturbance term and follows a normal
distribution with a mean value of 0; 𝑢
is a trade
non efficiency term, which refers to the factors
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
222

affecting the efficiency of bilateral trade. Generally,
it is human factors that cause the variables in the trade
group, such as government integrity, trade freedom,
financial freedom, etc., which are independent of 𝜃
.
It is usually assumed that they obey normal
distribution or tail normal distribution; The
expression of the model is as follows:
(,)
it it it
hZ a
μ
ε
=+
(3)
In formula (3): 𝑍
is the influencing factor of
trade non efficiency term, 𝛾 is the parameter to be
estimated and 𝜀
is the random disturbance term. In
this study, battese and coelli (1995) proposed to
substitute the trade inefficiency model into the
stochastic frontier gravity model. It means to
substitute equation (3) into equation (2), and
obtained:
[
]
ln ln ( ) ( , )
it it it it it
Yfx hZa
β
θε
=+−+,
(4)
If equation (4) is regressed, the stochastic frontier
gravity model and trade inefficiency model can be
estimated at the same time.
3.2 Empirical Model
3.2.1 Stochastic Frontier Gravity Model
Combined with the analysis of previous scholars,
generally, important objective factors that will not
occur significantly in the short term, such as total
GDP, population, geographical distance, whether it is
China's border country and other variables, are placed
in the stochastic frontier gravity model. The variables
such as government integrity, currency freedom,
trade freedom, financial freedom, whether there is a
trade agreement or whether to join the trade
organization are uniformly placed in the trade non
efficiency item. Build a specific stochastic frontier
gravity model.
it 0 1 2 3 4
ln ln ln ln ln , 0
it it it i it it it
OFDI GDP CAP DIS BO
ββ β β β θμμ
=+ + + + +− ≥
(5)
In (5): 𝑂𝐹𝐷𝐼
it
represents the total stock of China's
direct investment in country i in period t; 𝐺𝐷𝑃
、
𝐶𝐴𝑃
respectively represent the economic scale and
population of country i in period t; 𝐷𝐼𝑆
indicates
the geographical distance from Beijing, China to the
capital of country i ; 𝐵𝑂
indicates whether country
I and China have a common border. A dummy
variable is used here. If two countries have a border
for child labor, the variable is set to 1, otherwise it is
0. 𝜃
is a random disturbance term and 𝑢
is a
trade non efficiency term.
3.2.2 Trade Inefficiency Model
By referring to the previous literature, this paper uses
the variables of government integrity, currency
freedom, trade freedom, financial freedom, whether
there is a trade agreement, whether to join the trade
organization and so on to construct the trade
inefficiency index system. The specific measurement
model is as follows:
01 2 3 4 5 6
ln ln ln ln ln ln
it it it it it it it it
GOV CUR GRA FIN AGR ORG
μγγ γ γ γ γ γ
ε
=+ + + + + + +
(6)
In equation (6): 𝐺𝑂𝑉
refers to the government
integrity of country i in period t. 𝐶𝑈𝑅
、𝐺𝑅𝐴
、
𝐹𝐼𝑁
represents the monetary freedom, trade
freedom and financial freedom of country i
respectively; 𝐴𝐺𝑅
indicates whether China has
signed a free trade agreement with country i; 𝑂𝑅𝐺
is whether country i is a member of WTO; 𝜀
is a
random perturbation term.
3.3 Sample Selection and Data Source
The strategy of “One belt, one road” was put forward
in 2013. Some countries were excluded because of a
serious lack of data. The data from the remaining
2013-2019 were selected from the year of 2013. The
data were analyzed by Frontier 4.1 soft. The
explanation of each variable, data source, expectation
and impact on dependent variables can be shown
from table 1.
3.4 Empirical Test and Result Analysis
3.4.1 Applicability Test of Model
In this study, the maximum likelihood ratio LR
statistic𝐿𝑅 = −2(𝑙𝑛 𝐻
−𝑙𝑛𝐻
) is used to judge the
effectiveness of the stochastic frontier gravity model
and the specific form of the model setting. Assuming
the original hypothesis𝐻
:𝛾 = 0, we could compare
the calculated LR statistics with the segment critical
value at the 1% significance level, so as to judge
whether to reject or accept the original hypothesis. 𝛾
can be expressed as𝛾=𝛿
/(𝛿
+𝛿
). Among them,
between 0 and 1, if the original hypothesis is
accepted, the model can be estimated directly by
ordinary least square method; If it approaches 1, it
indicates that the random frontier gravity model
should be used for estimation.
The Trade Potential and Trade Efficiency of the â
˘
AIJOne Belt, One Roadâ
˘
A
˙
I Countries along the Border and Their Impact on Chinaâ
˘
A
´
Zs
Foreign Direct Investment: Based on the Stochastic Frontier Gravity Model
223
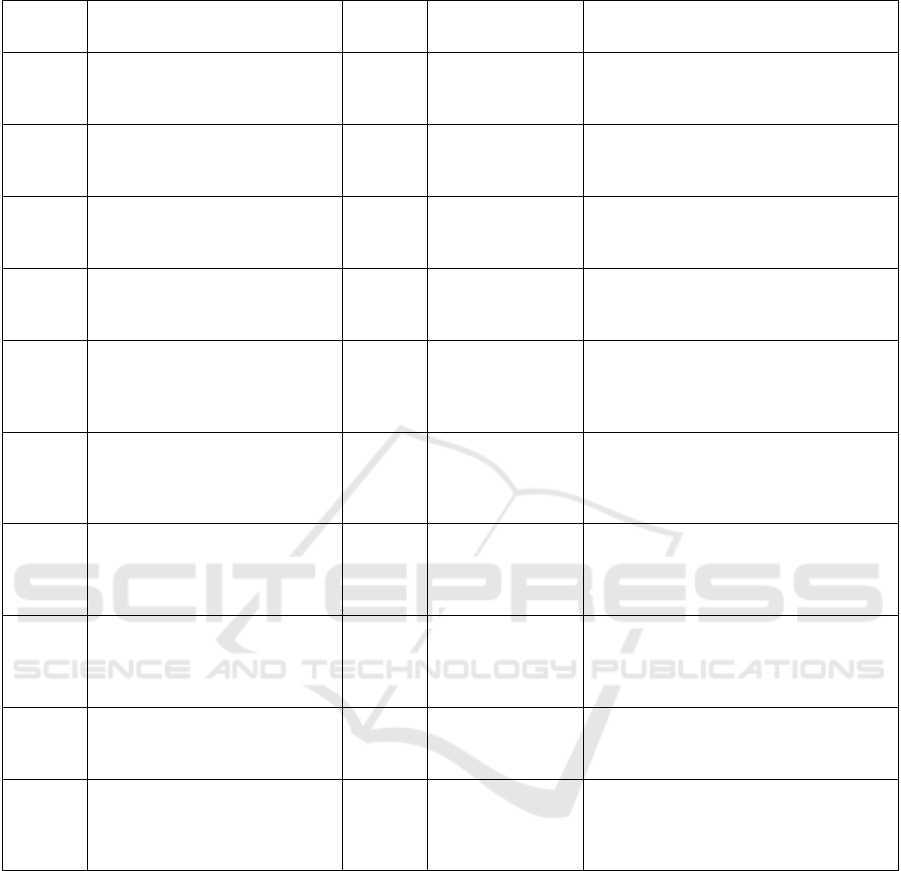
Table 1: The explanation of each variable, data source, expectation and impact on dependent variables.
Variable Meaning Expecte
d
Symbol
Data Sources Theoretical Description
ln
it
GDP
GD
P
of countr
y
i
/
USD + Worl
d
Ban
k
Database
The large
r
the economic scale of the
invested country, the Greater China's
direct investment in the country
ln
it
CAP
Population of country i
/
p
erson + Worl
d
Ban
k
Database
The large
r
the
p
opulation of the investe
d
country, the Greater China's direct
investment in the country
ln
it
D
IS
Distance
b
etween China an
d
country i / km
- French CEPII
database
The close
r
China is to a country, the
Greater China's direct investment in that
country
ln
i
BO
Whethe
r
China an
d
country i
have a common border
+ French CEPII
database
If the investe
d
country has a common
border with China, China's direct
investment in the country will be greater
ln
it
GOV
government integrit
y
- American Heritage
Foundation
Database
The more honest the government of the
invested country is, the less resistance
China has to direct investment in the
country
ln
it
CUR
Degree of monetar
y
freedo
m
in
country i
-
American Heritage
Foundation
Database
The highe
r
the degree of monetary
freedom of the invested country, the
smaller the resistance of China's direct
investment in the country
ln
it
GRA
Degree of trade freedo
m
of
country i
- American Heritage
Foundation
Database
The highe
r
the degree of trade freedo
m
of
the invested country, the smaller the
resistance of China to direct investment in
the country
ln
it
F
IN
Degree of financial freedom in
country I
- American Heritage
Foundation
Database
The highe
r
the degree of financial freedo
m
of the invested country, the smaller the
resistance of China to direct investment in
the country
ln
it
A
GR
Whethe
r
China signe
d
a free trade
agreement with country i
- China Free Trade
Zone Service
Network
If a
b
ilateral free trade agreement is
signed, the less resistance China has to
direct investment in the country
ln
it
ORG
Whethe
r
countr
y
i is a membe
r
of
the world trade organization
- Official website of
the World Trade
Organization
If the investe
d
country is a membe
r
of the
world trade organization, the less
resistance China has to direct investment
in that country
3.4.2 Analysis of Model Regression Results
As can be shown from table 2, in the estimation of
trade potential and trade efficiency, the GDP of
countries along the line has a positive correlation and
significant effect on China's foreign investment,
which shows that the higher the economic
development level of countries along the line, the
more can promote China's foreign direct investment,
which is consistent with the expected theory.
Population is also an influencing factor of trade
potential
and trade efficiency, which has a negative
inhibitory effect on China's foreign direct investment,
and the results are significant, which is obviously
inconsistent with the expected theory. China's “one
belt, one road”, is mostly a small country in
developing countries and a small country in
developed countries. This is also the reason why the
results are not consistent with the theoretical
expectations, according to the estimated results. The
leamer's non trade equilibrium interpretation applies
only to developed countries such as the United States.
The distance between the countries along the line and
China is negatively correlated, indicating that the
farther the countries along the line are from China,
the higher the cost, and the more unfavorable it is for
China's foreign direct investment. Whether there is a
common
border between the countries along the line
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
224
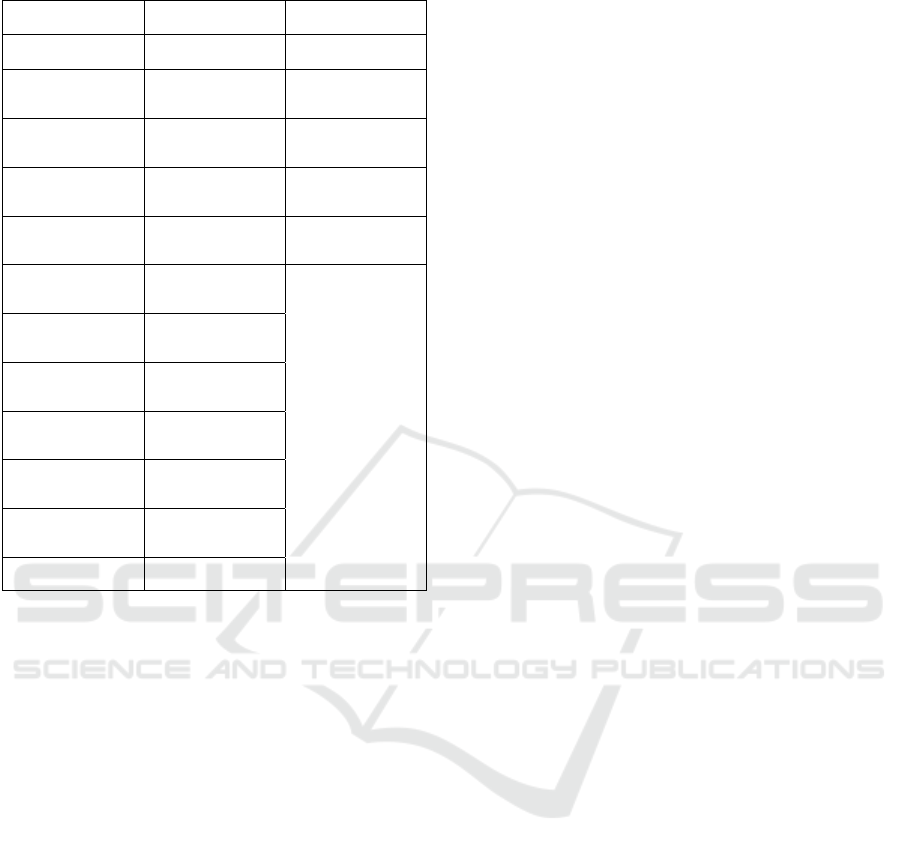
Table 2: Model regression results.
variable coefficient
t
-ratio
0.157
4.41096
ln
it
GDP
0.342
1.0809741
ln
it
CAP
-0.687
-1.0875752
ln
it
D
IS
-0.179
-4.0355547
ln
i
BO
-0.329
-1.2719382
ln
it
GOV
-0.423
ln
it
CUR
-0.108
ln
it
GRA
-0.107
ln
it
F
IN
-0.192
ln
it
A
GR
-0.892
ln
it
ORG
-0.805
gamma 0.53
and China has a significant impact, indicating that
bordering with China will promote foreign direct
investment. The trade potential and trade efficiency
measured by the level of government integrity are
significantly negatively correlated, indicating that the
more perfect the government system is, the greater
the amount of foreign direct investment is, which is
obviously consistent with the expectation. The
improvement of government system shows that the
political risk is small, which is conducive to China's
investment, which is also an important reason to
include it into the variables of trade potential and
trade efficiency. Different from previous studies, this
paper adds monetary freedom as a variable of trade
potential and trade efficiency. The results show that
this variable has a greater impact on trade potential
and trade efficiency, which means that the higher the
monetary freedom, the greater the amount of China's
foreign direct investment. A country's trade freedom
refers to the country's non-tariff barriers. It controls
the trade freedom by restricting imports directly and
indirectly. If the government reduces the trade
freedom, it will inevitably inhibit imports and affect
China's foreign direct investment. The degree of
financial freedom of a country includes the degree of
distribution of credit funds, the degree of government
service and regulation of financial institutions, and
the difficulty of financial services to the real
economy. If the degree of government regulation of
financial institutions is increased, it will inevitably
inhibit imports. Therefore, the improvement of
financial freedom will promote trade potential and
trade efficiency. Other variables, such as whether the
two sides have signed a free trade agreement and
whether the countries along the line have joined the
free trade organization, are consistent with the
theoretical expectation.
4 CONCLUSION AND ADVICE
Based on the above research conclusions, the paper
puts forward the following countermeasures and
suggestions: first, make full use of the Asian
infrastructure investment bank and the Silk Road
Fund, improve the overall trade facilitation level of
the region, and constantly explore the trade potential
and realize the common prosperity of the countries
along the line; Second, on the factors affecting trade
efficiency, targeted measures should be formulated to
improve China's export trade efficiency with
countries along the economic corridor of the new
Eurasian Continental Bridge. China's one belt, one
road, along with its economic development, will
enhance its efficiency in the export of trade, such as
strengthening bilateral and multi field cooperation,
improving customs clearance efficiency, improving
the quality of infrastructure, facilitating trade and
transport efficiency, and improving the quality of
logistics services. Third, upgrade green financial
services. As the saying goes, "economy is the body,
finance is the blood, and the two coexist and prosper".
China's “one belt, one road” and other countries will
be able to trade with the improved financial
supporting services. Mr. Chen Yulu, vice president of
the central bank, believes that the most important
thing in China's current financial reform is to
establish a world-class green financial evaluation
standard system. The development of green finance
is one of the biggest highlights of China's financial
reform in recent years and an important thrust for the
financial industry to better serve China's real
economy and help supply side structural reform. In
addition, Mr. Yi Gang, governor of the central bank,
believes that stable monetary policy and active fiscal
policy are the most important and best policies in the
short term, at most in the medium term, and also the
second best choice to make up for China's GDP
growth gap; Fourth, deepen China’s strategy of the
“one belt, one road”, the financial cooperation of the
countries along the border, enhance the degree of
The Trade Potential and Trade Efficiency of the â
˘
AIJOne Belt, One Roadâ
˘
A
˙
I Countries along the Border and Their Impact on Chinaâ
˘
A
´
Zs
Foreign Direct Investment: Based on the Stochastic Frontier Gravity Model
225

financial freedom, strengthen the government's
supervision over financial institutions, and increase
the scale of credit capital allocation.
REFERENCES
CHEN Chuang-Lian, XIE Xue-zhen, LIN Yu-Ting.
Analysis of global trade efficiency and trade potential
and its influencing factors[J]. International Trade
Issues, 2016(07):27-39.
Chen Lin, Xie Xuezhen, Liu Lin. Trade Efficiency and
Trade Potential of China's Exports: 1980-2015[J].
Feng Gen-yao, CHEN Xiao. Trade efficiency and export
potential of cultural products between China and the
fulcrum countries along the "Belt and Road"——
Estimation based on stochastic frontier gravitational
model[J]. Journal of Shaoxing University of Arts and
Sciences (Humanities and Social Sciences),
2019,39(06):64-72.
HABYARIMANA Jean D’Amour, WU Xiang Feng.
Motives and Determinants of China’s Foreign Direct
Investment in Rwanda[J]. International Journal of
Economic Behavior and Organization, 2017, 5 (2).
International Economic and Trade Exploration,2018,34 (1):
33-50.
International Trade Issues (2): 3-12.
Juma Makaranga. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), Quality
of Institutions and Economic Growth: Evidence from
African Economies[D]. University of International
Business and Economics,2019.
Kevin Honglin Zhang. Does International Investment Help
Poverty Reduction in China? [J]. Chinese
Economy,2006,39(3).
Li Cuiping." Research on China's Foreign Trade Efficiency
under the Background of the Belt and Road Initiative:
Based on the Empirical Data of the New Eurasian Land
Bridge of 19 Countries[J]. Research on Technology
Economics and Management, 2021(02):112-117.
Li Haiwei, Ni Sha. Research on the Trade Environment and
Potential between China and Countries along the "Belt
and Road": An Empirical Test Based on HT Model[J].
Journal of Shanxi University: Philosophy and Social
Sciences Edition, 2020(3):73-85.
Li Helu, Jin Meizhen. FDI Environment and Promotion
Policy for China Money in Korea[J]. The Journal of
Korea Research Society for Customs,2011,12(4).
LI Ping. Trade potential and trade efficiency between China
and countries along the "Belt and Road" and its
determinants: An empirical study based on the
stochastic frontier gravitational model[J]. International
Business Research,2018,39(5):5-16.
Li Xiao, Zhang Yuxuan, Chen Xiaoxin. A Study on China's
Trade Potential with The Belt and Road Participating
Countries: A Case Study of Final Consumer Goods
Imports[J]. Nankai Economic Research, 2020(01):45-
69.
Li Xiaozhong, Lü Peipei. Research on the Export Trade
Potential and Trade Efficiency of China's Equipment
Manufacturing Products: An Empirical Study Based on
the "Belt and Road" Countries[J]. International Trade
Issues, 2019(01):80-92.
Liang Wang and Yuanyuan Wu, (2016), "The Trade
Potential of the Silk Road Economic Belt: An Analysis
Based on the 'Natural Trading Partner' Hypothesis and
the Stochastic Frontier Gravitational Model," The
Economist, Vol. 4, pp. 33-41.
Quan Yi, Gao Junxing." The Belt and Road Initiative and
the New Strategy for The Development of China's
Coastal Opening-up[J]. Fujian Forum (Humanities and
Social Sciences Edition), 2019(12):106-114.
Suresh K. Chadha, Bulbul Singh, Vivek S. Natarajan.
Interaction among foreign direct investment, economic
growth and foreign trade: evidence from India and
China[J]. Int. J. of Process Management and
Benchmarking,2014,4(2).
Tan Xiujie, Zhou Maorong. 2015. Trade Potential and
Influencing Factors of the Maritime Silk Road in the
21st Century: An Empirical Study Based on Stochastic
Frontier Gravitational Model[J].
WANG Yan-fang, CHEN Shu-mei, GAO Jia-hui." The
Impact of the Belt and Road Trade Network on China's
Trade Efficiency: A Comparison with TPP, TTIP, and
RCEP[J]. Asia-Pacific Economics, 2019(1):49-55.
Yang Yiting. An Empirical Analysis of China's Trade
Potential and Trade Efficiency with the Belt and Road
Countries[J]. Monthly Price, 2019(05):47-54.
Zhang Huiqing. Research on the trade potential between
China and regions along the "Belt and Road"[J].
International Trade Issues,2017(07):85-95.
Zhang Yuling, Zhang Xia, Chen Meng. Research on trade
potential, efficiency and influencing factors between
China and countries along the Maritime Silk Road: An
Empirical Analysis Based on Stochastic Frontier
Gravitational Model[J]. Journal of Yili Normal
University (Social Science Edition), 2020,38(02):56-
65.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
226
