
The Impact of Satisfaction and Environmental Uncertainty on
Commitments Mediated by the Franchisee’s Trust
Makartiningrum, D. Adriel, A. K. Ilyas and Lim Sanny
Business Management Program, Management Department,
BINUS Business School Master Program Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, 11480, Indonesia
Keywords: Satisfaction, Environmental Uncertainty, Commitment, Trust, Franchise.
Abstract: This study aims to analyze the effect of environmental satisfaction and uncertainty on commitment and its
indirect effects through trust mediator variables. The research sample is franchisee, especially in the field of
food and beverages. Data analysis using SPSS and Sobel Test. The results showed that there was a positive
and significant effect of Franchisee Satisfaction on Franchisee Trust, positive and significant influence
between Environmental Uncertainty on Franchisee Trust, positive influence of Franchisee Trust on
Commitment, further Franchisee Satisfaction had a positive and significant effect on Commitment with
Franchisee’s Trust as a mediating variable, and Environmental Uncertainty has a positive and significant
effect on Commitment with Franchisee’s Trust as a mediating variable.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today’s highly developed digital era, there are
many businesses, both large and small, in society,
especially in Indonesia. One of the businesses that is
currently on the rise is about franchising or
franchising, especially in the field of food and
beverages where there are more competitors. From
year to year, the prospect of franchise business in
Indonesia is increasingly promising. General
Chairperson of the Indonesian Franchise and
Licensing Association (Wali), Levita Ginting Supit,
said the franchise business in the country continues to
experience positive growth. In 2018, the franchise
business in the country experienced a growth of 3%
with a turnover of IDR 150 trillion. In 2019, it is
projected that the franchise business can grow by 5%
(FLEI, 2019). In addition, this franchise is also
supported by the improvement of infrastructure and
investment in the trade sector. The concept of
franchising is just learning and running a system that
has been determined by a certain brand, so there is no
need to create a new brand.
This franchise business can be said to be a
strategic business because even though it was built
from a small business, it was formed in a mature
concept. In the franchise business, the risk of failure
can be minimized, because the franchisor has
provided everything to support the franchisee,
including surveys, marketing and promotion
methods, licensing, raw materials, management,
work standards (SOP), interior design, strategies and
so on (Latan et al., 2018). Several franchise
businesses are currently under increasing pressure by
having to always innovate, otherwise this will make
the business worse off. The challenge of this franchise
business is that business people must be innovative
and creative. The reason is, the emergence of various
franchises and many foreign franchises have entered
Indonesia. ”Like it or not, franchising has to be
creative,” said Levita (2019).
Meanwhile, in other conditions in 2020, around
the world began to talk about the Covid-19 virus. This
virus was first known to infect humans at the end of
December 2019 in the city of Wuhan - China. Then
in January 2020, the National Health Commission of
China informed that this virus can be transmitted
from human to human (Sheth et al., 2012). In this
case, the whole world is experiencing changes in all
their daily activities. Including in terms of the
economy, the economic turmoil caused by the Covid-
19 pandemic hit Indonesia like a perfect storm which
at least had three major impacts on the economy,
Suryo said the first impact was making household
consumption or purchasing power which is the
support for 60 percent of the economy to fall deep
enough. This is evidenced by data from the Central
Makartiningrum, ., Adriel, D., Ilyas, A. and Sanny, L.
The Impact of Satisfaction and Environmental Uncertainty on Commitments Mediated by the Franchisee’s Trust.
DOI: 10.5220/0011243800003376
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2021), pages 221-227
ISBN: 978-989-758-602-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
221

Statistics Agency (BPS) which recorded that
household consumption fell from 5.02 percent in the
first quarter of 2019 to 2.84 percent in the first quarter
of 2020. The second impact, namely the pandemic,
caused prolonged uncertainty so that investment also
weakens and implies cessation of business. The third
impact is that the entire world is experiencing an
economic downturn, causing commodity prices to fall
and Indonesia’s exports to several countries have also
stopped (Morgan et al., 1994).
Based on data, especially in the food and beverage
franchise business sector in Indonesia, for example,
PT Fast Food Indonesia Tbk (FAST), the KFC
franchise rights holder acknowledged the cessation of
operations in some companies, due to the impact of
the corona virus or Covid-19. This termination made
FAST close 115 KFC outlets (Davies et al., 2011).
Then for the current beverage business from Taiwan,
Chatime, to change its operating hours, according to
the applicable mall operating hours to close several
stores in several cities during the pandemic period,
there are 39 outlets that have started to stop operating,
which are spread throughout the cities of Indonesia
(Minarikova et al., 2020). This creates a condition of
uncertainty in terms of denomination or environment
uncertainty. Unpredictable environmental uncertainty
(such as climate change or natural disasters) or the
level of change in the market (such as customer
desires, competitor challenges and technological
changes) that lead companies to respond either now
or in the future (Minarikova et al., 2020).
The relationship between the Franchisor and
Franchisee has an important role in the franchise
business. (Latan et al., 2018) state that the important
thing in building relationships in the franchisee field
is to develop a vertical marketing system, for example
franchising and exclusive distribution where
marketers can develop long-term relationships and
contracts between buyers and sellers. In this case,
forming relationships, trust and commitment are three
important factors. Commitment and trust are key
because it encourages marketers to (1) work in
maintaining investment relationships by working
with partners, (2) refuse to take short-term
alternatives in order to expect longterm benefits with
partners, (3) see potential high risk actions as wise
because they believe that partners will not act
opportunistically (Justitia et al., 2019).
The trust that is built between the franchisor and
the franchisee is in the form of control that is
dependent on the two. According to (Sanny et al.,
2017), franchisors generally rely on franchisees to
sell their brands but still with strict rules. So that the
franchisee depends on the franchisor for promotional
support and managerial support such as conducting
training. Therefore, the franchisor needs to maintain
the trust that has been given. When the control
between the two is missed until the franchisee doesn’t
trust the franchisor, the contract between the two of
them becomes out of sync, which causes the
franchisee to start not following the existing rules
because they have lost trust.
According to (Allen and Meyer, 1990),
franchisors have a perception that the income they
receive is generally higher than their franchisees. This
means that franchise royalties are usually based on
gross sales figures, while franchisee’s profits are
strongly influenced by operating costs. Then, the
revenue from the franchisor is a collection of a
predetermined percentage of the total income or
profits obtained from the franchisee, so if there is a
problem in terms of an economic downturn, the
franchisor will still get a profit according to that
percentage. So that if there are problems related to the
economy, there can be conflict friction between the
two because of the mismatch of perception. In this
case, trust and commitment must be built on both
parties, trust is a factor that underlies a relationship so
that with mutual trust the relationship between the
two parties is strong enough.
Based on previous researchers who have
conducted research on franchise and trust businesses,
such as research by (labrague et al, 2018) which
tested a model of trust and compliance in franchise
relationships, other researchers, (Chu, 2003) tested
the bright side and the dark side of trust: The
mediating effect of the franchisor owner’s trust in
performance. Research by (Siagian and Cahyono,
2014), regarding the influence of environmental
uncertainty on trust relationships, as well as research
conducted by (Morgan et al., 1994) regarding the
influence of environmental strategy, environmental
uncertainty and management commitment to
corporate environmental performance: The role of
environmental management accounting. Finally, the
research conducted by (Alzola, 2013), regarding the
effect of environmental uncertainty, organizational
commitment, and information asymmetry on the
relationship between budget participation in
manufacturing companies in Surabaya.
According to several previous studies that have
been mentioned above, research has not been found
that combines the variables of Satisfaction,
Environmental Uncertainty, Commitments and Trust.
Therefore, we will conduct a research entitled The
Impact of Satisfaction and Environmental
Uncertainty on Commitments Mediated by The
Franchisee’s trust. The results of this study are
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
222
expected to help franchisees, especially in the field of
food and beverage companies, to be more optimal in
running their business.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The development of the franchise at this time can be
said to be worldwide, even its development has been
very rapid in Indonesia, both international franchises
and local brands. This is driven by the entrepreneurial
spirit and creativity of the community to build their
economic independence. Franchise is a form of
business strategy that aims to expand the reach of its
business in increasing market segment and sales.
Satisfaction from the franchisee side is found when
someone’s expectations match the perceived
performance of a given product or service. Loyalty is
earned when a customer repurchases a service or
product or recommends it to a potential new
customer. Satisfaction has a direct positive
correlation with loyalty (Padin et al., 2017).
Commitment is defined as an attitude that has a
strong desire to remain in an organization, tries hard
according to the wishes of the organization, and
believes in the acceptance of organizational values
and goals (Hogevold et al., 2019). Organizational
commitment is defined as an emotional relationship
between employees and the organization which
consists of affective commitment, normative
commitment, and ongoing commitment.
Trust is a trust based on integrity and reliability as
well as dependence between consumers and providers
(Rusman and Karim., 2017). According to (Hogevold
et al., 2019) describes several indicators of trust such
as best service, consistent, complete, valuable, and
keeping promises. Then (Wasiati, 2019) add that trust
is the willingness of a company to depend on its
business partners. According to (Mowday et al, 1979)
trust is a belief from one party regarding the
intentions and behavior of the other party, thus trust
is defined as an expectation that service providers can
be trusted or relied on in fulfilling their promises.
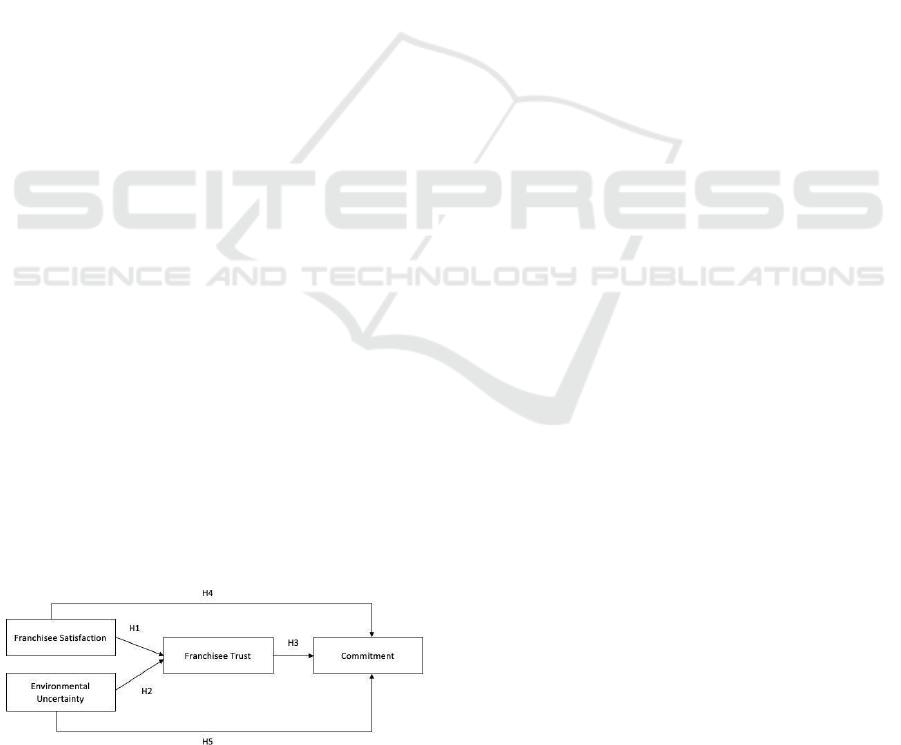
Figure 1: Research model.
Satisfaction is a manifestation of the other’s
capacity to fulfil relational norms, and this can
generate trust. The perception of expectations
regarding the quality of the franchise exchange is of
course how to produce a relationship between the two
parties, namely the Franchisee and Franchisor.
Satisfaction in economic terms is based on
distributive equity and equity exchanges, and leads
directly to trust in the franchisor and his competencies
(Kasali, 2018). Meanwhile, trust can be defined as a
willingness to trust in another partner in a business
context where actions taken by one partner can make
another vulnerable (Etikan et al., 2016). Based on this
description, our first hypothesis is:
2.1 H1: Franchisee Satisfaction Has a
Positive Impact on Franchisee
Trust
Under environmental uncertainty, one expects the
level of trust in the organization to change because
the circumstances we interact with may change;
otherwise, the imminent interaction seems to be over.
Therefore, environmental uncertainty limits the
development of trust within the firm due to growing
behavioral uncertainty. The higher the environmental
uncertainty, the greater the need to incorporate risk
into decisions, and the greater the need for trust. As
Sako and Helper (1998) in (Etikan et al., 2016), the
greater the level of environmental uncertainty, the
greater the benefit of being able to trust a trading
partner, because trust facilitates decision making in
unforeseen circumstances or environmental
uncertainty.
2.2 H2: The Effect of Environmental
Uncertainty on Franchisee Trust
If in partnership both parties trust each other, they
will be confident in their reliability and integrity
which will then result in a commitment from each
party. As business partners who can repeatedly
interact with each other, the trust and commitment
that has been built will be able to grow (Labrague et
al, 2018) in (Chu, 2003). Based on the perspective of
the sales process, Svensson et al., (2010) argue that
trust is an antecedent to commitment.
2.3 H3: Franchisee Trust Has a
Positive Impact on Commitment
Franchisees get satisfaction based on how well the
relationship with the franchisors can meet their
expectations (Kotler, 2012) Based on research
The Impact of Satisfaction and Environmental Uncertainty on Commitments Mediated by the Franchisee’s Trust
223
conducted by (Justitia et al., 2019) regarding the role
of commitment and relationship satisfaction on
franchisee loyalty, found that in testing the
commitment between the franchisee and the
franchisor, the results showed that the effect of
commitment was lower than franchisee satisfaction.
In this study, the franchisee seems less satisfied with
the franchisor’s attitude. The franchisor’s attitude is
one of several dimensions that are asked of the
franchisee in addition to support from the franchisor,
payment time, payment method and time to receive
materials. In particular, it is said that although the
franchisor provides all facilities to the franchisee
based on the franchise agreement, the franchisor does
not consider the franchisee’s opinion, especially in an
effort to develop a marketing strategy to increase
sales of the products it sells.
2.4 H4: Indirect Influence of
Franchisee Satisfaction on
Commitment with Franchisee’s
Trust as a Mediating Variable
Based on previous research that tested the Effect of
Environmental Uncertainty on Commitment, it was
stated that testing for Environment uncertainty had a
positive effect on Organizational Commitment (Latan
et al., 2018). Organizational commitment in this study
is because organizational commitment shows strong
belief and support for the values and goals that the
organization wants to achieve (Minarikova et al.,
2020). A strong organizational commitment within
the individual will cause individuals to strive to
achieve organizational goals in accordance with the
interests that have been planned. In this era of
disruption, uncertainty is something that is of concern
to both employees and companies. Uncertainty
affects employee motivation at work (Davies et al.,
2011) Individual beliefs or commitments in taking
jobs, identify with workrelated roles, they will
become committed to doing work and behave in
accordance with the expectations of the job (Sheth et
al., 2012).
3 METHODOLOGY
The population in this study were food and beverages
franchisees in Jakarta areas. The technique used is
convenience sampling. Convenience sampling (also
known as Haphazard Sampling or Accidental
Sampling) is a type of non-probability or non-random
sampling in which members of a target population
meet certain practical criteria, such as easy
accessibility, geographic proximity, availability at
certain times, or willingness to participate .
Convenience Sampling is a sampling that is quite
affordable, easy and the subject is readily available.
Of the total population, it is possible that the number
of samples collected from this quota sample consists
of 50-100 respondents who have business food and
beverages franchisees.
4 RESULTS AND FINDINGS
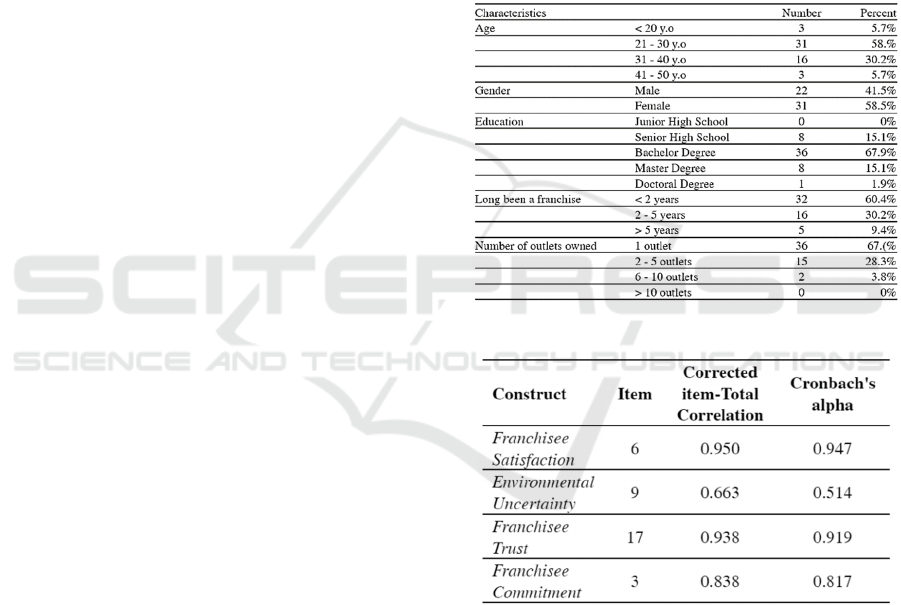
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics of the Respondent.
Table 2: Reliability Consistency Test Results.
Through the results of the reliability test of the four
variables, it is known that the first variable, namely
Franchisee Satisfaction, has a Cronbach Alpha
coefficient value of 0.947 which means that the
internal consistency is very good (r
> 0.9). The second
variable, Environmental Uncertainty has a Cronbach
Alpha coefficient value of 0.514, meaning that the
internal consistency is categorized as less reliable (r
<0.6). The third variable, Franchisee Trust, has a
Cronbach Alpha coefficient of 0.919, meaning that
the internal consistency is very good (r
>0.9). And the
last variable, Franchisee Commitment, has a
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
224

Cronbach Alpha coefficient value of 0.817 meaning
that the internal consistency is categorized as good
(r
> 0.8).
Table 3: Result of Normality Test between Variables.
Construct
Kolmogorov-
Smirnov Z
P
Franchisee
Satisfaction &
Trust
0.095 0.200
Environmental
Uncertainty &
Trust
0.131 0.083
Franchisee
Trust &
commitment
0.069 0.200
Through the results of the correlation test using
the Kolmogorov-Smirnov 1-Samples Menu by
looking at the significance value (p), variables that
have a normal distribution will have a p value
(Asymp. Sig.)
> 0.05 and an abnormal distribution is
p
<0.05. From the first three tests, Franchisee
Satisfaction Trust has a normal distribution with a
KolmogorovSmirnov Z value = 0.095 and a
significance value p = 0.200 (p
> 0.05). Second,
Environmental Uncertainty Trust has a normal
distribution with a Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z value =
0.131 and a significance value p = 0.083 (p
> 0.05).
And finally, Franchisee Trust commitment has a
normal distribution with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z
value = 0.069 and a significance value p = 0.200 (p
>
0.05).
Table 4: Results of Hypothesis 1, 2 and 3 Regression Test.
Variable
Regression
Coefficient
thitung Sig.
Franchisee
Satisfaction &
Trust
14.463 4.605 0.000
1.87 8.053 0.000
Environmental
Uncertainty &
Trust
-2.212 -0.385 0.702
1.939 7.203 0.000
Franchisee Trust
& commitment
0.724 0.982 0.332
0.143 7.708 0.000
In the results of the above calculations, hypothesis
1 has a sig value. of the independent variable
Franchisee Satisfaction, which is equal to 0.000
<0.05 so that it has a significant influence on the
dependent variable, namely trust, and the same as the
trust variable on the dependent variable Franchisee
Satisfaction has a value of 0.000
<0.05, which means
that it has a significant influence between the two
variables. In this case, both variables have a
significant effect.
In the results of the above calculations, hypothesis
2 has a sig value. from the independent variable
Environmental uncertainty, which is 0.702> 0.05, so
it does not have a significant effect on the dependent
variable, namely trust, and the trust variable on the
dependent variable Environmental uncertainty has a
value of 0.000
<0.05 which means it has a significant
effect. In this case, when compared, the trust variable
has a significant influence compared to the
environmental uncertainty variable.
In the results of the above calculations, hypothesis
3 has a sig value. from the free variable trust which is
equal to 0.332> 0.05 so that it does not have a
significant effect on the dependent variable, namely
the commitment, and the trust variable on the
commitment bound variable has a value of 0.000
<0.05 which means that it has a significant effect. In
this case, when compared, the variable commitment
has a significant effect compared to the trust variable.
Table 5: Results of Hypothesis 1, 2 and 3 Regression Test.
Variable p-value
Franchisee Satisfaction,
Commitment & Trust
0.0047
0.0050
0.0044
Franchisee Trust,
Environmental
Uncertainty &
Commitment
0.0001
0.0001
0.0000
From the results of the above calculations using
the Sobel test, in Hypothesis 4, the indirect effect of
Franchisee Satisfaction on Commitment with trust as
mediation, has a value of 2,824 with P value: 0.0047,
0.0050, and 0.0044 where the P value
<0.01 which
means that trust mediates the relationship Indirectly
variable Franchisee Satisfaction with Commitment.
From the results of the above calculations using the
The Impact of Satisfaction and Environmental Uncertainty on Commitments Mediated by the Franchisee’s Trust
225

Sobel test, in Hypothesis 5, the indirect effect of
Environmental Uncertainty on Commitment with
trust as mediation has a value of 2,824 with a P value:
0.0001, 0.0001, and 0.0000 where the P value
<0.01
which means that trust mediates the relationship
indirectly the Environmental Uncertainty variable on
Commitment.
5 CONCLUSION
on the results of data analysis described in chapter IV,
both hypothesis 1, hypothesis 2 and hypothesis 3 are
accepted and have an influence on this study. Where
hypothesis 1 shows that satisfaction has a positive
effect on trust, hypothesis 2 shows that environmental
uncertainty has a positive effect on trust, and
hypothesis 3 on trust has a positive effect on
commitment. On the results of data analysis described
in chapter IV, the hypothesis with the mediation
variable Trust tested using the sobel test is also
accepted and Trust as the mediating variable is
proven to have a direct effect. For hypothesis 4 with
P values: 0.0047, 0.0050, and 0.0044 where the P
value < 0.01, which means that trust mediates the
indirect relationship of the Franchisee Satisfaction
variable to Commitment. Then hypothesis 5 with the
value of P: 0.0001, 0.0001, and 0.0000 where the
value of P
< 0.01, which means that trust mediates the
indirect relationship of the variable Environmental
Uncertainty to Commitment.
REFERENCES
Franchise business. FLEI 2019: Franchise Business
Believed to Grow 5% / Bisnis waralaba. FLEI 2019:
Bisnis Waralaba Diyakini Tumbuh 5% Tahun Ini.
(2019). Diunduh 16 Desember 2019. Dari:
https://ekonomi.bisnis.com/read/20190905/12/114495
9/flei-2019-bisnis-waralaba-diyakini-tumbuh-5-tahun-
ini
Get to know the franchise business. Get to know the
problems that often occur in a franchise business /
Mengenal bisnis waralaba. Mengenal Problem yang
Sering Menimpa Bisnis Franchise. (2019). Diunduh 03
April 2020. Dari: http://kerajaanbisnis.com/mengenal-
problem-yang-sering-menimpa-bisnis-franchise/
Franchise business constraints. Predicted Franchise
Business Growth Reach 10 Percent / Kendala bisnis
waralaba. Pertumbuhan Bisnis Waralaba Diprediksi
Mencapai 10 Persen. (2019). Diunduh 10 februari 2020.
Dari: https://bisnis.tempo.co/read/1221712/pertumbu
han-bisnis-waralaba-diprediksi-mencapai-10-persen
Corona Virus: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and When
to See a Doctor Immediately / Virus Corona: Penyebab,
Gejala, Pencegahan, dan Kapan Harus Segera ke
Dokter. (2019). Diunduh 06 Agustus 2020. Dari:
https://www.kompas.com/tren/read/2020/03/31/16200
0665/virus-corona--penyebab-gejala-pencegahan-dan-
kapan-harus-segera-ke-dokter?page=all.
Three Great Impacts of the Covid-19 Pandemic on the
Indonesian Economy / Tiga Dampak Besar Pandemi
Covid-19 bagi Ekonomi RI. (2020). Diunduh 06
Agustus 2020. Dari: https://republika.co.id/berita/
qdgt5p383/tiga-dampak-besar-pandemi-covid19-bagi-
ekonomi-ri.
KFC closes 115 outlets due to Covid-19 / KFC Tutup 115
Gerai karena Covid-19. (2020). Diunduh 06 Agustus
2020. Dari: https://economy.okezone.com/read/2020/
05/21/278/2217647/kfc-tutup-115-gerai-karena-covid-
19
List of temporarily closed Chatime stores! / Daftar Store
Chatime yang Tutup Sementara! (2020). Diunduh 05
Agustus 2020. Dari: https://indonesia.chatime.com.tw/
daftar-store-chatime-yang-tutup-sementara/
Latan, H., Jabbour, C.J.C., Jabbour, A.B.L.S., Wamba,
S.F., & Shahbaz, M. (2018). Effects of environmental
strategy, environmental uncertainty and top
management's commitment on corporate environmental
performance: The role of environmental management
accounting. Journal of Cleaner Production, 297-306
Sheth, J., Parvatiyar, A., & Sinha, M. (2012). The
Conceptual Foundations of Relationship Marketing:
Review and Synthesis. Economic Sociology_The
European Electronic Newslatter, Cologne, 13(3), 4-26.
Morgan, Robert, M & Shelby, D.H. (1994). The
Commitment – Trust Theory of Relationship
Marketing. Journal of Marketing, 20-38.
Davies, M.A.P., Lassar, W., Manolis, C., Prince, M., &
Winsor, R.D. (2011). A model of trust and compliance
in franchise relationships. Journal of Business
Venturing, 321-340.
Minarikova, D., Mumdziev, N., Griessmair, M., &
Windsperger, J. (2020). The bright side and dark side
of trust: The mediating effect of franchisor trust on
performance. Managerial and Decision Economics,
41(1), 116-129.
Zanini, M.T.F., & Almeida, A.L.C. (2009). The impact of
environmental uncertainty on trust relationships. 44 (4),
313-326.
Latan, H., Jabbour, C.J.C., Jabbour, A.B.L.S., Wamba,
S.F., & Shahbaz, M. (2018). Effects of environmental
strategy, environmental uncertainty and top
management's commitment on corporate environmental
performance: The role of environmental management
accounting. Journal of Cleaner Production, 297-306.
The Effect of Environmental Uncertainty, Organizational
Commitment, Information Asymmetry, on the
Relationship Between Budget Participation and
Budgetary Slack in Manufacturing Companies in
Surabaya/ Soka, Y. G. (2013). Pengaruh Ketidakpastian
Lingkungan, Komitmen Organisasi, Informasi
Asimetri, Terhadap Hubungan Antara Partisipasi
Anggaran dan Senjangan Anggaran Pada Perusahaan
ICRI 2021 - International Conference on Recent Innovations
226

Manufaktur di Surabaya. Skripsi Universitas Katolik
Widya Mandala Surabaya.
Justitia, A., Semiati, R., & Ayuvinda, N. R. (2019).
Customer satisfaction analysis of online taxi mobile
apps. Journal of Information Systems Engineering and
Business Intelligence, 5(1), 85-92.
Sanny, L., Abdurachman,E., Simatupang,B & Heriyati, P.
(2017). Franchising Performance from Franchisee
Perspective: Case in Education Franchising in
Indonesia. Global Business Review, 18(3), 1-12.
Allen, N. J., & Meyer, J. P. (1990). The measurement and
antecedents of affective, continuance and normative
commitment to the organization. Journal of
Occupational Psychology, 63(1), 1 – 18
Labrague, L. J., McEnroe – Petitte, D. M., Tsaras, K., Cruz,
J. P., Colet, P. C., & Gloe, D. S. (2018). Organizational
commitment and turnover intention among rural nurses
in the Philippines: Implications for nursing
management. International Journal of Nursing
Sciences, 5(4), 403 – 408.
Chu, Y. (2003). The drivers and antecedents of satisfaction,
trust, commitment and loyalty among Chinese
customers. Expert System Via Application, 24, 124-
142.
Ziqmund William. (2003). Marketing. South-Western
College Pubik.
Kotler, P. dan Keller. (2012). Marketing Management 14th
edition. PT. Indeks Kelompok Gramedia, Jakarta
Siagian, Hotlan & Edwi Cahyono. (2014). Analisis Website
Quality, Trust dan Loyalty Pelanggan Online Shop.
Jurnal Manajemen Pemasaran, 8(2), 55-61.
Monroy dan Alzola. (2005). An analysis of Quality
Management in Franchise Systems. European Journal
of Marketing, 39, 585
Padin, C., Ferro, C. and Svensson, G. (2017), “Validity and
Reliability of Satisfaction as A Mediator Between
Quality Constructs in Manufacturer–Supplier
Relationships Through Time and Across Contexts”,
Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 24(1), 1-
17.
Hogevold, N., Svensson, G., & Neira, C.O. (2019). Trust
and commitment as mediators between economic and
non-economic satisfaction in business relationships: a
sales perspective. Journal of business & Industrial
Marketing.
Rusman, R.F.Y dan Karim, I. (2017). The Influence of
Relationship Marketing among Franchisee and
Franchisor in Fried Chicken Local Franchise.
International Journal of Social Science and
Development, 1(2), 163-169.
Wasiati, H. (2019). The Influence of Environmental
Uncertainty, Entrepreneurial Orientation, Innovation
Risk Taking, and Organizational Commitment Against
Organizational Performance. UPAJIWA
DEWANTARA VOL. 3.
Mowday, R. T., Steers, R. M.,&Porter, L.W. (1979). The
measurement of organizational commitment. Journal of
Vocational Behavior, 14, 224–247.
Kasali, R. (2018). Self Disruption, Yogyakarta: Mizan. Lee,
De-Chih., Li-Mei, H., Mei-Ling, C. (2012). Empirical
Study on the Influence among Corporate Sponsorship,
Organizational Commitment, Organizational
Cohesiveness and Turnover Intention. Journal of
Management and Sustainability. Vol. 2 No. 2, Pp. 43-
53
Etikan, I., Musa, S. A., & Alkassim, R. S. (2016).
Comparison of convenience sampling and purposive
sampling. American journal of theoretical and applied
statistics, 5(1), 1-4.
The Impact of Satisfaction and Environmental Uncertainty on Commitments Mediated by the Franchisee’s Trust
227
