
External and Internal Factors Affecting the Socio-economic Situation
of the EAEU during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Alexandra A. Kaskova
a
and Lyudmila A. Trofimova
b
Saint Petersburg State University of Aerospace Instrumentation, Saint-Petersburg, Russia
Keywords: Pandemic, Eurasian Economic Union, Socio-economic Situation, External Environment Factors, Internal
Environment Factors, Saint Petersburg, Sustainable Development.
Abstract: The global spread of the new coronavirus infection has had a strong destructive effect on the socio-economic
situation in the EAEU countries, which required the search for factors that could quickly influence its
improvement. The analysis showed that the factors of the external and internal environment can have both
positive and negative impact on the socio-economic situation in the EAEU. Particular attention should be paid
to the role of internal factors and, first of all, the effectiveness of the work of authorities at all levels, because
they are the ones who are able to control other factors and set the directions for their development, relying on
the resource potential.
1 INTRODUCTION
The pandemic of the new coronavirus infection has
become a serious challenge for the entire world
community. In a short period of time, this caused a
number of negative socio-economic consequences in
many countries, which led to a very deep recession in
the global economy. According to UN estimates, the
global economy contracted by 4.3% in 2020
compared to 2019 due to the spread of COVID-19 and
the widespread introduction of restrictive measures to
contain it (United Nation, 2021). This was the largest
decline since the Great Depression.
One example of the negative impact of the
pandemic is the deterioration of the socio-economic
situation in the countries of the Eurasian Economic
Union. A sharp deterioration in external economic
conditions and the introduction of internal restrictive
measures to limit the spread of coronavirus infection
have led to a weakening of export demand, a decrease
in investment inflows, a deterioration in the business
climate, a decrease in migration flows, a decrease in
the performance of many sectors of the economy, a
reduction in budget revenues, an increase in
unemployment and poverty in each EAEU country
(Sorokina, 2021; Selishcheva, 2021). In this regard,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8379-2602
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3839-8507
additional difficulties have been created for the
implementation of the Concept of Sustainable
Development, proposed by the United Nation in the
90s of the XX century.
In fact, the successful functioning of the EAEU is
a derivative of the successful functioning of the
economies of its member countries. Thus, it can be
argued that the socio-economic problems that have
arisen in the EAEU countries negatively affect the
development of the Union as a whole and
significantly reduce the possibilities of achieving the
ambitious goals of Eurasian integration.
The situation is complicated by the fact that there
are currently no unambiguous forecasts regarding the
timing of the end of the pandemic. In particular, this
is due to the fact that the SARS-CoV-2 virus mutates
rapidly, new more aggressive strains appear, while
the rate of vaccination in the EAEU countries is
growing at an insufficient rate. As of November 1,
2021, only 16.76% of the total population has been
vaccinated in Armenia, in Belarus — 29.22%, in
Kazakhstan — 44.04%, in Kyrgyzstan — 15.21%, in
Russia — 39.72% (Minfin, 2021).
The ambiguity of epidemiological forecasts
complicates the fight against the consequences of a
pandemic and the choice of its strategy. This requires
404
Kaskova, A. and Trofimova, L.
External and Internal Factors Affecting the Socio-economic Situation of the EAEU during the COVID-19 Pandemic.
DOI: 10.5220/0011121400003439
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific and Practical Conference "COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals" (RTCOV 2021), pages 404-409
ISBN: 978-989-758-617-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
a search for factors that can affect the socio-economic
situation of the integration association.
2 METHODOLOGY
The theoretical basis of this study was the work of O.
L. Goikher, U. Kanykei and others in the field of the
content and characteristics of external and internal
factors of economic systems. Certain aspects of the
functioning of the Eurasian economic were
considered in the works of A.V. Bredikhin V.E.
Frolov, T.A Meshkova and others. The socio-
economic consequences caused by the coronavirus
pandemic were described in the works of L.E. Slutsky
and E.A. Khudorenko.
In addition, numerous various analytical materials
were used, which contain certain aspects of the socio-
economic development of the EAEU countries during
the pandemic, prepared by the United Nations, the
World Bank, the World Trade Organization, the
Eurasian Economic Commission, the Central Bank of
the Russian Federation and the Eurasian
Development Bank.
This work was based on such theoretical methods
as analysis, synthesis, and generalization.
3 RESULTS OF THE STUDY
Considering the factors affecting the socio-economic
situation in the EAEU, it is important to note that this
is a macroeconomic concept. According to the
authors, it characterizes not only the current state of
the social and economic spheres, but also the
possibilities of their development in a specific time
period.
The EAEU is a regional integration association of
five countries, which ensures the freedom of
movement of goods, services, capital, labour and the
conduct of a coordinated, agreed or unified policies in
key sectors of the economy to achieve sustainable
economic growth in the long term (Treaty on the
Eurasian Economic Union, 2021).
Based on these provisions and on the research of
Goikher and Laryushkina (2013), we can conclude
that the Union has all the features characteristic of
economic systems, including:
the interconnectedness of system elements;
the certain territory;
the presence of multifunctional connections
between the elements;
the presence of socio-economic relations;
the motivation of the participants;
the presence of various mechanisms of
interaction (Goikher and Laryushkina, 2013).
Consequently, based on the principles of
functioning of such systems, the EAEU is influenced
by factors of both external and internal environment.
Traditionally, the internal environment of any
economic subject is understood as a set of factors that
are controlled by this subject and affects his activities.
In turn, the external environment arises and exists
independently of the activity of an economic subject,
but at the same time it has a certain influence on it. In
contrast to the internal environment, it is
characterized by greater uncertainty and the rate of
change (Panasyuk, Pudovik and Vakhterova, 2019).
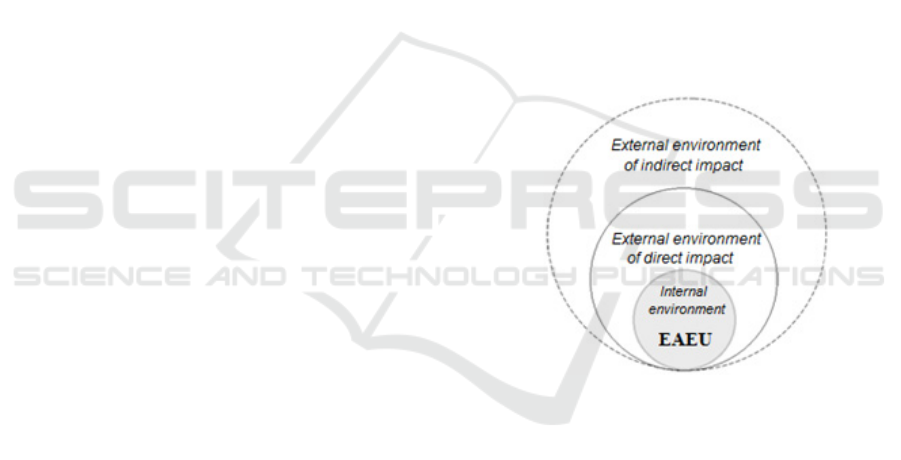
The external environment of direct impact includes
factors that directly and purposefully affect the
activity of an economic subject. On the contrary, the
external environment of indirect impact includes
factors that affect it indirectly and may not have a
quick impact. It is important to note that both
environments exist in close relationship (Figure 1).
Figure 1: External and internal environment of the
integration association.
There are many factors of the external and internal
environment that differ in their effects. The analysis
of these factors is complicated by the fact that some
of them affect individual countries, and only later can
transfer the effect to the entire association. Due to the
complexity of the analysis of all factors, it is
advisable to further consider them in generalized
groups.
The following factors of the internal environment
affecting the socio-economic situation of the EAEU
can be noted:
activities of supranational and national
authorities;
production and resource potential;
the development of legal and financial
institutions;
External and Internal Factors Affecting the Socio-economic Situation of the EAEU during the COVID-19 Pandemic
405

the state of public infrastructure;
the educational level of the population;
the level of scientific, technical and innovative
development, etc.
The specificity of the internal environment
determines that among the indicated factors, a special
role belongs to the activities of supranational and
national authorities, because they can control other
factors and determine the directions of their
development, relying on resource potential.
Thus, the activities of the supranational
authorities of the EAEU (Supreme Eurasian
Economic Council, Eurasian Economic Commission)
are mainly aimed at shaping a common agenda for
Eurasian integration and at making decisions, orders
and developing recommendations that relate to the
economic interaction of the member states. At the
same time, responsibility for the practical
implementation of many acts remains in the
competence of national government bodies, including
at the level of individual administrative-territorial
units (cities, regions, etc.).
The importance of administrative-territorial units
and territorial authorities in achieving the goals of
Eurasian integration is steadily increasing, because
they are able to coordinate their implementation,
taking into account local specifics and available
resources. Moreover, many of these units can become
drivers of the Union's socio-economic development
due to the existing opportunities. Mainly, these are
the largest cities of the EAEU, which have a
developed industry, transport system, scientific,
educational and cultural spheres. Thanks to this, they
are able to take an active part in political and socio-
economic processes of both national and
supranational scale (Bredikhin, 2017).
For example, Saint Petersburg is such a city,
because the issues of Eurasian integration occupy a
special place in its activities. Currently, the city is the
most important political and diplomatic center in the
EAEU. It is a frequent meeting place for the political
elites of the member states, and is also a platform for
events dedicated to integration issues. In addition,
Saint Petersburg is actively developing partnerships
with many cities and regions of the EAEU countries.
Among them: Yerevan, Minsk and Minsk region,
Alma-Ata and Nur-Sultan, Osh and Bishkek
(Government of Saint Petersburg, 2021). The city
also has a practice of signing “diagonal” cooperation
agreements with Belarus and Kyrgyzstan (Frolov,
2015). At the same time, occupying leading positions
in a number of indicators of socio-economic
development among Russian regions, it is able to
significantly influence the socio-economic situation
of the integration association. The city receives on its
territory huge migration flows from the EAEU
countries and actively develops trade and investment
relations with them (Trofimova and Kaskova, 2021).
Turning to the factors of the external environment
of direct impact on the socio-economic situation of
the EAEU should consider:
the influence of third countries;
the influence of international organizations and
development institutions.
The context of influence of third countries can
imply both cooperative and confrontational relations.
Of course, cooperative relations can largely
contribute to the formation of a favorable socio-
economic situation in the EAEU. For example, at
present the Union is actively developing relations
with the countries that are members of ASEAN,
BRICS and SCO, with the aim of mutual exchange of
experience and expansion of economic cooperation.
Also, the international dialogue on the Latin
American direction is intensively developing: the
Union has documented relations with the Andean
Community, the Pacific Alliance and the Southern
Common Market (Meshkova, Izotov, Demidkina and
Kofner, 2019).
At the same time, there are rather problematic
relations in the Euro-American vector, which is
mainly associated with the introduction of sanctions
by Western countries against Russia and Belarus, as
well as the reciprocal acceptance of counter-sanctions
by these countries. The policy of mutual sanctions
significantly complicates the development of
international economic cooperation, interferes with
negotiation processes and has a significant
destabilizing effect on the socio-economic situation
in these countries. According to some estimates, the
sanctions against Belarus, which were imposed due to
disagreement with the results of the presidential
elections in August 2020, could bring the total
economic damage to the country in the amount of 7-
8% of GDP (DW Akademie, 2021). In turn, the
damage to Russia is estimated at more than $50
billion after the imposition of sanctions in 2014 due
to the Ukraine crisis (TASS, 2021).
As for the influence of international organizations
and institutions on the socio-economic development
of integration associations, today these structures
perform a number of important functions. They act as
research centers for various socio-economic
problems, developing ways to solve them
(recommendations, humanitarian and financial
assistance, etc.) and coordinating international
cooperation in problem areas. This is confirmed by an
analysis of the interaction of the EAEU countries with
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
406

international organizations and institutions.
Unfortunately, the EAEU cannot take full advantage
of the advantages of this interaction due to the strong
politicization of economic processes.
Considering the factors of the external
environment of indirect impact, it should be noted
that they set the general directions for the
development of the entire world economic system
and, therefore, are of the most complex nature
(Kanykei, 2018). In general terms, these include:
pandemics,
a global competition,
the cyclical nature of the world economy,
socio-demographic trends,
the acceleration of the pace of scientific and
technological progress, etc.
In particular, the problem of the COVID-19
pandemic today determines many trends in world
development and has a direct impact on all other
specified factors.
Thus, the spread of coronavirus infection led to a
decrease in world trade in goods by 8% in 2020
compared to 2019. Trade in services decreased by
21% over the same period (WTO, 2021). Forecasts
for 2021 are quite optimistic: the world economy is
expected to recover by 5.6% compared to the
previous year, and world trade may grow by 10.8%
(World Bank, 2021). However, many countries
continue to strengthen their policies of imposing
barriers and restrictions on international trade due to
unfavourable external conditions and the protracted
nature of the pandemic (Ministry of Economic
Development of the Russian Federation, 2021). Of
course, this negatively affects the development of
global competition and reduces the opportunities for
economic recovery in individual countries by
increasing export volumes.
An equally important aspect of the impact of the
pandemic on world economic development is the
exacerbation of global imbalances, which can lead to
a systemic crisis even in conditions of post-СOVID
economic recovery. According to the Central Bank of
Russia, the likelihood of a systemic crisis could
significantly increase “if a rapid and significant
tightening of monetary policy in the United States is
superimposed on the bursting of bubbles in asset
markets” (Bank of Russia, 2021).
It should also be noted that the pandemic had a
serious impact on the territorial mobility of the
population both between countries and within
individual states due to the introduction of a huge
number of internal restrictions and the closure of
borders. The widespread decline in labour migration
has contributed to increased unemployment and
poverty in many countries. This has become a serious
problem for the EAEU countries, and mainly for
Russia, which receives huge migration flows from
allied countries on its territory and largely depends on
the labour of migrants. According to the EEC, in 2020
the migration growth of Russia from other EAEU
member states decreased by more than 10 times: in
2019 it was 95.9 thousand people, in 2020 – 6.6
thousand people (Eurasian Economic Commission,
2021).
An important trend provoked by the pandemic is
the strengthening of the role of science and an
increase in its funding (Slutsky and Hudorenko,
2020). Thus, the scientific community was tasked
with the early development of a vaccine and treatment
for COVID-19.
The increase in the growth of e-commerce, the
widespread transition to distance learning in
universities and schools, the transfer of many
enterprises to remote work, led to the acceleration of
digitalization, which became part of the competitive
indicators for enterprises and countries.
Thus, factors of the external and internal
environment can have both positive and destructive
effects on the socio-economic situation of the EAEU,
which is confirmed by the analysis performed. The
pandemic has changed the conditions for the
functioning of economies, which sets before the allied
countries both the task of overcoming its negative
consequences and the task of adapting economies to
new conditions. Of course, the solution of these tasks
can be favoured by the expansion of interaction with
third countries and international organizations and
institutions. Unfortunately, the peculiarities of the
political situation can prevent the establishment of
this interaction and further shift the emphasis towards
the factors of the internal environment, which were
previously described.
4 DISCUSSION
According to the experts of the Accounts Chamber of
Russia, the spread of COVID-19 and the socio-
economic problems provoked by it seriously
worsened the possibilities of achieving the entire list
of Sustainable Development Goals that were
established by the UN (Accounts Chamber of Russia,
2021). The pandemic not only cancelled out previous
gains in improving living standards and well-being of
the population, but also created risks for increasing
inequality between countries. According to IMF
forecasts, the economies of developed countries will
be able to recover their pre-pandemic indicators as
External and Internal Factors Affecting the Socio-economic Situation of the EAEU during the COVID-19 Pandemic
407
early as 2022, but the vast majority of developing
countries may take “many more years” due to
extremely high inflation rates, growing budget
deficits and a significant increase in the volume of
public external debt (IMF, 2021). It should be noted
that these obstacles exist in most of the EAEU
countries. In 2020, in relation to 2019, inflation in the
EAEU as a whole amounted to 5.4%. Moreover, the
average inflation rate in the EAEU in the first quarter
of 2021 amounted to 6.7%, which significantly
exceeds the target values (Eurasian Economic
Commission, 2021).
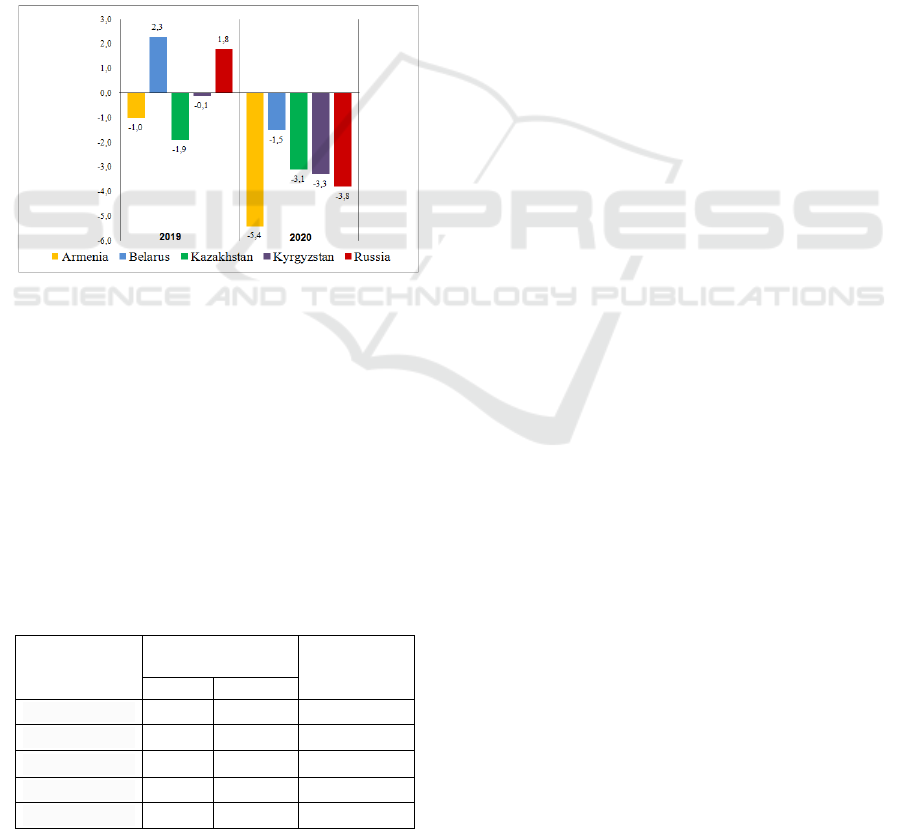
In 2020, there was an increase in the budget deficit
in all EAEU countries due to a decrease in revenues
and an increase in budget spending on health care and
measures to support the economy and the population
(Figure 2).
Figure 2: Budget deficit/ surplus, % of GDP (Eurasian
Economic Commission, 2021
).
In 2020, the size of the republican budget deficit
increased in Armenia, Belarus, and Kyrgyzstan to
5.4% of GDP, 3.1% of GDP and 3.3% of GDP,
respectively. In turn, budget surpluses were replaced
by deficits in Belarus (1.5% of GDP) and Russia
(3.8% of GDP).
Due to the lack of own funds for economic
recovery, the EAEU countries, except for Russia,
increased external borrowing, which affected the
growth of external public debt (Table 1).
Table 1: Public external debt in the EAEU in 2019-2020.
Country
Public External
Debt, US $ bln
Year-on-year
growth, %
2019 2020
Armenia 5.8 6.0 ▲4.6
Belarus 17.1 18.6 ▲8.4
Kazakhstan 15.2 16.4 ▲7.6
Kyrgyzstan 3.9 4.2 ▲9.5
Russia
41.6 39.1 ▼6
Source: (Eurasian Economic Commission, 2021).
Russia continued the course to reduce the external
debt burden, even in the context of the pandemic. On
the contrary, other countries of the Union actively
resorted to borrowing from other organizations and
international development institutions, including the
IMF, IBRD, EBRD, ADB, IFC and others. However,
an increase in external public debt with insufficient
GDP growth is associated with great financial risks
for the EAEU countries. According to EDB forecasts,
the economies of Armenia, Kyrgyzstan will not be
able to reach the pre-crisis level in 2021, while the
protracted nature of the spread of COVID-19 and its
socio-economic consequences can only contribute to
a further increase in external borrowing (Eurasian
Development Bank, 2021).
According to the authors, the current situation has
shown the importance of creating its own financial
support mechanism within the EAEU and confirmed
the conclusions about the important role of its own
resources and reserves.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Currently, the global spread of the new coronavirus
infection has had a strong destructive impact on the
socio-economic situation of the EAEU countries.
This required a search for factors that can quickly
affect its improvement. The factors of the internal and
external environment were identified as influencing
factors. Their interaction and significance in a given
time interval have been described.
The results of the study showed that the specificity
of the internal environment is associated with a
special role that belongs to the activities of
supranational and national authorities. They are the
ones who are able to control other factors and
determine the directions of their development.
Unfortunately, at the present stage they cannot fully
express themselves, due to the fact that the Union is a
fairly young association, which is just entering the
stage of revealing its integration potential.
In this situation, it is proposed to pay particular
attention to the role of internal factors and, first of all,
to the efficiency of the work of authorities at all levels
and the presence of their own resource potential. At
the same time, much attention should be paid to
constant analysis of the current socio-economic
situation and mutual exchange of experience with
third countries.
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
408

REFERENCES
Accounts Chamber of Russia, 2021. How coronavirus
affects the achievement of the Sustainable
Development Goals. https://ach.gov.ru/news/kak-
koronavirus-vliyaet-na-dostizhenie-tseley-ustoychivo
go-razvitiya-usugublenie-problem-i-zelenye-p.
Bank of Russia, 2021. Main directions of the unified state
monetary policy. https://cbr.ru/Content/Document/File/
126064/on_project_2022(2023-2024).pdf.
Bredikhin, A.V., 2017. The place and role of cross-border
agglomerations in the Eurasian Economic Union,
Gumanitarnyye nauki. Vestnik Finansovogo
universiteta (Humanitarian sciences. Bulletin of the
Financial University), 1 (25), pp. 64-72.
DW Akademie, 2021. The fourth package of EU sanctions
will squeeze the Belarusian economy. https://www.dw.
com/ru/chetvertyj-paket-sankcij-evrosojuza-sozhmet-
belorusskuju-jekonomiku/a-58004389.
Eurasian Development Bank, 2021. Macroeconomic Outlook
2022. https://eabr.org/upload/iblock/bed/EDB-
Macroreview_November-2021_Summary_EN.pdf.
Eurasian Economic Commission, 2021. EAEU statistics.
http://www.eurasiancommission.org/ru/act/integr_i_ma
kroec/dep_stat/union_stat/Pages/default.aspx.
Frolov, V.E., 2015. Saint Petersburg as one of the key points
in the development of Eurasian integration. Eurasian
integration: economics, law, politics, 2, pp. 147-154.
Goikher, O. L., Laryushkina, A. A., 2013. Economic
system: concept, types, properties. Vestnik GUU
(Bulletin of the SUM), 16, pp. 246-250.
Government of Saint Petersburg, 2021. Cooperation with
foreign partners. https://kvs.gov.spb.ru/en/cooperation-
with-foreign-cities-and-regions/st-petersburg-countries
-world/stpetersburg-member-states-cis/.
IMF, 2021. Overcoming Divides and Removing Obstacles
to Recovery. https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2
021/10/05/sp100521-md-curtain-raiser-overcoming-
divides-and-removing-obstacles-to-recovery.
Kanykei, U., 2018. The main external factors determining
the development of the national economy, Innovatsii i
investitsii (Innovation and Investment), 1, pp. 63-67.
Kaskova, A.A., Trofimova, L.A., 2021. The role of Saint
Petersburg in the Eurasian Economic Union, European
Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences
EpSBS, 116, pp. 928-936.
Meshkova, T.A., Izotov, V.S., Demidkina, O.V., Kofner,
Y.C., 2019. The EAEU in a changing geopolitical
context: priorities for international cooperation, RUDN
Journal of Political Science, 1, pp. 7-33.
Minfin, 2021. Coronavirus: statistics by country.
https://index.minfin.com.ua/reference/coronavirus/geo
graphy/.
Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian
Federation, 2021. Results of foreign economic activity
of the Russian Federation in 2020 and the first half of
2021. https://www.economy.gov.ru/material/file/
ab03f167412ee7cbc60d8caf776bab70/itogi_ved_v_20
20g_i_1_polugodie_2021.pdf.
Panasyuk, M. V., Pudovik, E. M., Vakhterova, D. A., 2019.
Evaluation method of external environment factors
influencing on socio-economic development of a
region, Gorizonty ekonomiki (Economic horizons),
3(49), pp. 68-72.
Selishcheva, T. A., 2021. Impact of the COVID-19
pandemic on the economy of the Eurasian Economic
Union member countries and the prospects of its
restoration. Izvestiya Sankt-Peterburgskogo
gosudarstvennogo ekonomicheskogo universiteta
(Bulletin of the Saint Petersburg State University of
Economics), 3(129), pp. 36-42.
Slutsky, L.E., Khudorenko, E.A. 2020. EAEU: pandemic
takeaways, Comparative Politics Russia, 11 (4), pp.
123-134.
Sorokina, O.V., 2021. Economic growth in the EAEU
countries in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic,
Kant, 1(38), pp. 64-68.
TASS, 2021. How Russia responded to Western sanctions.
https://tass.ru/info/10064165.
Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union, 2014.
https://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/acc_e/kaz_e/W
TACCKAZ85_LEG_1.pdf.
United Nation, 2021. World Economic Situation Prospects.
https://www.un.org/development/desa/dpad/wp-
content/uploads/sites/45/WESP2021_FullReport.pdf.
World Bank, 2021. Global Economic Prospects, June 2021.
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handl
e/10986/35647/9781464816659.pdf.
WTO, 2021. World Trade Statistical Review 2021.
https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2021_e/
wts2021_e.pdf.
External and Internal Factors Affecting the Socio-economic Situation of the EAEU during the COVID-19 Pandemic
409
