
Problems of Minimizing the Socio-economic Consequences of
COVID-19 Distribution in the Context of Ensuring Political Stability
Oleg Evgenyevich Grishin
1,2 a
, Olga Alekseevna Nesterchuk
1,3 b
and Sergey Ivanovich Popov
1c
1
Peoples' Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), Moscow, Russia
2
Russian State Social University, Moscow, Russia
3
Russian Academy of National Economy and Public Administration under the President of the Russian Federation,
Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Covid 19, Pandemic, Political Stability, Economic Policy, Government Management, Sustainable
Development.
Abstract: In the article, the authors analyze the range of problems associated with the consequences of the spread of
coronavirus infection, making the study focus on resolving socio-economic issues in the context of ensuring
political stability. The urgency of the study is determined by the presence (absence) of the effectiveness of
the functioning of information and communication channels in the social sphere, concerning messages about
public health, prevention of outbreaks of epidemics and pandemics. Recommendations of a socio-political
nature to mitigate the identified negative consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, based on the regional
characteristics of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are in demand. The impact of the pandemic
on the world economy, regional partnerships, socio-economic factors of human existence is noted. It is shown
that different states solve the problems of fighting the virus in different ways. The authors believe that when
solving state problems of minimizing the socio-economic consequences of the spread of COVID-19 in the
context of ensuring political stability, an integrated interdisciplinary approach is required. It has been
demonstrated that it is quite difficult for governments to assess the effects and find effective answers to solving
the problem of minimizing the consequences of the spread of a pandemic coronavirus infection because of its
scale. Some directions of reducing the negative socio-economic consequences of the spread of COVID-19 are
given, taking into account provision of political stability. The authors complement the existing study
approaches to solving the problem of reducing the degree of negative factors affecting the deterioration of the
socio-economic situation in communities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The demand for the study is due to the economic,
political and social consequences during the COVID-
19 pandemic and after its completion. It is important
to compare the actions of governments in
authoritarian and democratic states, to compare the
actions of global and regional international
organizations, to analyze changes in the world order,
the consequences for the socio-economic and
political systems of different countries. It is necessary
to carry out a comprehensive study when studying the
consequences of a pandemic in the context of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0669-1012
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8776-2694
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2171-5817
ensuring political stability. During the pandemic,
different states have transformed their economic
policies in different ways. They calculate human and
economic costs using macroeconomic models in the
short and long term. Economic policy during a
pandemic involves the use of study approaches to
crisis management to find the effectiveness of
monetary policy, fiscal policy and possible economic
solutions in the post-pandemic period. An analysis of
the situation before and after the pandemic is
necessary to develop effective measures of state
policy to revive the national economy, starting with a
basic analysis of the transformation of development
Grishin, O., Nesterchuk, O. and Popov, S.
Problems of Minimizing the Socio-Economic Consequences of COVID-19 Distribution in the Context of Ensuring Political Stability.
DOI: 10.5220/0011117600003439
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific and Practical Conference "COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals" (RTCOV 2021), pages 203-207
ISBN: 978-989-758-617-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
203

to specific tasks of economic policy in each country
in the context of the regional economy and the
conditions of life of society [3; 8; 11]. Therefore, the
stated problem is of interest to political scientists,
sociologists, economists, which once again
emphasizes its scale and urgency of the study. The
core of the study is based on the negative impact on
the national and global economy. The social policy of
the state shall be aimed at correct modeling and
comprehensive regulation of the dynamics of the
pandemic of coronavirus infection by state authorities
and administration, and their significant efforts in the
field of unknown parameters of mass disease,
disclosure of new waves of the pandemic, it is also
necessary to obtain additional information to create
and regulate quarantine measures.
2 STUDY METHODS
When studying the issues of minimizing the socio-
economic consequences of the spread of COVID-19
in the context of ensuring political stability, the
authors used systemic, structural-functional and
interdisciplinary approaches to the problem under
study. The study basis was the publications of
domestic and foreign authors - specialists in the field
of public administration and political stability,
political scientists, sociologists and economists. The
study methods were content analysis of mass media,
participant observation, event analysis, case studies.
3 STUDY RESULTS
The authors believe that minimizing the socio-
economic consequences of the spread of COVID-19
is an integral part of political stability. Stability is a
stable state that is not subject to significant changes.
Stable development, therefore – the ability to
constancy of any parameters of the dynamic state, the
preservation of basic elements during the transition
from one qualitative status to another, from the old to
the new one. As a rule, political stability is considered
as a qualitative condition (property) of the stability of
the system, that is, its state in which the potential is
maintained to autonomously realize relative
constancy within the system and to remain in its
previous specified parameters. “Political stability is
an opportunity that remains with the constancy of
integratively significant parts (even under conditions
of destabilization of some parts of the system), the
likelihood of developing and adapting to
transformations” [1]. The authors agree with this
statement. Political stability, in general terms, implies
a phased, progressive, step-by-step growth of certain
indicators of the vital activity of society and the state,
characterizing them as an integral well and jointly
functioning organism. Political stability can be
viewed as a pivotal factor for socio-economic
stability and security.
It is stated that there are many points of view,
studies, forecasts and practical projects that illustrate
the various directions and paths that states and
societies can follow in the field of sustainable
development and political stability when the
pandemic ends to prepare for a possible repetition of
this kind of crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic has
caused severe human suffering and significant
damage to national economies, affecting both wealthy
and developing countries. It is predicted that the
consequences of the pandemic will be protracted [4].
In this regard, states need to include a wide range of
activities to maintain sustainable development and
political stability in their countries. Currently, there is
an urgent need to create an innovative methodology
to overcome the global crisis provoked by the
coronavirus infection, which has caused serious
damage to the world economy, exacerbating the
problem of poverty (impoverishment), causing a
number of deprivations and jeopardizing the ability to
earn a normal livelihood. Taken together, such
negative impacts can maximize the implementation
of sustainable development programs and preserve
the political stability of states and societies, as well as
form, with the proper approach, new methods and
ways to provide a basis for future government efforts
to restore the previous socio-economic situation.
The analysis showed that Russia ranks sixth in the
ranking of countries calculated in terms of gross
domestic product for October of 2021 [5]. Wherein,
China firmly occupies the leading first place, despite
the fact that it was there that the pandemic began. This
is primarily due to tough and timely measures taken
to curb the spread of the disease. China's GDP is
expected to grow by 8 % in 2021 and by 4.9 % in
2022 [10]. In Russia, small businesses, tourism,
fitness, shoe and clothing stores, and grocery stores
have suffered the most. The population's ability to pay
has fallen sharply. Wherein, food delivery services
have grown exponentially.
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
204
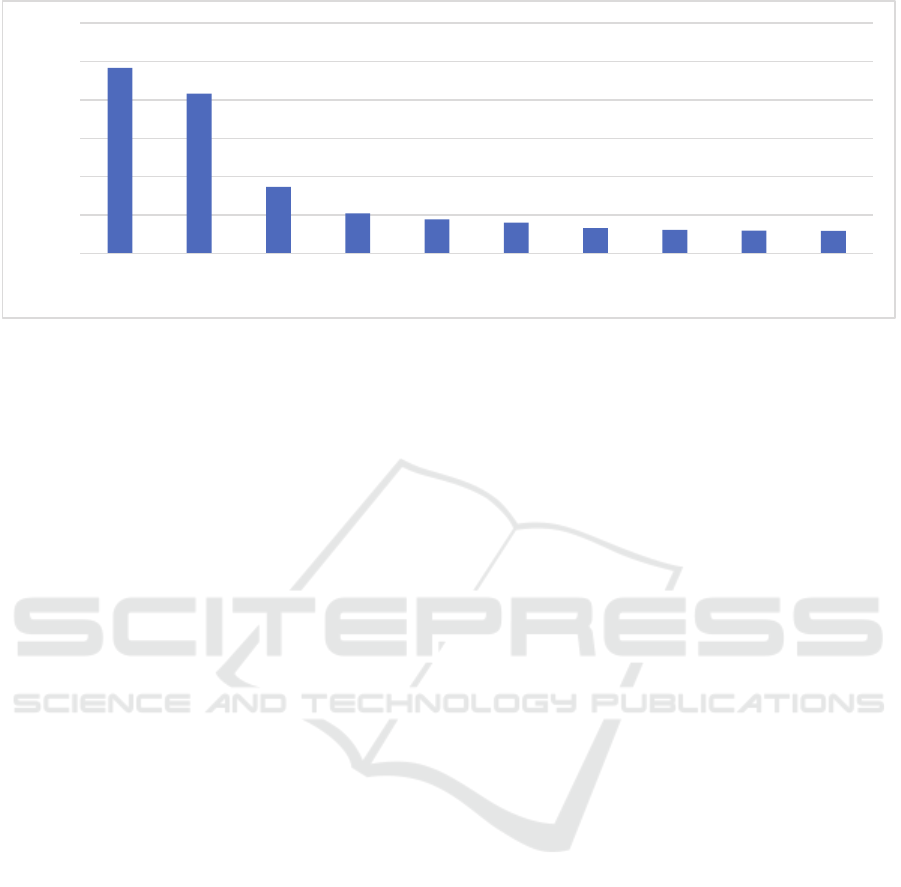
Figure 1: Ranking of countries by gross domestic product in 2021 [5].
The analysis showed that it is quite difficult to
assess the effects and find the correct answers to
government authorities and authorities and specialists
involved in solving the COVID-19 problem due to its
scale. Basically, the study focus is on six main areas:
public health, economics (tourism, agriculture, self-
sufficiency, etc.), finance, social tensions, public
policy and regional partnerships [2]. The
normalization of these areas presupposes the search
for urgent solutions for the system of state
management of the economy and development in
order to balance the life of communities.
Wherein, the original point of view is expressed
by the professor of economics at the University of
UCLA O. Itskhoki, who believes that it was a big
surprise that the lockdown does not have such a
strong effect on economic activity. In his opinion, the
United States gave an interesting example, there are
many states that have implemented different policies
of state regulation of the pandemic. California had
tougher measures, Texas less. However, their
economic trajectories don't diverge very much.
Further, he notes that people themselves strongly
regulate their economic behavior, and the economy is
not so strongly connected with the course of the
pandemic [7].
Therefore, the relevance of the study is necessary
in the context of analyzing the social nature of the
COVID-19 pandemic and the level of its impact, in
its attachment to specific territories and regions,
human-environmental interaction, this is especially
important for the Russian Federation due to its
territorial scale. The limitation of socio-economic
mobility carries a socio-psychological burden for the
population, and, as a rule, economic costs affecting
the representation of the state during this crisis period.
In this regard, adaptive socio-economic instruments
formed and implemented by the Russian state on the
basis of socio-political theories, research and
practices are important.
4 RESULT DISCUSSION
The global pandemic crisis has reduced industrial and
commercial activities, the use of transport, which in
turn has led to a decrease in environmental pollution.
Slowing down economic activity requires the
commitment of public administration to the formation
of new regulations for economic recovery based on
the principles of sustainable development. The
coronavirus has shown the fragility of an economic
system based on maximizing profits and siphoning
resources. This model gave rise to many problems, in
this regard, it is necessary to revise the social goals of
business and create a new sustainable world with the
help of innovative economic tools. Let's suppose that
the new economic policy can be based on energy and
environmental transition plans and projects and on a
circular economy.
The COVID-19 pandemic and the security
measures consolidated with it hit the global economy
and affected the basis of the existing socio-economic
and business models, which have so far undergone
complex multifaceted multifaceted changes.
Industrialized countries are experiencing a prolonged
economic decline and a slowdown in growth rates,
usually associated with demographic and
technological development, growing demand for
asset savings, and etc. This becomes an additional
burden on government budgets. These kinds of trends
limit monetary and tax policies aimed at stabilizing
the economy [9].
The pandemic has exacerbated inequality among
countries and increased the crisis in the economy and
politics, eliminating the tendencies of neoliberalism
0
5 000
10 000
15 000
20 000
25 000
30 000
China USA India Japan Germany Russia Indonesia Brazil United
Kingdom
France
Problems of Minimizing the Socio-Economic Consequences of COVID-19 Distribution in the Context of Ensuring Political Stability
205

with a detrimental effect on the development of
democracy and increased the opportunities for a "left
turn" [6]. The authors of the article agree with this
statement.
It is important to note that the specificity of the
socio-economic policy of Russia was manifested
during the period of the spread of coronavirus
infection. COVID-19 has forever changed the lives of
people around the world, including in Russia. This
situation prompted the state and society to form and
implement different approaches to public
administration and regulation in the socio-economic
and political spheres, to strive for a common constant
desired future. The measures of social and economic
support for Russians are of a large-scale and
unprecedented nature. Currently, a search for new
views on political leadership and public
administration is underway, considering the negative
results of the pandemic, this follows from the
experience of the new management paradigms that
will subsequently allow to effectively cope with
unpredictable and rapidly changing crisis conditions,
complex and ambiguous.
In the context of the crisis and the search for a
balance of systemic social measures implemented by
the state on an ongoing basis, the need for organizing
new models of safe life for citizens, teleworking,
communication, business communications, as well as
building new organizational foundations of health
care that will be able to withstand the challenges of
the pandemic and other potential threats to the life and
health of citizens. Wherein, striving for an effective
result, without causing the development of social
dependency in society.
In a pandemic, many countries are hesitant to
adopt aggressive methods and methods to contain the
spread of coronavirus, believing that this will cause
significant damage to their national economies. A
dilemma arises between saving lives and economic
development. The analysis shows that, nevertheless,
the tough measures of the governments make it
possible to effectively cope with the unfavorable
situation. Enhanced border and entry controls, travel
control throughout the country are among them. Such
measures can negatively affect the stock market, on
the other hand, other restrictions practically do not
affect the stock market return. Therefore, public
policy can be very effective in the fight against
coronavirus. It is therefore important to strike a
balance between tough tackling the pandemic and
economic development.
Therefore, governments in low-income countries
generally find it difficult to cope with the increased
demand for health services, requiring rapid
government and policy decisions to protect the most
vulnerable social groups and affected sectors of the
economy. The analysis of models of socio-economic
assistance to citizens and regions as complex systems
and structures, their modification during a pandemic
is in demand. It is necessary to build a system of
indicators for measuring the effectiveness of the fight
against coronavirus infection in nation states,
describing them using socio-political and
macroeconomic indicators (GDP, government
spending, inequality, infrastructure formation, and
etc.).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Therefore, the analysis showed that insufficient study
and, as a result, the lack of harmonious formation and
implementation of measures to minimize the socio-
economic consequences of the spread of COVID-19
can lead to impoverishment of the population
(poverty) and environmental degradation. It is
necessary to have a clear conceptual framework for
understanding the main problems of sustainable
development in developing and developed countries.
It is necessary to use interdisciplinary and holistic
approaches to assessing the interdependencies
between pandemic threats, industrial activities,
economic risk, poverty and social vulnerability to
facilitate the development and adoption of effective
socio-political decisions in the context of ensuring
political stability actually while minimizing the
socio-economic consequences of the spread of
COVID-19.
The peculiarity of the situation with the
coronavirus infection pandemic lies in the uniqueness
of the actions of the governments of different
countries, which in turn predetermines the wealth of
crisis management experience that shall be studied.
The actions of political leaders and political
institutions were transformed, a new awareness of
cross-border threats emerged, which spread to health
care, economic and socio-political systems.
Therefore, it is necessary to investigate new
mechanisms of the state's socio-economic policy in
the current crisis situation in the context of ensuring
political stability.
The global pandemic affects the social sphere of
an individual's life. It demonstrated that for all the
coverage of the disease, the response to it is local in
nature, as a rule, within one state. In this regard,
effective response methods depend on the level of
development of public administration, the political
situation, use of social technologies and innovations,
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
206

on the perception and behavior of citizens. The
coronavirus pandemic has affected the rich and the
poor, urban and rural segments of the economy,
developed and developing countries and communities
in different ways. It has shaped a new political agenda
for the medium and maybe long term period.
Innovative developments are needed in the
application of socio-economically effective methods
for assessing socio-political risks, especially in the
context of a lack of budgetary resources. This is
especially important for assessing socio-economic
risks in developing countries, given the
underdeveloped regulatory institutions and limited
resources. Overcoming the socio-economic risks
contributes to preservation and maintenance of the
political stability of communities.
We need new approaches to building a model of
interaction "state - business - society". Support and
regulation from the state is required by the affected
sectors of the economy, this is also an important
social task (creation of new jobs, subsidies,
investments, and etc.), thereby affecting the
sustainable development of the national economy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study was carried out with the support of the
Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. The code of
the research and development topic "Technologies for
Ensuring Political Stability in Modern Russia" is
100701-0-000.
REFERENCES
Balbek, R.I., 2019. Technologies for ensuring political
stability in conditions of external destabilizing influences
(on the example of the Republic of Crimea), 51.
Campbell Y., Connell J., 2021. COVID in the Islands: A
comparative perspective on the Caribbean and the
Pacific. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
Singh, S., Singh, L., Vatta, K.l., 2021. Covid-19 Pandemic
and Economic Development. Springer Nature
Singapore Pte Ltd.
Filho W.L., 2021. COVID-19: Paving the Way for a More
Sustainable World. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Danilov, D., 2021. Ranking of the countries of the world in
terms of GDP in 2021: where is Russia?, https://top-
rf.ru/places/161-reiting-stran-mira-po-vvp.html.
Filho, A.S., 2021. The Age of Crisis. Palgrave Macmillan,
Cham. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Karpova, A., 2021. The effect of COVID-19: how the world
economy is experiencing a pandemic and what the
year 2021 will be like, https://www.forbes.ru/karera-
i-svoy-biznes/416461-effekt-covid-19-kak-
mirovaya-ekono mika-perezhivaet-pandemiyu-i-
kakim.
Vidaković, N., Lovrinović, I., 2021. Macroeconomic
Responses to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Springer
Nature Switzerland AG.
Oliveira Martins, J., Roeger, W., 2021. How will COVID-
19 affect an already fragile global economy? Int Econ
Econ Policy, 18: 453–455.
Sheng, L., 2022. How COVID-19 Reshapes New World
Order: Political Economy Perspective. Springer Nature
Singapore Pte Ltd.
Problems of Minimizing the Socio-Economic Consequences of COVID-19 Distribution in the Context of Ensuring Political Stability
207
