
Economic Education: Future Standards as a Main Reference Point
for the Economics Specialist’s Education
Olga Kvashina
a
, Ekaterina Nikiforova
b
and Julia Streletskaya
c
Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education «Velikie Luki State Agricultural Academy»,
Lenina Str., 2, Velikie Luki, Russia
Keywords: Educational Standard, Competence, Basic Professional Educational Program, Accelerated Learning,
Advanced Education Model, Digital Economy Specialist.
Abstract: This paper presents the main aspects of the development of economic education in Russia, as well as the
foreign higher education experience. The modern teaching practice in economic areas shows that the
economist and manager, as profession, will not be needed in society in a few years. Business leaders want to
see a specialist who has digital technologies knowledge, and is able to make competent and quick management
decisions. Sustainable development requires an advanced model for training a comprehensively competent
specialist for economic sectors in the shortest possible time. At the same time this specialist must highly
qualified, for example, have a master`s degree.
1 INTRODUCTION
The consequence of the COVID-19 and new strains
spread affects not only the country's economy, but
also the higher education system, in particular the
economic higher education.
The main document for the students higher
education is the Federal State Educational Standard.
Over the past decades, the State Standard of the 2nd
generation (Since, 2005), the Federal State
Educational Standard of the 3rd generation (FSES, or
FGOS) (Since, 2009) have been in effect in higher
education. In 2020, the FSES for higher education
with a preamble 3++ was adopted in economic
education areas.
The need for the development of the 3rd
generation FSES for higher education (FSES HE) was
associated with the ongoing processes of Russia's
integration into the Bologna Process.
In our opinion, over the entire period of the
European model of education implementation, the
formation of specialist for work in the sectors of the
national economy has not been brought to a common
denominator. Is higher education, i.e. bachelor's
degree, a priority? Or one needs a specialist level, or
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1171-9665
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7061-4735
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8399-2794
a master's degree, to perform the amount of work
assigned to a modern young specialist.
The development of the 3rd generation standards
was carried out in accordance with the experience
noted in the framework of the TUNING project. The
project is focused on the implementation of the
graduate's competence model (Zakharova, Kuzenkov,
2016) and the regulatory requirements for both
academic (general competence) and professional
(professional competence) components of the future
bachelors education. The distinctive features of the
FSES 3rd generation, in addition to teaching students
on a competency-based basis, were also the
introduction of a credit-modular educational system
and the measurement of the education complexity in
credit units (c.u.).
However, it should be noted that this model has
been being tested for already 10 years and has shown
that in the realities of time it needs to be improved
within the following aspects:
- introduction of methodological principles to
form a list of competencies;
- revision and structuralization of professional
competencies considering the type of activity;
Kvashina, O., Nikiforova, E. and Streletskaya, J.
Economic Education: Future Standards as a Main Reference Point for the Economics Specialist’s Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0011112100003439
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific and Practical Conference "COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals" (RTCOV 2021), pages 143-148
ISBN: 978-989-758-617-0
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
143

- weak correlation of the formed list of
competencies with sections of the main educational
programs;
- horizontal structure of the main educational
program, which limits the implement of the modular
principle of structuring the educational content.
In the current FSES HE 3+ which has been now
operating for more than 10 years, the key innovations
were:
- division of bachelor's degree programs into the
academic and applied parts;
- lack of study cycles and a list of studied subjects;
- formation of competencies in three groups –
general cultural, general professional and
professional in accordance with the types of activities
that the main professional educational program
(MPEP) is focused on;
- strengthening the role of using the information
and educational environment with an indication of the
requirements imposed on it, as well as the use of
distance learning technologies and e-learning.
The positive aspects of the FSES HE 3+
implementation were: the expansion of the of
universities freedom to independently form the MPEP,
the opportunity to chose forms, methods and means
of teaching (Bedny, B., Kuzenkov, O., 2017). Such
flexibility in the formation of the MPEP, the content
of teaching, and a set of competencies were aimed to
maximaze integration of education and the labor
market (Kuzenkov O., Zakharova I., 2018). However,
the factor limiting the integration was the low
correlation level between the results of mastering the
MPEP , i.e. the list of formed competencies and the
requirements of employers - generalized labor
functions outlined in professional standards. This
determined the need to modernize the FSES HE 3+
and switch to the new edition of the FSES HE 3++.
In August 2020, the FSES HE 3++ were approved
in economic education areas.
The standards analysis showed that the new
edition is focused on participating in the formation of
the employers' MPEP. General cultural competencies
have been replaced with universal ones. There is a
need for constant monitoring of the labor market, the
range of practices has been expanded in some
economic areas, there is no division into academic
and applied bachelor's degrees.
The innovations are made just on time, but we
believe that the question of getting a high-quality
education in 4 years remains open, as well as the
possibility of shortening the period of study for
students who have completed the secondary
vocational stage of education, continuing to pursue
higher education under the bachelor's degree
programs.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The methodological basis of this research is the
scientific works of Russian and foreign specialists in
the field of formation of modern higher education
systems, preparation of regulatory documents for the
implementation of educational activities within the
requirements of the employers. We also consider the
possibility of introducing elements of studying in
specialized classes created on the basis of schools that
actively interact with the universities. In this study we
use methods of system analysis, generalization and
comparison of data, monographic and others methods.
The scientific novelty of our research consists in
the development of a model of an economic education
system in the field of organizing reduced studying in
related programs of secondary vocational education,
bachelor's and master's degree programs. The current
trends of entering the arket of a specialist with in-
depth knowledge of the digital economy aspects were
also taken into account.
We believe that on summarizing the results
obtained, it is possible:
- to attract a wider target audience for higher
economic education on a paid basis;
- to transform economic education in a way that
will allow regional universities, in particular,
agricultural universities, to develop standards
themselves and approve them on the basis of an
educational organization for the most popular
professions in which the employer is interested;
- to work more closely with students of 8th — 9th
grades, and also to use the employer's base for
organizing and conducting practical training;
- to facilitate the early identification of students
who are able to success in science and study under
additional professional programs, using distance
learning formats with the help of the methodology for
assessing the quality of educational services.
We also believe that Russian education in the 20s
of the third millennium is in a pronounced bifurcation
phase – at a radical turning point of its development.
The future forms, paradigms and models of education
will be influenced by the civilization evolution.
Education, as its important global component, should
contribute to those forms of development that will
implement the survival strategy of humanity to the
greatest extent, not only with the use of IT
technologies, but also preserving the biosphere.
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
144
The ways of improving higher education and its
sustainable development within the framework of
new standards, the emergence of qualitatively new
professions should include:
- unified systems of electronic educational
websites for obtaining information (their accessibility
from any student's location);
- use of information technologies thanks to the
development of mobile means of transmitting and
processing information within the walls of the
university and at its expense;
- shortening of studying periods for those
categories of students who work in the specialty, or
have been taught in related programs of secondary
vocational education.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
Currently, most of the field of studies in economic
specializations are not provided with on-budget
places. They are implemented on paid educational
services basis. In addition, the Unified State Exam
(USE) system shows over the past few years that most
school graduates choose those subjects that are not for
admission to economic educational areas: social
studies, mathematics (major level). It becomes quite
difficult to pass the threshold level. Many 9th year
graduates enter secondary vocational educational
institutions (SVE).
The obtained SVE degree allows one to pass the
entrance tests on the university base without passing
the Unified State Exam. However, there are other
disadvantages that graduates with a SVE degree
might encounter:
- on average, vocational education takes 3 years
and 10 months, while an ordinary school graduate
spends 2 years to receive a secondary general
education;
- young men are not granted with a deferral from
the army. That is a compulsory service in the armed
forces, after which a small percentage goes to higher
school on a full-time basis;
- according to the FSES HE 3++, the student credit
units, that does not allow to retest the studied
discipline. Thus, it is not always possible to shorten
the period of study by one calendar year, only if the
curricula with the same names of the subjects studied
is formed;
- acceleration of studies is possible only in a
related field and with reimbursement of tuition costs
(in the absence of on-budget places);
- additional costs, teaching according to an
individual curriculum are acceptable only for a
certain target audience.
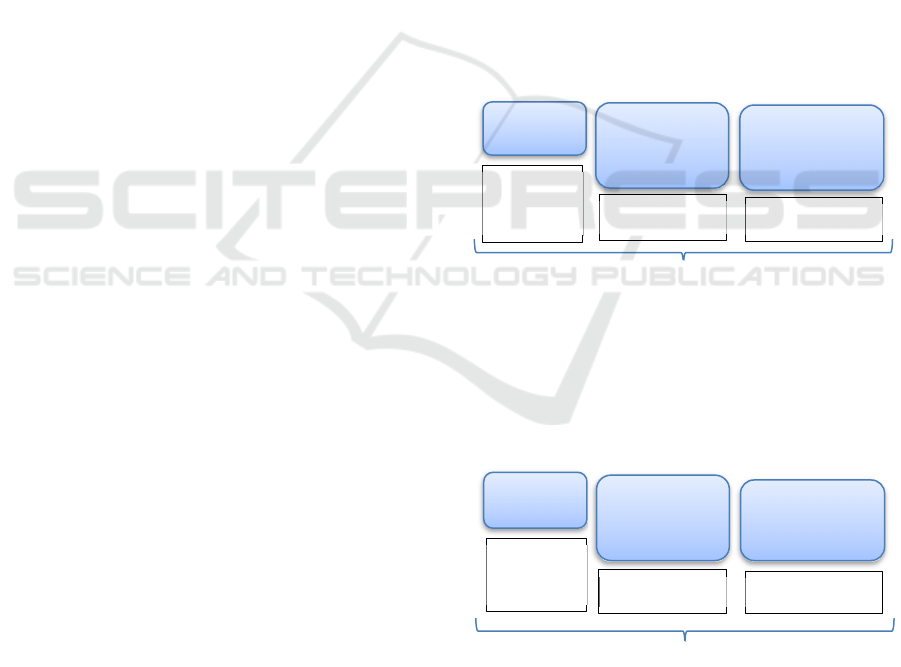
According to the standard scheme (Fig.1), a
graduate student spends 9 years and 10 months before
receiving a higher education diploma if they studies
according to the 3-level education system: SVE -
Bachelor's degree - Master's degree. If an educational
institution develops and approves an internal
educational standard, taking into account the
comparison of all the features that restrain the
reduction of the education time, then in this case the
student can save 1.5 years (Fig.2). It should be noted
that in Russia only about 20 universities can
independently develop their standards. More than 800
universities in Russia work strictly according to the
FSES!
In the last few years, the model shown in Figure 2
has been used in practice by educational
organizations that represent all levels of education,
but it became possible to shorten the duration of
Master's programs within the FSES HE 3++.
Figure 1: Standard 3-level educational system.
In the last few years, the model shown in Figure 2
has been used in practice by educational
organizations that represent all levels of education,
but it became possible to shorten the duration of
Master's programs within the FSES HE 3++.
Figure 2: Express 3-level educational system.
Within the Master's degree in Economics the new
standard was approved in August 2020. It is just on
time to onboard undergraduates in 2022 and to
develop programs with the duration reduced by 0.5
years.
SVE
3 years
and 10
months
HE:
Bachelor’s
degree
4 years
HE: Master’s
degree
2 years
9 years 10 months
SVE
3 years 10
months
HE:
Bach\elor’s
degree
3 years
HE: Master’s
degree
1,5 years
8 years 3 months
Economic Education: Future Standards as a Main Reference Point for the Economics Specialist’s Education
145

As a part of the pilot project, we propose to
consider a model (Fig.3) in which school education
can also be involved.
For making students of 8th – 9th grades receive
additional education there should be classes focused
on Economics and ongoing 2-year education plan
which includes such subjects as Management,
Marketing, Economics, Introduction to the
Specialization (Accounting), History of Economic
Studies, Philosophy etc. Upon successful completion
of final works (abstracts, reports, projects) students of
9th grade will be able to get an additional educational
certificate. The received document can be equal to
primary vocational education, then learning process
will be reduced by another 1 year.
Figure 3: Express 4-level training system.
The model presented in Figure 3 aligns the
learning time period of school student with a graduate
student who has completed full-time learning at SVE
level. It is clear that the duration of learning at the HE
level will be reduced by 1.5 years.
There is a rational link in the proposed model:
classes focused on Economics can be issued at a
university. Students gain knowledge in the field of
Economics and Management, get used to the classes
organization within SVE and HE systems. In the
future, studying under SVE helps to acquire practical
skills and get acquainted with the specifics of the
future profession.
To implement this model, modern educational
platforms, qualified teachers who are able to work
with teenagers, and the educational organizations
interested in early career guidance among students are
needed.
The main steps to the implementation of this
model are preparation of documentation, licensing,
specification of the MPEP, which is agreed with the
employer. Taking into account the realities of the time
and the advanced development of economic sectors,
each educational institution should know the labor
market, develop competitive advantages in the field
of provided education, and also monitor professional
trends.
The analysis carried out during the research on
modern approaches in Russian education allowed us
to identify a number of triggers that determine the
trends for improving the system of economic
education:
- the external triggers should be the global trends
that operate in almost all areas of human activity and
have a direct impact on the educational field;
- the derived triggers will be the consequences of
"external triggers" that have independent significance
and relevance for the development of the education
system;
- system triggers will indicate trends and attitudes
already established in the education system;
- possible trends and attitudes should be
considered as promising triggers which can be
profitably used for the development of education
systems and their output to optimal scenarios for the
selected pilot projects;
- internal system triggers and trends should reflect
the specifics of education levels with general and
particular problems for each level of education.
Optimists believe that by 2030, people in
developed countries will be mainly involved into the
types of work robots and artificial intelligence will
not be able to perform due to either tasks’ "simplicity"
(economically inefficient) or high complexity. A
significant part of the working production activity
will become creative. Other people, on the other hand,
will work less with technical objects and more with
other people.
The economy of the future will require not only a
high-leveled "hard skills" for the production of mass
goods and services, but also conditions for conscious
consumption in order to create unique products. The
hand made and uniqueness trend will become stronger.
The future of specialists in Economics does not seem
bright either.
In leading companies, the traditional "workplace"
is gradually disappearing. The development of local
and distributed production systems (3D printing,
remotely-controlled robots and simulators) brings
them closer to the end user.
Many things already have to be studied remotely,
but not all students have high motivation within the
distance education conditions, and in the modern
world such a skill to study remotely acquires
additional value.
The exclusion of people from the field of
education due to digitalization and distance learning
without the "presence effect" can lead to the
disappearance of communicative and intercultural
competencies and drop in the emotional intelligence
level.
SVE
HE:
Bachelor’s
degree
HE:
Master’s
degree
2 years 10
months
3 years
1,5 years
8 years 3 months (-1 year)
Schoo
l 8th-
9th
1 year of
study
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
146

As a result of the economic imbalances expansion,
the society differentiation by income increases. The
reduction of old production technology chains
combined with digitalization is already having a
strong impact on wages and employment of the
middle class representatives: they cannot afford
prestigious education (hence, Russia will get a chance
to develop education and educational tourism).
All over the world, children from rich families
study in prestigious educational institutions, which
also receive additional funding from private non-
profit foundations in addition to government funding.
Children in difficult life situations and children from
poor families, end up in ordinary schools. In such
educational institutions, a "cycle of social insolvency
reproduction" is already formed. It generally leads to
decrease in quality and effectiveness of the education
system. In Russia, significant work has to be done to
reverse this trend, otherwise, there is a risk of
increased school segregation and institutionalized
inequality of opportunities. And already at this stage,
a model of civilized development of the education
system is needed.
4 DISCUSSION OF THE
RESULTS
The main outline of the new civilization development
model and its most important subsystem – education
- have already been formed abroad. However,
Russian universities need at least 10 years to bring
standards for the tool that would allow to form highly
qualified specialists.
Sustainable development (SD) is not just one of
the new global strategies, but an evolving worldwide
movement that the future of all mankind and its fate
depends on. This is a completely new form (model)
of the the entire world development, that is now on
the path of reducing existential risks and its own
survival (Ilyin I., 2017).
The Sustainable Development Goals are a
continuation of both the targets of all previous UN SD
documents and the Millennium Development Goals
(MDGs). The MDGs identified eight international
development goals as priorities, they were
implemented by UN member states in 2000 and were
mostly completed by 2015 (Ursul, A., Ursul, T., 2017).
We believe that it is necessary to revise the FSES
HE 3++ as soon as possible (in particular, for both
secondary and higher education), in order to eliminate
those shortcomings that hinder progress, freeze the
possibility of opening new specializations that are
already in demand. A specialist in digital economy
has to study for 2 years if they chooses a master's
degree program. Yet there is no professional standard
in this field. Hence, the labor functions recommended
in the FSES HE 3++ for the formation of the
graduate’s necessary competence become odd.
The availability of higher education in Russia, the
soft conditions applied when evaluating a student
during exams or final certification have led to the
emergence of pseudo-specialists who are not able to
perform elementary tasks, or make administrative
decisions. Even upon the strict selection of specialists
among the candidates with higher education
undertaken in state institutions, incompetent ignorant
and not able to work graduates of universities, very
often working not according to the profile of their
education, carry out their work. Therefore, at the
completion stage of education in the SVE programs,
a strict selection for admission to higher education
should be carried out. One needs practical experience,
that is, in the last year of study, the vocational
education curriculum must necessarily provide for
work in production for 3-4 months.
Since 2021, instead of the practice concept of
practice, practical training has appeared at all levels
of education. Since "practical training in the
implementation of academic subjects, courses,
modules is organized by conducting practical classes,
workshops, laboratory work and other similar types
of educational activities involving the participation of
students in the performance of certain elements of
work related to future professional activities," then in
the future, a close relationship with production
organizations and enterprises should be established.
If specialized classes are created at leading
enterprises, then the teaching staff of the university
will be partially unloaded, and the production teacher
will be able to make a choice among students who are
interested in their future profession.
For many years, production teachers were not
motivated, there was no interest in organizing and
conducting practical training. Only with financial
support from the state and timely assistance from the
university it is possible for students to work
systematically in the workplace. And when assigning
a student's salary during the training, they will have
an interest and responsibility for performing the
assigned work.
It should also be noted that quotas for targeted
education are provided in universities. In general, this
is 10% of the total number of on-budget places
allocated for all educational programs. The range of
enterprises with which it is possible to sign an
agreement for targeted education is quite narrow. This
Economic Education: Future Standards as a Main Reference Point for the Economics Specialist’s Education
147

is another problem of higher education: specialists are
needed, yet there are no resources, no mentors, no
data on available vacancies in order to make efforts in
their training, to raise a qualified employee who, after
graduation, can be employed at this enterprise.
To develop a system of targeted training, it is
necessary to clearly identify in the development
strategy of the industry, educational institution or
enterprise the importance of human resources, the
creation of a personnel reserve for the future, the
graduate's interest in working in the desired
profession after graduation.
The availability of information resources, the
reliability of the information provided, the ease of
search and visual reproduction are important
components for an applicant to enroll in one’s
university. And in order to want to study both under
the SVE and under the HE programs, all conditions
must be created – from the social environment to the
career growth formation when hiring.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the acquired at the university experience,
such as the formation and development of curricula in
economic study fields, the development of MPEP,
educational and methodological documentation on
subjects, trainings, state final certification and other
documentation, we have formulated a number of
measures that must necessarily be carried out in the
near future when finalizing the FSES HE 3++ in
economic education areas:
- the increase the variety of educational programs
(Senashenko, V., 2018): it is necessary to diversify the
courses presented in the plans, dividing them into
workshops, research subjects and subjects involving
the use of special software products (1C, simulation
modeling, robotics, business navigators, etc.);
- the implementation of an independent quality
assessment system (testing, qualification exams)
(Blinov, V., Yesenina, E., Klink, O., Kurteeva, L.,
Satdykov, A., Faktorovich, A. 2017);
- the new standards require at least 3-4
professional competences based on the education area
in order to indicate the necessary and sufficient level
of all implemented competences;
- the correct organization of the educational
process, trainings directly at enterprises (the structure
and amount of trainings within the bachelor's degree
program consist of about 2000 hours in accordance
with the FGOS HE 3+ and FGOS HE 3++. It is an
order of magnitude more than the additional
vocational education programs (AVE), and allows
students to master any professional competence and
labor functions, if the educational process is
organized correctly, in terms of production conditions,
and get the exact professional experience that the
employer needs);
- to provide accelerated training in bachelor's and
master's degree programs in related areas of
education on the basis of internal local acts (or by
developing standards on the university basis);
- education at all its levels "should not remain on
the periphery of global development as a traditionally
falling behind component of this process, but must
become its particularly important advancing
"catalyst" ..." (Ursul, A.., Ursul, T. 2017).
REFERENCES
Zakharova, I., Kuzenkov, O., 2016. Experience in
implementing the requirements of the educationaland
professional standarts in the field of ICT in Russian
education. 11st 1thInternational Scientific-Practical
Conference Modern Information Technologies and IT-
education, SITITO.
Bedny, B., Kuzenkov, O., 2017. Integrated training
programs for highly qualified scientific and
pedagogical personnel. Integration of education, 4 (89).
pages 637-650.
Kuzenkov O., Zakharova I., 2018. Mathematical programs
modernization based on Russian and international
standards. Modern information technologies of the IT
education market, 1. pages 233-244.
Ilyin I., 2017. Education for sustainable development:
global context. Globalistics And Geopolitics, 2.
Ursul, A., Ursul, T., 2017. New Goals of Sustainable
Future. The Journal Philosophy and Cosmology, 18.
Questions and answers regarding the legal regulation of
practical training of students, ATP Consultant Plus,
MN-5/207304 (30.10.2020).
Senashenko, V., 2018. Levels of coupling of the higher
education system and the sphere of work. Higher
education in Russia, 3. pages 38–47.
Blinov, V., Yesenina, E., Klink, O., Kurteeva, L., Satdykov,
A., Faktorovich, A. 2017. Professional standards: from
idea to practice. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing
RU.
Ursul, A., Ursul, T. 2017. The phenomenon of futurization
in education for sustainable development. Values and
meanings, 6 (52). pages 8–20.
RTCOV 2021 - II International Scientific and Practical Conference " COVID-19: Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
(RTCOV )
148
