
Decision Support System of Social Assistance in Bitung City
by using AHP Method
Alfrets Septy Wauran, Anthon Kimbal and Roby Lumbu
Department of Electrical Engineering, Manado State Polytechnic, Manado, Indonesia
Keywords: Bitung City, Decision Support System, AHP.
Abstract: Information and data from all SKPs under the Bitung City Government are integrated in a data center. So,
they can be accessed in real time by users, both government and community. There are several algorithms
that can process data and provide the desired information such as Data Mining, Artificial Intelligence and
Decision Support Systems. Decision Support System is a computer system application that can assist
decision makers in solving problems. In addition to population problems, a decision support system can
help government to solve social problems. In this study, we created a decision support system using the
Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) algorithm which will calculate optimal decisions in solving population
and social problem. This system will be used to calculate the priority of social assistance in Bitung City.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bitung City is a Maritime City which is the only
Special Economic Zone in Sulawesi. Bitung City is a
maritime city where most of the people depend on
the sea and beach products such as fishing industry,
coastal tourism, fish canning factories and ports. As
we know that Bitung City has the largest seaport in
Eastern Indonesia. Given its very strategic location
as a maritime city, most of the city's revenue comes
from the maritime sector. To improve the economy
and income of the people of Bitung City, the
government needs an integrated and reliable
information system. If it is not supported by a good
reliable information system, the management of
resources in Bitung City will not be optimal given
the limited human ability to manage information
manually. Therefore, this becomes a serious problem
because valuable data and information in Bitung
City cannot be accepted and utilized properly by the
community due to lack of knowledge and utilization
of information technology. To realize Bitung City as
a Digital City, an Integrated Big Data system is
needed to be able to quickly access data and
information stored in the Data Centre. The stored
data in the system can be a population data,
employment, correspondence and so on. These data
can be used to find solutions for all problems that
occur in the community. For example, population
data that must be assisted economically by the data
on fishermen that must be assisted in the
procurement of fishing equipment, fishery industry
data, scholarships for those who cannot afford but
excel, data on marine natural resources that can be
used for evaluation in inviting tourism investors, as
well as marine tourism data that can be developed or
new tourism potential areas according to the
appropriate parameters and criteria. In determining
the beneficiaries and analizing these investments,
they still use manual evaluation by decision-making
employees. This results are dishonest and subjective
results. Likewise, the results obtained by the
analizing of population data are very inaccurate due
to invalid data and limited human memory capacity
in determining the priority of beneficiaries.
Therefore, a computer application integrated with
Bitung City Big Data is needed in the form of a
Decision Support System. The Decision Support
System that will be made is using the AHP method
which is known to be very accurate in calculating
the statistical problem. Population data can be
retrieved and collected quickly. So, the data can be
used directly to be calculated and aggregated based
on criteria and as a final result is the order of
priorities and optimal decisions that must be taken.
This decision support system can solve many social
problem in Bitung City.
Wauran, A., Kimbal, A. and Lumbu, R.
Decision Support System of Social Assistance in Bitung City by using AHP Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0010958600003260
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science (iCAST-ES 2021), pages 1045-1048
ISBN: 978-989-758-615-6; ISSN: 2975-8246
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1045

2 RESEARCH LITERATURE
2.1 Decision Support System
Decision Support System (DSS) is a system that
interactively provides information, modeling, and
data manipulation where the system is used to assist
decision making in semi-structured and unstructured
problems, where no one knows for sure how
decisions should be made (Alter , 2002). Decision
Support Systems (DSS) are generally built to find a
solution to a problem with several available options
(alternatives) based on knowledge, or evaluate an
opportunity based on existing data. Where the
decision support system is called the DSS
application. To find solutions to certain unstructured
management problems, DSS applications use a
flexible, interactive, and adaptable CBIS (Computer
Based Information System) (Kusrini, 2007).
The objectives of the Decision Support System are
(Turban, 2005):
1. Assist managers in making decisions on semi-
structured problems.
2. Provide support for the manager's judgment and is
not intended to replace the manager's function.
3. Increasing the effectiveness of decisions taken by
managers more than improving their efficiency.
4. Computing speed.
5. Increased productivity.
6. Quality support.
7. Competitive.
8. Overcome cognitive limitations in processing and
storage.
2.2 Analitical Hierarkhi Process (AHP)
The main principle of the AHP method is to enter
human perception into a functional hierarchy. In
solving decision-making problems using the AHP
method, the following are the principles that must be
understood (Kusrini, 2007):
1. Create a Hierarchy
A complex system of problems can be better
understood by breaking it down into supporting
elements, arranging the elements hierarchically, and
combining them or synthesizing them.
2. Assessment of criteria and alternatives.
This assessment is carried out by pairwise
comparisons in the matrix. According to Saaty
(1988), a scale of 1 – 9 is the best representation for
expressing opinions on a problem.
3. Determine Priorities.
For each criterion and alternative, a pairwise
comparison must be made. The relative comparison
value of all alternative criteria can be adjusted
according to the predetermined judgment to produce
weights and priorities by manipulating the matrix or
by solving mathematical equations.
4. Logical Consistency (logical consistency)
Consistency is the first where similar objects can be
grouped according to uniformity and relevance.
Second, it concerns the level of relationship between
objects based on certain criteria.
Basically the procedures or steps in the AHP method
consist of (Kusrini, 2007):
1. Defining the problem and determining the desired
solution, then compiling a hierarchy of the problems
encountered.
2. Determine the priority of the elements.
3. Synthesis.
Consideration of synthetic pairwise comparisons to
produce overall priorities.
4. Measuring consistency
The final result of this step yields max
5. Calculate the consistency of the Index using the
following formula:
CI = (λ, max – n) / n (1)
where n = number of elements
6. Calculate the Consistency Ratio (CR) using the
following formula:
CR = CI/IR (2)
Where CR = Consistency Ratio
CI = Consistency Index
IR = Index Random Consistency
7. Check the consistency of the hierarchy with the
following tests:
If the CR value is more than 10% (0.1), then the
assessment of the data is inconsistent and must be
corrected. And if the CR value is less than or equal
to 10% (0.1), then the data assessment is correct.
3 RESULT
3.1 Dashboard (Main Page)
Figure 1: Dashboard.
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1046
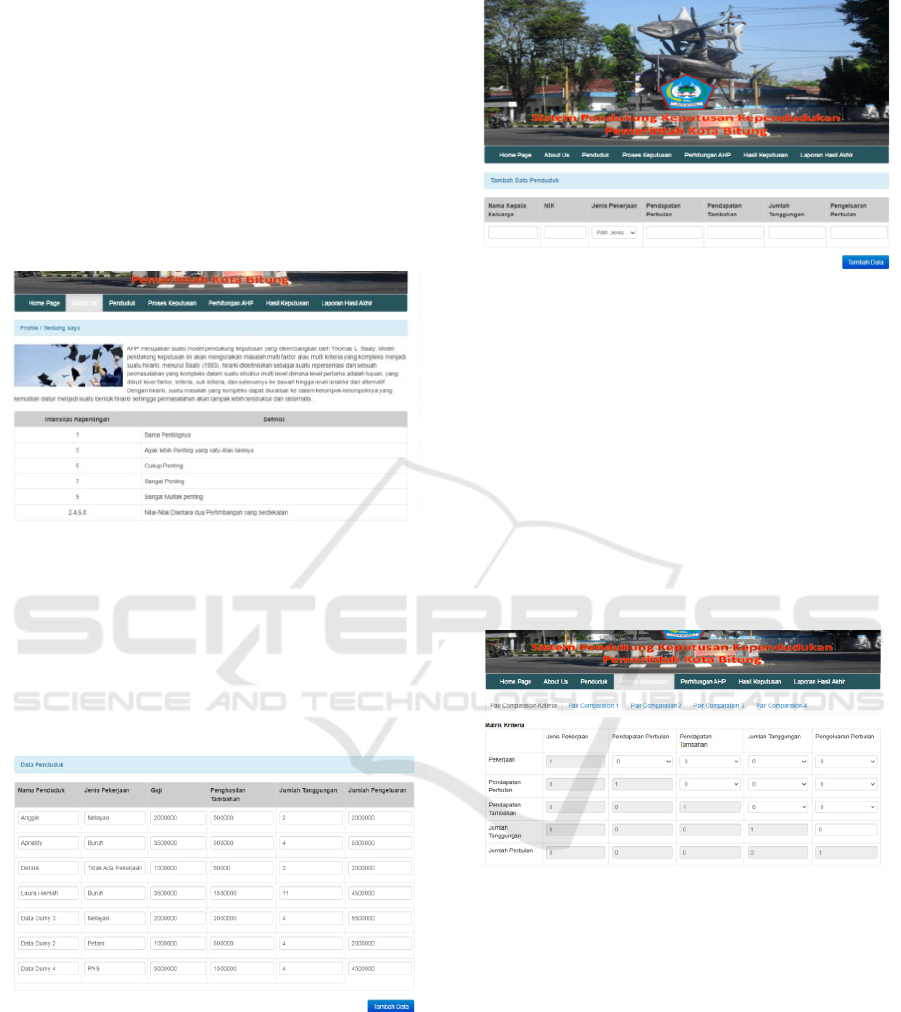
The figure 1 shown the main page of the decision
support system. User can get information about the
population data, decision support system, the system
process, and the result of the decision support
system
.
3.2 Information Page
This page consist of the information about the value
of criteria in the decision support system. The value
is shows the priority of the criteria.
Figure 2: Information Page.
3.3 Demography Data
This page shows the job of the people, salary,
additional salary, dependents, and expense. Base on
this criteria, we decide the value. This value will be
used to calculate the final mark and rank of the
person.
Figure 3: Demography Data.
3.4 Demography Data Entry
We will fill-in the data in the figure 4 completely to
calculate final value and the rank. There are the
fields of the name of the head of family, Regency
Registration Number, Occupation, the monthly
income, additional income, the number of family
and the monthly expense.
Figure 4: Demography Data Entry.
3.5 Value Criteria in AHP
We can set the value of criteria matrix by input the
all value in the empty box below. The figure below
is called ‘pairs matrix’. The priority of criteria are:
1. The Salary
2. Expense
3. The Dependents
4. Additional Salary
5. The Job
Figure 5: Pairs Matrix.
3.6 Process of Decision Support System
After fill-in the value of pair matrix, we can
calculate the valid of our AHP values. The values of
Consistency Index and Consistency Ratio must be
less then 1. So, the value of CI and CR below is less
than 1, it means that the matrix is good and can be
used.
Decision Support System of Social Assistance in Bitung City by using AHP Method
1047
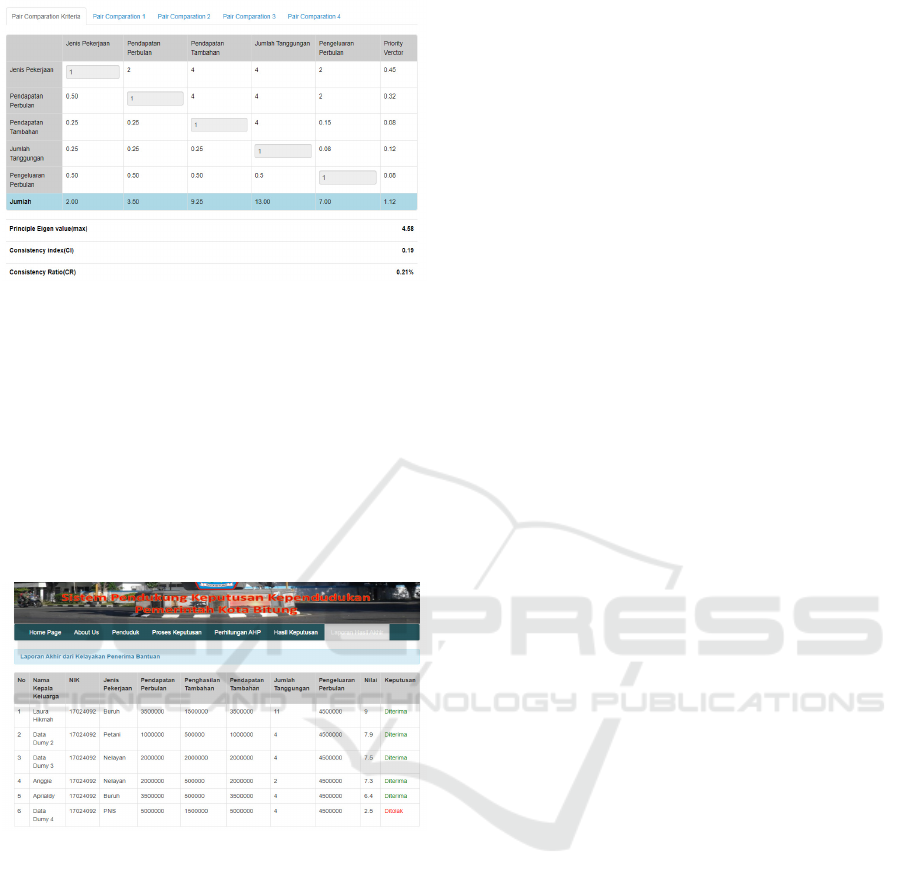
Figure 6: Value CI dan CR.
3.7 Report of Rank Social Assesment
Finaly, we can calculate the all value of criteria
based on the value in pair matrix to get the final
value and rangking. It’s shown by the figure below.
There several value are not accept because they not
fulfil the criteria of social assist. The top ranking are
more priority than the ranking below. So we can
calculate the final value and list the ranking to show
who has the higher priority of social assist.
Figure 7: Report of Calculation and Ranking.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The Result shows that the decision support system
can calculate the value of criteria to get the final
score with its ranking of priority. In this system we
can decide the value of each criteria and have the
calculation of the validity of our pair matrix. By this
system the asesment of the social assistance will be
more fair and accurate because the people has no
interference to decide the score and ranking. This
system can make report automatically to have a
transparency result.
REFERENCES
Ahmad Faisol, M Aziz Muslim dan Hadi Suyono, 2014,
Komparasi Fuzzy AHP dengan AHP pada Sistem
Pendukung Keputusan Investasi Properti, Jurnal
EECCIS Vol.8, No.2, Desember 2014
Alter, S. Decision Support Systems : Current Practice and
Continuing Challenges. Reading, Mass. : Addison-
Wesley Pub., 1980. 316 p. ISBN 0-201-00193-4
Fauziah Mayasari Iskandar, Arief Andy Subroto dan
Rekyan Regasari, 2013, Sistem Pendukung Keputusan
Seleksi Beasiswa PPA dan BBM Menggunakan
Metode Fuzzy AHP, SMATIKA Jurnal Volume 03,
Edisi 01, 2013
Kusrini, 2007, Konsep dan Aplikasi Sistem Pendukung
Keputusan, Andi Offset, Yogyakarta. Kusrini, 2007
Norhikmah, Rumini dan Henderi, 2013, Metode Fuzzy
AHP dan AHP Dalam Penerapan Sistem Pendukung
Keputusan, Seminar Nasional Teknologi Informasi
dan Multimedia, STMIK AMIKOM Yogyakarta, 19
Januari 2013
Nurdin, 2015, Fuzzy Optimization Method in the Search
and Determination of Scholarship Recepients System
at the University, International Journal of Computer
Applications Technology and Research, Volume 4 –
Issue 7, 512 – 516, ISSN : 2319-8556, 2015
Saifulloh dan Kusrini, 2016, Sistem Pendukung
Pengambilan Keputusan Penentuan Beasiswa
Menggunakan Metode Fuzzy-AHP, Cogito Smart
Journal/Vol.2/No.2/Desember 2016
Turban Efraim, 2005, Decision Support System and
Intelligence System, Pearson/Prentice Hall 2005
iCAST-ES 2021 - International Conference on Applied Science and Technology on Engineering Science
1048
