
The Effect of Tax Administration, Tax Knowledge and Tax Sanctions
on Taxpayer Compliance
Annisyah Aprillia
1
and Dwi Kartika Sari
2
1
Business Management Major, Batam State Polytechnic, Indonesia
2
Business Administration Study Program, Batam State Polytechnic, Indonesia
Keywords: Tax Administration, Tax Knowledge, Sanctions Taxation, Individual Taxpayer Compliance.
Abstract: This study aims to identify and analyze whether the effect of tax administration, tax knowledge and sanctions
taxation to compliance of individual taxpayers. The method of this thesis is the research instrument test,
classic assumption test, multiple linier regression test and hypothesis testing. Independent variables in this
study are tax administration, knowledge of taxation and tax sanctions, while the dependent variable is the
individual taxpayer compliance. The number of population in this study is not known how many individual
taxpayers are registered using a sample from Paul Leedy obtained 139 people as a sample. The type of data
used is primary data. The results of this study prove that simultaneously tax administration, knowledge of
taxation and tax sanctions have an effect on individual taxpayer compliance. Partially, the variables of tax
administration and tax sanctions have an effect on individual taxpayer compliance. Meanwhile, tax knowledge
has no effect on individual taxpayer compliance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Duty income is perhaps the most elevated supporter
of state incomes which will then, at that point be
utilized for all state interests, for example,
government financing and framework advancement.
Expense income keeps on encountering an
unprecedented increment, this is clear from the 2018
income information gathered as much as 1,618.1 T
and in 2019 it expanded by 10.4%.
Hence, the Directorate General of Taxes (DGT)
keeps on searching for approaches to advance
potential assessment incomes for the state depository,
numerous things are being done and one of them is
the duty change program. there are 5 reasons why
assessment change should be done, in particular: (1)
the low degree of citizen consistence; (2) The expense
income target builds each year; (3) the quantity of HR
isn't corresponding to the increment in the quantity of
citizens, hardships in oversight and law requirement;
(4) The advancement of the computerized economy
and mechanical advancement is exceptionally fast;
(5) Rules that expect the improvement of exchange
exchanges.
This duty organization change program and action
has been completed for quite a while, in particular in
1983 which has the accompanying attributes: (1)
hierarchical design of capacities, (2) Through the
foundation of a client delegate and grievance place
for every citizen recharging administration to oblige
obligatory protests. charges (Rahayu, 2010).
Citizens who don't consent will affect tax
avoidance, tax avoidance, sneaking and carelessness,
bringing about a lessening in public assessment
income (Budhiningtias and Bimantara, 2017). That is
the reason resident consistency is a significant part for
the remainder of the world.
Consistency is where residents satisfy their every
responsibility and exercise their right of judgment
(Rahayu, 2010). Simultaneously, as indicated by the
choice of the priest of money 544/KMK.04/2000
consistence is a demonstration of the citizen in
satisfying his duty commitments as per the
arrangements of the enactment and expense execution
guidelines in power in a country.
In research directed by Clement Olatunji Olaoye,
Abiodun Rafiat Ayeni-Agbaje, Abiola Peter Alaran-
Ajewole (2017), Natrah Saad (2014), Damajanti and
Karim (2017), Ompusunggu (2015) their examination
shows charge information influences citizen
consistence decidedly.
Different investigations directed by Khuzaimah
and Hermawan (2018), Halawa and Saragih (2017) in
Aprillia, A. and Sari, D.
The Effect of Tax Administration, Tax Knowledge and Tax Sanctions on Taxpayer Compliance.
DOI: 10.5220/0010936800003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 149-154
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
149

their investigation show that assessment authorizes
significantly influence charge consistency.
Thinking about the above premise, the specialist
will lead an examination named "The Influence of
Tax Administration, Tax Knowledge and Tax
Sanctions on Individual Taxpayer Compliance."
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Tax
As indicated by Mardiasmo (2013:1) Taxes are
responsibilities made by people to the state and seen
from the law, are coercive and don't get
correspondence that is felt to be direct and can be
applied to meet all state needs. Furthermore, in light
of the overall arrangements and tax collection
systems in the KUP Law Number 28 of 2007 Article
1 Paragraph 1 assessment implies it is compulsory to
partake locally, the two people or elements to the state
and it is upheld as indicated by the law of backhanded
pay, and is utilized to address the issues of the local
area. individuals' flourishing.
2.2 Tax Administration
As indicated by Olaoye, Ayeni-Agbaje, and Alaran-
Ajewole (2017:133) charge organization is a strategy
or system made with the goal that citizens complete
their commitments to the public authority. The duty
organization is straightforwardly taken care of by the
directorate general of tax collection to be evaluated,
gathered and observed its encouraging as per the set
up charge laws and guidelines. There are 5 (five)
pointers of assessment organization, in particular: (1)
Law; (2) Public Administration; (3) Sociology; (4)
Psychology; (5) Economics.
2.3 Tax Knowledge
Information is extremely significant for citizens to
satisfy their commitments, particularly information
about charges. A citizen can be supposed to be loyal
in the event that he can know what his commitments
are. On the off chance that the citizen doesn't know
about the rudiments of tax collection, it will be hard
for him to enlist himself, round out a warning letter
(SPT), not realize how much duty he should pay and
store the assessment (Rahayu, 2010).
As per Rosyida (2018) there are 3 (three) pointers
of authoritative responsibility, to be specific as
follows: (1) Understanding the duty work; (2)
Taxpayer's information on charge guidelines; (3)
Knowing the expense rate and methods for making
good on charges.
2.4 Tax Sanctions
As demonstrated by the entire lawful course of action
and rules, charge sanctions are utilized as an
assurance to be consented to/agreed. Then again in
various terms as an obstruction with the point that
residents don't manhandle the standards of tolls
(Mardiasmo, 2013).
As per the arrangements of Article 7, Article 28 of
the 2007 KUP, if the Taxpayer doesn't present the Tax
Return (SPT) inside the predefined time limit, and as
far as possible agrees with the arrangements of
Article 3, passage 3, and Article 3, section 4 of the
Law on charge sanctions, executed, the General
Regulation of Taxation Number 28 of 2007 which
peruses as follows:
1. For period notification letters, the latest deadline
is the 20th (twentieth) day after the end of the
tax period.
2. For individual annual tax returns, the deadline is
3 (three) months after the end of the tax year.
3. For corporate tax annual notification, the
deadline is 4 (four) months after the end of the
tax year.
The indicators of tax sanctions are (1)
administrative sanctions and (2) criminal sanctions.
2.5 Tax Compliance
As per the Big Indonesian Online Dictionary, Edition
V, 2016 devoted resembles complying (orders, etc);
restrained. While dutifulness has the significance of
loyal nature, submission. Consequently, consistence
is faithful and dependent upon the guidelines that
have been set. As indicated by Marcori (2018), it is a
necessity for citizens to comprehend, recognize,
regard and sit tight for the pertinent duty guidelines
and desire to satisfy their assessment commitments.
Resident consistency can be deciphered as a
condition wherein residents do a great deal of
expenditure on their privileges and responsibilities.
The markers of expense consistence are (1) Service
Quality; (2) Education level; (3) Timeliness in
making good on charges.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
150
3 METHOD
3.1 Population and Sample
The populace in this examination were singular
citizens enlisted at KPP Pratama Batam Utara with an
example of 139 individuals.
3.2 Method
The exploration methodology utilized is quantitative
examination strategies. The aftereffects of this test
come from the responses to the poll that have been
appropriated to the example which will then, at that
point be handled and broke down.
This investigation utilizes 3 (three) free factors
specifically charge organization, charge information
and expense sanctions and the reliant variable is
singular citizen consistence. This assessment utilizes
different direct assessments with the accompanying
conditions:
Y= α + β1X1 + β2X2 + β3X3 + β4 + e
Description :
Y : Taxpayers Compliance
α : Constant
β1 : Tax Knowledge Coefifficient
β2 : Tax Administration Coeeficient
β3 : Sanctions Taxation Coefficient
X1 : Tax Administration Variable
X2 : Tax Knowledge Variable
X3 : Sanctions Taxation Variable
e : Error
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
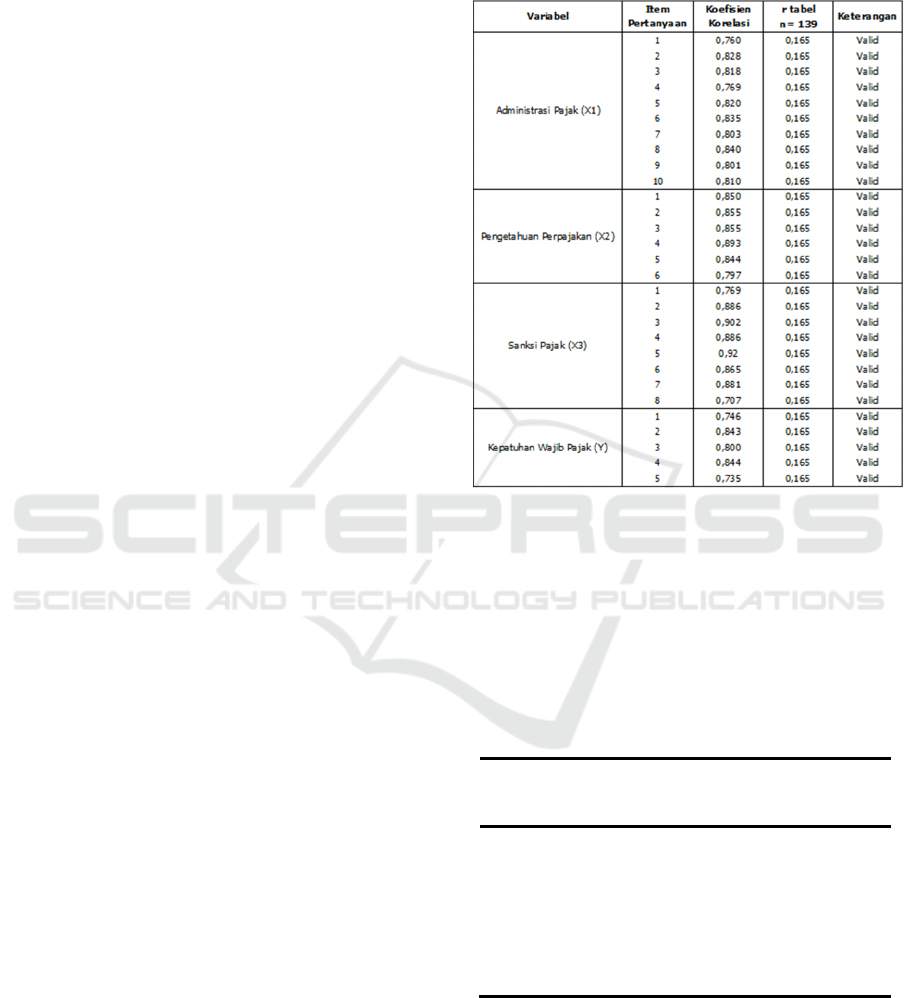
4.1 Validity Test
The legitimacy test was endeavored to gauge whether
the survey was legitimate. (Ghozali, 2016). it was
reasoned that all things had rcount > rtable, in
particular at a critical degree of 5% (α = 0.05) and
(N=139-2) so the reference number was 137. Thusly,
rtable = 1.165 was acquired. The end is that the
inquiry things in this examination are substantial.
Coming up next are the consequences of testing the
authenticity of this examination:
Table 1: Validity Test
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
4.2 Realibility Test
On the off chance that the Cronbach Alpha worth is
more noteworthy than 0.6, the exploration poll is
dependable Sugiyono (2018:268). It is realized that
the survey is solid, on the grounds that Cronbach's
Alpha worth is more prominent than 0.6.
Table 2: Realibility Test
Variable
Nilai Alpha
Cronbach
(Y) Tax Compliance 0,853
(X1) Tax Administration (X1) 0,941
(X2) Tax Knowledge (X2) 0,922
(X3) Sanctions Taxation (X3) 0,946
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
4.3 Normality Test
Routineness test for deposits utilizing Kolmogorov-
Smirnov. The importance level utilized is = 0.05. The
The Effect of Tax Administration, Tax Knowledge and Tax Sanctions on Taxpayer Compliance
151
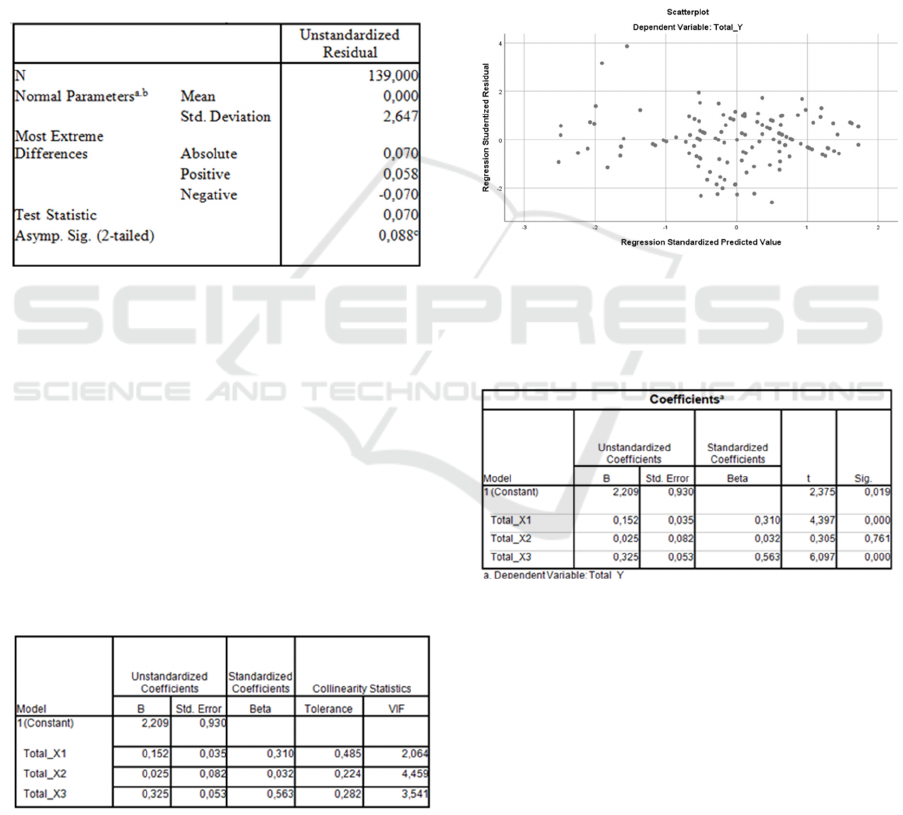
justification settling on the decision is to take a gander
at the conceivable number P, with the going with
conditions.
In the event that the likelihood worth of P 0.05, the
suspicion of ordinariness is met.
In the event that the likelihood P < 0.05, the suspicion
of ordinariness isn't met.
Since the worth of Kolmogorov-Smirnov is 0.070
while the worth of Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed) got 0.088
higher than the degree of significance of 0.05 then
reasonableness is met.
Table 3: Normality Test
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
4.4 Multicollinearity Test
To see the presence or nonattendance of
multicollinearity, it is awesome to see the change
expanding factor (VIF) esteem. A VIF worth of more
than 10 shows an autonomous factor,
multicollinearity happens (Ghozali, 2016).
In this examination, there were no manifestations
of multicollinearity on the grounds that the VIF
esteem was under 10 with a resistance esteem above
0.1.
Table 4: Multicollinearity Test.
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
4.5 Heteroscedasticity Test
To recognize the presence of heteroscedasticity
appearances, it will in general be seen from the
presence or nonattendance of explicit models on the
disipate plot chart between SRESID on the Y turn,
and ZPRED on the X pivot (Ghozali, 2016). It very
well may be found in the picture underneath that there
is no unmistakable example, and the specks spread
above and beneath the number 0 on the Y pivot, so
there is no heteroscedasticity.
Figure 1: Scatterplot
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
4.6 Multiple Linier Regresion Test
Table 5: Multiple Linier Regresion Test
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
This assessment is relied upon to have the option
to choose the heading of the connection between the
self-sufficient variable and the reliant variable,
whether or not every free factor has a positive or
negative relationship. Can be found in the table
beneath that the outcomes are sure factors.
4.7 T Test
As indicated by Sugiyono (2018: 275) the inspiration
driving the T test is to check whether there is a
deficient or reformist connection between the self-
ruling variable and the reliant variable. On the off
chance that the likelihood is < 0.05, the hypothesis is
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
152
viewed as enormous, and alternately with the
supposition that the likelihood is > 0.05, theory is
considered immaterial. The consequences of the T
test can be found in table 5.
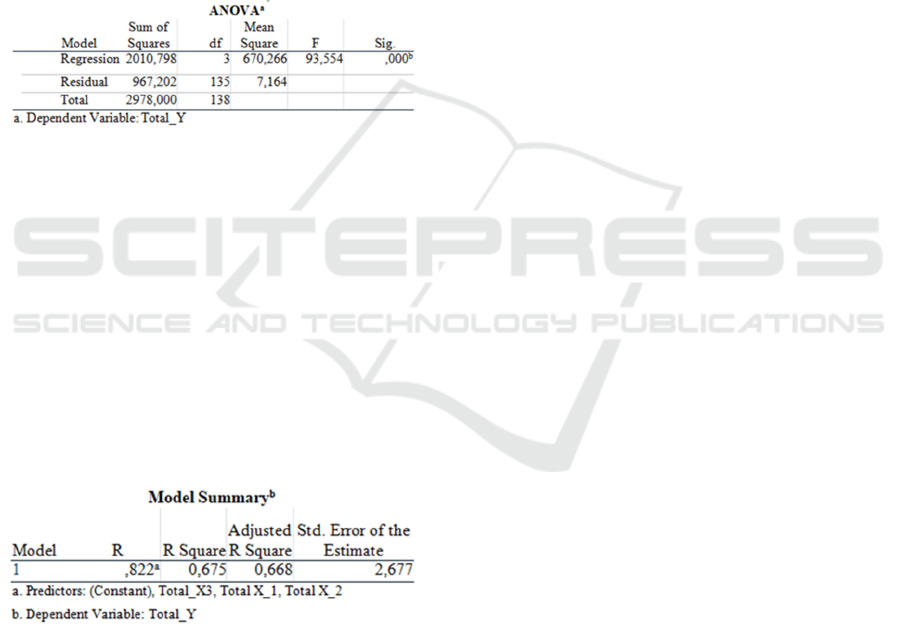
4.8 F Test
According to Ghozali (2016: 96) the purpose of this
simultaneous hypothesis test (Test F) is to prove that
all independent variables together significantly affect
the significance of the dependent variable or not. if
the significance value of F is 0.05 then it can be used
to predict the dependent variable. The following are
the results of the F test.
Table 6.
Source : Output SPSS, 2021
4.9 Coefficient of Determination (R2)
Describes changes in the dependent variable with
coefficients ranging from zero to one. The smaller the
coefficient value means the dependent variable has a
very limited ability to explain changes in the variable.
A value close to 1 indicates that the dependent
variable provides almost all the information needed to
predict changes in the dependent variable (Ghozali,
2016). The following is the result of the coefficient of
determination.
Table 7: Coefficient of Determination (R2)
Source : Outpus SPSS, 2021
4.10 Discussion
In light of the examination of the coordinated data,
the accompanying can be acquired:
1. Duty Administration Variable (X1) on
Individual Taxpayer Compliance (Y) gets
4.397, more noteworthy than 1.978 t table with
a meaning of 0.000 <0.05, for that the proposed
speculation is acknowledged. implies that Tax
Administration (X1) significantly affects
Individual Taxpayer Compliance (Y) at a huge
degree of = 5%.
2. Information on Taxation (X2) on Individual
Taxpayer Compliance (Y) got by 0.305 lower
than 1.978 t table with a meaning of 0.761 >
0.05, then, at that point the accommodation of
the speculation is dismissed. This shows that
Tax Knowledge (X2) doesn't to some degree
influence the Individual Taxpayer Compliance
variable (Y) at a huge degree of = 5%.
3. Duty Sanctions (X3) on Individual Taxpayer
Compliance (Y) are gotten at 6,097 and surpass
ttable 1,978 at an importance level of 0.000 <
0.05, the proposed speculation is acknowledged.
It implies that the Tax Sanction (X3) has no
huge impact on Individual Taxpayer
Compliance (Y) with a meaning of = 5%.
5 CONCLUSION
In light of the consequences of the investigation, the
accompanying ends can be drawn:
1. Duty Administration has incomplete impact on
Individual Taxpayer Compliance.
2. Duty information somewhat has no impact on
Individual Taxpayer Compliance.
3. Duty Sanctions somewhat influence the
Compliance of Individual Taxpayers.
4. Duty Administration, Tax Knowledge and Tax
Sanctions simultaneously affect Individual
Taxpayer Compliance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Thanks to Mrs. Dwi Kartikasari, S.T., MBA. Mr.
Rahmat Hidayat., S.AB., M.AB Mr. Fandy Bestario
Harlan, S.T., M.MT. and all academic ranks and staff
of the Department of Business Management and
Batam State Polytechnic.
REFERENCES
Budhiningtias, M., & Bimantara, F. W. (2017). The
Influence of the Quality of the SPT Information System
on the Improvement of Taxpayer Satisfaction at the
The Effect of Tax Administration, Tax Knowledge and Tax Sanctions on Taxpayer Compliance
153

Merauke Pratama Tax Service Office. Unikom
Scientific Magazine Journal, 15, 123–136.
https://jurnal.unikom.ac.id/jurnal/unjuk-kualitas-
sistem.6d
Damajanti, A., & Karim, A. (2017). Effect of Tax
Knowledge on Individual Taxpayers Compliance.
Economics & Business Solutions Journal, 1, 1–19.
Directorate General of Taxation. Tax Reform in Indonesia.
www.pajak.go.id
Directorate of State Budget Preparation. (2019). State
Budget 2019.
https://www.kemenkeu.go.id/media/11213/buku-
information-apbn-2019.pdf
Ghozali, I. (2016). Multivariate Analysis Application with
IBM SPSS 23 Program. Diponegoro University.
Halawa, Jenita; Saragih, J. L. (2017). The Influence of Tax
Awareness, Tax Sanctions, Fiscus Attitudes, on
Compulsory Compliance at KPP Pratama Lubuk
Pakam. Journal of Accounting and Financial Research,
3(2), 243–256.
https://doi.org/10.1234/akuntansi.v3i2.449
Khuzaimah, N., & Hermawan, S. (2018). The Effect of
Taxpayer Understanding Level, Taxpayer Awareness,
and Tax Sanctions on Taxpayer Compliance. JIATAX
(Journal of Islamic Accounting and Tax), 1(1), 36.
https://doi.org/10.30587/jiatax.v1i1.447
Marcori, F. (2018). The Influence of Taxpayer Awareness,
Fiscus Service and Tax Sanctions on Individual
Taxpayer Compliance Conducting Small and Medium
Enterprises. Accounting journal.
http://ejournal.unp.ac.id/students/index.php/akt/article/
view/3791
Mardiasmo. (2013). 2013 Revised Edition of Taxation.
Andi.
Minister of Finance Decree no. 544 of 2000: regarding the
criteria for taxpayers who can be given a preliminary
refund of tax overpayments, (2000).
Olatunji Olaoye, C. (2017). Tax Information,
Administration and Knowledge on Tax Payers'
Compliance of Block Molding Firms in Ekiti State.
Journal of Finance and Accounting, 5(4), 131.
https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jfa.20170504.12
Rahayu. (2010). Indonesian taxation: concepts and formal
aspects. Graha Ilmu.
Saad, N. (2014). Tax Knowledge, Tax Complexity and Tax
Compliance: Taxpayers' View. Procedia - Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 109(1), 1069–1075.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.12.590
Sudrajat, Ajat; Ompusunggu, A. P. (2015). Utilization of
Information technology, Tax Socialization, Tax
Knowledge, and Tax Compliance. Journal of
Accounting and Taxation Research, 2(2), 193–202.
Sugiyono. (2018). Quantitative Research Methods.
Alphabet.
KUP Law Number 28 of 2007, (2007).
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
154
