
Human Resources Professional Transformation:
An Introduction of New Concepts
Abd. Rasyid Syamsuri, Ritha F. Dalimunthe, Parapat Gultom and Elisabet Siahaan
Faculty of Economy and Business, Universitas Sumatra Utara, Jl T.F Hanafiah, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Competence, Commitment, Work Contribution, Demography, Human Resources Professional
Transformation, Employee Productivity
Abstract: Conceptually this research develops a model with a new concept as renewal called Human Resources
Professional Transformation (HRPT). This concept is a synthesis to fulfil theoretical needs in answering
problems in the role and function of human resource management. Specifically, this concept aims to build
individual abilities/talents of line division of human resources in determining work from the business context
side with run the roles and functions of human resources which include Competence, Commitment, Work
Contribution, Demography (including age, education, gender, and work experience) so as to increase
employee productivity as a competitive advantage of the company.
1 INTRODUCTION
Organizations should organize human resources as
well as possible because the role of human resources
is the sole key of all activities or the activities to keep
a life span and achievement of success. In terms of
business strategy, an organization can succeed if it
has a sustainable competitive benefit (better than
competitors and able to maintain that benefit over a
long period of time), (Noe, et al., 2016). The
industrial revolution era 4.0 opens the opportunity for
human resources in having mastered concerning to
the latest technological developments. So that, it is
important to implement skills improvement programs
or renewal of skills of human resources based on the
recent needs of the industry, the competency needed
is human resources that have talents, this is because
talent is the key or crucial factor for the industry 4.0
successful implementation, (Rohida, 2018).
According to Fang, (2018), technology has
transformed the way to access the information and
how to conduct business. A major impact will occur
in the workplace because of this change. How the
workforce structured and organized must change
substantially, which has a lot of impacts on human
resource management. The change of functional in
the operation of human resources to let the
professionals’ human resources to get more strategic
works is the way to redefine human resource
management. Technology will not replace, but 'add'
many ways to do a job.
The concept of empowering human resources
with this new paradigm becomes a valuable asset for
companies that can be done by applying the concept
of human capital to encourage human role and
function as an integral part of the business processes
of a company. This shows that humans have a big role
in developing a company, so that management
requires a broad attention from management by
developing or maintaining it as an important element
in making strategic decisions. The study conducted
by Sukoco and Prameswari, (2017) regarding
"Human capital approaches to the management of
human resources productivity", found that in
Indonesia there are many companies that have not
implemented optimal human capital approaches. The
human maintenance capital-based human resources
requires not a little amount of money, but this is not a
problem if the impact is provided, they are a number
of advanteges obtained by the company or the rate of
return from the amount of money spent to finance the
labor management. GS Becker (1964, 1993) stated
that, humans are resources and a capital that produce
returns and every expenditure made in order to
promote the quality and quantity of capital investment
activity. The approach of human capital emphasizes
that, the role of humans is one of the primary capital
in a company with anunlimited value and amount,
which can be managed in a process, and able to make
Syamsuri, A., F. Dalimunthe, R., Gultom, P. and Siahaan, E.
Human Resources Professional Transformation: An Introduction of New Concepts.
DOI: 10.5220/0010935800003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 451-461
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
451

additional value for the company in achieving its
goals.
The survey which conducted by The Boston
Consulting Group and the World Federation of
People Management Association stated that
Indonesian companies face the issues in the quality
and quantity of expertise at all stages of the
organizations. Indonesia is predicted to the lack
supply of professional workers at managerial level. In
this research, it is explained that the problem
experienced by manufacturing companies in
Indonesia is because they do not have the experts
needed by the company. This shows projections
regarding inequality of needs and availability of
labor, especially in managerial level. ( Boston
Consulting Group (BCG ) research results and the
World Federation of People Management
Associations (WFPMA ) published in 2013. Many of
challenges are still faced in expanding the
manufacturing industry sector in Indonesia. First, the
bad quality of Human Resources is showed by less
competitive labor productivity and a high level of
rigidity (labor) in the labor market. Secondly, the
unavailability of reliable energy at competitive prices.
Third, logistical efficiency and support of the
manufacturing industry are still not enough. Fourth,
industrial policies that have not been integrated
between related institutions and the center. Fifth, The
unbalanced industrial structure which creates
dependence on raw and auxiliary materials overseas.
Sixth, the non- balanced industrial posture with the
largest composition in micro and small scale
industries is still not optimal. Seventh, especially in
diversity terms, the sources of industrial are still
limited, (Communication Ministry-Bank Indonesia,
2016).
Research conducted by Heuvel and Bondarouk,
(2017) stated that, HR Analytics in 2025 will become
an established discipline, that has proven to have an
impact on the results of business, and has a huge
influence on strategic and operational decision
making. Their research gives contribution to the HR
analytics development, as a field of research that is
able to inform businesses easily, by exploring how
HR analytics will be seen in the future time. HR
analytics showed that the responsibility for
identifying and measuring people as a stimulation
of business results. This lies in the function or
department of Human resources.
The goal of developing aligned HR policies and
practices to form a coherent system is referred to the
achievement of " horizontal integration" among the
human resources activities. Achieving vertical and
horizontal integration HR professionals are needed to
work together with line managers and employees. In
short, the strategic of vertical integration is about
human resource management , that are
comprehending the organization and its context,
Horizontal integration is building a clear HR system,
effectiveness demostration about how the HR system
influences the organization, and Performance
partnerships namely Professionals of human
resources cooperative work with the line managers
and with non-management employees , (Schuler and
Jackson, 2005). Jackson, et al., (2014) also added
that, HR formal professionals design, HR policies in
the field of business plans, supervisors change
policies into daily practices . Human resources
professionals have become more actively involved in
the process of business planning; formal policies
have become more subjective in interpretations by
individual managers when they try to respond the
certain situations and constantly changed;
employees with high abilities/talents often negotiate
contracts and working conditions.
The shifting of this paradigm has resulted in
roles of human resources professionality who
originally just acted as the administrative personnel
into a more comprehensive and strategic role. Krishna
and Prasad, (2012) stated that HR Professionals have
contributed to make a significant progress to the
company's performance. HR professionals face the
increase of accountability to ensure that HR practices
and function can boost business results. The
transformation of HR was initially focused on
making HR operations work efficiently and
effectively through standardization of processes and
technology. The next generation of HR
transformation is closely related to the company's
strategy and creates business value through HR
services . The servcices handle the most company's
urgent strategic challenges.
Successful transformation of HR is able to
increase additional human resources value for
business, (Ulrich, et al., 2009). If the professionals of
human resources really become business partners,
then their aim have to be a business goal.
Transforming HR professionals into business
partners is not its the final goals; This means to reach
the strategic, business-oriented goals. Ulrich and his
team also stated that senior HR professionals are
responsible for make sure that HR practices and
functions are aligned and stimulate the business
achievement. In order to conduct this function,
competency, commitment, work contribution and
demographics, the age of the employee, education,
gender and employee productivity are needed.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
452

Laine, et al., (2017) stated strategic position and
the role of business partners in general was built in
HR competencies. According to Kinicki and Fugate,
(2016), needs of competency are the wants to be
qualified, knowledgeable, and able to finish an
action, task, or goal. They suggest that a manager is
able to give real resources, time, relationships, and
training to develop employee competencies by
ensuring that employees have the knowledge and
information needed to do at work place.
Competence can improve credibility by showing
well business instincts, technical capabilities, and
professionalism . Competences can also be used as a
personal evaluation of the ability to do a job .
Oh, et al., (2015) stated that managers of human
resources- Human resources and human capital
(broadly representing their competence in doing
some works) related to their commitment to the
positively of human resources for example.
Company in HR (widely represents organizational
support for their work). In Bagaeva et al., (2018)
research, it was also stated that the competency
approach provides many opportunities to express the
professional and personal aspects needed in reaching
organizational high level efficiency in all aspects.
The chances to focus on key aspects of personal and
business quality which influence the final results.
At the same time, using the concept of competency
is very likely to express the expected knowledge and
skills from the employees who effectively fulfill their
duties.
Commitment focuses on building employee’s
value propositions to make sure that employees
will provide value to the organization and receive
the value in turn, (Ulrich, 2013). Companies that
achieve success with process management tend to
increase commitment in the process of intensity and
expand its influence in many processes, (Benner and
Tushman, 2003). According to Chadwick, et al.,
(2014), Line Manager's active involvement is one of
the important mechanisms that change the top
management's strategic with respect to commitment-
based HR into an HR system based on actual
commitments. Without the line managers active
involvement, the strategic emphasis of top managers
may still unrealize. Therefore, the commitment-
based HR system company implementation,
especially in the settings in which the system is
contrary with tradition, potentially could be a middle
management real indicator acceptance for manager's
strategic emphasis.
Workplace involvement is an essential factor in
the commitment level and loyalty shown by each
employee to the organizations. In addition, the
relationship between workers' trust in the authority of
decision making and their commitments to the
organization is a self- preservation. In a high levels of
trust environments, commitment in organizations is
greatly reduced when leaders failed to manage
procedures and results fairly, it shows that in a low
trust environment, establishing a clear rule of
procedure and the distribution of results is a chance,
because this will have a positive effect on employee
commitment as far as fair procedures and fair or
profitable results can be delivered as well. Whereas,
the failure to set some clear rules about procedures
and results is a threat in environments with high levels
of trust, because it has a potential to ruin the
employee’s commitment if the procedure is unfair or
create unfavorable results, (Seifert, et al., 2016).
For further research stated that, the role of Human
Resources divisions is needed in the human resources
implementation, (Trullen, et al., 2016). From their
research, it was stated that HR can contribute in the
implementation of the effectiveness HR practices by
line managers. The contribution of their research
involves the development of new theories in the HR
Practices implementation by focusing on the role of
organizations other than line managers, namely the
department of human resources that can influence the
results of the implementation of HR Practices. This
can be done by giving high- quality human resources
and sufficient technical advice for the field. Research
Trullen, et al., (2016), found evidence of HR practices
that were not implemented effectively, this was
shown when the HR department remained passive,
implementation would likely to fail. In addition, their
research also adds the widely accepted structure by
highlighting the different ways where HR
departments can shape business success. Facilitating
the implementation of effective HR practices, which
are the cornerstone of the effectiveness of HR in the
whole aspects (this is based on the viewpoint (Wright
and Nishii, 2013). The further contribution of their
research was to provide professional HR with
practical advice. It’s about how to handle the
implementation of HR Practices by line managers. As
a recommendation from research Trullen, et al.,
(2016), the results of the analysis they conducted
shows that the line manager implementation behavior
must be well understood in a similar manner to the
other productive work behaviors.
According to Marcus and Gopinath, (2017),
demography is an important factor that is considered
in the most human resource and management
decisions because it influences work behavior and
employee productivity. Their study analyzed the
impact of demographic variables such as age and
Human Resources Professional Transformation: An Introduction of New Concepts
453

gender in the employee perceptions of the corporate
practice involvement. Demographic variables, they
are: age and gender are chosen based on their
relevance. Jiang, et al., (2015), added that the
frequency and quality of interactions between
employees and other organizational members can be
affected by the existence of demograoic inquality. It
also influence th relevancy and credibility of
information received from other sources, and thus
affect the alignment between perceptions of HR
manager practices and coworkers and employees'
perceptions of HR practices.
Productivity can be defined as a relative concept
and the ratio of output divided by inputs, that cannot
be proven to increase or decrease without
measurement, either changes from competitors or
other standards at some points of time, (Hossain, et
al., 2018). From their research, the productivity of
employees means the output of a worker at a certain
time such as hours, days, weeks or months with the
effectiveness of employees. It measures the ability of
employees or a group of workers as well. Delmas and
Pekovic, (2018) added that the organizational team
work in combination with environmental practices
should lead to higher work productivity because the
association would enable the employees to increase
the diversity and their interpersonal contacts’ wealth
by working across departments and permitting the
development of relationships with workers in outside
their own unit.
Based on the explanations that have been stated, it
can be stated that the research on the Human
Resources Professional Transformation (HRPT) has
three strong foundations. First; there is a need to
collaborate HR analytics as an area of research that
can easily inform businesses, by seeing how HR
analytics will be seen in the future . HR analytics
shows that the responsibility for identifying and
measuring humans as a stimulation of business
results lies in the function or division of HR.
Second; HR professionals must be more actively
engaged in the business planning process to respond
the specific situations and change quickly. Third;
Successful HR transformation will increase the
business additional value of human resources . If HR
professionals really become business partners, then
the goal is business, (Heuvel and Bondarouk, (2017);
Zeidan and Itani (2020), Jackson, et al., (2014);
Ulrich, et al., (2009)).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Synthesis of Human Resources
Professional Transformation
Theory of Human Capital is a classic study theory of
GS Becker, (1964, 1993) which discusses the results
of investing in knowledge and skills in a person. In
theory investment in individual education and
training is the same as a set of business investments.
GS Becker, (1964, 1993) suggests that human capital
is knowledge contained in humans. Because human
resources contain knowledge and skills, as well as
economic development for the advancement of
technological and scientific knowledge that depends
on the accumulation of human resources itself. Roos,
et al., (1997) suggests that human capital comes from
knowledge, attitudes and intellectual agility of the
employees. Human capital focus on training policies
and human resource management that allow
managers to see all investments implemented in the
short term of time.
Human Capital Theory inspires many researchers
to consider the resources used by companies in
special forms of investment in human capital. BE
Becker and Huselid (1998) stated that the role of
human capital as a potential source of sustainable
competitive benefit, such as, work knowledge and
workers, intellectual capital, and work systems for
high performance. The existence of intellectual assets
and organizational systems by developing the assets
are used as important parts in making strategic
decisions. Furthermore, BE Becker, et al., (2001)
states that the strategic role of human resources or
human capital will implicitly focus on the productive
behaviour of people in the organization. This is
because tautologically, people in the organization can
influence the organization's environment. They also
suggested that strategic behaviour is a subset of
productive behaviour that directly functions in
implementing the company's strategy.
Boudreau and Ramstad, (2004) states that the
evolution of Human Resources (HR) and
measurement of HR will require a science decision
for human capital, which actually informs and refines
the decisions about human resources. This term is
referred to a talent that focuses on hidden talent and
real talent from employees who have potential. This
new science decision will focus on providing
excellent HR processes and programs, by providing a
concept for identifying decisions about human capital
and the most importantly how to logically connect
those decisions with the effectiveness of
organizational. Human capital/intellectual capital/
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
454

human resources/talents are the resources which
found in the employees and how organizing is
recognized as important point for strategic to achieve
success and competitive advantage, (Boudreau and
Ramstad, 2007). They also argued that human capital
is a decision needed to improve resources in an
organization that does not only cover individual
abilities but includes motivations and opportunities to
be faced.
According to Lawler III and Mohrman, (2003),
Professionals in Human Resources need to have more
effective strategic business partners. Ulrich, (1998),
argued further that HR professionals must make the
transition from strategic business partners to become
contributors in their organizations. In this regard,
Losey, (1999) also argues that HR professional
groups see many chances to change human capital
strategies into long- term competitive benefits. Thus,
part of the strategy to be creative and improve
productivity is to have the competencies needed to
achieve the result, (Long and Ismail, (2011). By doing
work for an organization with existing HR
professionals, successful organizations can be
characterized from the following three aspects,
namely leadership, individuals (talent), and ability.
Individuals need to be more productive to provide any
strategy, organizations need to have the right abilities;
and throughout the organization, leadership have to
be shared widely. These three organizational
dimensions can be seen as the result of human
resources, to lead the human resource professionals,
(Ulrich, 2014). Of the three domains, this study uses
individuals (talent) to determine the work of human
resources in achieving results seen from the business
context.
Individual abilities (talent or human capital) use a
simple formula which is able to help HR
professionals and managers to develop more
productive talents: namely (Talents= Competence
*Commitment *Contribution), (Ulrich, 2014). The
three elements of these similarities need to be fully
integrated in order to manage talent (individual
abilities) HR professionals. According to his theory
competence means that an individual who has the
knowledge, expertise and value needed to do a work.
Competence is obviously considered important
because an inability can led to poor decision making.
Ulrich, (2014), also argues that in the past decade,
competence and commitment have become an axis
for talent. The next generation of employees may be
competent (capable of doing work) and committed, if
the employees make a real contribution through work.
Their productivity can also decrease If their interest
in what they do decreases. Contributions occur when
employees feel that their personal needs are fulfilled
through their participation in the organization.
The human resources future logic starts with the
direction in which HR must add a value. This
direction has to be connected with business, both the
business context that form decision making and
certain stakeholders of the business strategy, (Ulrich,
2013). Ulrich also developed a STEPED framework
that was linked to the business context. This
framework consists of some trends they are: Social,
Technological, Economic, Political, Environmental,
and Demographic trends. From this framework this
research leads to Demographic trends, namely trends.
Specifically, HR professionals have to approach
the work from outside / inside and provide value by
knowing the context of business for an organization.
Human resources will need Specific actions in order
to add value of targets for HR work (individual,
organizational, and leadership) and areas for HR
investments (Human resources function, practices,
people, and analytics), (Ulrich and Dulebohn, 2015).
HR professionals can consume this HR work target to
face an obstacle. HR professionals must also realize
that not only external business factors can affect work
within the organization, but also the HR work nature
itself and how the work will be finished. The view of
Ulrich and Dulebohn, (2015) with the purpose of
adding value, and as part of the approach of work in /
out of HR, is very helpful in achieving the targets or
HR work results. Furthermore, the approach of HR
work outside/ in will build a talent and improve the
work of employees. A strategy also needs to be given
to individuals/employees so that they become more
productive and able to adjust their behaviour in
supporting the strategy.
Management infrastructure that understands and
able to implement the company's strategy is the base
of the HR strategy that creates value. In general, the
role of professionals in the field of HR function is
supposed to lead to these efforts. This implies that
there is a beginning of the traditional functional
orientation by HR managers and also a broader
strategic role comprehending that HR may have in the
company, (BE Becker, et al., (2001).
Huselid, et al., (1997), also summarized that most
companies had demonstrated the acceptable levels of
technical competence and potency of human
resources, none of the capabilities of traditional
human resources were not reduced in a value. The
value was not sufficient to meet the needs of a broader
HR strategy. Competencies that HR managers need to
develop and have the greatest impact on company
performance are business and strategic of HR
competencies.
Human Resources Professional Transformation: An Introduction of New Concepts
455

Schuler and Walker, (1990), suggested that HR
strategies are a sequence of processes and activities
distributed by human resources and line managers in
solving business problems related to people. Through
the HR strategy, HR management try to add value by
identifying these issues, assessing them, evaluating
and resolving the important problems for
organizational competitiveness which eventually
leads to the organization success. Furthermore, a
number of complementary activities that leads to the
creation of the HR strategy are found: First, in
response to the lots of changes in the environment,
attention and more pressure in HR. Second, issue
orientation is used to frame the human and business
resource agenda. Third, human resource concerns are
treated as business issues related to individuals and
become an integral part of successful organizational
change. Fourth, line managers get involved in human
resource problems.
Losey, et al., (2005), argued that a business
context can be built through: Positive psychology
contracts with belief and respect, are supported by
progressive management practices designed
monitoring their implementation. These are o the
chances for employees to share comprehensive
information about their organization and participation
in decision making. Good design and flexible work
that stimulates people to take part and grow. talent
developments can be achieved through selection,
induction, and careful learning. Positive leadership at
whole levels of work with the same goals and values.
Getting value from differences as a goal to achieve
business success. Organizational climate that
respects and recognize the behaviour is needed for the
organization achievements. Decentralized self -
management and teams that make the decisions.
A more specific explanation stated by Yeung, et
al., (1999) stated that the organizational effectiveness
learning styles depends on conformity with the
broader business context, namely culture, business
strategy and characteristics of industry. In the recent
stages of the research, they did, they were convinced
that organizations could generate new ideas
differently due to the business context. In turn, they
found that different organizational learning styles
produced different performance results. Although
organizational learning styles often overlap in
organizations significantly, it is clear that successful
organizations develop their abilities through one type
of learning to grow, develop, and adapt to changing
business environments.
According to Argyris and Schon, (1978) argues
that organizational learning is a metaphor that
requires us to re-examine organizational ideas.
Individual assemblies regulate when members
arrange regulations for decision delegation and
collective membership. In regulating regulatory
behaviour, they act for collectives in ways that reflect
the task system. Just as the theory of individual
actions can be inferred from individual behaviour, the
theory of organizational action can be inferred from
the pattern of organizational action. Organizational
learning occurs when members of an organization act
as agents of learning for organizations, responding to
changes in the organization's both of internal and
external environment by detecting and correcting
errors in the theory used, and instilling the results of
their investigations in person, through pictures,
organizational maps.
The four categories of HR Analytics, this research
leads to the structure. Then Heuvel and Bondarouk,
(2017) stated that the findings regarding the structure
of HR Analytics can be divided into three parts: the
positioning of HR analytics in organizations, the
internal and the external factors involved. Related to
this, the categories of the internal actors involved are
categories that lead to the business context. This is
also supported by the statement of Heuvel and
Bondarouk, (2017) from the research conducted that
HR analytics will have a main influence on decision
making in organizations in the future. Furthermore, as
a function, human resources analytics tends to
influence the arrangement and role of HR.
Zeidan and Itani (2020) added that organizations
must pay attention to the need in improving their HR
analysis capabilities, this can be done by further
investing in HR technology. The more investment
that is put into an HR analysis, the higher the rate of
return on investment that goes to the HR division and
organizational results. HR analysis, which refers to
business and technology, will be beneficial for
organizations to have entities that support other HR
functions in decision making and overall business
strategy. The HR Division should truly go through a
revolution with the introduction and application of
HR Analysis. Therefore, it is important for
organizations to run this division thoroughly in order
to take a more strategic role and be more capable in
achieving business goals and objectives.
In addition, Marler and Boudreau, (2016), argues
that in evaluating HR Analytics one of the theoretical
perspectives categories that explains about
management strategy as the cause-and-effect
relationships of the main social science disciplines,
they propose a theoretical framework that explains
the main cause and effect relationships one of them is
the HR strategy by (BE Becker, et al., 2001). The
views of BE Becker, et al., (2001) suggest that
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
456

professionals in Human Resources are increasingly
challenged to take part in making more strategic
perspective on their part in the organization.
According to of Schuler and Jackson (2005), the
professional human resources who are responsible in
designing and managing HR systems must enhance
an understanding of HR that cuts all HR activities like
practices and policies. This means, the HR strategy
implies that HR professionals have to maintain the
capacity operation as HR generalists rather than HR
specialists. Jackson, et al., (2014) also states that
human resource professionals use the name "HR
Strategy" widely to signal their belief. They believe
effective HR contributes to the business
effectiveness. As a result of the process of finding
Losey, et al., (2005) determined that the future of HR
employees-and HR professionals have to develop
business acumen, functional expertise, talent
management skills, leadership change, and
partnership/relationship skills, while also learning
how to use and applying technology. They also added
that the challenge of other skills transformation was
to enhance business acuity and push the process
generally in various industries and have discipline
under one organization.
The perspective of HR transformation that can
successfully increase the additional value of human
resources for business because human resources
transformation must begin with an obvious
understanding of the business context. Ulrich, et al.,
(2009) defined HR Transformation as an integrated,
harmonious, innovative approach. The business focus
to redefine how HR work is conducted in an
organization. This can help organizations meet the
needs made to customers, investors and other
stakeholders. They also stated that the idea of HR
transformation was aimed at HR professionals. HR
professionals must understand the principles of HR
transformation to be able to apply it to a much better
position. Sousa and Dias (2020) added that HR
transformation is aimed at the shift from an
administrative function to a more strategic-oriented
and integrated business function. The reorientation
mentioned, intended to contribute that HR is not only
to play an important role in the overall business
strategic planning but also acts to clarify and direct
employees about the desired organizational goals.
The explanation and understanding of the Human
Resource Analytics, Human Resources Professionals
and Human Resources Transformation that have been
put forward, it can be summarized as a temporary
basis for draw conclusions that Human Resource
Analytics is a portfolio of Human Resource
Professionals and Transformation related to human
capital role as a potential source of sustainable
competitive advantage to increase employee
productivity. The description of the literature that has
been presented is the basis of the flow of the synthesis
of the concept of Human Resources Professionals
Transformation which is contained in the appendix.
Human Resources Professional Transformation
is the ability of line-division managers of HR who are
innovative and adaptive toward the change to achieve
the effectiveness of organization. In the process of
implementing the professional transformation of
human resources, companies collaborate on the
ability of individuals/talents (line managers) to
determine work in achieving results seen from the
side of the business context. Collaboration HR
Professionals Transformation is a relationship of an
HR analytics to carry out the evolution of work with
competitive strategies in the face of competition and
the success of the company.
In the process of Human Resources Professional
Transformation, line managers so must develop more
productive talents as a skill to maintain
competitiveness and competitive advantage of the
company. These skills are applied in the form of
commitment, having competence, being able to
contribute to work that is seen based on demographics
(age, education, gender and work experience) to
increase employee productivity. In achieving success
in competitive competition, companies must be able
to adjust the innovation strategy of human resource
management as a process of company activities to
solve business problems.
Based on the results of the synthesis of Human
Resources Analytics, Human Resources
Professionals and Human Resources Transformation
who request further research, it can be stated that the
three concepts require new concepts to answer and
solve problems in human resource management. The
new concept offered to answer this problem gap is the
Human Resources Professional Transformation as
well as updates to this research. According to Barney,
et al., (2011) one of the implications of a theory of
maturity is declared critical, located when followed
by revitalization or decline. Thus, it can be concluded,
the concept of Human Resources Professional
Transformation as renewal has met the requirements.
2.2 Proposition of Human Resources
Professional Transformation
Flow and the description of its concept synthesis
raises the following propositions: "Human Resources
Analytics, Human Resources Professionals and
Human Resources Transformation as an integrated
Human Resources Professional Transformation: An Introduction of New Concepts
457

approach in the company's competitive advantage on
the concept of" Human Resource Professional
Transformation "that has the potential to increase
Employee Productivity". The proposition of this
study explains that the Human Resources
Professional Transformation Influences Employee
Productivity from the concepts of Human Resource
Analytics, Human Resources Professionals and
Human Resources Transformation as an integrated
approach in the company's competitive benefits. This
section must be in one column.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The developments of new concepts through theories
synthesis that promote the findings of the new
concept Human Resources Professional
Transformation from the Functional objective
perspective. Functional objectives emphasize
conformity between activities, the capabilities of the
human resources department, and business activities
and changes. The new concept has an important role
in theory as a construct that strengthens the theory of
Human Resources aimed in the ability of individuals/
talents of line managers of the HR division to
determine work as a corporate strategy in achieving
more productive results. This new concept is also
expected to contribute in strengthening the theoretical
basis of the Human Resources Analytics,
Professionals and Transformation as a sustainable
competitive advantage.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This article is part of the author's scientific work and
dissertation publication. The author would like to
express his gratitude to Universitas Sumatera Utara.
REFERENCES
Argyris C, Donald A. S. 1978. Organizational Learning: A
Theory of Action Perspective. Philippines, Addison-
Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.
Bagaeva I, Iliashenko O, Borremans A. 2018. Theoretical
and methodological aspects of the competence
approach to the evaluation of the organization’s
personnel, MATEC Web of Conferences, published by
EDP Sciences,
https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201819305060Moo
re, R., Lopes, J., 1999. Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. SCITEPRESS.
Barney J. B., Ketchen D. J., Jr, Wright M, 2011. The Future
of Resource-Based Theory: Revitalization or
Decline? Journal of
Management, 37 (5), 1299-1315.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206310391805
Becker B. E, Huselid M. A. 1998. High Performance Work
Systems and Firm Performance: A Synthesis of
Research and Managerial Implications Research in
Personnel and Human Resources Management, (16),
53-101. Jai Press Inc. ISBN: 0-7623-0368-9
Becker B.E., Huselid M. A dan Ulrich, D. 2001. The HR
Scorecard Linking People Strategy and Performance.
Massachusetts, Harvard Business School Press.
Becker Gary S. 1964, 1975, 1993. Human Capital A
Theoretical and Empirical Analysis, with Special
Reference to Education Third Edition. By The National
Bureau of Economic Research All rights reserved.
Published 1993. Chicago and London, The University
of Chicago Press.
Benner J. M, Thusman M. L 2013. Exploitation,
Exploration, And Process Management: The
Productivity Dilemma Revisited. Academy of
management review.
Boudreau J. W., Ramstad P. M. 2004. Talentship And
Human Resource Measurement And Analysis: From
Roi to Strategic Organizational Change, CEO
Publication.
Boudreau J. W., Ramstad P. M. 2007. Beyound HR.
Massachusetts, Harvard Business School Press
Chadwick C., Super J. F., Kwon K. 2014, Resource
Orchestration In Practice: Ceo Emphasis on Shrm,
Commitment-Based HR Systems, and Firm
Performance. Strategic Management Journal Published
online EarlyView in Wiley Online Library,
https://doi.org/: 10.1002/smj.2217
Communication Ministry-Bank Indonesia, 2016, Accessed
at https://infopublik.id/read/180764/transformasi-
industri-manufaktur-kunci-daya-saing-global-
indonesia.html?show
Delmas, M. A., & Pekovic, S. 2018. Organizational
Configurations for Sustainability and Employee
Productivity : A Qualitative Comparative Analysis
Approach. https://doi.org/10.1177/0007650317703648
Fang M. 2018. Viewpoints, Six trends in the future of human
resource management. Willis Towers Watson. All
rights reserved.
Heuvel S. Van den, Bondarouk T. 2017. The rise (and fall?)
of HR analytics: a study into the future application,
value, structure, and system support. Journal of
Organizational Effectiveness: People and
Performance. 4 (2) Published online in Emeraldinsight,
https://doi.org/10.1108/JOEPP-03-2017-0022
Hossain M. S, Khatun M., Sardar M. M. 2018. Does
Employee Involvement Really Increase Employee
Productivity?-An Employee Perception Based Study.
Published by GPH - Journal of Business Management,
1 (1) 5
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
458

Huselid M. A, Jackson S. E., Schuler R. S., 1997. Technical
And Strategic Human Resource Management
Effectiveness As Determinants Of Firm Performance.
Academy of Management Journal 40, (1) 171–188
Jackson, S. E., Schuler, R. S., & Jiang, K. 2014. The
Academy of Management Annals An Aspirational
Framework for Strategic Human Resource
Management: An Aspirational Framework for Strategic
Human Resource Management, 6520 (January).
https://doi.org/10.1080/19416520.2014.872335
Jiang K., Hu J., Liu S., Lepak D. P. 2015. Understanding
Employees’ Perceptions Of Human Resource
Practices: Effects Of Demographic Dissimilarity To
Managers And Coworkers. Journal of Human Resource
Management, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Published online
EarlyView in Wiley Online Library,
https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21771
Kinicki A, Mel F. 2016. Organizational behavior: a
practical, problem-solving approach. New York
McGraw-Hill Education
Krishna G.S.R, Prasad N.G.S 2012. Transforming HR
Professionals into Business Partners. European Journal
of Business and Management ISSN 2222-1905
(Paper), ISSN 2222-2839 (Online) 4 (4).
Lawler III E. E, Mohrman S. A. 2003. HR as a Strategic
Partner: What Does It Take to Make It Happen? Center
for Effective Organizations Marshall School of
Business Los Ageles, University of Southern
California
Laine P, Stenvall J, Tuominen H. 2017. A Strategic role for
HR: is it a competence issue?. Nordic Journal of
Business (NJB) 66 (1)
Losey M. R. (1999). Mastering The Competencies Of HR
Management, 38(2), 99–102.
Losey, Meisinger S., Ulrich D. 2005. The Future of Human
Resources Management, New Jersey, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc., Hoboken.
Long C. S, Ismail W. K. 2011. An analysis of the
relationship between HR professionals’ competencies
and firms’ performance in Malaysia. Routledge Taylor
& Francis Group:The International Journal of Human
Resource Management, 22(5), 3, 1054–1068
Marcus A., Gopinath N. M. 2017. Impact of The
Demographic Variables on The Employee
Engagement-An Analysis. ICTACT Journal on
Management Studies, 5-3(2), ISSN: 2395-1664
(Online), https://doi.org/10.21917/Ijms.2017.0068
Marler J. H., Boudreau J. W. 2016. An evidence-based
review of HR Analytics. The International Journal of
Human Resource Management, Routledge Taylor &
Francis Group: 5192 (November), 1–24.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2016.124469
Noe R. A, Hollenbeck J. R, Gerhart B, Wright P. M. 2016.
Fundamentals Of Human Resource Management, Sixth
Edition, New York Mc Graw Hill Education.
Oh S. I, Blau G, Han J. H & Kim S. 2015. Human Capital
Factors Affecting Human Resource (HR) Managers’
Commitment to HR and The Mediating Role of
Perceived Organizational Value on HR. Journal of
Human Resource Management, Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Published online EarlyView in Wiley Oline Library,
https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21768
Rohida, L., Sos, S., & Si, M. 2018. Pengaruh Era Revolusi
Industri 4.0 terhadap Kompetensi Sumber Daya
Manusia. Jurnal Manajemen Bisnis Indonesia, 6(1),
14–136.
Roos J, Roos G, Dragonetti N. C, Edvinsson L. 1997.
Intellectual Capital Navigating the Nevv Business
Landscape, London Macmillan Press Ltd
Schuler R. S, Jackson S. E. 2005. A quarter-century review
of human resource management in the US: The growth
in importance of the international perspective.
Management Revue, ISSN 1861-9916, Hampp,
Mering, 16(1), 11-35. Published online in Econstor,
https://doi.org/10419/78888
Schuler R. S, Walker J. W. 1990. Human Resources
Strategy: Focusing on Issues and Action. Academy of
Management
Seifert M, Brockner J, Bianchi E. C, Moon H. 2016. How
Workplace Fairness Affects Employee Commitment-
New research offers insights into the effects that fair
procedures and outcomes-or a lack of them-have on
employees’ commitment to an organization. MIT Sloan
Management, 57(2)
Sousa M. J, Dias I. 2020. Business Intelligence for Human
Capital Management. International Journal of Business
Intelligence Research, 11(1), DOI:
10.4018/IJBIR.2020010103
Sukoco I, Prameswari D. 2017. Human Capital Approach
to Increasing Productivity Of Human Resources
Management. Jurnal AdBispreneur, 2(1)
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG). 2013. Growing
Pains, Lasting Advantage-Tackling Indonesia’s
Challengers, May
Trullen, J., Stirpe, L., Bonache, J., Division, M., &
Valverde, M. 2016. The HR department ’s contribution
to line managers ’ effective implementation of HR
practices, 1997, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-
8583.12116
Ulrich D. 1998. A New Mandate for Human Resources.
Harvard business review, January-February
Ulrich D, Allen J. Brockbank W, Younger J, Nyman M.
2009. HR Transformation: Building Human Resources
from the Outside In. The RBL Institute, USA, McGraw-
Hill Books
Ulrich D. 2013. Are We There Yet? What’s Next for HR.
The RBL Group Oracle/Accenture White Paper, April
Ulrich D. 2014.The future targets or outcomes of HR work:
individuals, organizations and Leadership. Human
Resource Development International, 17:1, 1-9,
Routledge Taylor & Francis Group:
https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2013.825144
Ulrich D, Dulebohn J. H. 2015. Are We There Yet? What’s
Next for HR. Human Resource Management Review.
Elsevier Inc, dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2015.01.004
Wright P. M, Lisa H. N. 2013. Strategic HRM and
Organizational Behavior: Integrating Multiple Levels
Human Resources Professional Transformation: An Introduction of New Concepts
459

of Analysis. CAHRS working paper series,
digitalcommons, Cornell University ILR School
Yeung A.K., Ulrich D, Nason S.W., Mary A.V.G 1999.
Organizational Learning Capability, New York, Oxford
University Press, Inc.
Zeidan S., Itani N. 2020. HR Analytics and Organizational
Effectiveness. International Journal on Emerging
Technologies 11(2): 683-688(2020).
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
460
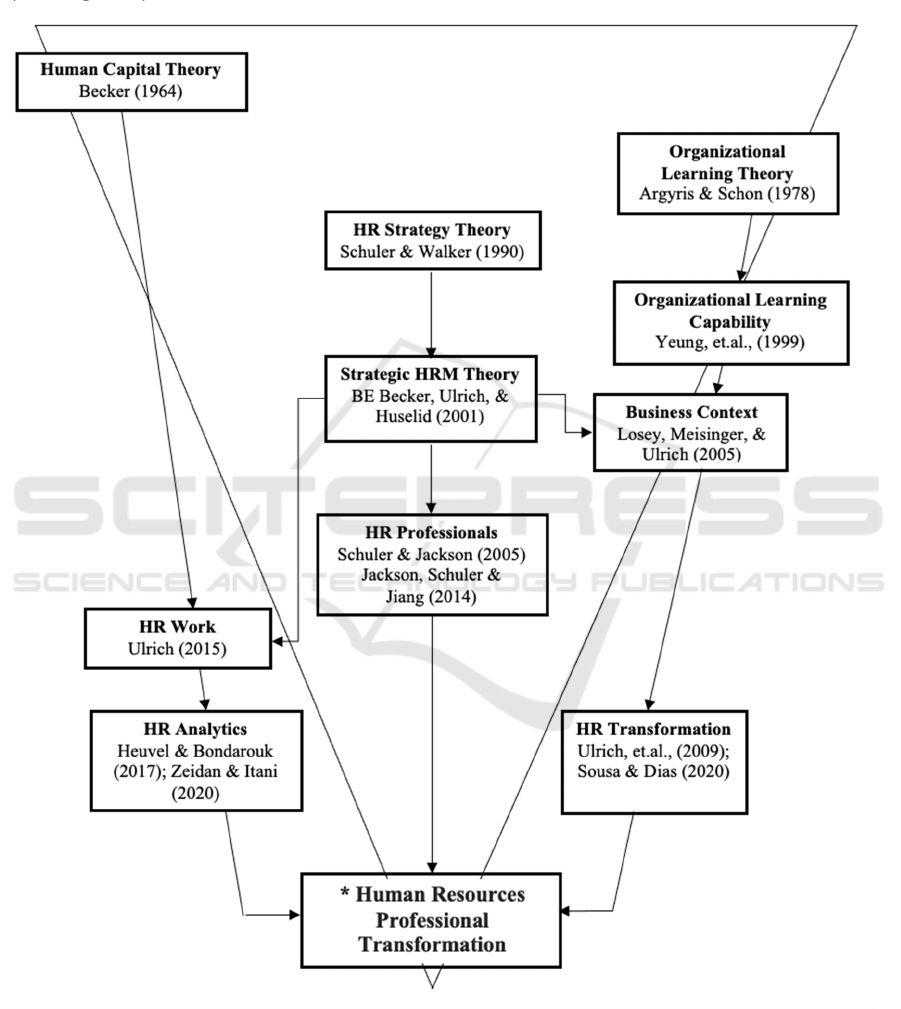
APPENDIX
*HR Professional Transformation*
Synthesis pathway of Human Resources Professional Transformation
Human Resources Professional Transformation: An Introduction of New Concepts
461
