
Does the Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance, and Privacy Concern
Effect on the Online Impulse Buying Tendency?
Anisha Rizka Femilia and Mega Mayasari
Managerial Accounting Study Program, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Jl.Ahmad Yani, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: Online impulse buying; novelty; advertising value; relevance; privacy concern; social media advertising
Abstract: Online impulse buying is a factor that can generate profit for online retailers and advertisers. Currently, buying
and selling activities do not only occur face-to-face, but can be done through an e-commerce which offers
many conveniences. Marketing methods are also increasingly developing through social media. This research
is a quantitative study which aims to test the effect of novelty factors, advertising value, relevance, and privacy
concern on the tendency to make impulsive online purchases. Respondents used were students majoring in
Business Management at Batam State Polytechnic with a sample of 108 students with a sampling technique
using purposive sampling. This study uses multiple linear regression analysis techniques. The results of this
study indicate that the relevance and privacy concern have a significant effect on the tendency to make online
impulse. Meanwhile, the novelty and advertising value variables did not have a significant effect on the online
impulse buying tendency.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the increasingly rapid development of the
era, marked by the development of increasingly
advanced technology. One form of technological
development is the digital economy. The digital
economy can be interpreted as a market consisting of
digital technology that facilitates trade in goods and
services through electronic commerce (OECD,
2013). E-commerce is a form of digital economy. we
can carry out buying and selling activities using the
internet network or online without having to set up a
shop (Kristiadi, 2017).
Indonesia was the country with the fastest e-
commerce growth out of 10 other major countries
with a growth of 78% in 2018 (Widowati, 2019).
There are more than 50% of existing purchases
originating from impulse buying which indicates the
importance of impulse buying (Amos, Holmes, &
Keneson, 2014). Other studies say that impulse
buying accounts for about 40% of all online spending
(Verhagen & Van Dolen, 2011).
Online shopping platforms are not the only factor
that can influence impulsive online purchases.
Another factor that can cause the tendency to make
impulsive online purchases is a marketing strategy
with advertising (Pratomo & Ermawati, 2019).
Advertising can be done through print media,
television, browsers, etc. The latest phenomenon in
marketing is the use of social media by sellers,
especially their partnerships as influencers on social
media to attract consumers' interest in goods and
services to drive traffic to their online stores (Ryu &
Park, 2020). Influencer advertising is a growing area
that offers fast and targeted access to an engaged
audience that is less expensive than traditional
advertising (Siqueira Jr., Pena, Horst, & Molina,
2019). The value of advertising affects potential
customers' intentions to buy the advertised product
(Martins, Costa, Oliviera, Goncalves, & Branco,
2019). Social trust can be seen from the results of
using social media platforms for shopping by users
who do not have a personal relationship with each
other (Alalwan, et al., 2019). This study will examine
the effect of novelty, advertising value, relevance,
and privacy concern on the tendency of impulsive
online purchases.
The idea of this research from (Dodoo & Wu,
2019). This research is different from previous
research. Previous research was conducted in the
United States, while this study was conducted in
Indonesia. Seeing the many online shopping
platforms in Indonesia with all the new features that
are interesting and easy at this time, will affect
impulsive online purchases (Kristanto, Suharto, &
444
Rizka Femilia, A. and Mayasari, M.
Does the Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance, and Privacy Concern Effect on the Online Impulse Buying Tendency?.
DOI: 10.5220/0010935700003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 444-450
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Aly, 2020). Therefore, researchers are interested in
raising this topic for research. This study uses
multiple linear regression as an analytical tool in this
study, because the researcher follows the opinion of
(Jogiyanto, 2012) that the Likert scale is grouped into
interval data, therefore this study can use multiple
linear regression. Previous research used a sample of
students from a university in the United States, while
this study used a sample of students majoring in
Business Management at the Batam State
Polytechnic. This study will use data collection
techniques with surveys using questionnaires to
students majoring in Business Management at the
Batam State Polytechnic through online media. Based
on the explanation of the background above, the
research to be studied has the title The Effect of
Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance, and Privacy
Concern of the Online Impulse Buying Tendency.
2 LITERATURE STUDY
2.1 Theoretical Review
2.2.1 Social Influence Theory
Social influence theory distinguishes between
different types and levels of social commitment:
compliance, identification, and internalization.
Theory (Kelman, 1958) explains how various
commitment mechanisms change attitudes toward
target behavior. For example, obedience occurs when
a person accepts influence because he or she expects
to get a positive reaction from another person or
group with a normative commitment. Identification
occurs when system users adopt behaviors to create
satisfying and self-determining relationships with
other people or groups with affective commitment.
Internalization occurs when system users adopt
behaviors due to content, which they find conform to
their own values with internal motivation.
2.1.2 Theory of Economic Growth
Growth theory is generally associated with models,
mechanisms, interpretations, and predictive
frameworks that describe the economic drivers of a
country's growth. The basis of growth theory is that
there are external technologies that are sustainable
and advanced. Advances are linked in the form of
new elements, new Markets, and new operations. In
e-commerce itself there is a trade called Business to
Consumer (B2C). The growth of a country's B2C e-
commerce is driven by external factors from
developed or leading countries (Ho, Kauffman, &
Liang, 2007).
2.1.3 Online Impulse Buying Tendency
Impulsive online buying tendencies are the extent to
which individuals tend to make unwanted, immediate
and non-reflective purchases (Weun, Jones, & Beatty,
1998). According to the theory (Beatty & Ferrell,
1998) sudden and direct purchases without any
intention before shopping either to buy certain
products or to perform certain buying tasks.
2.1.4 Novelty Categorization Theory
Novelty Categorization Theory or NCT proposes the
independence of a bond. NCT shows that in general,
people are curious and will approach new events
based on the motivation to know (Kagan, 1972). New
events can be interesting and arouse curiosity
(Berlyne, 1960). Novelty can also be threatening with
the possibility of carrying some risks (Bornstein,
1989). According to (Zajonc, 1998), there is a close
relationship between repeated exposure and positive
influence so that one does not conclude that novelty
is inherently a bad thing.
2.1.5 Social Media Advertising
According to (Joseph, 2011) there are 3 activities that
can be done in social media, namely: 1) Media
Maintenance: Taking care of social media by posting
regularly on social media such as Twitter, Instagram,
Facebook, and others. 2) Social Media Endorsement:
Looking for public figures who have a lot of time to
support a company's social media in order to increase
interest in the products sold by the company. 3) Social
Media Activation: Create unique activities to enhance
Word of Mouth (WoM). WoM will significantly
increase interest in the company's products. (Ducoffe,
1995) also said that entertainment has a positive
effect on advertising value, pleasure for the
advertisements displayed also has an effect on
customer ratings.
2.2 Empirical Review
According to (Dodoo & Wu, 2019) research, the
perceived personalization of social media advertising
positively affects the perception of novelty, perceived
relevance and advertising value. According to
research of (Sofi & Nika, 2017), intrinsic factors
influence impulse buying decisions. Consumers who
have high cognitive dissonance will make higher
impulsive purchases. According to the research of
Does the Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance, and Privacy Concern Effect on the Online Impulse Buying Tendency?
445

(Evans, Phua, Lim, & Jun, 2017), the language of
disclosure in paid advertising positively affects ad
recognition, which then interacts with the memory of
the audience who saw the ad.
According to research (Sohn & Kim, 2020); 1)
81% of respondents have used social commerce
services; 2) 52% of respondents access social
commerce services whenever they want; 3) 56.9% of
respondents are satisfied using social commerce
services, this shows that the potential for repurchase
and overall social commerce growth is quite high.
The research of (Hermanda, Sumarwan, & Tinaprilla,
2019) has shown that social media influencers have a
significant positive effect on the brand image of local
cosmetic products and consumer self-concepts.
Another conclusion is that brand image has a
significant positive effect on consumer buying
interest, in contrast to the effect of self-concept. In
addition, the results of the study state that influencers
do not have a significant effect on consumer buying
interest, but produce a significant positive influence
indirectly through the brand image variable.
The research of (Sreejesh, Justin, Crolyn, & Jose,
2020) says that the clarity of the message conveyed
redirects the user's attention to the ad, and develops
better advertising effectiveness. According to
research (Jonathan & Mulyadi, 2019), security is a
key variable that affects a customer's purchase
decision. Privacy, security and trust simultaneously
have an influence on customer decisions in making
purchases. How online stores can provide
convenience to users affects customer decisions in
making purchases.
2.3 Hypothesis Development
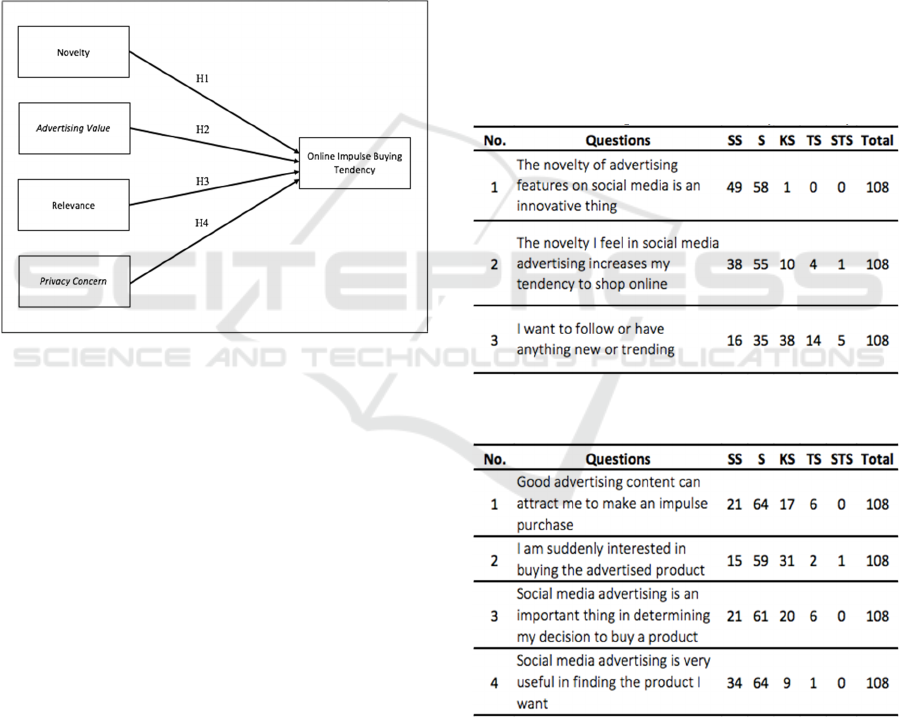
2.3.1 Perceived Novelty
Impulse buying is also a response to novelty (Larose,
2001). This statement is supported by empirical
evidence from research (Yu & Bastin, 2010) which
finds that novelty is the most critical factor
influencing consumer impulse buying. Research
(Hausman, A., 2000) also found that there is a
positive relationship between novelty as an indicator
of impulsive buying tendencies. The results of
previous studies are also in accordance with the
theory (Kagan, 1972) which says that humans have a
tendency to know new things. Based on the
description above, the hypothesis is proposed:
H1: Novelty perceived by customers has a
positive effect on the online impulse buying
tendency.
2.3.2 Advertising Value
There are two important engines in advertising value,
namely: Informativeness and Irritation.
Informativeness refers to the extent to which
advertising can provide information to viewers
(Ducoffe, 1995). Irritation occurs when the
advertising message conveyed can disturb the viewer
(Ducoffe, 1995). Customer perceptions of advertising
value can also influence the tendency of impulsive
online purchases. Impulse buying can be triggered by
heuristic processes such as whether a product gives
rise to the urge to buy or not (Verplanken & Sato,
2011). Based on the description above, the hypothesis
is proposed:
H2: Advertising value has a positive effect on
the online impulse buying tendency.
2.3.3 Perceived Relevance
Social media ads created by studying the online
activity of customers and tailoring the advertising
content to the needs and interests of the customers
based on their browsing history. This results in
customers feeling that the ads displayed are
personalized and relevant to what customers think.
This statement is also in accordance with the results
of previous research (Dodoo & Wu, 2019), namely,
perceived relevance explains the impact of
personalization on the online impulse buying
tendency. Perceived relevance affects attitude
changes and affects the tendency of irregular
customer behavior (Dodoo & Wu, 2019). Based on
the description above, the hypothesis is proposed:
H3: Relevance perceived by customers has a
positive effect on the online impulse buying
tendency.
2.3.4 Privacy Concern
There are two types of routine internet activity,
namely: Consumption of online information and
opening e-mails from unknown sources (Chen,
Beaudoin, & Hong, 2017). The consumption of
information referred to refers to viewing news, health
information, product descriptions, and reading e-mail
and financial account information (Coiro & Dobler,
2007). The vulnerability of the occurrence of privacy
problems causes many users to be reluctant to buy
products online. Research (Dodoo & Wu, 2019) says
that privacy problems tend to arise from the use of
individual information, whereas impulse buying
consists of spontaneous purchases without careful
consideration, this makes it difficult to establish a
relationship between privacy concerns and the
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
446
tendency to buy impulsively online. Security is also a
key variable that can influence customer decisions in
making purchases (Jonathan & Mulyadi, 2019).
Based on the statement and the results of previous
research, the researcher argues that privacy concern
has no influence on the tendency of impulsive online
purchases. Based on the description above, the
hypothesis is proposed:
H4: Privacy concern has a negative effect on
the online impulse buying tendency.
Based on the description of the theoretical study,
literature review, and hypothesis development that
have been described previously, the research model
can be seen in Figure 1:
Figure 1: Research Model.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is a type of quantitative research. The
source of data used in this research is primary data.
The instrument used in this research is a
questionnaire. The questionnaire consists of 2 parts,
the first part is the content and the second part is the
respondent's data. The research questionnaire used a
5-point Likert scale. The sample used in this study
amounted to 108 respondents. The sampling
technique used is non-probability sampling, with the
type of purposive sampling. Samples were taken in
accordance with the criteria used in this study. This
research was conducted at the Batam State
Polytechnic. The object of this research is the active
students of Batam State Polytechnic with an age
range of 18-24 years.
The data analysis technique used multiple
regression analysis using SPSS 25 software.
Descriptive statistical analysis will be used in this
study. The classical assumption test that used in this
study are multicollinearity and heteroscedasticity test.
Test the hypothesis using a partial significant test (t
test). The regression equation in this study is as
follows:
Y = α + b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
+ b
4
X
4
+ ε
(1
)
4 RESULTS
The population data used in this study are the active
students of Politeknik Negeri Batam. The criteria is
students with an age range of 18-24 years as many as
108 students or respondents.
4.1 Theoretical Review
Below is a descriptive statistical analysis table:
Table 1: Descriptive statistical analysis novelty.
Table 2: Descriptive statistical analysis, advertising value.
Does the Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance, and Privacy Concern Effect on the Online Impulse Buying Tendency?
447
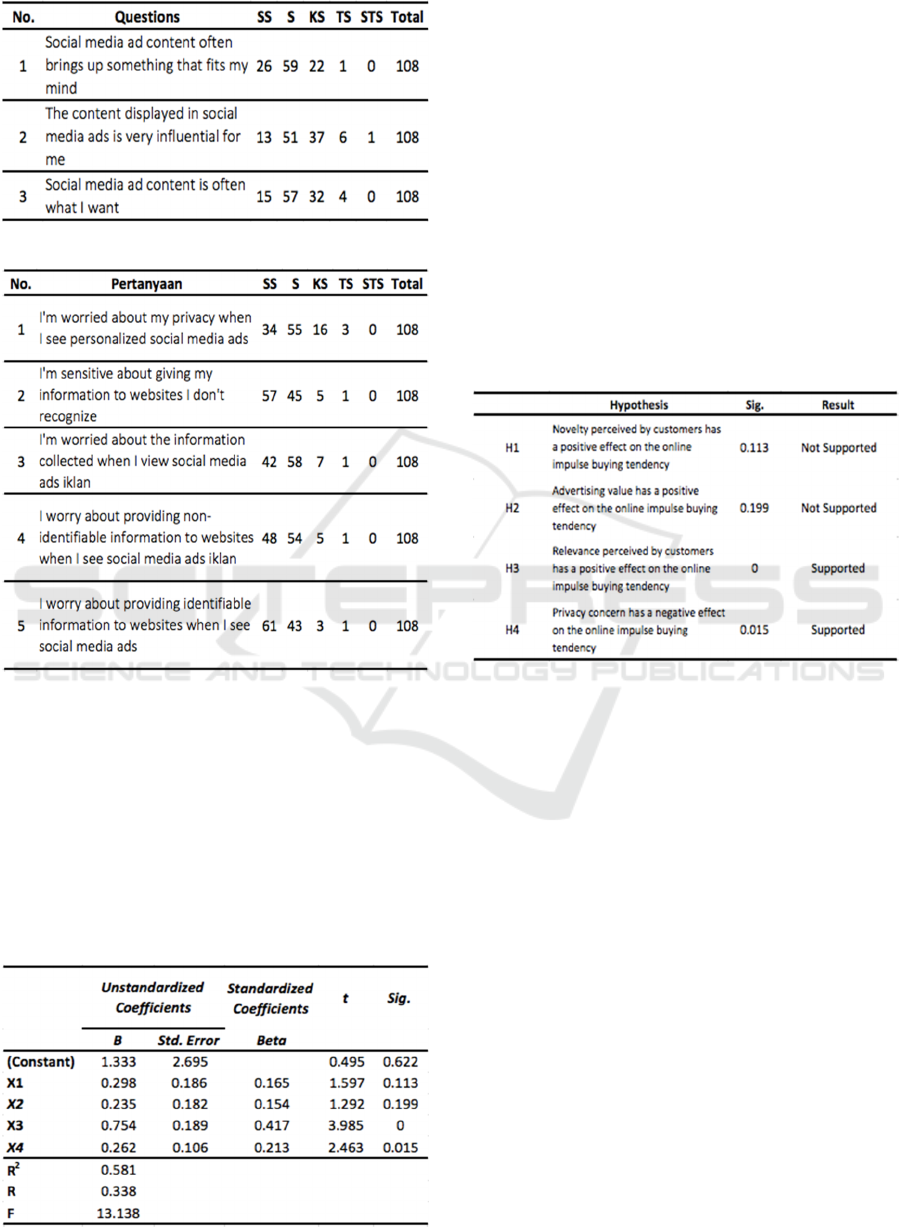
Table 3: Descriptive statistical analysis, relevance.
Table 4: Descriptive statistical analysis, privacy concern.
4.2 Multiple Regression Analysis
Previously, this study had tested the classical
assumptions test. Normality test, heteroscedasticity
test, and multicollinearity test. The results of these
tests are normal or free from problems. Testing
research hypotheses using multiple regression
analysis that is processed through the application of
statistics SPSS 25. The author has done testing with
SPSS that are attached on the following table:
Table 5: Multiple Regression Analysis.
Based on the above table, the regression equation
for this study is:
Y = 1.333 + 0,298KB + 0,235AV +
0,754RE + 0,26PC
(2
)
Adjusted R2 value shows a value of 0.581. It
means that the dependent variable of online impulse
buying tendency is influenced by the independent
variables (Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance,
and Privacy Concern) by 58% (0.581) and the rest is
explained by other factors outside the research model.
4.3 Data
Analysis
The following is a summary table of test results from
this study:
Table 6: Data Analysis.
4.3.1 Novelty Perceived by Customer Has a
Positive Effect on the Online Impulse
Buying Tendency
Based on the results of the hypothesis in table 6 shows
that H1 is not supported, that is, novelty does not have
a significant effect on the tendency to make impulsive
online purchases. This is because novelty does not
encourage people to make impulse purchases online.
The results of this study are in accordance with
previous research (Dodoo & Wu, 2019) which states
that perceived novelty cannot predict the impulse to
make impulse purchases. Novelty is enough to be an
attitude or change, but not enough to encourage
purchase. This is also supported by the theory
(Kagan, 1972) which states that humans have a
curiosity about new things
4.3.2 Advertising Value Has a Positive
Effect on the Online Impulse Buying
Tendency
Based on the results of hypothesis testing which can
be seen in table 6, it shows that H2 is not supported.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
448

These results can be interpreted that advertising value
has no significant effect on the online impulse buying
tendency. The results of this test are in line with
previous research (Dodoo & Wu, 2019) which states
that advertising value cannot be ascertained as a
determinant of the online impulse buying tendency.
Customers need to process the ads they see in order
to provide an assessment. The evaluation made of the
advertisement inhibits the urge to make an impulsive
decision.
4.3.3 Relevance Perceived by Customer Has
a Positive Effect on the Online Impulse
Buying Tendency
The results of the hypothesis test generated in this
study indicate that H3 is supported, which means the
relevance or suitability of the perceived customer for
advertisements, products, and perceptions have a
significant positive effect on the online impulse
buying tendency. The test results for the third
hypothesis are in line with previous research (Dodoo
& Wu, 2019) which states that perceived relevance
has a positive influence on the online impulse buying
tendency. This result is also reinforced by the theory
(Kelman, 1958) which says that internalization occurs
when system users adopt behavior due to content,
which they find appropriate or relevant to their own
values
4.3.4 Privacy Concern Has a Negative Effect
on the Online Impulse Buying
Tendency
Based on the results of the hypothesis testing that has
been carried out, it shows that H4 is supported.
According to (Coiro & Dobler, 2007) this privacy
security problem can occur when performing
activities such as viewing news, health information,
product descriptions, and reading e-mail and financial
account information from unknown sources. The
existence of these problems makes customers to make
purchases online. The results of this study are
strengthened by previous research (Jonathan &
Mulyadi, 2019) which says that security is also a key
variable that can influence customer decisions in
making purchases. Customers will consider before
making a purchase, so that impulsive purchases do
not occur.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the test results that have been described
previously, conclusions can be drawn, namely: (1)
Novelty does not significantly affect on the online
impulse buying tendency; (2) Advertising value has a
positive effect on the online impulse buying
tendency; (3) Relevance perceived by customers has
a positive effect on the online impulse buying
tendency; (4) Privacy concern has a negative effect on
the online impulse buying tendency.
This research still has limitations that need to be
addressed for the development of similar research in
the future. First, the sample used in this study was
only students majoring in Business Management at
the Batam State Polytechnic. Second, this study only
focuses on impulse buying. Third, the collection of
questionnaires is quite time consuming due to the
long-time feedback from respondents.
Based on the limitations of this study that have
been described previously, the following suggestions
can be considered for further research. First, further
research is expected to use a wider and more general
sample. Second, further research is expected to add
independent variables that are assumed to affect the
tendency to make impulsive online purchases.
REFERENCES
Alalwan, A. A., Algharabat, R. S., Baabdullah, A. M.,
Rana, N. P., Raman, R., Dwivedi, R., et al. (2019).
Examining the impact of social commerce dimensions
on customers' value cocreation: The mediating effect of
social trust. Consumer Behavior, 434.
Amos, C., Holmes, G., & Keneson, W. (2014). A meta-
analysis of consumer impulse buying. Journal of
Retailing and Consumer Services.
Beatty, S., & Ferrell, M. (1998). Impulse buying: modeling
its precursors. Journal of Retailing.
Chen, H., Beaudoin, C. E., & Hong, T. (2017). Securing
Online Privacy: An Empirical Test on Internet Scam
Victimization, Online Privacy Concerns, and Privacy
Protection Behaviors. Computers in Human Behavior
Coiro, J., & Dobler, E. (2007). Exploring the online reading
comprehension strategies used by sixth-grade skilled
readers to search for and locate information on the
Internet. Reading Research Quarterly.
Dodoo, N. A., & Wu, L. (2019). Exploring the anteceding
impact of personalised social media advertising on
online impulse buying tendency. Internet Marketing
and Advertising, 88.
Dodoo, N. A., & Wu, L. (2019). Exploring the anteceding
impact of personalised social media advertising on
online impulse buying tendency. International Journal
Marketing and Advertising, 74.
Does the Novelty, Advertising Value, Relevance, and Privacy Concern Effect on the Online Impulse Buying Tendency?
449

Ducoffe, R. H. (1995). Why consumers like Facebook
brands: the role of aspirational brand personality in
consumer behavior. Journal of Promotion Management,
103-127.
Evans, N. J., Phua, J., Lim, J., & Jun, H. (2017). Disclosing
Instagram Influencer Advertising: The Effects of
Disclosure Language on Advertising Recognition,
Attitudes, and Behavioral Intent. Journal of Interactive
Advertising, 146.
Hausman, A. (2000). A multi-method investigation of
consumer motivations in impulse buying behavior.
Journal of Consumer Marketing.
Hermanda, A., Sumarwan, U., & Tinaprilla, N. (2019). The
Effect of Social Media Influencer on Brand Image,
Self-Concept, and Purchase Intention. Journal of
Consumer Sciences.
Jogiyanto, H. (2012). Teori Portofolio dan Analisis
Investasi. Edisi Ketujuh. Yogyakarta: PT BPFE
Yogyakarta.
Jonathan, I. R., & Mulyandi, M. R. (2019). Pengaruh
Privasi, Keamanan, dan Kepercayaan Terhadap
Keputusan Pembelian Masyarakat dalam E-Commerce.
Prosiding Seminar dan Lokakarya Kualitatif Indonesia
2019.
Joseph, T. (2011). APPS: The Spirit of Digital Marketing
3.0. Jakarta, Indonesia.
Kagan, J. (1972). Motives and Development. Journal of
Personality and Social Psychology.
Kelman, H. (1958). Compliance, Identification and
Internalization; Threes processes of attitude change.
Journal of Conflict Resolution.
Kristiadi, N. (2017, Agustus 15). E-Commerce, Manfaat,
dan Keuntungannya. Retrieved Januari 20, 2020, from
Kompasiana.com:
https://www.kompasiana.com/novikristiadi/5992634e9
3be2508e06c5402/e-commerce-manfaat-dan-
keuntungannya
Larose, R. (2001). On the Negative Effects of E-
Commerce: A Sociocognitive Exploration of
Unregulated On-line Buying. Journal of Computer-
Mediated Communication.
Martins, J., Costa, C., Oliviera, T., Goncalves, R., &
Branco, F. (2019). How smartphone advertising
influences consumers' purchase intention. Journal of
Business Research.
OECD. (2013). "Measuring the Internet Economy: A
Contribution to the Research Agenda" ECD Digital
Economy Papers, No. 226. Paris: OECD Publishing.
Pratomo, D., & Ermawati, L. (2019). Kecenderungan
Pembelian Impulsif Ditinjau dari Perspektif Islam
(Studi Kasus Pada Pengunjung Malioboro Mall
Yogyakarta). Jurnal Ekonomi & Ekonomi Syariah.
Ryu, S., & Park, J. (2020, July). The effects of benefit-
driven commitment on usage of social media for
shopping and positive word-of-mouth. Journal of
Retailing and Consumer Services.
Siqueira Jr., J. R., Pena, N. G., Horst, E., & Molina, G.
(2019). Spreading the Word: How Customer
Experience in a Traditional Retail T Setting Influences
Consumer Traditional and Electronic Word-of-mouth
Intention. Electronic Commerce Research and
Applications.
Sohn, J. W., & Kim, J. K. (2020). Factors that in uence
purchase intentions in social commerce. Technology in
Society.
Sreejesh, S., Justin, P., Crolyn, S., & Jose, P. (2020).
Consumer response towards social media advertising:
Effect of media T interactivity, its conditions and the
underlying mechanism. International Journal of
Information Management.
Verhagen, T., & Van Dolen, W. (2011). The influence of
online store beliefs on consumer online impulse buying:
a model and empirical application. Information &
Management.
Verplanken, B., & Sato, A. (2011). The psychology of
impulse buying: an integrative selfregulation approach.
Journal of Consumer Policy.
Weun, S., Jones, M. A., & Beatty, S. E. (1998).
Development and validation of the impulse buying
tendency scale. Psychological Reports.
Widowati, H. (2019, April 25). Indonesia Jadi Negara
dengan Pertumbuhan E-Commerce Tercepat di Dunia.
Retrieved Maret 15, 2020, from
databoks.katadata.co.id:
https://databoks.katadata.co.id/datapublish/2019/04/25
/indonesia-jadi-negara-dengan-pertumbuhan-e-
commerce-tercepat-di-dunia
Yu, C., & Bastin, M. (2010). Hedonic shopping value and
impulse buying behavior in transitional economies: a
symbiosis in the mainland China marketplace. Journal
of Brand Management.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
450
