
Determine Factors of Accounting Student Satisfaction in Online
Learning
Hana Ainubie and Muhammad Ramadhan Slamet
Managerial Accounting, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Jl Ahmad Yani, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: Online Learning, Course Structure, Online Tutorials Flexibility, Online Tutorials Quality, Technology
Quality, Student Satisfaction
Abstract: This study aims to determine the influence of course structure, flexibility of online learning, quality of online
learning, and quality of technology on student satisfaction in online learning. This research uses independent
variables namely course structure, online tutorials flexibility, online tutorials quality, and technology quality.
The dependent variable used is student satisfaction. This study used primary data with data collection
techniques using questionnaires (web-based questionnaires) that were distributed to students of D3
Accounting and D4 Managerial Accounting in 2020/2021 Politeknik Negeri Batam. Sample withdrawal
technique using cluster sampling method. The testing method in this study used multiple regression analysis
with the help of SPSS statistical application program Version 25. The results showed that the course structure,
online tutorials flexibility, online tutorials quality, and technology quality significantly influenced student
satisfaction in online learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the development of technology, all aspects are
closely related to digitization, so that obtaining
information is no longer difficult because it can be
done in real time. The use of technology in the field
of education is also developing, namely with the
existence of e-learning. Michael (2013) explained
that e-learning is electronic learning that uses
information and communication technology and then
held with the aim of learning to use electronic devices
or computers to support the learning process. E-
learning makes the learning process happen anywhere
and anytime, then with the geographical separation
between students and teachers, it encourages more
people to be involved in learning (Harsasi &
Sutawijaya, 2018).
Today, online learning is the main learning
method, due to the Covid-19 outbreak and in
accordance with the circular letter from
Kemendikbud Number 36962/MPK.A/HK/2020
regarding online learning and working from home in
order to prevent the spread of corona virus disease
(covid-19). This is also carried out by universities,
one of which is Politeknik Negeri Batam. Politeknik
Negeri Batam applies distance education starting on
March 16, 2020 in accordance with circular letter No.
289/PL29/III/2020 concerning vigilance and
prevention of the spread of Covid-19 infection within
Politeknik Negeri Batam.
Given the increase in learning using e-learning
during this pandemic, student satisfaction is
important in assessing online learning related to the
quality of online learning. Based on research by
Harsasi & Sutawijaya (2018), it explains that there are
4 factors that influence student satisfaction, namely
course structure, online tutorials flexibility, online
tutorials quality and technology quality.
Research by Eom, Wen, & Ashill (2006) explains
that the lesson structure has two components, namely
learning objectives/expectations and lesson
infrastructure. Which learning objectives /
expectations must be explained in a syllabus which
includes what topics will be studied, expected class
participation in online conferences, group
assignments and so on. While the learning
infrastructure relates to an explanation of the overall
use of the online learning site or e-learning so that it
can be understood.
In the research of Sun, Tsai, Finger, Chen, & Yeh
(2008) revealed that online learning is different from
conventional classroom learning, which is not limited
by space, time and location. Therefore, students have
426
Ainubie, H. and Ramadhan Slamet, M.
Determine Factors of Accounting Student Satisfaction in Online Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0010935500003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 426-434
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

a high degree of flexibility and many opportunities
for independent study. This makes the flexibility of
online learning to play an important role in student
satisfaction and has been shown to have a significant
effect on student satisfaction.
Sun, Tsai, Finger, Chen, & Yeh (2008) said that
of all the independent variables in their research, the
quality of online learning had the strongest
relationship with student satisfaction. Because it
includes the overall lesson design, teaching materials,
and so on. According to him, for a higher level of
satisfaction such as scheduling lessons, the
arrangement and types of discussions and teaching
materials must be prepared properly. This is to help
students solve their curriculum and technical
difficulties, can reduce students' frustration levels in
online learning, thus making the learning experience
better.
Research by Harsasi & Sutawijaya (2018) says
that the implementation of information and
communication technology has been used in the field
of education, especially universities. Many higher
education institutions use e-learning as a modern
learning solution. Therefore, the quality of
technology is one of the factors determining student
satisfaction.
This research is a replication study which refers to
previous research conducted by Harsasi & Sutawijaya
(2018). Researchers used the same variables as
previous studies, namely using course structure,
online tutorials flexibility, online tutorials quality,
and technology quality as independent variables and
using student satisfaction as the dependent variable.
As for what distinguishes it from previous research, it
is related to research respondents, where the
researcher uses Accounting students at the Politeknik
Negeri Batam class of 2020/2021 as the sample.
Although many previous studies have discussed
the determinants of student satisfaction in online
learning, there are still differences in the results of
each previous study. The researcher's contribution is
to identify whether the lesson structure, online
learning flexibility, online learning quality, and
technology quality can affect the satisfaction of
Politeknik Negeri Batam Accounting students during
the application of online learning. Differences in the
results of previous studies are also an important
aspect in conducting this research. The researcher
hopes that this research can provide an overview and
suggestions for the application of online learning.
2 THEORITICAL STUDY
2.1 Constructivism Learning Theory
The theory of constructivism learning according to
Piaget (1977) is to believe that learning is a self-
discovery process, which is a process that a person
goes through because of interacting and observing the
environment (self-discovery learning). Piaget
believed that people learn and construct their own
knowledge. This constructivism learning theory also
states that there is a change in the role of the teacher
who usually explains material from class to class,
now becomes a mediator and facilitator during the
online learning process.
2.2 Technology Acceptance Model
(TAM)
Considering internet-based online learning, the
theoretical perspective of technology adoption is very
appropriate to predict the satisfaction of internet-
based learning (Arbaugh, 2000). Davis, Bagozzi, &
Warshaw (1989) revealed that the Technology
Acceptance Model (TAM) shows that beliefs and
attitudes towards a technology are the main
determinants of whether a technology will be
adopted. There are 2 main variables in this model,
namely the perception of the usefulness of a
technology and the perception of the ease of use of a
technology. Davis (1989) said, first, people tend to
use or not use the application according to their
beliefs, whether it can help in doing a better job. This
refers to the first perception of the usefulness of a
technology. Second, even if potential users believe
that a particular application is useful, they may at the
same time believe that the system is too difficult to
use and that the performance benefits of using the
application outweigh the expected effort of using the
application. This means that in addition to usability,
use is also theorized to be influenced by perceived
ease of use. Perceived usefulness is defined as the
extent to which a person believes that using a
particular system will improve job performance.
2.3 Literature Review
The study of Eom, Wen, & Ashill (2006) used
American students enrolled in online learning without
meeting on campus as a sample, whose main research
objective was to investigate the determinants of
student perceived learning outcomes and satisfaction
in distance education using an e-learning system. In
this study, lesson structure is considered an important
Determine Factors of Accounting Student Satisfaction in Online Learning
427

variable that affects success during the online
learning process. Researchers say the structure of the
lesson will be highly correlated with user satisfaction
and perceived learning outcomes, especially when
teaching materials are organized into logical and
easy-to-understand components. And also, clear
communication regarding learning objectives and
procedures, it will increase the level of student
satisfaction and perceived learning outcomes.
The research of Sun, Tsai, Finger, Chen, & Yeh
(2008) used students from 2 public universities in
Taiwan as a sample, this study aims to investigate the
factors that influence student satisfaction in the use of
e-learning. The researcher revealed that the definition
of online learning flexibility is students' perceptions
of the efficiency and effects of adopting the use of e-
learning during their work, study and travel hours.
This makes flexibility an important role in student
satisfaction. Because online learning is different from
classroom learning in general, which is not limited by
space, time and location, it allows students to have a
high degree of flexibility and have many
opportunities for independent study. By using e-
learning, it eliminates the awkwardness associated
with face-to-face communication in conventional
classrooms. Students can express their thoughts
without shame and ask questions through online
discussions.
Becta (2002) says that using e-learning provides
opportunities for students to develop at a pace and
learning time that suits them, to get the information
they need. By using e-learning students can meet
with other students virtually to ask questions, discuss
problems, and even participate in a study forum or
group assignment without having to leave their daily
activities. E-learning provides opportunities for
students to get access whenever they want, and is able
to involve other students and lecturers globally.
In a study by Mages & Garson (2010) which
investigated whether online tutorials can effectively
meet the needs of students and scholars seeking
information on how to properly use the APA style
citation rule. Researchers are part of the library's
initiative to foster information literacy and prevent
accidental plagiarism, by designing high-quality
online tutorials to teach students to cite sources
correctly. With good quality online tutorials, it can
increase participants' understanding. The results
showed that 98% of respondents said the online
tutorial was very useful and increased their
understanding of APA style.
The research of Harsasi & Sutawijaya (2018)
which uses Open University (UT) students enrolled in
4 core courses in the management department who
have taken online learning as a sample, examines
what are the determinants of student satisfaction
during the online learning process. The research uses
lesson structure, online learning flexibility, online
learning quality and technology quality as
independent variables. And using student satisfaction
as the dependent variable. Researchers say with the
advancement of knowledge, methods, and techniques
related to the field of information and communication
technology; it is possible to make significant changes
in educational practice. As with the quality of
technology, are students able to access online
learning anywhere, do not experience problems
during the online learning process, are they easy to
use, and so on.
2.4 Hypothesis Development
2.4.1 Course Structure
Students can understand teaching materials well and
have a high interest in learning, if the teaching
materials provided are well structured, the learning
objectives are clear, and most importantly easy to
understand. In constructivism learning theory it is
said that a person learns and builds his own
knowledge by interacting and observing the
environment. This is what makes students better off
when they learn independently at their own time and
at their own pace. Based on the description above, the
hypothesis is proposed:
H1: Course Structure has a significant effect on
Student Satisfaction
2.4.2 Online Tutorial Flexibility
By using e-learning, students can access teaching
materials without limitation of time and place. This
makes students have a high level of flexibility and
have many opportunities for independent study. This
is supported by the technology acceptance model
(TAM) with one of the perceptions, namely the
perception of the usefulness of a technology. The use
of technology in online learning makes it easier for
students to manage their own study time, not being
tied down in the learning process because it can be
done anywhere and anytime, which makes student
learning activities more effective. So that students can
balance their work, family, and personal activities
without having to put aside learning. Based on the
description above, the hypothesis is proposed:
H2: Online Tutorials Flexibility has a significant
effect on Student Satisfaction
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
428
2.4.3 Online Tutorial Quality
A well-designed online learning is one of the factors
for students in considering online learning itself. This
is because quality is an important factor that
influences the learning effect and satisfaction during
online learning. In the technology acceptance model
(TAM), the belief that a technology is useful and easy
to use affects the attitude of users towards the
technology which will then determine their decision
to adopt the technology. In the case of online learning,
do students experience / do not experience difficulties
in using the features, whether during the internet-
based online learning process can improve the quality
of learning, and so on. Based on the description
above, the hypothesis is proposed:
H3: Online Tutorials Quality has a significant effect
on Student Satisfaction
2.4.4 Technology Quality
Advances in knowledge, methods, and techniques
related to the field of information and communication
technology enable significant changes to educational
practice. Rodriguez, Ooms, & Montañez (2008)
revealed that most students feel comfortable with
activities that use technology, such as using e-mail to
send assignments, displaying learning videos on
computers and so on. Arbaugh (2000) said that in the
context of online learning, showing the perceived
usefulness and ease of use of delivery media will
improve students' attitudes towards their learning
experience. Based on the description above, the
hypothesis is proposed:
H4: Technology Quality has a significant effect on
Student Satisfaction
Based on the description of the theoretical study,
literature review, and hypothesis development that
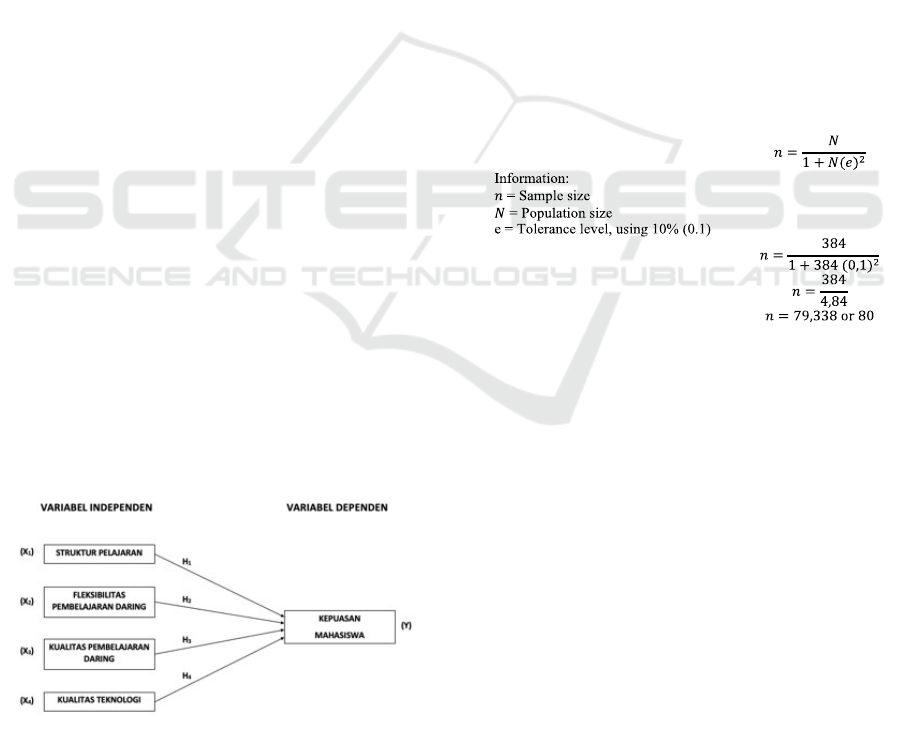
have been described previously, the research model
can be seen in Figure 1:
Figure 1: Research Model.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses a quantitative approach, which is a
systematic, planned, and structured research that aims
to prove the influence between variables (Hermawan,
2019). There are 2 types of variables used in this
study, namely the independent variable and the
dependent variable. The independent variables used
are course structure, online tutorials flexibility, online
tutorials quality, and technology quality. The
dependent variable used is student satisfaction. This
research data is primary data which uses a research
instrument in the form of a questionnaire adopted
from previous research (Harsasi & Sutawijaya, 2018).
The object of this research is Accounting students
of D3 Accounting and D4 Managerial Accounting at
Politeknik Negeri Batam class of 2020/2021 who get
Introductory Accounting courses or Basic Financial
Accounting in their online learning, both the morning
regular class, the employee class (evening), and the
industrial class totaling 384 students. To determine
the sample size, it is carried out through a statistical
approach using the slovin formula (Sugiyono, 2016):
Figure 2: Sample Size.
Based on the results of calculations using the
Slovin formula, the number of samples to be studied
in this study were 80 samples.
In this study, the researcher used a probability
sampling technique, namely cluster sampling. Then
data processing using SPSS version 25. The data
analysis techniques used are descriptive statistics,
validity tests, and reliability tests. The classical
assumption test used is the normality test,
multicollinearity test, and heteroscedasticity test. And
the hypothesis test used in this study is multiple linear
regression and individual parameter significance test
(T test).
4 RESULTS
In this study, a sampling technique was used in the
form of probability sampling, namely cluster
Determine Factors of Accounting Student Satisfaction in Online Learning
429

sampling with respondents taken, namely students/I
study programs of D3 Accounting and D4 Managerial
Accounting class 2020/2021 Politeknik Negeri
Batam. The population used in this study amounted
to 384 based on predetermined criteria. The sample
used in this study were 80 respondents.
4.1 Descriptive Statistical Analysis
Below is a descriptive statistical analysis table:
Table 1: Descriptive Statistical Analysis.
4.2 Instrument Test Results
4.2.1 Validity Test
To find out whether a list of questions/statements is
feasible or not, that is by conducting a validity test on
the question items (Sujarweni, 2019). The results of
R (Correlation coefficients) are compared with R
Tables where df = n-2 with sig 5%, in this study using
as many as 30 respondents, the df obtained = 28 and
the R table value = 0.361. Statement items can be said
to be valid if R Count > 0.361. The following are the
results of the validity of the research data:
Table 2: Validity Test.
Based on the table above, it is known that all items
in the statement list have an R greater than R Table,
which means that all statement items from the
variables used in this study are declared valid to be
used as measuring instruments.
4.2.2 Reliability Test
The reliability test is a measure of the stability and
consistency of respondents in answering a list of
questions/statements (Sujarweni, 2019). A variable
can be said to be reliable if it has a Cronbach's alpha
value greater than 0.60. The results of the reliability
test are shown in the following table:
Table 3: Reliability Test.
Based on the table above, it is known that all
variables have a Cronbach's alpha value greater than
0.60. So, it can be concluded that the questionnaire
used is reliable.
4.3 Classic Assumption Test
4.3.1 Normality Test
In this study, the normality test of the Kolmogorov
Smirnov one sample method was used to determine
whether the data distribution was normally
distributed or not. The decision-making criteria is that
if the significance value is > 0.05 then the data is said
to be normally distributed. The results of the
normality test are shown in the following table:
Table 4: Normality Test.
Based on the table shows a significance value of
0.200 > the Kolmogorov-Smirnov value of 0.05. So,
it can be concluded that the data is normally
distributed.
4.3.2 Multicollinearity Test
A good regression model should not have a
correlation between the independent variables. It can
be seen through the Tolerance and Inflation Factor
(VIF) values, the VIF value must be < 10 and the
N Min. Max. Mean
S
td.
Deviation
Course Structure 80 8 20 14,96 2,441
Online Tutorials
Flexibility 80 10 35 24,55 5,384
Online Tutorials Quality 80 16 34 24,59 4,292
Technology Quality 80 20 40 28,94 5,328
Student Satisfaction 80 10 25 17,51 3,379
Variabel
Item R Hitung R Tabel Keterangan
Course
Structure
MK1 0,765 0,361 Valid
MK2 0,676 0,361 Valid
MK3 0,813 0,361 Valid
MK4 0,837 0,361 Valid
Online
Tutorials
Flexibility
F1 0,835 0,361 Valid
F2 0,897 0,361 Valid
F3 0,816 0,361 Valid
F4 0,748 0,361 Valid
F5 0,922 0,361 Valid
F6 0,683 0,361 Valid
F7 0,704 0,361 Valid
Online
Tutorials
Quality
Q1 0,602 0,361 Valid
Q2 0,729 0,361 Valid
Q3 0,815 0,361 Valid
Q4 0,606 0,361 Valid
Q5 0,784 0,361 Valid
Q6 0,770 0,361 Valid
Q7 0,674 0,361 Valid
Technology
Quality
TC1 0,559 0,361 Valid
TC2 0,757 0,361 Valid
TC3 0,870 0,361 Valid
TC4 0,820 0,361 Valid
TC5 0,674 0,361 Valid
TC6 0,748 0,361 Valid
TC7 0,760 0,361 Valid
TC8 0,688 0,361 Valid
Student
Satisfaction
S1 0,904 0,361 Valid
S2 0,716 0,361 Valid
S3 0,644 0,361 Valid
S4 0,653 0,361 Valid
S5 0,730 0,361 Valid
Variabel
Jumlah
Item
Reliabilitas
Alpha
Cronbach
Cut Off
Alpha
Cronbanch
Keterangan
Course S
t
ruc
t
ure 4 0.767 0.60 Reliabel
Online Tutorials Flexibility 7 0.903 0.60 Reliabel
Online Tutorials Quality 7 0.819 0.60 Reliabel
Technology Quali
t
y 8 0.873 0.60 Reliabel
Student Satisfaction 5 0.767 0.60 Reliabel
Unstandardlized Residual
Kolmogorov Smirnov 0.05
Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed) 0.200
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
430

tolerance value > 0.1. The results of the
multicollinearity test are shown in the following
table:
Table 5: Multicollinearity Test.
It can be seen that the Tolerance value > 0.1 and the
VIF value < 10, it can be concluded that there is no
multicollinearity in the regression model.
4.3.3 Heteroscedasticity Test
In this study using the heteroscedasticity test with the
glejser test, which is regressing between the
independent variables and the absolute value of the
residual (Priyastama, 2017). If the significance value
between the independent variable and the absolute
residual is more than 0.05, then there is no
heteroscedasticity. The results of the
heteroscedasticity test are shown in the following
table:
Table 6: Heteroscedasticity Test.
The results above show that the significance value of
the four independent variables is more than 0.05, so it
can be concluded that there is no heteroscedasticity.
4.4 Hypothesis Testing Results
4.4.1 Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
Multiple linear analysis is an analysis to measure the
magnitude of the influence between two or more
independent variables on one dependent variable
(Priyastama, 2017). The results of multiple linear
regression calculations are shown in the following
table:
Table 7: Multiple Regression Analysis.
4.4.2 Hypothesis Test
Table 8: Hypothesis Test.
Based on the table above, the regression equation
formed is:
Y = -1,933 + 0,228X
1
+ 0,098X
2
+
0,386X
3
+0,144X
4
+e
(1
)
4.4.3 T Test
Using the statistical method of partial t-test to
determine whether the hypothesis is accepted or
rejected. The test is carried out using a correlation
significance of 0.05 in order to find out each of the
independent variables on the dependent variable
partially (Santoso, 2018). The results of the statistical
analysis of the t test are shown in the following table:
Table 9: T Test.
4.5 Data Analysis
The following is a summary table of test results from
this study:
Table 10: T Summary of Test Result.
Collinearity Statistics
Tolerance VIF
Course Structure 0.575 1.739
Online Tutorials Flexibility 0.536 1.866
Online Tutorials Quality 0.380 2.629
Technology Quality 0.434 2.304
Sig.
Course Structure 0.944
Online Tutorials Flexibility 0.095
Online Tutorials Quality 0.513
Technology Quality 0.050
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F Sig.
Regression 702.597 4 175.649 66.070 .000
Residual 199.390 75 2.659
Total 901.988 79
Unstanda
r
d
i
zed
Coefficients
S
tanda
r
d
i
zed
Coefficients t Sig.
B Std. Error Beta
(Constant) -1.933 1.285
-1.504 .137
Course Structure .228 .099 .165 2.299 .024
Online Tutorials Flexibility .098 .047 .156 2.098 .039
Online Tutorials Quality .386 .069 .490 5.564 .000
Technology Quality .144 .052 .227 2.750 .007
Unstandardized
Coefficients
S
tandardized
Coefficients
t Sig.
B
Std.
Error Beta
(Constant) -1.933 1.285
-1.504 .137
Course S
t
ruc
t
ure .228 .099 .165 2.299 .024
Online Tutorials
Flexibility .098 .047 .156 2.098 .039
Online Tu
t
orials
Quality .386 .069 .490 5.564 .000
Technology Quality .144 .052 .227 2.750 .007
Hypothesis Hypothesis Statement Sig. Result
H1
Course structure significantly affects student
satisfaction
.024 Supported
H2
The flexibility of online learning significantly
affects student satisfaction
.039 Supported
H3
The quality of online learning significantly affects
student satisfaction
.000 Supported
H4
Technology quality significantly affects student
satisfaction
.007 Supported
Determine Factors of Accounting Student Satisfaction in Online Learning
431

4.5.1 Effect of Course Structure on Student
Satisfaction
Based on the results of the hypothesis in Table 10, it
shows that H1 is supported, namely the course
structure affects student satisfaction, because the
measurement of the lesson structure based on the
statement indicators in the questionnaire has a
significant effect on student satisfaction. The results
of this study are consistent with previous research by
Eom, Wen, & Ashill (2006) which stated that students
can understand teaching materials well and have a
high interest in learning if the teaching materials
provided are well structured, clear learning
objectives, and easy to understand.
Research conducted by Swan, Matthews, Bogle,
Boles, & Day (2012) states the same thing that the
lesson structure affects the process of a learning and
satisfactory learning outcomes for students, if the
educational institution manages the lesson structure
into an interesting component. This is also supported
by constructivism learning theory which says
someone is better off when they learn independently
at their own pace and time. With an easy-to-
understand lesson structure, it will increase students'
enthusiasm and interest in learning.
4.5.2 Effect of Online Tutorial Flexibility on
Student Satisfaction
Based on the results of the hypothesis in Table 10, it
shows that H2 is supported, namely the flexibility of
online learning affects student satisfaction, because
the measurement of online learning flexibility based
on the statement indicators in the questionnaire has a
significant effect on student satisfaction. The results
of this study show the same results as previous
research conducted by Sun, Tsai, Finger, Chen, &
Yeh (2008) which stated that students have a high
degree of flexibility and have many opportunities for
independent study because students can access
teaching materials without time restrictions. and
place.
The same thing was also expressed by research
conducted by Becta (2002), that e-learning makes it
easier for students to access various subjects anytime
and anywhere, then students can manage their own
study time and how long they want to study. This is
also supported by the theory of technology
acceptance model (TAM) with one of its perceptions,
namely the usefulness of a technology, with the
existence of technology in online learning that makes
it easier for students to manage their own study time
so that they are not bound by time and place so that
learning activities are more effective.
4.5.3 Effect of Online Tutorial Quality on
Student Satisfaction
Based on the results of the hypothesis in Table 10, it
shows that H3 is supported, namely the quality of
online learning affects student satisfaction, because
measuring the quality of online learning based on the
statement indicators in the questionnaire has a
significant influence on student satisfaction. The
results of the study show the same results as previous
research. Sun, Tsai, Finger, Chen, & Yeh (2008)
stated that one of the factors that influence the
satisfaction effect of online learning is well-
designed/managed online learning.
Research conducted by Mages & Garson (2010)
also states the same thing, it is said that there is a need
for good quality online learning to meet student
understanding. This is supported by the TAM theory
which says that useful and easy-to-use technology
affects user attitudes which will then determine their
decision to use the technology. However, research
conducted by Harsasi & Sutawijaya (2018) states that
the quality of online learning does not affect student
satisfaction due to the lack of quality of online
learning, especially in education providers in
Indonesia. Online learning is not yet fully
implemented, and also the lack of interaction from
students and lecturers during the implementation of
online learning. So, this is a special concern for
education providers in Indonesia to pay more
attention to the quality of online learning.
4.5.4 Effect of Technology Quality on
Student Satisfaction
Based on the results of the hypothesis in Table 10, it
shows that H4 is supported, namely the quality of
technology affects student satisfaction, because the
measurement of technology quality based on the
statement indicators in the questionnaire has a
significant effect on student satisfaction. The results
of the research conducted have the same results as
previous research conducted by Harsasi & Sutawijaya
(2018) which states that advances in knowledge in the
field of technology allow significant changes to
educational practice. Like whether students can
access and also use the technology. The research of
Rodriguez, Ooms, & Montañez (2008) also stated that
most students prefer activities that use technology.
For example, sending assignments via e-mail.
This is also supported by the TAM theory which
states the extent to which a person believes that using
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
432

technology will improve his work performance, and
also the extent to which a person believes that using
technology will make him free from effort. In the
context of online learning, showing the perceived
usefulness and ease of use of delivery media will
improve students' attitudes towards their learning
experience. However, research conducted by Sun,
Tsai, Finger, Chen, & Yeh (2008) revealed something
different, it was said that the quality of technology did
not affect student satisfaction in online learning. This
is because most e-learning systems are built and
implemented in an environment that has a high-speed
network, making it easy to carry out activities online.
So that students do not have to worry about technical
difficulties during the online learning process.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research that has been
described previously, the conclusions of this study
are:
a) The lesson structure directly has a positive and
significant effect on student satisfaction. This is
because the presentation of material at the Batam
State Polytechnic is well structured which is
related to learning objectives, learning materials,
and also the structure of teaching materials. So
that students feel it is easier to get and understand
teaching materials even though they are online.
This makes students have a great interest in
learning independently. We hope you find the
information in this template useful in the
preparation of your submission.
b) The flexibility of online learning directly has a
positive and significant effect on student
satisfaction. Because online learning provides
flexibility in managing time between studying and
other activities, so students can manage their time
more effectively. Students can also set when they
want to access teaching materials, and can also
access teaching materials wherever they want.
Unlike during conventional learning, online
students can get teaching materials even though
they don't come to campus. Students can also
determine their own study time and how long they
want to study. This makes students feel more
effective when learning is done online.
c) The quality of online learning directly has a
positive and significant effect on student
satisfaction. This is because so far online learning
at the Pliteknik Negeri Batam has good quality,
then has an attractive appearance so that students
are interested in opening the e-learning system
and accessing teaching materials, then it is easy to
use its features so that students do not find it
difficult to get teaching materials.
d) The quality of technology directly has a positive
and significant effect on student satisfaction. This
is because thanks to technology students can
access learning anywhere and anytime, have
useful functions, and help in getting/learning
material. Especially in Batam City which has
access and fast internet network, making it easier
for students to apply online learning.
REFERENCES
Arbaugh, J. B. (2000). VIRTUAL CLASSROOM
CHARACTERISTICS AND STUDENT
SATISFACTION WITH INTERNET-BASED MBA
COURSES. JOURNAL OF MANAGEMENT
EDUCATION, 32-54.
Batam, P. N. (2020). SURAT EDARAN Nomor:
289/PL29/III/2020. Batam: Politeknik Negeri Batam.
Becta, A. (2002). E-learning and teaching in library: An
information service. London: Facet.
Davis, F. D. (1986). A Technology Acceptance Model for
Empirically Testing New End-User Informations
Systems Theory and Results. MASSACHUSETTS
INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY: Sloan School of
Management.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease
of Use, and User Acceptance of Information
Technology. IT Usefulness and Ease of Use, 319-340.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989).
USER ACCEPTANCE OF COMPUTER
TECHNOLOGY: A COMPARISON OF TWO
THEORETICAL MODELS*. Management Science
Vol. 35, No. 8, 982-1003.
Eom, S. B., & Ashill, N. (2016). The Determinants of
Students’ Perceived Learning Outcomes and
Satisfaction in University Online Education: An
Update*. Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative
Education Volume 14 Number 2, 185-215.
Eom, S. B., Wen, H. J., & Ashill, N. (2006). The
Determinants of Students’ Perceived Learning
Outcomes and Satisfaction in University Online
Education: An Empirical Investigation. Decision
Sciences Journal of Innovative Education Volume 4
Number 2, 215-235.
Harsasi, M., & Sutawijaya, A. (2018). DETERMINANTS
OF STUDENT SATISFACTION IN ONLINE
TUTORIAL: A STUDY OF A DISTANCE
EDUCATION INSTITUTION. Turkish Online Journal
of Distance Education-TOJDE January 2018 ISSN
1302-6488 Volume: 19 Number: 1 Article 7, 89-99.
Kebudayaan, M. d. (2020, Maret 17). Kemendikbud Nomor
36962/MPK.A/HK/2020. Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia.
Mages, W. K., & Garson, D. S. (2010). Get the cite right:
Design and evaluation of a high-quality online citation
Determine Factors of Accounting Student Satisfaction in Online Learning
433

tutorial. Library & Information Science Research 32,
138-146.
Michael, A. (2013). Michael Allen’s Guide to E-learning.
Canada: John Wiley & Sons.
Piaget, J. (1977). Equilibration of cognitive structures. New
York: Viking Press.
Priyastama, R. (2017). Buku Sakti Kuasai SPSS.
Yogyakarta: Start Up.
Rodriguez, M. C., Ooms, A., & Montañez, M. (2008).
Students’ Perceptions of Online-learning Quality given
Comfort, Motivation, Satisfaction, and Experience.
Journal of Interactive Online Learning Volume 7,
Number 2, 105-125
Santoso, S. (2018). Menguasai Statistik dengan SPSS 25.
Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo.
Sugiyono. (2013). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. (2016). Qualitative Research Methods,
Quantitative and R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sujarweni, V. W. (2019). SPSS UNTUK PENELITIAN.
Yogyakarta: Pustaka Baru Press.
Sun, P.-C., Tsai, R. J., Finger, G., Chen, Y. Y., & Yeh, D.
(2008). What drives a successful e-Learning? An
empirical investigation of the critical factors
influencing learner satisfaction. Computers &
Education 50, 1183-1202.
Swan, K., Matthews, D., Bogle, L., Boles, E., & Day, S.
(2012). Linking Online Course Design and
Implementation to Learning Outcomes: A Design
Experiment. Internet and Higher Education. 15(2), 81-
88.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
434
