
Do Monetary Instruments Affect Conventional Bank Loans to
MSMEs?
Dina Yeni Martia
1
, Afriyanti Hasanah
2
, Siti Atika Liasari
1
, Endah Purwanti
1
and Kenneth Pinandhito
1
1
Accounting Department, Politeknik Negeri Semarang, Prof. Sudarto, Semarang, Indonesia
2
Business Management, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Ahmad Yanin, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: MSME, BI 7 Days RR, SBI, Bank Indonesia Certificate
Abstract: This research aimed to analyse the effect of SBI and BI 7 Days RR on the UMKM credit of conventional
Banks in Indonesia in 2017-2019. The method used is a quantitative approach by applying multiple linear
regression models. The research used statistical data obtained from the official website of the Financial
Service Authority and Bank Indonesia's interest rate from the official website of Bank of Indonesia. This
research showed that in the 2017-2019 period, the Bank Indonesia Certificate (SBI) variable has no significant
effect on MSMEs credit of conventional banks in Indonesia. Meanwhile, the BI 7 Days RR variable had a
significant positive effect on UMKM credit of conventional banks in Indonesia in the 2017-2019 period.
Simultaneously, the results showed significant effects between SBI and BI 7 Days RR variables on the
MSMEs credit of conventional banks in Indonesia in 2017-2019. This research showed that the SBI and BI 7
Days RR variable significantly impacted conventional bank credit expansion to the MSMEs sector.
1 INTRODUCTION
Micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are
believed to have an essential meaning in economic
development and development in both developing
and developed countries. The MSME sector in
developed countries is used as an economic driver to
trigger economic growth, innovation, and
technological progress. The developed countries in
question are the United States, Japan, France, and the
Netherlands (Tulus, 2009).
As one of the most prominent players in
Indonesia's economy, MSMEs have proven to be
economic drivers after the economic crisis. In
addition, MSMEs have saved the Indonesian
economy from the economic crisis (Singgih, 2007).
MSMEs have a role to be able to encourage
Indonesia's economic growth. MSMEs have proven
not to be affected by the crisis. In fact, every year, the
number of MSMEs continues to increase. The large
number of workers entering Indonesia is the impact
of the increase in the number of MSMEs. According
to data from the Central Statistics Agency, MSMEs
absorbed 114 million workers in 2013 (Statistik,
2021).
The significant role of MSMEs in the Indonesian
economy does not make this industry out of trouble.
One of the obstacles faced by MSMEs is limited
funds. The fund's majority of MSMEs come from
personal savings or informal sources such as
households. On the other hand, the government also
helps by financing the MSME sector. According to
the Central Statistics Agency data, the number of
loans issued continued to increase during 2016-2019.
In 2019, the MSME loan ratio was IDR 1,098.14
trillion. Compared to the previous year Statistik
(2021), this figure has increased by 6.34%.
The government's efforts to improve the
performance of MSMEs are carried out by providing
ease of use of funds for the MSME sector. Two Bank
Indonesia credit programs initiated this allocation,
namely small investment loans (KIK) and fixed
working capital loans (KMKP). In addition, Bank
Indonesia has issued Bank Indonesia Regulation
(PBI) No. 3/2 / PBI / 2001, which requires banks to
extend credit to small businesses for 20% of their total
loans. The regulation was issued as a trigger for banks
to increase their allocation of funds to the MSME
sector (Ramadhan and Beik, 2013).
As a supporter of the dual currency system, Bank
Indonesia issues Bank Indonesia Certificates (SBI) as
a conventional medium of exchange. As a monetary
instrument, SBI has its transmission line to the
physical sector, which will affect the amount of the
loan. In order to increase the role of the National Bank
58
Martia, D., Hasanah, A., Liasari, S., Purwanti, E. and Pinandhito, K.
Do Monetary Instruments Affect Conventional Bank Loans to MSMEs?.
DOI: 10.5220/0010921500003255
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2021), pages 58-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-605-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

as an intermediary institution, it is necessary to
increase the opportunities for lending to business
actors, especially in the small, medium and micro
business sector (Meydianawathi, 2007).
In the MSME sector, transferring funds from
banks is influenced by internal and external factors.
Profitability is an internal factor for banks to guide
credit. At the same time, monetary instruments have
become an external factor for bank lending. It is the
reason for doing this research; the role of monetary
instruments will affect credit distribution in
conventional banking businesses in the MSME
sector.
Based on previous research examined by
Ramadhan and Beik (2013), it shows that
simultaneously the distribution of MSME loans, both
Islamic and conventional banking, is significantly
influenced by the SBIS Islamic monetary instrument
and the conventional SBI interest rate instrument.
However, the relationship between SBI and SBIS on
MSME lending or financing is negative. Meanwhile,
Devi and Cahyono (2020) research shows that are
simultaneously lending to
the MSME sector in conventional banking in
Indonesia is influenced by SBI, inflation, and the BI
Rate. Meanwhile, lending to the MSME sector in
Islamic banking in Indonesia is also influenced
simultaneously by SBIS, inflation and the BI Rate.
Based on the conventional model, the BI Rate only
partially affects MSME credit in conventional
banking in Indonesia. While in the sharia model, the
provision of MSMEs in Islamic banking in Indonesia
is only partially influenced by inflation.
Another study conducted by Ichwani and Dewi
(2021) showed that partially the BI 7 Day RR and BI
Rate had an influence on lending to MSMEs in the
short term. At the same time, the research examined
by Wirathi and Putra (2014) shows that partially the
distribution of MSME loans at Commercial Banks in
Bali Province is significantly affected by the BI Rate.
Based on previous research, we are interested in
examining the allocation of MSME funds by
Indonesian conventional banks from January 2017 to
December 2019. This research quantitatively
analyses the effect of BI 7 Days RR and SBI on
MSME loans in Indonesia. The purpose of this study
was to determine the impact of Bank Indonesia's
policies on the determination of reference interest
rates (BI exchange rates) and conventional currency
instruments (Bank Indonesia Certificates) on
Indonesian conventional bank loans to the MSME
sector.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Micro, Small and Medium
Enterprises (MSMEs)
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
refers to a business activity established by the
community in individuals or business entities. In-Law
Number 20 of 2008 concerning Micro, Small and
Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), it is stated that
MSMEs have different criteria. The criteria for
MSMEs are regulated in article 6 paragraphs 1-3,
which state that the classification of micro, small and
medium enterprises is based on the value of net worth
and sales for one year. In addition, another aspect that
forms the basis for differences in the number of
employees in each business. The number of
employees absorbed in the MSME sector indicates
that this sector can contribute to the national
economy.
According to Hastuti et.al., (2020), small and
medium enterprises (MSMEs) are business activities
that can provide various kinds of benefits to the
community. The positive impacts of small and
medium enterprises (MSMEs) are expanding
employment opportunities, high community income
and the realization of equity in Indonesia. In addition,
the existence of MSMEs can strengthen the economy
and play a role in achieving national stability.
2.2 Credit
Credit or a loan is commonly called an activity carried
out by the bank with other parties based on an
agreement or agreement. Credit can be implemented
because of the trust of each party. Based on trust in a
party in need, money, goods, or services are given
with the condition that they must be paid back under
the agreement of both parties.
According to Astiko (1996), credit can make
purchases or loans with an agreement. In terms of
payment, both loan principal and loan interest can be
paid according to the predetermined credit maturity
date. Credit is something that society needs. It is
because credit can encourage and facilitate trade
activities and can meet the needs of the community.
2.3 Bank Indonesia Certificate
Bank Indonesia Certificates (SBI) are instruments
with competitive returns and are free from the risk of
default. The guarantor of the SBI (Bank Indonesia
Certificate) is the government, so the risk of bad loans
is more negligible (Ferdian, 2008).
Do Monetary Instruments Affect Conventional Bank Loans to MSMEs?
59
Bank Indonesia Certificates (SBI) are securities in
the form of short-term debt. Bank Indonesia issues
SBIs (Bank of Indonesia Certificate) in IDR currency.
In the context of currency control, Bank Indonesia
Certificates are used as an open market operation tool
for Bank Indonesia to carry out transactions on the
money market both with banks and other parties.
Interest rate determination is carried out based on an
auction system. If the determination of the SBI
interest rate is high enough, it will impact
conventional bank investment where conventional
banks will prioritize investment in SBI instruments
compared to lending (Sugema, 2010).
2.4 BI 7 Days RR
According to Setianingsih (2018) the BI interest rate
is the interest rate set by Bank Indonesia, which
reflects the attitude of monetary policy. BI interest
rates are announced to the public every month by the
Board of Directors of Bank Indonesia.
Bank Indonesia has conducted monetary
operations through managing liquidity in the money
market. By conducting monetary operations, Bank
Indonesia's monetary policy targets can be achieved.
Since August 19th, 2016, a new benchmark interest
rate has been introduced by Bank Indonesia, with the
name BI 7 Days Repo Rate. The new interest rate
serves to strengthen Bank Indonesia's monetary
operating framework. However, the implemented
monetary policy will not change even though Bank
Indonesia has introduced a new benchmark interest
rate policy (Haryanto and Widyarti, 2017).
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Population and Sample
In this study, the population in the form of MSME
loans from Indonesian conventional banks. In
addition, the saturated sampling technique is a
sampling technique in this study. In determining the
sample from a population, it is necessary to pay
attention to relatively few population elements. The
research sample was all Indonesian conventional
bank MSME loans in 2017-2019.
3.2 Method of Collecting Data
In this study, the data was obtained in the form of
additional data from other available sources. The data
used in this study came from several sources, namely
banking statistics issued by the Financial Services
Authority by Keuangan (2021) and BI 7 Days RR
issued by Bank Indonesia.
3.3 Analysis Methods and Variable
Measurement Data
The research method is quantitative. This research
uses multiple linear regression analysis methods
using SPSS version 25.0 application. The
independent variables used are Bank Indonesia
Certificates (SBI) and BI 7 Days RR. While the
dependent variable used is MSME credit.
The author will summarize the variables
discussed so that the empirical model used by the
author in this study can be expressed as follows (Devi
and Cahyono, 2020):
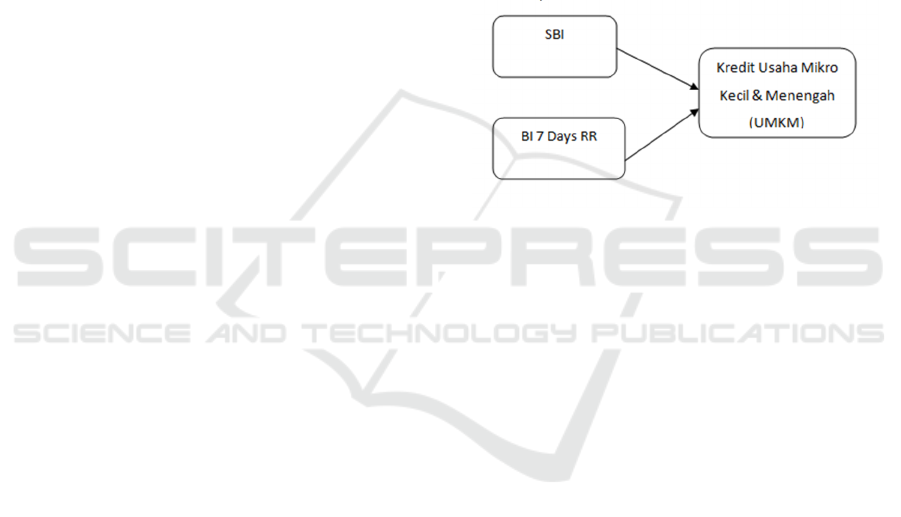
Figure 1: Research framework.
With the model equation as follows:
Y = α+β_ (1) X_1+β_2 〖 X〗_2+ et
Information:
Y = MSMEs Loan
α = Constant
β_1 β_2 = Regression Coefficient
X_1 = Bank Indonesia Certificate
X_2 = BI 7 Days RR
e = Error
The multiple linear regression method is an analytical
technique used in research. The hypothesis can be
stated in this study as follows:
H1: BI 7 Days RR and Bank Indonesia Certificates
(SBI) have a partial effect on MSME loans of
Indonesian conventional banks.
H0: BI 7 Days RR and Bank Indonesia Certificates
partially have no significant effect on MSME loans of
Indonesian conventional banks.
Ha: BI 7 Days RR and Bank Indonesia Certificates
(SBI) partially have a significant effect on MSME
loans of Indonesian conventional banks.
H2: BI 7 Days RR and Bank Indonesia Certificates
(SBI) simultaneously have a significant effect on
MSME loans of Indonesian conventional banks.
H0: BI 7 Days RR and Bank Indonesia Certificates
simultaneously do not affect MSME loans of
Indonesian conventional banks.
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
60
Ha: BI 7 Days RR and Bank Indonesia Certificates
(SBI) simultaneously affect MSME loans of
Indonesian conventional banks.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Statistic Descriptive
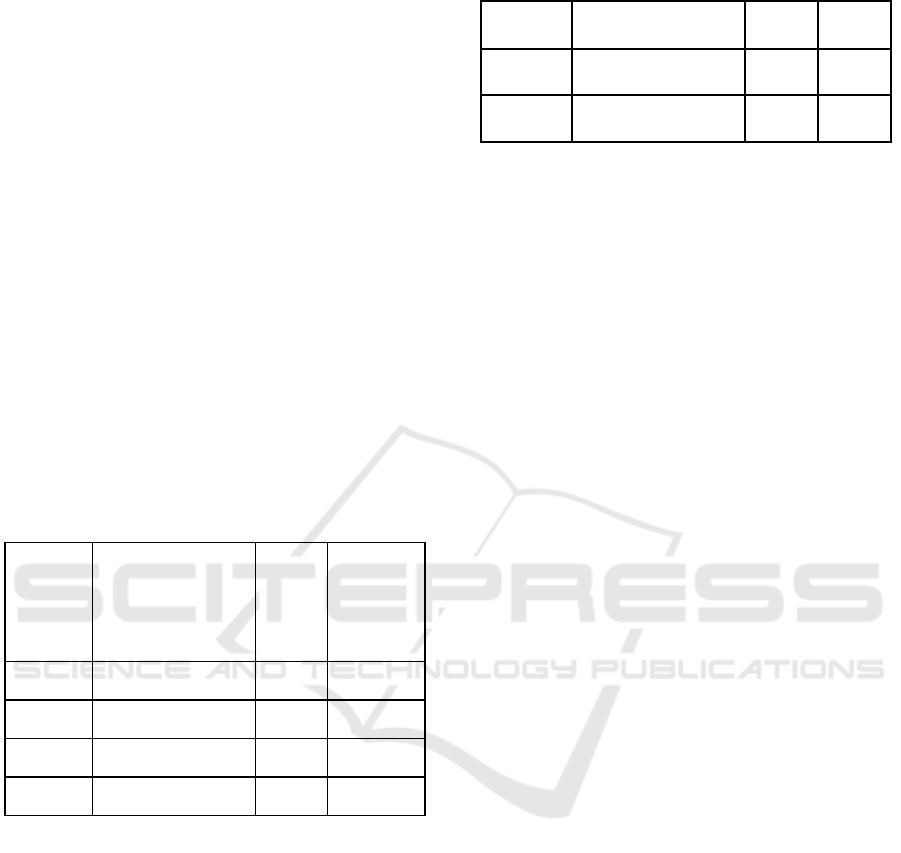
The following are SBI Indonesia Bank Certificate
data from BI 7 Days Repo Rate and MSMEs lending
from January 2017 to December 2019. The minimum
Indonesian Bank Certificate during 2017-2019 is IDR
1,109 billion in December 2017, with the maximum
amount issued is IDR 40,805 in May 2019. While the
lowest 4.25% BI-7 Days Repo Rate was regulated in
the 3rd quarter of 2017, and the highest is 6.00% from
November 2018 until June 2019. The smallest loan
disbursed was IDR 780,179 in January 2017, while
the largest disbursement was IDR 1,044,764 billion in
November 2019. It is increasing significantly during
the observation years.
Table 1: Statistic Descriptive.
Bank Indonesia
Certificate (IDR
Billion)
BI 7
Day RR
MSMEs
Loan
(IDR
Billion)
N statistic 36 36 36
Minimum 1109 4,25% 780179
Maximum 40805 6,00% 1044764
Mean 18217,36 5,10% 917487,69
Source: Processed Data, 2021
4.2 Multiple Linear Regression
Analysis
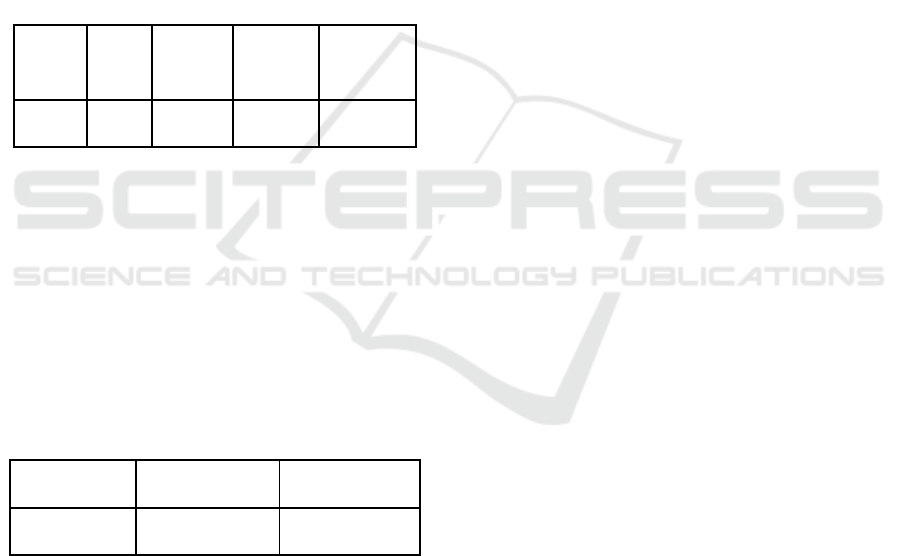
Table 1 shows that the SBI variable has a regression
coefficient of 0.618. However, it is not significant.
Whilst the regression coefficient of the BI-7 Days
variable is 7274828,079. It shows that the BI-7 Days
positively affect MSME credit, meaning that the
larger the BI-7 Days, the more credit distribution to
MSMEs will be. With the increase in BI-7 Days
everyone unit, the MSME credit variable has
increased by 7274828,079 percent and vice versa.
Table 2: Multiple Linear Regression Results.
Model Coefficient t-stat Sig.
SBI 0.618 0.634 0.531
BI Rate 7274828.079 3.709 0.001
Source: Processed Data, 2021
Based on the t-test result, it can be analysed that
the t-test value for the SBI variable is 0.634, and the
significance level is 0.531. The significance value of
the data above is more than 0.05. It shows that the SBI
variable does not have a significant positive effect on
the MSME credit variable. It can also be interpreted
that this SBI variable does not have a partial influence
on MSME credit. On the other hand, the t-test result
on the BI-7 Days variable is 3.709, and the
significance level is 0.001. The significance value is
less than 0.05, so it can be concluded that the BI
interest rate variable has a significant positive effect
on the MSME credit variable. In other words, the BI-
7 Days variable partially affects MSME loans.
4.3 The Effect of SBI on MSMEs Loan
Based on the partial regression test results, it can be
seen that Bank Indonesia Certificates (SBI) do not
have a significant positive effect on conventional
bank MSME loans in Indonesia because the
significance value of SBI> 0.05 is 0.531. In the t-test
calculation, it is known that the SBI variable is 0.634,
so it can be concluded that in the Indonesian
conventional banking industry, SBI does not have a
significant effect on MSME loans. Using the results
of the t-test that has been carried out, the analysis
results reject the new hypothesis, which means that
the SBI portion does not affect MSME loans.
4.4 The Influence of BI-7 Days on Fund
Distribution to MSMEs
Based on the partial regression test results, it can be
seen that BI-7 Days has a significant positive effect
on MSME loans of Indonesian conventional banks.
The calculation shreds of evidence that the
significance value of BI-7 Days is 0.001 or <0.05. In
the t-test calculation, it is known that the BI-7 Days
variable is 3.709. It can be concluded that BI-7 Days
has a significant positive effect so that there is a one-
way relationship between the BI-7 Days variable and
MSME Credit. By using the results of the t-test, the
results of the analysis accept the following
Do Monetary Instruments Affect Conventional Bank Loans to MSMEs?
61
hypothesis: BI-7 Days has a partial effect on MSME
loans.
The results of this study are contrary to previous
research conducted by Osei and Asenso (2015),
which showed that BI-7 Days had a negative effect on
lending. It shows that the increase in BI-7 Days will
increase bank interest rates and cause lending to
decline. Vice versa, the decline in BI-7 Days will
cause credit demand to increase.
4.5 Coefficient of Determination R2
R2 (Coefficient of Determination) in this study was
0.416 or 41.6%. It means that the magnitude of the
influence of SBI, BI-7 Days on MSME loans is
41.6%, while other variables influence the other
58.4% (error value).
Table 3: Coefficient of Determination (R
2
).
Model R R
Square
F
Change
Sig F
Change
0.645 0,416 11,765 0.000
Source: Processed Data, 2021
4.6 F-test
Based on the table of F test results, it is known that
the F value in this study is 11.765. Meanwhile, based
on the results of the significance of 0.000 <0.05, it is
concluded that all independent variables (namely
Bank Indonesia Certificates (SBI) and BI-7 Days)
have a significant positive effect on the dependent
variable (MSME credit).
Table 4: F test Result.
Model F Sig.
1 11.765 0.000b
Source: Processed Data, 2021
5 CONCLUSION
Based on research using multiple linear regression
analysis to test the hypothesis, it was concluded that
partially, Indonesian conventional bank MSME loans
during 2017-2019 were not significantly affected by
the Bank Indonesia Certificate (SBI) variable.
Meanwhile, the BI-7 Days RR variable significantly
affects traditional Indonesian bank MSME loans
during 2017-2019.
Meanwhile, the study results show that
simultaneously the variables of Bank Indonesia
Certificates (SBI) and BI-7 Days RR significantly
influence the distribution of Indonesian conventional
bank loans to the MSME sector during 2017-2019.
It is hoped that the next researcher can further
develop this research by adding other variables and
extending the research time and data volume so that
the results obtained are more precise and
comprehensive.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We gratefully thank to Politeknik Negeri Semarang
and Politeknik Negeri Batam for the support.
REFERENCES
Astiko, S. (1996). Pengantar Manajemen Perkreditan.
Yogyakarta: Andi Yogyakarta.
Devi, W. L., and Cahyono, E. F. (2020). Analisis Pengaruh
Sertifikat Bank Indonesia (SBI), Sertifikat Bank
Indonesia Syariah (Sbis), Inflasi Dan Bi Rate Terhadap
Penyaluran Dana Ke Sektor UMKM Oleh Perbankan
Syariah di Indonesia. Jurnal Ekonomi Syariah Teori
dan Terapan, 7(3), 499-512.
Ferdian, I. R. (2008). SBI, Instrumen Moneter atau
Instrumen Investasi. Republika. Senin, 21.
Haryanto, S. B., and Widyarti, E. T. (2017). Analisis
pengaruh NIM, NPL, BOPO, BI Rate dan CAR
terhadap penyaluran kredit bank umum go public
periode tahun 2012-2016. Diponegoro Journal of
Management, 6(4), 942-952.
Hastuti, P., Nurofik, A., Purnomo, A., Hasibuan, A.,
Aribowo, H., Faried, A. I.,Saputra, D. H. (2020).
Kewirausahaan dan UMKM: Yayasan Kita Menulis.
Ichwani, T., and Dewi, R. S. (2021). Pengaruh perubahan
BI rate menjadi BI 7-day reverse repo rate terhadap
jumlah kredit UMKM. Jurnal Manajemen dan Bisnis,
1(1), 67-76.
Keuangan, O. J. (2021). Statistik Perbankan Indonesia
Retrieved from www.ojk.go.id
Meydianawathi, L. G. (2007). Analisis Perilaku Penawaran
Kredit Perbankan Kepada Sektor UMKM di Indonesia
(2002-2006). Buletin Studi Ekonomi, 12(2), 134-147.
Osei, A. E., and Asenso, J. K. (2015). Regulatory capital
and its effect on credit growth, non-performing loans,
and bank efficiency: Evidence from Ghana. Journal of
Financial Economic Policy.
Ramadhan, M. M., and Beik, I. S. (2013). Analisis
pengaruh instrumen moneter syariah dan konvensional
terhadap penyaluran dana ke sektor usaha mikro kecil
ICAESS 2021 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
62

dan menengah (umkm) di indonesia. Al-Muzara'ah,
1(2), 175-190.
Setianingsih, D. (2018). Pengaruh Inflasi, Bi Rate,
Sertifikat Bank Indonesia Syariah, Dan Financing to
Deposit Ratio Terhadap Pembiayaan Usaha Mikro
Kecil Dan Menengah Pada Bank Umum Syariah Dan
Unit Usaha Syariah di Indonesia Periode 2014–2017.
Skripsi. IAIN Surakarta.
Singgih, M. N. (2007). Strategi Penguatan Usaha Mikro
Kecil Menengah (UMKM) Sebagai Refleksi
Pembelajaran Krisis Ekonomi Indonesia. Jurnal
Ekonomi Modernisasi, 3(3), 218-227.
Statistik, B. P. (2021). Statistik Indonesia 2021. Retrieved
from https://www.bps.go.id/
Sugema, I. (2010). BI Masih Pertahankan Bunga SBI. In:
Kontan.
Tulus, T. (2009). UMKM di Indonesia. Jakarta: Ghalia
Indonesia.
Wirathi, I., and Putra, I. B. G. (2014). Pengaruh LDR, BI
Rate, CAR, NPL terhadap Penyaluran Kredit UMKM
di Bank Umum Provinsi Bali Periode 2004. I-2013. IV.
E-Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan Universitas Udayana,
3(12), 44499.
Do Monetary Instruments Affect Conventional Bank Loans to MSMEs?
63
