
Implementing a Digital Workspace based on Model Composition
Architecture
Nisrine El Marzouki
1
, Mohamed El Mehdi El Aissi
1
, Yassine Loukili
1
, Chaimae Ouali- Alami
1
a
,
Younes Lakhrissi
1
b
and Oksana Nikiforiva
2
1
SIGER Laboratory, Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University, Fez, Morocco
2
FCSIT, Riga Technical University, Riga, Latvia
ouali-alami@hotmail.com, Oksana.Nikiforova@rtu.lv
Keywords: Covid-19, Digital workspace, Model composition, Model Driven Architecture, Liferay, Prototype.
Abstract: In the era of covid-19 and with the policy of confinement in order to overcome the pandemic of the
coronavirus, telework is a mode of work organization, which has obvious virtues. It notably makes it possible
to avoid tiredness and lost time in transport, to contribute to the fight against climate change by reducing
pollution, to reduce fuel consumption and therefore to increase the purchasing power of households, and also
to better organize his working time by staying at home. However, the use of Information and Communication
Technologies (ICT) is a necessity, in this context digital workspaces are presented as a strong and powerful
platform which implements several ready-to-use modules and also the possibility of adding blocks or what is
called in digital workspace jargon a portlet. We will study in this article the architecture of Liferay digital
workspace and its ability to present us reusable portlets, so we will refer to the composition of the models in
the context of Model Driven Architecture in order to propose a complete and global prototype that meets the
expected needs.
1 INTRODUCTION
A digital work space designates a set of online tools
that allow remote access to digital resources. This
term is commonly used in colleges, high schools and
universities to designate an internet portal. We also
talk about the digital work environment, virtual
office, online binder and collaborative work platform.
Initially, the digital workspace aims to modernize
teaching and pedagogy, but with the pandemic
coronavirus, digital workspace also allow to enter and
make available to students and their parents, teachers,
administrative staff and more generally to all
members of the educational community of school
education or higher education, depending the
authorizations of each user, educational and
pedagogical content, administrative information
relating to school life, the teachings and operation of
the establishment as well as online
documentation.(Jacobs, 1963) (Bailey, 2017).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3862-9149
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2718-7090
A digital workspace allows users to register online
for activities offered by the establishment, to
subscribe to mailing lists, to participate in community
spaces.
The objectives are therefore to promote the
sharing and communication of resources and
practices by providing to each user a workspace and
storage whose resources are accessible at any time
from any place with an Internet connection. Secondly,
the objective is to diversify educational resources and
supports (audio resources, video supports, etc.) but
allow the organization of school life through an
increase in the use of information and communication
technologies in the establishment, allow the reduction
of assistance and maintenance costs.
In the context of MDA (Model driven
architecture) a digital workspace is generally used to
designate this integrated set of digital services from
the point of view of users. A digital workspace can be
seen as a project or a solution.
572
El Marzouki, N., El Aissi, M., Loukili, Y., Ouali- Alami, C., Lakhrissi, Y. and Nikiforiva, O.
Implementing a Digital Workspace based on Model Composition Architecture.
DOI: 10.5220/0010811600003101
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Modelling and Machine Learning (BML 2021), pages 572-577
ISBN: 978-989-758-559-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The “digital workspace solution” designates the
application components and implementation services
offered by publishers / integrators and other service
providers (operators, hosts) linked to project leaders
by service commitments. It respects the digital
workspace reference architecture.
The reference architecture presents an organized
view of the various services offered by the digital
workspace, services which must be adapted to the
needs and uses of the educational community. It
should be noted that the client part of digital
workspace is today intended to be multi-channel,
multi-support and that it goes beyond the simple web
browser client by presenting mobile clients, the other
digital workspace part that it understands
materializing the needs of increasing exchange and
collaboration between users. In this article, we will
study a powerful digital workspace, which is Liferay.
Liferay (Genevois, 2011) is an excellent solution for
a corporate portal. Our contribution is to identify the
behaviour of this digital workspace in the context of
model composition based on model driven
architecture, in order to propose a global prototype
using the prerequisite modules presented by Liferay.
The remainder of this paper is structured as
follows: section 2 presents the global architecture of
a digital workspace. Section 3 presents Liferay portal
as a solution for digital workspace. A model
composition solution based on Liferay portal will be
presented in section 4. In section 5, we conclude the
paper with a summary of our future research.
2 DIGITAL WORKSPACE
2.1 Digital Workspace Offering
The Digital workspace, also called "single portal" or
"virtual office", brings together services for staff and
users.
The Digital workspace extends the use of digital
technology in general, a vector of success for all
students, and good communication between the
different actors in this success.
Management staff must both master and support the
development of digital educational tools.
This requires a marked involvement of the
management team, a quick handling of the tool (user-
friendliness, ergonomics) and an internal work as a
team.
Information, training, support and conditions for
developing the tool are essential so that all users can
appropriate it.
Concretely, the digital workspace allows us to steer
the establishment and open it up to its environment by
(Miller, 2016) (Leclercq, 2007) (Poyet, 2009):
Facilitating discussion with teams and partners,
communicate and inform in real time all users;
Facilitating exchange and sharing resources
and practices;
Providing to each user a workspace and storage
space accessible at any time and regardless of
the location (home, classrooms, computer
rooms, etc.);
Diversifying the educational resources and
available supports like video, sound resources,
manuals and digital resources;
Offering a pooling space for each team:
personalized support and any other
organization requiring interdisciplinary
communication;
Offering individualized student monitoring
systems: help, support, personalized
educational success programs, and online
educational resources;
Offering collaborative working tools trough
out blogs and shared files;
Offering equipment and tools management to
users: computer, multimedia room, meeting
room, videoconferencing, audioconferencing,
mobile classes, teleservices (registration,
modification of data, online payment, etc.);
Management of licenses and activation keys for
students and teachers for access to digital
resources etc.
2.2 Digital Workspace Architecture
The core of the digital workspace communicates with
the presentation module according to a protocol using
XML metalanguage. The presentation layer converts
the XML flow into a flow adapted from the client of
the user. This translation also takes place during the
feedback of information from the client to the digital
workspace. The presentation layer communicates
with a Web browser according to the HTML protocol.
The digital workspace communicates with the bricks
through the application interface according to
standardized protocols using XML metalanguage
(see Figure 1).
Implementing a Digital Workspace based on Model Composition Architecture
573
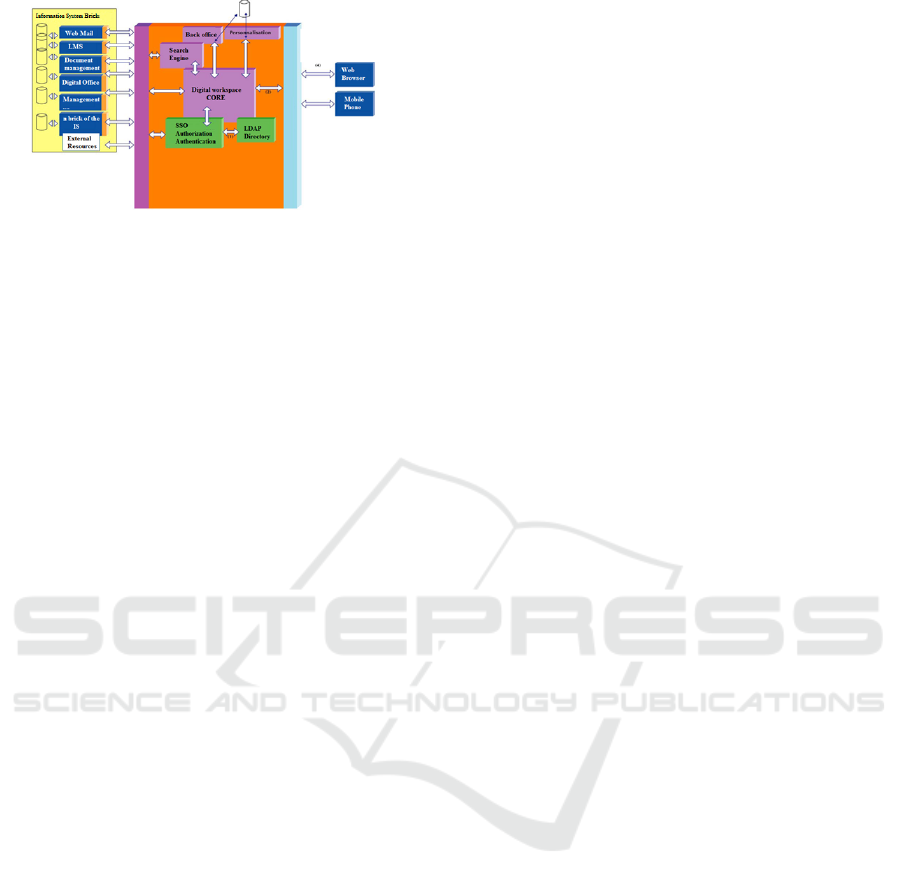
Figure 1: Digital workspace architecture (Genevois, 2011).
The search engine is able to carry out request from all
information system bricks. Security does not appear
on this architecture because it is present in all trade
flows. The protocol used to communicate with the
directory is LDAP V3. (Poyet, 2006) (Poyet, 2011).
3 PRESENTATION OF LIFERAY
Liferay Enterprise Portal is an open source American
JEE portal, which presents an interface allowing the
construction of several pages by assembling blocks
with drag and drop actions in order to obtain simple
ergonomic.
Liferay is an excellent solution for a corporate portal,
allowing the standardized integration of all existing
applications, offering portal animation and
configuration settings for pages and modules, with
ergonomics always worked, thus attracting users.
(Jacobs, 1963) (Bailey, 2017)
We will focalize on this article to Liferay for several
reasons:
Simpletoadminister;
Widely used for the creation of business
solutions for companies;
CompatibleJSR-168(APIPortlet);
JEE compatible (it can be deployed on JEE
application servers from IBM, Oracle, SUN,
etc.);
Available in Tomcat version (JSP / Servelet);
Available in JBoss / Tomcat / Jetty version;
Integrates with classic RDBMS (Oracle,
Mysql, PostgreSQL,);
OpenSource;
Offersseveralready-to-usePortlets;
Documentationavailable;
Amongthenewportals.
3.1 Liferay Architecture
The common digital workspace services offered by
LifeRay are: Registration to the workspace, Unique
identification and management profiles,
personalization of the environment, Management of
user groups, search engine, Notes, Notifications,
Forum, Calendar, Wiki, Management of the storage
environment.
A portal is made up of members; they can belong
to groups and/or belong to organizations.
Organizations can be grouped into hierarchies.
Members, groups and organizations can belong to
communities that have common interests. The fact of
grouping the users facilitates the specification of the
access rights of some users. A user can belong to
several groups, organizations and communities
(Puimatto, 2006) (Attaran, 2019). There are three
types of communities:
Open: A user can join or leave an open type of
community when he wants to help the portlet
“Communities”.
Restricted: A Restricted type community requires
sending a request to the community administrator to
join it.
Hidden: A community of type Hidden is like a
community of type Restricted except that it is not in
the list of communities in the portlet “Communities”.
(Khachouch, 2020)
3.2 Roles
Liferay identify four types of roles in its architecture:
The owner: The owner has all the access, he has
all the access rights on all the portal pages and
on all the features offered by Liferay. Simple to
administer;
The administrator: A portal can have several
administrators. An administrator has all the
same rights as the owner except that he cannot
assign members as administrators;
Power Users: They are simple users who have
additional powers;
Single users: These are the simple users of the
portal.
3.3 Pages
A portal on Liferay is organized according to a set of
public pages and private pages. The private pages and
the public pages have the same structure, the only
difference between them is the access rights. For
example, the public pages of a user on the portal are
seen by all the members of the portal. On the other
hand, the private pages are not seen and access only
by himself, even the portal administrator cannot
access the members private page. Each user on the
portal has private pages and public pages. Each
community
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
574
has private pages and public pages. Each organization
in the portal has private pages and public pages.
(Khachouch, 2020) (Korchi, 2020)
4 LIFERAY AND MODEL
COMPOSITION
4.1 Main Contribution: Liferay Design
in the Context of Model
Composition
With Liferay we can create several portlets which can
be grouped together to build a generic platform. In the
context of model composition, these portlets can be
represented as models. Based on the Spring IoC and
Hibernate frameworks, it allows us to easily create
our models, the persistence layer and the service
layer, so this tool generates the Spring and Hibernate
configuration files necessary for the setting operation.
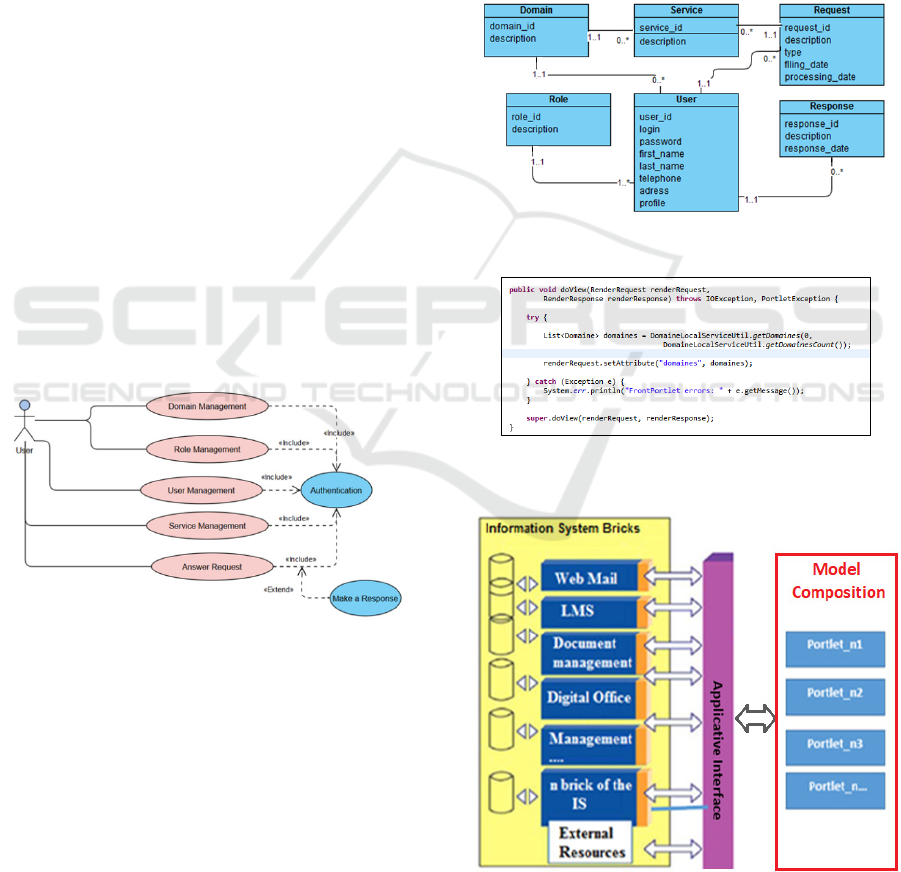
Use Case Diagram: After authentication, each user
has the right to submit a request for inspection to the
department concerned, after processing the response
is sent to their mailbox and also in the form of a
notification accompanied by the various details
within the digital workspace itself. The administrator
according to the department to which he is affiliated,
he has the right to process the various user requests.
(Khachouch, 2020)
Figure 2: Liferay Use Case diagram.
Class Diagram: Each user can access several
services depending on their role and area of activity.
A user can make several requests and get an
answer.
A service has a very specific request, which is in
its role can be intended for several services.
With Liferay, we can create a service builder. A
service builder is nothing else than a XML file that
contains the definition of our entities and relations
between them, a service builder is always associate
with a Liferay project as a portlet.
The Layer Model contains all our entities. The
persistence layer, responsible for requests and
operations on our database entities. The Service layer,
performing all technical and business operations
other than those of the previous layers. The Utility
layer, this layer represents a glue in the global
architecture and it’s mainly called within our portlets.
As shown in figure 4, we present an example of the
portlet skeleton referring to the example provided in
the class diagram, we have developed the domain part
by calling the services used
“DomaineLocalServiceUtil” and associated methods
“getDomaineCount”.
Figure 3: Liferay Class Diagram.
Figure 4: Example of using the classes generated in a
portlet.
Figure 5: Liferay digital workspace in the context of model
composition (Bailey, 2017).
Implementing a Digital Workspace based on Model Composition Architecture
575
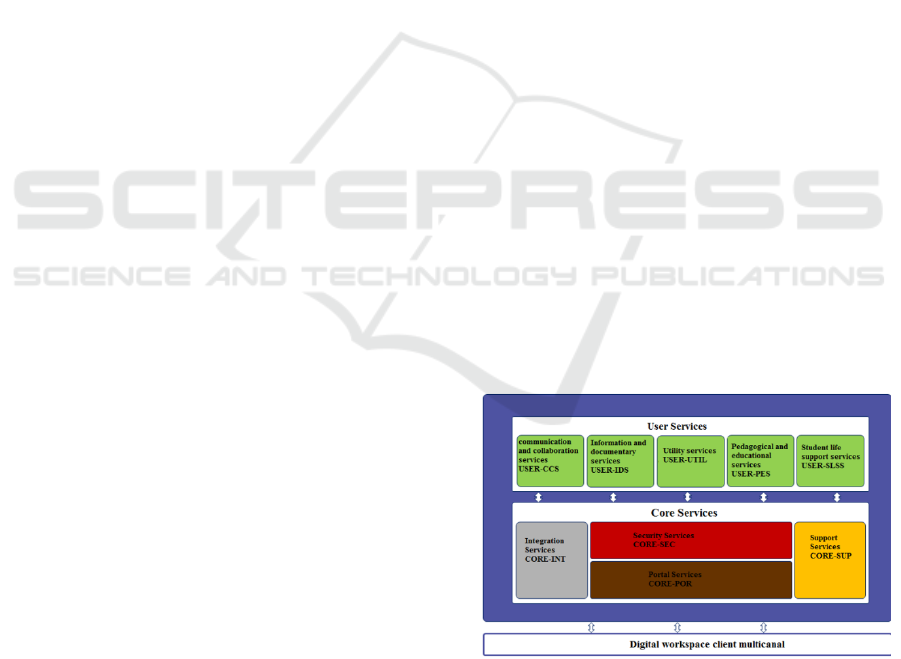
The reference architecture in the figure 5 presents
an organized view of the various services offered by
the digital workspace, services which must be
adapted to the needs and uses of the educational
community.
It should be noted that the client, part of a digital
workspace, is today intended to be multi- channel,
multi-support and that it goes beyond the simple web
browser client by presenting mobile clients, the other
part of a digital workspace answers the needs of
increasing exchange and collaboration between users.
The qualities expected of digital workspace (quality
of service, adaptability, extensibility and security) are
made possible by the capacities provided by the base
services and user services. The base services (core)
are those on which all user services are based. User
services are divided and organized into service
typologies which take in consideration the
pedagogical and educational dimension. (Bailey,
2017)
4.2 Use of Digital Services
As shown in figure 6, in terms of basic services, there
are: Integration services, Import / export of data, Call
for external services, Presentation of services to the
outside, Provision of data to services, Security
services, Identification and authentication,
authorization, propagation of identity information,
application of security policy, detection and
prevention of security breaches, portal services
presentation, portal customization, multichannel
management, search engine, support services,
operation, administration of back office and User
assistance.
In terms of user services, there are:
Communication and collaboration services, email,
spaces for exchange and collaboration, instant
messaging, information display, web publishing,
audio and video conference, Information and
documentary services, research, individual student
monitoring and room equipment reservation.
5 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVES
The use of the digital workspace must be
accompanied by a reliable IT environment: functional
IT equipment and stable software. In order to support
its deployment in the establishment, it is appropriate
to set up a steering committee. This committee could
be endowed with several functions, in particular in the
field of editorial policy (management of sections,
management of roles, publication rights).
The precautions to be taken arise from the legal
difficulties caused by the online services
implemented by the establishment and from data
protection (access, processing, protection, integrity
and backup). The following points should be
carefully considered: guarantee the integrity of IT
systems (responsibility which can be shared with
other partners if the data is outsourced). This
responsibility includes:
establishment by the academic filter; file security
relating to data processing and files and
confidentiality of data.
Many researches have been done in the same
stream of works, but most of them focused generally
on the university architecture, that satisfy the
institution needs and presents functional details,
without interesting to the complexity of developing
this kind of systems. With the prototype that we
propose based on a model composition concept and
using as a strain Liferay digital workspace which
propose a portlet concept in order to overcome the
complexity of developing a huge system and
managing the security gaps by treating the system like
bricks and offering ready-to-use portlets, from this
prototype we are looking to guarantee the continuity
of the school outside the walls, especially in the era
of the covid-19.
In our future work, we plan to use and expand this
architecture in order to develop several portlets that
will fill the gaps in term of our need, while allowing
a composition of these portlets and also promoting the
reuse and flexibility of these bricks in a model
composition frame.
Figure 6: Structure of a digital workspace prototype in the
context of model composition (Bailey, 2017).
BML 2021 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIG DATA, MODELLING AND MACHINE LEARNING (BML’21)
576

REFERENCES
Jacobs, I.S., 1963. Fine particles, thin films and exchange
anisotropy. Magnetism, pp.271-350.
Bailey, D., 30. online small business tools to use in 2017.
[online] https://blumint.co/30- online-small-business-
tools-use-2017.
Digital workspaces: what uses in teaching? Online file of
the Educnet site (MEN):
http://www.educnet.education.fr/dossier/espaces-
numeriques-de-travail [accessed on July 2020]
Genevois, S., 2011. Internet or the new figures of spatiality,
In Poyet, F., Develotte, C., Education in the digital age.
INRP.
Miller, P. and Marsh, E., 2016. The digital renaissance of
work: Delivering digital workplaces fit for the future.
Routledge.
Leclercq JM, Boissière J., 2007. The digital workspace
project: building a trusted digital school system for the
whole educational community, digital workspace and
extended school.
http://www.cndp.fr/archivage/valid/93838/93838-
15542-19530.pdf [accessed on July 2020]
Poyet, F., Genevois, S., 2009. Integration of Digital Work
Environments in Teaching Practices: Between
Continuities and Ruptures, In Rinaudo, J-L, Poyet, F.,
Digital Environments in Schools. Lyon, INRP.
Poyet, F., Baconnier, B., 2006. Digital work environments
in schools, The letter from the Scientific and
Technological Watch-INRP.
Poyet, F., 2011. School culture and digital culture in
tension, In Poyet, F., Develotte, INRP.
Puimatto G., 2006. Digital educational networks.
Regulators, actors and vectors of the evolution of
practices and the organization of educational
establishments and institutions (Doctoral dissertation,
Paris 13).
Attaran, M., Attaran, S. and Kirkland, D., 2019. The need
for digital workplace: increasing workforce
productivity in the information age. International
Journal of Enterprise Information Systems (IJEIS),
15(1), pp.1-23.
Khachouch, M.K., Loukili, Y., Benjelloun, S., Korchi, A.,
Lakhrissi, Y., Moumen, A. and Aghoutane, B., 2020,
December. E-learning techniques and technologies
analysis for a moroccan virtual university perspective.
In 2020 IEEE 2nd International Conference on
Electronics, Control, Optimization and Computer
Science (ICECOCS) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Korchi, A., Benjelloun, S., El Aissi, M.E.M., Khachouch,
M.K., El Marzouki, N. and Lakhrissi, Y., 2022. Toward
Moroccan Virtual University: Technical Proposal. In
WITS 2020 (pp. 189-199). Springer, Singapore.
Implementing a Digital Workspace based on Model Composition Architecture
577
