
Digitalization of Education in Arts and Humanities
for Sustainable Development
Svetlana Karkina
1a
, Elena Dyganova
1b
and Manuel Carlos Felgueiras
2c
1
Institute of Philology and Intercultural Communication, Kazan Federal University, Kremlevskaya str., Kazan, Russia
2
School of Engineering (ISEP), Instituto Politécnico do Porto, Porto, Portugal
Keywords: Sustainable development, education, Art and Humanities, digital tools, Online Learning.
Abstract: The paper explains the perspectives of education in Arts and Humanities in the digital age in the aspect of
leading trends such as economic, political and cultural development of the modern world in accordance with
Sustainable Development goals. The literature review lets us state the gap among the number of researches
that cover the issue of sustainable development in the field of Arts and Humanities and others include
engineering and environmental science. Using a sustainable approach as a methodological tool allowed to
shift the point of view from the development of the educational process equipment to the problem of cultural
ecology in order to preserve social and cultural values in the digital age, particularly, in online education. The
research based on methods of the average rating of students` musical performance records and the value
orientations questionnaire. The obtained results demonstrate a high level of creativity criterion in students`
performances prepared during the online lessons and the significance of moral, spiritual, and cultural values
for students – future music teachers. In conclusions were stated the crucial role of subjects in Arts and
Humanities for the cultural ecology as part of the sustainable development movement due to the digitalization
of education.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to the technological progress the digitalization
covering all educational system components offering
new opportunities for its development. Through the
last decades, computer equipment became a
fundamental tool of a classroom, and libraries were
shifted to the digital format that provides e-sources
for any type of educational activity. Moreover, the
2020th year demonstrated the transformation in
education in a case of emergency, when traditional
face-to-face ways were replaced by online learning.
For this reason, teachers from all over the world were
gathered new methods for delivering knowledge,
organize students` activity and provide assessments
of the educational results.
Capturing all educational subject fields, the
digitalization spread the Arts and Humanities, where
brought new challenges. Despite a wide range of
advantages such as the availability of cultural heritage
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2176-5910
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2875-5109
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4202-5551
by the means of e-books, virtual museums, digital
collections of arts, online courses, necessary to point
to some limits for the educational process
implementation. Considering the pivotal role of
personal interaction in this field we have to highlight
that the discussion in an online environment cannot
exactly mimic face-to-face conversation. Successful
learning languages or philosophical disputes need
another approach for organizing online than in the
traditional classrooms.
Besides human capacity needs to be kept during
the digitalization in performance arts where digital
tools today allow to cover the most part of
professional functions include composing of music,
performing, critics and others (Bauer, 2014). Such
devices as multifunctional working station Korg i3
and BioMuse for reading human`s brain activity,
digital musical instruments synthesizing and
reproducing sounds are able to replace all types of
musician professional activity (Shirieva & Dyganova,
Karkina, S., Dyganova, E. and Felgueiras, M.
Digitalization of Education in Arts and Humanities for Sustainable Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0010672300003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 587-592
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
587
2020). In such a context, the crucial role takes the
issue to figure out the place of personality and human
capacity as a significant component of cultural
ecology. By comparison it seems to be appropriate to
cite the known words of Steve Jobs that “Technology
alone is not enough” (Lehrer, 2011) that sound even
more meaningful in relation to such fragile and
vulnerable phenomena as human culture.
The step toward the cultural ecology was included
in the document ‘2030 Agenda” set by the United
Nations General Assembly in 2015 for the purpose to
achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. Despite
there is no goal in this document, dedicated to culture
and integration cultural aspects, there are several
points direct references to culture, include:
Goal 4.7 refers to the fact that all students
receive knowledge and skills, necessary to
promote sustainable development, in particular
by education, recognition of cultural diversity,
and the contribution of culture to sustainable
development;
Goal 8.3 aims to promote the development of
policies that support development of creativity
and innovation;
Goal 8.9 and 12.b refer to the need to develop
and implement strategies development of
sustainable tourism, including through local
culture, and the need to create monitoring tools
in this area;
Goal 11.4 emphasizes the need for efforts to
protect and protect the world cultural and
natural heritage.
These points demonstrate the valuable role of culture
in the successful realization of the “2030 Agenda”
while all of them in total summarize the aspects of
cultural ecology as an important component of
sustainable development.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In order to study the relevance of the Sustainable
Development approach in different subject fields, a
literature review was provided. Using the Web of
Science database and sample strategy: The title
includes “Sustainable Development” and the type of
publication “article” the data were collected.
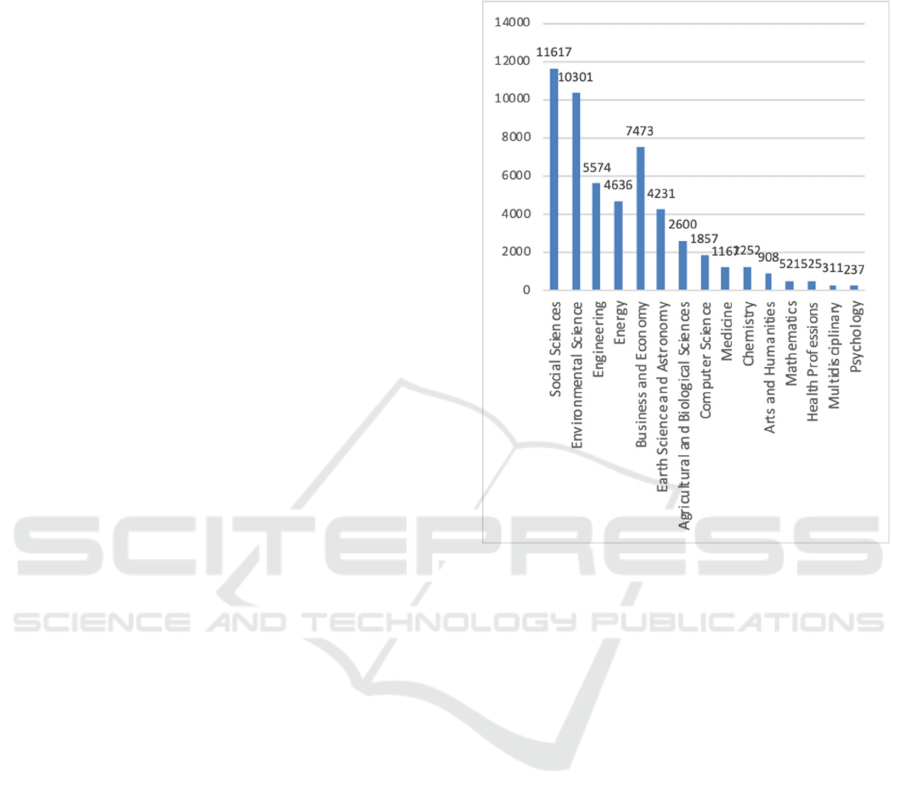
The analysis of the data let us stated that the
importance of Sustainable Development in the field
of Art and Humanities was confirmed by researchers
from all over the world by the number of papers
which number some less than a thousand. While this
number less than in Environmental science or
Engineering – the subject fields normally pay more
attention to a sustainable approach, at the same time
it is higher than in Psychology or Mathematics (see
Figure 1).
Figure 1: Distribution of articles with the words Sustainable
Development in the title indexed in Web of Science
Wide range of aspects in the field of Arts and
Humanities were covered by researchers through all
over the world.
The term “cultural ecology” was coined by
Steward as the way to adapt people culture in the
surrounding environment reflecting the harmony
between people and nature (Steward, 1955). The
definition of cultural ecology was described by
Lichachev as the complexity of architecture, literature
and arts, language, and all human cultural heritage
(Lichachev, 2000). According to his works, the
culture was built by humanity, while different levels
touch together with nature in the existence. The same
topic emphasized by Barkova as an approach in the
process of modern art development were the
fundamental ideas such as unity and person harmony,
nature and culture point the critical strategy towards
humans` return to nature (Barkova, 2012).
Modern researchers covered a vide range of
ecology issues in relation with culture and art
(Karkina et al., 2020). The implementation of the
Forest School model based on the interconnectivity
between art and ecology offers “outdoor curriculum
arts-based environmental education could provide
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
588

valuable learning experiences” (Hunter-Doniger,
2020). The inspiration of “Chinese traditional art
forms and architectural thoughts, landscape ecology
or landsenseology emphasizes the integration of
human physical senses, psychological perceptions
and sustainable development concept into the
regional Ecol-environmental research and planning-
construction-management, which is an inheritance
and development to ancient Chinese” promotes
ecological ideas and sustainable development
consciousness (Zhao & Xiao, 2020). Furthermore,
based on the connection between sustainability and
art researchers explain the significant role of artist
and designer in the ecologies issues by taking care of
students` creative skills (Tan, 2019).
The relevance of sustainable approach
implementation as a valuable trend in culture and arts
was found in the field of design due to saving the
environment “by improving the health and well-being
of people and other living beings and ecosystems”
(Yao et al., 2018). Besides, the pivotal role of careful
management in the art festivals and tourism moving
stated by Quinn in order to promote “the socially
sustaining function of festivals and of encouraging
sustainable approaches to tourism development”
(Quinn, 2006).
Some researchers offer an arts-based approach for
promotion sustainability, for instance, as in the
British village project by the means of dialogic
practices and site-specific theatre established the
importance of “context-based meaning finding” that
allows engaging “people in place through processes
in which communities yield their own, context and
time-specific interpretations of sustainable
development” (Eernstman & Wals, 2013).
Towards to overcoming violence and preventing
terrorism other researchers explore the role of Islamic
Museum of Australia and highlight the meaning of
arts-based initiatives “as ‘soft’ and ‘non-threatening’
tools promote sustainable development, facilitate
social inclusion and retain value over time with
important policy implications” (Azmat et al., 2017).
Due to reach sustainability in urban ecology by
the means of live music researcher figure out “three
different dimensions for social value (social capital,
public engagement and identity) and three for cultural
value (musical creativity, cultural vibrancy and talent
development)” (Hoeven & Hitters, 2019).
Some cultural ecology issues demonstrate the
value of musical education for Sustainable
Development. Bogomolov points the opportunity to
transform vibrational characteristics of an
ecological
system into sound form that would allow to convert
them into the “music” of ecological systems as a “new
direction for creative understanding of the state of
nature” (Bogomolov et al., 2020). For the purpose to
improve the musical education system Li provides a
“new theoretical perspectives and practical approach
for the reform of preschool music teaching which is
also another new exploration and attempt on the
theory of ecology in education and curriculum” (Li,
2019).
In the field of piano education “suggest that
teachers can adopt the generative teaching method to
form the piano teaching ecosystem for teaching
objectives”, content, ideas and design (Fan, 2019).
Follow a “Canadian poet Robert Bringhurst found
inspiration for New World Suite No. 3, a complex
poem for three voices in four movements, in the
natural polyphony of the Earth and in the vast world
of polyphonic music” (Serrano, 2019) the researcher
noted that the Suite reminds about mandatory moral
imperative regulate the dwelling humans on Earth.
Due to the digitalization process progression
researchers propose self-training as a basis “to return
a view among both to the ecological/environmental
field and the artistic/aesthetic field” for musical
educators (Gomes & Saheb, 2019). The crucial role
for necessary “to redirect culture away from
economic prescriptions and to focus on ecological
approaches to ‘value’” pointed as an important
strategy for modern reality (Bailey et al., 2019).
The value approach features using the concept of
“art” in Science not less than in Humanities, includes
engineering that contains the explanation of it as a
“kind of mastery that comes from an intimate
familiarity with real circuits, actual devices”
(Horowitz & Hill, 2015). This example demonstrates
the correlation between two huge fields which is
bridged by issues of values carried by arts. In such
context, it seems pivotal to offer the purpose of the
study to characterize the role of aesthetic values
providing by subjects in the Arts and Humanities in
order to bridge the gap between humans and the
digital environment in order to save the uniqueness of
human capacity as a significant component for
Sustainable Development.
3 METHODS
The research work was based on the educational
process at Kazan Federal University. The data were
collected by the means of two methods:
questionnaire average rating of the students`
musical performance works, prepared in online
interaction with teachers
Digitalization of Education in Arts and Humanities for Sustainable Development
589

questionnaire on values orientations
implemented by the means of Google form
(Motkov & Ogneva, 2008)
statistical methods of median and standard
deviation
In the experimental work have taken part 120
students studied in the bachelor program for future
music teachers. During the experiment, they learned
in an online way due to the case of emergency with
COVID19 on the platform Microsoft Teams and
using online courses created by authors of the
research.
4 ANALYSIS OF RESULTS
The experimental work included students learning in
piano class. During the pandemic time, all lessons
were shifted to the online way. Students created the
records of their performance and sent them to the
teacher, after that they received the teacher`s
instructions and recommendations for future
improvements of musical performance. Students`
piano performance works were evaluated on a tenth
point scale according to the next criteria: technical
level, correspondence to the text, artistic
expressiveness, emotionality, creativity. The highest
level of each criterion received 10 marks, while the
lowest could receive 0 mark. The results of average
rating of the students` works presented in the Table 1.
Table 1: Average rating of the students` musical
performance works.
Criteria Number of
students
Median Standard
deviation
Technical level
120
7 0.786630
Correspondence
to the text
6
0.819235
Artistic
expressiveness
8
0.995645
Emotionalit
y
8 1.002178
Creativit
y
9 0.984232
The analysis was based on statistical methods
such as the median, which allowed to count and
average points without limitation such as kind or
asymmetric of distribution, and standard deviation
was used for counting the level of differences
between the students` test results. Through the
analysis were concluded that the highest level (9
points), students reached in the criterion of creativity.
This result corresponds to the research of Pike, when
students had been studying to play piano by skype and
received any instruction in such a way only (Pike,
2017). During the analysis of this work were
established the highest level of creativeness in the
performances in comparison with the traditional face-
to-face way, because students were free for choosing
their body and hand position near the piano. The
conclusions of Pike were confirmed in our
experimental work, where students felt themselves
more free than near a teacher. So, not only in creative
criterion, but also in artistic expressiveness and
emotionality (8 points). Indeed such criteria as
technical level and correspondence to the text reached
less points (7 and 6 respectivamente), let us to
conclude about necessary, at least, to combine online
and face-to-face way in teaching piano. Using the
standard deviation method demonstrated no
statistically significant differences among obtained
data, and proved their appropriate quality.
Another valuable conclusion from of the analysis
the performance result was the possibility to teach
piano by the means of digital technology, as well as
improve human creative capacity which students
demonstrated much more successfully in comparison
with performance after the face-to-face study process
only.
The second stage of the experimental work
included ten values that a responded must assess by
five scales: in the aspect of the significance and
implementation of life values and reasons of their
realization, such as external reasons, personal
capacity, personal efforts. Questions were followed
by five-point Likert scale questions (using strongly
agree; agree; neither agree nor disagree; disagree;
strongly disagree) exploring respondents’ value
orientation. For each answer student received a mark
from 1 to 5 points according to the Likert scale. The
total result of each student could be from 1 to 5. The
results of the attitude survey were presented in the
Table 2.
Table 2: Questionnaire on students` values orientations.
Criteria Number of
students
Median Standard
deviation
Si
g
nificance
120
4.23 1.234151
Im
p
lementation 3.78 0.925362
Life values and
reasons of their
realization
3.89
0.884545
Personal
ca
p
acit
y
4.45
0.902398
Personal efforts 4.48 0.887262
The analysis of the results demonstrated the
significance of different values for students. The
lowest level was reached for Live values and reasons
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
590

for their realization (3.89) and implementation (3.78)
showed less interest of students – future music
teachers to external environment than moral and
spiritual culture. More points than the previous two
were obtained to the next value significance (4.23)
which was in the middle. The highest result was
obtained for the personal capacity (4.45) and personal
efforts (4.48) which demonstrated its pivotal role
among students` value orientations.
Using the method of standard deviation
demonstrated the minimum diversity between all the
students` average results, while all the results were
approximately equal or less than 1.
Based on this analysis were concluded that
students, who learn music as a professional subject,
appreciate social and cultural values more than
substantive what correspondent to regular personal
features not only musicians, but all persons who
studied, teach or doing arts.
5 DISCUSSION
In order to define the role of sustainability in Arts and
Humanities were establish a point of view on it as the
crucial factor of successful economical growth in the
countries where the government supports arts. Hunt
noted in his research the role of arts such as “much
more than money. It suggests a willingness to learn
and a commitment to the long-term. While in
economic terms it means sustained success in
competition, publicly-funded arts define success as
producing something society values” (Hunt & Shaw
2008).
Furthermore, some researchers emphasize social
and cultural values as fundamental part of economical
growing which principles were stated by Australian
Research Institute for Environment and Sustainability
include the movement to balance and harmony
between human and environment (Drew, 2020).
The digitalization of Arts and Humanities
provides modern equipment for fruitful work in some
cases changes the point of view on the humans`
activity. Using this equipment allow to produce
sounds expressing artistic ideas without special skills
or musical education. Digital technologies today
provide the music-making process as a more quicker
and easier, while a person not needs to know the
elements working process, but has an opportunity to
correct mistakes at any time (Humberstone, 2014). As
a matter of this fact using digital musical technologies
provides the easiest way to create a musical
background for movies, TV shows for which
electronic sound is quite enough.
In strict contrast, the implementation through arts
the most important function of human capabilities
such as creativity needs is shifting its role from
applied mean to self-valuable. For this purpose, a
person who uses digital devices needs to keep an open
mind and critical thinking for using them following
the inspiration and inner feeling of harmony (Price,
2013). This way allows to use digital tools for taking
care of cultural ecology as a valuable part of
sustainable development.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The digital development brings new opportunities to
human life challenging some fundamental issues such
as creative capacity and its role in the future. In order
to establish the proper way to implement new digital
equipment in such fields as Arts and Humanities they
are needed to be study as a part of global purpose as
cultural ecology. This concept points the necessary to
reach harmony in human existence in close contact
with nature and the urban environment. Study the
cultural ecology include figure out the ways for
taking care of cultural heritage as well as point its
critical role in economy and politics which
understand the necessity to keep balance among all
parts of the human society include culture.
The sustainable approach to Arts and Humanities
as an educational field means to change focus from
the applied tasks to the core of the professional
activity such as providing social and cultural values
in order to translate it to the young generation. The
digitalization of this field required the improvement
of the ability to keep an open mind and critical
thinking about computer technologies and follow the
inspiration in using them as a guarantee to keep
unique human capacity as the main value for
sustainable development.
7 LIMITATIONS
The paper has a limitation such as a comparative data
analysis among value orientations among students,
who enrolled the bachelor programs in the field of
Arts and Humanities and students who studied on any
Science program. In order to eliminate this gap, we
have a plan to establish in the future experiment,
which will combine students, learning different
subject fields.
Digitalization of Education in Arts and Humanities for Sustainable Development
591

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work is performed according to the Russian
Government Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan
Federal University.
REFERENCES
Bauer, W.I. (2014). Music learning today: Digital
pedagogy for creating, performing, and responding to
music, Oxford University Press. New York.
Shirieva, N.V., Dyganova E.A. (2020). Music education in
the age of transgumanizm. In World of Science,
Pedagogy and Psycology, 3.
https://mir-nauki.com/PDF/56PDMN320.
Lehrer, J. (2011). Steve Jobs: "Technology alone is not
enough". The New Yorker. Retrieved from
http://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/steve-
jobs-technology-alone-is-not-enough.
Steward, J.H. (1955). Theory of Culture Change. The
Methodology of Multilinear Evolution. University of
Illinois Press, Urbana.
Lichachev, D.S. (2000). Russian culture, Iskusstvo.
Moskow.
Barkova, E.V. (2012). Philosophy of culture in
ecologoorientirovannoy perspective. Culture. Science.
Integration, 2.
Karkina S.V, Batyrshina G.I, Valeeva R.A. (2020) A
sustainable approach to music education: Towards a
cultural ecology in the digital age. ACM International
Conference Proceeding Series.
Hunter-Doniger, T. (2020). Seeing the forest through the
trees: at the intersection of Forest Kindergartens and
art-based environmental education. Journal of
Adventure Education and Outdoor Learning, DOI:
10.1080/14729679.2020.1771388.
Zhao, Y., Xiao, L. (2020). Analysis on the landsense
creation of Chinese classical poetry and mountains-
and-waters painting based on landsenses ecology.
International Journal of Sustainable Development &
World Ecology, 27:3, 292-296, DOI:
10.1080/13504509.2020.1726835.
Tan, M.K.B., 2019. Art and Design Education in the
Ecology of Care. In International Journal of Art &
Design Education, 38(4), SI.
Galeeva, Z.N., Yao, M.K., Emanova, J.G., Pushkar, T.
(2018). Development of sustainable design: directions
and problems. Amazonia Investiga, 7(15).
Quinn, B., 2006. Problematizing “Festival Tourism”: Arts
Festivals and Sustainable Development in Ireland.
Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 14.
Eernstman, N., Wals, A.E.J., (2013). Locative Meaning-
making: An Arts-based Approach to Learning for
Sustainable Development. In Sustainability
(Switzerland), 5(4).
Azmat, F., Ferdous, A., Rentschler, R., Winston, E. (2017).
Arts-based initiatives in museums: Creating value for
sustainable development. Journal of Business
Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.10.016.
Hoeven, A., Hitters, E., (2019). The social and cultural
values of live music: Sustaining urban live music
ecologies. CITIES, 90.
Bogomolov, A., Nevezhin, V., Piskun, E., Khokhlov, V.,
(2020). Models of Frequency Characteristics of
Ecological Systems and their Conversion to Sound
Form. International Conference on Efficient
Production and Processing, ICEPP 2020, Prague,
Czech Republic, 27-28 February 2020.
Li, X.B. (2019). Research on Preschool Music Education
from the Perspective of Ecology. EKOLOJI, 28(107).
Fan, J. (2019). Research on Piano Education from the
Perspective of Music Eco-environment Psychology.
EKOLOJI, 28(107).
Serrano, L.M.M. (2019). Polyphony and ecology: The
green world in Robert Bringhurst's New World Suite
No. 3. Journal of Postcolonial Writing, 55(2).
Gomes, Y.L., Saheb, D. (2019). Teaching the human
condition: a reflection on environmental education,
music and self-training. Remea-Revista Electronica do
Mestrado em Educacao Ambiental, 36(2).
Bailey, R., Booth-Kurpnieks, C., Davies, K., Delsante I.
(2019). Cultural Ecology and Cultural Critique. ARTS,
8(4), DOI: 10.3390/arts8040166.
Horowitz, P., Hill, W. (2015). The Art of Electronics.
Cambridge University Press. England, 3
rd
Edition.
Motkov, O.I., Ogneva T.A. (2008). Methodics of Value
orientation, Prosvesheniye, Moskow.
Pike, P.D. (2017). Improving music teaching and learning
through online service: A case study of a synchronous
online teaching internship. International Journal of
Music Education, 35(1).
Hunt, C., Shaw, P. (2008). A Sustainable Arts Sector: What
Will it Take? Platform papers, 15.
Drew, C. (2020). Education for Sustainable Development,
Explained!
https://helpfulprofessor.com/education-for-sustainable-
development/.
Humberstone J. (2014). The place of Music in 21st Century
Education.
https://www.coursera.org/learn/music-education?
Price, D. (2013). Open: How we’ll work, live and teach
from the inside out, Crux Publishing. London. England.
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
592
