
Motivation Management of Professional Activity of Teachers as
Factor of Sustainable Education in Sports Schools
Elena Zakharova
a
and Svetlana Bernikova
b
Kurgan State University, Kurgan, 640020, 63 Sovetskaya str., p. 4, Russia
Keywords: Motivation, Motivation Management, Sustainable Education, Organizational and Pedagogical Conditions,
Motivational Environment, Material Motivation, Moral Stimulation.
Abstract: The article deals with the problem of improving the motivation management of professional activity of
teachers as a factor of sustainable education in sports schools. The article presents a theoretical analysis of
the issues of formation and development of teachers’ motivation in educational organizations. The results of
diagnostics of motivation of professional activity of couches-instructors in sports school are described. The
indicators of external and internal motivation of teachers are determined. The article analyzes the factors of
attraction of the profession of a coach-instructor, the most attractive of which was the opportunity to realize
abilities and capabilities and the least attractive is the level of salary. The levels of formation of the
motivational environment of a sports school are revealed. The motivation of professional development of
teachers was at a high level, the motivation of teaching and educational activity of teachers was at a middle
level and the motivation of innovative activity was at a low level. The positive characteristics and main
disadvantages of the motivational environment of the institution are also identified. The article presents the
organizational and pedagogical conditions developed in the course of the research and a set of measures to
improve the motivation management of couches-instructors.
1 INTRODUCTION
In modern conditions of modernization of education,
most teachers experience difficulties. They are related
to the frequent changing requirements for the
organization and implementation of the educational
process, the need for innovation, the development of
new curricula and programs, and the mastery of
information and communication technologies. At the
same time, salary in the new conditions remains the
same and does not correspond to the efforts, spent by
teachers. All these lead teachers to a feeling of
anxiety, stress, a decrease in self-esteem.
Accordingly, the motivation of labor activity is
reduced. The administrations of educational
organizations are in similar conditions. Therefore, it
is necessary to find the best methods and forms of
motivation of employees to successful, creative
activities that contribute to the support of sustainable
education.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0672-2317
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6232-9018
Sports educational organizations are no
exception. Here it is more difficult to motivate the
coaching staff, that have to work in conditions of
gyms in need of repair, outdated equipment or its
lack, low salary. There is also the problem of
attracting young personnel to work in sports schools,
since they prefer to choose private halls, fitness
centers, where salaries are much higher (Nosova,
2016). This problem is of particular relevance in
small subsidized towns. Here, sports youth, having
received education, prefer to go to more successful
large cities rather than work in fitness centers. Thus,
the relevance of the problem of teachers’ motivation
in a sports school of a small city is not in doubt.
2 METHODOLOGY
The methodological and theoretical basis of the
research was the works on the motivation of foreign
scientists: M. Mescon, A. Maslow, F. Herzberg, D.
456
Zakharova, E. and Bernikova, S.
Motivation Management of Professional Activity of Teachers as Factor of Sustainable Education in Sports Schools.
DOI: 10.5220/0010670200003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 456-462
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

McClelland, V. Vroom and others; as well as works
of domestic scientists: A. M. Moiseeva, M. M.
Potashnik, S. A. Shapiro, A. P. Egorshin, O. S.
Vikhanskiy, E. P. Ilyin, N. S. Pryazhnikov, M. V.
Kitaeva and many others.
The classical research methods were used in the
research: studying and analyzing literature,
corresponding to the problem, as well as documentary
sources and information resources; interviewing,
questionnaires, methods of motivation diagnostics,
methods of mathematical statistics, summative
assessment.
The purpose of the research was to study the
theoretical and practical aspects of the problem of
motivation of couches-instructors as a factor of
sustainable education in a sports school, to conduct
experimental work on its study, diagnostics and to
develop management recommendations. Research
tasks were to carry out a theoretical analysis of the
problem of the formation and development of
motivation of teachers; to run diagnostics of
motivation of couches-instructors in a sports school;
to develop organizational and pedagogical conditions
for effective management of motivation of sports
school teachers and directions of their
implementation.
The scientific novelty of the research consists in
determining organizational and pedagogical
conditions for effective management of the
motivation of the professional activities of teachers of
a sports school. The theoretical significance of work
is in receiving characteristics of motivation of
couches-instructors of a sports school and in defining
organizational and pedagogical conditions of
management of teachers’ motivation a sports school.
The practical significance is in the fact that the use of
the developed conditions and activities for their
implementation will contribute to increasing the
effectiveness of the activities of couches-instructors,
and therefore the school itself, and can also be used
in the management practice of other educational
organizations.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
Let us consider the theoretical aspects of the problem
of forming motivation of teachers in educational
institutions.
3.1 Literature Review
Researchers understand the role of labor motivation
in different ways. M. Mescon sees the motivation of
labor as one of the independent functions of
management and believes that it manifests itself in the
desire of a person to satisfy his needs through labor
(Mescon et al., 2017). O. S. Vikhanskiy characterizes
motivation as the encouragement of an employee to
work under the influence of internal and external
factors (Vikhanskiy, 1999). Yegorshin A.P. believes
that if the activity is motivated by internal factors, a
person does not need remuneration. When the
motives of activity arise under the influence of the
outside, there is an external motivation, which is
based on rewards (positive external motivation) or
punishments (negative external dominant)
(Yegorshin, 2013).
Scientists consider content and procedural
theories of motivation. In psychological and
pedagogical literature, content theories of foreign
scientists are discussed in detail. A. Maslow believes
that a person works to satisfy his needs (Maslow,
2019). F. Herzberg identifies factors of labor activity:
external, or hygiene (remuneration, rest, comfortable
conditions) and internal, or content (interesting and
creative work, career growth, success, satisfaction
with work). Hygiene factors, according to the
scientist, do not stimulate the employee, but their
absence negatively affects the activity. However,
content factors are good motivators (Herzberg, 2007).
According to D. McClelland, the motivation of a
person to work is formed under the influence of the
most significant needs for achievement, affiliation,
power, avoidance. For example, if a teacher wants to
achieve something, he will show initiative, autonomy,
responsibility, he seeks to achieve goals in more
effective ways, which encourages him to improve
himself (McClelland, 2007). H. Heckhausen revealed
this trend: when a person seeks success and achieves
it, he explains it with internal reasons, that is, with his
abilities, hard work, determination; and those workers
who do not show much effort, blame external reasons
for their failures: conflict with the boss, colleagues,
lack of funds, time, etc. (Heckhausen, 2003).
Procedural theories explain the reasons for the
formation of motivation. According to Expectancy
theory by V. Vroom, successful motivation of an
employee is possible when the result of his work
satisfies the employer, and remuneration for work
corresponds to the expectations of the performer.
(Musagitova, 2018). According to the theory of S.
Adams, a person expects a fair assessment and
remuneration of his work by an employer. Porter-
Lawler combined the ideas of V. Vroom and S.
Adams, believing that a person’s motivation to work
is formed under the influence of expectancy for fair
remuneration for the work done (Mermann, 2019).
Motivation Management of Professional Activity of Teachers as Factor of Sustainable Education in Sports Schools
457

3.2 Teacher Motivation Management
Let us consider the peculiarities of managing the
motivation of teachers in an educational organization.
According to E.O. Kuroedova, in educational
institutions, the management of motivation of
teachers is the sphere of administration activity on
organizing the work of employees (Kuroedova,
2006). M.V. Prokhorova believes that thanks to the
management, the educational organization retains its
structure, functionality, implementation of goals and
objectives of educational activities, as well as
motivation of teachers (Prokhorova, 2016). The
motivation function has a great influence on the
success of organization management. The creation of
a competent motivation system in the organization
makes it possible to increase its efficiency and
effectiveness due to the high quality of each teacher’s
work on condition that he is satisfied with his
activities. The administrator needs to realize a
motivation system, which includes direct (salary
system) and indirect (system of additional non-
monetary compensation) material motivation, as well
as non-financial motivation (Vitic et al., 2016).
3.3 Material and Moral Incentives for
Teachers
The main part of a teacher’s income is the salary,
which consists of two parts: basic and stimulating.
According to N. S. Zotkina, an effective salary system
encourages employees to work optimally, while
ineffective one leads to dissatisfaction, worsening of
labor discipline, and quality decrease (Zotkina et al.,
2017). In addition to salaries, there are regular
additional payments: salary increment and extra pay.
According to the Law “On education in the Russian
Federation”, an educational institution can
independently determine the indicators and sizes of
bonuses for employees (Federal Law, 2012). Salary
increments (for seniority, for high achievements in
labor and high level of qualification, for the duration
of continuous work, etc.) are fixed by a collective
agreement. Some salary increments are established
legislatively (Article 144 of the Labor Code of the
Russian Federation). Extra pays (for special working
conditions, for overtime work, for concurrent service,
class management, etc.) are regulated by Article 149,
151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
(Federal Law, 2018).
In addition to salary increment and extra pay for
pedagogical workers, an incentive fund is provided.
To determine incentive payments, a commission
should be created at a school which includes the
administrators of the organization, trade union
workers and teachers.
In order to improve social and economic aspects
of the institution, administration needs to implement
specific social programs (Alabugin et al., 2017). In
this regard, material incentives should be used in
combination with non-financial (moral) incentives,
which are based on public recognition, an adequate
assessment of the employee’s merits. Forms of moral
incentive can be: awarding honorary distinction,
memorable gifts, expressing gratitude, publications
about distinguished labor of an individual or team;
creation of flexible working hours; stimulation with
free time. Such incentive may also be corporate
holidays, the main goal of which is to unite the team
on the basis of informal communication, to welcome
newcomers into the team, to create the image of the
organization (Adetunji, 2017).
Thus, in order to manage the motivation of
teachers effectively, the administrator needs to ensure
the correct interaction of material and non-financial
incentives, to develop and improve them constantly
in accordance with the goals and objectives of the
educational organization.
4 DISCUSSION
To study the process of managing teachers’
motivation in a sports school, we carried out
experimental work. Its goal was to diagnose teachers’
motivation of a sports school and to develop
organizational and pedagogical conditions and
practical recommendations for improving the
management of its development. The study was
carried out on the basis of the municipal budgetary
institution of supplementary education “Sports school
for children young people No. 1 named after A. A.
Semenov" in the city of Kurgan. 32 trainers and
teachers participated in the experiment. The
qualifications of most teachers correspond to the
profile of work and position. 24 people (75%) have
higher education, 8 people have secondary vocational
(25%).
To analyze the process of managing the
motivation of pedagogical workers, documentation
was studied on the working conditions, on stimulation
and motivation of couches-instructors. They were a
collective agreement, a regulation on the
remuneration of workers, a regulation on the
procedure for charging salary increment and social
extra pay to official salaries of employees from the
incentive fund, etc. (The official website, 2019).
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
458
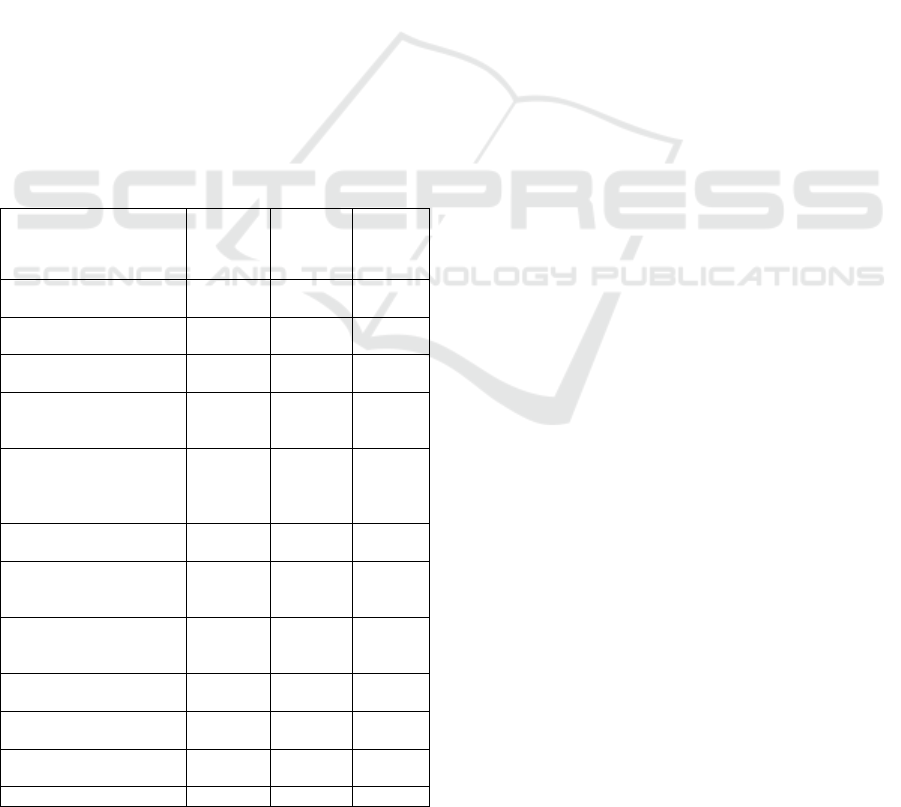
4.1 Factors of Attractiveness of the
Profession
In accordance with the goal and objectives of the
ascertaining stage of the experiment, the diagnostics
of the attraction factors of couches-instructors’
profession was carried out according to the
methodology of V. A. Yadov in the modification of
N. V. Kuzmina, A. A. Rean (table 1).
We ranged profession attraction factors for
couches-instructors of a sports school. The most
attractive motivational factors were the following:
work correspondence to abilities, capabilities (84%),
as well as the possibility of their realization (69%);
favorable working regime (72%); correspondence of
work to values and beliefs (66%); the possibility of
professional self-realization (66%); social
recognition and respect (63%). The obtained data
correspond to the results of the questionnaire of
trainers on the most significant professional qualities
(on a 10-point scale): moral qualities - 9.2;
psychological and pedagogical training - 8.9; love to
work, communication skills - 8.8; knowledge of the
sport - 8,6; willpower - 8.1 (Emanova et al., 2020).
Table 1: Attraction factors of teachers’ profession of sport
school.
Attraction factors
Significan
ce
coefficient
Absolute
value,
people
Relative
value, %
1. Work corresponds to my
abilities, capabilities
0.67 27 84
2. Favorable working
regime
0.48 23 72
3. Work allows realizing
capabilities, needs
0.41 22 69
4. Content of work
corresponds to my beliefs,
values
0.35 21 66
5. Possibility of
professional self-
realization and career
developmen
t
0.35 21 66
6. Opportunity to achieve
social recognition, respect
0.29 20 63
7. Professional activities do
not interfere into personal/
family interests
0.23 19 59
8. Work gives certain
advantages, benefits,
privileges
0.23 19 59
9. Ability to work with
people
0.16 18 56
10. Importance of
profession in society
- 0.16 13 41
11. Work does not cause
overfatigue
- 0.67 5 16
12. Salary suits - 0.75 4 13
Among the least attractive factors (having minus
coefficient) are: dissatisfaction with salary (87%);
work causes overfatigue (84%); decrease of the
prestige of the profession in society (59%).
Thus, most school couches-instructors work with
pleasure, as they are engaged in their favorite
occupation and they are professionals. At the
beginning of the year they have a clear idea of what
results should be achieved by the end of the year in
order to keep their reputation and not to give rise to
criticism from the administration. However,
achieving maximum results is complicated due to
insufficient material and technical means. There is
not enough training and safety equipment, the sizes of
the halls do not meet international standards. The
halls are in a high worn-out state, the ventilation
system does not work well, etc. Gratification is
limited mainly to forms of moral encouragement. The
leading motive for couches-instructors is to keep or to
increase their professional reputation.
4.2 Indicators of Motivation of
Professional Activity of Teachers
The results of the diagnostics of motivation of
teachers of “Sports school for children young people
No. 1” are presented in the table 2. It was carried
out according to the methodology “Motivation of
professional activity” by K. Zamfir in the
modification of A. Rean.
According to data processing, the result was
obtained which shows that in the studied sports
school the dominant labor motivation was internal
(IM - on average 3.8 points out of 5 possible). The
teachers receive satisfaction from the training process
and have the opportunity to realize their abilities.
Among the external motives for couches-instructors,
the leading ones were positive motives (EPM - on
average 3.35 points): salary, the need to earn
reputation from students and colleagues; career
growth. The least significant of the external
motivations was negative (ENM - on average 2.67
points): fear and avoidance of criticism, censure
about their work. As a result, we received the formula
IM > EPM > ENM, which characterizes a favorable
motivational complex. Thus, in a sports school the
trainers are stimulated by the training process itself,
first of all, to a lesser extent they are stimulated by
salary and, to the least extent, by the fear of
punishment.
Motivation Management of Professional Activity of Teachers as Factor of Sustainable Education in Sports Schools
459
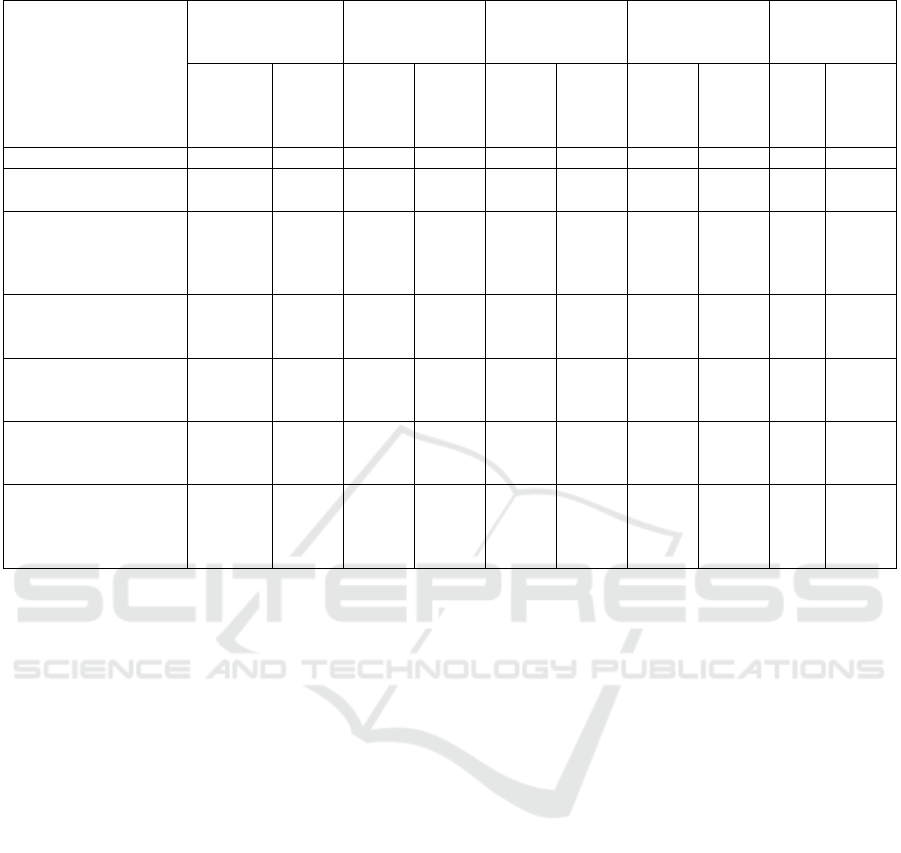
Table 2: Motivation measures of professional activity of sports school teachers.
Measures
Manifestation of
measures
To very little
extent (1 point)
To little extent
(2 points)
Neither to great
nor to little
extent
(
3
p
oints
)
To quite great
extent
(
4
p
oints
)
To very great
extent
(
5 баллов
)
relative
value,
%
absolu
te
value,
p
eople
relativ
e
value,
%
absolu
te
value,
p
eople
relativ
e
value,
%
absolu
te
value,
p
eople
relativ
e
value,
%
absolu
te
value,
p
eople
relat
ive
valu
e,%
absolu
te
value,
p
eople
1. Salar
y
3.1 1 12.5 4 25 8 34.4 11 25 8
2. Desire to be
p
romote
d
3.1 1 34.4 11 37.5 12 18.7 6 6.3 2
3. Desire to avoid
criticism from
administrator or
collea
g
ues
9.4 3 31.3 10 56.2 18 3.1 1 0 0
4. The desire to avoid
possible punishments
or troubles
6.3 2 34.3 11 40.6 13 12.5 4 6.3 2
5. Need for social
prestige and respect on
the part of others
3.1 1 9.4 3 34.3 11 34.4 11 18.8 6
6. Satisfaction from
process itself and
work result
0 0 6.3 2 15.6 5 46.8 15 31.3 10
7. Possibility of most
complete self-
realization in this
activity
0 0 6.3 2 40.6 13 40.6 13 12.5 4
4.3 Results of Diagnostics of the
Motivational Environment of the
School
To collect information about the motivational
environment, we conducted a questionnaire of the
pedagogical team according to the methodology of
V.S. Lazarev. The level of environmental
development was determined based on the total
average: 0 - 54 points show low level, 55 - 109 show
middle level, 110 - 162 show high level. The analysis
of diagnostics data of motivational environment of
educational activity of sports school revealed the
average level of formation of this indicator: average
93.5 points out of 162 possible (5.2 out of 9 possible)
or 58% of maximum level.
The following motivational measures turned out
to be the highest: teachers experience positive
emotions in work more often (average 7.8 points out
of 9). The trainers have a clear idea of work results (7
out of 9); results expected of trainers correspond to
their capabilities (6.7 out of 9).
The weakest aspects of the motivational
environment of educational activities are: teachers’
dissatisfaction with the fairness of encouragement
(5.1 out of 9); organizational conditions required to
achieve results (4.8 out of 9); lack of awareness
among educators of the criteria for encouragement
(4.5 out of 9); little attraction of the forms of
encouragement used; (3.5 of 9); availability of
material conditions necessary to achieve results (3.2
of 9).
The diagnostics of the motivational environment
of innovative activity of a sports school revealed a
low level of formation of this indicator: on average
57.5 points out of 162 possible (3.2 out of 9 possible)
or 35.5% of the maximum level. The most acute
problems related to innovation were identified:
excessive tension required to implement innovation
(average point 3.5 out of 9); lack of material and
technical conditions for effective use of innovation
(2.7 out of 9); the lack of a system of rewards for
innovation and little attraction of the forms of rewards
used (2.5 out of 9). The administration’s insufficient
attention to the material and moral motivation of
innovators is, in our opinion, one of the main reasons
that teachers do not seek to master and introduce
innovations in the training process.
The analysis of the diagnostic data of the
motivational environment of professional
development of teachers revealed a high level of this
indicator: an average point of 117 out of 162 (6.5 out
of 9) or 72% of the maximum level. Therefore,
couches-instructors have good opportunities and
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
460

motivation for professional development. So, in a
sports school there is an opportunity to advance in
qualification grades (from third to highest), in
positions (from coach, senior coach to methodologist,
senior methodologist and administrator). Teachers in
the process of training sportsmen, with their
participation in competitions, receiving prizes,
categories, as well as in the process of advanced
training, gain appropriate points and increase the
qualification category.
The main shortcomings of the motivational
environment of professional development of trainers
were revealed: uncertainty in the fair distribution of
bonuses (average point 4.5 out of 9); low value of
rewards (4.2 out of 9); lack of material and technical
conditions necessary to achieve high results of
training activities (3.7 out of 9).
4.4 Organizational and Pedagogical
Conditions for Effective
Management of Teachers '
Motivation
The analysis of measures of motivation of
professional activity of the pedagogical team,
motivation environment of a sports school allowed us
to formulate organizational and pedagogical
conditions of effective management of motivation of
professional activity of teachers in a sports school and
events corresponding to them.
1. Availability of prospects for professional
development of teachers. Activities on the
implementation of the condition are: organization of
interviews with teachers on the creation of individual
development trajectories; holding seminars and
workshops on methodological work; formation of a
plan-schedule for the further training of teachers;
mentoring of young couches-instructors; conducting
professional competitions.
2. Creating a favorable psychological climate in
the team and a positive motivational environment.
Activities to implement the condition are: classes of
the “Club for psychological support of trainers”,
including psychological games, trainings for
communication interaction, self-regulation of
psycho-emotional conditions, prevention of
professional burnout; organization of corporate
holidays.
3. Ensuring individual approach to employee
activities. Activities to implement the condition
include: individual work of the administrator with
each teacher (conversations, consultations);
promotion of participation in competitions, trainings
of personal growth.
4. The existence of a system of moral and material
incentives for the activities of teachers. Areas of
activity are: adjustment of the “Regulations on the
remuneration of teachers”; development of the
“Regulation on the intangible stimulation of
teachers”; approval of the composition of the
commission on the distribution of incentive
payments, on the assessment of the performance of
coaches; organization of intra-school competitions,
actions, flash mobs; delivery of certificates of honor
and letters of thanks.
5. Improvement of the methodological and
material and technical base necessary for the effective
work of teachers. Implementation activities are as
follows: compiling a register of needs; equipping the
sports halls and workplaces of trainers with the
necessary equipment, technical means;
methodological support of trainers’ activity;
organization of methodological assistance and
psychological support for young trainers in
preparation for classes.
6. Creation of comfortable working conditions for
teachers. Areas of activity consist of: ensuring
sanitary and hygienic standards in the school
premises; improvement of coaching rooms,
recreation areas, food areas, delivery of drinking
water; regular medical examinations; providing
employees with the membership to the gym and pool;
registration and provision with trip tickets to health
camps and sanatoriums for employees and their
children.
5 CONCLUSION
In the course of the study of motivation of teachers in
a sports school, the theoretical analysis of the problem
was carried out. The experimental work revealed the
following: the most attractive factors of the
profession for couches-instructors is the
correspondence of work to abilities, the possibility of
their implementation. The least attractive factor is
dissatisfaction with salary. The activity of teachers is
motivated by the content of their work, the desire to
achieve positive results. Motivation of training
activities of trainers is at the middle level, motivation
of innovation activity is at the low level, motivation
of professional development of teachers is at the high
level. The main disadvantages of the motivational
environment are the lack of the necessary material
and technical conditions for achieving high results; a
poorly developed remuneration system;
dissatisfaction with the fairness of encouragement.
Organizational and pedagogical conditions for the
Motivation Management of Professional Activity of Teachers as Factor of Sustainable Education in Sports Schools
461

effective management of motivation of teachers of a
sports school have been developed. They are a
prospect of professional development of pedagogical
workers, a creation of a favorable psychological
climate in the team and a positive motivational
environment, ensuring an individual approach to staff
activities; the existence of a system of moral and
material incentives for the activities of teachers, an
improvement of the school’s methodological and
material and technical base, creation of comfortable
working conditions of teachers. The practical
implementation of the proposed organizational and
pedagogical conditions will contribute to increasing
the efficiency of managing the motivation of teachers
as a factor of sustainable education. The increase of
the interest of couches-instructors in the results of
their activities will increase the quality of education
and teachers’ pedagogical skills, give an additional
stimulus to improve their qualifications.
REFERENCES
Adetunji, A.M. (2017). Main problems of motivation and
stimulation of labor in the organization, International
scientific review, 4: 2542-0798.
Alabugin, A.A., Kardapoltsev, K.V., and Aliukov, S.V.
(2017). Theoretical and Methodological Approaches to
Improving Management of Integration Processes of
Potentials of Balanced Enterprise Development,
Proceedings of The 30th International Business
Information Management Association Conference,
pages 1359-1365.
Vitic, S.V., Koptyakova, S.V., and Balynskaya, N.R.
(2016). Methodology for assessing the efficiency of
labor – related incentives at an enterprise. Asian
Journal of information Technology, 18: 250-260.
Vikhanskiy, O.S. (1999). Management, M.: Gardarika.
Yegorshin, A.P. (2013). Motivation and stimulation of work
activity: Educational manual, M.: NIC Infra-M.
Emanova, S., Ryleeva, A., Zakharova, E., and Bernikova,
S. (2019). Role of Healthy Environment in Preserving
and Strengthening Students’ Well-Being in Institutions
of Secondary and Additional, ESES 2019.
Zotkina, N., Kopytova, A, Zenkina, M., and Zhigunova, O.
(2017). Implementation of the principles of rational
incentive system in modern conditions on an example
of sectoral enterprises matec, International Science
conference SpbWOSCE, 106.
Kuroedova, E.O. (2006). Psychological foundations of
motivation of labor activity, Materials of the annual
scientific session “The Role of business in the
transformation of the Russian society", 2: 120-131.
McClelland, D. (2007). Human motivation, Spb: Priester.
Maslow, A. (2019). Motivation and personality.
Translation from the English, St. Petersburg: “Peter”.
Mermann, E. (2019). Staff motivation. Motivation tools for
organizational success, M.: Humanitarian Center.
Mescon, M., Albert, M., and Hedowrie, F. (2017).
Fundamentals of Management, Publishing house:
Williams.
Musagitova, Y.Ya. (2018). Application of the motivational
theory of V. Vroom in practical activities, Skif. Student
science issues, 2: 2587-8204
Nosova, T.A. and Konyaeva, E.A. (2016). Ways to improve
motivation and motivation of young teachers in the
educational organization, International Conference on
Education and New Learning Technologies materials
of the I international research and practice conference,
74-84.
The official website of the Municipal budgetary institution
of additional education “Sports School for children and
young people No. 1 named after A.A. Semenov" of the
city of Kurgan, https://www.acrobatika45.ru/
Prokhorova, M.V. (2016). Structure of motivation of labor
activity at different stages of organizational
development, Bulletin of Nizhny Novgorod
Lobachevsky University, 1(1): 363-369.
Federal Law “On amendments to the labor code of the
Russian Federation” dated 28.02.2008 No. 13-FL,
http://base.garant.ru/12159064/
Federal Law “On education in the Russian Federation”
dated 29.12.2012 No. 273-FL,
http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_
140174/
Heckhausen, H. (2003). Motivation and activity, St.
Petersburg: Peter; M.: Meaning.
Herzberg, F., Mosner, B., and Sniderman, B.B. (2007).
Motivation for work, Moscow: Top.
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
462
