
Integrity and Integration of Educational Space as a Factor of
Stability and Quality of Education in the Trans-Urals Region
Svetlana Emanova
a
, Anastasia Ryleeva
b
and Elena Khomutnikova
c
Kurgan State University, 64000, St. Soviet, building 4, Kurgan, Russia
Keywords: Integration, Stability, Quality of Education, Region.
Abstract: The attention of researchers in this work is focused on the forms of integration in the educational space of the
Trans-Ural region, the peculiarities of its implementation in the conditions of a village, a small town and a
regional center. Integration is considered by the authors as a means of preserving the integrity of the
educational space, through the interaction, the relationship of its participants. The article provides data on the
ways of cooperation aimed at stabilizing the educational process at all levels of education. The effectiveness
and quality of the existing integration models were revealed in the process of researching 3,670 students, the
same number of parents and 455 teachers. In the course of the study, it was concluded that the conditions for
the successful integration of all types of educational institutions are the interaction of the structural elements
of the educational space and the effectiveness of ties in the process of cooperation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The relevance of the article is due to the fact that the
modern scientific paradigm in the field of pedagogy
is actively studying the processes of integration of
education and various socio-cultural phenomenas.
Let us note the studies affecting these problems in
foreign countries. A. Khozhanova, G. Zvezdina, M.
Elagina in their work, substantiate the need for the
integration of organizations of a technical and
professional orientation for the response of the
educational systems of Kazakhstan. R. Ali, D.
Lepeshev, K. Kulambayeva, S. Dossanova, A.
Kukubayeva, N. Ivankova also touch upon the
problems of the Republic of Kazakhstan and describe
educational modules, focusing on ways to integrate
seven modules into one lesson. O. Erez, A.Y. Degani
on the integration of music schooling and social
policy in Israel. K.A. Allee-Herndon, A.B.
Kaczmarczyk, R. Buchanan analyze the ability of
future primary school teachers to integrate an
educational component related to social justice and
the necessary knowledge in school subjects in
teaching English and social studies. The integration
of education and various related industries in the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1387-6987
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4699-5096
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7139-3230
interaction of government, universities and industrial
enterprises is written by authors such as Z.B. Chen,
W. Zhang, L. Li, M.He, J .Wang.
The problems of the integrity and integration of
the educational space were considered by many
scientists:
aspects of the relationship between lesson and
extracurricular work, basic and additional
education: E.B. Evladov, V.I. Kazarenkov, Z.A.
Kargin, N.A. Morozova, M.O. Checkov;
studies on the problems of integration of general
and additional education, the specifics of its
organization and software: V.A. Berezina, V.V.
Belova, E.B. Evladova, I.V. Kalish, L.G.
Loginova, A.V. Zolotareva, S.L. Paladyeva.
Forms of integration are distinguished depending
on the level of integration (from lowest to highest); in
general, the following forms are distinguished:
cooperation, association, merger.
Cooperation and association as forms
characterized by a minimum and average degree of
mutual rapprochement of the subjects of integration
can be discussed in relation to the integration of
institutions of general and additional education of
children. Merger as a form characterized by the
Emanova, S., Ryleeva, A. and Khomutnikova, E.
Integrity and Integration of Educational Space as a Factor of Stability and Quality of Education in the Trans-Urals Region.
DOI: 10.5220/0010669500003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 413-419
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
413

maximum degree of mutual convergence of the
subjects of integration, most often describes the
integration processes within one educational
institution.
Concept "integration" occurs in various fields.
Today they talk about political, social, industrial,
economic, financial, cultural, scientific and
educational integration (Sorokina, 2008).
The issues of practical integration in the
pedagogical process are reflected in many scientific
works (S.M. Arefieva, S.Yu. Burilova, V.V. Guzeev,
V.A. Klenikova, V.M. Panfilova, V.B. Sinnikov,
S.Yu. Strashnyuk and others.) Practical integration
implies the use of different techniques, methods and
learning paths. First of all, this is the creation of
integrated courses, the integration of subjects and
their components.
Historically, integration in Russian education,
according to S.V. Omelchenko (Omelchenko, 2006)
took place in three stages: turn of the XIX-XX
centuries – 20th - unified labor school; 50th – 70th -
introduction of interdisciplinary connections; 80th –
90th - interaction, interpenetration (integration itself).
In a modern reading, according to T. K. Sozykina,
integration in education provides conditions
(Sozykina, 2014): implementation of individual
educational trajectories of students; life and
professional self-determination; ability development;
formation of key competencies of students. Career
guidance, as a process of choosing and acquiring a
future profession, is an important part of the
educational process. With its help, students develop
willingness to work and planning a professional
career.
Today, digitalization has had a huge impact on
modern career guidance, which means the translation
of information into digital, the transition to digital
services and the automation of processes. The term
"digitalization" appeared in connection with the
strengthening of information and communication
technologies (Ryleeva et al., 2019).
With the advent of digital technologies, a huge
range of opportunities opens up in career guidance
work, which makes it possible to solve the main task
of career guidance - to increase the motivation of
students for independent professional self-
determination. The use of modern information and
communication technologies can help achieve this
goal and increase the competitiveness of young
people in the labor market. Digitization of vocational
guidance has helped to make this process not only
more "flexible", but also to solve the territorial
problem. Career guidance became available for
children living in regions who lacked vocational
guidance at school. Coverage has become greater
than with conventional career guidance.
All of the above contributes to an increase in the
level of professional self-determination of the student
and the formation of a holistic view of the modern
labor market and professions among schoolchildren,
motivates to take a more serious approach to choosing
a profession, and with the help of various Internet
methods in the field of choosing a future profession,
you can tentatively identify your personal and
professional interests and inclinations (Amirov,
2016).
In accordance with paragraph 1.3 of the protocol
of the meeting of the National Council under the
President of the Russian Federation for Professional
Qualifications dated June 25, 2020 No. 45, the
Ministry of Labor of Russia, together with the All-
Russian Research Institute of Labor, the Ministry of
Labor of Russia and ANO "Digital Economy" were
recommended to develop standard modules
containing descriptions of the competencies of the
digital economy, for inclusion in professional
standards. To describe in professional standards
specific requirements for workers, the key
competencies of the digital economy should be
presented in professional standards in the form of
digital competencies - sets of skills and knowledge
necessary to perform labor actions using digital
technologies. By digital competence of teachers, we
mean the ability of teachers to use information and
communication technologies in their work in
combination with pedagogical (didactic)
understanding and awareness of its strategic
importance in the educational process.
Modern digital competencies are associated with
the fact that the teacher was forced to start work in a
fundamentally new, digital environment. Interaction
with other participants in the educational process:
directly with schoolchildren, with colleagues, with
the administration and parents, it became necessary to
carry out in a new format. When organizing education
using distance technologies, most teachers tried to
simply transfer their practices to a digital
environment, but this approach was not productive.
That is why teachers need new competencies to work
in a new environment.
To date, two forms of organization of distance
learning have been formed. The first form involves
communication with children in real time, that is,
conducting online lessons, during which the teacher
interacts with all students at once. At the same time,
for remote teamwork, he can use online whiteboards,
joint screens, mobile applications and chats to
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
414

communicate, involve students in the discussion, and
prevent distractions.
The second form involves off-line interaction
between a teacher and children. Various digital
technologies are used here. These can be recorded
lessons and lectures, quizzes, online assignments, and
so on.
Both distance learning formats require students to
have certain resources. The most pressing issue is
whether children have a computer and a high-speed
Internet connection. Modern telephones may well
replace a computer, but the remoteness of a settlement
from a district or regional center does not always
allow for the operation of an uninterrupted Internet.
The younger the generation, the higher its digital
literacy. Today's children actually have digital skills
from birth, but at the same time, they want to learn
only if they are really interested. The school is faced
with the task of creating such conditions so that
teachers can meet the necessary competencies.
Unfortunately, the spring events showed that not
everything that teachers were taught and that was
previously considered necessary was useful to them
in practice. However, thanks to this, errors and
shortcomings were discovered. This means that today
they can be eliminated, the education system as a
whole can be improved and, of course, the new
necessary competencies of the teacher can be
developed.
The federal project "Digital Educational
Environment" provides for the creation of a digital
educational environment starting from school and in
general in each region of the country. Such a modern
digital educational environment will ensure the
organization of educational and extracurricular
activities of students, including the management of
school life, with all the necessary digital devices.
The federal project is aimed at solving a number
of problems that will allow introducing new methods
of teaching and upbringing at all levels of general
education, developing new educational technologies,
ensuring the development of basic skills and abilities
in students, as well as increasing motivation for
learning and involving them in the educational
process. In addition, to create a modern safe digital
educational environment that ensures high quality
and accessibility of education of all types and levels.
T.K. Sozykina emphasis is placed on the close
interaction of general and additional education
(Sozykina, 2014).
The integration of basic and additional general
education programs as a trend in the development of
the modern education system is reflected in the
Federal State Educational Standard of General
Education in the provisions providing, in particular,
the inclusion of extracurricular activities in the main
educational program of the school.
Today, a certain system of views and approaches
has developed in defining the concept of integration
in the pedagogical process, revealing various aspects
of its content. In general, in pedagogy, integration is
understood as the highest form of expression of the
unity of goals, principles and content of the
organization of the process of teaching and
upbringing, the result of the functioning of which is
the formation of a qualitatively new integral system
of knowledge and skills in students. A comprehensive
study of the problem of integration in education has
confirmed its importance and positive impact on the
pedagogical process.
2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Modern approaches to the organization of the
educational process, presented in the Federal State
Educational Standard of GE, imply the design of
educational environments that ensure the
development of the interests, abilities and inclinations
of students. At the same time, the elements of an
integrated educational environment include: objects
of the surrounding reality; subjects of the process of
performing various types of educational activities;
means, methods, forms of organization and
implementation of training and education processes;
methodological association that ensures interaction
between teachers of secondary schools and teachers
of additional education for children; development and
maintenance of individual educational routes for the
development of students' abilities; an integrated
author's program as a model of joint activities of a
teacher of a general education school, a teacher of
organizing additional education for children and a
child. In this regard, new requirements are imposed
on the professional competence of teachers who carry
out pedagogical activities in the conditions of the
requirements of the Federal State Educational
Standard. (Ryleeva et al., 2019).
The problem of integrating the educational space
as a factor of stabilization and quality in the Trans-
Urals region was associated with the need to develop
and implement models of interaction between
educational organizations of various types:
kindergartens, schools, institutions of additional
education, special institutions. As a result of the
regional stage of the competition of social and
educational projects, such models became:
"Professions of the future" (profiling), "Digitalization
Integrity and Integration of Educational Space as a Factor of Stability and Quality of Education in the Trans-Urals Region
415
of the educational environment" (distance education),
"Lesson - abilities - activities - creativity" (activities
of resource (support) centers), "Give me your hand -
friend"(social partnership in education).
The profiling model "Professions of the future"
operates according to the "kindergarten - school -
vocational education" scheme and solves the issues of
primary vocational guidance (kindergarten, primary
school), professional self-determination (senior
classes of secondary schools) and professional
identification (students of secondary vocational
education and junior high school students).
The model "Digitalization of the educational
environment" allows the introduction of innovative
forms of interaction, the use of distance technologies
that allow participants to master integrated skills: to
navigate in various subject areas of knowledge; work
with large flows of information; create their own
databases.
The activity of resource (support) centers is
organized within the framework of the project "Lesson
- Abilities - Activity - Creativity", organically
combines the capabilities of educational and cultural
institutions, contributes to the improvement of the
creative development of both students and teachers.
Social partnership in education operates within the
framework of the "Give a hand - friend" project and
creates opportunities for the implementation of
children's and youth projects of interaction with
society.
2.1 Diagnostics of the Level of
Effectiveess of the Implementftion
of Existing Integration Models
The main goal of this work is to check the
effectiveness of the implemented models and projects
in the integrative educational space of micro societies
in the Trans-Ural region, satisfaction with the
educational activities of students, their parents (legal
representatives) and teaching staff.
The questionnaire for parents, included questions
identifying the degree of satisfaction with educational
services, priority areas for their children, attitudes
towards digitalization and distance technologies in
education, assistance in professional self-
determination.
Students were asked to fill out a questionnaire to
determine the priority motivation in choosing an
activity, satisfaction with the learning process and
additional educational programs, attitude to distance
education.
The teachers determined the conditions for the
efficiency and quality of integration processes in their
microsociums and determined the leading tasks of
digitalization.
The total sample of respondents was 7795
persons: from parents - 3670 persons, from
schoolchildren - 3670, from teachers - 455 persons.
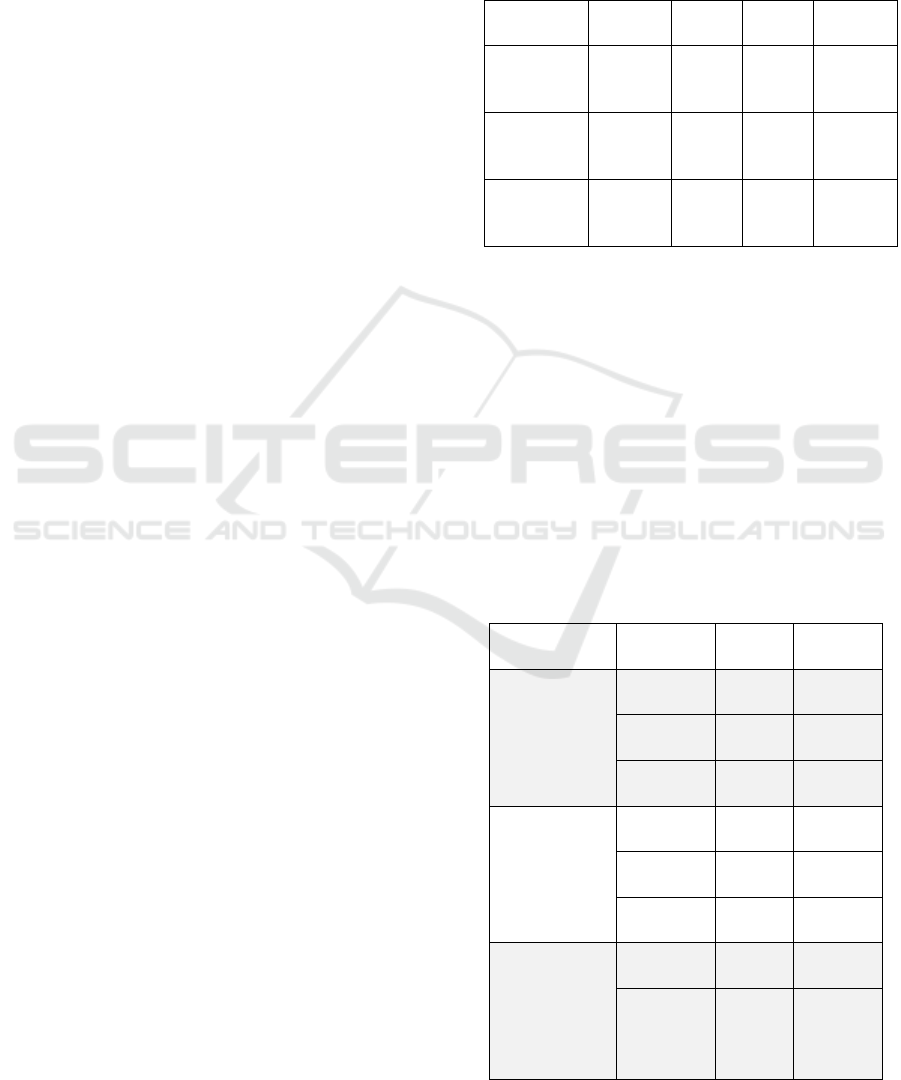
Table 1: Sample by municipalities.
Municipali
ty
schoolc
hildren
parent
s
teache
rs
total
Vargashi
(workers'
settlement)
670 570 55 1295
Kurtamysh
(small
town)
900 700 150 1750
Kurgan
(regional
center)
2100 2400 250 4750
The results of the survey indicate the satisfaction
of various interests and needs of children,
understanding of the significance of parents of the
importance of creating a single educational
environment for the development of the child.
The analysis of the students' answers made it
possible to reveal an opinion about those aspects of
the educational and upbringing process, which were
organized in accordance with their interests and
hobbies.
After analyzing Table 2, we can conclude that all
factors of satisfaction of parents and children with the
quality of education are positive dynamics.
Table 2: Analysis of the satisfaction of students and their
parents with the educational space in the region.
Questions Answer
options
Parents
Children
1. I receive
help in self-
determination
and choosing a
future
profession
a) yes 1480
(40%)
2790
(76%)
b) partly 740
(20%)
740
(20%)
c) no 740
(20%)
140(4%)
2. I can use
digital
technologies
a) yes 3350
(91%)
3650
(99.5%)
b) partly 300
(7.5%)
20
(0.5%)
c) no 20
(0.5%) 0
3. I'm
satisfied with
the quality of
the teachers'
work
a) yes 3480
(95%)
3670
(100%)
b)
sometimes
170
(4.5%)
0
c) no 20
(0.5%)
0
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
416
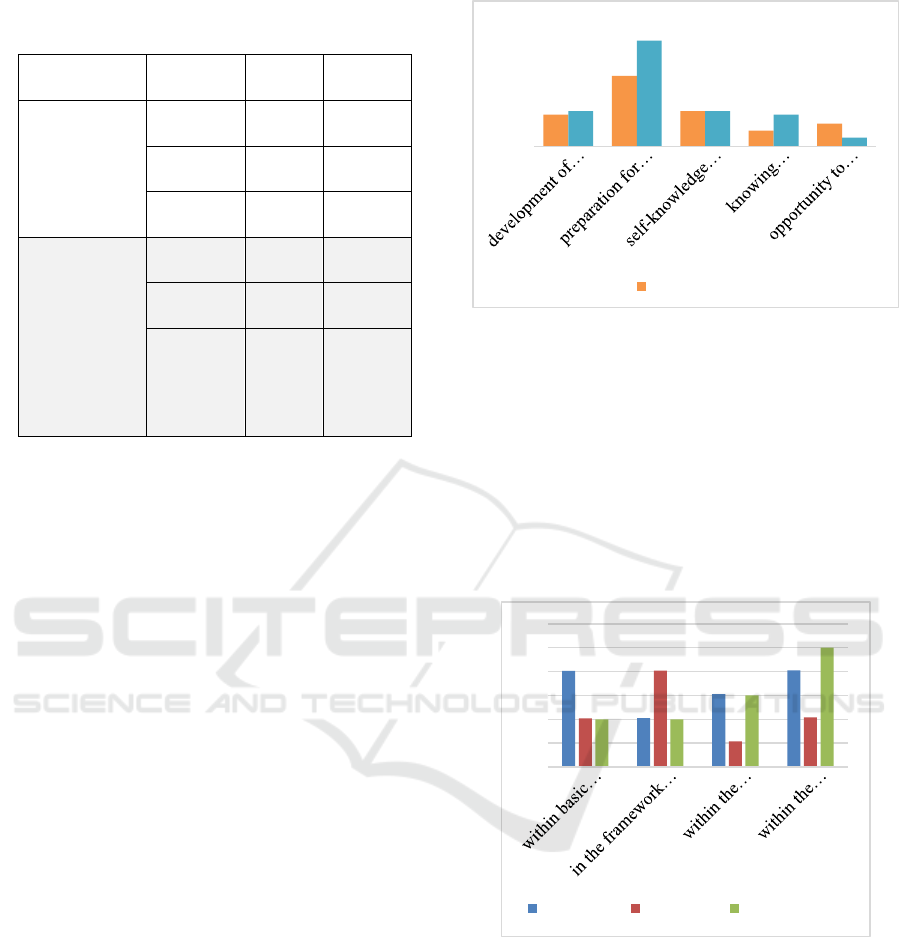
Table 2: Analysis of the satisfaction of students and their
parents with the educational space in the region (cont.).
Questions Answer
options
Parents
Children
4. I'm satisfied
with the
quality of
additional
education
a) yes 3340
(91%)
3670
(100%)
b) partly 310
(8.5%)
0
c) no 20
(0.5%)
0
5. All
conditions
have been
created in the
microdistrict
for the
development
of their
interests
a) yes 3480
(95%)
3650
(99.5%)
b) not
always
170
(4.5%)
20
(0.5%)
c) no 20
(0.5%)
0
The parents noted the content of the vocational
guidance work. 40% of the respondents said with
confidence that their children will continue their
education in the already chosen areas in
extracurricular activities.
Assessment of parents' satisfaction with the
quality of educational services showed that only 6%
of survey participants find it difficult to assess the
quality of educational services in society. The total
level of satisfaction with educational services was
94%, which corresponds to a high level.
95.5% of parents are satisfied with the
professionalism of teachers, 0.5% are partially
satisfied.
The survey showed a high interest of parents in
the educational process, orientation towards joint
activities with teachers and children.
99.5% of children believe that all conditions have
been created in the microdistrict for the development
of their interests. The vocational guidance work
carried out by teachers satisfies schoolchildren by
76%.
Assessing the qualities of a teacher, the guys put
in the first places: 95% - benevolence; 94% - an
interesting person knows how to interest; 86% are
fair; 92% is able to understand.
To the questions "What do you see the meaning of
the interaction between the school and the institution
of additional education?" a significant number of
answers (60%) are related to preparation for a
profession.
Figure 1: Parents' opinion on the meaning of additional
education in the life of their children at the beginning and
at the end of the implementation of the project
"Professions of the Future"
Most of the parents surveyed believe that the
participation of children in a variety of activities, both
at school and outside it, motivates them to self-
education.
As a result of a survey of teachers, the possibilities
of digital education were identified.
Figure 2: Opinion of educators on the possibilities of digital
education.
Figure 3 presents a diagram showing the tasks
that, according to the respondents, are solved by
distance technologies in education.
18
40
20
9
13
20
60
20
18
5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
registering
40,3
20,5
30,5
40,5
20,4
40,4
10,8
20,8
20 20
30
50
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
countryside small town regional center
Integrity and Integration of Educational Space as a Factor of Stability and Quality of Education in the Trans-Urals Region
417

Figure 3: Tasks solved by distance technologies in
education.
Choosing the priority of tasks in the development
of the personality of students, the teachers were
unanimous. Big points were scored by tasks such as
providing an opportunity to study at a convenient
time and place (16.2%), developing intellectual
abilities (16.1%), then providing an opportunity to
expand their circle of communication (15.0%),
forming skills in working with volumes of
information, developing independence in finding and
using the necessary information (14.9%), increasing
the level of knowledge (13.9%), developing
motivation for self-education (12.0%) and finally,
developing self-control skills (10, 6%). None of the
proposed tasks was rejected, as well as an opinion
was expressed about excluding any of the tasks from
the list, or adding another option.
Monitoring of the social activity of participants in
educational relations in the region recorded an
increased interest of respondents to socially
significant projects: "School of Responsible
Parenting", "Family Heirloom", "My Pedigree",
"History of My Little Homeland", "Professions of My
Family", "Defender of My Motherland", "Take care
of your child", "Victory Road", festival of projects
and research works "Rainbow".
Students and their parents take an active part in
various competitions, contests, shows, festivals,
exhibitions.
Integration capabilities allow meeting the needs
of all layers of the microsociety.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The satisfaction of parents and students with the
quality of educational services provided, both in rural
areas and in the regional center, is an assessment of
the stability of integrative processes in the
educational space of the region. The survey showed
that the assessment received from parents and
children is very high. Thus, the share of those who are
satisfied with the quality of educational services
averaged 99% in the region (answers "Satisfied
completely" and "Rather satisfied"). The number of
those who are “rather dissatisfied” with the quality of
education is very insignificant and amounted to 1%.
Those, who found it difficult to estimate, are 0%.
REFERENCES
Ali, R., Lepeshev D., Kulambayeva, K., Dossanova, S.,
Kukubayeva, A., and Ivankova, N. (2021). Updating
the content of education through the integration of
seven modules, Propositos y representaciones, 9: e965.
Allee-Herndon, K.A., Kaczmarczyk, A.B., and Buchanan,
R. (2021). Is it "just" planning? Exploring the
integration of social justice education in an elementary
language arts methods course thematic, Journal for
multicultural education.
Amirov, A.Zh. (2016). Possibilities of using information
technologies in vocational guidance work with young
people, Young scientist, 26 (130): 623-624.
Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Li L., He, M., and Wang, J. (2021).
Evaluation of Urban Industry-Education Integration
Based on Improved Fuzzy Linguistic Approach,
Mathematical problems in engineering, 2021: 6610367.
Erez, O. and Degani, A.Y. (2021). Songs of subordinate
integration: music education and the Palestinian Arab
citizens of Israel during the Mapai era, Ethnic and
racial studies, 44 (6): 1008-1029.
Khozhanova, A., Zvezdina, G., and Elagina, M. (2019).
Strategic management of an educational organization of
a technical and professional orientation in the context
of integration processes in the post-Soviet educational
space, International Conference on Trends in the
Development of Psycho-Pedagogical Education in the
Conditions of Transitional Society (ICTDPP), 70:
02006.
Omelchenko, S.V. (2006). The concept of integration in the
pedagogical process, Man. Sport. Medicine, 16: 14-17.
Ryleeva, A.S., Emanova, S.V., Sokolskaya, M.A., and
Kazantseva, E.A. (2019). Features of pedagogical
activity on development of communicative universal
learning actions at younger school students, The
International Scientific and Practical Conference
"Current Issues of Linguistics and Didactics: The
Interdisciplinary Approach in Humanities and Social
Sciences".
16%
16%
15%
15%
14%
14%
10%
provides the opportunity to study at a convenient
time and place
develops intellectual abilities
provides an opportunity to expand their circle of
communication
forms skills of working with volumes of information
increases the level of knowledge
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
418

Sorokina, I.O. (2008). Theoretical foundations of the
concept of "integration" and the principles of its
implementation, Management in Russia and abroad.
Sozykina, T.K. (2014). Efficiency of integration of general
and additional education in a modern educational
institution in the context of the implementation of the
Federal State Educational Standard, Interactive
Education, 25.
Semenova, I.Yu. (2020). Career guidance in the context of
digital transformation of the education system, Digital
education: a new reality: materials of the All-Russia.
scientific. conf. with international participation, pages
59-62.
Integrity and Integration of Educational Space as a Factor of Stability and Quality of Education in the Trans-Urals Region
419
