
Sustainable Development of Industrial Regions: Economic Aspect
(the Case of the Kemerovo Region)
Olga Zonova
a
, Oksana Sheveleva
b
and Ekaterina Slesarenko
c
Department of Finance and Credit, T.F. Gorbachev Kuzbass State Technical University, Kemerovo, Russian Federation
Keywords: Sustainable Development, Industrial Region.
Abstract: Sustainable development of the Russian Federation, including its individual territorial entities, is a strategic
area of socio-economic development. The Kemerovo Region is an old-industry region with a traditional
techno-economic paradigm, where degradation of natural landscapes, environmental pollution, and morbidity
of the population act as “sore” points of sustainable development and generate an outflow of a significant part
of the population. Structural analysis of the gross regional product of the Kemerovo region - Kuzbass revealed
imbalances in favor of mining during the post-Soviet period. It is also a regrettable fact that the share of
investments aimed at environmental protection and rational use of natural resources in the total investments
is extremely small, which has a disturbing effect in the further implementation of the concept of sustainable
development. We believe that it is the quality of structural changes that determines the sustainability of
economic development and the stabilization of its growth in the long term. The presented indicators
characterizing the sectoral makeup of the economy of the Kemerovo region - Kuzbass demonstrate the
transition of the economy from the late industrial type with a predominance in its structure of industries
producing goods with high added value to the early industrial type, specializing in the extraction of natural
resources. Increasing production potential is limited by the growth of the extractive industries, which poses a
threat to environmental safety and, in general, limits the potential for sustainable development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The concept of sustainable development appeared
almost 30 years ago and has received worldwide
recognition in connection with the need for a
coordinated and joint solution of global problems.
The problem for humanity is that economic growth
destroys and depletes the natural environment, leads
to environmental degradation, and this, in turn,
undermines the very process of economic growth.
Currently, humanity is facing the risk of irreversible
destruction of the environment, which can lead to the
destruction of the mainstays of civilization and the
extinction of living nature (Safonov et al, 2013). It
concerns not particular crises - energy, economic,
social, etc., but the global world crisis of the "man-
environment" relationship.
Sustainable development involves finding a
compromise between the exploitation of the natural
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9891-6281
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9469-2460
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0030-646Х
environment and the ability to meet the needs of
current and future generations. The very definition of
sustainable development raises questions: What
environmental impact can be considered acceptable?
How to quantify the limit of anthropogenic impact on
the environment? We believe that the rate of
destruction of the environment by humans exceeds
the capabilities of modern science in understanding
them and does not allow fully assessing what is
happening (Barkhatov and Benz, 2020). In this
connection, the way out of the crisis is seen, first of
all, in a change in techno-economic paradigm by
modernizing primary industries, the formation and
development of processing industries that create a
product with high added value, as well as in the
development of the service sector.
Environmental, social and economic factors have
become drivers of growth on the path to sustainable
development in accordance with the Decree of the
President of the Russian Federation of 04.02.1994
Zonova, O., Sheveleva, O. and Slesarenko, E.
Sustainable Development of Industrial Regions: Economic Aspect (the Case of the Kemerovo Region).
DOI: 10.5220/0010668400003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 355-359
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
355
No. 236 "On the Concept of the Russian Federation's
Transition to Sustainable Development". Currently,
within the framework of the concept of sustainable
development, 12 national projects are being
implemented, including "Environment",
"Demography", "Digital Economy of the Russian
Federation". It should be noted that the institutional
environment in the Russian Federation is being
formed, and the global trend of further development
has been identified (Barkhatov and Benz, 2020). It is
possible that the strengthening and reforming of the
institutional framework for sustainable development
should be more stringent, since for almost 30 years
the current situation has not been resolved, but is
somewhat aggravated.
2 METHODS
The study is based on the use of a dialectical system
method, which allows describing both the current
state of an object and the process of its development.
Consideration of the current state of an object
involves the study of structural and functional
elements that internally interact with each other.
Whereas the characteristic of the development
process consists in describing the level of functioning
and changes in the object of research (Mingaleva and
Oborin, 2017).
Also, we consider it important to apply a systems
approach to the analysis of sustainable development of
the region. It involves taking into account the
historically established specialization of the region, in
connection with which, when planning the prospects
for further sustainable development of the region, it is
necessary to identify precisely the problems of
modernization and structural transformation of its
economy. In the process of analysis, it is necessary to
identify the main driving forces (resources) for further
socio-economic development and conditions that have
a disturbing effect (Mingaleva and Oborin, 2017).
We consider it expedient to apply the
anthropocentric approach, which prevails in the
works of most researchers of sustainable
development of territories. The use of this approach
is explained by several circumstances:
improving the quality of life is the goal of the
strategic development of the state, as well as
the goal of sustainable development;
human activity is aimed at meeting her/his
needs, which is also closely related to
sustainable development issues.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The object of the research is the concept of
sustainable development of an industrial region. The
subject of the research is economic limitations on the
implementation of the concept of sustainable
development.
The Kemerovo Region is a typical industrial
region with a conventional sectoral makeup that
requires serious restructuring and modernization of
the economy to implement the principles of
sustainable development, which is currently
happening at a fairly low rate (Table 1).
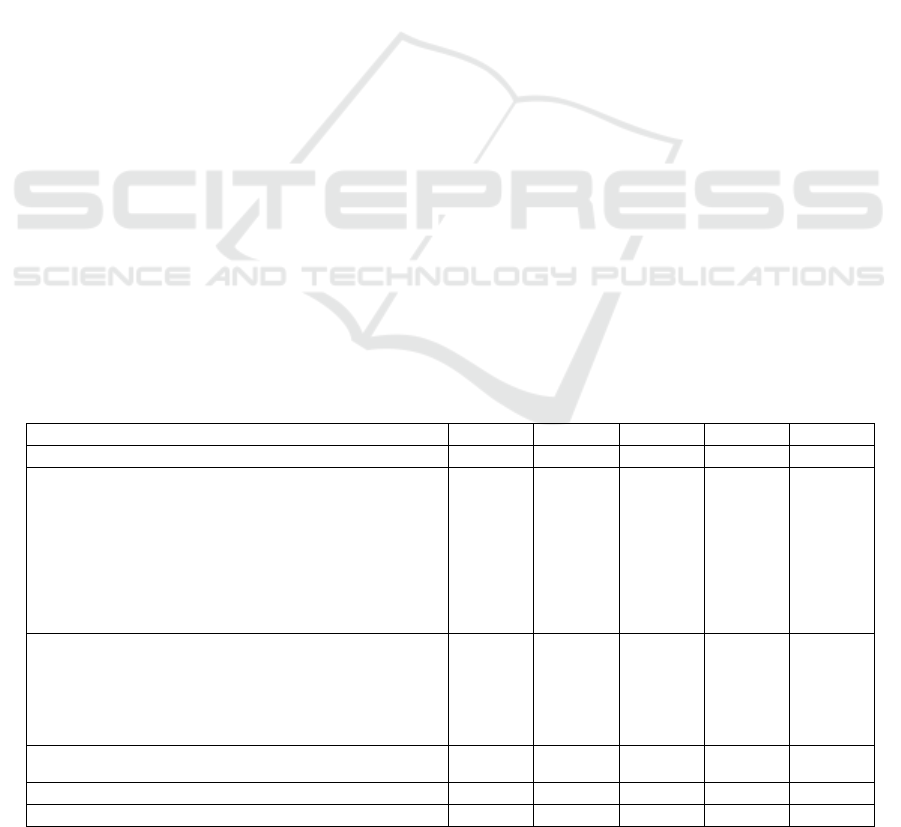
Table 1: Pattern of investments in fixed assets, investment accumulation rate and depreciation of fixed assets.
Indicato
r
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Fixed capital investments, million rubles 170470 165666 215237 248665 297946
including by types of fixed assets:
non-residential buildings, structures
share of buildings and structures in the fixed assets,%
machinery, equipment, vehicles
share of machinery, equipment, vehicles in the fixed assets, %
intellectual property objects
share of intellectual property objects in the fixed assets, %
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
63122
29.3
123453
57.4
524.6
0.2
73217
29.4
143136
57.6
1733
0.7
101513
34.1
160879
54.0
1973
0.6
including by type of economic activity:
mining
share of share of mining in the total volume, %
processing industries
share of processing industries in the total volume, %
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
80577
53.9
14570
9.8
94600
51.7
19148
10.5
123134
55.1
25377
11.3
Including investments in fixed assets aimed at environmental
protection and rational use of natural resources, million rubles
2058
1669
3150
2954
5110
Investment accumulation rate, %
20.2 18.3 19.6 19.6 26.8
Depreciation of fixed assets (in mining),%
- - 53.4 52.2 50.7
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
356

The economy of the Kemerovo region, as before,
is natural capital intensive and the transition to a new
qualitative level of economic growth is becoming
very problematic.
The economy of the Kemerovo region, as before,
is natural capital intensive and the transition to a new
qualitative level of economic growth is becoming
very problematic. This type of economic
development follows an extensive path and in
conditions of increasing technological potential of
developed and developing countries, it is determined
by an extremely unstable macroeconomic trend.
In modern conditions of the development of
convergent technologies, the sixth wave of
innovations, the sustainability of economic growth
and the development of old-industry regions is
determined by the direction of shifts occurring in the
structure of the economy, and, first of all, in the
structure of reproduction. Thus, structural shifts in
investment in fixed assets by type of economic
activity (Table 1) reveal clear distortions in favor of
the extraction of minerals throughout the entire post-
Soviet period. It is also a regrettable fact that the share
of investments aimed at environmental protection and
rational use of natural resources in the investments
pattern is extremely small and amounts to no more
than 2%, and investments in intellectual property
objects - less than 1%.
Thus, it is the quality of structural changes that
determines the sustainability of economic
development and the stabilization of its growth in the
long term (Uskova, 2020). The presented indicators
characterizing the sectoral makeup of the economy of
the Kemerovo region - Kuzbass demonstrate the
transition of the economy from the late industrial type
with a predominance in its structure of industries
producing goods with high added value to the early
industrial type, specializing in the extraction of
natural resources. The increase in the production
potential of Kuzbass is limited by the growth of the
mining sector, which poses a threat to environmental
safety and, in general, hinders the potential for
sustainable development.
On the other hand, the strengthening of the
industrial orientation of economic growth does not
have a negative environmental effect if high-tech
industries take the lion's share in the structure of
industrial production (Stupen and Taratula, 2019).
But in the Kemerovo region, the situation is
somewhat different.
The rate of accumulation of investments in fixed
assets in GRP in 2015-2018 is almost stable and
amounts to about 20%. In 2019, the accumulation rate
was 26%. Intensive growth and a high rate of gross
fixed capital formation provide only at first high rates
of economic growth and are mandatory, but
insufficient conditions for the implementation of the
concept of sustainable development. The value of this
indicator for the Kemerovo region is low.
Undoubtedly, when a certain level of economic
development is reached, a relatively lower rate of
capital investments will be required to ensure a given
growth as a result of more efficient use of
investments.
The unsatisfactory dynamics of investments in
fixed assets is currently one of the main conditions
that have a disturbing effect on the transition of the
economy to the trajectory of sustainable
development. At the same time, the possibilities of
production growth due to the better use of fixed assets
are extremely limited due to the high level of their
depreciation (over 50%).
According to the chosen logic of the study, let us
turn to the analysis of the ongoing structural changes
in the regional economy (Table 2).
Structural changes in the economy are the drivers
of economic growth. Of course, over time, structural
changes are inevitable due to the differentiated
influence of technological innovations in a number of
industries, different elasticities of demand for goods,
works and services.
Structural changes in output by sectors of the
Kemerovo region's economy in dynamics over 15
years show a decrease in the share of agriculture and
processing in GRP, an increase during the analyzed
period and a slight decrease by the end of 2019 in the
share of mining.
The share of agriculture in the GRP is declining
despite the fact that agricultural products can be an
export commodity. In the context of forced import
substitution due to the imposition of sanctions,
consumer preferences shifted towards the support of
the domestic producer.
We believe that one of the priority measures for a
coal-mining region should be the diversification of
exports (as an option, agricultural products, in
particular, raw materials or certain types of their
primary processing) in order to reduce the
dependence on fluctuations in hydrocarbon prices.
An interesting fact is that, despite the volatility of
energy prices, the transition of a number of countries
to low-carbon development strategies, reduced
demand for coal, the use of renewable energy sources,
the share of production in the GRP structure of the
Kemerovo region is stable. In our opinion, an
alarming trend is the reduction in the share of
processing industries in the GRP of the Kemerovo
Sustainable Development of Industrial Regions: Economic Aspect (the Case of the Kemerovo Region)
357
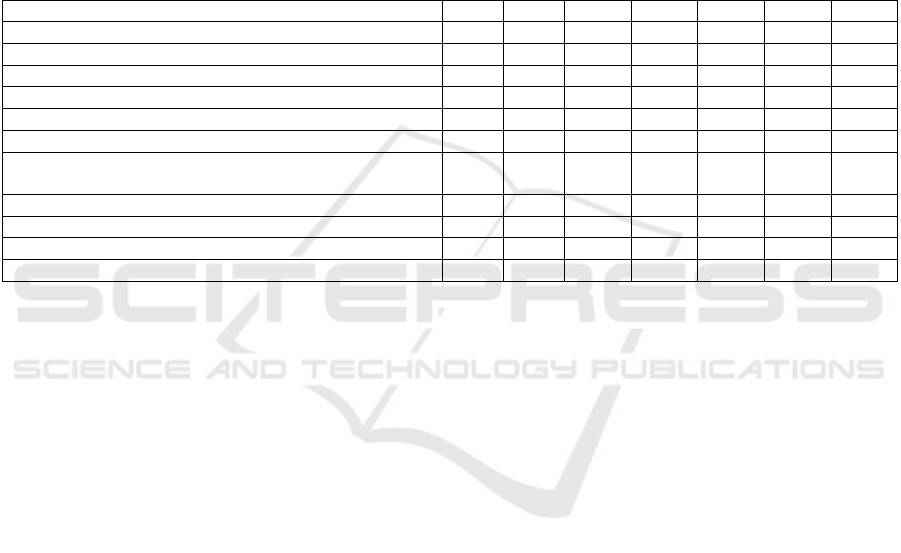
Region, despite the fact that processing industries are
recognized as a powerful driver of economic growth.
At the same time, the focus on the development of
processing industries can also limit the possibilities of
transition to sustainable development.
Structural change must be multidimensional. We
believe that the service sector, including high-tech,
also has significant growth potential. However, in the
Kemerovo region - Kuzbass, the share of activity in
the field of information is stable, being at a rather low
level during 2016-2019, and accordingly, there are
also opportunities for economic growth.
A positive trend in the implementation of the
sustainable development strategy is the increase in the
share of education and healthcare in the GRP for the
period under study. We believe that investments in
human capital are fundamental factors for sustainable
growth (Lazareva et al, 2020; Dematteis, 2009;
Sheveleva et al, 2019).
As part of the implementation of the concept of
sustainable development, it is necessary to take into
account not only the needs of the economy, but also
the needs of a person (Ostanina, 2020).
Table 2: The structure of the Kemerovo region economy.
Indicato
r
2005 2010 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Share of a
g
riculture and forestr
y
in GRP,% 3.3 3.4 4 3.0 2.2 1.9 22
Share of mining in GRP,% 27.1 31.4 25.8 29.7 36.5 35.9 26.3
Share of processing industries in GRP¸% 16.9 18.9 17.9 15.4 13.9 14.6 14.0
Share of construction in GRP,% 5.3 4.6 3.9 3.8 3.3 3.6 5.4
Share of trans
p
ort and communications in GRP,% 9.4 8.9 9.2 - - - -
Share of trans
p
ortation and stora
g
e in GRP,% - - - 6.0 6.1 6.2 7.1
Share of activities in the field of information and
communication in GRP,%
- - - 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.4
Share of education in GRP,% 3.0 2.7 3.6 3.3 3.0 3.0 3.6
Share of healthcare in GRP,% 3.8 4.1 5.0 4.6 4.1 4.4 5.4
Share of wholesale and retail trade in GRP,%
13.8 9.4 9.9 9.3 8.7 8.6 10.0
Share of financial services in GRP,%
0.4 0.4 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.2
The interrelation of economic and social
components of sustainable development is extremely
close, therefore, further limitations of economic
growth can be such social problems as an aging
population, a decrease in the number of able-bodied
citizens, an increase in morbidity, disability,
mortality, a decrease in the birth rate, and migration
outflow.
These issues cannot be ignored when
implementing the concept of sustainable
development, since taking these factors into account
can provide an increase in labor productivity, an
increase in GRP, and a reduction in financial costs to
support the dependent population or persons with
disabilities.
Also, a promising direction, in our opinion, is the
formation and development of closed-cycle
production (Azzahidi et al, 2020; Zonova et al, 2016),
which will reduce the burden on the environment
through the processing of industrial and household
waste. And this, in turn, involves sorting waste,
organizing its reception and transportation to the
place of direct processing, i.e. development of
processing industries.
Thus, it is obvious that the currently implemented
regional economic policy does not contain a vector
for sustainable economic development, since it is not
aimed at stimulating positive structural changes
(Zonova et al, 2016; Bereznev et al, 2017; Sheveleva
et al, 2020). We consider structural changes positive
if they result in an increase in entrepreneurial activity
(especially in the sector of high-tech and information-
intensive services), the emergence of new market
entities, the development of reproductive relations
(the emergence of new forms of investment in high-
tech business, modification of connections between
entities, the emergence of new sources of capital
accumulation, etc.).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The industrial region continues to increase its
production potential, structural changes in investment
demonstrate the strengthening of extractive
industries. Depressing is the fact that there are almost
no significant changes in the investment pattern,
which testifies to the consolidation of the raw
material orientation of the economy.
In industrial regions, the issues of quality of life
are most urgent. Degradation of natural landscapes,
environmental pollution, morbidity of the population
act as "sore points" for further socio-economic
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
358

development and generate an outflow of the able-
bodied population, in particular the component that
has a high innovative potential (scientists,
researchers, engineers).
In order to achieve the goals of sustainable
development of the Kemerovo Region and
typologically homogeneous regions with a
predominant mining-type economic activity we
consider it necessary to give the regional economic
policy a vector aimed at stimulating positive
structural changes that ensure the formation of a
highly competitive innovation environment.
REFERENCES
Azzahidi, A., Bengrich, M., Omrane, A. (2020). Innovation
for Sustainable Development.
10.1201/9781003097921-2.
Barkhatov, V., Benz, D. (2020). Sustainable Development
in Russia. Just a Theory? 10.1007/978-3-030-44711-
3_12.
Bereznev, S., Zonova O., Lubkova, Е. (2017). The
innovative strategy of social and economic
development of mining region. E3s web of conferences.
04002.
Dematteis, G., 2009. The Territorial Sustainability of
Development. Lotus International, 140: 84-88.
Krohmer, R., Nestmann, F. (2011). Conceps for a
Sustainable Development in Russia. Wasserwirtschaft,
101: 10-11.
Lazareva, E., Anopchenko, T., Murzin, A. (2020). Human
Capital in the System of Urban Territory. Sustainable
Development Management. 10.1007/978-3-030-16091-
3_28.
Magopets, D., Svitlana, O., Iryna, M. (2020). Strategic
Planning for the Sustainable Development of
Territories. International Journal of Economics and
Business Administration, VIII. 259-272.
10.35808/ijeba/547.
Mingaleva, Z., Oborin, M. (2017). Author Constructing
Research Methodology for Territorial Sustainable
Development. Moscow University Economics Bulletin,
3-24. 10.38050/01300105201731.
Ostanina, U. (2020). Management of sustainable
development of territories. E3S Web of Conferences,
208: 08016. 10.1051/e3sconf/202020808016.
Safonov, G., Bobylev, S., Perelet, R., Davydova, A. (2013).
Sustainable Development in Russia.
Sheveleva, O., Slesarenko, E., Kudrevatykh, N.,
Kumaneeva, M. (2020). The Role of Investment and
Innovation Activities of Coal Mining Enterprises in
Increasing the Level of Environmental Safety of
Country and Region. E3s web of conferences: Vth
International Innovative Mining Symposium, 04008.
Sheveleva, O., Slesarenko, E., Kudrevatykh, N., Mamzina,
T. (2019). The unity of the trajectory of sustainable
development of the mining region and ensuring its
environmental safety. E3S Web of Conferences, 134:
03007.
Stupen, M., Taratula, R. (2019). The assessment of
economic efficiency of rural territories sustainable
development. Vìsnik L’vìvs’kogo nacìonal’nogo
agrarnogo unìversitetu. Arhìtektura ì
sìl’s’kogospodars’ke budìvnictvo, 85-89.
10.31734/architecture2019.20.085.
Uskova, T. (2020). Territories’ Sustainable Development
and Modern Management. Methods. Problems of
Territory's Development. 10.15838/ptd.2020.2.106.1.
Zonova, O., Slesarenko, E., Nekhoda, N. (2016). Social
Technologies for Management: Opportunities for Coal-
mining Enterprises. Coal in the 21st Century: Mining,
Processing and Safety, 125-129.
Sustainable Development of Industrial Regions: Economic Aspect (the Case of the Kemerovo Region)
359
