
Research on the Quality of Economic Development of Regional
Innovation Systems, Taking into Account Human Potential
Karina A. Nevmatulina
1a
, Alexander A. Tsvyrko
2b
and Natalya A. Azarova
3c
1
Karaganda University of Economics Kazpotrebsoyuz, Karaganda, Kazakhstan
2
Central Russian Institute of Management, Eagle, Russian Federation
3
Department of World and National Economics, Voronezh State Forestry University named after G.F. Morozov, Voronezh,
Russian Federation
Keywords: Innovation, Regional Economy, Human Potential, Regional Innovation Systems.
Abstract: The high quality of the economic development of the region allows increasing the efficiency of public
production: for this, the cost of productive labor and means of production deceases per unit of regional income,
and economic development improvement, the role of scientific and technological progress of the quality of
products increases. These economic processes lead to an empowerment in the quality of life of the population,
as well as the effectiveness of social policy, and the environmental friendliness of the economic development
of the region. As a result, regional innovative economic systems must be significantly modernized. The
previous functioning type of extensive economic relations that developed through mining ultimately led to
negative environmental consequences. "The ability to achieve a new quality of economic development in the
regions is a major challenge. In order to solve it, it is necessary to overcome the high level of social
differentiation, insufficient life expectancy, and prevent excessive exploitation of the environmentally
friendly component of natural potential" (Management of innovative development of the region: monograph,
2008). That is why it is now a priority to find an alternative as well as more sustainable economic models that
should provide conditions for improving the well-being of the population in the region and, at the same time,
be sufficiently environmentally friendly. To solve this problem, it is necessary to give a clear quantitative
assessment of the quality of economic development of regional innovation systems, which will provide a
unified approach to the analysis of all indicators of the state of the region.
1 INTRODUCTION
Regional innovative economic systems are a dynamic
set, where both the resources of a given region and
the result of their use are of the most effective
importance for the country's economy. Therefore, the
issues of their quantitative measurement, determining
the quality of their development have not been
sufficiently studied. In particular, a single integrated
approach to how to assess the quality of economic
development of regional innovation systems has not
yet been developed, including the concept of a single
indicator for measuring it is controversial. This
situation gives rise to a dispute over the quality of the
development of the country's economy as a whole.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0839-9071
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0240-7985
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8244-8922
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The question of studying the concept of "regional
innovative economic systems" is a new one.
Therefore, the purpose of this work is to develop a
single indicator for assessing the quality of economic
development of regional innovative economic
systems, which will help to reveal the economic
content of this concept and develop the necessary
quantitative methodology.
An accurate understanding of the problems of
spatial and regional economic problems can be based
on basic economic facts:
1) This is the predominance of natural mining
regions;
Nevmatulina, K., Tsvyrko, A. and Azarova, N.
Research on the Quality of Economic Development of Regional Innovation Systems, Taking into Account Human Potential.
DOI: 10.5220/0010665500003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 165-171
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
165

2) This is the winning concentration in economic
development;
3) This is the role of costs for domestic and
external transport and communications.
A regional economy is a framework within which
the spatial nature of economic systems can be
understood. Determining the factors driving the
distribution of economic activity in space, and
recognizing that changing this distribution will have
important consequences for people and communities
- is the goal of the study. Therefore, today the most
pressing area of research on regional innovative
economic systems is the so-called synergy of closed-
loop economics. In conclusion, the quality of
economic development is determined by the
functioning of economic models that are based on the
principle of an innovative cycle, that is, continuous
innovative development, and not on the constantly
increasing extraction of natural resources.
Environmental degradation and ongoing climate
change demonstrate the need to dominate innovative
economic models that are sustainable over the long
term.
Thus, all the specifics of the regional economy
can be concluded in the following issues: "what?
where? why and how? ".
The first, "what?" refers to all types of economic
activity: not only to production enterprises in the
narrow sense of the word like farms and mines, but
also to other types of enterprises, households, as well
as private and public institutions. The question
"where?" refers to the location of one economic
activity in relation to another activity; "it includes
issues of proximity, concentration, variance, and
similarity or inconsistency of spatial structures, and it
can be discussed either broadly, for example, between
regions or at the meso-level, in terms of zones,
surroundings and sites". Questions "why? and how?"
belong to the competence of a scientist-economist.
The regional economy is a relatively young
branch of the economy. Until recently, most
economists ignored the question of "where?" finding
many problems that they could deal with without
giving their analysis any spatial dimension.
"Geographers lacked awareness of the specifics of
explanation in the categories of human behavior and
institutions to explain "why?" and resorted to simple
description and mapping. Urban planners were still
concerned about the physical and aesthetic aspects of
the idealized urban layout" (Zinovieva, Azarov,
Heavenly, 2021).
This minor situation has been largely corrected
over the past few decades. People who call
themselves different professional labels - economists,
geographers, environmentalists, city and regional
planners, regional scientists and urbanists - came
together to develop analytical tools and skills and
apply them to some of the most pressing problems of
that time.
"The study of theories of economic development
is connected with the combination of the concepts of
the "vicious circle of poverty" and the concept of
"sustainable development". This concept of the so-
called "vicious cycle of poverty" was applied in the
analysis of the development of the economies of low-
developed countries. According to this theory of
quasi-stable equilibrium, its author, H. Leibenstein,
revealed a relationship between the prospect of
population growth and a possible change in certain
economic conditions, which in turn ensures
fluctuations in the economy due to an improvement
or deterioration in per capita income "(Nureyev,
2000).
"This abstract theory focuses on the dangers
caused by the decline in per capita income in the
territory. Another view of the "vicious cycle of
poverty" theory is that this problem is caused by the
narrowness of the domestic market and insufficient
resources for innovation. The theory of the "vicious
circle of capital shortages" by R. Nurkes strongly
links the economic backwardness of the Territory
with specific institutional conditions, especially with
indicators such as the low qualification of the labor
force and the underdevelopment of secondary and
higher education systems in terms of the level of
vocational training "(Nureyev, 2000).
"As a result, a continuation of the theory of
"vicious circles of poverty" was such a concept that
gave the concept of the possibility of a transition to
self-supporting growth, authored by the scientist W.
Rostow. This concept was to justify the transition
from a single traditional society to an innovative
society of the Western type. In the concept of W.
Rostow, economic development synonymizes the
concept of a high growth rate" (Nureyev, 2000).
"In its interpretation, social and institutional
changes do not seriously affect the development of
the economy, and the indicator "the ratio of the level
of investment to the level of growth of GNP" comes
to the fore. In his opinion, a sufficiently large
injection of capital resources is necessary for the
successful modernization of the national economy.
As a result, self-sustaining growth will begin. It is not
possible to mobilize these resources on an absolutely
voluntary basis. The State must therefore ensure the
forced saving of the population. These savings are the
result of a special monetary and fiscal policy of the
State. The inefficiency of fiscal capital could be offset
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
166

by the import of monetary capital. The term
"economic development" refers to profound
structural changes. These changes cover completely
all the main sectors of the national economy, which is
called the theory of "big push"(Nureyev, 2000).
The "theory" model with two deficits "was to
describe the relationship between the development of
the processes of internal accumulation of monetary
resources in the country and the reduction of sources
of external financing. The theory of the "two-deficit
model" explains "economic development" by
crowding out external sources of financing by
domestic ones. Replacement of imported goods with
domestic ones, which will be the basis for
overcoming external monetary and financial
dependence" (Nureyev, 2000).
"Therefore, the main disadvantage of these
concepts is that they focus on the use of a fairly
limited economic factor in developing countries -
capital. However, the error of these economic theories
was the failure to take into account the possibilities
given by the use of such a relatively excessive
resource in some territories as labor"(Nureyev, 2000).
The study of the concept of "economic
development" in the understanding of J. Schumpeter
(Shpaltakov, 2017), determines the ability to
implement such innovations in which the
entrepreneur will initiate this innovation.
Considering the economic theories of Keynesians,
whose research base was a change in the technical and
economic parameters of the economy. However, the
socio-economic prerequisites of these studies did not
affect.
Neoclassical theories of economic development
were based on an equilibrium combination of capital
accumulation and population growth trends. These
two indicators provided a combination of the
development of the two-component component of the
Territory's economy - agricultural and industrial
sectors. W. Lewis, A. Hirschman, S. Schatz, J. Fey
and G. Ranis, as founders of the theory of dualist
economics, assumed that urbanization of the
population, including the movement of labor
resources from agriculture to industry, ensures the
development of the economy as a whole. But the
quality of economic development in this theory was
not considered. Economist G. Murdal, who ensures
the humanization of economic growth in terms of
paying special attention to the means of solving social
problems, criticized the main theories of growth.
There was a distinction in the understanding of
economic growth and development. If economic
growth does not generate income growth for the
majority of the population, it contributes to instability
in the economy, technological stagnation, corruption
and bureaucracy. Leaving aside the economic
situation of the majority of the population, this
economic growth did not contribute to the qualitative
development of the population living in this territory.
By development, this researcher understood the
degree of satisfaction with the basic needs of the
majority of the population (Shpaltakov, 2017).
And after some time, the time has come for the
institutional approach to dominate the understanding
of economic development. This approach was
developed by T. Schultz, as a prominent
representative of the economic school, which founded
an understanding of investment in human capital.
"Human capital combines all the productive qualities
of workers, including the totality of knowledge,
skills, motivation and mental energy. By means of
preparation of the human capital for processes of
production, investments into expenses for education,
education, health care, prerequisites for his
functioning in an effective form" are created"
(Pavlova, 2011). This trend will, in the author's
opinion, ensure economic development.
At the same time, special importance is attached
to the formation of models of regional innovation
systems through the education system and the
accumulation of scientific and technical potential.
According to simplified models, the regional
innovation system includes: (a) organizations that
produce and use knowledge; b) participants ensuring
the activity of the former; c) a single sociocultural
space. "Thus, the basic idea of modern concepts is
that economic development should be accompanied
by the corresponding synergistic development of
social infrastructure, improvement of the quality of
life of the population, state of ecology, improvement
of the institutional basis of economic activity"
(Pavlova, 2011). This conditions the quality of
economic development of regional innovation
systems.
3 RESULTS OF THE STUDY
The essence of regional innovation systems is a
complex of organizations that provide the territory
with the production of new knowledge, new
professional experience, skills and skills. These
industries contribute to the financial, economic, legal
and information support of innovative processes in
the region. The innovative potential of economic
development is the basis of the regional innovation
system. With the standard method of assessing the
economic development of regional systems, it was
Research on the Quality of Economic Development of Regional Innovation Systems, Taking into Account Human Potential
167
possible to determine only the level of development
of production. But taking into account international
trends in assessment, one can say that such an
assessment is insufficient. This is due to the
understanding that human capital will be the basis for
the economic development of regional innovation
systems. And "the development of such aspects as
education, health, the state of the environment, equal
opportunities in the economic sphere, personal
freedom and a culture of life provides the basis for
growth and further development" (Stroeva, 2021).
International organizations assess the level and
quality of life of the population of the economy in a
particular territory according to various indicators.
The competent use of statistical information allows
the calculation of many indicators characterizing
these processes. It is therefore necessary to assess the
quality of economic development of regional
innovation systems. The regional innovation system
is based on the national system, in terms of copying
its development trends as a subsystem element. To
equalize the economic situation of regions and
maximize their potential (economic, social and
environmental), this assessment is based on a specific
innovation strategy, unique opportunities and abilities
of each regional territory. To address "the problem of
such an assessment, it is necessary to identify and
limit the list of indicators. These indicators can be
seen as indicators of the innovative state of the region
based on the functioning of the regional innovation
infrastructure" (Pavlova, Pavlova, 2011).
"The integrated indicator of the functioning of the
regional innovation infrastructure should be a
multidimensional complex" (Stepanova, 2021),
which includes the following elements:
Costs of high-tech health care in the region;
Level of demographic growth (fall);
average real incomes of the population in the
region;
Environmental welfare costs;
Level of environmental protection;
Social component of economic well-being
(level of schools, universities, institutions of
secondary vocational education);
Availability of business clusters for innovative
support of regional economic development.
"Some researchers are invited to assess the
following types of efficiency of the innovation
system: social, economic, environmental,
demographic; social and economic" (Zinovieva,
Azarov, Heavenly, 2021).
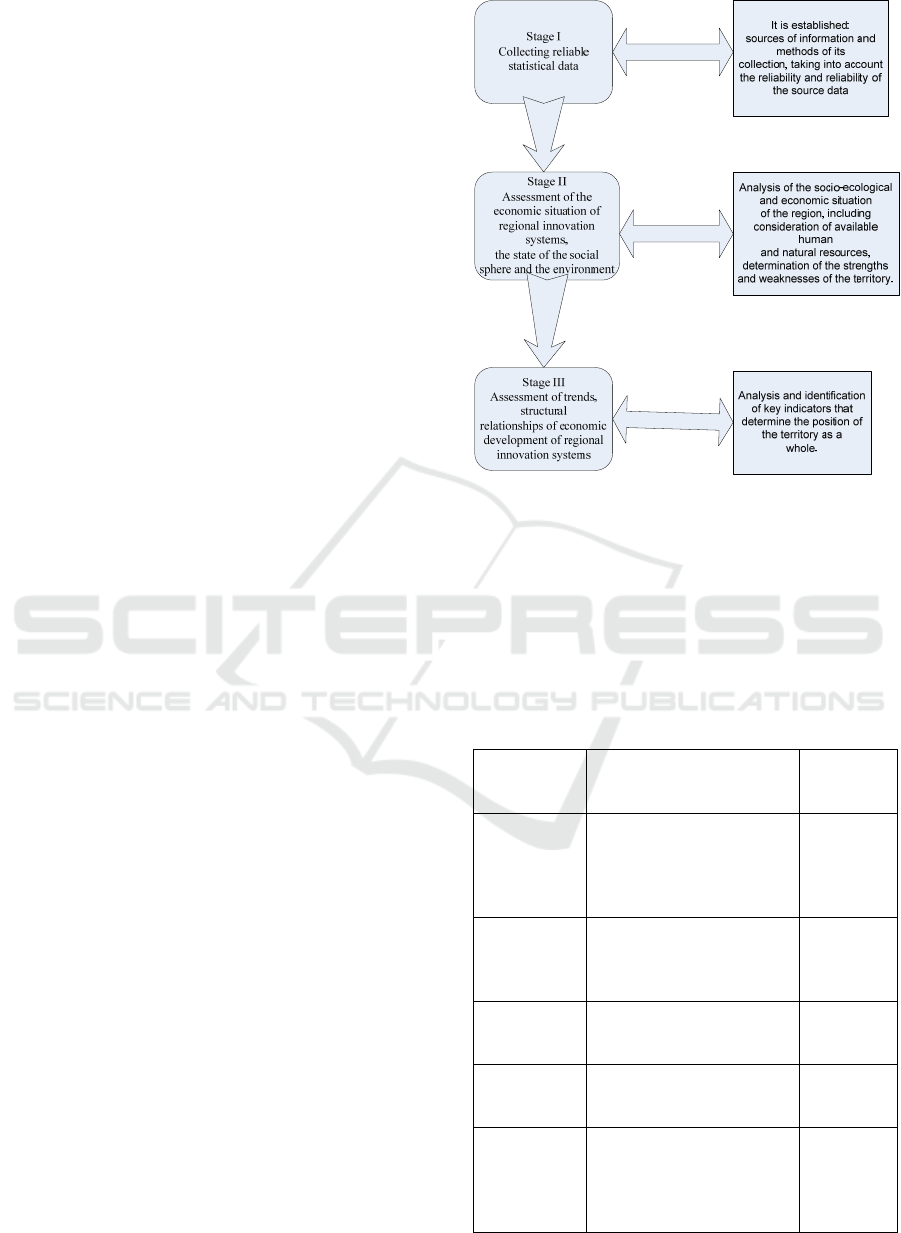
The proposed algorithm for assessing the
functioning of the regional innovation system
consists of a list of consecutive stages.
Figure 1: Algorithm for assessing the quality of economic
development of regional innovation systems.
"At each stage, a certain task has been identified
for solving, sources of information, ways of their
collection are established, reliability and reliability of
initial data are assessed, i.e. the task of collecting
reliable statistical data is solved" (Stroeva, 2021).
Table 1: Indicators of analysis of innovative potential of the
region.
Indicator
group
Type of indicators Source of
statistical
information
Level of
education of
the
population in
the region
Proportion of employees
with higher and secondary
education in the total
population of the region
Statistics
Innovation
and technical
components
Share of innovative
enterprises in the region
according to the balance
sheet
Statistics
Calculation
data
Financial
component
Share of technological
innovation costs in the
region
Statistics
Scientific
component
Proportion of researchers
performing research and
development in the region
Statistics
Environment
al component
Share of waste technology
development costs in the
region. Sum of specific
emissions and waste
g
eneration
Statistics
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
168

By highlighting the main blocks of innovation
potential of the region, the main indicators for
analysis can be identified.
4 DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
"An index refers to a specific construct formed by a
combination of indicators. The process of
constructing an index is often one way to create a new
concept at the empirical level of knowledge or to
replace the inaccurate concept of the theoretical level
with a more accurate one. The construction of the
index can be considered as a way to obtain values of
a latent characteristic that is not directly measurable
using certain transformations of the values of the
observed characteristics (indicators)" (Pavlova,
Pavlova, 2011). "An index as a construct of indicators
is considered to be the empirical equivalent of its
corresponding concept. The purpose of introducing
indicators and indices is to assess the situation (state,
situation) in some areas of research, on the basis of
which a forecast of possible developments should be
given and recommendations to ensure the
achievement of the development goals of the systems
under consideration" (Stepanova, 2021). The
algorithm for constructing the index reflecting the
quality of economic development of regional
innovation systems takes into account the
methodology for calculating the "human
development index", which includes the arithmetic
mean of three private indices:
"index of the scientific component, based on
the share of scientists performing scientific
research and development in the region"
(Carrot, 2020);
The education index, measured as the
aggregate index of the proportion of employees
with higher and secondary education in the
total population of the region;
Index of knowledge-intensive GDP per capita,
taking into account the share of innovative
enterprises in the total number of enterprises
and the share of costs of these enterprises for
technological innovations in the regional
economy;
Eco-innovation index, which includes the cost
of developing waste management technologies
in the region and the sum of specific emissions
and waste generation.
The calculations use unified minimum and
maximum values of statistical indicators: from 0 and
up to 100%.
Each private index is calculated using the
formula:
minmax
min
ii
ii
xx
xx
i
I
(1)
"A number of Russian researchers note regional
innovation systems specific to the index, taking into
account human potential, such as the insufficient
reasoning of the accepted limits for changing baseline
indicators, and the almost free substitution of baseline
indicators. The proposed integral indicator should
include three blocks: economic, qualitative and
social, environmental. Private indicators are built on
the basis of block data, which in turn consist of
normalized values of individual indicators"
(Astakhin, Tretyakova, 2019). "When building a
consolidated index of the quality of economic
development of regional innovation systems, it is
necessary to proceed from the real possibility of
obtaining certain indicators necessary for
calculations. The statistical indicators included in the
index should meet the following requirements:
representativeness, according to which all the main
indicators of the information block under
consideration should be presented in this list;
information accessibility, according to which the
indicators involved in further analysis should be
available for their statistical registration" (Zinoveva,
Yakovlev, Pecherskaya, 2019).
"Therefore, they must be included in the
nomenclature of official statistical indicators, or
calculated from the values of the latter; Information
reliability, according to which the statistics and
private indicators used should adequately reflect the
state of the economic development dimension under
analysis. The method of rationing is based on the
determination of the "most favorable" and "least
favorable" values of each indicator according to the
totality of territories" (Bahur, Nebesnaya, Azarova,
2020). "The formula for rationing the values of
indicators that have a positive impact on the quality
of economic development of regional innovation
systems has the form" (Bahur, Nebesnaya, Azarova,
2020):
leastmost
leastfact
norm
yy
yy
y
(2)
for indicators that have a negative effect, the
formula is transformed as follows:
.
..
leastmost
factmost
norm
yy
yy
y
(3)
Research on the Quality of Economic Development of Regional Innovation Systems, Taking into Account Human Potential
169

where y
norm
is the normalized value of the
indicator;
Y
fact
- actual value of the indicator;
Y
most
- the most favorable value of the indicator;
Y
least
- the least favorable value of the indicator.
"This approach allows the assessment procedure
to take into account the positive or negative impact of
a factor on the quality of economic development of
regional innovation systems, taking into account the
impact on human development, based on the meaning
or nature of the indicator related to it" (Yakovleva, et
al., 2018). It is proposed to calculate indicators for
each of the areas (educational, health, cultural and
social) according to the arithmetic average formula:
n
y
I
n
i
i
j
1
(4)
where it is the development index j of the sphere.
"Further analysis and comparison of the obtained
integral assessments of the state of economic
development of regional innovation systems, their
graphical representation and interpretation are carried
out. The integral indicator for assessing the quality of
economic development of regional innovation
systems (I) is proposed to be calculated using the
geometric mean formula" (Yakovleva, et al., 2018):
3
321
31
III
I
(5)
where ωj - weight coefficients, and their sum it is
equal to 1.
"The implementation of the proposed evaluation
system, taking into account the algorithm, will allow
the researcher to quantify the quality of economic
development of regional innovation systems, taking
into account the impact on the formation of human
potential, to conduct a comparative analysis in the
context of the subjects of the Russian Federation.
Complex approach ensures validity of study results"
(Yakovleva, et al., 2018).
5 CONCLUSION
In this regard, it is interesting to analyse innovative
economic systems in the following areas: as a channel
for technology diffusion, as a competitive
environment and as export opportunities.
There are three possible channels for technology
diffusion: import, direct investment and technology
trade. As for imports, the effect of increasing the
domestic technological level and productivity
through the import of high-quality foreign goods was
recorded. Direct investment can also increase
productivity in both the initial and subsequent stages
of the supply chain. In addition to the side effect
through the supply chain, also point to the side effect
of technologies in the same industry. The last is
technology trading. Trade in technology in the form
of licensing is considered particularly important for
innovation in the chemical and pharmaceutical fields.
It can also be said that technical guidance and training
of workers can help to accelerate the distribution of
these goods.
Competitive environment, innovative economic
systems as an export opportunity. Free trade is
believed to increase competition. It was pointed out
that the impact of competition on innovation was to
ensure discipline in companies and improve
efficiency, but it was also hypothesized that
investment in R & D would not be possible due to
reduced profits from competition. They are not
incompatible with each other, and there are
hypotheses and empirical studies that determine
which effect is better depending on the degree of
fierce competition and the level of technology. As a
management strategy, there are times when we
introduce inexpensive innovations to increase the
efficiency of companies and management in
conditions of competition and pressure, and there are
times when we carefully differentiate products
through innovation and avoid competition.
The third point is the relationship between export
and innovation. It is usually said that export
companies are more productive, but as for causation,
economic discussions until the early 2000s said that
high-performance companies would enter the import
market. However, recent empirical studies have
shown that, for example, the expansion of export
opportunities has increased the motivation for
innovation, which together leads to increased
productivity.
Finally, the linkage between trade and innovation
through the liberalization of economic systems is an
important issue. Free trade and the investment
environment are in themselves a framework for
promoting innovation, and it can be said that
interaction with a wider range of policy areas is also
important to be linked to real innovation. In this
regard, it is important to train absorption capacity in
a broad sense. This also means the ability to absorb
and learn technology, focusing on individuals, but
also includes broader policy contexts: stable
macroeconomics, market regulation.
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
170

In practice, the quality of economic development
of regional innovation systems reflects many
indicators. Therefore, solving the problem of
quantifying these indicators allows us to determine
the prospects of this study.
REFERENCES
Management of innovative development of the region:
monograph, 2008. Ed. Egorshina A.P., Nizhny
Novgorod: NIMB, 283 p.
Nureyev, R., 2000. Theories of development: a new
understanding of dualism. Economic issues, 10: 134-
154.
Nureyev, R., 2000. Theories of development: neoclassical
models of the formation of a market economy.
Economic issues, 5: 145-158.
Shpaltakov, V.P., 2017. Shumpeter on the problems of
innovative development. Innovative economy and
society, 2(16): 25-34.
Pavlova, S. N., 2011. Methodological Foundations for
Assessing the Innovative Development of the Region.
Russian Economic Online Journal, 3: 180-193.
Zinovieva, I. S., Azarov, N. A., Heavenly, A. Yu., 2021.
Eco-economic indicators of sustainable development of
regions in the context of ensuring the quality of life of
the population. Bulletin of Transbaikal State
University, 27(2): 114-122. DOI 10.21209/2227-9245-
2021-27-2-114-122.
Stroeva, O.A., Lavrikova, N.I., Alekhina, T.A., Semenova,
E.E., Stepanova, M.A., 2021. Development of
Organizational Diagrams and Governance Mechanisms
of Region’s Economy. Modern Global Economic
System: Evolutional Development vs. Revolutionary
Leap. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 198:
1807-1816. Springer,
Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69415-
9_199
Pavlova, S. N., Pavlova S. N., 2011. Comprehensive
assessment of innovation: theory, methodology,
practice. Akad. Sciences Rep. Sakha (Yakutia),
Moscow Department of Education and Science of the
Russian Federation, Federal State Scientific.
Establishment of the "In-t regional economy of the
North". Yakutsk: Sphere, 21 pages.
Stepanova, Yu. N., 2021. Collection of system-forming
components of the concept of developing the innovative
potential of business entities. Region: systems,
economics, management, 1(52): 224-230. DOI
10.22394/1997-4469-2021-52-1-224-230.
Carrot, S. S., 2020. Determinants of innovative activity of
enterprises of the regional ecosystem. Society and
Economic Thought in the 21st Century: Development
Paths and Innovations: Materials of the VIII
International Scientific and Practical Conference,
Voronezh: Publishing and Printing Center "Scientific
Book", pages 138-143.
Astakhin, A. S., Tretyakova, L. A., 2019. Life Modeling
Management of Regional Socio-Economic Systems.
Bulletin of Voronezh State University of Engineering
Technologies, 81(4(82)): 218-225. DOI
10.20914/2310-1202-2019-4-218-225.
Zinoveva, I. S., Yakovlev, A. V., Pecherskaya O. A., 2019.
Methods of application of intellectual technologies of
decision support for maximizing economic
effectiveness of regional economy in the conditions of
its sustainable development. Advances in Intelligent
Systems and Computing, 726: 337-343. DOI
10.1007/978-3-319-90835-9_39.
Bahur, O., Nebesnaya, A. Yu., Azarova N. A., 2020. Study
on the competitiveness of Russian-made wood panels
in the development of import-substituting industries.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental
Science: International Forestry Forum "Forest
ecosystems as global resource of the biosphere: calls,
threats, solutions", Voronezh: IOP Publishing, P.
012037. DOI 10.1088/1755-1315/595/1/012037.
Yakovleva, E. A. Nebesnaya, A. Y. Fomina, N. N. Azarova
N. A., 2018. Monitoring Regional Development Based
on Green Indicators. European Research Studies
Journal, 21(S1): 535-543.
Research on the Quality of Economic Development of Regional Innovation Systems, Taking into Account Human Potential
171
