
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME)
Navya Martin Kollapally
1
, Yan Chen
2
and James Geller
1
1
Department of Computer Science, New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, U.S.A.
2
Department of Computer Information Systems, Borough of Manhattan Community College, New York, U.S.A.
Keywords: Healthcare Inequity, Ontology, Minority, Taxonomy, Ontology Evaluation.
Abstract: Healthcare inequity, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), is a systemic difference in
healthcare services received by different population groups, based on race, ethnicity, gender, sexual
orientation, etc. The Covid-19 pandemic has heightened the awareness of differences in care received by
racial and ethnic minorities in the US. We have investigated the physical, psychological, and emotional harm
that people of colour were exposed to during this time. It is necessary to record data about unequal treatment
to identify and eradicate existing institutional racism in healthcare. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) rely to
a high degree on “coded” terms from terminologies and ontologies. Such a biomedical ontology can be used
for standardization, integration and sharing of data, knowledge reuse, decision support, etc. No ontology for
racial differences exists in US healthcare. This motivation leads us to the development of such an ontology to
record the physical, emotional, and psychological effects resulting from differences in treatment that citizens
receive, based on their identity. Differences exist not only inside of healthcare organizations, but also occur
even before entering them. We present the first version of such a Health Ontology for Minority Equity
(HOME) along with ontology evaluation methods that we applied.
1 INTRODUCTION
The word ontology in computer science refers to a
representation that helps in knowledge sharing and
reasoning (Noy & McGuinnes, 2001). A biomedical
ontology helps in organizing and standardizing
medical data. Ontologies have become important
means for the utilization and integration of
biomedical big data (Caviedes & Cimino, 2003).
More specifically, an ontology helps with defining
concepts, relationships between them, and sometimes
instances in a way that can be easily interpreted by
humans and computer applications. It provides a
terminology framework to reduce data heterogeneity
and allows data to be shared between information
systems. For example, data annotation, wherein data
and the description of metadata are coded by unique
IDs helps in achieving interoperability.
The objective of this paper is to argue for the
necessity of a dedicated ontology for healthcare terms
specifically relevant to minority patients and to
present a design, implementation, and evaluation of a
first version of such an ontology.
A few of the famous biomedical ontologies are the
Disease Ontology (DO) (Schriml, 2018), which
semantically integrates diseases and other medical
terms. The Gene Ontology (GO) (Ashburner, 2000)
represents information about biological processes,
cellular components, and molecular functions. On-to-
knowledge (York, Steffen, & Rudi, 2004) and
Methontology (Fernandez-Lopez, Gomez-Perez, &
Juristo, 1997) are two of the popular ontology
development methods (Kuziemsky & Lau, 2010).
Ontology development goes through steps including
specification, conceptualization, formalization,
implementation, and maintenance (Pan et al., 2019).
The World Wide Web consortium (W3C) Web
Ontology Language (OWL) is widely used for
ontology representation.
This paper describes the motivation, design, and
development of an ontology to report physical,
emotional, and psychological harm, which may or
may not result in hospitalization. This kind of harm is
disproportionally faced by minority members in the
US. The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 describes the background behind the
proposed ontology. Section 3 cites other work related
to medical ontology development and design. Section
4 describes our method of implementation. Section 5
contains details about the design and implementation
of the HOME ontology. Section 6 covers the Protégé
implementation of the HOME ontology. Section 7
Kollapally, N., Chen, Y. and Geller, J.
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME).
DOI: 10.5220/0010639800003064
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2021) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 17-27
ISBN: 978-989-758-533-3; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
17

deals with techniques of ontology evaluation that we
used. Section 8 discusses open issues and Section 9
suggests future work. Section 10 contains
conclusions. This paper does not cover ethical
decision making and situation handling skills.
2 BACKGROUND
Racism, both structural and interpersonal, negatively
affects the mental and physical health of millions of
people, preventing them from attaining their highest
level of health (Walensky, 2021). The COVID-19
pandemic has displayed another stark example of
health disparities faced by racial and ethnic minority
populations.
Racial inequality persists in education
(UNCF.Org, n.d.) and healthcare. Research shows
that minority groups, throughout the United States,
experience higher rates of illness and death across a
wide range of health conditions, including diabetes,
hypertension, obesity, asthma, and heart disease
when compared to their White counterparts (Office of
Minority health resource center, 2021). Additionally,
the life expectancy of non-Hispanic Black Americans
is four years lower than that of White Americans
(CDC, Health Equity, 2021). De facto racial
segregation and low socio-economic status are factors
contributing to this disparity.
Denial of early screening and nutritional
counseling are common among the communities of
minority members. Minority members constitute a
higher proportion of frontline workers (e.g., postal
service employees), which puts them at higher risk of
exposure to communicable diseases and physical
injury, but they are often unable to afford high quality
insurance coverage, which would ensure quality care.
There is evidence that suggests that Black men are
3.23 times more likely than White men to be killed by
police officers during their lifetime (Harvard School
of Public Health, 2020). Based on information from
more than two million 911 calls in two US cities,
researchers concluded that White officers dispatched
to Black neighbourhoods fired their guns five times
as often as Black officers dispatched for similar calls
to the same neighbourhoods (Clark, 2020). These are
a few scenarios in which minority people receive
different treatment based on race and ethnicity, even
before they enter the healthcare system, but that affect
their well-being. It is important to gather data
showing the differences in treatment experienced by
minority population members, which will help in
alleviating intentional and unintentional biases
(Cimino, 2020). Hence development of a specific
ontology is needed for representing this knowledge.
The UMLS (Unified Medical Language System)
(NLM, 2021AA) is a repository of biomedical
vocabularies developed by the US National Library
of Medicine. It integrates and distributes 218 medical
terminologies, containing 4.44 million concepts and
16.1 million unique concept names. The UMLS
includes the Metathesaurus, the Semantic Network,
and the Specialist Lexicon and Lexical tools
(Bodenreider, 2004). The Metathesaurus is the
biggest component of the UMLS. The Metathesaurus
identifies concepts and useful relationships between
them and preserves the meanings, concept names, and
relationships from each source vocabulary, which
helps in the creation of more effective and
interoperable biomedical information systems and
services, including Electronic Health Records (EHR).
The biomedical terminologies that we have
considered in this research are MedDRA (MSSO,
23.0), Medcin (NLM, 2021AA), ICD-11 (CDC, ICD-
11 CM, 11th), NCIt (NCIthesaurus, 21.03e) and
SNOMED CT (SNOMED CT, n.d.).
The Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities
(MedDRA) was developed by the International
Council on Harmonization of Technical
Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use
(ICH). It covers drugs, advanced therapies, and some
medical device information. “MedDRA contains
terms for signs, symptoms, diseases, syndromes,
diagnoses, indications, investigations, medication
errors, quality terms, procedures and some terms for
medical and social history” (Brown & Wood, 1999).
Medcin® was created and is maintained by
Medicom systems. Medcin is a point-of-care
terminology, intended for use in Electronic Health
Record (EHR) systems (MEDCIN, 2004). Several
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems are
embedded with Medcin. “This facilitates the creation
of fully structured and numerically codified patient
charts that enable the aggregation, analysis, and
extensive mining of clinical and practice management
data related to a disease, a patient or a population”
(National Library of Medicine, 2008).
ICD-11 is the 11th revision of the International
statistical Classification of Diseases and related
health problems, a medical classification created by
the World Health Organization (WHO) (World
Health Organization, 2019) that will come into effect
in January 2022. In this paper, we have used version
09/2020 of ICD-11 MMS (Mortality and Morbidity
Statistics) to investigate the extracted concepts. It
contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms,
abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances,
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
18

and external causes of injuries and diseases. Versions
of ICD (e.g., ICD-10-CM) are used by health
insurers, national health program managers, data
collection specialists and others in global health to
determine the allocation of health resources. The
ICD-11 also reflects progress in medicine and
includes the tools to code unsafe workflows in
hospitals.
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) thesaurus
(NCIt) has been produced by NCI Enterprise
Vocabulary Services (EVS). “The NCI thesaurus
covers vocabulary for cancer-related clinical care,
translational and basic research, public information
and administrative activities” (National Cancer
Institute, 2020).
The Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine-
Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT: SNOMED is not
considered an acronym) was created by the College
of American Pathologists (CAP). “SNOMED CT
aims to improve patient care through the development
of systems to record health care encounters
accurately” (SNOMEDCT_US, 2020).
BioPortal is a web portal that provides access to a
library of biomedical ontologies and terminologies
via the NCBO web services. It serves as a repository
for biomedical ontologies, containing 868 ontologies
as of May 2021. BioPortal enables ontology users to
find out the biomedical ontologies that exist for a
topic, what a particular ontology might be good for,
and how individual ontologies relate to one another
(Noy, Shah, & Dai, 2008). Open Biological and
Biomedical Ontology (OBO) Foundry (Smith,
Ashburner, & Rosse, 2007) is recognized as “gold
standard” repository (Norris, Hastings, Marques, &
Finnerty Mutlu, 2021) of interoperable ontologies,
which, as of May 2021, contains 263 ontologies.
3 RELATED WORK
Atal et al., (2016) defined an automatic classification
of registered clinical trials. In their work, they have
developed a knowledge-based approach to associate
clinical trial concepts with diseases from a Global
Burden of Disease list (GBD). They used MetaMap
(Aronson, 2020) to extract the UMLS concepts from
health conditions and scientific titles, linked the
UMLS concepts with ICD-10 codes, and classified
those ICD-10 codes according to GBD categories.
Specifically, the classification is based on the
recognition of diseases in the free text description of
the trials and the mapping of concepts between
medical taxonomies. This enabled a comparison
between global health research and global burden
across diseases.
Grimes et al. (Grimes, Brennan, & O'Connor,
2020) defined a taxonomy of potential negative
reactions experienced by people who are
disseminating medical results to the wider
community using Twitter. In their work, 142
prominent medical practitioners and scientists were
invited to take part in a survey. There were 101
responses. Based on the survey a non-exhaustive
taxonomy was developed, which contained five
major categories, namely 1) Discreditation attempts,
2) Dubious amplification of pseudoscientific
narratives, 3) Malicious complaints/abuse of
regulatory frameworks, 4) Interpersonal Harassment
and 5) Mispresentation (i.e., Misrepresentation).
The National Institute for Occupational Safety
and Health (BLU, 2012) NIOSH in conjunction with
the CDC has developed a taxonomy of occupational
injury and illness incidents. The Bureau of Labour
Statistics (BLS) developed the Occupational Injury
and Illness Classification System (OIICS) to
characterize occupational injury and illness incidents.
The taxonomy is organized according to the nature of
injury, part of body affected, source of injury and
event of injury. They have also developed a graphical
tree interface that is searchable and includes
descriptive details.
He et al. (He, 2020) defined a taxonomy for
Coronavirus disease knowledge and data integration
(CIDO). They emphasized the FAIR principles which
intend to make data Findable, Accessible,
Interoperable and Reusable.
To the best of our knowledge, there does not exist
an ontology of medical harm specifically focused on
minority populations.
4 METHODS
We investigated BioPortal and OBO Foundry to
determine whether any ontology exists that
specifically addresses injuries resulting from racism
and implicit bias in society. For this purpose, we
started with formulating permutations of common
terms used to describe race and ethnicity and used the
search functionalities of BioPortal and OBO Foundry
to check whether they exist in the target ontology
repositories. In some cases, the autocomplete
function in BioPortal discovered partially matching
terms that were different from our permutations, but
relevant.
In the second phase, we investigated the entire list
of BioPortal and OBO foundry ontologies to locate
ontologies addressing minority hazards that were
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME)
19

missed in the first phase. When ontologies such as
“International classification of external cause of
injuries” in BioPortal where located, we explored the
classes of the specific ontology to identify whether
minority populations are mentioned in the design of
the ontology.
We also investigated biomedical vocabularies for
specific terms in the context of racism, inspired, e.g.,
by news reports. For many of the injury terms that we
encountered, we did not find a corresponding concept
in any of SNOMED CT, ICD-11, NCIt, MedDRA or
Medcin. We also explored whether postcoordination
could be utilized to record such situations or findings.
The postcoordination feature that has long existed in
SNOMED CT is also implemented in ICD-11. For
example, in ICD-11, we investigated how to represent
“Victim Suffocated to death by police using spit
hood.” We tried to represent it using “asphyxiation”
and added “legal intervention” as an “associated
with” field, but when we did that the ICD-11 browser
displayed the error message “Ignored as the selection
does not have a code and therefore cannot be used as
a postcoordination value.” We alternatively tried to
code the concept using PE60 “Assault by threat to
breathing, suffocation from object covering mouth or
nose” coordinated with XE2Z7 “Perpetrator-victim
relationship, official or legal authority, police” as an
“aspect of injury.” The final code obtained after
postcoordination was therefore PE60 & XE2Z7. The
fact that an injury like this couldn’t be recorded
without using the “heavy duty tool” of
postcoordination inspired us to develop the Health
Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME).
5 DEVELOPMENT OF HEALTH
ONTOLOGY FOR MINORITY
EQUITY (HOME)
In developing the Health Ontology for Minority
Equity (HOME), we have focused on injuries that are
“differently experienced” by minority members. The
classification is based on events at a healthcare
institution or in educational, workplace, law
enforcement, and “society at large” settings. To
identify relevant concepts, we researched scientific
journals through PubMed and Medline, using
keywords such as “Health disparity minority,”
“Implicit bias,” “Health inequity,” “Racial profiling,”
etc. We also used free text Google searches to extract
incidents of police shootings, workplace harassment,
and sub-standard care faced by Black and Latinx
populations. We then traversed the UMLS
Metathesaurus to identify the codes (CUIs) for these
concepts in our target ontologies. If we could not find
the concepts of interest, we looked for synonyms. If
there were no synonyms either, we extended the
search to potential parents of the desired concepts.
Whenever we successfully located a desired concept,
we added it to our list of relevant concepts. When we
could not identify a concept (or synonym) we
“invented” a concept name and added it to the list.
Then we organized all concepts in the finalized list
into an ontology by introducing IS-A links, until
every concept was reachable from the root.
Table 1 shows a few of the concepts and their
codes that we found in our target ontologies. When a
concept and its synonyms were completely missing,
we entered ‘No’ in the corresponding cell of the table.
To identify synonyms for the extracted concepts, we
searched the UMLS for each concept and identified
synonyms suggested by the UMLS. Then we refined
our search to our target ontologies and extracted the
corresponding codes for the desired concept, broader
concepts and narrower concepts in the UMLS.
If neither a relevant concept nor synonyms for it
were identified, then we used alternative terms in our
investigation, based on partial matches. For example,
the term “Procedure violation” did not yield an exact
match in the UMLS. Therefore, we used “Protocol
violation,” based on a partial match listing in the
UMLS, which yielded a result in the NCIt.
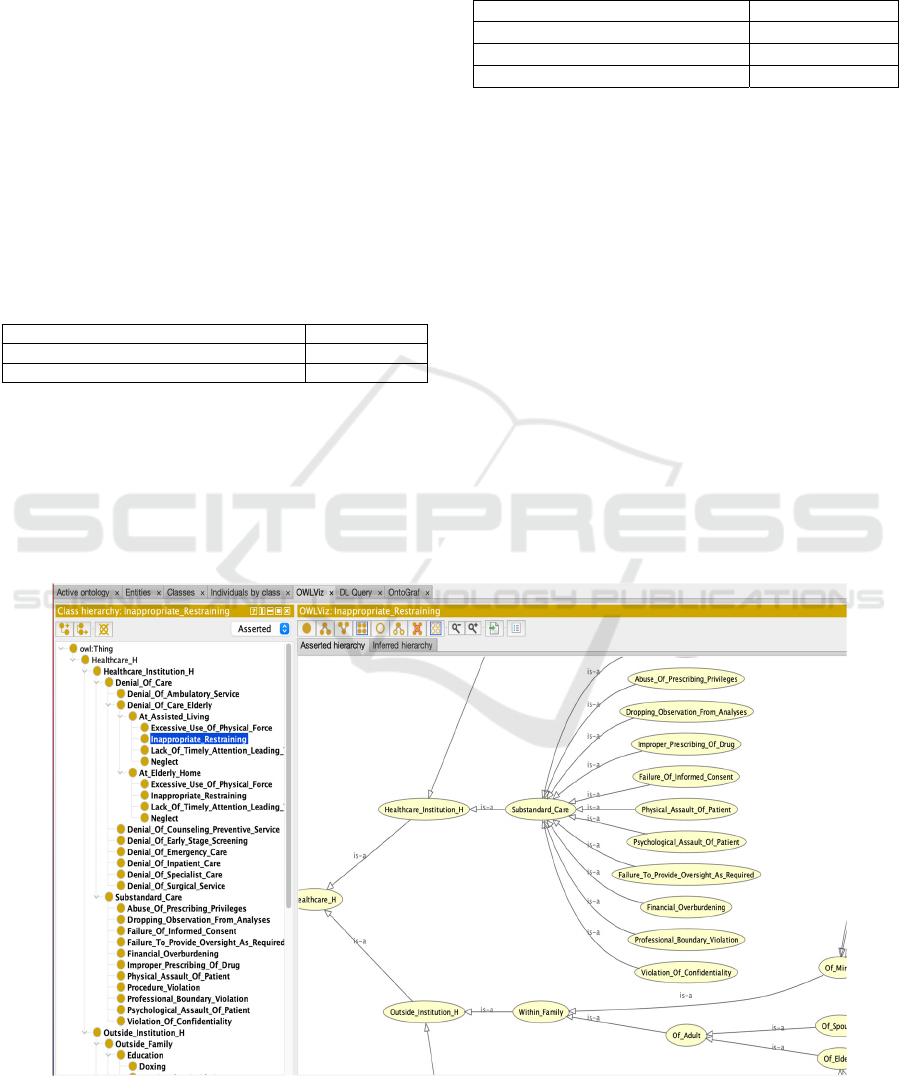
Figure 1 shows a partial view of the HOME
ontology. Strictly speaking, every triple of two
concepts connected by an IS-A link should be
readable as an English sentence with the child
concept as the subject of the sentence. For example,
the triple “Denial_of_care_elderly IS-A
Denial_of_care” can be read as a reasonably clear
(although not “elegant”) English sentence. However,
in many cases, this requirement will lead to very long
and even unnatural concept names.
Tree (or Directed Acyclic Graph - DAG)
diagrams of ontologies are easier to understand and
more natural than indented text, for example, because
all children of a concept are directly connected to the
parent. However, such diagrams become unwieldy
when concept names are very long. Thus, we had to
compromise and shorten some concept names. Thus,
many concepts in HOME are “hazards,” but we
dropped the word “hazard” to shorten the concept
names.
For example, we shortened Within-family-hazard
IS-A Outside-institution-hazard to Within-family IS-
A Outside-institution-h. When ontology diagrams
become very large, there is also a diminishing return
of the visual display. Thus, we are showing only parts
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
20
Table 1: Evaluated terminologies and synonyms considered with corresponding codes if present in biomedical vocabularies.
Terminology SNOMED CT ICD-11 MedDra NCIt Medcin Examples of Synonyms
Protocol violation 416237000 QC1Z No C142185 No
Interventions not carried out, Procedure
violation, Procedure not done.
Financial
overburdening
225827005 VA55 No No 4720
Victim of financial abuse, Health drain on
financial resources.
Abuse of prescribing
privileges
879970005 PL14 10079146 C100355 No
Medications not Prescribed for pain, At risk
for medication error, Medication errors and
other product use errors, non-administration
of necessary drug.
Physical assault of
patient
370927008 No No No No
Injury of a patient or staff member resulting
from a physical assault (i.e., battery) that
occurs within or on the grounds of the
healthcare facility.
Violation of
confidentiality
No No No No 4726 Denial of right to privacy
Failure of informed
consent
No No No No No
Failure to provide
oversight as required
405365001 No No No No Incorrect operative procedure performed
Dropping observation
from analysis
No XE4BB No C62848 No
Incorrect, inadequate, or imprecise result or
readings
Denial of inpatient
care
No QB14 No No No
Unavailability or inaccessibility of health care
facilities, Unspecified reason for
unavailability of medical facilities
Denial of ambulatory
services
No No No No No
Denial of emergency
care
No No No No No
Denial of early-stage
screening
171152003 No No C150884 No
Screening not wanted (situation), Met
eligibility criteria but was not needed
Denial of surgical
services
No QB15 No C63098 No
Medical services not available in current
medical facility, Inadequate medical device
service
of HOME in Figure 1 and later in Figure 2. A
complete ontology file exists at the GitHub link
https://github.com/HOME-Ontology/HOME.
6 PROTÉGÉ IMPLEMENTATION
Protégé is the most widely used ontology editing
environment with numerous plugins available for
additional processing such as visualization. We have
implemented the HOME ontology in Protégé 5.5 in
OWL format. Thus, Figure 2 shows a partial screen
capture of the Protégé OWLViz visualization of
HOME. Protégé refers to “concepts” as “classes,” and
allows adding annotations to classes. The class Thing
is predefined in Protégé and is used as the root of
every ontology. Below we will use “class” and
“concept” interchangeably, even if one can draw
distinctions.
A reasoner is a program that infers logical
consequences from a set of explicitly asserted facts or
axioms and typically provides automated support for
reasoning tasks such as classification, debugging and
querying. Standard reasoner services are Consistency
checking, Subsumption checking, Equivalence
checking and Instantiation checking (Drummond,
Horridge, & Dameron, 2006). Consistency checking
using a reasoner is an important functionality in
Protégé. There are different reasoning tools to check
the consistency of an OWL ontology, including
HermiT, Racer, Pellet and Fact++ (Mohamad &
Zeshan, 2012).
We performed consistency checking in Protégé by
utilizing HermiT Version 1.4.3.456. HermiT is
implemented using the Java language. HermiT
checks the OWL files for consistency of the ontology
and to identify hierarchical relationships between the
classes. This reasoner is based upon the hyper tableau
calculus (Abburu, 2012), which allows the reasoner
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME)
21
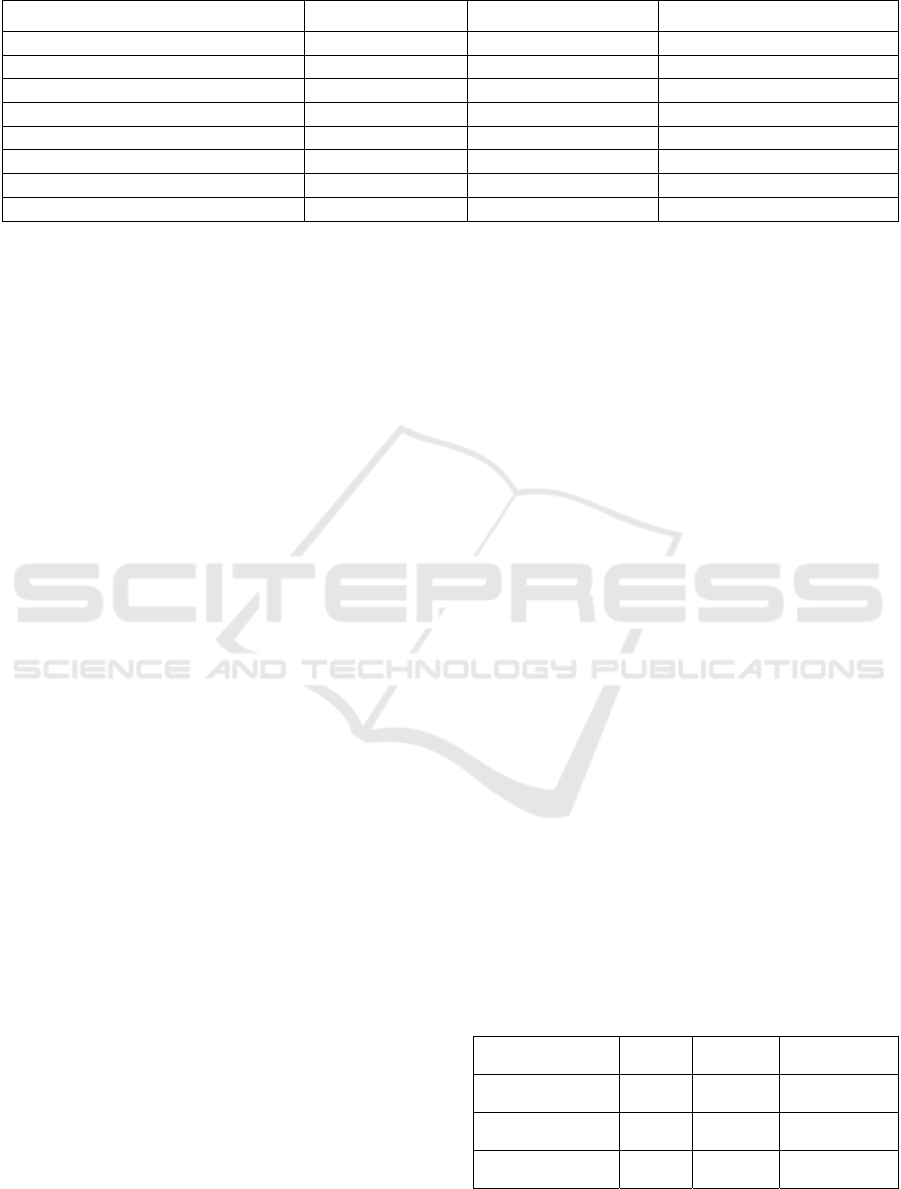

Table 2: Few rows of datasheet provided for HOME evaluation.
Child Relation Parent Question
Financial overburdening Is-a Substandard Care
Abuse of prescribing power Is-a Substandard Care
Procedure violation Is-a Substandard Care
Professional boundary violation Is-a ??? Substandard Care Is this a correct child?
Failure of Informed consent Is-a ??? Substandard Care Is this a correct child?
Failure to provide oversight as required Is-a ??? Substandard Care Is this a correct child?
Inappropriate restraining at Elderly home Is-a ??? Substandard Care Is this a correct child?
Lack of timely attention at assisted living Is-a ??? Substandard Care Is this a correct child?
to avoid some of the nondeterministic behaviour
exhibited by tableau calculus used in FaCT++ and
Pellet.
7 ONTOLOGY EVALUATION
Ontology evaluation is defined as the process of
deciding the quality of an ontology considering a set
of evaluation criteria. Depending on the kind of
ontology being evaluated (Amith, He, & Bian, 2018).
Ontology evaluation can be segmented into ontology
verification and ontology validation based on context
(Gómez-Pérez, 2004). Ontology verification
confirms that the ontology has been built according to
specified ontology quality criteria. Ontology
validation checks whether the meaning of the
definition matches with the conceptualization the
ontology is meant to specify. The four main methods
of ontology evaluation are gold-standard comparison,
application-based evaluation, data sources
comparison, and human-centric evaluation. Based on
our investigation of BioPortal and OBO Foundry, we
have used human expert evaluation, OntoMetrics and
Ontology Pitfall Scanner (OOPS) to evaluate HOME.
7.1 Human Expert Evaluation
We involved a medical subject matter expert (co-
author on this paper), with extensive experience in
ontology evaluation, to assess the HOME ontology.
For the evaluation, we started with a spreadsheet (part
of which is shown in Table 2) with 29 randomly
chosen parent-child pairs from the ontology. These
were pairs that we presented to the evaluator as
correct, to give her a flavour of the concepts in the
ontology. (The evaluator was not asked whether she
disagreed with any of those pairs as being correct, but
did not report any problems with them on her own.)
Then we added 30 more parent-child pairs taken
from the ontology, but we did not tell the evaluator
that we considered them correct. Finally, we added 41
parent-child pairs where both the parent and the child
existed in the ontology, but they were not connected
by a direct IS-A link. In other words, we considered
those pairs “incorrect.” We did not tell the evaluator
that those were considered incorrect parent-child
pairs. Thus, a total of 100 pairs were presented to the
evaluator, of which she had to evaluate 71.
The task of the evaluator was to determine for
every one of those 71 pairs, whether it should be in
the ontology or not. We then applied a statistical
measure to determine whether her choices “mostly”
agreed with what is in the ontology.
We chose this strategy in order to force the
evaluator to think about every one of the 71 parent-
child pairs. Had we given the whole ontology with no
incorrect pairs to her, there would have been a great
temptation to automatically say “correct” on every
pair. (See discussion on this issue.)
To evaluate the statistical significance of her
results, we used Fisher’s exact test. This test assumes
the input data is mutually exclusive and is usually
employed for small sample sizes. Fisher's exact test
gives more accurate results compared to the Chi-
square test for small samples, but the former is
computationally heavy. We used online software
(Calculator, 2018) to compute the p-value for Fisher's
exact test. We obtained a p-value of 0.018, which
implies that the evaluation was statistically
significant, since it is the case that 0.018 < 0.05 (a
common threshold). Thus, the expert was in good
agreement with our choices. Table 3 shows the input
contingency table used for Fisher's exact test.
Table 3: 2X2 Confusion Matrix input.
Confusion Matrix
IS-A
child
Not IS-A
child
Marginal row
total
Evaluated as an IS-
A child
30 30 60
Evaluated as not an
IS-A child
1 10 11
Marginal column
total
31 40 71
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
22
7.2 OntoMetrics Evaluation
OntoMetrics is an open-source Java implementation
that utilizes Java libraries of Protégé. OntoMetrics
operates as a web service and supports three different
kinds of metrics, namely general metrics, schema
metrics and graph metrics.
The steps that we performed using OntoMetrics
were as follows: Firstly, we uploaded our OWL
ontology file, which is in RDF-XML format, to
OntoMetrics to calculate quality metrics for the
ontology. Secondly, we obtained an XML download
file of the calculated ontology quality metrics.
Thirdly, we extracted the calculated values for the
uploaded HOME ontology. Results of the evaluation
are listed in Tables 4, 5, and 6.
Table 4: Base Metrics Evaluation.
Logical Axioms coun
t
135
Class coun
t
82
Total count 217
In Table 4, “Logical Axioms count” describes the
number of the logical relations in the Ontology.
Logical axioms take into account Disjoint classes,
Equivalent classes and Subclass axioms. A sample
logical axiom inferred from HOME is:
DisjointClasses: Baton, Pepper Spray,
Rubber_Bullet, Stun_Grenades, Taser, Tear_Gas.
“Class count” is the number of concepts. The sum of
these two numbers is listed as the “Total count.”
Table 5: Schema Metrics Evaluation.
Inheritance Richness (IR) 1.390244
Relationshi
p
Richness
(
RR
)
0.155556
Axiom/Class ratio 2.646341
Class/Relation ratio 0.607407
Inheritance Richness (IR) is a good measure of
how well knowledge is grouped into different
categories and sub-categories in the Ontology (Table
5). An ontology with a high IR (Rodrıguez, Sicilia, &
Garcıa, 2012) would be a deep ontology, which
indicates that the ontology covers a specific domain
in a detailed manner. An ontology with a low (close
to zero) IR would be a shallow (or horizontal)
ontology, which indicates that the ontology
represents a wide range of general knowledge with a
low level of detail.
Relationship Richness (RR) is defined as the ratio
of non-inheritance relationships (P) to the total
number of relationships, i.e., the sum of subclass
relationships (SC) and non-inheritance relationship
(P) as in Formula 1.
Since HOME consists mostly of class-subclass
relationships, we obtained a value of RR close to zero.
RR represents the diversity of relations in the
ontology (Rodrıguez, Sicilia, & Garcıa, 2012).
Figure 1: Partial OWLViz visualization of HOME Ontology in Protégé 5.5.
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME)
23
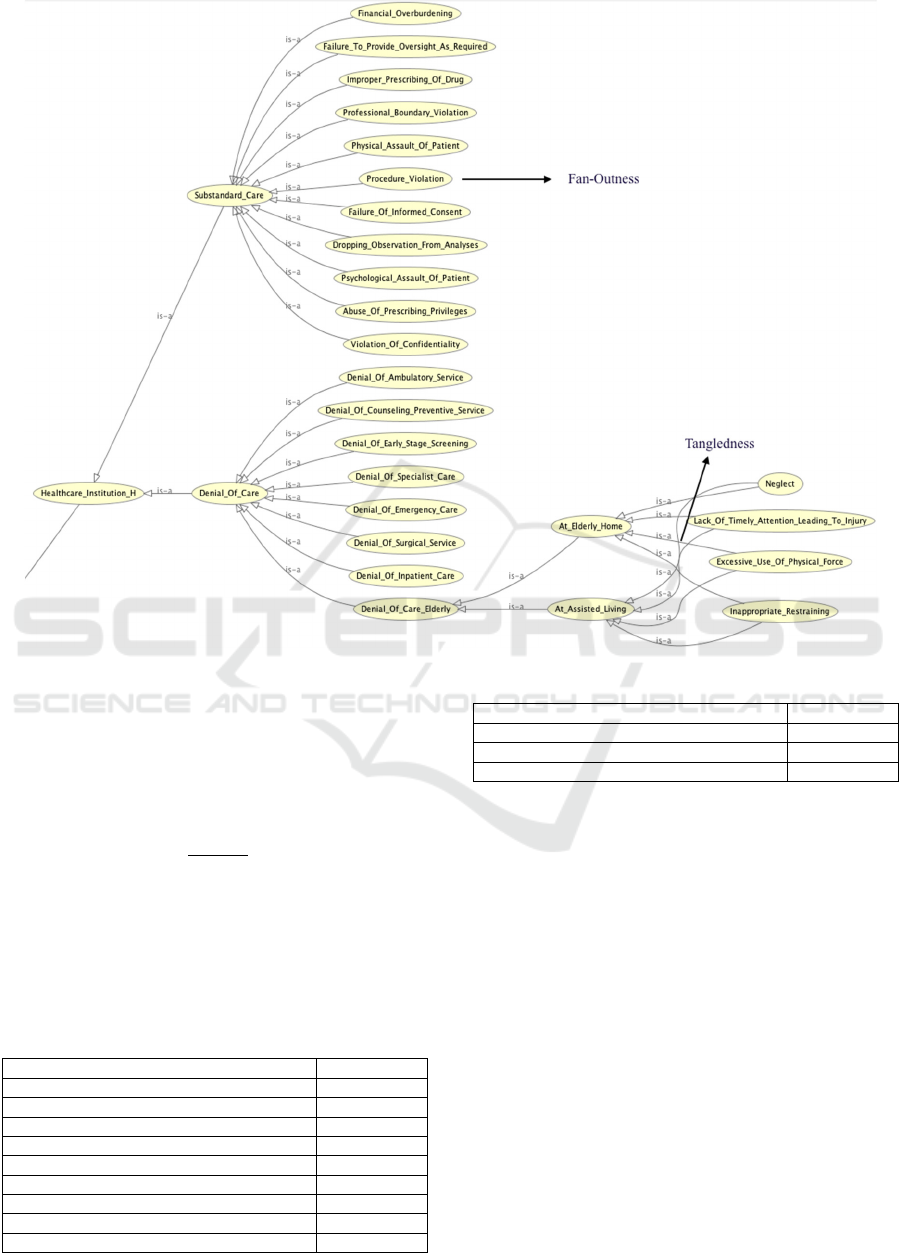
Figure 2: Logical representation of a portion of HOME outlining Fan-outness and Tangledness.
The Axiom/Class ratio is defined as the average
number of axioms per class. Similarly, the
Class/Relation ratio is the ratio of classes to relations
(sum of inheritance and non-inheritance relations) in
the ontology.
𝑅𝑅
𝑃
𝑆𝐶
𝑃
(1)
Table 6 shows the graph metrics from OntoMetrics,
most of which describe graph properties. Detailed
explanations can be found in the OntoMetrics Wiki
(Lantow, 2016) and in (Gangemi, Catenacci,
Ciaramita, & Lehmann, 2005).
Table 6: Graph Metrics Evaluation.
Absolute root cardinality 1
Absolute leaf cardinality 58
Absolute sibling cardinality 82
Absolute depth 662
Average depth 5.33871
Maximal depth 7
Absolute breadth 124
Average breadth 4.592593
Maximal breadth 14
Ratio of Leaf Fan-Outness (LFO) 0.707317
Ration of Sibling Fan-Outness (SFO) 1.0
Tangledness 0.243902
Total number of paths 124
Average number of paths 17.71428
7.3 Ontology Pitfall Scanner
We also used the Ontology Pitfall Scanner (OOPS),
which is a RESTful web service that helps in
identifying some of the common pitfalls in an
ontology. A few of them are reasoning, logic, and
naming pitfalls, etc. On evaluating our ontology, we
observed that the critical pitfall “polysemous
elements” is not present in HOME. However, OOPS
returned an evaluation report of three minor pitfalls
as shown in Figure 3 (P04, P07, and P08). P04 is
about creating unconnected ontology elements, P07 is
merging different concept in the same class and P08
is missing annotations. At this initial evaluation, these
minor pitfalls appear to be irrelevant, since the
construction of the ontology is still in progress.
Figure 3 is screen capture of OOPS.
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
24

Figure 3: Screen displays our result after analysing HOME
using OOPS.
8 DISCUSSION
We developed HOME in such a way that researchers,
system developers, and clinicians can find correct
vocabulary terms referring to events such as “Denial
of ambulatory services” or “Physically abused by law
enforcement personnel.” This is especially important
when data is recorded in EHRs. When properly
recorded, such data will document the disparities
faced by minority citizens.
The first step when addressing such problems is
documenting them and the first step to document
problems is to develop the language to express them.
Our HOME ontology is intended to bridge the current
gaps in expressiveness of medical ontologies in
diversity coverage. This ontology can be made richer,
and more breadth could be added with the
involvement of stakeholders contributing new
knowledge from their clinical practices.
8.1 Limitations
It is remarkable that there are 30 false positives in the
evaluation. We can think of three possible reasons for
that. One reason is that to avoid any possible biases
of the evaluator, she was not briefed on the fact that
there would be “many” incorrect pairs. Another
reason is that some of the incorrect pairs were
“parent-grandchild” links. In other words, the
connection between the two concepts was not
incorrect at all, it was just “too far away.” For
example (Figure 2), it would be fair to say that
“Neglect” IS-A “Denial-of-care,” however, in our
hierarchy “Neglect” is a great-grandchild of “Denial-
of-care.” From this viewpoint, saying that it is a child
would be incorrect.
One can argue that “Inappropriate-restraining-of-
elderly” can be a child of either “Denial-of-care” or
“Substandard-care,” but we assigned it to be a child
of the former. This problem could have been avoided
by making “Substandard-care” a child of both, as
multiple inheritance is permitted in this ontology.
9 FUTURE WORK
In future work, we plan to add more depth to our
ontology, addressing more specific situations of
injury, both emotional and physical. We are also
planning to interview clinicians to find more
scenarios in which they do not perceive that they have
the exact terms they need to record a “minority-
affecting” situation in their EHRs.
We will revisit every part of the ontology to
determine whether more concepts need to be assigned
multiple parents.
In future evaluation work, we will be more precise
in the choices and instructions given to the evaluator,
for example by specifying the possibility of a pair of
concepts being in a parent-grandchild relationship.
This should reduce the number of false positives. We
also intend to recruit more than one evaluator for the
next generation of this ontology.
10 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have designed, developed, and
implemented (in Protégé 5.5) HOME, an ontology for
representing hazards faced by minority citizens that
may or may not result in hospitalization. HOME was
developed to bridge the gap of missing concepts for
hazards especially affecting Black, Latinx and Asian
community members in ontology repositories such as
BioPortal and OBO foundry. To find the specific
missing terms and concepts for coding such injuries,
we investigated terminology repositories such as
SNOMED CT, ICD-11, MedDra, etc. The initial
version of HOME consists of 82 classes and 135
logical axioms, which in turn are divided into 20
disjoint class axioms and 115 IS-A links (subclass
axioms). HOME was evaluated by a human expert,
with a statistical significance of p=0.018, computed
by Fisher's exact test. We also used OntoMetrics and
OOPS to evaluate the HOME ontology.
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME)
25

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Research reported in this publication was supported
by the National Center for Advancing Translational
Sciences (NCATS), a component of the National
Institute of Health (NIH) under award number
UL1TR003017. The content is solely the
responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily
represent the official views of the National Institutes
of Health.
REFERENCES
Abburu, S. (2012). A Survey on Ontology Reasoners and
Comparison. International Journal of Computer
Applications, 33-39.
Amith, M., He, Z., & Bian, J. (2018). Assessing the practice
of biomedical ontology evaluation: Gaps and
opportunities. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 80, 1-
13.
Aronson, A. (2020). MetaMap - A Tool For Recognizing
UMLS Concepts in Text. (NIH, Producer) Retrieved
April 2021, from https://metamap.nlm.nih.gov
Ashburner, e. a. (2000, May). Gene ontology: tool for the
unification of biology. Retrieved from
http://geneontology.org
Atal, I., Zeitoun, J., & Neveol, A. e. (2016). Automatic
classification of registered clinical trials towards the
Global Burden of Diseases taxonomy of diseases and
injuries. Bioinformatics 17.
BLU. (2012, Oct). OIICS Code Trees. Retrieved April
2021, from Occupational Injury and Illness
Classification System:
https://wwwn.cdc.gov/wisards/oiics/
Bodenreider, O. (2004). The Unified Medical Language
System (UMLS): integrating biomedical terminology.
Nucleic acids research, 32, D267–D270.
Brown, E. G., & Wood, L. e. (1999, Feb 20). The medical
dictionary for regulatory activities. Drug Saf, 109-17.
Calculator, F. E. (2018, November 13). Retrieved from
https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/fisher/default2.a
spx
Carratala, S. (n.d.). Center for American Progress.
Retrieved from Health Disparities by Race and
Ethnicity:
https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/race/reports/
2020/05/07/484742/health-disparities-race-ethnicity/
Caviedes, J. E., & Cimino, J. J. (2003, Oct 20). Towards the
development of a conceptual distance metric for the
UMLS. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, Page 77-85.
CDC. (11th). Retrieved April 2021, from ICD-11 CM:
https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en
CDC. (2019, Sep 5). Racial and Ethnic Disparities Continue
in Pregnancy-Related Deaths. Retrieved April 2021,
from CDC Newsroom:
https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2019/p0905-
racial-ethnic-disparities-pregnancy-deaths.html
CDC. (2021, April 12). Retrieved April 2021, from Health
Equity: https://www.cdc.gov/healthequity/racism-
disparities/index.html
Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. (2021, April 19).
Retrieved April 2021, from Tracking the COVID-19
Recession’s Effects on Food, Housing, and
Employment Hardships:
https://www.cbpp.org/research/poverty-and-
inequality/tracking-the-covid-19-recessions-effects-
on-food-housing-and
Cimino, J. J. (2020, Sep 18). Is Biomedical Informatics
Abetting Systemic Racism? Retrieved from
https://www.uab.edu/medicine/informatics/news-
events/institute-news/144-special-seminar-on-
biomedical-informatics-and-systemic-racism
Clark, C. (2020, June 24). Texas A&M Study: White Police
Officers Use Force More Often Than Non-White
Colleagues. Retrieved April 2021, from Texas A&M
Today: https://today.tamu.edu/2020/06/24/texas-am-
study-white-police-officers-use-force-more-often-
than-non-white-colleagues/
Coleman-Jensen, R. M. (2019). Household food security in
the United States in 2018. U.S. Department of
Agriculture, Economic Research Service.
Drummond, N., Horridge, M., & Dameron, O. e. (2006). A
Practical Introduction to Protégé OWL. Retrieved April
2021, from
https://protege.stanford.edu/conference/2006/submissi
ons/slides/OWLTutorial_Part1.pdf
Fernandez-Lopez, M., Gomez-Perez, A., & Juristo, N.
(1997). METHONTOLOGY: from ontological art
towards ontological engineering. Engineering
Workshop on Ontological Engineering .
Gangemi, A., Catenacci, C., Ciaramita, M., & Lehmann, J.
(2005). A theoretical framework for ontology
evaluation and validation. SWAP.
Grimes, D., Brennan, L., & O'Connor, R. (2020).
Establishing a taxonomy of potential hazards associated
with communicating medical science in the age of
disinformation. BMJ Open, doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-
2019-035626.
Gómez-Pérez. (2004). Ontology evaluation. In Handbook
on Ontologies. International Handbooks on Information
Systems (pp. 251-274). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Harvard School of Public Health. (2020, June 24).
Retrieved April 2021, from Black people more than
three times as likely as white people to be killed during
a police encounter:
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-
news/blacks-whites-police-deaths-disparity/
Harvard School of Public Health. (2020, June 24).
Retrieved April 2021, from Black people more than
three times as likely as white people to be killed during
a police encounter:
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-
news/blacks-whites-police-deaths-disparity/
Hauschild V, H. K. (2017). A Taxonomy of Injuries for
Public Health Monitoring & Reporting. U.S. Army
Public Health Center (APHC).
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
26

He, Y. Y. (2020). CIDO, a community-based ontology for
coronavirus disease knowledge and data integration,
sharing, and analysis. Sci Data.
Kuziemsky, C. E., & Lau, F. (2010, April 12). A four stage
approach for ontology-based health information system
design. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 50(3), 133-
148.
Lantow, B. (2016). Retrieved from
https://ontometrics.informatik.uni-
rostock.de/wiki/index.php/Base_Metrics
MEDCIN. (2004). Retrieved April 2021, from
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/sourcereleased
ocs/current/MEDCIN/index.html
Mohamad, R., & Zeshan, F. (2012). Medical Ontology in
Dynamic Healthcare Environment. Procedia Computer
Science. Procedia Computer science, 340-348.
MSSO, M. (23.0). MedDRA. Retrieved April 2021, from
Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities:
https://www.meddra.org/about-meddra/evolving-
meddra
National Cancer Institute. (2020, Oct 20). Retrieved April
2021, from Vocabulary for Cancer Research:
https://datascience.cancer.gov/resources/cancer-
vocabulary
National Library of Medicine. (2008). Retrieved April
2021, from MEDCIN (MEDCIN) - Synopsis:
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/sourcereleased
ocs/current/MEDCIN/index.html
NCIthesaurus. (21.03e). Retrieved April 2021, from
https://ncithesaurus.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/
NLM. (2021AA). UMLS Terminology Services. Retrieved
April 2021, from UMLS Metathesaurus Browser:
https://uts.nlm.nih.gov/uts/umls/home
Norris, E., Hastings, J., Marques, M., & Finnerty Mutlu, A.
(2021). Why and how to engage expert stakeholders in
ontology development: insights from social and
behavioural sciences. J Biomed Semant, 12(4).
Noy, N. F., & McGuinnes, D. L. (2001). Ontology
Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First
Ontology. Retrieved April 2021, from Stanford
Knowledge Systems Laboratory and Stanford Medical
Informatics:
https://protege.stanford.edu/publications/ontology_dev
elopment/ontology101-noy-mcguinness.html
Noy, N., Shah, N., & Dai, B. (2008). BioPortal: A Web
Repository for Biomedical Ontologies and Data
Resources. Proceedings of the Poster and
Demonstration Session at the 7th International
Semantic Web Conference (ISWC2008). Germany.
Office of Minority health resource center. (2021, April 5).
Retrieved from U.S Deaprtment of health and Human
services:
https://www.minorityhealth.hhs.gov/omh/browse.aspx
?lvl=3&lvlid=61
Pan, H., Zhu, Y., Yang, S., Wang, & Wei, Z. (2019,
December). Biomedical ontologies and their
development, management, and applications in and
beyond China. Journal of Bio-X Research, 2(4), 178-
84.
Rodrıguez, D., Sicilia, M. A., & Garcıa, E. (2012).
Empirical findings on ontology metrics. Expert
Systems with Applications, 39(8), 6706-6711.
Schriml, L. M. (2018). Disease Ontology. Retrieved from
https://disease-ontology.org
Smith, B., Ashburner, M., & Rosse, C. (2007). The OBO
Foundry: coordinated evolution of ontologies to
support biomedical data integration. Nat Biotechnol,
1251-1255.
SNOMED CT. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2021, from
https://browser.ihtsdotools.org/?perspective=full&con
ceptId1=405703008&edition=MAIN/2021-01-
31&release=&languages=en
SNOMEDCT_US . (2020, March 31). Retrieved April
2021, from National Library of Medicine:
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/source
releasedocs/snomedct_us.html
UNCF.Org. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2021, from K-12
Disparity Facts and Statistics: https://uncf.org/pages/k-
12-disparity-facts-and-stats
Walensky, R. P. (2021, April 12). Racism and Health.
Retrieved April 2021, from Health Equity:
https://www.cdc.gov/healthequity/racism-
disparities/index.html
Westbrook, L. (2014, Nov 27). BBC. Retrieved April 2021,
from Tamir Rice shot 'within two seconds' of police
arrival: https://www.bbc.com/news/av/world-us-
canada-30220700
World Health Organization. (2019). Retrieved April 2021,
from International Statistical Classification of Diseases
and Related Health Problems (ICD):
https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/classific
ation-of-diseases
York, S., Steffen, S., & Rudi, S. (2004). On-To-Knowledge
Methodology (OTKM). International Handbooks on
Information Systems, 117-132.
Health Ontology for Minority Equity (HOME)
27
