
Information Security in Banks
Yulia V. Evdokimova
1
a
, Elena N. Egorova
1
b
and Olga V. Shinkareva
2
c
1
Russian State Social University, Wilhelm Pic Str., Moscow, Russia
2
Moscow City University, Selskokhozyaystvenny Drive, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Bank Information Security Risks, Payment Infrastructure, Targeted Attacks, Perimeter and Host Security,
Information Security Incidents, Transactions.
Abstract: The study examined key issues of information security of banks in the Russian Federation. The issues of
standardization within the framework of information security of banks, the main risks of banks were studied.
The main crimes in the field of information security threatening banks were considered. The main elements
of the information security system in banks are presented. Data on information security incidents during the
transfer of funds, on embezzlement carried out by cheaters in banks were analysed. The data on distribution
of attacks on banks by their types are given. The main requirements to which the equipment used by banks to
protect information security should meet are considered. We studied the changes that are taking place in banks
taking into account the requirements of our time, the growth of the quality of banking services and their
security, the growing risks and the need to minimize them.
1 INTRODUCTION
Risks in the field of information security are
associated with the loss of confidentiality, integrity or
availability of the organization's information assets.
Risks of information security are closely related to
other risks in other areas, in finance, in the field of
quality, ecology, labour protection or industrial
security (Evdokimova, 2020). Digitisation of the
business, the growing number of changes in the
organization's information infrastructure, the newly
emerging cyber threats and cyberattacks require an
adequate response from specialists.
As a result, in modern conditions, the construction
of an integrated information security system in banks
is turning into a continuous process of introducing
more and more new methods and tools for protecting
and improving existing ones.
2 METHODOLOGY
As part of the study, data on the development of
information security in the banking sector of the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1721-1368
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0403-7391
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2291-3516
Russian Federation were systematized and analysed.
The goal of the study was the need to structure and
summarize data to identify specific threats in the field
of information security of banks and the possibility of
their minimization.
3 RESULTS
Financial organizations historically, together with the
oil and gas industry and telecom, are one of the
leaders in the formation of integrated information
security systems, the use of the most modern
technologies and solutions in them. The risks of
information security in the banking sector cause
serious reputational and financial losses. The terms
"operational risk" and "information security risk"
appeared in the Bank of Russia Standard on
Information Security in 2004 (Standard STO BR
IBBS 1.0- 2004, 2004). The improvement of this
standard has led to the fact that the risk-oriented
approach has been steadily developing, the
requirements for information security of the bank
have been tightened. In 2010, Recommendations in
Evdokimova, Y., Egorova, E. and Shinkareva, O.
Information Security in Banks.
DOI: 10.5220/0010617800003170
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security (INFSEC 2021), pages 81-86
ISBN: 978-989-758-531-9; ISSN: 2184-9862
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
81

the field of standardization of the Bank of Russia
were put into effect: "Methodology for assessing the
risks of violation of information security" (Bank of
Russia, 2009). Credit institutions are constantly faced
with information security risks associated with the
implementation of information security threats, they
can be caused by shortcomings in the processes of
ensuring information security by banks, which is
associated with technological and other events,
shortcomings in the application software of
automated systems and applications, as well as with
possible inconsistency of these processes of the
bank's activities (Regulation the Bank of Russia from
04/08/2020 № 716-P, 2020).
The ISO 31000 standard provides the following
risk assessment: it is a process that is a continuous
systematic action to apply strategic and tactical
actions, procedures, tools to form communications,
advice, identification, assessment, analysis, risk
monitoring (ISO 31000, 2018.).
First of all, it is necessary to identify the main
crimes in the field of information security that
threaten banks. The most dangerous in financial
institutions are attacks on the payment infrastructure.
In this case, the credit institution incurs large-scale
direct financial losses.
Further, attacks on bank processing centers with
withdrawal of funds through ATMs can be
distinguished. These attacks can be conditionally
divided into two categories. The first category
includes the infection of the ATM management
subsystem or through it the ATMs themselves, with
the subsequent submission of a command to issue
cash. The second category includes hacking of
processing with subsequent crediting to previously
received cards of significant amounts. Then these
funds are cashed through ATMs of various banks.
Attacks on remote banking systems should also be
highlighted. As a rule, they are implemented through
infection of devices from which clients remotely
manage accounts. Of course, many banks have
introduced transaction confirmation technologies
with one-time codes obtained, for example, through
SMS, but various social engineering methods are
actively used to lure these codes from customers.
Fraud using social engineering methods is gaining
momentum, mainly used to lure people into their
payment card data and one-time transaction
confirmation codes. Initial ringing is usually done
programmatically.
There are also internal threats, these are abuses by
employees of the financial organization itself.
The elements of the information security system
in banks can be divided into two categories:
protection of the perimeter of the organization's
computer network and protection of internal hosts.
Perimetre protective equipment included:
firewall systems;
attack detection/prevention systems;
DLP system modules for mail and web traffic
control;
content filtering systems when employees of
the organization access the Internet;
antivirus tools on the mail server and Internet
access proxy server and a number of other
tools.
Host Protection Uses:
antivirus tools;
Personal firewall systems;
system host modules - Intrusion Detection
Systems and Intrusion Prevention Systems;
-DLP System Host Modules (Data Loss
Prevention) - as protection against accidental
data leaks;
means of controlling employee's use of
peripheral devices, primarily USB drives.
Many endpoint security solutions have begun to
combine a significant portion of the listed
functionality.
Now, more and more often in the perimeter and in
the host part began to add protection against targeted
attacks. These are attacks aimed at specific banking
organizations. They are not massive and prepare for a
long time. Attackers study the information systems of
the attacked object, find out which software is used
for various purposes. The targets of the attack are
very limited by any scope or objectives of specific
information systems and/or people. Malicious
software is specifically developed for attack so that
standard antivirus and security tools used by the
object and sufficiently well studied by intruders
cannot detect a threat. Most often, these are zero-day
vulnerabilities and special communication algorithms
with the perpetrators/customers of the attack
(TAdviser, 2021).
Recently, as part of information security, software
developers have been paying attention to the
interaction of perimeter and host security tools to
increase the effectiveness of detecting and countering
modern cyberattacks.
Banks widely practice a process, systematic
approach based on the interconnection of managerial,
technological, legal, information. Business processes.
A specific security tool is a tool built into the bank's
general information security system. The following
processes are distinguished:
malware protection;
data leakage protection;
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
82
protection of electronic document management
systems;
protection of computer networks;
protection of information in mobile users;
management of access rights;
Vulnerability management;
monitoring and response to information
security incidents;
management of information assets;
information security risk management;
-conformance control (compliance);
-secure software development;
improving the competence of employees in
matters of information security.
In financial organizations, information security
systems cover the protection of payment processes
and payment infrastructure. This component is given
key attention in banks. Information security threats
attributed to illegitimate transactions are now
common and do not lose their relevance. Transactions
between the user and the banking system are the least
secure and most frequent objects of cybercrime.
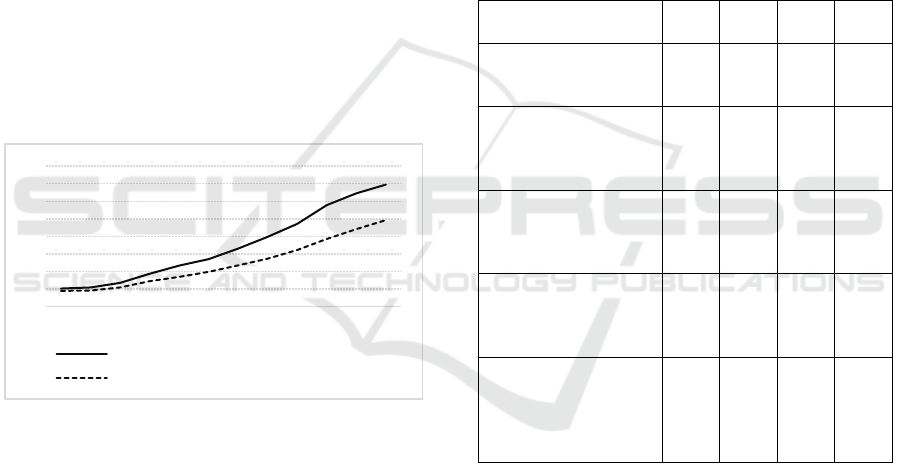
The share of cashless settlements in Russia is
growing (see figure 1).
Figure 1: Dynamics of the share of cashless operations in
Russia (Sberbank, 2020).
Technology, digitalization of the banking sector,
demanded by the market, is gaining momentum. In
this regard, the introduction of contactless mobile
payments using Apple Pay, Google Pay and other
similar applications is extremely fast. Russia has
become the largest market in Europe in terms of
operations using digital wallets.
This spread of cashless payments entails an
increase in information security risks in banks. Risks
are associated with the organization of the payment
process itself and with the possible loss of control of
the bank over it, and with the risk of fraud through
users of payment systems.
To manage risks in the process of organizing
payments, there are a number of standards and
mandatory standards that the bank must comply with.
However, the whole point is that from the point of
view of the system, fraudulent payments can satisfy
all the necessary requirements to confirm the
voluntary intention of the client. Payment fraud
schemes aimed at users have become systematic in
recent years. Multiple customer misleading schemes
are used. A large number of complaints come from
victims over the age of 60. "Tech Support Fraud"
quantity is increasing - operation of user trust in
technical support.
The Bank of Russia data on information security
incidents during the transfer of funds are as follows
(see Table 1).
Table 1: Volume of operations carried out without the
consent of customers for the 1st and 2nd quarters of 2019
and 2020 (Bank of Russia, 2020).
Indicator
2019
Q1
2019
Q2
2020
Q1
2020
Q2
ATMs, terminals,
imprinters, million
rubles
157
111
112
127
Payment of goods and
services on the
Internet, million
rubles
669
603
926
1122
Remote Banking
System for Physical
Persons, million
rubles
397
460
559
728
System of remote
banking services for
legal persons, million
rubles
105
194
231
193
Volume of
transactions using
electronic means of
payment, trillions of
rubles
24
23,1
19,4
22,5
The total amount of embezzlement of funds is
5723.5 million rubles, the average cost of theft is: for
individuals - 10 thousand rubles, for legal entities -
152 thousand rubles. According to the structure, the
main number of incidents is related to transactions for
payment of goods and services on the Internet (CNP-
transactions) and methods of social engineering
(fraud). The concentration of incidents falls on
Moscow and the Central Federal District, St.
Petersburg, Ural, Volga and Far Eastern Federal
Districts (Bank of Russia, 2020).
The distribution of attacks on banks by their types
made it possible to trace the following patterns (see
Table 2).
0,0%
10,0%
20,0%
30,0%
40,0%
50,0%
60,0%
70,0%
80,0%
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
share of cashless transactions in card expenditure transactions
share of cashless trade turnover in total expenses of citizens
Information Security in Banks
83
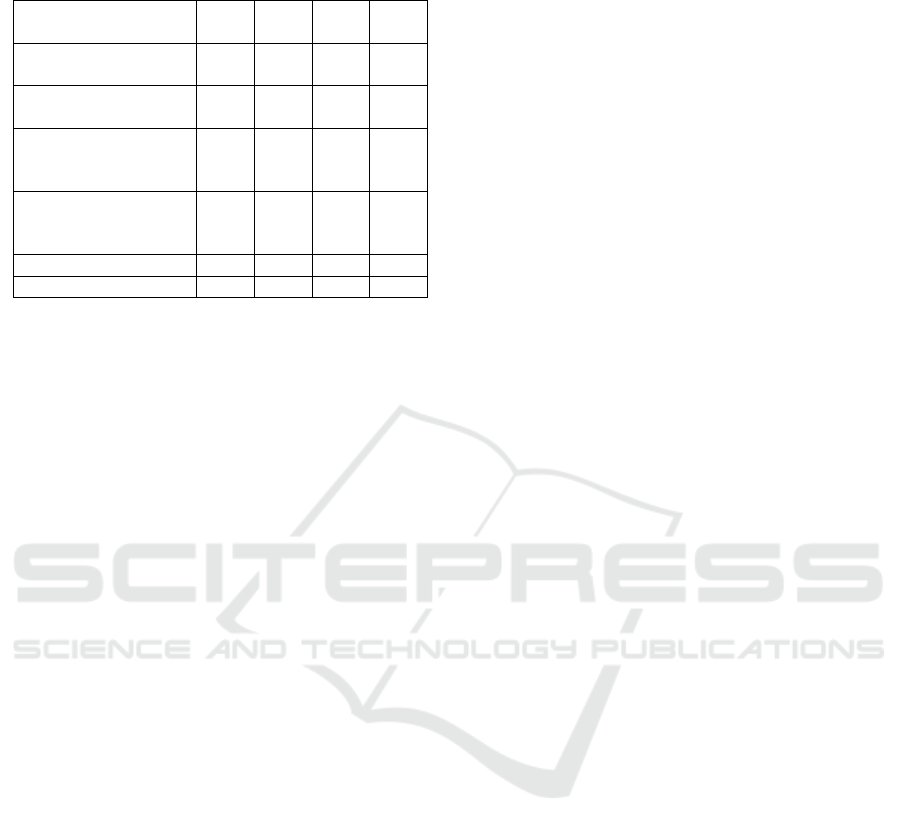
Table 2: Number of attacks on banking organizations by
their types in units (Bank of Russia, 2020).
Indicator
2019
Q1
2019
Q2
2020
Q1
2020
Q2
Phishing mailings by
customer
554
340
432
583
Attacks using social
engineering methods
6
466
4
462
4
806
4
589
Attacks on banks
using malicious
software
172
251
102
103
Attacks exploiting
software
vulnerabilities
223
430
165
186
Other types of attacks
224
113
131
113
Total
7639
5596
5636
5574
Attacks using social engineering methods
predominate for all study periods in the number of
cases, accounting for more than 80% of the total
number of attacks.
4 DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
The specifics of information security in banks is that
serious information security efforts are aimed at
protecting the payment infrastructure and payment
processes. It should be noted that most banking
transactions and most of the information processed in
the bank relate to bank secrecy, the task of ensuring
its protection can be solved only by building a
complex security system. You should also not forget
about the threats to information security associated
with personal data. Banks process them in significant
volumes, and they must be protected in accordance
with federal law 152 "About Personal Data" (Federal
Law from 07/27/2006 № 152-FL, 2006).
"The main directions for the development of
information security of the credit and financial sector
for the period 2019-2021" formed by the Bank of
Russia, as the main goals and objectives of today,
include ensuring cyber stability, operational
reliability and continuity of banks, as well as their
need to counter attacks in order to ensure the interests
of consumers of financial services (Bank of Russia,
2019).
The Bank of Russia considers the main areas of
development of banking informatization and
protection by regulating the use of big data, artificial
intelligence, robotization and the Internet of things in
the credit and financial sphere. Special attention is
paid to data processing using digital technologies.
The initiative of the Bank of Russia is the massive use
of cryptography in the financial market. The
controversy of this issue is related to a number of
legal and administrative barriers from the positions of
the Federal Security Service. The Bank of Russia will
stimulate actions on import substitution. However,
there are (at the moment) no alternative foreign
remedies, which will make it difficult for banks to
fulfill these requirements. Much attention will be paid
to the education of information security specialists:
from the preparation of an educational professional
standard and the identification of the need for
specialists to the introduction of certification of
employees of financial organizations at the
University of the Central Bank. In addition, it is
planned to teach students and university students the
basics of cybersecurity. The information security of
credit and non-credit financial institutions, according
to this document, should be ensured at the level of
infrastructure, application software and applications.
The level of bank information security will be
determined by the indicators established by the Bank
of Russia. Such indicators include compliance of
supervised organizations with the requirements of
state standards in terms of information protection,
business continuity, risk management and
outsourcing. For applications, certification will be the
criterion for assessing their level of protection and
quality. Special attention is also paid to the need for
international cooperation, taking into account the fact
that threats in the field of cybersecurity are universal.
Such threats are cross-border, change the formed
business models. The necessary tasks in this area are
the exchange of information on cyber threats, the
development of unified standardized approaches in
the cybersecurity field, the establishment of an
experience exchange in regulating and introducing
financial technologies in the framework of bank
information protection and security. Accelerated
banking sector digitalization due to the pandemic
entailed the intense emergence of new services,
which will certainly become the sphere of interests of
attackers, so the development of warning positions
should be ahead of the onset of possible negative
events. Such innovations should be mandatory and
universal for the entire banking sector in the
framework of optimizing information security.
Changes in regulatory documents for financial
organizations in 2021 are obvious. In 2019, the Bank
of Russia approved two new provisions for banks-
672-P and 683-P. They regulate unified rules for
ensuring information security in banks on the basis of
the national standard in the field of financial
transactions (GOST R 57580.1-2017). This standard
is a list of 343 security processes in 8 key areas:
access control protection, network protection,
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
84

information infrastructure integrity and security
control, malicious code protection, data loss
prevention, incident management, virtualization
protection, and mobile security. In addition, the
standard includes 65 requirements for organizing and
managing information protection. There are three
levels of information protection: minimum, standard
and enhanced. For each of the points of the standard,
it is indicated how they should be provided depending
on the level of information security: at the standard
level, a significant part of information security
processes is implemented by organizational
measures, with an enhanced level, more stringent
requirements are put forward for the implementation
of technical solutions (software or software and
hardware), while at the minimum level, meeting part
of the requirements is not necessary (National
standard of the Russian Federation GOST R 57580.1-
2017, 2017.).
Since January 1, 2021, changes entered Provision
683-P of the Bank of Russia (Regulation Bank of
Russia from 04/17 /2019 № 683-P, 2019.). Banking
organizations should ensure compliance assessment
according to GOST R 57580.1-2017 at least once
every two years. From January 1, 2021, banks need to
provide a third level of security. An appropriate
methodology has been developed that defines six
levels of conformity, from zero (no protection
systems) to fifth (compliance with all items of the
standard on an ongoing basis with proper control). At
the zero level of compliance, organizational and
technical measures of the information protection
system process are not implemented or are
implemented in isolated cases. There are no common
approaches to their implementation and monitoring of
implementation. At the first level, the organizational
and technical measures of the information protection
system process are implemented in a small number,
randomly and/or occasionally. There are also no
common approaches to implementation and control.
At the second level, organizational and technical
measures are implemented in a significant number on
an ongoing basis. General implementation
approaches are established in isolated cases.
Monitoring and improvement of the implementation
of organizational and technical measures of the
information protection system process is practically
not carried out. The third level of compliance adds
control and improvement of the implementation of
organizational and technical measures of the
protection system process, although they are carried
out randomly and/or sporadically. At the fourth level
of conformity, organizational and technical measures
are implemented in full and on an ongoing basis in
accordance with the general approaches established
in the organization. Control processes and
improvement of the information protection process
are mainly implemented. The fifth level of
compliance adds continuous monitoring and
necessary timely improvement of organizational and
technical measures of the information protection
system process
The main requirements of the Regulations of the
683-P in the framework of countering threats to
information security in banks contain the following
requirements are:
assessment of compliance with the National
Standard GOST R 57580.1-2017;
two-stage modernization of the information
protection system;
penetration testing and vulnerability analysis;
certification of vulnerabilities;
application of personal data protection
measures;
recommendations for clients on information
security;
recording of information protection incidents;
Information Security Requirement for Business
Processes.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The main requirements to be met by the equipment
used by banks to protect information security should
be attributed to these. how: functionality, reliability,
simplicity and ease of use at an acceptable cost. The
role of effective security interactions with each other
and with information security management systems is
also growing. As a rule, different products of the same
manufacturer are effectively integrated with each
other, but today the needs of the informatization
market are aimed at ensuring effective interaction and
from the solutions of different manufacturers.
The fact of warning is extremely important, that
is, banks faced with the inevitable need to invest in
promising research and development so that
information security systems can improve not in
connection with the crimes that occurred, but allow
preventing, among other things, completely new,
previously unknown types of attacks.
Solutions in the field of information security of
the bank require constant improvement and
development. They must be adequate to modern
threats, which, in turn, are also constantly developing
and improving.
Information Security in Banks
85

REFERENCES
Federal Law from 07/27/2006 № 152-FL, 2006. About
Personal Data
ISO 31000, 2018. Risk Management – Management
National standard of the Russian Federation GOST R
57580.1-2017, 2017. Security of financial (banking)
operations. Protecting the information of financial
institutions. Basic set of organizational and technical
measures
Regulation the Bank of Russia from 04/08/2020 № 716-P,
2020. On requirements for the operational risk
management system in a credit institution and a
banking group
Regulation Bank of Russia from 04/17 /2019 № 683-P,
2019. On the establishment of mandatory requirements
for credit institutions to ensure the protection of
information during banking activities in order to
counter the implementation of money transfers without
the consent of the client
Bank of Russia (2009). Recommendations in the field of
standardization RS BR IBBS-2.2-2009. Ensuring
information security of organizations of the banking
system of the Russian Federation. Methodology for
assessment of risks of violation of information security
Bank of Russia (2020). Overview of reporting on
information security incidents during the transfer of
funds in the I and II quarters of 2019/2020
Bank of Russia (2019). The main directions for the
development of information security of the credit and
financial sector for the period 2019-2021
Standard STO BR IBBS 1.0- 2004, 2004. Ensuring
information security of organizations of the banking
system of the Russian Federation
Evdokimova, Y., Egorova, E. and Shinkareva, O. (2020).
Information technology in financial sector Russian
Federation - Driver of the formation of the Russian
economy, E3S Web of Conferences, 208, 03017.
Sberbank, 2020. Rating of "cashless" cities and regions.
Results of 2019
TAdviser, 2021. APT - Targeted or Targeted Attack
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
86
